Jack Delano Row houses, Baltimore 1940



“The economy is continuing to improve..” Nuff said.
• Yellen Leans Toward Near-Term Rate Rise Without Detailing Timing (BBG)
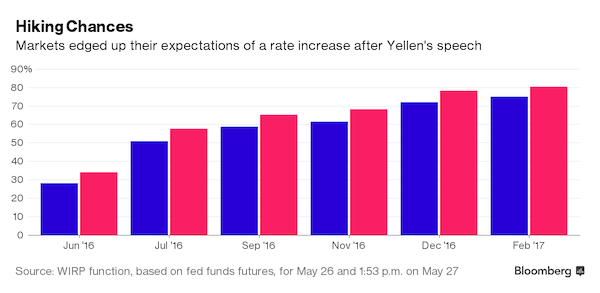
Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen threw her support behind a growing consensus at the central bank in favor of another interest rate increase soon, while steering clear of specifying the timing of such a move. “It’s appropriate – and I’ve said this in the past – for the Fed to gradually and cautiously increase our overnight interest rate over time,” Yellen said Friday during remarks at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. “Probably in the coming months such a move would be appropriate.” Yellen will host her colleagues on the Federal Open Market Committee in Washington June 14-15, when they will contemplate a second interest-rate increase following seven years of near-zero borrowing costs that ended when they hiked in December.
A series of speeches by Fed officials and the release of the minutes to their April policy meeting have heightened investor expectations for another tightening move either next month or in July. “The economy is continuing to improve,” she said in a discussion with Harvard economics professor Gregory Mankiw. She added that she expects “inflation will move up over the next couple of years to our 2% objective,” provided headwinds holding down price pressures, including energy prices and a stronger dollar, stabilize alongside an improving labor market.
Several regional Fed presidents, ranging from Boston Fed President Eric Rosengren to San Francisco’s John Williams, have in recent weeks urged financial market participants to take more seriously the chances of a rate hike in the next two months, pointing to continued signs of steady if unspectacular growth in the U.S. economy and the waning of risks posed by global economic and financial conditions. Yellen suggested that a rate rise would be appropriate if economic growth picks up and the labor market continues to improve – two developments that she said she expects to happen.

Trump sees a whole other world than Yellen does. Take your pick.
• Trump: Only ‘Dummies’ Believe Fed’s Unemployment Figure (Crudele)
Donald Trump, if elected president, will investigate the veracity of US economic statistics produced by Washington — including “the way they are reported.” I caught up with Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, by phone Tuesday morning, and we had a frank talk about the economy and what is making his campaign tick. “When you look at some of these [economic] numbers they give out and then you go out and see people dying to get a job all over the country, I mean, it’s not jibing with what’s really going on,” Trump said. “The economy is not doing well,” Trump said. “You know, John, I’m getting 20,000 to 25,000 people every time I make a speech, and they are not there just because of the border,” he added, referring to his vow to build a wall between the US and Mexico.
“They are there because — and you know — if you put out a job notice, you’ll get thousands of people showing up to pick up a job,” Trump said. As I’ve mentioned before, I first met Trump decades ago and we used to talk once in a while, but haven’t for many years. Trump says he thinks the US unemployment rate is close to 20% and not the 5% reported by the Labor Department. Anyone who believes the 5% is a “dummy,” he said. The Federal Reserve, of course, always quotes the 5% figure and may raise interest rates based on that belief in the coming months. But even the Fed must not be too certain since it produces its own version of the jobless number, something I’ve already written about. Trump has said in the past that the Fed is also in his cross hairs for an audit. (I would recommend he look into how the Fed interferes with the markets.)
As I’ve been reporting for years, the official unemployment rate is conveniently reduced by a number of factors — each in place during both Democratic and Republican administrations. One of these factors, for example, is out-of-work people who have stopped looking for work for more than a year because they may have grown frustrated by the lack of jobs. They are not counted in the unemployment rate. A less popular unemployment stat, called the U-6, which measures some of these idled souls plus others who are forced to work part-time because they can’t find a 40-hour-a-week gig, stands at 9.7%. The truly frustrated aren’t counted at all.

It’s stunning, really, that this man still gets to dig his country ever deeper in. He hasn’t delivered on f**k all.
• Japan’s Abe Plans Up to $90.7 Billion Stimulus (BBG)
Japan Prime Minister Shinzo Abe plans to propose a fiscal stimulus package of as much as 10 trillion yen ($90.7 billion) after warning Group of Seven leaders that the global economy faces significant risk of another crisis, according to the Nikkei newspaper. Abe will seek a second supplementary budget worth 5 trillion yen to 10 trillion yen after July’s upper-house election, the Nikkei reported Saturday without attribution. Proposals will include accelerating the construction of a magnetic-levitation train line from Nagoya to Osaka, issuing vouchers to boost consumer spending, increasing pay for child-care workers and setting up a scholarship fund, the Nikkei said. “When you want to get the economy going, as long as demand in Asia is weak, you need additional public spending,” Martin Schulz at Fujitsu Research Institute in Tokyo, said by phone.
“Since private spending is still not picking up, the government is simply taking up the slack.” Abe is getting closer to delaying an increase in Japan’s sales tax, saying Friday he’ll make a decision before an upper-house election this summer on whether to go ahead with a planned hike in the levy next April to 10%, from 8%. A formal announcement of a two-year delay is expected Wednesday at the close of the parliamentary session, the Nikkei reported. This would be the second postponement by Abe, as the tax was initially scheduled to be raised in October 2015. An increase in the levy in 2014 pushed Japan into a recession. Abe had previously said the tax hike would be delayed only if there was a shock on the scale of a major earthquake or a corporate collapse like that of Lehman Brothers.
Since the previous tax hike, the economy has swung between contraction and growth, with consumer spending remaining weak. Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda has struggled to spur inflation despite record asset purchases and negative interest rates. Consumer prices excluding fresh food fell 0.3% in April from a year earlier, after dropping by the same amount in March, data released Friday showed. Meanwhile, the yen has surged about 9% versus the dollar this year, threatening profits for exporters including Toyota and weighing on the nation’s stock market. The benchmark Topix index has fallen 13% in 2016.

Compliments of the globalized and chemicalized food industry.
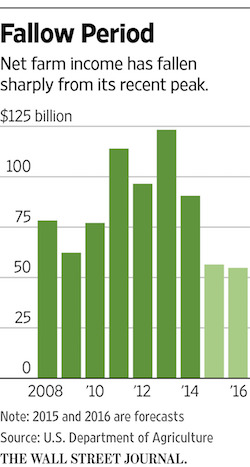
• US Farm Belt Banks Tighten the Buckle (WSJ)
Banks are tightening credit for U.S. farmers amid a rise in delinquencies, forcing some growers to turn to alternative sources of loans. When U.S. agriculture was booming this decade, banks doled out ample credit to strong performers and weaker growers alike, said Michael Swanson, an agricultural economist at Wells Fargo. But with the farm slump moving into its third year, banks have become pickier, requiring some growers to cough up more collateral and denying financing outright to some customers who need it to pay for seeds, crop chemicals and rent. Farmers this year have been grappling with low commodity prices, mounting debt and weaker incomes.
Claude Sem, chief executive of Farm Credit Services of North Dakota, said he asked some farmers to put up more land or machinery to back loans this spring. Collateral requirements could increase for more farmers if crop prices remain low, he said, noting that the cash price for wheat in northern North Dakota recently was about $4.50 a bushel, roughly a dollar below what it costs many farmers to raise the crop. “Below break-even, everything tightens up,” Mr. Sem said, adding that falling land values also have spurred lenders to boost collateral requirements, with cropland prices down as much as 20% in some parts of North Dakota.With traditional bank loans harder to come by, farmers are turning to sources like CHS Inc., a large farmer-owned cooperative in the U.S., which operates grain elevators and retail stores across the Midwest. CHS said its loans to farmers increased 48% in both number and volume in the 12 months to March and have more than doubled since 2014. It “suggests there are many farmers struggling to obtain financing,” said Randy Nelson, president of the co-op’s financing subsidiary, CHS Capital.

Lemmings ‘R’ Us.
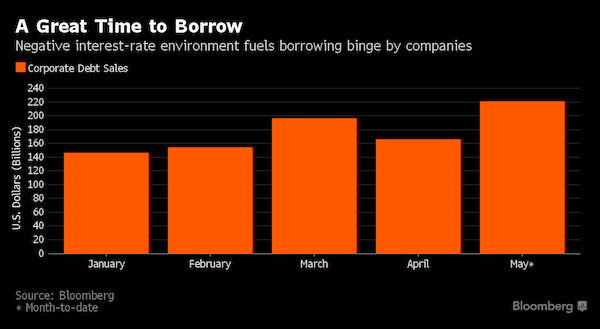
• Companies Go on Worldwide Bond Bender With $236 Billion of Sales (BBG)
A borrowing binge by companies globally is poised to make May one of the the busiest months ever, thanks to investors who continue to devour the relatively juicy yields on corporate debt in a negative-rate world.\ Global issuance of non-financial company debt will be in excess of $236 billion by month-end, according to data compiled by Bloomberg, led by computer maker Dell, which sold $20 billion of bonds to back its takeover of EMC in the year’s second-biggest corporate offering. In Europe, companies sold €48.5 billion ($54.2 billion) making it the busiest May on record. U.S. borrowers including Johnson & Johnson and Kraft Heinz did deals of more than €1 billion.
The surge in issuance is unlikely to satisfy investors who hoped to boost their income by buying company debt when easy-money monetary policies push yields on more than $9 trillion of bonds worldwide below zero. The extra yield investors demand to hold company debt globally relative to safer government bonds remains near year-to-date lows, while concessions on newly issued notes have fallen over the course of the month. “Deals continue to be very much oversubscribed,” said Travis King, head of investment-grade credit at Voya Investment Management, which oversees $203 billion. “It is very difficult to get bonds, especially in the hotter deals.” For investors who placed more than $80 billion of orders for Dell’s bond sale, the problem may get worse next month.
Seasonal declines in issuance, combined with decisions by some companies to accelerate debt sales to May, indicate June volumes in the U.S. will be in the $75 billion to $85 billion range, about half of this month’s supply, according to Bank of America. Vincent Murray, who heads U.S. fixed-income syndicate at Mizuho in New York, said the flow of new deals kept his team kept busy all month. While bond issuance will be less than $100 billion in June, some opportunistic companies may take advantage of low rates in the weeks ahead to issue debt, he said. “The market has remarkably weathered the storm of all this supply,” Murray said. “The fact that supply hasn’t affected the spreads in the marketplace may attract some more issuers that were thinking of passing.”

“..until the mid-1990s, the sum of runnable liabilities was steady at about 40% of U.S. GDP. That number peaked in early 2008 at 80%, but remains above historical levels, at about 60% of GDP.” And that does not include derivatives.
• Clinton Lurks in Shadows When Sparring With Sanders on Banks (BBG)
There is no universal definition for “shadow bank.” At its broadest, it’s any institution that borrows money and invests in financial assets, but is neither a bank, nor regulated like one. This can include insurance companies, hedge funds, private equity firms, and government-sponsored entities such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. In debates, Clinton brings up hedge funds and insurance companies. But her published plan hints at a more precise definition: if it’s runnable, it’s a shadow bank. A research note last year from economists at the Federal Reserve Board in Washington describes “runnables” – short-term funds at financial institutions that can evaporate in a panic. Bank deposits over $250,000 are uninsured, and therefore runnable.
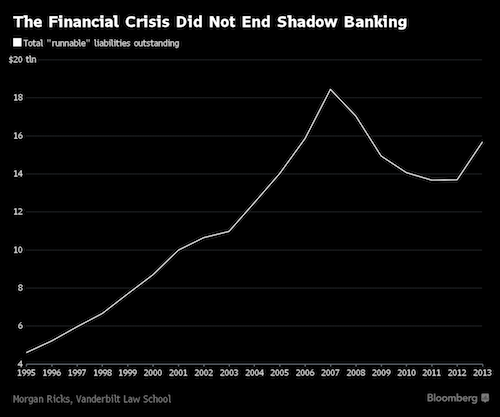
So are shares in money-market mutual funds; they should be considered investments, but in practice are not expected to lose principal. Repurchase agreements, also on the list, allow a borrower to sell a stock or bond, along with a promise to buy it back, often in a day or two. Short-term corporate debt, called “paper,” is similarly runnable. According to the Fed economists’ research, until the mid-1990s, the sum of runnable liabilities was steady at about 40% of U.S. GDP. That number peaked in early 2008 at 80%, but remains above historical levels, at about 60% of GDP. The definitions differ slightly, but this is consistent with patterns measured by Morgan Ricks at the Vanderbilt University Law School in Nashville, and by the the Financial Stability Oversight Council, a group of representatives from several regulators.
Runnables, said Ricks, are the “central unsolved problem of financial reform.” Ricks, who was a senior policy adviser at the Treasury Department in 2009 and 2010, takes a historical view of financial runs. Before the U.S. began insuring bank deposits in 1933, bank runs happened about once a decade. Since then, even during the financial crisis, they’ve been rare. But the risk moved outside the banks. Paul McCulley coined the term “shadow bank” during the Kansas City Fed’s 2007 Jackson Hole conference on economic policy. Then the chief economist of Pimco, McCulley laid out the systemic danger hidden in bank-like firms that relied on uninsured short-term funding. By the end of the next year, Bear Stearns, Lehman Brothers, and Merrill Lynch all collapsed. None of these were banks, but all had seen runs on short-term funding. “These are all species of the same genus,” said Ricks.

The wholesale destruction of cities and communities is not done.
• Toronto’s Red-Hot Market Sends Property Values Soaring (Star)
Toronto’s blistering housing market has prompted a 30% jump in residential property values over the last four years, according to the company that assesses real estate in the province. City homeowners will receive assessment notices — their first since 2012 — from the Municipal Property Assessment Corp. (MPAC) beginning next week showing a 7.5% annual increase in their property values. That’s well above the 4.5% provincial average, but lower than the double-digit increases in some 905-area communities such as Richmond Hill and Markham. The average assessed value for a single-family detached home in Toronto is $770,000, up about $200,000 on average from the last assessment in 2012. Toronto condo values increased 2.9% on average to $363,000, about $35,000 higher than four years ago.
Although assessments are linked to property taxes, homeowners should not panic about a steep rise in taxes, says MPAC. “Just because the assessment does increase doesn’t necessarily mean that this is going to have an impact on their taxes,” said Greg Martino, director of valuation and customer relations MPAC. Municipalities, not MPAC, determine property tax rates. How much an individual owner pays depends on where their assessment ranks compared to the city average. Owners whose properties are assessed above the 7.5% average will pay more. Those with below-average assessments pay less. In Toronto, virtually every property will be assessed at a higher rate than it was in 2012. If two properties were assessed at $500,000 in 2012, each would share an equal portion of the city’s tax burden. But if they are reassessed and one home remains at $500,000 but the other is now valued at $600,000, the higher valued property now carries a bigger tax responsibility.

Force interest rates up by just 1% and you have mayhem.
• UK House Prices Compared With Earnings ‘Close To Pre-Crisis Levels’ (G.)
House prices as a multiple of average earnings are “within a whisker” of record levels set before the financial crisis, a City consultancy has warned. The average UK house price is now 6.1 times average earnings, close to the peak of 6.4 it hit before the downturn, Fathom Consulting said. A rise in interest rates from their current low of 0.5% would lead to a correction, it said, although a return to “normal” rates was some way off. Prices have been pushed up by the availability of cheap home loans, and would need to fall by 40% to bring the ratio back to the pre-2000 average of 3.5 times earnings, it added. During the financial crisis, banks and building societies withdrew from lending, particularly to borrowers with small deposits.
But since then, the government’s funding for lending scheme made loans cheaper for borrowers with substantial equity, and then help to buy brought back 95% mortgages. Lenders are now cutting ratesand easing lending criteria. Fathom said this cheap borrowing had been the biggest driver for demand for homes. “Since 2013, the demand for housing has been turbocharged by chancellor [George] Osborne’s help-to-buy policy and the search for yield – which has resulted in the accumulation of housing wealth as an investment alternative for low-yielding financial assets,” it said. “As a consequence, house prices are now close to an all-time high of more than six times disposable income.”
The firm said couples buying together were increasingly taking on large loans relative to their income. Before the crisis fewer than 30% of joint mortgages were taken at more than 2.75 times income , but now that proportion has risen to more than a third. Fear of destabilising the “fragile arithmetic” that underpinned the housing market meant the Bank of England was unlikely to increase the base rate from its current record low of 0.5% until at least 2018, it said, regardless of the EU referendum result. “If it were to tighten Bank rate, it could trigger a rapid correction in the UK housing market and compound the slowdown in economic growth,” it said.

“Making Brexit a success will be the end of the EU. It cannot happen.” Brexit, period, will be the end.
• Paris and Berlin Ready ‘Plan B’ For Life After Brexit (FT)
European leaders have stepped-up secret discussions about a future union without Britain, drawing-up a “plan-B” focused on closer security and defence co-operation in the event of a UK vote to leave the EU. At several overlapping meetings in recent weeks — in Hanover, Rome and Brussels — EU leaders and their most trusted aides have discussed how to mount a common response to Brexit, which would be the bloc’s biggest setback in its 60-year history. More than a dozen politicians and officials involved at various levels have sketched out to the Financial Times the ideas for concerted action to “double down on the irreversibility of our union” — as well as the many internal divisions that stand in their way.
Rather than attempt a sudden lurch to integrate the eurozone, Chancellor Angela Merkel and President François Hollande are instead eyeing a push to deepen security and defence co-operation, a less contentious initiative that has appeal beyond the 19-member euro area. Foremost is the challenge of managing expected financial and political turmoil in the aftermath of a Brexit vote. Beyond the first statements to reassure markets, officials expect a special gathering of EU leaders — without Britain — to discuss the bloc’s response. A summit of all 28 leaders is already scheduled for June 28-29. “Everybody will say: ‘We’re sorry, this is a historical disaster but now we have to move on.’ And then they will say ‘OK, David [Cameron], goodbye, because now we have to meet as 27 leaders,’” said one senior diplomat intimately involved in the planning.
“That will be rather a decisive moment: will the 27 find the energy, the convergence of views to define a common agenda or whether it will be only the 19?” French officials are wary of Brexit contagion spreading to other member states and the lift it would provide to anti-EU insurgents like the National Front’s Marine Le Pen. They are determined to send a tough and punitive message to show divorce will be costly for Britain. “Playing down or minimising the consequences would put Europe at risk,” said one senior French official. “The principle of consequences is very important — to protect Europe.” Another leading European politician central to the Plan B process said: “Making Brexit a success will be the end of the EU. It cannot happen.”

There are a few smart people working at the IMF. But they don’t make policy. Neoliberals do.
• Neoliberalism Increases Inequality and Stunts Economic Growth: IMF (Ind.)
Key parts of neoliberal economic policy have increased inequality and risk stunting economic growth across the globe, economists at the IMF have warned. Neoliberalism – the dominant economic ideology since the 1980s – tends to advocate a free market approach to policymaking: promoting measures such as privatisation, public spending cuts, and deregulation. It is generally antipathetic to the public sector and believes the private sector should play a greater role in the economy. The ideology was initially championed by Margaret Thatcher and Ronald Reagan in Britain and America, but was ultimately also adopted by centre-left parties worldwide, under “third way” figures like Tony Blair.
The approach has long been the target of criticism from the radical left and parts of the reactionary right – but has been endorsed as common sense by centrist parties across the world for decades. Now a paper published in June 2016’s issue of the IMF’s Finance and Development journal warns that, after nearly forty years of neoliberalism, the approach is jeopardising the future of the world economy. “Instead of delivering growth, some neoliberal policies have increased inequality, in turn jeopardising durable expansion,” the senior IMF economists who drew up the paper said. The authors say that while the liberalisation of trade has helped lift people out of poverty in the developed world and some privatisations have raised efficiency, other aspects of the policy platform had seriously misfired.
“There are aspects of the neoliberal agenda that have not delivered as expected,” they said, focusing specifically on austerity and the freedom of capital to move across borders. “The benefits in terms of increased growth seem fairly difficult to establish when looking at a broad group of countries. “The costs in terms of increased inequality are prominent. Such costs epitomize the trade-off between the growth and equity effects of some aspects of the neoliberal agenda. “Increased inequality in turn hurts the level and sustainability of growth. Even if growth is the sole or main purpose of the neoliberal agenda, advocates of that agenda still need to pay attention to the distributional effects.”
They go on to say that throwing open national borders to multinational corporations has had “uncertain” growth benefits but quite clear costs – due to “increased economic volatility and crisis frequency” which they say is more evident under neoliberalism. On the issue of austerity, the authors say there is strong evidence that there is no reason for countries like Britain to inflict austerity on themselves. “Austerity policies not only generate substantial welfare costs due to supply-side channels, they also hurt demand – and thus worsen employment and unemployment,” they say. “In sum, the benefits of some policies that are an important part of the neoliberal agenda appear to have been somewhat overplayed.”

“During the Middle Ages, avarice had been considered to be among the most mortal of the seven deadly sins..”
• How the Deadly Sin of Avarice Was Rehabilitated as Self Interest (Evon.)
In the aftermath of the stock market crash of 1987, the New York Times headlined an editorial “Ban Greed? No: Harness It,” It continued: “Perhaps the most important idea here is the need to distinguish between motive and consequence. Derivative securities attract the greedy the way raw meat attracts piranhas. But so what? Private greed can lead to public good. The sensible goal for securities regulation is to channel selfish behavior, not thwart it.” The Times, surely unwittingly, was channeling the 18th century philosopher David Hume: “Political writers have established it as a maxim, that in contriving any system of government . . . every man ought to be supposed to be a knave and to have no other end, in all his actions, than his private interest. By this interest we must govern him, and, by means of it, make him, notwithstanding his insatiable avarice and ambition, cooperate to public good.”
The idea that base motives could be harnessed for the public good is what I term economic alchemy. And in Hume’s time it was definitely a new way of thinking about how society could be governed. During the Middle Ages, avarice had been considered to be among the most mortal of the seven deadly sins, a view that became more widespread with the expansion of commercial activity after the twelfth century. So it is surprising that self-interest would eventually be accepted a respectable motive, and even more surprising that this change owed little to the rise of economics, at least at first. How this came about, you will see, is a remarkable story, one that is finally running its course in light of mounting evidence not only that people are not really all that knavish, but also that treating citizens as if they were knaves may lead them to act is if they really were knaves! But I am getting ahead of the story.
It all began in the sixteenth century with Niccolò Machiavelli. “Anyone who would found a republic and order its laws” he wrote in his Discourses, “must assume that all men are wicked [and] . . . never act well except through necessity . . . It is said that hunger and poverty make them industrious, laws make them good.” Hume, it seems was channeling Machiavelli! It was the shadow of war and disorder that made self-interest an acceptable basis of good government. During the seventeenth century, wars accounted for a larger share of European mortality than in any century for which we have records, including what Raymond Aron called “the century of total war,” which happily is now finished.
Writing after a decade of warfare between English parliamentarians and royalists, Hobbes (in 1651) sought to determine “the Passions that encline men to Peace” and found them in “Feare of Death; Desire of such things as are necessary to commodious living; and a Hope by their Industry to obtain them.” Knaves might be preferable to saints or at least likely to be more harmless. The year before Adam Smith wrote in his Wealth of Nations (1776) about how the self-interest of the butcher, the brewer, and the baker would put our dinner on the table, James Boswell’s Dr. Johnson gave Homo economicus a different endorsement: “There are few ways in which a man can be more innocently employed than in getting money.”

“[One] great myth we’re seeing play out is that of Obama as some kind of peaceful guy who’s trying to get rid of nuclear weapons. He’s the biggest nuclear warrior there is. He’s committed us to a ruinous course of spending a trillion dollars on more nuclear weapons. Somehow, people live in this fantasy that because he gives vague news conferences and speeches and feel-good photo-ops that somehow that’s attached to actual policy. It isn’t.”
• Silencing the United States as It Prepares for War (Pilger)
Returning to the United States in an election year, I am struck by the silence. I have covered four presidential campaigns, starting with 1968; I was with Robert Kennedy when he was shot and I saw his assassin, preparing to kill him. It was a baptism in the American way, along with the salivating violence of the Chicago police at the Democratic Party’s rigged convention. The great counter revolution had begun. The first to be assassinated that year, Martin Luther King, had dared link the suffering of African-Americans and the people of Vietnam. When Janis Joplin sang, “Freedom’s just another word for nothing left to lose”, she spoke perhaps unconsciously for millions of America’s victims in faraway places.
“We lost 58,000 young soldiers in Vietnam, and they died defending your freedom. Now don’t you forget it.” So said a National Parks Service guide as I filmed last week at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington. He was addressing a school party of young teenagers in bright orange T-shirts. As if by rote, he inverted the truth about Vietnam into an unchallenged lie. The millions of Vietnamese who died and were maimed and poisoned and dispossessed by the American invasion have no historical place in young minds, not to mention the estimated 60,000 veterans who took their own lives. A friend of mine, a marine who became a paraplegic in Vietnam, was often asked, “Which side did you fight on?” A few years ago, I attended a popular exhibition called “The Price of Freedom” at the venerable Smithsonian Institution in Washington.
The lines of ordinary people, mostly children shuffling through a Santa’s grotto of revisionism, were dispensed a variety of lies: the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki saved “a million lives”; Iraq was “liberated [by] air strikes of unprecedented precision”. The theme was unerringly heroic: only Americans pay the price of freedom. The 2016 election campaign is remarkable not only for the rise of Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders but also for the resilience of an enduring silence about a murderous self-bestowed divinity. A third of the members of the United Nations have felt Washington’s boot, overturning governments, subverting democracy, imposing blockades and boycotts. Most of the presidents responsible have been liberal – Truman, Kennedy, Johnson, Carter, Clinton, Obama.
The breathtaking record of perfidy is so mutated in the public mind, wrote the late Harold Pinter, that it “never happened …Nothing ever happened. Even while it was happening it wasn’t happening. It didn’t matter. It was of no interest. It didn’t matter … “. Pinter expressed a mock admiration for what he called “a quite clinical manipulation of power worldwide while masquerading as a force for universal good. It’s a brilliant, even witty, highly successful act of hypnosis.”

Is Russia the only party to turn to?
• ISIS Advance Traps 165,000 Syrians at Closed Turkish Border (HRW)
There are two walls on the Turkey-Syria border. One is manned by Turkish border guards enforcing Turkey’s 15 month-old border closure who, according to witnesses, have at times shot at and assaulted Syrian asylum seekers as they try to reach safety in Turkey – abuses strongly denied by the Turkish government. The other is a wall of silence by the rest of the world, including the United Nations, which has chosen to turn a blind eye to Turkey’s breach of international law which prohibits forcing people back to places, including by rejecting them at the border, where their lives or freedom would be threatened. Both walls are trapping 165,000 displaced Syrians now scattered in overcrowded informal settlements and fields just south of Turkey’s Öncupınar/Bab al-Salameh border crossing and in and around the nearby Syrian town of Azaz.
In April, 30,000 of them fled ISIS advances on about 10 informal displacement camps to the east of Azaz, which came under ISIS attack, and one of which has since been hit by an airstrike that killed at least 20 people and injured at least 37 more. Turkish border guards shot at civilians fleeing ISIS and approaching the border. Now aid agencies operating in the area say that between May 24 and 27, another 45,000 fled a new ISIS assault on the area east of Azaz and are now stuck in and around Azaz too. Aid agencies say there is no question all 165,000 would seek asylum in Turkey if the border were open to them.