
NPC “Largest electric locomotive and Congressman John C. Schafer” 1924



Shanghai closed down another 3.42%. Capital is taking the Concorde out of the country.
• China Stocks Slump Again Despite Signs Of Government Support (Reuters)
China stocks tumbled again in late trading on Thursday, underscoring fragile investor confidence in the market as worries about the world’s second largest economy persist. Trading volumes were thin, suggesting many investors stayed on the sidelines. Shares were marginally lower in the morning, as statements by a slew of companies that the government had invested in them boosted some counters. But in mid-afternoon, prices began to drop. The CSI300 index of the largest listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen fell 3.2%, to 3,761.45, while the Shanghai Composite Index lost 3.4%, to 3,664.29 points.
The SSEC is now down about 7% since China devalued the yuan by nearly 2% on Aug. 11. On Wednesday, the indexes had reversed sharp losses to end higher, as roughly 30 Chinese listed companies, many small caps, disclosed holdings by government-backed investors in an apparent attempt to sooth market panic following the previous session’s 6% tumble. “Even as the government has the will to put a floor under the market, whether it has the ability to do so is in doubt,” said Hou Yingmin, analyst at AJ Securities, citing adversities including an anaemic economy, capital outflows and ugly technical patterns. “Without fresh money inflows, any rebound is not sustainable.”
Most sectors fell, with transport and real estate shares leading the decline. Analysts have said further yuan depreciation would trigger fresh capital outflows, putting pressure on the property market. But investors nevertheless bet on companies with investments from state-backed investor Central Huijin, and state margin lender China Securities Finance Corp (CSFC), which was tasked with propping up share prices during crisis.

Not looking good for Beijing.
• China Strengthens Yuan By Most In 2 Months; Massive Liquidity Injection (ZH)
The PBOC set the Yuan fix 0.08% stronger – the biggest ‘strengthening in 2 months, which is interesting because following The IMF’s confirmation of a delay to Yuan inclusion in the SDR basket to Oct 2016 (pending a year-end decision and asking for more flexibility), Offshore Yuan forwards notably devalued (shifting 350pips higher to 6.65, the highest/weakest Yuan in a week) pricing a 20 handle (or 3%) devaluation by August 2016. Overnight saw another CNY110bn liquidity injection rescue from The PPT in the afternoon session (saving SHCOMP from a close below the 200DMA) and tonight we see promise to recap Ag Bank along with another CNY 120bn reverse repo injection. Shanghai margin debt declined for a 2nd day in a row and Chinese stocks look set to open weaker.

“Authorities have to walk a thin line between boosting exports and satisfying the IMF’s requirements for the yuan to obtain reserve status, while at the same time ensuring financial stability.”
• China Central Bank Injects Most Funds Since February (Bloomberg)
China’s central bank injected the most funds in open-market operations since February as intervention to prop up the yuan strained the supply of cash and drove a key money-market rate to a four-month high. The People’s Bank of China pumped a net 150 billion yuan ($23 billion) into the financial system this week, data compiled by Bloomberg show. That’s the most since before the Chinese New Year holiday, when seasonal demand for cash spikes. The authorities are providing another 170 billion yuan through loans and an auction of deposits. The injections come after China surprised investors by devaluing the yuan last week and shifting to a more market-oriented exchange rate. Under the new system, PBOC intervention has partly replaced the daily reference rate’s role in guiding currency moves.
Yuan purchases risk driving borrowing costs higher at a time of slowing economic growth unless the monetary authority releases additional cash. “Front-end rates have been edging up, likely resulting from tighter liquidity conditions amid intervention,” said Frances Cheung at Societe Generale in Hong Kong. “The PBOC needs to step up its open-market operations to offset the liquidity withdrawal on the foreign-exchange side.” Authorities have to walk a thin line between boosting exports and satisfying the IMF’s requirements for the yuan to obtain reserve status, while at the same time ensuring financial stability. The overnight repurchase rate, a gauge of liquidity in the banking system, rose three basis points to 1.80% as of 1 p.m. in Shanghai, according to a weighted average from the National Interbank Funding Center. That’s the highest since April 23 and reflects increased demand for cash.

“..it is more heavily indebted than America was when its crisis began—even relying on official statistics which undoubtedly understate the real situation..”
• Is This The Great Crash Of China? (Steve Keen)
Banks in the West effectively ignore what the government wants: in the West, the political class is effectively subservient to the financial class. But in China, despite its economic transformation, the political class remains dominant: any Chinese entity that ignores a government directive does so at its peril. Things are not as they were in the 1980s, when every answer to every question that I and my group of touring Australian journalists asked began with “We followed the directives of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China”.
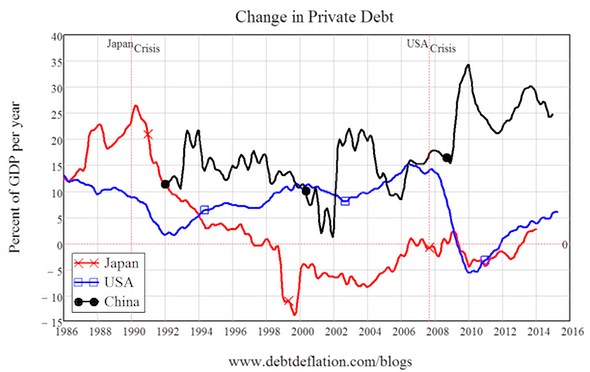
But it’s still not good for your health to flout Central Committee policy. So the Chinese banking system and its satellites lent like crazy to any company and many individuals, and one of the biggest credit bubbles in history—possibly the biggest ever—took off. In 2010, the increase in private debt in China was equivalent to 35% of GDP. That dwarfs the rate of growth of credit in both Japan and the USA prior to their crises: Japan topped out at just over 25% per year, and the USA reached a “mere” 15% of GDP per year.
As I have argued for a decade now, crises begin when the rate of growth of credit slows down in heavily indebted countries. China was not heavily indebted in 2008, which is why it could take the credit growth path out of the Global Financial Crisis. But now it is more heavily indebted than America was when its crisis began—even relying on official statistics which undoubtedly understate the real situation—and the momentum of debt may well carry it past the peak level reached by Japan after its Bubble Economy collapsed in the early 1990s.
So China is having its first fully-fledged capitalist crisis. To date its response to it has been to try to sustain the unsustainable: to transfer the bubble from housing to the stockmarket, and to keep the stockmarket rising like some production target for wheat from the bad old days before the fall of the Gang of Four. It can’t be done. At some point, the Chinese government is going to have to make the transition from generating a credit bubble to trying to contain its aftermath.

Ambrose is the odd one out.
• China’s August Scare Is A False Alarm As Fiscal Crunch Fades (AEP)
The situation in China is desperate but not serious, to borrow an old Viennese saying. Countries with a tight exchange controls and state banking systems may come to grief in the long-run, but they do not face the sort of financial collapse seen in the US and Europe in 1931 or 2008. China’s central bank (PBOC) has already warned that it will deploy the coercive might of the Communist regime to stop anybody smuggling money abroad under false pretexts, invoking laws covering “money laundering and terrorist financing.” It said violators will be “severely punished”. They will be sent to the proverbial asbestos mines of Sichuan. This is the sort of liberalisation that Xi Jinping does best. Given the sanctions and given that China has a trade surplus of $600bn or 6pc of GDP – and is therefore accumulating foreign exchange at blistering pace, ceteris paribus – there is no chance whatsoever that reserve losses will spin out of control.
Jens Nordvig from Nomura says China has $3.65 trillion reserves to cover foreign currency debts of $1.135 trillion, a ratio of 322pc. This a far cry from the East Asia Crisis in 1997-1998 when the ratio was 59pc in Malaysia, 33pc in Thailand, 27pc in Indonesia, and 22pc in Korea. All these countries had current account deficits. China most emphatically does not. “We think the authorities will remain in control of the situation. This may mean that the worst shock effect is behind us, although ultimately the economic data will provide the final verdict,” he said. On cue, the economy is already coming back to life after hitting a brick wall over the winter. Credit growth jumped to a 31-month high in July. The monetary base has grown at a 20pc rate over the last three months, implying an economic spike later this year.
It is worth remembering what has just happened in China. The country is recovering from a ferocious monetary and fiscal shock. The authorities refused to react as falling inflation caused one-year lending rates to ratchet up to 5pc in real terms from zero in late 2011. This was deliberate, of course. Premier Li Keqiang intended to break the back of the property bubble and wean the country off its $26 trillion credit dependency. But pricking bubbles is no easy task. The authorities overshot. The crunch came just as fiscal policy went awry. Budget spending contracted in the first quarter. This was certainly not intended. While details remain murky, it appears that banks refused to roll over short-term loans used by local governments to finance a raft of existing projects.
They feared that these loans were no longer covered by a state guarantee under new rules. “It caused huge disruption,” said Capital Economics. At the same time, the regions saw a sudden-stop in lending for new projects as well. Local governments were prohibited from fresh bank borrowing in January. Under the so-called “debt swap” plan there was supposed to be a seamless transition from loans to bond issuance, but the bond market was not up and running until May. This is why China crashed into a recession in the first half of the year. Wisely or not – depending on your economic religion – the Communist Party has now reverted to stimulus as usual. The local governments issued almost $200bn of bonds over the two months of July and August. Beijing coyly describes its fiscal spending as “proactive”. Turbo-charged would be another way of putting it.

I’m not.
• Should We Be Afraid Of China’s ‘Value Chain’? (CNBC)
The devaluation of the yuan may have a tougher impact on global companies than previously imagined, as China’s drive to produce and consume higher-quality goods intensifies. The shockwaves of the People’s Bank of China’s devaluation of its currency are still resonating around the world’s markets, but in the medium to long-term, it’s manufacturers who may hurt the most. Western companies from Apple to Burberry will face a tough time finding out whether they can rely on their cachet in China even when their goods becoming more expensive. China’s wealth has grown by leaps and bounds since the gradual opening up of its economy began in the 1980s.
Its per capita GDP in 2014 was $12,608.87, when adjusted for purchasing power, more than double what it had been just a decade before. The Chinese leadership’s current five-year economic plan (2011 to 2015) is specifically aimed at moving the economy’s fast-paced growth away from the low-cost manufacturing it had become famous for, towards consumption. Tactics included greater investment in research and development, higher-end manufacturing, and services targeted at the country’s burgeoning middle class.
In May, the Made in China 2025 plan has been billed by Premier Li Keqiang as an attempt to “redouble our efforts to upgrade China from a manufacturer of quantity to one of quality.” He pledged in May to “seek innovation-driven development, apply smart technology, strengthen foundations, pursue green development” – all of which is aimed at avoiding the “middle income trap”, where a country gets stuck at a certain level of economic development. Worryingly for those countries which have done well out of exporting to China in recent years, the plan includes sourcing 70% of key components within China’s borders by 2025.

“Euro area policymakers have lived on one myth after another..”
• Eurozone: The Case Against ‘Cash For Reform’ (Martin Sandbu)
“Euro area policymakers have lived on one myth after another,” says Ashoka Mody, a former deputy director at the International Monetary Fund. “A process of groupthink coalesces around these myths: ‘We know it’s not going to work but we need to make it work and we need to seem supportive’ — and before you know it they start to believe it. And because there is no democratic accountability, they are free to make one error after another in terms of economic and political logic.” The eurozone establishment has largely internalised the idea that “cash for reform” is necessary to keep the euro together.
The most direct challenge to it, from Greece’s Syriza party, was defeated when other countries — most notoriously Germany — made clear they would rather force Greece out of the euro than consider alternatives to offering refinancing in return for control over fiscal and reform policies. The idea that “there is no alternative” also motivates the efforts to “complete” Europe’s economic and monetary union. These efforts at deeper integration, epitomised most recently in the so-called “Five Presidents’ Report” — written by the heads of the most influential eurozone and EU institutions — proceed from the notion that the euro was flawed at birth and needs significant repairs to function properly. [..]
This article examines four widely-held preconceptions about Europe’s single currency. First, that the euro eroded the export competitiveness of the weaker countries. Second, that the resulting debt made official bailouts necessary. Third, that a monetary union can work only in the presence of a “fiscal union” — large budget transfers between countries to insure against downturns. And fourth, that the weaker countries must undergo deep structural reforms to be able to stay in the euro.
Each of these claims has had an outsize influence on policy. The research reported below shows that they should not be taken for granted.

Fraport is rumored not to have paid its Greek VAT in many years.
• Greece’s First Privatization Deal Since Third Bailout Hits Snag (Bloomberg)
Greece’s first privatization agreement since the country’s third bailout hit a snag just one day after the government announced the deal’s approval. A government council overseeing state asset sales said on Tuesday that Fraport AG and a unit of Greece’s Copelouzos Group had won a 40-year concession to operate 14 regional airports for €1.2 billion. Fraport commented afterward that the decision was “not tantamount to the conclusion of a contract but rather offers a basis for the resumption of negotiations.” The Greek government said Wednesday that it had approved the contract based on previous agreements, and that any effort to seek a renegotiation “wouldn’t be limited to the issues raised by the company.”
Fraport is “working toward a positive outcome,” said Joerg Machacek, a company spokesman. The airport deal is meant to be the first in a series of privatizations that Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras agreed to undertake in return for the third bailout package worth as much as €86 billion. The most pressing matter is obtaining funding to avoid a default Thursday when Greece must pay €3.2 billion to the ECB. Under the current proposal, Fraport would invest €1.4 billion to upgrade the airports by the end of the concession. The German company would also pay an annual lease of €22.9 million for the airports, which include the holiday islands of Mykonos and Santorini.

It’s simply a bad bad deal. Strike it.
• Fresh Doubts Raised Over Privatization Of 14 Greek Airports (Xinhua)
Fresh doubts were raised on Wednesday after the government finalized a €1.23 billion deal with the German consortium Fraport-Slentel on Tuesday to privatize 14 regional airports in Greece. The sale of the airports’ operation rights for 40 years was the first privatization to be concluded under the third bailout that was ratified by the Greek parliament on Friday. It was also the first privatization to be carried out since the left-led government coalition assumed power after the general elections in January. The announcement sparked mixed reactions in Greece. Some members of opposition parties welcomed the deal as a step towards boosting development. At the same time, they criticized the government for wasting precious time by delaying decisions for months.
Meanwhile, the ruling SYRIZA party’s hardliners denounced the “sell off” in a statement. Left Platform accused the government of “handing a great gift to the German government in return for the new catastrophic bailout.” The president of the Federation of Greek Civil Aviation Workers (OSYPA), Vassilis Alevizopoulos, warned of strike actions and lawsuits in Greek and European courts to “safeguard Greek public interests,” speaking to local VIMA radio station on Wednesday. Critics argued that the funds the German consortium would invest in the upgrade of the airports under the contract were insufficient and the cost will undoubtedly be transferred to travelers. In this climate of prolonged economic and political uncertainty in Greece, the German investors would most likely seek “more guarantees” from the government, Kathimerini reported.
However, Greek government sources stressed that if the consortium should wish to renegotiate the contract, there would be an in-depth dialogue on all issues. The agreement on the concession of the 14 airports that included the airports of Thessaloniki in northern Greece, and airports on islands such as Corfu and Mykonos, was initially scheduled to close in late 2014, but was frozen in the pre-election period. SYRIZA, which initially opposed the entire privatization program since the beginning of Greek bailouts in 2010, had previously said that the terms of the tender would be reviewed. But according to Tuesday’s official announcement, no amendments were made on the finalization of the privatization. [..]Greek ministers argued that privatizations would take place under changed conditions in comparison to the past “to benefit Greek economy and people.”

“..the MoU is really a “surrender document” that eclipses the country’s economic sovereignty and ensures that Greece’s depression — already deeper than America’s Great Depression — will get worse.”
• Stiglitz: “Deep-Seatedly Wrong” Economic Thinking Is Killing Greece (Parramore)
Bad economic ideas inflict untold human suffering. When they come cloaked in a fog of Orwellian obfuscation, their poison and effects can spread with little hindrance. The public is misled. Power plays are hidden from view. In Greece, where suicide rates have risen sharply in the wake of austerity measures, people lose hope. Joseph Stiglitz, who has been following the Greek crisis closely and is recently returned from Athens, sets himself to the task of cutting through the fog. His plain English and fearless use of moral language to expose the ugliness behind economic and political abstractions lend clarity to a situation that is not just bringing a nation to its knees, but threatening to destroy the European project and bring on a future of conflict and hardship.
In discussing Greece’s Third Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) and its draconian terms, Stiglitz observes that the MoU is really a “surrender document” that eclipses the country’s economic sovereignty and ensures that Greece’s depression — already deeper than America’s Great Depression — will get worse. An economy that is seeing youth unemployment reaching up to 60% is likely to lose another 5% in GDP. That is over and beyond the 25% plunge in GDP the country has been hit with since the imposition of austerity measures. Socially conservative Germans, Stiglitz warns, are doubling down on the discredited notion that austerity policies help economies recover in times of crisis.
In reality, the insistence on keeping wages down, stripping away bargaining power from workers, forcing small business owners to pay taxes a year in advance, and cutting pensions will only hamper demand and lead to a deepening spiral of debt. (Stiglitz emphasizes that hardly any of the money loaned to Greece has actually gone to help the Greeks themselves, but rather private-sector creditors – namely German and French banks). Reflecting on a recent panel at Columbia University with Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble followed by a dinner, Stiglitz said, “My heart goes out to Greece, even more so after meeting Schäuble.”

The Dutch are clueless. They blame SYRIZA for what’s ailing Greece. For Pete’s sake, get a life.
• Dutch Lambast Greece For Creating ‘Complete Chaos’ (Telegraph)
German MPs voted to back a third bail-out for Greece on Wednesday as Dutch prime minister Mark Rutte fought back a no confidence vote over his decision to support the €86bn rescue plan. After a three-hour debate, Berlin’s Bundestag approved a new rescue package for Greece with a majority of 454 votes to 113. Eighteen MPs also abstained, marking Angela Merkel’s biggest insurrection during her decade in office. Of her ruling CDU/CSU parliamentarians, 63 MPs voting against the package, more than the 60 coalition MPs who voted “no” in an initial vote in July. But the approval was enough to secure the disbursement of €13bn from the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) – the eurozone’s bail-out fund.
However, less than €1bn will go directly to the Greek government and €3.2bn will be used to immediately pay back a maturing bond held by the ECB on Thursday. It is the first injection of rescue cash to the Greek economy since August 2014 after eight months of ill-tempered talks and political crisis in the eurozone. EU policymakers hailed the agreement on Wednesday evening. Pierre Moscovici, the euro’s economics chief, said the deal would mark a “new chapter based on reforms, fairness and shared trust” between Greece and its creditors. Ratification from the German parliament was crucial in securing the deal. Wolfgang Schaeuble, Germany’s finance minister, told lawmakers that a deal was in the “interest of Europe”, but admitted that backing for a third bail-out deal was “not easy” and there was “no guarantee of success”.
“If Greece stands by its obligations and the programme is completely and resolutely implemented, then the Greek economy can grow again,” he said. “The opportunity is there. Whether it will be used, only the Greeks can decide.” Dutch finance minister Jeroen Dijsselbloem, who is also president of the Eurogroup, said reaching an accord was difficult. “Greece has seen decades of bad policies and six months of complete chaos,” he told his parliament. The Dutch backlash was led by right-wing politician Geert Wilders, who has called for the Netherlands to withdraw from the European Union. “Today we are here to prevent Dutch PM Rutte from indulging in his favorite hobby: sending money to Greece, this time €5bn,” Mr Wilders told the Dutch parliament on Wednesday.
Mr Wilders said Mr Rutte had reneged on a pledge in September 2012 that “enough is enough” and that Greece would get no more financial help from the country. “He’s the Pinocchio of the low countries. This is betrayal,” said Mr Wilders. “We need this money to support health care and the elderly. This government hates the elderly.” Mr Rutte said he took “responsibility” for his comments, but defended the government’s decision to back a bail-out, claiming that “no-one could have foreseen” in 2012 how the situation in Greece would evolve. “The new Greek government has caused great damage,” he said.

Crucial for Greece: bank recapitalization. The rest is circle jerk only.
• European Bailout Fund To Disburse First Greek Tranche On Thursday (Reuters)
The European Stability Mechanism will disburse the first tranche of funds from Greece’s bailout loan on Thursday, the Greek finance ministry said after the ESM board approved a rescue of up to €86 billion on Wednesday. Athens will receive €13 billion on Thursday morning, the ministry said, of which about €12 billion will be used to pay down debt, including an earlier bridge loan and money owed to the ECB. “Nearly one billion euros will be made available to the Greek state, a sum that can be used to pay arrears,” the finance ministry said in a statement.
The new bailout package of up to €86 billion for 32.5 years includes up to €25 billion to recapitalize Greek banks, of which 10 billion will be immediately available, according to the ministry. Athens needed the funds in time to make a €3.2 billion debt payment to the ECB on Thursday. The initial €13 billion tranche will be paid in cash, while the €10 billion euros for the recapitalization of banks will be sent to a segregated account in the form of ESM notes.

“..economic pain was designed into the Greek rescue. Unable to devalue Greece’s currency, the bailouts’ architects—other eurozone countries and the IMF—tried to push down prices and wages in a process called “internal devaluation.”
• The Fisherman’s Lament – A Way of Life Drowned by Greece’s Crisis (WSJ)
Dimitris Stathakis, 75 years old and wearing no shoes, is at work on the aft deck of the North Aegean, a fishing boat docked in the Greek port of Nea Michaniona. The boat’s 14-man crew is prepping for a night at sea. Bags of ice are tossed aboard. Someone brings a delivery of white Styrofoam boxes. It is baking hot. Mr. Stathakis has his shirt on his head to keep the sun off. He is mending nets with flicks of a plastic shuttle and assessing the state of a profession he took up in his teens. “This is the end,” he says. “This is the worst. There is no life anymore.” The fisherman’s lament is as old as the seas. And Greeks have earned a living from fish for eons. It is the country’s second-largest agricultural export, behind fruit and nuts but ahead of olive oil and cheese.
Six years of economic crisis, however, have left this way of life in a shambles. A collapse in household buying power has demolished demand for fish, and with it fishermen’s income. Aquaculture companies, once a shining star in the marine economy, are drowning in debts. Fish processors are struggling with high costs for finance and relentless price pressure among strapped shoppers. Few think the woes will end soon. The Greek government has signed up to a new bailout, with more years of belt-tightening ahead. The first notches came last month, in laws rushed through parliament at the behest of Greece’s creditors: Fishermen face higher pension contributions, while fish processors face new, higher taxes on processed food.
Meantime, Greek banks are only dribbling out cash to customers—further strangling already weak demand. Sales at North Aegean Sea Canneries SA, one of Greece’s largest fish processors, dropped 20% at the beginning of the crisis. The company is facing a long recovery. Nikolaos Tzikas, an owner, says he had hoped to crawl back to 2011 levels this year. “Now,” he says, “I don’t know.” The travails of Greece’s fish industry show how years of crisis and bailouts have left the country’s economy in worse shape than before—and why the next episode may well meet the same fate. In a way, economic pain was designed into the Greek rescue. Unable to devalue Greece’s currency, the bailouts’ architects—other eurozone countries and the IMF—tried to push down prices and wages in a process called “internal devaluation.”
The hope was that lower costs would make Greek industries nimbler and more competitive, juicing a sustained economic recovery. Instead, the loss of income has killed consumption. People are too poor to buy stuff and the banks too weak to give them credit, and the effects ripple up the economic chain. “Internal devaluation did not do any good for the Greek fishing, aquaculture and processing sector,” says Lamprakis Avdelas, a fishing expert at a government-affiliated institute in Athens.

“..the price of oil in five years’ time has collapsed in recent months.”
• Get Used To Cheap Oil, Derivatives Markets Say (Reuters)
Oil prices will stay low for years to come, derivatives markets say, keeping a lid on inflation and helping boost global growth. Oil has more than halved in value over the last year, thanks to huge oversupply, and many oil companies, particularly in the United States, say they may soon have to rein in production, tightening supply, unless the market recovers. That has led many analysts to predict that oil – on average around 5% of companies’ costs – will see price rises later this year or in 2016, pushing up inflation. But oil derivatives tell another story. Contracts for delivery of crude oil in the future on the big commodities markets such as the New York Mercantile Exchange and the InterContinental Exchange show the price of oil in five years’ time has collapsed in recent months.
U.S. crude now costs around $42 a barrel for delivery next month, and only about $20 more for delivery in 2020. Prices of oil for future delivery are usually much more stable than volatile near-term prices, holding their value even when the spot market crashes. But the recent oil-price rout looks different. Prices for all futures months for years to come, also known as the futures price “curve”, have come down sharply. “The curve is saying prices will stay low for some time,” said Amrita Sen, oil analyst at consultancy Energy Aspects.

All that’ll be left is the lethal tailings ponds.
• As Canada’s Oil Debt Soars to Record, an Industry Shakeout Looms (Bloomberg)
Canadian energy companies’ debt loads are the heaviest in at least a decade, boosting concern that some won’t survive the collapse in crude prices. Trican Well Service, Canada’s largest fracking service provider, said last week it may be unable to continue because it’s in danger of breaching the terms of its debt. It’s the latest firm to see crude’s descent to a six-year low sap the cash flow needed to meet financial obligations. Oil’s plunge has pushed a measure of the average debt burden among Canadian energy firms to the highest since at least 2002, and another measure of their ability to make interest payments to the third-lowest level in a decade, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
Facing some of the highest production costs in the world and carrying more debt than U.S. peers, the Canadian industry has become ripe for acquisitions. “Your ability to be an ongoing entity is certainly decreased,” said Jason Parker, head of fixed-income research at Bank of Montreal. “You’ll see larger, more financially affluent entities coming in and picking away at those properties.” Energy companies in the Standard & Poor’s/TSX Composite Index had an average of 3.1 times more debt than earnings as of their latest quarterly report, the highest ratio in Bloomberg data going back to the middle of 2002. That measure, a gauge of a firm’s ability to repay its obligations where a higher number indicates greater difficulty, has surged this year amid the global oil glut that’s depressed prices and earnings.
Another ratio, measuring how much greater earnings are than interest expenses, plummeted to the third least in a decade at the end of last year, suggesting there’s less money to service the borrowings. The heavy crude that many Canadian firms pump sells at almost the widest discount in a year relative to the U.S. benchmark. At $24.22 per barrel on Wednesday, the price is below the cost of production for many companies. For James Jung, who rates the debt of Canadian oil companies at DBRS Ltd. in Toronto, that divides the country’s industry into winners and losers, with those who have stronger balance sheets and lots of cash in a position to take advantage as more peers struggle with debt.

That’s one Ponzi industry I wouldn’t mind seeing killed off.
• Cheap Oil’s Making It Tough for Ethanol to Pay the Bills (Bloomberg)
Cheap crude oil may make it hard for ethanol companies to pay their bills on time. The lowest oil prices in six years are hitting biofuel producers two ways: They’re making ethanol less attractive as a blend for gasoline, and emboldening the arguments of petroleum backers who say the U.S. law mandating consumption of the fuel alternative is obsolete, Standard & Poor’s Ratings said in a report Wednesday. “The most noteworthy trend in the energy industry during the past year has been the precipitous decline in commodity prices, and chief among these has been plummeting oil prices,” Michael Ferguson, a credit analyst at S&P, wrote. “The lower oil prices may present a difficult rationale for blending ethanol.”
Crude oil has fallen 57% in the past year to $40.80 a barrel on the New York Mercantile Exchange, the lowest since March 2009. Gasoline has plunged 42% and ethanol has dropped 31%. Regulatory support has also waned. In May, the Environmental Protection Agency proposed reducing the amount of ethanol required to be mixed with gasoline from statutory levels set in 2007, citing changing driving habits and fuel use since then. That’s not reason enough to abandon the policy, according to Growth Energy, a Washington-based trade group. “Cheap gas and cheap oil is never a certainty, and often it is the exception,” Tom Buis, chief executive officer of the lobby, said in an e-mailed statement.
The Renewable Fuels Association, also a Washington-based trade group, said the S&P report “is really out of step with the realities of the market place today.” Low-priced crude oil lowers gasoline costs and makes ethanol less attractive for blending beyond government mandates. An additive, ethanol is used to boost gasoline supply and lower prices. “Consumers are saying, ‘I’ve already got cheap gas, why do I need this ethanol?’” Ferguson, the report’s author, said in a telephone interview Wednesday.

Australia.
• Banks Have Treated Our Housing Market Like A Ponzi Scheme (David)
Australia’s big four banks are among the largest and most profitable financial institutions in the world. Despite this, it is mathematically impossible that these banks, primarily focused on domestic retail operations, could be as big and profitable as they currently are without one of the following taking place: either each of these banks, in their individual capacity, has solved (at the same time, in the same country, and as a first in the history of banking) the ultimate recipe for infinitely profiting from an exponentially-growing stock of private debt; or they are all engaged in activity which is incredibly risky. Looking at the balance sheets of these four banking leviathans they have clearly taken on abnormal sums of risk to invest in a single, all-in, one-way bet on the housing market.
As my colleague Philip Soos and I told the House of Representatives’ economics committee inquiry into home ownership last week, the evidence suggests that on the back of irrational exuberance, Australia is experiencing what can only be described as a classic debt-financed speculative housing bubble with every metric that evidenced the bubble in the US and Ireland present within our economic system today. Between 2002 and 2015, the mortgage books of National Australia Bank, ANZ, Commonwealth Bank and Westpac grew by 388%, 435%, 475% and 554% respectively. Put another way, the big four’s mortgage books escalated from a combined $242bn to a whopping $1.13tn, surging at such a consistent rate it would make Bernie Madoff proud.
What the Australian banking system has developed is an uninterrupted growth model which shares a similar risk profile as a Ponzi or pyramid scheme by lending ever-larger sums of debt to homebuyers and property investors year after year. If this growth model is interrupted, however, and banks cannot expand their mortgage books further, housing price inflation halts and will then plunge.

Only choice left that will stop the shelling.
• Rebels In Ukraine’s Donetsk Plan Referendum On Joining Russia (Xinhua)
Leaders of the self-proclaimed “Donetsk People’s Republic” are planning to hold a referendum on seceding from Ukraine and joining Russia, the Donetsk-based Ostrov news agency reported Wednesday. The referendum is scheduled to be held in two to four weeks after the Oct. 18 local elections, said the news agency. The ballot papers for the referendum designed in the colors of the Russian flag have already been printed, it said. Neither the rebel leadership nor the Ukrainian authorities have commented on the report yet.
In July, leaders of pro-independence insurgents in Donetsk region said they would hold local elections on Oct. 18 without Kiev’s supervision as they believed that the Ukrainian government has not fulfilled its obligations under the Minsk peace agreement. Last week, violence in eastern Ukraine has sharply escalated after several weeks of relative calmness. On Sunday night, at least 11 people, including nine civilians, were reportedly killed in Donetsk region, marking the worst casualties in the conflict since early June.

Hilarious.
• China’s Building a Huge Canal in Nicaragua, But We Couldn’t Find It (Bloomberg)
Deep on the southeastern side of Lake Nicaragua, along a bumpy dirt road that climbs gently through lush-green forest, sits the tiny town of El Tule. It is quintessential rural Central America: Chickens roam outside tin-roofed homes while pigs stand tied to trees, awaiting slaughter; the sound of drunk locals singing along to ranchera music greeted visitors on a recent rain-soaked afternoon. The village, if you listen to Nicaraguan officials, is a key point in what will be the biggest infrastructure project the region has ever seen, the construction of a $50 billion canal slated to run 170 miles from the country’s east to west coast. Awarded two years ago by President Daniel Ortega to an obscure Chinese businessman named Wang Jing, the concession calls for El Tule to be ripped up, erased essentially, in order to make way for the canal right before it plunges into the lake and then meets the Pacific Ocean a few miles later.
The idea is that the waterway will attract many of the larger vessels that the Panama Canal — located just 300 miles to the southeast — has historically struggled to accomodate. A construction deadline of 2020 has been set. Yet a four-day tour through El Tule and surrounding areas slated for crucial initial development only seemed to corroborate the belief, harbored by many analysts inside and outside Nicaragua, that this project isn’t going to get done. The townspeople haven’t seen any signs of canal workers in months. And the work that was done was marginal. A handful of Chinese engineers were spotted late last year making field notations on the east side of the lake; early this year, a dirt road was expanded and light posts were upgraded at a spot on the west side where a port is to be built.
Juharling Mendoza, a 32-year-old local entrepreneur, is so convinced that the project won’t proceed that he’s constructing a two-story house with three guest rooms and an attached convenience store just outside of El Tule. He says bluntly: “There isn’t going to be a canal.”

These people are completely nuts. Sending dogs on refugees says it all.
• British Police Head To Calais To Stymie Migrant Smuggling Activity (Guardian)
British police will be deployed to Calais to target people-smuggling gangs as part of a new agreement aimed at alleviating the ongoing migrant crisis at the French port. In the first visit to Calais by a UK government minister since the crisis escalated at the start of the summer, home secretary Theresa May will travel to the town on Thursday to confirm a joint declaration with Bernard Cazeneuve, the French minister of the interior. Their deal will see officers from the UK based in a new command and control centre in Calais alongside their French counterparts and Border Force personnel. The work of the police contingent will be led by two senior commanders – one from the UK and one from France. They will report regularly to May and Cazeneuve on the extent of immigration-related criminal activity on both sides of the Channel.
Officials said the move was aimed at disrupting organised criminals, who attempt to smuggle migrants illegally into northern France and across the Channel into Britain, by ensuring intelligence and enforcement work is more collaborative. Britain and France will also work jointly to ensure networks are dismantled and prosecutions are pursued, sources said. Fresh measures included in the new agreement include: • The deployment of extra French policing units and additional freight search teams, including detection dogs • The investment of UK resources including fencing, CCTV, flood lighting and infrared detection technology to secure the Eurotunnel railhead • The tightening of security within the tunnel itself, with Eurotunnel helping to increase the number of guards protecting the site • The creation of a new “integrated control room” covering the railheads at Coquelles • A security audit to be carried out by specialist French and British police teams to underpin the design of the improvements.

The moral bankruptcy of Europe.
• Refugee Chaos in Macedonia: ‘Life-Threatening for Women and Children’ (Spiegel)
A dangerous bottleneck has formed in the Macedonian border town of Gevgelija, an important hub for refugees traveling to Western Europe. Those trying to reach the trains here face extreme heat, dangerous crowds and police bullying. It’s Monday, earlier this week, and what can be seen unfolding along the route to Macedonia is no less than mass migration, with around 200 people making their way along the Balkans route to Western Europe on this day alone. They have come here from Aleppo, Homs, Kobani, Tartus, Hama and Damascus. Indeed, much of Syria’s population appears to be fleeing at the moment, as they attempt to make their way to safety. The group walks along the railway tracks that lead from the Greek village of Idomeni to the town of Gevgelija in Macedonia.
“Good luck, Kobani!” a family from Damascus calls out as they pass by a group of Syrian Kurds. “Good luck, Damascus,” they respond. But they don’t make it very far. They soon encounter five Macedonian police officers waiting along the tracks on the dusty, trampled earth. They order the people to wait without telling them why or for how long. The Syrians take off their backpacks and set them on the ground. Women and children look for a place in the shade. Over the next five hours, the waiting group swells to around 400 people. Not all are Syrians. A few Iraqis have also made it here. Some are now claiming to be Syrian, which would give them greater chances of success with their asylum applications and expedited procedures. A Syrian man points to eight young men and women from Africa.
“Everyone here is from Syria now, even those people over there,” he says, grinning. The people here all have at least one thing in common: They arrived in Europe during recent days via one of the Greek islands located near the Turkish coast – Kos, Lesbos or Chios. Each day, around 1,000 to 1,500 people arrive on the islands, a greater number than ever seen before. Most want to continue on to Western Europe as quickly as possible. The massive surge of refugees has created a dangerous bottleneck on the main route through the Balkans.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 20 2015