
Frances Benjamin Johnston “Courtyard at 1133-1135 Chartres Street, New Orleans” 1937



The dog ate my homework?!
• Saudi Arabia and UAE Blame Non-OPEC Producers For Oil Price Slide (FT)
The oil ministers of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates have blamed the oil price rout on producers outside of OPEC and reaffirmed their stance to keep output at current levels. Ali al-Naimi, Saudi Arabia’s oil minister, said a lack of co-operation from countries outside the cartel was a key contributor to the near 50% slide in crude oil prices since the middle of June. “The kingdom of Saudi Arabia and other countries sought to bring back balance to the market, but the lack of co-operation from other producers outside OPEC and the spread of misleading information and speculation led to the continuation of the drop in prices,” he said at an energy conference in Abu Dhabi on Sunday, according to Reuters. “Let the most efficient producers produce,” he added.
Speaking at the same gathering, Suhail bin Mohammed al-Mazroui, the UAE energy minister, said one of the principal reasons for the price falls was “the irresponsible production of some producers from outside OPEC”. The comments from the two Gulf producers underline their commitment to production targets that stand at 30m barrels day, despite calls from some poorer OPEC members to reduce output to bolster prices. OPEC’s production policy and concerns about a supply glut have seen the price of Brent crude — the international oil benchmark — fall below $60 a barrel, hitting its lowest level in more than five years last week. At the conference, Mr Al-Mazrouei echoed a previous statement, saying “OPEC is not a swing producer” and “it’s not fair that we correct the market for everyone else”.
The UAE is thought to have the closest views to Saudi Arabia, a Gulf ally as well as the cartel’s largest producer and de facto leader. Ahead of last month’s OPEC meeting in Vienna, Mr Al-Mazrouei told the Financial Times: “Yes, there is an oversupply but that oversupply is not an OPEC problem.” He also said that non-OPEC countries and high-cost production – such as oil from US shale fields – should play a role in balancing the market. He says lower prices would help cut excess supplies from more expensive oilfields while preserving the share of lower-cost OPEC producers. The “market will fix it”, he said in November.

Too optimistic. To do this kind of calculation, you have to look at where financing came from, and how it’s leveraged and hedged.
• Calculating The Breakeven Price For The Median Bakken Shale Well (Zero Hedge)
A lot of data has been thrown around recently concerning the Bakken shale wells of North Dakota in an attempt to figure out the necessary oil price required to break even on the investment. In order to get a clearer picture of the financial situation in Bakken, it is necessary to develop a financial model of the median Bakken well. With a discount rate of 15%, the median well has a profitability index of 1.02 (after federal income tax) if $66 per barrel is used. (A profitability index of 1.0 indicates a break even situation at the discount rate that was used in the model). This means that at $66 per barrel, half the wells are uneconomic. If oil prices settle out at this price it can be expected that the number of wells drilled should be reduced by about half. The median Bakken well has the following attributes:
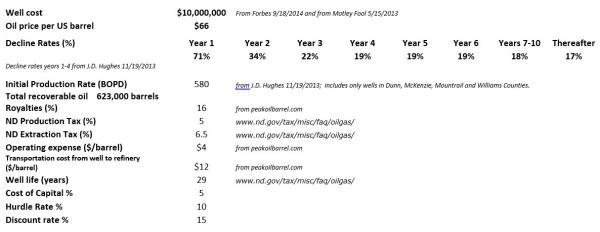
If the current oil price of $55 per barrel is used, the initial production rate has to be increased to 800 BPD in order to break even. According to the J.D. Hughes data, 25% of the wells have an initial production rate of 1000 BPD or more. Accordingly, if oil prices settle out at the current price, the number of wells drilled will be about a quarter of the present number. Some people have stated that this shale industry exists only due to abnormally low interest rates. If we use $100 per barrel and increase the discount rate to 20%, the median well has a profitability index of 1.6, which is profitable. The well is still making over 200 BPD after payout. My conclusion is that the shale development would still be profitable in a normal interest rate environment. The production data used in this model are from only 4 counties, Dunn, McKenzie, Mountrail, and Williams. Very few wells have been economic outside of these 4 counties. Therefore, when these 4 counties become saturated with wells, the Bakken play is over.

Not an overly impressive sum-up.
• How Oil Price Fall Will Affect Crude Exporters – And The Rest Of Us (Observer)
John Paul Getty’s formula for success was to rise early, work hard and strike oil. But a dependence on the black stuff can create its own problems, especially when the price tumbles as it has over the last few months. The price of a barrel of Brent crude has almost halved from $115 in the summer to stabilise around $60 last week. Most forecasters expect the cost of oil to remain low well into next year. Getty became a billionaire oil magnate after four years of speculative drilling in the Saudi Arabian desert proved to be worth the risk. Now the house of Saud appears willing to wait almost as long for its own victory. The plan, agreed with OPEC, maintains output, ignoring demands for cuts to push the price back up again.
As the dominant OPEC member, and keen to protect its own market share, the Saudis have forced the others to take the long view with a strategy that aims to put out of business all those producers that have flooded the market in the last few years and dragged the price lower. US fracking firms, where production costs are high, should be the first to feel the financial pain. But there will be collateral damage to others too. Iran may find itself running out of cash. And then there is Russia, which is heading for a deep recession next year as gas prices follow oil to lows not seen in 10 years. There will be winners too. The UK, now a net importer of oil, has already benefited by an estimated £3m-a-day reduction in fuel costs. Businesses will gain from cheaper energy, and cheaper petrol in effect puts more cash in consumers’ pockets. Taken in the round, global GDP could rise by 0.2% to 0.5% as the wheels of trade are lubricated a little more.

If you yourself can’t hike your ourput, it’s easy to tell others not to do it either.
• UAE Urges All World’s Oil Producers Not To Raise Output In 2015 (Reuters)
The United Arab Emirates oil minister urged all of the world’s producers on Sunday not to raise their oil output next year, saying this would quickly stabilize prices. “We invite everyone to do what OPEC did and take a step to balance the market through not offering additional products in 2015, and if everyone abides by (the) OPEC decision, the market will stabilize and it will stabilize quickly,” Suhail Bin Mohammed al-Mazroui said. He was speaking to reporters on the sidelines of a meeting of ministers of the Organisation of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) in Abu Dhabi. OPEC’s decision late last month to leave its output ceiling unchanged,rather than cutting it, was followed by a fresh plunge of oil prices. Iranian Oil Minister Bijan Zangeneh said last week that the continuing price slide was a “political conspiracy”; Iran needs a high oil price to ease pressure on its state finances. But Mazroui said on Sunday: “There is no conspiracy, there is no targeting of anyone. This is a market and it goes up and down.”

Hey, well, if Goldman says it …
• Goldman Sees Little Systemic Risk For Banks From Oil Price Drop (MarketWatch)
A larger share of lending to the energy sector came from high-yield debt rather than through traditional bank loans and as a result there is little scope for systemic risk to the U.S. banking system from a drop in oil prices, according to a research note from Goldman Sachs economist team. Government data puts energy-related loans on commercial banks at a bit more than $200 billion, the team said Friday in a note, a modest share of the sector’s $14.3 trillion in assets. However, regional banks have a disproportionate exposure to energy-related loans could find the recent drop in prices more challenging, the report said.
Fed Chairwoman Janet Yellen said last week that oil’s nearly 50% drop from its summers highs remains a net positive for the economy. She played down risk to the U.S. banking sector. Robert Brusca, chief economist at FAO Economics, said hedge fund players have already taken some big hits since energy was such a prevalent theme in the sector. “If the oil price continues to weaken and stays low for an extended period we could see problems emerge,” Brusca said in a note to clients. He noted a separate study by Goldman’s investment research unit that shows that $1 trillion in oil investment projects planned for the next year globally are no longer profitable with Brent crude below $70 a barrel. The analysis excluded U.S. shale.

Germany’s industry will not take much more of this.
• Russian Crisis Kills Big German Gas Deal (CNNMoney)
Fallout from the Russian crisis continues to spread with the cancellation of a big gas deal with Germany. BASF said it had dropped plans to hand full control of its gas storage and trading business to Russia’s Gazprom in exchange for stakes in two Siberian gas fields. State-controlled Gazprom is the leading supplier of natural gas to western Europe and has been looking to develop its marketing and distribution activities in the region. The chill in relations between Germany and Russia killed the asset swap deal, which covered BASF businesses with €12 billion ($14.6 billion) in sales. Sanctions imposed on Russia over its behavior in Ukraine place restrictions on new energy projects and equipment, and also prevent Russian companies borrowing in Western financial markets.
The cancellation has forced the German chemicals company to restate its accounts for last year, and to mark down profits in 2014, at a combined cost of €324 million ($395 million). BASF and Gazprom have worked together for more than 20 years, and will continue to operate the gas trading business as a joint venture. Other big energy deals have already fallen victim to the deterioration in relations with the West. President Vladimir Putin announced earlier this month that Gazprom had scrapped plans to build a new $40 billion gas pipeline to southern Europe, bypassing Ukraine. With Russia unable to raise new finance from European and U.S. investors, Gazprom may have struggled to fund construction of the pipeline. Some EU states were also nervous that the project would make them even more dependent on Russian gas at a time when they’re looking to diversify their energy supplies.

But no, that’s not deflation … After all, it’s all about semantics.
• ECB’s Constancio Sees Negative Inflation Rate In Months Ahead (Reuters)
European Central Bank Vice President Vitor Constancio said in a magazine interview he expected the euro zone inflation rate to turn negative in the coming months but that if this was just a temporary phenomenon, he did not see a risk of deflation. Annual inflation in the euro zone slowed to 0.3% in November as energy prices fell, putting it well below the ECB’s target for inflation close to but just below 2%. In early December the ECB had forecast 0.7% inflation for 2015 but Constancio told Germany’s WirtschaftsWoche oil prices had fallen by an extra 15% since then and that, while this should support growth and so drive up inflation in the longer term, it created a tricky situation in the short-term.
“We now expect a negative inflation rate in the coming months and that is something that every central bank has to look at very closely,” Constancio was quoted as saying in an interview due to be published on Monday. But he said that several months of negative inflation would not translate into deflation: “You’d need negative inflation rates over a longer period for that. If it’s just a temporary phenomenon, I don’t see a danger.” Constancio said the euro zone was not in deflation and there was also not a risk of this for every country in the single currency bloc. He added that rising productivity in countries like Ireland and Spain could, for example, create scope for wage rises, which would counter deflation dangers.

“.. while the social democrats think big, Italy’s rightwing parties are declaring the whole thing unaffordable. Not just the Olympics, but the foreign wars, what’s left of the foreign aid budget and, most pressingly, the euro.”
• For Rome, All Roads Seem To Lead Away From A Single Currency (Observer)
When Italian prime minister Matteo Renzi confirmed last week that Rome would enter a bid to host the 2024 summer Olympic Games, it was a moment that divided the nation. How could the country afford the £10bn, or even £20bn-plus bill to stage the Olympics when the Italian economy has failed to grow in every quarter since 2011 and the national income is the same as it was in 1997? Renzi dismissed his critics, saying: “Our country too often seems hesitant. It’s unacceptable not to try… or to renounce playing the game.” What he meant was that Italy is a premiership team and should therefore be prepared to compete with the best. Yet while the social democrats think big, Italy’s rightwing parties are declaring the whole thing unaffordable. Not just the Olympics, but the foreign wars, what’s left of the foreign aid budget and, most pressingly, the euro. Silvio Berlusconi’s Forza Italia, Beppe Grillo’s Five Star Movement and the Northern League all agree that Italy cannot hope to compete with northern European rivals inside the same currency zone.
Between them they represent almost 45% of the Italian electorate, rising to almost 50% once Eurosceptic parties are included. These three parties hate each other almost as much as they loathe Renzi’s Democrats. But, still, this discontent with the euro, and the almost intuitive understanding of the single currency’s ability to set Italian workers against German and Austrian rivals with only one obvious loser – Rome – illustrates how the euro project is crumbling. Only a couple of years ago, Italy would have stood aside from all the hand-wringing about the euro. Middle-income Italians were solidly in favour of a project of which they saw themselves as founding members. And more importantly, their vast savings and property values were in euros. Any attempt to withdraw would almost certainly entail a devaluation of 50% or more and the destruction of 50 years of scrimping.
Roberto D’Alimonte, professor of politics at Rome’s Luiss university, says growing discontent with the euro is still an emotional response to domestic austerity cuts and could not be translated into an outright vote against the euro. He says a referendum calling for a withdrawal would be lost. So for the time being, a splintered rightwing opposition and an incoherent response to the euro allow Renzi to forge ahead. But D’Alimonte warns that the resurgence of the Northern League is a sign of growing discontent. An opinion poll earlier this month gave the 41-year-old party leader, Matteo Salvini, a personal popularity of 26% and his party 10%. D’Alimonte says these polls underestimate the powerful surge enjoyed over recent months by the Northern League, which has also reached out to discontented southerners. Salvini calls the euro a “criminal currency” and wants to demolish a Brussels consensus he says is strangling European politics.
The successor to party founder Umberto Bossi, who was brought down by a financial scandal, Salvini is also an admirer of Vladimir Putin and friend of French National Front leader Marine Le Pen. To the shock of many on the left, he has overtaken Grillo as the cheerleader for an Italy that accepts demotion to the second division. “The Europe of today cannot be reformed, in my opinion,” he told the Foreign Press Association in Rome. “There’s nothing to be reformed in Brussels. It’s run by a group of people who hate the Italian people and economy in particular.” When asked whether he worried about spooking the financial markets with his radical plans to withdraw from the euro, impose a single flat tax rate of 15% and deport illegal immigrants, he said: “I don’t want to reassure anyone at all.”

Those numbers should be much higher.
• Poll Shows Majority Of Brits Want To Quit EU (RT)
Among the six European states participating in the poll questioning EU membership, the British appeared most certain of all that they want to leave the union with only 37% against breaking ties. The French OpinionWay poll showed that 42% of British respondents want to leave the EU, while 37% are for staying in the union and the rest 21% are not sure of the answer, Le Figaro reported on Friday. Britain’s PM Davis Cameron promised last year to hold a vote on Europe in a referendum by the end of 2017 if the Conservatives win the next general election. Cameron has been under domestic pressure from politicians to quit the EU sooner. The second place among the six European states surveyed was taken by the Netherlands with 39% for breaking the relationship with EU and 41% of responders against leaving European partnership. The least eager ones to say goodbye were the Spanish with 67% against the notion and only 17% for EU exit.
Among the 3,500 respondents, the French were 22% for and 55 against, while the Germans were 22% and 64 respectively. Most of Italy’s respondents said they would stay in the union – 58%, only 30 were against. Amid the ongoing Eurozone crisis that started in 2009, the member states have cut government spending to try and reduce their budget deficits. EU member countries pushed by austerity policing Germany have been struggling to come out of the crisis. Last week German Chancellor Angela Merkel criticized France and Italy for taking insufficient reforms to curb spending. “The European Commission has drawn up a calendar according to which France and Italy are due to present additional measures” Merkel said to newspaper Die Welt adding that she agrees with the commission. In November the EU commission approved two countries’ budgets which guaranteed that they would impose more austerity measures in 2015.

And many more than MarketWatch lets on.
• Retirement Index Shows Many Still At Risk (MarketWatch)
Every three years, with the release of the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances (SCF), we update our National Retirement Risk Index (NRRI). The NRRI shows the share of working-age households who are “at risk” of being unable to maintain their pre-retirement standard of living in retirement. Constructing the NRRI involves three steps: 1) projecting a replacement rate—retirement income as a share of pre-retirement income—for each member of the SCF’s nationally representative sample of U.S. households; 2) constructing a target replacement rate that would allow each household to maintain its pre-retirement standard of living in retirement; and 3) comparing the projected and target replacement rates to find the percentage of households “at risk.” The NRRI was originally created using the 2004 SCF and has been updated with the release of each subsequent survey.
Our expectation was that the NRRI would improve sharply in 2013; it certainly felt like a better year than 2010. The stock market was up, and housing values were beginning to recover. But the ratio of wealth to income had not bounced back from the financial crisis, more households would face a higher Social Security Full Retirement Age, and the government had tightened up on the percentage of housing equity that borrowers could extract through a reverse mortgage. On balance, then, the Index level for 2013 was 52%, only slightly better than the 53% reported for 2010. This result means that more than half of today’s households will not have enough retirement income to maintain their pre-retirement standard of living, even if they work to age 65—which is above the current average retirement age—and annuitize all their financial assets, including the receipts from a reverse mortgage on their homes. The NRRI clearly indicates that many Americans need to save more and/or work longer.

Strange use of the word ‘native’.
• Despite Job Growth, Native US Employment Still Below 2007 (HA)
Additional findings:
• The BLS reports that 23.1 million adult (16-plus) immigrants (legal and illegal) were working in November 2007 and 25.1 million were working in November of this year — a two million increase. For natives, 124.01 million were working in November 2007 compared to 122.56 million in November 2014 — a 1.46 million decrease.
• Thus BLS data indicates that what employment growth there has been since 2007 has all gone to immigrants, even though natives accounted for 69% of the growth in the +16 population.
• The number of immigrants working returned to pre-recession levels by the middle of 2012, and has continued to climb. But the number of natives working remains almost 1.5 million below the November 2007 level.
• However, even as job growth has increased in the last two years ( November 2012 to November 2014), 45% of employment growth has still gone to immigrants, though they comprise only 17% of the labor force.
• The number of natives officially unemployed (looking for work in the prior four weeks) has declined in recent years. But the number of natives not in the labor force (neither working nor looking for work) continues to grow.
• The number of adult natives 16-plus not in the labor force actually increased by 693,000 over the last year, November 2013 to November of 2014.
• Compared to November 2007, the number of adult natives not in the labor force is 11.1 million larger in November of this year.
• In total, there were 79.1 million adult natives and 13.5 million adult immigrants not in the labor force in November 2014. There were an additional 8.6 million immigrant and native adults officially unemployed.
• The percentage of adult natives in the labor force (the participation rate) did not improve at all in the last year.
• All of the information in BLS Table A-7 indicates there is no labor shortage in the United States, even as many members of Congress and the president continue to support efforts to increase the level of immigration, such as Senate bill S.744 that passed in the Senate last year. This bill would have roughly doubled the number of immigrants allowed into the country from one million annually to two million.
• It will take many years of sustained job growth just to absorb the enormous number of people, primarily native-born, who are currently not working and return the country to the labor force participation rate of 2007. If we continue to allow in new immigration at the current pace or choose to increase the immigration level, it will be even more difficult for the native-born to make back the ground lost in the labor market.

Problem is: who’s going to buy all that stuff?
• Go West, Young Han (Asia Times)
November 18, 2014: it’s a day that should live forever in history. On that day, in the city of Yiwu in China’s Zhejiang province, 300 kilometers south of Shanghai, the first train carrying 82 containers of export goods weighing more than 1,000 tons left a massive warehouse complex heading for Madrid. It arrived on December 9. Welcome to the new trans-Eurasia choo-choo train. At over 13,000 kilometers, it will regularly traverse the longest freight train route in the world, 40% farther than the legendary Trans-Siberian Railway. Its cargo will cross China from East to West, then Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Poland, Germany, France, and finally Spain. You may not have the faintest idea where Yiwu is, but businessmen plying their trades across Eurasia, especially from the Arab world, are already hooked on the city “where amazing happens!” We’re talking about the largest wholesale center for small-sized consumer goods – from clothes to toys – possibly anywhere on Earth.
The Yiwu-Madrid route across Eurasia represents the beginning of a set of game-changing developments. It will be an efficient logistics channel of incredible length. It will represent geopolitics with a human touch, knitting together small traders and huge markets across a vast landmass. It’s already a graphic example of Eurasian integration on the go. And most of all, it’s the first building block on China’s “New Silk Road”, conceivably the project of the new century and undoubtedly the greatest trade story in the world for the next decade. Go west, young Han. One day, if everything happens according to plan (and according to the dreams of China’s leaders), all this will be yours – via high-speed rail, no less. The trip from China to Europe will be a two-day affair, not the 21 days of the present moment. In fact, as that freight train left Yiwu, the D8602 bullet train was leaving Urumqi in Xinjiang Province, heading for Hami in China’s far west.
That’s the first high-speed railway built in Xinjiang, and more like it will be coming soon across China at what is likely to prove dizzying speed. Today, 90% of the global container trade still travels by ocean, and that’s what Beijing plans to change. Its embryonic, still relatively slow New Silk Road represents its first breakthrough in what is bound to be an overland trans-continental container trade revolution. And with it will go a basket of future “win-win” deals, including lower transportation costs, the expansion of Chinese construction companies ever further into the Central Asian “stans”, as well as into Europe, an easier and faster way to move uranium and rare metals from Central Asia elsewhere, and the opening of myriad new markets harboring hundreds of millions of people. So if Washington is intent on “pivoting to Asia,” China has its own plan in mind. Think of it as a pirouette to Europe across Eurasia.

What did it say, exactly?
• The Fed’s Too Clever By Half (Guy Haselmann, Scotiabank)
Yesterday I received an email from a well-known hedge fund manager which in its entirety read as follows: “At the end of the day, the Fed is confused and confusing, so if you spend too much time addressing their comments you end up confusing as well”. In this light, I will detail one observation in this note that leaves me to conclude that the post-FOMC market reaction is farcical. Bear with me while I explain. The FOMC meeting was slightly hawkish for two simple reasons.
1) The Fed slightly moved forward its time frame for the first rate hike to the April-June time frame when Yellen stated, “It is unlikely the Federal Open Market Committee will raise rates for at least the next couple of meetings”. This statement is indeed wishy-washy enough as to allow the Fed flexibility around the comment; nonetheless, the center point for ‘lift-off’ was moved forward.
2) Yellen said the drop in the price of oil would have a transitory effect on inflation and was seen as “tax cut” for the consumer and businesses.
These were the only new pieces of information that emerged from the meeting. How would a day-trader have reacted in normal markets? The US dollar would have risen. Oil would have fallen despite the rise in the dollar. The front end of the Treasury market would have dropped (i.e. higher yields). And, equities would have gone down. All of these occurred except for equities which exploded higher in wild grab-fest fashion. Why? The explanation centers around the fact that the Fed left the words “considerable period” in the statement, even though the Fed changed how it used those words. Many headlines read, “Fed kept considerable period”. This is misleading. The FED did NOT say that it “expects to maintain the target range for the federal funds rate for a consider time”. Rather, the Fed kept the original language that it expects to maintain the target…..for a considerable time following the end of its asset purchase program in October. There is a big difference between the two.
Why make it backward looking? Using the statement in this manner is no different than saying, ‘we still believe what we said at the last meeting’. The markets already knew the Fed expected rates to be maintained after the end of QE, but what about its assessment from today forward? They actually even changed how the words “considerable time” were used to make them completely meaningless. They wanted to emphasize the word “patient” (even though the market already knew it would be patient). In order to keep the “considerable time” words, the FOMC said its patience is consistent with that earlier statement of “consider time”. If they did not do this in order to purposefully make sure those exact words were in the statement, then the entire sentence is completely meaningless.

Women and children first, Cameron’s favorite victims.
• Women To Take Brunt Of UK Welfare Cuts (RT)
New analysis has shown that women will suffer the most from a freeze in tax credits and benefits that the Chancellor, George Osborne, has said will be introduced if the Tories win the general election. Labour commissioned the research from the House of Commons Library after Osborne announced in September that he would save £3 billion a year by freezing working age benefits, which Labour say would hit 10 million households. Labour has consistently said that freezes and cuts to working age benefits hit women the hardest as large numbers of women are in part time work and because of child care they have to rely more on tax credits.
The analysis showed that Osborne’s plan would save up to £3.2 billion by 2018 and that £2.4 billion of these savings will be provided by women compared to just £800 million by men. “These figures show how, once again, women will bear the brunt of David Cameron’s and George Osborne’s choices. This follows four years of budgets, which have taken six times more from women than men – even though women earn less than men,” said the Labour shadow chancellor, Ed Balls. Balls said that 3 million working people will be worse off because of the proposed cut in tax credits; in reality the freeze will cost a one-breadwinner family £500 a year. Labour is pushing hard to convince voters that their way of dealing with the deficit is fairer and less damaging than the Tories.
They have said consistently that the deficit must be tackled but not in a way that hits the working poor. They have also said that the wealthy must do more and have said the 50p higher rate of income tax would be restored if they win the election. Labour’s announcement comes after a report compiled in September that called on the government to produce a “plan F” to tackle the deficit after it found that women were bearing a disproportionate amount of the burden. The Women’s Budget Group (WBG) found that single parents and single pensioners had lost the most from cuts that were being made to benefits and public services.

Be an asshole.
• How To Get Ahead At Goldman Sachs (Jim Armitage)
The Christmas break approaches but a select handful of Goldman Sachs rainmakers are counting down the clock to New Year’s Day – and a life of prosperity of which they only dared to dream. For these are the Goldmanites who have just been told they have made the grade as partners – a near-Olympian status that they take on from 1 January. There are 78 of them this year – 78 of the brightest, most ambitious and most driven men and women in the financial world. Goldman’s partnership-selection process is the stuff of legend in the City and on Wall Street. Once every two years, a pool of potentials is selected, then the candidates are evaluated by every partner with whom they have worked around the world in a process known as “crossruffing” – named after a cunning cardplayer’s move in bridge. The evaluations are, of course, completely confidential. Partnership selection is one of the secret ingredients that give Goldman its edge – that and paying the biggest bonuses on the block, of course.
As far as I’m aware, details of the testimonials from partners about their candidates have never been seen outside the firm. So it was quite a rarity to unearth an internal note of one the other week. It’s from a few years back – the 2008 partnership selection to be precise – but the process has remained the same for decades. So thrusting young Goldman executives aspiring to make the grade like CEO Lloyd Blankfein did all those years ago, read on. The bank stresses that selections are made according to candidates’ leadership qualities, teamwork, appreciation of “the significance of clients” – the usual stuff. But the testimonial memo makes the core message clear: this guy is great because he has an unnerving ability to make money for Goldman Sachs. Big money. And he makes this cash off the backs of the pension funds of the likes of you and me.
The banker, who is a well-known figure in his niche of the City, joined Goldman in the late 1990s, going on to be promoted to work in various divisions along the way. “Notable transactions”, the testimonial memo says, included making a killing (my words, not theirs) in helping to reorganise the pension-fund investments of WH Smith and Rolls-Royce not long before the global financial crisis hit. In the case of WH Smith, the memo says, he helped switch its pension pot from being invested in “cash equity and bonds” to “almost 100% synthetics” – derivatives contracts mainly of the type known as swaps. The trade was aimed at making the pension fund’s value less prone to being boosted or slashed by the vagaries of the financial markets. At the time, the deal was pretty famous – “innovative” was how pension fund trustees put it. It was certainly an innovation in the amount of money our banker helped Goldman make arranging the trade: “a total P&L [profit] exceeding $70m”, the memo says.

The Citi-written legislation passed this week.
• Derivatives And Mass Financial Destruction (Alasdair Macleod)
Globally systemically important banks (G-SIBs in the language of the Financial Stability Board) are to be bailed-in if they fail, moving the cost from governments to the depositors, bondholders and shareholders. There are exceptions to this rule, principally, small depositors who are protected by government schemes, and also derivatives, so the bail-in is partial and bail-out in these respects still applies. With oil prices having halved in the last six months, together with the attendant currency destabilisation, there have been significant transfers of value through derivative positions, so large that financial instability may result. Derivatives are important, because their gross nominal value amounted to $691 trillion at the end of last June, about nine times the global GDP. Furthermore, the vast bulk of them have G-SIBs as counterparties.
The concentration of derivative business in the G-SIBs is readily apparent in the US, where the top 25 holding companies (banks and their affiliated businesses) held a notional $305.2 trillion of derivatives, of which just five banks held 95% between them. In the event of just one of these G-SIBs failing, the dominoes of counterparty risk would probably all topple, wiping out the financial system because of this ownership concentration. To prevent this happening two important amendments have been introduced. Firstly ISDA, the body that standardises over-the-counter (OTC) derivative contracts, recently inserted an amendment so that if a counterparty to an OTC derivative contract fails, a time delay of 48 hours is introduced to enable the regulators to intervene with a solution. And secondly, derivatives, along with insured deposits, are to be classified as “excluded liabilities” by the regulators in the event of a bail-in.
This means a government that is responsible for a G-SIB’s banking license has no alternative but to take on the liability through its central bank. If it is only one G-SIB in trouble, for example due to the activities of a rogue trader, one could see the G-SIB being returned to the market in due course, recapitalised but with contractual relationships in the OTC markets intact. If, on the other hand, there is a wider systemic problem, such as instability in a major commodity market like energy, and if this instability is transmitted to other sectors via currency, credit and stock markets, a number of G-SIBs could be threatened with insolvency, both through their lending business and also through derivative exposure. In this case you can forget bail-ins: there would have to be a coordinated approach between central banks in multiple jurisdictions to contain systemic problems. But either way, governments will have to stand as counterparty of last resort.

Stockman on that same legislation.
• David Stockman Interview: The Case For Super Glass-Steagall (Gordon T. Long)

This should resound with many of you.
• There Is Hope In Understanding A Great Economic Collapse Is Coming (Snyder)
If you were about to take a final exam, would you have more hope or more fear if you didn’t understand any of the questions and you had not prepared for the test at all? I think that virtually all of us have had dreams where we show up for an exam that we have not studied for. Those dreams can be pretty terrifying. And of course if you were ever in such a situation in real life, you probably did very, very poorly on that test. The reason I have brought up this hypothetical is to make a point. My point is that there is hope in understanding what is ahead of us, and there is hope in getting prepared. Since I started The Economic Collapse Blog back in 2009, there have always been a few people that have accused me of spreading fear.
That frustrates me, because what I am actually doing is the exact opposite of that. When a hurricane is approaching, is it “spreading fear” to tell people to board up their windows? Of course not. In fact, you just might save someone’s life. Or if you were walking down the street one day and you saw someone that wasn’t looking and was about to step out into the road in front of a bus, what would the rational thing to do be? Anyone that has any sense of compassion would yell out and warn that other person to stay back. Yes, that other individual may be startled for a moment, but in the end you will be thanked warmly for saving that person from major injury or worse. Well, as a nation we are about to be slammed by the hardest times that any of us have ever experienced.
If we care about those around us, we should be sounding the alarm. Since 2009, I have published 1,211 articles on the coming economic collapse on my website. Some people assume that I must be filled with worry, bitterness and fear because I am constantly dealing with such deeply disturbing issues. But that is not the case at all. There is nothing that I lose sleep over, and I don’t spend my time worrying about anything. Yes, my analysis of the global financial system has completely convinced me that an absolutely horrific economic collapse is in our future. But understanding what is happening helps me to calmly make plans for the years ahead, and working hard to prepare for what is coming gives me hope that my family and I will be able to weather the storm.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle December 21 2014