
Bernard Pascucci Dancers on the Roof of the Opéra Garnier, Paris 1965

Yeah, we had a bit of a DDOS thing today. Sorry.
Haven’t seen one voice that makes sense in this Paris CON21 thing. I do remember what they said about everyone being on the same side of the boat.
• President Trump Announces US Withdrawal From The Paris Climate Accord (ZH)
It’s done. Bannon 1 – 0 Kushner. President Donald Trump announced the U.S. would withdraw from the Paris climate pact and that he will seek to renegotiate the international agreement in a way that treats American workers better. “So we are getting out, but we will start to negotiate and we will see if we can make a deal, and if we can, that’s great. And if we can’t, that’s fine,” Trump said Thursday, citing terms that he says benefit China’s economy at the expense of the U.S. “In order to fulfill my solemn duty to protect America and its citizens, the United States will withdraw from the Paris climate accord, but begin negotiations to re-enter either the Paris accord or really an entirely new transaction on terms that are fair to the United States, its businesses” and its taxpayers, Trump said.
As Bloomberg reports, Trump’s announcement, delivered to cabinet members, supporters and conservative activists in the White House Rose Garden, spurns pleas from corporate executives, world leaders and even Pope Francis who warned the move imperils a global fight against climate change. As we noted earlier, we should prepare for the establishment to begin its mourning and fearmongering of the disaster about to befall the world. Pulling out means the U.S. joins Russia, Iran, North Korea and a string of Third World countries in not putting the agreement into action. Just two countries are not in the deal at all – one of them war-torn Syria, the other Nicaragua. The Hill notes that many Republicans on Capitol Hill are likely to support pulling out of the Paris deal – 20 leading Senate Republicans, including Majority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.) asked Trump to do just that last week.
Withdrawing from Paris would greatly please conservative groups, which have orchestrated an all-out push in opposition to the pact. “Without any impact on global temperatures, Paris is the open door for egregious regulation, cronyism, and government spending that would be disastrous for the American economy as it is proving to be for those in Europe,” said Nick Loris, a fellow at the Heritage Foundation. “It is time for the U.S. to say ‘au revoir’ to the Paris agreement,” he said.


And use to NOT have their leader appear on TV. I’m thinking a decision by the new (American?!) campaign team installed after the Snap announcement. “Stay away from the camera, it can only do you harm!” Boris PM by July 1?
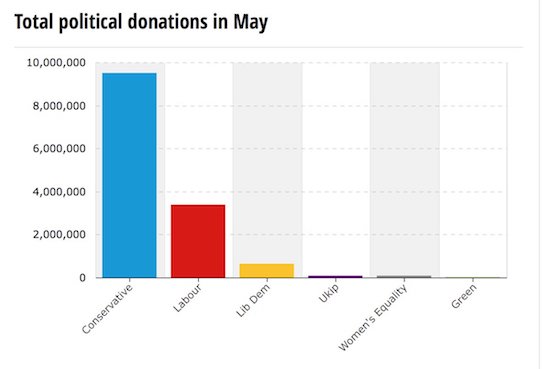
• Conservatives’ Donors Gave 10 Times As Much As Labour’s Last Week (G.)
The Conservatives raised more than 10 times as much as Labour last week, partly thanks to a donation of over £1m from the theatre producer behind The Book of Mormon and The Phantom of the Opera. John Gore, whose company has produced a string of hit musicals, gave £1.05m as part of the £3.77m received by the Conservatives in the third week of the election campaign. In the same time, Labour received only £331,499. The Electoral Commission only publishes details of donations over £7,500, so the smaller donors who make up most of Labour’s fundraising are not identified. Almost all Labour’s larger donations came from unions, including £159,500 from Unite. The new figures show the Conservatives have received £15.2m since the start of 2017, while Labour has received £8.1m.
The large donations came as the poll lead held by the Conservatives and Theresa May appeared to fall following controversies around her social care policy. In the week starting 17 May, the Liberal Democrats received £310,500, of which £230,000 came from the Joseph Rowntree Reform Trust and £25,000 came from the former BBC director general Greg Dyke. The Women’s Equality party received £71,552, with Edwina Snow, the Duke of Westminster’s sister who is married to the historian Dan Snow, giving £50,000. Ukip’s donations fell dramatically to £16,300 from £35,000 the previous week. Political parties can spend £30,000 for every seat they contest during the regulated period. There are 650 seats around the country, meaning that parties can spend up to £19.5m during the regulated period in the run-up to the election.

Money spent at the lower rungs of society tends to stay inside it.
• The Myths About Money That British Voters Should Reject (Chang)
Befitting a surprise election, the manifestos from the main parties contained surprises. Labour is shaking off decades of shyness about nationalisation and tax increases for the rich and for the first time in decades has a policy agenda that is not Tory-lite. The Conservatives, meanwhile, say they are rejecting “the cult of selfish individualism” and “belief in untrammelled free markets”, while adopting the quasi-Marxist idea of an energy price cap. Despite these significant shifts, myths about the economy refuse to go away and hamper a more productive debate. They concern how the government manages public finances – “tax and spend”, if you will.
The first is that there is an inherent virtue in balancing the books. Conservatives still cling to the idea of eliminating the budget deficit, even if it is with a 10-year delay (2025, as opposed to George Osborne’s original goal of 2015). The budget-balancing myth is so powerful that Labour feels it has to cost its new spending pledges down to the last penny, lest it be accused of fiscal irresponsibility. However, as Keynes and his followers told us, whether a balanced budget is a good or a bad thing depends on the circumstances. In an overheating economy, deficit spending would be a serious folly. However, in today’s UK economy, whose underlying stagnation has been masked only by the release of excess liquidity on an oceanic scale, some deficit spending may be good – necessary, even.
The second myth is that the UK welfare state is especially large. Conservatives believe that it is bloated out of all proportion and needs to be drastically cut. Even the Labour party partly buys into this idea. Its extra spending pledge on this front is presented as an attempt to reverse the worst of the Tory cuts, rather than as an attempt to expand provision to rebuild the foundation for a decent society. The reality is the UK welfare state is not large at all. As of 2016, the British welfare state (measured by public social spending) was, at 21.5% of GDP, barely three-quarters of welfare spending in comparably rich countries in Europe – France’s is 31.5% and Denmark’s is 28.7%, for example. The UK welfare state is barely larger than the OECD average (21%), which includes a dozen or so countries such as Mexico, Chile, Turkey and Estonia, which are much poorer and/or have less need for public welfare provision. They have younger populations and stronger extended family networks.
The third myth is that welfare spending is consumption – that it is a drain on the nation’s productive resources and thus has to be minimised. This myth is what Conservative supporters subscribe to when they say that, despite their negative impact, we have to accept cuts in such things as disability benefit, unemployment benefit, child care and free school meals, because we “can’t afford them”. This myth even tints, although doesn’t define, Labour’s view on the welfare state. For example, Labour argues for an expansion of welfare spending, but promises to finance it with current revenue, thereby implicitly admitting that the money that goes into it is consumption that does not add to future output.

We saw this in 2015, I think it was Qingdao port(?!). Now it turns out this is widespread. China is very corrupt.
• ‘Ghost Collateral’ Haunts China’s Debt-Laden Banking System (R.)
The banker at the other end of the phone line was furious, recalled Shanghai lawyer Wang Chaoyu. A pile of steel pledged as collateral for a loan of almost $3 million from his bank, China CITIC, had vanished from a warehouse on the outskirts of the city. Just several months earlier, in mid-2013, Wang and the banker had visited the warehouse and verified that the steel was there. “The first time I went, I saw the steel,” recalled Wang, an attorney at Beijing DHH Law Firm, which represents the Shanghai branch of CITIC. “Afterwards, the banker got in contact with me and said, ‘The pledged assets are no longer there.’” The trouble had begun in 2012, after CITIC loaned the money to Shanghai Hanning Iron and Steel, a privately held steel trader. Hanning failed to meet payments, according to a mediation agreement reviewed by Reuters, and CITIC took ownership of the steel.
It was when CITIC moved to retrieve the collateral that the banker visited the warehouse and discovered that the 291-tonne pile of steel was no longer there, Wang said. The bank is still in court trying to recoup its losses. The missing collateral is a setback for CITIC. But it is indicative of a much wider problem that could endanger the health of China’s financial system – fraudulent or “ghost” collateral. When bank auditors in China go looking, they too often find that collateral recorded on the books simply isn’t there. In some cases, collateral that has been pledged simply doesn’t exist. In others, it disappears as borrowers in financial distress sell the assets. There are also instances in which the same collateral has been pledged to multiple lenders. One lawyer said he discovered that the same pile of steel was used to secure loans from 10 different lenders.
With the mainland facing its slowest growth in over a quarter of a century, defaults are mounting as borrowers struggle to repay their loans. The danger of fraudulent collateral in this situation, say economists, is that it exacerbates the problem of bad debt for China’s banks, increasing the risk of financial turmoil. As growth slows, lenders can expect more nasty surprises, said Xin Qingquan at Chongqing University. More instances of fake collateral will arise, he said. [..] There are no official statistics or estimates of the problem. But fraudulent collateral is “a huge issue,” said Violet Ho, co-head of Greater China Investigations and Disputes Practice at Kroll, which conducts corporate investigations on the mainland. “Often you also see that the paperwork around collateral may be dodgy, and the bank loan officer knows, the intermediary knows, and the goods owner knows – so it’s essentially a Ponzi scheme.”
[..]Bad loans are mounting fast. Officially, just 1.74% of commercial bank loans were classified as non-performing at the end of March. But some analysts say lenders often mask the true level of bad debt and so the figure is likely much higher. Fitch Ratings said in a report last September that it had estimated non-performing loans in China’s financial system could be as high as 15% to 21%. This in a banking sector that has undergone a massive credit expansion. The value of outstanding bank loans ballooned to $17.2 trillion at the end of April from $5.8 trillion at the end of 2009, according to data from China’s central bank. In September last year, the Bank for International Settlements warned that excessive credit growth in China meant there was a growing risk of a banking crisis in the next three years.

ECB at 28% of Eurozone GDP. Fed at 23% of US.
• BOJ’s Balance Sheet Almost As Big As Japanese Economy (Nikkei)
The Bank of Japan’s assets apparently exceeded 500 trillion yen ($4.49 trillion) as of the end of May, growing to rival the country’s economy as the central bank continues its debt purchases under an ultraeasy monetary policy. The bank’s total assets stood at 498.15 trillion yen as of May 20. By the time the month ended Wednesday, its holdings of Japanese government bonds had increased by another 2.24 trillion yen. Assuming that the BOJ had not significantly reduced its non-JGB assets, its balance sheet almost certainly crossed over the 500 trillion yen mark into uncharted territory. The BOJ’s balance sheet began expanding at a rapid clip after Governor Haruhiko Kuroda launched unprecedented quantitative and qualitative easing in April 2013. At around 93%, the scale of the Japanese central bank’s assets in proportion to GDP has no close match. Latest data shows that the U.S. Fed held roughly $4.5 trillion in assets, which is equivalent to 23% of the country’s GDP.
The ECB’s balance sheet, at about €4.2 trillion ($4.71 trillion) is larger than the BOJ’s, but it still sits at around 28% of the eurozone GDP. The BOJ in September shifted its policy focus from QE to controlling the yield curve, but the bank is still snapping up JGBs to keep long-term rates at around zero. The central bank has stood firm on its pledge to continue expanding its balance sheet to boost currency supply until Japan’s consumer price inflation is steadily above 2%. This suggests that the BOJ’s balance sheet will continue expanding past the 500 trillion yen mark. This prospect makes some financial experts uneasy. Once the inflation target is finally met, and the BOJ starts raising interest rates, the bank will have to pay more in interest to financial institutions’ reserve deposits than it will earn from its low-yielding JGB holdings.

All hail Amazon.
• 25-30% Of US Shopping Malls To Close In The Next Five Years (LATimes)
Between 20% and 25% of the nation’s shopping malls will close in the next five years, according to a new report from Credit Suisse that predicts e-commerce will continue to pull shoppers away from bricks-and-mortar retailers. For many, the Wall Street firm’s finding may come as no surprise. Long-standing retailers are dying off as shoppers’ habits shift online. Credit Suisse expects apparel sales to represent 35% of all e-commerce by 2030, up from 17% today. Traditional mall anchors, such as Macy’s, J.C. Penney and Sears, have announced numerous store closings in recent months. Clothiers including American Apparel and BCBG Max Azria have filed for bankruptcy. Bebe has closed all of its stores.
The report estimates that around 8,640 stores will close by the end of the year. Retail industry experts say Credit Suisse may have underestimated the scope of the upheaval. “It’s more in the 30% range,” Ron Friedman, a retail expert at accounting and advisory firm Marcum said of the share of malls that he predicts will close in the next five years. “There are a lot of malls that know they’re in big trouble.” By ignoring new shopping centers being built, the research note took an overly simplistic view of the changing landscape of shopping centers, said analyst David Marcotte, senior vice president with Kantar Retail. “There are still malls being built,” Marcotte said. “Predominantly outlet malls and lifestyle malls.”

From May 11. h/t Tyler.
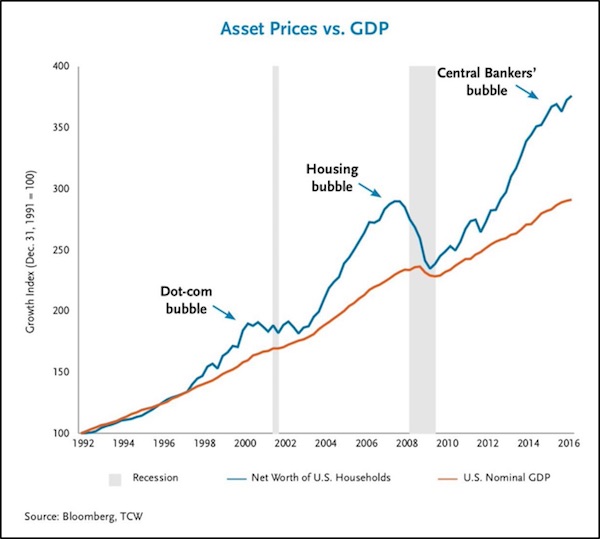
Now don’t get me wrong. Do I think Emmanuel Macron, a former Rothschild investment banker whose “ambition was always two steps ahead of his experience”, is the second coming of Charles de Gaulle? Do I think Donald freakin’ Trump is a modern day Andrew Jackson? Bwa-ha-ha-ha-ha-ha … good one! But here’s what I do think: • Something old and powerful is happening in the real world to crush the status quo political systems of every Western democracy. • Something predictably sad is happening in the political world to replace the old guard candidates with self-absorbed plutocrats like Trump and pretty boy bankers like Macron. • Something new and powerful is happening in the investment world to divorce political risk and volatility from market risk and volatility. The old force repeating itself in the real world is nicely summed up by these two charts, the most important charts I know. They’re specific to the U.S., but applicable everywhere in the West.
First, the Central Banker’s Bubble since March 2009 and the launch of QE1 has inflated U.S. household wealth far beyond what the nominal growth rate of the U.S. economy would otherwise support. This is a classic bubble in every sense of the word, with the primary difference from prior vast bubbles being its concentration and focus in financial assets — stocks and bonds — which are held primarily by the rich. Who wins the Academy Award for creation of wealth inequality in a supporting role? Ladies and gentlemen, I give you the U.S. Federal Reserve.
And as the second chart shows, this central bank largesse has sharply accelerated the massive shift in wealth to the Rich from the Rest, a shift which began in the 1980s with the Reagan Revolution. We are now back to where we were in the 1930s, where the household wealth of the bottom 90% of U.S. wage earners is equal to the household wealth of the top one-tenth of 1% of U.S. wage earners.
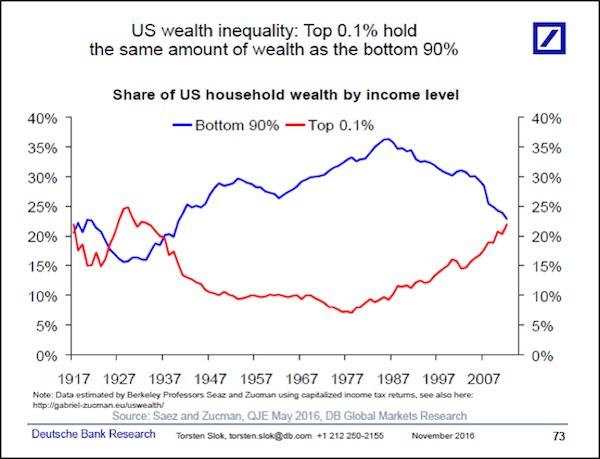
So look … I’m not saying that the current level or dynamics of wealth inequality is a good thing or a bad thing. I’m just saying that it IS. And I understand that there are insurance programs today, like social security and pension funds, which are not reflected in this chart and didn’t exist in the 1930s, the last time you saw this sort of wealth inequality. I understand that there are a lot more people in the United States today than in the 1930s. I understand that there are all sorts of important differences in the nature of wealth distribution between today and the 1930s. I get all that. What I’m saying, though, is that just like in the 1930s, there is a political price to be paid for this level of wealth inequality. That price is political polarization and electoral rejection of status quo parties.

At the local level, the US is in for something historic.
• Cities, States And School Systems Lose Millions To Credit Downgrades (IBT)
[..] downgrades of bonds issued by local governments raise the interest rates those governments must pay on holders of its debt, thereby costing those communities up to hundreds of millions of dollars annually, according to the report, which was released Wednesday by the non-profit Roosevelt Institute’s ReFund America Project and focused on recent downgrades by Moody’s in relatively impoverished, predominantly-black localities. The more recent report [..] took a granular look at a few communities whose budgets were impacted by downgrades, which drive the prices of bonds down while raising the interest rate at which the government has to pay its bondholders. New Jersey was set to lose $258 million annually as a result of a Moody’s ratings drop, the report calculated, using the spread between interest rates on bonds with different Moody’s credit ratings and the amount of debt affected by the downgrade.
Moody’s announced a downgrade of the New Jersey’s $37 billion in publicly-issued debt to A3, six levels below the agency’s top rating of Aaa, in late March. The agency attributed the downgrade to “significant pension underfunding, including growth in the state’s large long-term liabilities, a persistent structural imbalance and weak fund balances,” as well as a tax cut that would decrease revenues by $1.1 billion over the next four years. New Jersey’s city of Newark — which is 52.4% African American and 33.8% Hispanic, compared to 12.6% and 16.3%, respectively, on the national level, according to U.S. Census data — was slated to lose an estimated $10 million annually as a result of a Moody’s downgrade, the report calculated. Newark’s median household income was just over $33,000, compared to nearly $54,000 nationwide, as of 2015.
That year, Moody’s downgraded Newark’s $374 million in general obligation unlimited tax bonds to Baa3, one level above junk bond status. The rating change, Moody’s said in the press release, reflected “the city’s further weakened financial position since last year,” along with its “reliance on market access for cash flow, history of aggressively structured budgets typically adopted late in the year and uncertainty around continued financial support from the state of New Jersey.” Further west, Chicago Public Schools (CPS) also stood to suffer tremendously from a Moody’s rating drop. The report authors calculated that the school system would lose out on $290 million annually from a September 2016 Moody’s downgrade to B3, five ranks below the highest junk bond rating. Nearly 40% of students are African American, 46.5% are Hispanic and 80.2% are considered “economically disadvantaged,” according to October 2016 CPS data.

States falling one by one.
• S&P, Moody’s Downgrade Illinois to Near Junk, Lowest Ever for a US State (BBG)
Illinois had its bond rating downgraded to one step above junk by Moody’s Investors Service and S&P Global Ratings, the lowest ranking on record for a U.S. state, as the long-running political stalemate over the budget shows no signs of ending. S&P warned that Illinois will likely lose its investment-grade status, an unprecedented step for a state, around July 1 if leaders haven’t agreed on a budget that chips away at the government’s chronic deficits. Moody’s followed S&P’s downgrade Thursday, citing Illinois’s underfunded pensions and the record backlog of bills that are equivalent to about 40% of its operating budget. “Legislative gridlock has sidetracked efforts not only to address pension needs but also to achieve fiscal balance,” Ted Hampton, Moody’s analyst, said in a statement.
“During the past year of fruitless negotiations and partisan wrangling, fundamental credit challenges have intensified enough to warrant a downgrade, regardless of whether a fiscal compromise is reached.” Illinois hasn’t had a full year budget in place for the past two years amid a clash between the Democrat-run legislature and Republican Governor Bruce Rauner. That’s left the fifth most-populous state with a record $14.5 billion of unpaid bills, ravaged entities like universities and social service providers that rely on state aid and undermined Illinois’s standing in the bond market, where investors have demanded higher premiums for the risk of owning its debt. Moody’s called Illinois “an outlier among states” after suffering eight downgrades in as many years.
“The rating actions largely reflect the severe deterioration of Illinois’ fiscal condition, a byproduct of its stalemated budget negotiations,” S&P analyst Gabriel Petek said in a statement. “The unrelenting political brinkmanship now poses a threat to the timely payment of the state’s core priority payments.” Illinois’s 10-year bonds yield 4.4%, 2.5 percentage points more than those on top-rated debt. That spread – a measure of the perceived risk – is the highest since at least January 2013 and more than any of the other 19 states tracked by Bloomberg.

The new economy.
• Uber Burned Through Almost As Much Money As NASA Last Quarter (Simon Black)
Uber reported yesterday that its NET LOSS totaled more than $700 million last quarter, despite pulling in a whopping $3.4 billion in revenue. (This means they spent at least $4.1 billion!) That’s the latest in a string of massive, 9-figure quarterly losses for the company. The only question I have is– how much cocaine are these people buying? Seriously, it’s REALLY HARD to spend so many billions of dollars. You could have over 100,000 employees (‘real’ employees, not Uber drivers) and pay them $150,000 EACH and still not blow through that much money in a single quarter. Even if you think about Research & Development, Uber still managed to burn through almost as much cash as NASA’s $4.8 billion budget last quarter. The real irony is that this company is worth $70 BILLION. And Uber is far from alone. Netflix is also worth $70 billion; and like Uber, they can’t make money.
Over the last twelve months Netflix burned through over $1.7 billion in cash, and they made up for it by going deeper into debt. The list goes on and on– Snapchat debuted with a $30 billion valuation after its IPO, only to subsequently report that they had lost $2.2 billion in the previous quarter. Telecom company Sprint is still somehow worth more than $30 billion despite having over $40 billion in debt and burning through more than $6 billion over the last three years. And then there’s Twitter, a rudderless, profitless company that is still worth over $13 billion. This is pure insanity. If companies that burn through obscene piles of cash and have no clear path to profitability are worth tens of billions of dollars, it seems like any business that’s cashflow positive should be worth TRILLIONS. None of this makes any sense, and investing in this environment is nothing more than gambling. Sure, it’s always possible these companies’ stock prices increase even more. Maybe Netflix and Twitter quadruple despite continuing losses and debt accumulation. Maybe Bitcoin surges to $50,000 next month. And maybe the Dallas Cowboys finally offer me the starting quarterback position next season.

“One of those bubbles is global debt, especially government debt. The other is the even larger bubble of government promises.”
Hmm. Private debt is the biggie.
• The Next Recession May Be A Complete Reset Of All Asset Valuations (Mauldin)
Sometime this year, world public and private plus unfunded pensions will surpass $300 trillion. That is not even counting the $100 trillion in US government unfunded liabilities. Oops. These obligations cannot be paid. A time is coming when the market and voters will realize this. Will voters decide to tax “the rich” more? Will they increase their VAT rates and further slow growth? Will they reduce benefits? No matter what they decide, hard choices will bring political turmoil. And that, of course, will mean market turmoil. We are coming to a period I call “the Great Reset.” As it hits, we will have to deal, one way or another, with the largest twin bubbles in the history of the world. One of those bubbles is global debt, especially government debt. The other is the even larger bubble of government promises.
The other is the even larger bubble of government promises. History shows it is more than likely that the US will have a recession in the next few years. When it does come, it will likely blow the US government deficit up to $2 trillion a year. Obama took eight years to run up a $10 trillion debt after the 2008 recession. It might take just five years after the next recession to run up the next $10 trillion. Here is a chart my staff at Mauldin Economics created in late 2016 using Congressional Budget Office data. It shows what will happen in the next recession if revenues drop by the same percentage as they did in the last recession (without even counting likely higher expenditures this time).
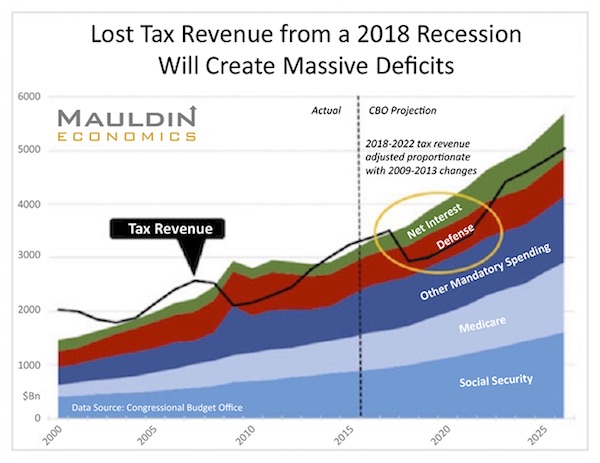
And you can add the $1.3 trillion deficit in this chart to the more than $500 billion in off-budget debt—and add a higher interest rate expense as interest rates rise. The catalyst could be a European recession that spills over into the US. Or it might be one triggered by US monetary and fiscal mistakes. Or a funding crisis in China, or an emerging-market meltdown. Whatever the cause, the next recession will be just as global as the last one. And there will be more buildup of debt and more political and economic chaos.

The trade will move elsewehere until it’s simply entirely banned.
• China’s Ivory Ban Sparks Dramatic Drop In Prices Across Asia (G.)
The price of raw ivory in Asia has fallen dramatically since the Chinese government announced plans to ban its domestic legal ivory trade, according to new research seen by the Guardian. Poaching, however, is not dropping in parallel. Undercover investigators from the Wildlife Justice Commission (WJC) have been visiting traders in Hanoi over the last three years. In 2015 they were being offered raw ivory for an average of US$1322/kg in 2015, but by October 2016 that price had dropped to $750/kg, and by February this year prices were as much as 50% lower overall, at $660/kg. Traders complain that the ivory business has become very “difficult and unprofitable”, and are saying they want to get rid of their stock, according to the unpublished report seen by the Guardian. Worryingly, however, others are stockpiling waiting for prices to go up again.
Of all the ivory industries across Asia, it is Vietnam that has increased its production of illegal ivory items the fastest in the last decade, according to Save the Elephants. Vietnam now has one of the largest illegal ivory markets in the world, with the majority of tusks being brought in from Africa. Although historically ivory carving is not considered a prestigious art form in Vietnam, as it is in China, the number of carvers has increased greatly. The demand for the worked pieces comes mostly from mainland China. Until recently, the chances of being arrested at the border slim due to inefficient law enforcement. But the prices for raw ivory are now declining as the Chinese market slows; this is partly due to China’s economic slowdown, and also to the announcement that the country will close down its domestic ivory trade.
China’s ivory factories were officially shut down by 31 March 2017, and all the retail outlets will be closed by the end of the year. Other countries have been taking similarly positive action on ivory, although the UK lags behind. Theresa May quietly dropped the conservative commitment to ban ivory from her manifesto, but voters have picked it up and there has been fury across social media. “All the traders we are speaking to are talking about what’s going on in China. It’s definitely having a significant impact on the trade,” said Sarah Stoner, senior intel analyst at the WJC. “A trader in one of the neighbouring countries who talked to our undercover investigators said he didn’t want to go to China anymore – it was so difficult in China now, and friends of his were arrested and sitting in jail. He seemed quite concerned about the situation,” said Pauline Verheji, WJC’S senior legal investigator.

Lip service.
• Audi Emissions Scandal Erupts After Germany Says It Detects New Cheating (R.)
Audi’s emissions scandal flared up again on Thursday after the German government accused the carmaker of cheating emissions tests with its top-end models, the first time Audi has been accused of such wrongdoing in its home country. The German Transport Ministry said it has asked Volkswagen’s luxury division to recall around 24,000 A7 and A8 models built between 2009 and 2013, about half of which were sold in Germany. VW Chief Executive Matthias Mueller was summoned to the Berlin-based ministry on Thursday, a ministry spokesman said, without elaborating. The affected Audi models with so-called Euro-5 emission standards emit about twice the legal limit of nitrogen oxides when the steering wheel is turned more than 15 degrees, the ministry said.
It is also the first time that Audi’s top-of-the-line A8 saloon has been implicated in emissions cheating. VW has said to date that the emissions-control software found in its rigged EA 189 diesel engine does not violate European law. The 80,000 3.0-liter vehicles affected by VW’s emissions cheating scandal in the United States included Audi A6, A7 and Q7 models as well as Porsche and VW brand cars. The ministry said it has issued a June 12 deadline for Audi to come up with a comprehensive plan to refit the cars. Ingolstadt-based Audi issued a recall for the 24,000 affected models late on Thursday, some 14,000 of which are registered in Germany, and said software updates will start in July. It will continue to cooperate with Germany’s KBA motor vehicle authority, Audi said.

This is supposed to be our biggest enemy? He makes far too much sense for that.
• Oliver Stone Quizzes Vladimir Putin On Snowden (G.)
Just a few hours after Megyn Kelly announced on NBC’s Today show that she would be interviewing Vladimir Putin in St Petersburg tomorrow at the International Economic Forum, Showtime released the first trailer and extended clip for The Putin Interviews, a sit-down with the Russian president conducted by the film-maker Oliver Stone for a four-part special that premieres on 12 June. Promoted as “the most detailed portrait of Putin ever granted to a Western interviewer”, The Putin Interviews spawned from several encounters over two years between Stone, director of politically oriented films including JFK and Nixon, and Putin. The interviews are to air as four one-hour installments, landing just a week after Kelly’s discussion with Putin, the centerpiece of her news magazine show on NBC, which premieres on Sunday night.
In the extended clip released on Thursday, Stone and Putin can be seen driving in a car with an English translator in the backseat, discussing topics such as Edward Snowden’s whistleblowing and Russian intelligence. “As an ex-KGB agent, you must have hated what Snowden did with every fiber of your being,” Stone asks in the clip. “Snowden is not a traitor,” Putin replies. “He did not betray the interests of his country. Nor did he transfer any information to any other country which would have been pernicious to his own country or to his own people. The only thing Snowden does, he does publicly.”

Oh well.
• Schaeuble Launches A Broadside Against Tsipras (K.)
Two weeks before a critical Eurogroup summit, German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble launched a broadside at Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras, claiming that the leftist premier has not shifted the burden of austerity away from poorer Greeks as he had pledged. In his comments, Schaeuble also maintained that party influence on the Greek public administration has increased rather than decreased during Tsipras’s time in power, noting that ruling party officials have been appointed to the country’s privatization fund. Greek government sources responded tersely to Schaeuble’s criticism. “The responsibility of Schaeuble in managing the Greek crisis has been recorded historically,” one source said. “There is no point in his ascribing it to others.”
Meanwhike Germany’s Die Welt reported that the ECB had similar views on the need for Greek debt relief to the IMF, and indicated that Schaeuble might be facing pressure to make unpopular decisions ahead of elections scheduled to take place in Germany in September. Tsipras, for his part, apparently sought to lower expectations in comments on Thursday. During a visit to the Interior Ministry, he said the government’s goal was “fulfilling the country’s commitments” linked to Greece’s third international bailout. He dodged reporters’ questions about whether he expected to leave a European Union leaders’ summit on June 22 wearing a tie – something he has pledged to do only when Greece secures debt relief. “The important thing is that I don’t leave with further burdens,” Tsipras said.
Aides close to Tsipras will be closely following a Euro Working Group meeting scheduled for June 8 for indications about what kind of deal creditors are likely to put on the table at the Eurogroup summit planned for June 15. If the solution that is in the works is deemed to be too politically toxic, it is likely that Tsipras will undertake another round of telephone diplomacy with key EU leaders such as German Chancellor Angela Merkel and French President Emmanuel Macron. He spoke to several prominent EU leaders earlier this week to underline the Greek government’s conviction that it has honored its promises to creditors and it is their turn to reciprocate with debt relief.

Promising. But.
• A New Antibiotic Multitool Could Beat The Toughest Bacteria (F.)
Doctors may soon have a new weapon in the long-running war between antibiotics and bacteria. It’s a Swiss Army knife of a drug that’s tens of thousands of times more effective in lab tests against dangerous antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Starting with the discovery of penicillin in 1928, scientists and doctors have been finding and making molecules that weaken or kill bacteria in a range of different ways to help humans survive infections. And as soon as humans started employing these antibiotics, bacteria began evolving to beat those attacks. That has started to become a huge problem. So-called superbugs like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) can ward off some of our most potent antibiotics, making infections by these bacteria extremely hard to treat.
Not only that, but their existence poses a strategic challenge as well, forcing doctors to think hard about when and where they use certain antibiotics, lest bacteria develop resistance to them and render them less effective. Vancomycin is one antibiotic that has stayed effective even as others have been been brought down by resistant bacteria. That’s because of the way vancomycin works: by latching onto one of the building blocks bacteria use to build their cell walls, like the microscopic equivalent of a bully stealing your shovel in the sandbox and not giving it back. (In this analogy, we’re on the bully’s side.) By interfering with such a critical cellular process in such a fundamental way, vancomycin makes it hard for bacteria to develop a simple mutation to defeat the antibiotic. That makes vancomycin one of our last lines of defense for treating infections like MRSA that others can’t.
It’s why the World Health Organization (WHO) added the drug to its list of essential medicines. Naturally, some bacteria have found ways to fight vancomycin, the most common being to substitute a different cell wall building block that the antibiotic can’t latch onto. Taking vancomycin out of doctors’ quivers would be a big blow. Which is why the WHO also lists vancomycin-resistant bacteria at number four and five on its list of the most threatening antibiotic-resistant microbes. So. To try to make sure vancomycin can beat those resistant bacteria, and stay effective for the next few decades—a reasonable lifetime for an antibiotic—chemists Dale Boger, Nicholas Isley and Akinori Okano at the Scripps Research Institute in California opened up the hood to make a few adjustments to the molecule.
After swapping out one part and bolting on a couple others, the group’s souped-up vancomycin was about 25,000 times more potent against resistant bacteria, and it had better endurance. They describe their work in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The major change was to the region of the molecule that grabs those cell wall building blocks, which are called D-alanyl-D-alanine. Resistant bacteria have learned to substitute the very similar D-alanyl-D-lactate, which your standard vancomycin can’t bind to very well, limiting its effectiveness. The researchers changed an oxygen atom for two atoms of hydrogen, making a new version of vancomycin that could hang onto either building block.








