
Arthur Rothstein Oregon or Bust, family fleeing South Dakota drought Jul 1936



Why should it? Just regulate the heebees out of them or close them down.
• Banking’s Toxic Culture ‘Will Take A Generation To Clean Up’ (Guardian)
Overhauling the broken culture of high street banking will take a generation to achieve, according to a report that found UK banks have received 20m customer complaints since the financial crisis. The report, by the thinktank New City Agenda, calculated that in the last 15 years the retail operations of banks had incurred £38.5m in fines and redress for mistreatment of customers. Andre Spicer, a professor at Cass Business School and the report’s lead author, said: “Most people we spoke to told us that real change will take at least five years. “There was some uncertainty as to how these changes were being translated into good practice at the customer coalface. Many culture change initiatives are fragile, and their success is not ensured. It’s clear to us that much work still needs to be done.”
The report concluded that it will take a generation to end a sales culture exposed by the 2008 crisis. It said UK banks did not address cultural change until the eruption of the Libor scandal in 2012, having failed to act after the emergence of mis-selling debacles such as the payment protection insurance scandal. “A toxic culture, decades in the making, will take a generation to clean up,” said the founders of New City Agenda, who are Labour peer Lord McFall, Conservative MP David Davis, and Liberal Democrat peer Lord Sharkey. They added: “Some frontline staff told us they still feel under significant pressure to sell. Complaints continue to rise and trust remains extremely low. Most of the people we talked to believed that real change, and as a consequence the better treatment of customers, will take some time to achieve.”

Will they ever stop using the word ‘unexpectedly’? It’s certainly a favorite over at Bloomberg, and not just there.
• Consumer Confidence in US Unexpectedly Dropped in November (Bloomberg)
Consumer confidence unexpectedly declined in November to a five-month low as Americans became less upbeat about the economy and labor market. The Conference Board’s index fell to 88.7 this month from an October reading of 94.1 that was the strongest since October 2007, the New York-based private research group said today. The figure last month was weaker than the most pessimistic estimate in a Bloomberg survey of economists. The decline this month interrupts a steady pickup in sentiment since the middle of the year and shows attitudes about the economy would benefit from bigger wage gains. While confidence slipped, buying plans picked up, indicating spending will be sustained on the heels of stronger job growth and lower fuel costs.
The drop this month “doesn’t change our view that the trend in consumer confidence is moving upwards,” said David Kelly, chief global strategist at JPMorgan Funds in New York. “Gasoline prices are down, the unemployment rate is down, home prices are gradually rising, and stock prices are certainly rising.” The median forecast of 75 economists in the Bloomberg survey called for a reading of 96, with estimates ranging from 93.5 to 99 after a previously reported October index of 94.5. The Conference Board’s measure averaged 96.8 during the last expansion and 53.7 during the recession that ended in June 2009.

I’m wondering how this squares with that GDP revision.
• Case Shiller Reports “Broad-Based Slowdown For Home Prices” (Zero Hedge)
While the just revised Q3 GDP surprised everyone to the upside, the Case Shiller index for September which was also reported moments ago, showed yet another month of what it called a “Broad-based Slowdown for Home Prices.” The bad news: the 20-City Composite gained 4.9% year-over-year, compared to 5.6% in August. However, this was modestly above the 4.6% expected. However, what was more troubling is that on a sequential basis, the Top 20 Composite MSA posted a modest -0.03% decline, the first sequential drop since February. And from the report itself: “The National Index reported a month-over-month decrease for the first time since November 2013. The Northeast region reported its first negative monthly returns since December 2013 and its worst annual returns since December 2012 due to weaknesses in Washington D.C. and Boston.”
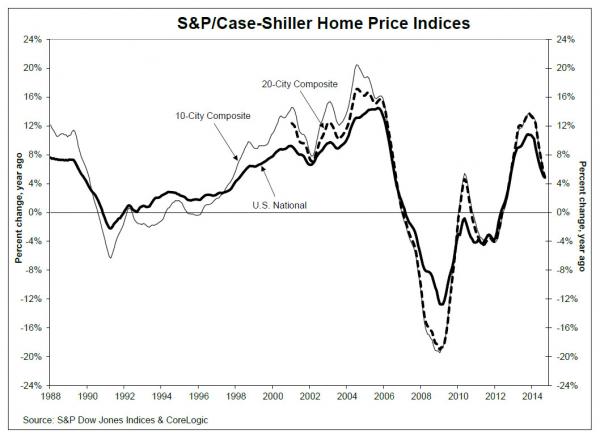

Some useful details.
• BEA Revises 3rd Quarter 2014 US GDP Growth Upwards to 3.89% (CMI)
In their second estimate of the US GDP for the third quarter of 2014, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) reported that the economy was growing at a +3.89% annualized rate, up +0.35% from their first estimate for the 3rd quarter but still down some -0.70% from the 4.59% annualized growth rate registered during the second quarter. The modest improvement in the headline number masks substantial changes in the reported sources of the annualized growth. The previously reported significant inventory draw-down almost vanished completely (dropping to a mere -0.12% impact on the headline number). Improving fixed investments added +0.23% to the headline, with nearly all of that improvement from spending for commercial equipment. Consumer spending for goods was also reported to be growing 0.27% in this report, while consumer spending for services was essentially unchanged (+0.02%).
Offsetting those upside revisions was a significant erosion in the previously reported export growth, which subtracted -0.38% from the headline. The contribution from imports in the headline number also weakened, taking the annualized growth down another -0.17%. Governmental spending was also revised down slightly, knocking another -0.07% from the headline. Nearly all of that downward revision to governmental spending was from reduced state and local investment in infrastructure. Despite the increased consumer spending, households actually took a disposable income hit in this revision – losing $146 in annualized per capita disposable income (now reported to be $37,525 per annum). This is down $344 per year from the 4th quarter of 2012. The spending growth reported above came exclusively from reduced household savings, which dropped a full 0.5% in this report.
As mentioned last month, softening energy prices play a major role in this report, since during the 3rd quarter dollar-based energy prices were plunging (and have continued their dive since). US “at the pump” gasoline prices fell from $3.68 per gallon to $3.32 during the quarter, a 9.8% quarter-to-quarter decline and a -33.8% annualized rate – pushing most consumer oriented inflation indexes into negative territory. During the third quarter (i.e., from July through September) the seasonally adjusted CPI-U index published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) was actually mildly dis-inflationary at a -0.10% (annualized) rate, and the price index reported by the Billion Prices Project (BPP — which arguably reflected the real experiences of American households) was slightly more dis-inflationary at -0.18% (annualized).
Yet for this report the BEA effectively assumed a positive annualized quarterly inflation of 1.40%. Over reported inflation will result in a more pessimistic growth data, and if the BEA’s numbers were corrected for inflation using the appropriate BLS CPI-U and PPI indexes the economy would be reported to be growing at a spectacular 5.42% annualized rate. If we were to use just the BPP data to adjust for inflation, the quarter’s growth rate would have been an astounding 5.52% annualized rate.

The smell of volatility on the morning.
• Refinancing Boom Exposing Risks in US Property Bonds (Bloomberg)
A $40 million penalty wasn’t enough to keep the owner of San Francisco’s Parkmerced apartment complex from the chance to lock in record-low interest rates and take advantage of the property’s $1.5 billion value. While a landlord willing to pay almost 63 times the average fee to refinance early is a bullish sign for commercial real estate, it’s less so for bond investors facing $295 billion of mortgages that come due during the next three years. That’s because the securities are increasingly tied to the market’s weakest properties, many of them financed during the peak of the real-estate boom in 2007, as the strongest are paid off. More property owners are jumping on a drop in financing costs and loosening terms to pay off their mortgages. That helped shrink the amount of debt maturing before the end of 2017 from $332 billion at the start of 2014, according to Bank of America data.
“If you’re a well-capitalized entity, you’re going to do it,” Richard Hill, a debt analyst at Morgan Stanley, said. That could leave commercial-mortgage bond investors “holding the bag on a bunch of lower-quality loans.” Properties such as skyscrapers, shopping malls, hotels and apartment complexes are attracting investors from sovereign wealth funds to insurance companies as they seek higher-yielding assets amid six years of Federal Reserve policies to hold short-term interest rates near zero. Wall Street banks are on pace to issue $100 billion of securities backed by commercial real estate this year after issuance doubled to $80 billion in 2013, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Sales, which peaked at $232 billion in 2007, are poised to climb to $140 billion in 2015, Credit Suisse Group AG analysts led by Roger Lehman forecast in a Nov. 21 report.
Sales of the securities also are being fueled by rules that will require banks to retain some portion of loans that are sold to investors as securities, according to Morgan Stanley’s Hill. That may increase financing costs when they take effect in 2016. Ray Potter, founder of R3 Funding, a New York-based firm that arranges financing for landlords and investors, said he’s advising clients not to wait to refinance as economists forecast the Fed will raise rates next year for the first time since 2006. There has been a surge in borrowers looking to refinance in the past couple of months, Potter said. “If you like that coupon, lock it in for 10 years,” he said. While the interest rate could dip even lower, it’s not worth the risk because “when it moves higher it moves fast,” he said.

“Japan remains doomed by its demographics and, of course, by its horrible debt.”
• Abe Sales Tax Backfiring With More Debt Not Less (Bloomberg)
What started as a plan to reduce Japan’s debt is turning into a reason to issue more bonds. Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s administration implemented a higher sales tax in April to boost revenue as government liabilities ballooned to 1 quadrillion yen ($8.5 trillion), more than double the nation’s yearly economic output. Consumption plunged and the economy fell into a recession, prompting companies including Mirae Asset Global Investments Co. and High Frequency Economics to predict even more sovereign debt sales to revive growth. “The government’s policies have failed,” Will Tseng, a money manager in Taipei at Mirae Asset, which manages about $62 billion, said in an e-mail Nov. 20. “They’re still issuing more debt and printing more money to try to help the economy. They’re in a really bad cycle.” He said he’s staying away from Japanese bonds.
The cost of protecting Japan’s debt from default surged for eight straight days and the yen tumbled to a seven-year low as Abe called a snap election and delayed plans to further increase the sales tax by 18 months. Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda on Oct. 31 boosted the amount of government bonds he plans to buy to as much as 12 trillion yen a month, a record. Japan will go back to its routine of borrowing more to fund plans to spur growth, said Carl Weinberg, the chief economist at High Frequency Economics in Valhalla, New York. What it needs to do is allow immigration to keep the population from shrinking, he said Nov. 18 on the “Bloomberg Surveillance” radio program. “The population and the economy are contracting, and the debt is growing, and that’s an unsustainable trend,” Weinberg said. “Japan remains doomed by its demographics and, of course, by its horrible debt.”

” .. Kuroda now has a budding mutiny on his hands. Many of his staffers think the central bank has already gone too far to weaken the yen and buy virtually every bond in sight.”
• Japan Is Running Out of Options (Bloomberg)
The New York Times recently lit up the Japanese Twittersphere with a cartoon that was a little too accurate for comfort. In it, a stretcher marked “economy” is loaded into an ambulance with “Abenomics” painted on the side; the vehicle lacks tires and sits atop cinder blocks. Prime Minister Shinzo Abe looks on nervously, holding an IV bag. The image aptly sums up Japan’s failure to gain traction in its push to end deflation. The Bank of Japan’s unprecedented stimulus and Abe’s pro-growth reforms have yet to spur a recovery in inflation and gross domestic product growth, and the country is yet again in recession. Worse, BOJ Governor Haruhiko Kuroda is rapidly running out of weapons in his battle to eradicate Japan’s “deflationary mindset.”
Minutes from the central bank’s Oct. 31 board meeting, at which officials surprised the world by expanding an already massive quantitative-easing program, show that Kuroda now has a budding mutiny on his hands. Many of his staffers think the central bank has already gone too far to weaken the yen and buy virtually every bond in sight. That’s a problem for Kuroda and Abe in two ways.
First, board members warned that the costs of further monetary stimulus outweigh the benefits. We already knew that Kuroda had only won approval for his shock-and-awe announcement by a paper-thin 5-4 margin, and that Takahide Kiuchi dissented when the BOJ boosted bond sales to about $700 billion annually. But the minutes suggest Kuroda came as close to any modern BOJ leader ever has to defeat on a policy move. Cautionary voices like Kiuchi’s worry that the BOJ could be “perceived as effectively financing fiscal deficits.” I’d say it’s too late for that. Of course the BOJ is acting as the Ministry of Finance’s ATM, just as Abe intended when he hired Kuroda. Still, the fact is that Kuroda’s odds of getting away with yet another Friday surprise are nil at best.
Second, maintaining stability in the bond market just got harder. The only way Kuroda can stop 10-year yields – currently 0.44% – from spiking as he tries to generate 2% inflation is by making ever bigger bond purchases. But fellow BOJ board members will be giving Kuroda less latitude to cap market rates. Japan is lucky in one way: Given that more than 90% of public debt is held domestically, Tokyo can the avoid wrath of the “bond vigilantes.” Kuroda further neutralized these activist traders by saying there’s “no limit” to what he can do to make Abenomics work. The fact that so many of his colleagues are skeptical of the policy, however, undermines Kuroda’s credibility. If markets begin to doubt his staying power, yields are sure to rise.

The entire world is a risk to world growth.
• Eurozone ‘Major Risk To World Growth’: OECD (CNBC)
The eurozone poses a serious danger for global growth, with the world’s economy already “in low gear”, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) said on Tuesday. “The euro area is grinding to a standstill and poses a major risk to world growth, as unemployment remains high and inflation persistently far from target,” the OECD said in the 96th edition of its Economic Outlook. The euro zone’s fledgling recovery—which started at the end of 2013—has been a cause for concern over recent months, with gross domestic product (GDP) rising only 0.2% quarter-on-quarter between July and September. Policymakers are also battling with very low inflation and high unemployment—around one-quarter of Spaniards and Greek remain without jobs.
The OECD sees euro zone economic growth at 0.8% this year. This is better than the economic contraction the currency union suffered in 2012 and 2013, but below average growth of 1.1% between 2002 and 2011. By comparison, the OECD expects the world’s economy to expand by 3.3% this year. As with the euro zone, this is an improvement on 2012 and 2013, but below the 2002-2011 average of 3.8%.”A moderate improvement in global growth is expected over the next two years, but with marked divergence across the major economies and large risks and vulnerabilities,” the OECD said.
A euro zone analyst at the Economist Intelligence Unit said the risks to the world economy posed by the euro zone were even larger than the OECD forecast.”The euro zone’s fundamental institutional deficiencies are now exacting a damaging price, by hampering the formulation and implementation of policy responses to the ongoing slump,” said Aengus Collins in a research note emailed after the OECD report.”In addition, the OECD overlooks political risk, which is rising sharply in line with voter disaffection.” Major countries expected to post solid growth include the U.S., which the OECD predicts will expand by 2.2% this year and 3.1% next. China, meanwhile, is seen growing by an impressive 7.3% in 2014, before slowing to 7.1% in 2015.

More interestingly, where will that leave Spanish and Italian bonds?
• Do German Bonds Face Japanification? (CNBC)
The euro zone’s long disinflation has spurred fears it will tumble all the way to Japan-style deflation, with some concerned yields on the continent’s safe-haven bond, the German bund, could remain depressed for the long haul. “While we are still not convinced that the euro zone is the new Japan, despite the many similarities in their economic predicaments, we are increasingly of the view that the 10-year Bund yield will remain exceptionally low for at least the next couple of years,” John Higgins, chief markets economist at Capital Economics, said in a note Wednesday. The 10-year bund is yielding around 0.75%, around all-time lows, compared with the 10-year Japanese government bond (JGB) at around 0.45% after a decades-long downtrend.
Japan’s central bank cut its benchmark interest rate to 0.5% in 1995, a move that pushed the 10-year JGB yield below 1% after three years, Higgins noted. “Investors did not know in 1998 that Japan’s key policy rate would remain near zero for the next 16 years (and counting). But the prospect of it remaining there for the foreseeable future was enough to keep the 10-year yield quite firmly anchored,” he said. “We see no reason why a similar outcome couldn’t happen in Germany,” as the bund yield fell below 1% after the ECB cut its main rate to 0.5% in mid-2013.

” .. new mortgage approvals hit a 17-month low of 37,076 in October. That total was down nearly a quarter from January’s 76-month high of 48,649. It was also down 16% year on year ..”
• UK Housing Market Cools Rapidly (Guardian)
Britain’s housing market is cooling rapidly as a result of tougher Bank of England mortgage market requirements, high prices and the uncertainty caused by the coming general election. The prospect of higher interest rates at some point in 2015 is also dampening demand. Figures from the British Bankers’ Association showed a sharp slowdown in mortgage approvals, while Nationwide building society has reported a drop in lending volumes. The BBA said that new mortgage approvals hit a 17-month low of 37,076 in October. That total was down nearly a quarter from January’s 76-month high of 48,649. It was also down 16% year on year. However, a house price crash is unlikely, according to new forecasts. Halifax’s forecasts for 2015 point to a further rise in values of 3% to 5% next year, despite uncertainty about the general election. Earlier this month Halifax reported that house prices fell during October and recorded their smallest quarterly increase in nearly two years.
The October survey by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors found that buyer inquires shrank for the fourth month running. Half-year results from Nationwide building society added to the gathering evidence of a weakening market, with net lending down by £2bn to £3.6bn in the six months to 30 September – although lending to landlords rose slightly. The society, which reported a doubling in pre-tax profits and higher savings inflows, said part of the reason net lending was down was tougher competition from other major mortgage providers, such as Halifax and Santander. “The BBA data add to now pretty widespread and compelling evidence that the housing market has come well off the boil,” said Howard Archer, an economist at IHS Insight. “The fact that mortgage approvals are substantially below their January peak levels – and falling – after lenders have got to grips with the new mortgage regulations points to an underlying moderation in housing market activity.”

“The Canadian, Australian and New Zealand dollars as well as the Brazilian real, Russian ruble and other emerging economies are all playing this game. Those countries want weaker currencies to offset declining commodity exports ..”
• Commodity Exporters Like Cheaper Currencies (A. Gary Shilling)
The U.S. dollar is strengthening for reasons that go beyond deliberate devaluations of the euro and yen. Major commodity exporters are also purposely pushing down their currencies as commodity prices drop. The Canadian, Australian and New Zealand dollars as well as the Brazilian real, Russian ruble and other emerging economies are all playing this game. Those countries want weaker currencies to offset declining commodity exports. In the past year, the head of the Reserve Bank of Australia has expressed sympathy for a weaker Aussie in view of soft mineral exports and a moderately growing economy.
Recently, the head of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand said that, even with the drop in the New Zealand dollar, the kiwi is at “unjustifiable” levels and isn’t reflecting the weakness in the global commodity market. Earlier, the kiwi was propelled by strong meat and dairy exports to China and robust prices for milk, which have plunged. New Zealand’s economic growth is in jeopardy. The Bank of Canada recently left its benchmark interest rate unchanged at 1% and expects inflation to be near its 2% target. But a decline in energy and other commodity prices has hurt the Canadian economy, which is growing at the same slow 2% rate as the U.S. The commodity bubble in the early 2000s prompted producers of industrial commodities, such as copper, zinc, iron ore and coal, to increase production. New output resulted just in time for the price collapse in the 2007 to 2009 recession.
The subsequent rebound didn’t hold and commodity prices have been falling since early 2011, no doubt due to excess supply of industrial commodities and slower growth in China, the world’s biggest commodity user. The price decreases are also due to sluggish expansions in developed countries and, in the case of agricultural products, good weather and more acreage being planted. So far this year, grain prices are falling, as are industrial commodity prices. Crude oil prices rose until mid-June, but have since dropped 25% and now are the lowest in six years. Spurred by fracking, U.S. oil output is exploding as economic softness in Europe and China and increased conservation have curtailed consumption. Copper, which is used in everything from plumbing fixtures to computers, is dropping in price as supply leaps and demand lags.

“Several months earlier, the stock market had begun to plunge violently. Soon there were layoffs and business closings and the economy was having a tough time getting back in gear.”
• On This Day, 138 Years Ago, The Idea Of QE Was Born (Art Cashin)
On this day in 1876, a group of influential, yet irate, Americans met in Indianapolis. Their primary purpose was to send a message to Washington on how to get the economy moving again. America at the time was going through a difficult and unusual period. Several months earlier, the stock market had begun to plunge violently. Soon there were layoffs and business closings and the economy was having a tough time getting back in gear. And for months now, strange things were happening, the money supply seemed not to be growing, real estate values were stagnant to slipping, and commodity prices were heading lower. (How unusual.)
So this group decided that what was needed was re-inflation (put more money in everyone’s hands, you see). The method they proposed was to issue more and more money. Cynics called them “The Greenback Party”. And on this day, the Greenbacks challenged Washington by running an independent for President of the United States. His name was Peter Cooper. He lost but several associate whackos were elected to Congress. To celebrate stop by the “Printing Press Lounge”. (It’s down the block from the Fed.) Tell the bartender to open the tap and just keep pouring it out till you say stop. Reassure the guy next to you (while you can still talk) that now we have more enlightened people in Washington. Try not to spill your drink if he falls off the stool laughing. There wasn’t much raucous laughter on Wall Street Monday, but the bulls were beaming with smiles as they managed to continue their string of bull runs.

” .. the stimulus policies of the Federal Reserve and other central banks have the power to drive stocks higher. But they will ultimately be self-defeating ..”
• A Bearish Hedge Fund Bets Against the Bulls and Still Profits (NY Times)
The stock market has been rising for years, hitting new highs almost every week. So how is it that one of Wall Street’s most bearish investors can claim to have profited strongly over this period? Universa Investments, a hedge fund founded by Mark Spitznagel, is one of the few firms that is set up with the aim of making money in an economic and financial collapse. In the market turmoil of 2008, Mr. Spitznagel earned large returns. Large pessimistic bets usually lose a lot of money when stocks are rising, as they have ever since 2009. But Universa is saying that its investment strategy has been able to produce consistent gains since then, including a 30% return last year, according to firm materials that were reviewed by The New York Times.
In comparison, the benchmark Standard & Poor’s 500-stock index in 2013 had a return of 32% with dividends reinvested. Insurance policies that pay out after disasters do not produce big returns when the catastrophe fails to occur. But since 2008, some investors have been looking for ways to ride the market higher while having bets in place that will notch up huge gains if the system teeters on the brink once again. At Universa, Mr. Spitznagel’s strategy stems from his skepticism toward government efforts to revive the economy. He acknowledges that the stimulus policies of the Federal Reserve and other central banks have the power to drive stocks higher. But they will ultimately be self-defeating, he contends.
This theory holds that another crash will occur when the Fed stops being able to stoke the economy. Universa’s strategy seeks to profit when confidence in the central banks is strong — and when it evaporates. “The Fed has created a trap in this yield-chasing environment,” Mr. Spitznagel said in an interview, during which he gave an overview of Universa’s approach. “It allows you to be long, but it gets you in position to be short when it’s all over,” he said.

Beggar thy neighbor, oil edition.
• Saudi Arabia Says No One Should Cut Output, Oil Will Stabilize
Saudi Arabia’s oil minister said tumbling crude prices will stabilize and there’s no need for producing nations to cut output. “No one should cut and market will stabilize itself,” Ali Al-Naimi told reporters a day before OPEC meets in Vienna. “Why Saudi Arabia should cut?The U.S. is a big producer too now. Should they cut?” Oil ministers from the 12 nations in the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries meet tomorrow in Vienna to discuss their combined production at a time when prices have fallen 30 percent since June. Crude fell in part on speculation that Saudi Arabia and other OPEC states wouldn’t take the necessary measures to curb a surplus. Venezuela’s Foreign Minister Rafael Ramirez met with officials from Saudi Arabia, Mexico and Russia yesterday. While they agreed to monitor prices, they made no joint commitment to lower their supplies.

It’s not going to happen. They are in too much distress.
• Pre-OPEC Producer Meeting Fails to Deliver Oil Output Cut (Bloomberg)
Nations supplying a third of the world’s oil failed to pledge output cuts after meeting in Vienna today. Russia can withstand prices even lower than they are now, the country’s biggest producer said. Officials from Venezuela, Saudi Arabia, Mexico and Russia said only that they would monitor prices. Crude futures sank to a four-year low in New York. OPEC meets in two days, with analysts split evenly over whether the group will lower output in response to the crash in prices. Crude fell into a bear market this year amid the highest U.S. production in 31 years and speculation that Saudi Arabia and other members of OPEC won’t do enough to curb a surplus. Prices are below what nine of group’s 12 members need to balance their national budgets, data compiled by Bloomberg show.
“All these countries are significantly affected by lower prices and want to see cuts, but it is a big step between having these talks and taking actual coordinated action to achieve this,” Richard Mallinson, geopolitical analyst at Energy Aspects, said by phone today. “The key is going to be what happens amongst OPEC members.” Brent, the global benchmark, fell as much as 2.1% in London, having gained 1% before the four-way meeting concluded. It settled at $78.33 a barrel. West Texas Intermediate sank 2.2% to $74.09, the lowest since Sept. 21, 2010. The discussions didn’t result in any joint commitment to reduce supplies, Rafael Ramirez, Venezuela’s Foreign Minister and representative to OPEC, told reporters after the meeting. All parties said they were worried about the oil price, he said.
“There is an overproduction of oil,” Igor Sechin, Chief Executive of OAO Rosneft, Russia’s largest oil company, said after the meeting. “Supply is exceeding demand, but not critically” and Russia wouldn’t need to cut production immediately even if oil fell below $60 a barrel, he said. Russia, Saudi Arabia, Mexico and Venezuela between them produced 27.8 million barrels a day of oil last year, according to data from BP Plc. Total global output was 86.8 million barrels daily, the oil company’s figures show. OPEC, which meets to discuss output in Vienna on Nov. 27, pumped 30.97 million barrels a day last month, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.

Too many opinions, too many variables.
• The Unbearable Over-Determination Of Oil (Ben Hunt)
You know you’re in trouble when the Fed’s Narrative dominance of all things market-related shows up in the New York Times crossword puzzle, the Saturday uber-hard edition no less. It’s kinda funny, but then again it’s more sad than funny. Not a sign of a market top necessarily, but definitely a sign of a top in the overwhelming belief that central banks and their monetary policies determine market outcomes, what I call the Narrative of Central Bank Omnipotence. There is a real world connected to markets, of course, a world of actual companies selling actual goods and services to actual people. And these real world attributes of good old fashioned economic supply and demand – the fundamentals, let’s call them – matter a great deal. Always have, always will. I don’t think they matter nearly as much during periods of global deleveraging and profound political fragmentation – an observation that holds true whether you’re talking about the 2010’s, the 1930’s, the 1870’s, or the 1470’s – but they do matter.
Unfortunately it’s not as simple as looking at some market outcome – the price of oil declining from $100/bbl to $70/bbl, say – and dividing up the outcome into some percentage of monetary policy-driven causes and some percentage of fundamental-driven causes. These market outcomes are always over-determined, which is a $10 word that means if you added up all of the likely causes and their likely percentage contribution to the outcome you would get a number way above 100%. Are recent oil price declines driven by the rising dollar (a monetary policy-driven cause) or by over-supply and global growth concerns (two fundamental-driven causes)? Answer: yes. I can make a case that either one of these “explanations” on its own can account for the entire $30 move. Put them together and I’ve “explained” the $30 move twice over. That’s not very satisfying or useful, of course, because it doesn’t help me anticipate what’s next.
Should I be basing my risk assessment of global oil prices on an evaluation of monetary policy divergence and what this means for the US dollar? Or should I be basing my assessment on an evaluation of global supply and demand fundamentals? If both, how do I weight these competing explanations so that I don’t end up overweighting both, which (not to get too technical with this stuff) will have the effect of sharply increasing the volatility of my forward projections, even if I’m exactly right in the ratio of the relative contribution of the potential explanatory factors. Here’s the short answer. I can’t.

Note: this is shale gas, not oil. That’s another bubble, and just as big.
• Who Will Wind Up Holding the Bag in the Shale Gas Bubble? (Naked Capitalism)
We’ve been writing off and on about how the sudden fall in gas prices has been expected to put a lot of shale gas development on hold. In fact, quite a few analysts believe that one of the big Saudi aims in refusing to support oil prices was to dent the prospects for competitive energy sources, not just renewables like wind and hydro power, but shale gas. Even though OilPrice reported that US rig count had indeed fallen as oil prices plunged, John Dizard at the Financial Times (hat tip Scott) gives a more intriguing piece of the puzzle: the degree to which production is still chugging along despite it being uneconomical. The oil majors have been criticized for levering up to continue developing when it is cash-flow negative; they are presumably betting that prices will be much higher in short order. But the same thing is happening further down the food chain, among players that don’t begin to have the deep pockets of the industry behemoths: many of them are still in “drill baby, drill” mode. Per Dizard:
Even long-time energy industry people cannot remember an overinvestment cycle lasting as long as the one in unconventional US resources. It is not just the hydrocarbon engineers who have created this bubble; there are the financial engineers who came up with new ways to pay for it.
And while the financial engineers will as always do just fine, lenders are another matter:
By now, though, there is an astonishing amount of debt that continues to build up on the smaller E&P companies’ balance sheets. According to Gavekal, the research group, even before the oil price plunge, aggregate debt-to-equity ratios in the smaller publicly traded energy companies are now at 93%, up from around 70% in 2012 and 2013, and around 50% between 2005 and 2011. This in a highly cyclical industry that used to go through periodic banker-driven shakeouts and even bankruptcies.

John Dizard from last Friday: the debt boom can’t stop without wreaking havoc across the industry.
• US Oil Producers Can’t Kick Drilling Habit (FT)
You would think, what with the recent oil price crash, the people who finance US oil and gas producers would have learnt their lesson. But not yet. For the past several years, and despite the once again widening gap between capital spending and cash flow, Wall Streeters have stepped in like an overindulgent parent to pay for the producers’ drilling habit. “Isn’t he cute!” they exclaim, as an exploration and production boy crashes another budget. “So talented! Did you see how many frac stages he can do now, and how tight his well spacing is?” Of course the exploration and production companies and their lenders have been to expensive accounting therapy sessions, where the concerned Wall Street family, accompanied by the sullen E&P operators, are told that they have to make a really sincere effort to match finding, drilling and completion expenditures to internally generated cash flow.
Everyone promises the accountant that that irresponsible land purchase or midstream commitment was the last mistake. From now on, cash flow break-even. Right. By now, though, there is an astonishing amount of debt that continues to build up on the smaller E&P companies’ balance sheets. According to Gavekal, the research group, even before the oil price plunge, aggregate debt-to-equity ratios in the smaller publicly traded energy companies are now at 93%, up from around 70% in 2012 and 2013, and around 50% between 2005 and 2011. This in a highly cyclical industry that used to go through periodic banker-driven shakeouts and even bankruptcies.
Particularly in the gas and natural gas liquids drilling directed sector, every operator (and their financier) is waiting for every other operator to stop or slow their drilling programmes, so there can be some recovery in the supply-demand balance. I have been hearing a lot of buzz about cutbacks in drilling budgets for 2015, but we will not really know until the companies begin to report in January and February. Then we will find out if they really are cutting back, using their profits on in-the-money hedge programmes to keep their debt under control, and taking impairment charges on properties that did not really pay off.

Nasty report.
• The Environmental Downside of the Shale Boom (NY Times)
Since 2006, when advances in hydraulic fracturing — fracking — and horizontal drilling began unlocking a trove of sweet crude oil in the Bakken shale formation, North Dakota has shed its identity as an agricultural state in decline to become an oil powerhouse second only to Texas. A small state that believes in small government, it took on the oversight of a multibillion-dollar industry with a slender regulatory system built on neighborly trust, verbal warnings and second chances. In recent years, as the boom really exploded, the number of reported spills, leaks, fires and blowouts has soared, with an increase in spillage that outpaces the increase in oil production, an investigation by The New York Times found. Yet, even as the state has hired more oil field inspectors and imposed new regulations, forgiveness remains embedded in the Industrial Commission’s approach to an industry that has given North Dakota the fastest-growing economy and lowest jobless rate in the country. [..]
Continental Resources hardly seems likely to walk away from its 1.2 million leased acres in the Bakken. It has reaped substantial profit from the boom, with $2.8 billion in net income from 2006 through 2013. But the company, which has a former North Dakota governor on its board, has been treated with leniency by the Industrial Commission. From 2006 through August, it reported more spills and environmental incidents (937) and a greater volume of spillage (1.6 million gallons) than any other operator. It spilled more per barrel of oil produced than any of the state’s other major producers. Since 2006, however, the company has paid the Industrial Commission $20,000 out of $222,000 in assessed fines.
Continental said in a written response to questions that it was misleading to compare its spill record with that of other operators because “we are not aware other operators report spills as transparently and proactively as we do.” It said that it had recovered the majority of what it spilled, and that penalty reductions came from providing the Industrial Commission “with precisely the information it needs to enforce its regulations fairly.” What Continental paid Mr. Rohr, the injured driller, is guarded by a confidentiality agreement negotiated after a jury was impaneled for a trial this September. His wife, Winnie, said she wished the trial had gone forward “so the truth could come out, but we just didn’t have enough power to fight them.”

You wish.
• Obama Climate Envoy: Fossil Fuels Will Have To Stay In The Ground (Guardian)
The world’s fossil fuels will “obviously” have to stay in the ground in order to solve global warming, Barack Obama’s climate change envoy said on Monday. In the clearest sign to date the administration sees no long-range future for fossil fuel, the state department climate change envoy, Todd Stern, said the world would have no choice but to forgo developing reserves of oil, coal and gas. The assertion, a week ahead of United Nations climate negotiations in Lima, will be seen as a further indication of Obama’s commitment to climate action, following an historic US-Chinese deal to curb emissions earlier this month. A global deal to fight climate change would necessarily require countries to abandon known reserves of oil, coal and gas, Stern told a forum at the Center for American Progress in Washington.
“It is going to have to be a solution that leaves a lot of fossil fuel assets in the ground,” he said. “We are not going to get rid of fossil fuel overnight but we are not going to solve climate change on the basis of all the fossil fuels that are in the ground are going to have to come out. That’s pretty obvious.” Last week’s historic climate deal between the US and China, and a successful outcome to climate negotiations in Paris next year, would make it increasingly clear to world and business leaders that there would eventually be an expiry date on oil and coal. “Companies and investors all over are going to be starting at some point to be factoring in what the future is longer range for fossil fuel,” Stern said.

Merkel has problems keeping her stance.
• Cracks Form in Berlin Over Russia Stance (Spiegel)
Within the European Union, the interests of the 28 member states are diverging in what are becoming increasingly clear ways. Taking a tough stance against Russia is generally less important to southern Europeans than it is to eastern Europeans. In the past, the German government had sought to serve as a bridge between the two camps. But in Berlin itself these days, significant differences in the assessment of the situation are starting to emerge within the coalition government pairing Merkel’s conservative Christian Democrats and the center-left Social Democrats (SPD). It’s one that pits Christian Democrat leaders like Merkel and Horst Seehofer, who heads the CDU’s Bavarian sister party, the Christian Social Union (CSU), against Foreign Minister Frank-Walter Steinmeier of the SPD and Social Democratic Party boss Sigmar Gabriel, who is the economics minister.
“The greatest danger is that we allow division to be sown between us,” the chancellor said last Monday in Sydney. And it’s certainly true to say that this threat is greater at present than at any other time since the crisis began. Is that what the Russian president has been waiting for? Last week, German Foreign Minister Steinmeier traveled to Moscow to visit with his Russian counterpart Sergey Lavrov. With Steinmeier standing at his side, the Russian foreign minister praised close relations between Germany and Russia. “It’s good my dear Frank-Walter that, despite the numerous rumors of recent days, you hold on to our personal contact.” Steinmeier reciprocated by not publically criticizing contentious issues like Russian weapons deliveries to Ukrainian separatists. Afterwards, Vladimir Putin received him, a rare honor. It was a prime example of just how the Russian strategy works.

Don’t want to be a prick, and I like the man, but so does he a bit.
• Europe Looks ‘Aged And Weary’: Pope Francis (CNBC)
Pope Francis has warned European politicians and policymakers that Europe is becoming less of a protagonist in the world as it looks “aged and weary.” Addressing the European Parliament in Strasbourg on Tuesday, Pope Francis, the spiritual leader of one billion Catholics worldwide, suggested that Europe risks becoming irrelevant. “Europe gives the impression of being aged and weary,feeling less and less a protagonist in a world which frequently looks on itwith aloofness, distrust and even, at times, suspicion…As a grandmother, no longer fertile and lively,” he said. “The great ideas that once inspired Europe…seem to have been replaced by the bureaucratic technicalities of Europe’s institutions.” Speaking at the plenary session of the parliament, he told lawmakers that they had the task of protecting and nurturing Europe’s identity “so that its citizens can experience renewed confidence in the institutions of the (European) Union and its project of peace and friendship that underlies it.”
Pope Francis’ visit to the European Parliament is the first by a pontiff since Pope John Paul II’s visit in 1988. He is also visiting the Council of Europe – the region’s human rights body – later on Tuesday. “I encourage you to work so that Europe rediscovers the best of its health,” he added. The pope also spoke about the importance of education and work. On the question of migration, a hot topic in Europe, Pope Francis said there needed to be a “united response.” “We cannot allow the Mediterranean to become a large graveyard,” he said, referring to the number of migrants who die during their attempts to cross the sea and reach Europe. “Rather than adopting policies that focus on self-interest which increase and feed conflicts, we need to act on the causes (for migration) and not only on the effects,” he added.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle November 26 2014