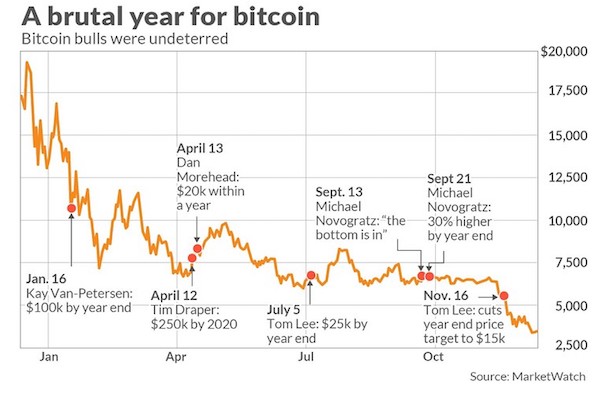
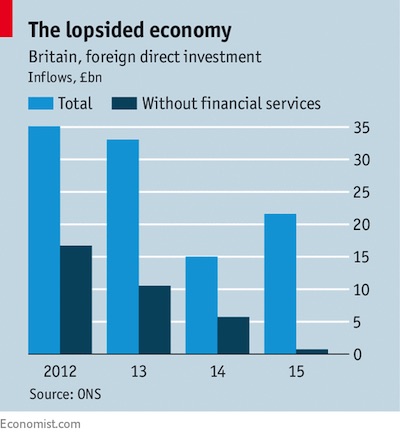
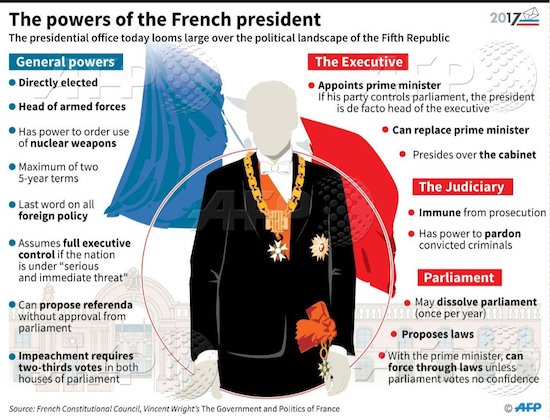
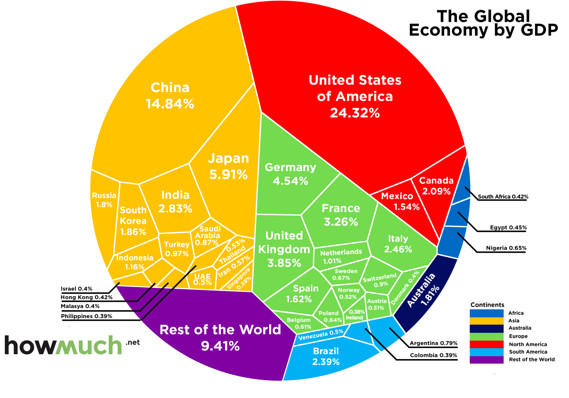
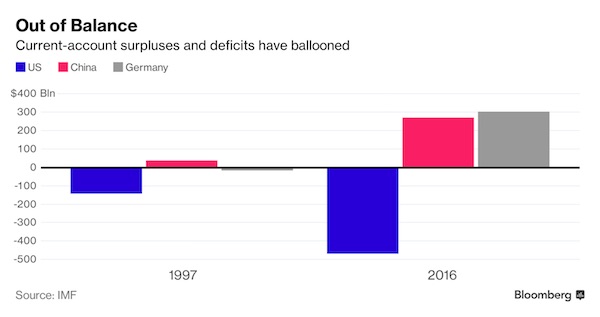
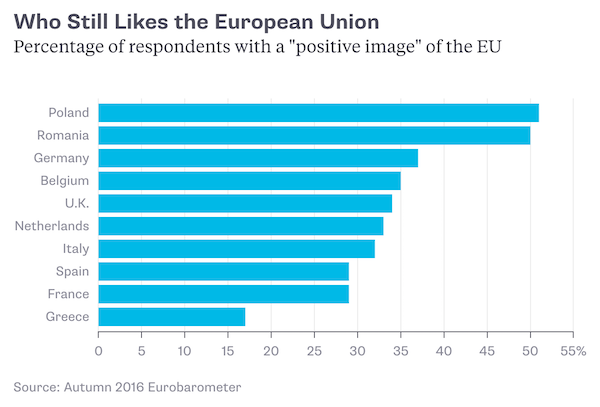
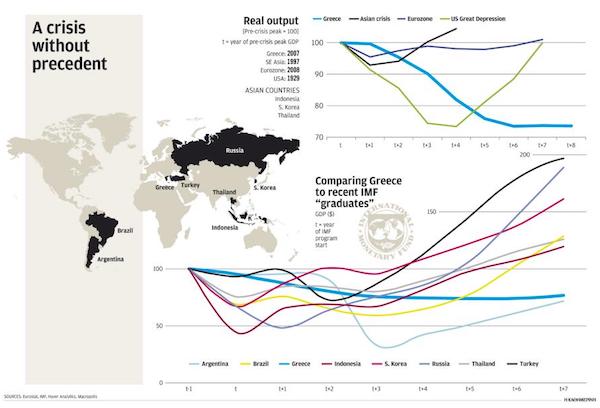
DPC Provision store. Caracas, Venezuela 1905



Wait a minute, just a few days ago we read that consumers keep the US economy going?!
• US Consumer Spending, Trade Data Signal Sluggish Growth (Reuters)
U.S. consumer spending barely rose in February and inflation retreated, suggesting the Federal Reserve could remain cautious about raising interest rates this year even as the labor market rapidly tightens. Monday’s report from the Commerce Department also showed consumer spending in January was not as strong as previously reported. That, together with other data showing a widening in the goods trade deficit in February, indicated economic growth remained sluggish in the first quarter. “It speaks to the weakening in domestic economic momentum at the start of this year, further reinforcing the Fed’s cautious monetary policy bias,” said Millan Mulraine at TD Securities in New York.
Consumer spending edged up 0.1% as households cut back on goods purchases after a downwardly revised 0.1% gain in January. Consumer spending, which accounts for more than two-thirds of U.S. economic activity, was previously reported to have increased 0.5% in January. When adjusted for inflation, consumer spending rose 0.2%. Inflation-adjusted consumer spending for January was revised down to show it unchanged rather than the 0.4% rise that was previously reported. Given labor market strength and cheap gasoline, economists speculated that consumption had been hampered by a massive stock market sell-off at the start of the year which eroded consumer confidence. In a separate report, the Commerce Department said the advance goods trade deficit widened to $62.9 billion in February from $62.2 billion, rising for a fourth straight month as an increase in exports was offset by a gain in imports.
Read more …

You can’t run a functioning democracy in a class system.
• Still The Land Of Opportunity? (BBG)
As the presidential primary season continues, much has been made of the appeal that candidates Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders hold for the angry, disaffected working class. Everyone seems to agree that this group is in trouble, and needs serious help. But which Americans exactly are part of the working class? There is no set definition. You can define class by wealth, but a young worker starting out on Wall Street and earning relatively little is hardly lower-class. You can define it by income, although that will be distorted by local differences in the cost of living, and by age (retirees have little income but usually more wealth). You also can define it by educational status. But perhaps the most important definition is in people’s minds. Gallup periodically asks people to place themselves in one of five classes – upper, upper-middle, middle, working and lower. Here are the results for the five categories:
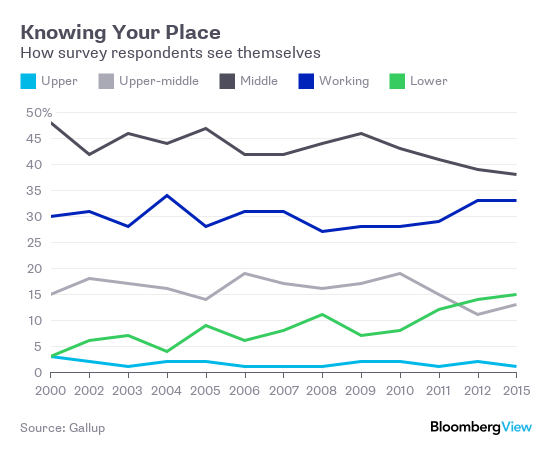
The percentages of Americans who consider themselves working class has stayed relatively stable. But the self-identified middle class has plunged by about 10 percentage points, matched by an even larger increase in the percentage of Americans who label themselves lower class. The self-identified lower class should probably be included in the working class that gets discussed in articles about Trump and Sanders. Why do fewer Americans identify as middle class? One obvious possibility is that the middle class has been spreading out, separating into a well-to-do upper-middle and an expanding working class. The evidence shows that something like this has been happening for decades now. Here is the U.S. Gini coefficient, a broad measure of income inequality:
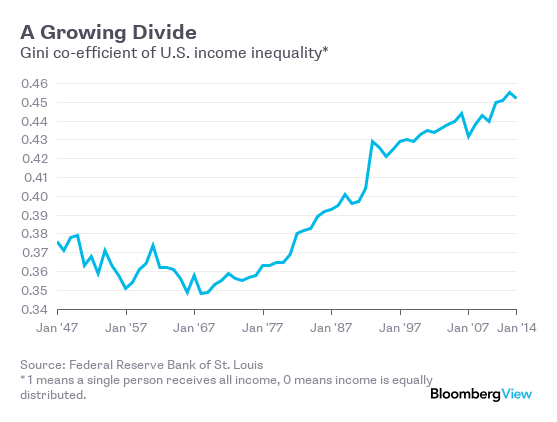
Income inequality has been steadily increasing since 1970, with especially big jumps in the early 1980s and early 1990s. That certainly seems likely to reduce the share of people who feel like they’re in the middle. But we don’t see a divergence – what we really see is a downward drift. Why? Perhaps slow growth has made everyone in the U.S. more pessimistic. Or perhaps inequality itself lowers everyone’s perception of their own class. People making $25,000 might compare themselves to people making $50,000, but people making $400,000 might compare themselves to people making $2 million. One development is that the difference between the working and upper-middle class incomes has widened, but the gap between the upper middle and the rich has absolutely exploded. That could be making everyone more pessimistic about where they stand in the hierarchy.
Read more …

The plunge in demand takes a long time to seep into people’s minds.
• It’s Official: The Oil Surge Was Driven By The Biggest Short-Squeeze Ever (ZH)
Two months ago, just before crude dropped to 13 year lows, we warned oil traders that there is “a constant short squeeze threat” because “oil shorts are at all-time highs”, adding that “we have seen extreme short positioning building up in the oil futures market. The quantity of short positions opened is at an all-time high for Brent, and still high for WTI futures.” We also warned that “a positive surprise could happen quite sharply, as short positions are likely to be squeezed by a profit-taking move. On WTI, the in-the-money short positions are really dominating at the front end of the curve while out-of-the-money long positions are dominating at the long end of the curve: the front end of oil curve could thus be more exposed to some profit-taking.”
It was, and just a few days later, the algos took this warning to heart and, courtesy of the most recurring headline (that of a “farcical” oil production freeze) as a recurring catalyst, unleashed an historic short squeeze. Actually make that a record short squeeze. Wait, that’s impossible: surely it was more than just shorts covering and oil rose because actual longs were piling in, one could say. One would be wrong, and it is now official: as crude soared 50% since Feb. 11, Bloomberg writes, the number of bets on increased prices has barely budged. “Instead, the upward pressure on prices appears to have come from traders cashing out of bearish wagers at an unprecedented pace. The liquidation of short positions during the last seven weeks covered by data from the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission was the largest on record.”
“The rally has come from shorts getting scared out of their positions, and you’re not seeing a lot of money coming in on the long side,” said John Kilduff at Again Capital, a New York hedge fund focused on energy. “It really calls into question the fortitude and staying power of the rally.” The details: “short positions on West Texas Intermediate crude, or bets that prices will fall, have dropped by 131,617 contracts since Feb. 2, the biggest liquidation in CFTC data going back a decade. To close out a bearish position, traders buy back futures and options, putting upward pressure on prices. In the same period, bullish wagers fell by 971. In the past 10 years, there have been only two other seven-week short-covering streaks, CFTC data show. The first started in September 2009 and the second in December 2012. Both were much smaller than the recent one and were accompanied by oil rallies.”
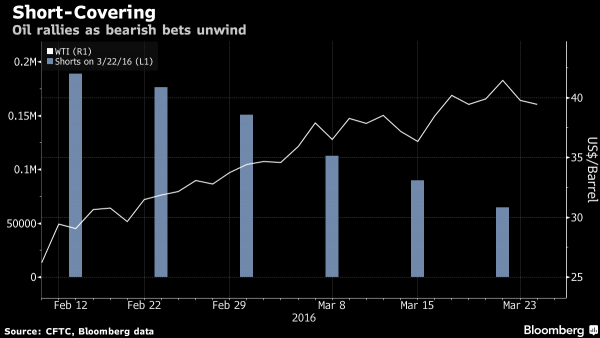
It gets better: as we showed previously, the irony is that as oil futures shorts were squeezed out, ETF longs actually declined instead of growing as absolutely nobody – except those who have to buy-in – believes this quote-unquote rally. Bloomberg notes that the rebound faltered a day after WTI prices touched a four-month high of $41.45 a barrel on March 22, tumbling 4% in New York after government data showed U.S. crude supplies surged the prior week to the highest level since 1930. Perhaps there are no more shorts left to squeeze, in which case watch out to the downside: “When energy markets get loaded to one side of the boat like that, you can have vicious reversals,” said Kilduff. And vice versa.
Read more …

The short-term consequences of highly leveraged long-term investments.
• Barclays Warns Commodities May Slump in ‘Rush for the Exits’ (BBG)
Commodities including oil and copper are at risk of steep declines as recent advances aren’t fully grounded in improved fundamentals, according to Barclays, which warned that prices may tumble as investors rush for the exits. Copper may slump to the low $4,000s a metric ton, from $4,945 in London last week, while oil could fall back to the low $30s a barrel, analyst Kevin Norrish said in a note. The risk for raw materials is that investors seek to liquidate bets on gains quickly and in unison, with potentially highly negative consequences, Norrish wrote in the note entitled “Buffalo Jump,” a term that describes a cliff where Native Americans herded bison to their death. “Investors have been attracted to commodities as one of the best performing assets so far in 2016,” he said in the March 28 report.
“However, in the absence of any concerted fundamental improvements, those returns are unlikely to be repeated in the second quarter, making commodities vulnerable to a wave of investor liquidation.” Commodities are headed for a quarterly advance amid speculation that prices may now be bottoming after they slumped 11% in the final three months of 2015 and 14% in the third quarter. Oil and copper have recovered from multi-year lows seen in the January and February, and Barclays estimated net flows into commodity products totaled more than $20 billion in the two-month period in the strongest start to a year since 2011. “Given that recent price appreciation does not seem to be very well founded in improving fundamentals, and that upward trends may prove difficult to sustain, the risk is growing that any setback will result in a rush for the exits that could again lead commodity prices to overshoot to the downside,” he said.
Investors were increasingly taking short-term bets on raw materials, not the long-term buy-and-hold strategy for diversification and inflation protection that underpinned inflows in the previous decade, he said. In addition, as commodities are among the few assets that have risen in the first quarter, that may make investors keener than usual to close out bets on gains, he said. “Key commodities markets such as oil and copper already face overhangs of excess production capacity and inventories, but also now face another obstacle in the recovery process, that of positioning, which is now approaching bullish extremes,” Norrish said.
Read more …

The backdrop is overproduction.
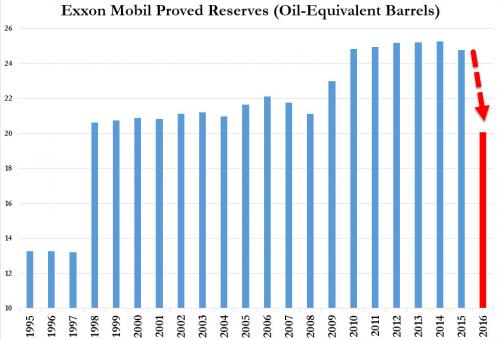
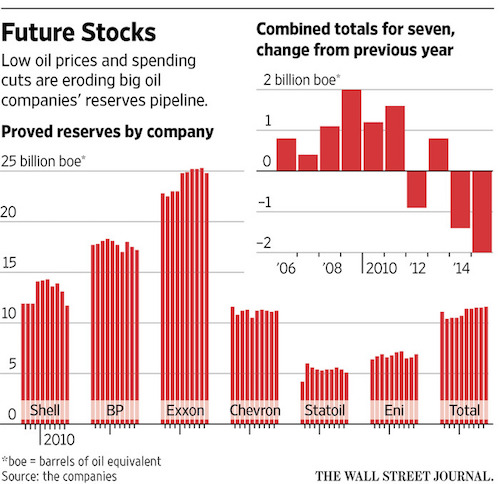
• Oil Firms Slow Exploration to Weather Low-Price Era (WSJ)
The world’s biggest oil companies are draining their petroleum reserves faster than they are replacing them—a symptom of how a deep oil-price decline is reshaping the energy industry’s priorities. In 2015, the seven biggest publicly traded Western energy companies, including Exxon Mobil and Shell, replaced just 75% of the oil and natural gas they pumped, on average, according to a Wall Street Journal analysis of company data. It was the biggest combined drop in inventory that companies have reported in at least a decade. For Exxon, 2015 marked the first time in more than two decades it didn’t fully replace production with new reserves, according to the company. It reported replacing 67% of its 2015 output.
In the past, shrinking reserves could send investors and executives into a panic over a company’s future prospects. These days, with ultralow oil prices, “it becomes less important” to replenish stockpiles, said Luca Bertelli, chief exploration officer at Italian oil producer Eni SpA. Eni has shifted spending away from high-risk, high-reward projects in favor of squeezing more out of fields that are already producing, he said. That shift shows how producers are responding to low prices by pulling back on new exploration in favor of maximizing profits. The risk is that cutting back on new projects now, when prices are low, could lead to shortages and price spikes in the future.
Historically, energy companies spent heavily in the present to find resources for the future—new wells that would replace the barrels they pump every day. When they decide they can extract the oil and gas economically, firms book those resources as proved reserves, untapped inventories to be exploited at a profit down the road. The current oil glut has forced companies to cut spending wherever they can. So they have pulled back on exploratory drilling and spending on new projects. Across the oil sector last year, companies approved just six new developments, according to Morgan Stanley researchers.
Read more …

Caught in a vicious circle.
• Saudi Economy Shows Deepening Signs of Strain (BBG)
The Saudi economy is showing deepening signs of strain under the weight of cheap oil. Saudi consumers withdrew and spent less money in February, according to central bank data released on Monday. M3, one of the broadest measures of money supply, shrank for the first time since at least 2000, when Bloomberg started tracking the data. While the kingdom still has one of the world’s largest foreign-currency reserves, cuts in government spending to shore up public finances are taking a toll on the economy. Growth may slow to 1.5% this year, according to the median estimate of a Bloomberg survey, the slowest pace since at least 2009. Saudi officials have repeatedly said that the nation can weather the slump in oil prices. Cash withdrawals through ATMs fell 8% after expanding for at least the previous five months, central bank data show. Point-of-sale transactions, an indicator of consumer confidence in the economy, dropped to 15.2 billion riyals ($4.1 billion).
And while bank credit to private businesses expanded about 10%, the growth likely reflects short-term borrowing, according to Monica Malik, the chief economist at Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank. “The rise in credit doesn’t indicate business expansion,” she said. “Actually, project activity has fallen substantially. All in all, lower government spending is taking a deepening toll on economic growth, and we can see it in the data.” The government is seeking to plug a budget deficit that reached about 15% of GDP in 2015. Authorities have also raised energy prices. Malik said the contraction of money supply likely reflects the government’s withdrawal of domestic deposits and the drop in net foreign assets, which declined 38 billion riyals. The pace of the drop was the slowest since October as Brent crude prices rebounded during the month. Oil exports make up about 70% of the government’s revenue.
Read more …

What Abenomics ia all about: Leading a horse to water.
• Can Anything Rescue Japan From The Abyss? (Tel.)
“Shunto” season has failed to grip Japan. The country’s annual Spring assault on wages seems to have passed with little more than a whimper this year despite being billed as one of the most anticipated economic events in Japan’s recent history. Translating as “spring wage offensive”, Shunto marks the annual Japanese ritual of wage bargaining between business groups and labour unions. This year’s negotiations have been preceded by months of feverish lobbying from prime minister Shinzo Abe who has urged the country’s business groups to raise wages and help smash Japan’s deflationary mindset once and for all. The issue has become the latest lightning rod in the country’s two decade struggle to ensure long-term economic prosperity. Higher salaries encourage consumption and are vital in raising inflation.
This in turn would help erode some part of Japan’s record 250pc of GDP debt pile. Abe’s calls have been echoed by some of the world’s most renowned economists. Olivier Blanchard, the former chief economist at the IMF and Adam Posen, a former BOE policymaker, have called for an unprecedented 10pc increase in nominal wages in 2016. In the last two years, average wages have risen by just 1pc. “What is needed is a jump-start to a wage-price spiral of the sort feared from the 1970s”, say Posen and Blanchard, who call for a “virtuous cycle” of wage growth, inflation, and lower debt to release Japan from economic stagnancy. But like so many of Tokyo’s radical attempts to extricate itself out of low growth and low inflation, the early signs show that Shunto has already fallen flat.
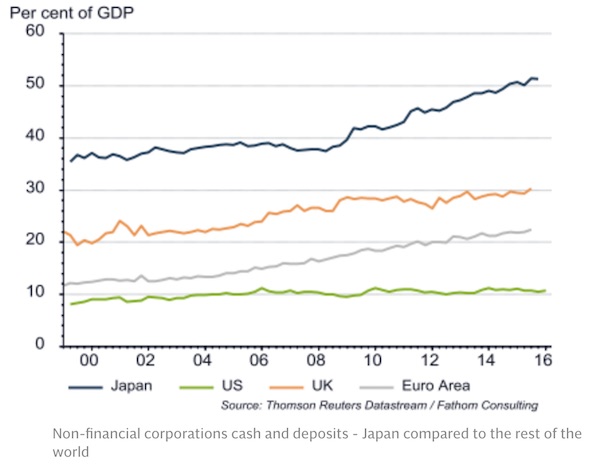
Car-making giant Toyota is reported to have agreed on a wage settlement which will boost its employees’ basic wages by just ¥1500 ($13) a month, despite recording bumper profits of ¥2.17 trillion ($19bn) last year. Overall, the fruits of 2016’s Shunto are set to be more meagre than those of last year. The March round of talks indicate wages hike demands from unions to be around 3.27pc this year, lower than the 3.74pc of 2015, according to analysts at UBS. This indicates the average eventual wage hike will be around 0.3pc in 2016 for the country’s 63.5m workers, down from 0.69pc agreed in 2015, calculate economists at JP Morgan. This reticence to raise wages puzzles economists. Nearly four years on from the start of the government’s Abenomics programme, Japanese companies are sitting on a record cash piles equivalent to nearly 50pc of the country’s entire GDP.
Read more …

The ignorance of the ‘experts’ is stunning.
• ECB’s Gloomy Price Outlook to Be Confirmed Just as QE Expands (BBG)
As Mario Draghi prepares to ramp up debt purchases starting Friday in his biggest assault against euro-area deflation risks, he’s about to get another sense of the magnitude of the challenge. Consumer prices in the currency zone probably fell for a second month in March and the unemployment rate remained in double digits in February, economists forecast in Bloomberg surveys before data this week. Another report is expected to say economic confidence was unchanged in the 19-nation region in March. Policy makers led by the European Central Bank president are expanding monthly asset buying to €80 billion from €60 billion and introducing new measures to lift inflation that hasn’t touched their near-2% goal since 2013.
While the economy is growing, it’s not gaining momentum, and a slow decline in unemployment has failed to spur enough demand to counter falling oil costs and ignite price gains. “The data will confirm that the ECB was right to act, and also may even need to do more in the future,” said Nick Kounis at ABN Amro in Amsterdam. “Underlying inflationary pressures are extremely weak and going in the wrong direction.” Draghi said this month that negative inflation rates may be “unavoidable” in the coming months and it’s “crucial to avoid second-round effects.” That concern prompted the ECB Governing Council to cut its deposit rate on March 10 and add a new series of long-term loans to banks, which will begin in June. The expansion of quantitative easing will start April 1.
“The window of action was now, we had a weak start to the year, and we’re seeing that feeding through to the numbers,” said Anatoli Annenkov at SocGen in London. He doesn’t expect any additional major ECB action this year, as policy makers wait to see how their new actions feed through to the economy. “The key to the ECB for getting inflation back on target is that we do need to see growth really pick up, and the recovery to take it to the next level,” said James Nixon, an economist at Oxford Economics in London. “It’s really the corporate sector that’s just sitting around with its hands in its pockets.”
Read more …

Europe needs normal interest rates, not crazy experiments.
• Europe’s Emerging Bubbles Need Structural Reform (Sinn)
The ECB’s latest policy moves have shocked many observers; while their goal – to prevent deflation and spur growth – is clear, the policies themselves are setting the stage for severe instability. The policies in question include setting the interest rate on the ECB’s main refinancing operations to zero; raising monthly asset purchases by €20bn to €80bn; and pushing the interest rate on money that banks deposit with the ECB further into negative territory, to -0.4%. Moreover, the ECB has launched a series of four targeted longer-term refinancing operations, which also carry negative interest rates. Banks receive up to 0.4% interest on ECB credit that they take themselves, provided they lend it out to private businesses.
These policies are, in essence, the latest in a string of attempts by the ECB to address the fallout of the collapse of the massive bubble that formed in southern Europe in the early years of the euro. This began with the announcement of the euro’s introduction at the 1995 EU Summit in Madrid, which caused interest rates to tumble. The inflationary credit bubble spurred in southern European countries by the persistence of lower interest rates undermined their competitiveness and drove asset and property prices to unsustainably high levels. When the bubble burst, the ECB tried to prevent the excessive prices from returning to equilibrium by using its printing press and promising unlimited coverage to investors. The latest ECB measures are more of the same.
Of course, when the financial crisis erupted in full force in 2008, following the collapse of the US investment bank Lehman Brothers, the ECB’s interventions were justified. But after the global economy started to recover during the latter part of the following year, the ECB’s moves became increasingly problematic, because they enabled countries to evade structural reform and hindered the necessary disinflation in the southern eurozone countries – or even halted it altogether, as in Portugal and Italy. Southern Europe had succumbed to the drug of cheap credit. But when private credit stalled and the symptoms of withdrawal began to appear, the ECB provided replacement drugs. Instead of treating the addiction, it created junkie economies that were unable to function without a fix.
[..] the worst effects of the ECB policy may be yet to come, if the eurozone’s still-sound economies also become credit junkies. There are already some worrying signs of this. Property markets in Austria, Germany, and Luxembourg have practically exploded throughout the crisis, as a result of banks chasing borrowers with offers of loans at near-zero interest rates, regardless of their creditworthiness. In Austria, property prices have risen by nearly half since the Lehman collapse; in Luxembourg, they have risen by almost one-third. Even Germany, Europe’s largest economy, has been experiencing a massive property boom since 2010, with average urban property prices having risen by more than one-third – and by nearly half in large cities. The country is undergoing a construction boom not seen since reunification. Real estate agents have only leftovers on offer.
Read more …

The entire world is affected.
• Investors Are in Denial About China’s Troubles (Balding)
Back in 2009, as China unleashed a massive fiscal stimulus and investment spree in response to the global financial crisis, the rest of the world was all too willing to believe the impossible. Aided by consultant research predicting decades of explosive growth, companies placed huge bets on China and expected to ride the never-ending boom to riches. Amid the gold rush, they bulked up to sell China t-shirts or tons of iron ore. They urged their governments to sign free-trade deals with Beijing. Commodity producers heedlessly expanded capacity, believing that 10% growth would continue indefinitely. Consumer brands rushed to set up flagships in third-tier Chinese cities. Shipping companies scrambled to build new fleets to meet an expected explosion in global trade.
However, as with so many previous bouts of irrational exuberance, this time wasn’t really different. The ruthless rules of supply and demand still applied. And now, the longer that painful decisions are delayed, the harder they’ll become. Commodities firms, in particular, are learning that lesson the hard way. As prices rose with Chinese demand, they made large upfront investments financed by borrowing – often on a 20-year timeline, in the expectation that growth would last and last. Now, with China’s economy slowing and the prices of everything from oil to metals plummeting, the bills are coming due. Major iron ore firms, which had predicted that Chinese steel demand would keep rising until about 2030, are now looking at substantial overinvestment and deteriorating credit. Dairy farmers, who increased their herds with future Chinese consumer demand in mind, are feeling the pinch as milk prices plunge.
After years of ramping up production to fuel China’s expected growth, oil-producing countries from Saudi Arabia to Norway are facing grim decisions about their public finances. Russia is rapidly draining its sovereign wealth fund. Venezuela is pleading with China for loans – on top of the nearly $60 billion already doled out – to stave off collapse. Pundits are warning that the large debt load of U.S. shale-gas and oil producers could pose greater risks than sub-prime lending did a decade ago. No less so than China, the rest of the world needs to face up to some new realities. First, the golden age of Chinese construction is over. There’s now enormous surplus capacity in virtually every industry that requires fixed-asset investment. Companies can no longer rely on the “Beijing put” of new government stimulus to boost growth.
Iron ore producers and copper miners all need to begin a painful process of downsizing and deleveraging – just as China’s bloated state-owned enterprises do. Producers around the world haven’t faced up to the new normal. Second, companies of all stripes have to put in the effort to understand China better. Expectations of double-digit growth, regardless of how poor the performance, have vanished. Luxury brands that once hoped their Beijing flagships would smooth the balance sheets at European headquarters need to recognize that different markets require different strategies, and that shops in China won’t run on autopilot. They need to compete. Third, companies and countries alike need to face up to their own irrational exuberance. Whether it’s failing to diversify, spending recklessly on the back of high prices, or taking on too much debt, fundamental mistakes can’t be blamed on China. Doing so only delays the inevitable.
Read more …

“Dongbei Special Steel’s missed payment comes just four days after the company disclosed that its former chairman, Yang Hua, was found dead by hanging at his home..”
• State-Owned Steelmaker Latest Chinese Company to Miss Bond Payment (BBG)
A state-owned Chinese steelmaker failed to make a 852 million yuan ($131 million) bond payment and expressed uncertainty about meeting a larger bill next week as the slowing economy weighs on debt-laden producers. Dongbei Special Steel, based in the northeastern city of Dalian, said it failed to repay the sum of interest and principal due Monday, according to a statement posted on the Chinamoney website. The company said in a separate statement that it also might not be able to repay 1 billion yuan due April 3 on a 90-day bill because of tight liquidity. The company sold 800 million yuan in one-year bonds last year with a coupon of 6.5%, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Chinese firms are struggling with surging debt burdens as Premier Li Keqiang seeks to weed out zombie corporations amid the country’s worst economic slowdown in a quarter century.
At least a dozen companies have defaulted on bonds over the past two years even as the central bank loosened monetary policy. Nanjing Yurun Foods, a sausage maker, and Zibo Hongda Mining, an iron ore miner, both said they defaulted on notes this month. Dongbei Special Steel’s missed payment comes just four days after the company disclosed that its former chairman, Yang Hua, was found dead by hanging at his home. The company said the death was under investigation by the relevant authority. Other Chinese steelmakers are also facing rising debt pressures. The northern city of Tianjin plans to set up a committee of creditors to help Bohai Steel “get out of trouble,” Caixin reported March 18. Minister of Human Resources Yin Weimin said Feb. 29 that about 1.8 million steel-and-coal workers would be laid off as the country cuts industrial overcapacity and reforms bloated state-owned enterprises.
Read more …

Overpaying for insurance. Now there’s a business model.
• The Credit Card Loophole That Gets Around China’s Capital Curbs (BBG)
More than 800. That’s how many times Hong Kong insurance agent Raymond Ng swiped the credit cards of a mainland Chinese client buying HK$28 million ($3.6 million) worth of insurance policies in the city earlier this month. Dozens, maybe more. That’s how many other agents are using similar tactics as a way around new restrictions on insurance policy purchases by mainlanders that are often used to evade capital controls and get their money out of China, according to interviews with five Hong Kong agents working for Prudential, AIA Group and two smaller insurance companies. “There are always ways around new restrictions,” said Ng, 30, who started selling insurance and investment products to mainland Chinese four years ago, declining to allow his company’s name to be used.
“Chinese customers are accelerating the pace of moving assets outside China, especially through insurance products.” Multiple credit-card swiping to buy insurance products, even hundreds of times, isn’t illegal in Hong Kong, but it allows individuals to exceed limits on insurance purchases by mainlanders meant to control capital outflows from China. The widespread practice shows just how eager Chinese remain to move money abroad amid a weakening economy and expectations of further declines in the yuan, potentially putting pressure on authorities to impose stricter curbs. Since February, Chinese regulators have moved to control the booming business of citizens buying insurance in Hong Kong, first by putting a $5,000 limit on each transaction and later by limiting electronic transfers for such purchases.
Previously there had been no limit on the use of the country’s China UnionPay credit and debit cards for buying the policies, giving individuals wanting to move money abroad a convenient way around the country’s foreign-exchange controls. Multiple card swipes mean the new curbs lose some of their effectiveness. When it imposed the $5,000 limit, the State Administration of Foreign Exchange said it would “closely monitor” cardholders and insurers for cases where cards have been swiped multiple times, though the regulator stopped short of banning multiple card use to purchase individual policies.
Read more …

A great 21st century Great Con story. Which features, what a surprise, China’s shadow banking system.
• How Con Man Used China To Launder Millions (AP)
Gilbert Chikli was rolling in money, stolen from some of the world’s biggest corporations. His targets: Accenture. Disney. American Express. In less than two years, he made off with at least 6.1 million euros from France alone. But he had a problem. He couldn’t spend the money. A tangle of banking rules designed to stop con men like him stood between Chikli and his cash. He needed to find a weak link in the global financial system, a place to make his stolen money appear legitimate. He found it in China. “China has become a universal, international gateway for all manner of scams,” he said in an interview with The Associated Press. “Because China today is a world power, because it doesn’t care about neighboring countries, and because, overall, China is flipping off other countries in a big way.”
A visionary con man, Chikli realized early on — around 2000, the year before China joined the WTO – the potential that lay in the shadows of China’s rise, its entrenched corruption and informal banking channels that date back over 1,000 years. The French-Israeli man told the AP he laundered 90% of his money through China and Hong Kong, slipping it into the region’s great tides of legitimate trade and finance. Today, he is in good company. Criminals around the world have discovered that a good way to liberate their dirty money is to send it to China, which is emerging as an international hub for money laundering, AP has found. Gangs from Israel and Spain, North African cannabis dealers and cartels from Mexico and Colombia are among those using China as a haven where they can safely hide money, clean it, and pump it back into the global financial system, according to police officials, European and U.S. court records and intelligence documents reviewed by AP.
In a regular briefing with reporters Monday, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Hong Lei said the government “places great emphasis” on fighting crimes such as money laundering and is working to expand international cooperation. “China is not, has not been, nor will be in the future a center of global money laundering,” he said. Chikli is widely credited in France with inventing a con that has inspired a generation of copycats. Chikli’s scam, called the fake president or fake CEO scam, has cost companies around the world $1.8 billion in just over two years, according to the FBI. And the damages are rising fast.
Read more …

Getting nervous.
• Central Melbourne Apartment Values Fall 30% (AFR)
Apartments in central Melbourne are being resold at discounts of up to 30% from their original off-plan purchase price, sales data shows. Not all units have fallen in value – some have risen – but analysis of a handful of transactions shows many apartments have failed to hold their value between original purchase and resale, typically a few years later. One property where prices have fallen is 27 Little Collins Street, which includes 171 apartments in a 32-storey tower above a Sheraton-branded hotel, completed by developer Golden Age in July last year. A three-bedroom, two-bathroom apartment occupying 140 square metres and with two car parks sold for $1,565,000 in August, a 28.7% discount on its November 2010 purchase price of $2,195,000.
A two-bedroom unit in the same building fell almost 23% in less than a year, when it was bought for $1,075,000 last April, having previously been purchased for $1,320,000 in June 2014. A number of smaller apartments without car parks suffered falls ranging from almost 4% to 8% between 2010 and their resale last year. Melbourne’s surge in new apartments led to predictions more than a year ago than an oversupply was likely to push prices down. While greater supply would limit rental income growth, as long as interest rates remained low there was unlikely to be a big correction in prices because buyers could still fund the gap between rental income and their mortgage payments, said BIS Shrapnel analyst Angie Zigomanis.
“Anyone who’s bought an apartment off-plan and then looks to onsell within a couple of years will probably be looking at a 10% decline, but [up to a] 40% decline – there might be the odd example – it’s definitely not going to be the norm,” Mr Zigomanis said. “At the broader level those price falls will be mitigated by lower interest rates and the fact that people aren’t necessarily going to be obliged to put their property on the market.”
Read more …

“When the grifters can’t cash their checks — or move their pixels into the accounts receivable column — they will be immobilized. Of course, if that happens, so will everything else, including your ability to buy any more frozen pizzas.”
• The Great Nausea (Jim Kunstler)
[..] the latest meme spreading across the web wires is how deeply the voters divide by sex: men flocking around Trump (or Machine Gun Ted Cruz), and the ladies standing at each mighty column of Hillary’s azure pant-suit. Yes, a national war of the sexes. Just what we need with all our shit falling apart. This sorry diversion results not from the triumph of feminism, as widely believed, but actually from the failure of American manhood. Proof of that, of course, is the ascendance of Trump, this punch-line of a political leader with all the gravitas of a hood ornament. History repeats itself, first as tragedy, second as farce – thank you, Karl Marx, O peevish mischief-maker squirming upon your fabled boils!
Finally, what will take the Deep State down is not some lance-wielding armored savior on a white horse but the awful undertow of financial implosion that awaits as the seasons of 2016 turn. When faith in our money and the instruments represented in it goes, look out below. There are so many rifts in the international banking system that the vista begins to look like the spring ice break-up on the Lake of Nations. When the grifters can’t cash their checks — or move their pixels into the accounts receivable column — they will be immobilized. Of course, if that happens, so will everything else, including your ability to buy any more frozen pizzas. Trump, Cruz, Hillary, and Bernie are signs that this poor paralyzed country needs to go through a convulsion to flush out all the toxic idiocy of this historical moment.
Trigger warning: it may be the messiest revolution in history when it finally comes, there is so much dross to clear out of the system. Trump and Hillary are like two giant fistulas obstructing the national bowel. Of course, a lot of sentient Americans do not want their nation dying on the toilet like Elvis. The indignity of it! In the name of the founding fathers, please, someone, fetch the enema bag. Events still lie hidden like bear traps on the path to “Decision 2016” as they like to say on the cable networks. Somewhere in London, Singapore, Shanghai, or New York, a 25-year-old coked-out Forex trader is going to tap the untoward keystroke that brings down a derivatives avalanche… or two brothers of Allah in some Berlin row-house will go forth one bright morning in vests of Semtex… and finally enough will be enough.
Read more …

The most vulnerable go first.
• Worst Bleaching On Record For Great Barrier Reef (AFP)
Aerial surveys of Australia’s Great Barrier Reef have revealed the worst bleaching on record in the icon’s pristine north, scientists said Tuesday, with few corals escaping damage. Researchers said the view was devastating after surveying some 520 reefs via plane and helicopter between Cairns and the Torres Strait in the north of Queensland state. “This will change the Great Barrier Reef forever,” Terry Hughes, an expert on coral reefs from James Cook University, told the Australian Broadcasting Corporation. “We’re seeing huge levels of bleaching in the northern thousand kilometre stretch of the Great Barrier Reef.” Just over a week ago, the Australian government revealed bleaching at the World Heritage-listed site was “severe” but noted that the southern area had escaped the worst.
Bleaching occurs when abnormal environmental conditions, such as warmer sea temperatures, cause corals to expel tiny photosynthetic algae, draining them of their colour. Hughes, convener of Australia’s National Coral Bleaching Taskforce, agreed in a statement that the southern reef had “dodged a bullet due to cloudy weather that cooled the water temperatures down”. But he said in the far north – the most remote and pristine areas – almost without exception, every reef showed consistently high levels of bleaching. “We flew for 4,000 kilometres in the most pristine parts of the Great Barrier Reef and saw only four reefs that had no bleaching,” he said. “The severity is much greater than in earlier bleaching events in 2002 or 1998.” Fellow James Cook University expert James Kerry said more surveys were to follow, but the damage seen from the air in the north was severe, often falling into the highest category of level four, meaning 60% of the coral was bleached.
Read more …

Not unreasonable. But. But they would have to be accepted in full as Germans, both by officials and by the people. Canada’s model is exemplary in this.
• Germany Wants Refugees To Integrate Or Lose Residency Rights (Reuters)
German Interior Minister Thomas de Maiziere said he is planning a new law that will require refugees to learn German and integrate into society, or else lose their permanent right of residence. The initiative comes after voters punished Chancellor Angela Merkel’s conservatives in regional elections earlier this month, giving a thumbs-down to her open-door refugee policy and turning in droves to the anti-immigrant party Alternative for Germany (AfD). Around 1 million migrants arrived in Germany last year – many fleeing conflict and economic hardship in the Middle East and Africa – and de Maiziere said around 100,000 more had arrived so far this year. Germany expected that in return for language lessons, social benefits and housing, the new arrivals made an effort to integrate, he told ARD television.
“For those who refuse to learn German, for those who refuse to allow their relatives to integrate – for instance women or girls – for those who reject job offers: for them, there cannot be an unlimited settlement permit after three years,” he said. De Maiziere, who belongs to Merkel’s conservatives party, added that he wanted “a link between successful integration and the permission for how long one is allowed to stay in Germany.” Vice Chancellor Sigmar Gabriel welcomed the draft law, which is planned for May. “We must not only support integration but demand it,” Gabriel told mass-selling daily Bild. Gabriel’s Social Democrats, the junior partner in Germany’s ruling coalition with Merkel’s conservatives, also suffered losses in this month’s elections in three German states.
Read more …

“The United States [..] has meanwhile pledged just 7% of the nearly 171,000 considered to be its fair share, it showed. The Netherlands also stood at 7%, Denmark at 15 and Britain at 22, Oxfam said.
• Rich Countries Resettle Barely 1% of Syrian Refugees (AFP)
Wealthy countries have resettled only a fraction of the nearly five million refugees who have fled Syria, Oxfam said on Tuesday, urging them to step up and do their share. The British charity called on wealthy countries to resettle at least 10% of the 4.8 million Syrian refugees registered in the region surrounding the war-ravaged nation by the end of the year. So far, rich countries have pledged fewer than 130,000 resettlement spots, and only around 67,100 people – a mere 1.39% of the refugees – have made it to their final destinations since 2013, Oxfam said. The charity issued its report ahead of an unprecedented UN-hosted conference in Geneva on Wednesday, where countries will be asked to pledge resettlement spots for Syrian refugees. As the brutal conflict enters its sixth year, most of the people who have fled are located in Syria’s immediate neighbours such as Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan and Iraq.
But as the war has dragged on and conditions have worsened in the surrounding states, Syrians have increasingly set their sights on Europe, accounting for most of the more than one million migrants who risked their lives crossing the Mediterranean last year. They are also believed to be heavily represented among the more than 7,500 people, including many children, who have died trying to make the crossing since 2014. Wednesday’s conference, which will be opened by UN Secretary General Ban Ki-moon, will aim to ensure “global responsibility sharing” for the crisis sparked by Syria’s brutal conflict, which has claimed more than 270,000 lives. “To date the response to calls of increased resettlement of vulnerable refugees has been disappointing, and the conference is an opportunity for states to mark a change of course,” the Oxfam report said.
The charity said its analysis showed only three of the world’s wealthy countries – Canada, Germany and Norway – had pledged more resettlement spots than what was considered their “fair share” according to the size of their economies. Five other countries, Australia, Finland, Iceland, Sweden and New Zealand had meanwhile pledged more than half of their fair share, while the remaining 20 nations included in the analysis fell far short, Oxfam said. Thus, France had only so far pledged to take in 1,000 Syrian refugees, or only four% of the nearly 26,000 considered to be its fair share, the report said. The United States, which has resettled 1,812 Syrian refugees and said it will take in 10,000 more, has meanwhile pledged just 7% of the nearly 171,000 considered to be its fair share, it showed. The Netherlands also stood at 7%, Denmark at 15 and Britain at 22, Oxfam said.
Read more …

The old new route is going strong. After a few days of – weather related- declining arrivals on Lesbos, numbers are rising there again as well.
• Nearly 1,500 Migrants Rescued Off Libya In Past 2 Days (AFP)
Nearly 1,500 migrants, including many women and children, have been rescued in the Mediterranean off the coast of Libya over the past two days, the Italian coastguard said Monday. A total of 1,482 people were picked up in about a dozen rescue operations at sea on Sunday and Monday, according to the Italian coastguard which coordinated the search and rescue efforts. They did not release the nationalities of the migrants and refugees.
They said 730 people were rescued on Sunday and 752 on Monday. They did not provide a breakdown of the number of children and women on board. The UN refugee agency said last week that nearly 14,500 migrants had arrived in Italy via Libya since the start of the year, up 42.5% on the same period a year earlier. Libya has long been a stepping stone for migrants seeking a better life in Europe, with Italy some 300 kilometres across the sea. European leaders fear that a recent deal with Ankara to stem the flow of migrants arriving in Greece via Turkey will increase crossings attempts from Libya.
Read more …