William Henry Jackson Steamboat Metamora of Palatka on the Ocklawaha, FL 1902



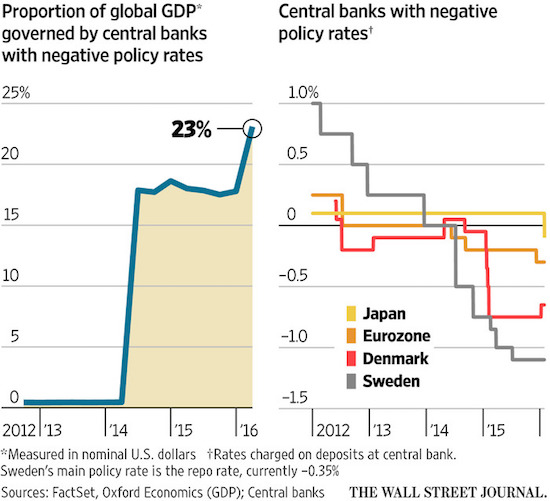
The essence, as Steve Keen keeps saying, is that negative rates on reserves are madness, because banks can’t lend out their reserves. Something central bankers genuinely don’t seem to grasp, weird as that may seem. Which speaks volumes, and shines a very bleak light, on the field of economics.
• Bank Of Japan’s Negative Rates Are ‘Economic Kamikaze’ (CNBC)
The Japanese central bank has only dug the country deeper into a hole by adopting negative interest rates, Lindsey Group chief market analyst Peter Boockvar said Friday. “I think it’s economic kamikaze,” he told CNBC’s “Squawk Box.” “Let’s tax money and hope things get better. Let’s create higher inflation for the Japanese people, who are barely seeing wage growth. And let’s amp up the currency battles, and hope everything gets better.” The Bank of Japan surprised markets on Friday by pushing interest rates into negative territory for the first time ever. By doing so, the BOJ is essentially charging banks for parking excess funds. The fact that the vote was split shows that BOJ Governor Haruhiko Kuroda got a lot of pushback to advance the policy, Boockvar said. “If this means now that they’re out of bullets with [QE], and this is their last hope, then I think this is a mess,” he said.
In a statement released along with the rate decision, the BOJ said the Japanese economy has recovered modestly with underlying inflation and spending by companies and households ticking up. But the bank warned that increasing uncertainty in emerging markets and commodity-exporting countries may delay an improvement in Japanese business confidence and negatively affect the current inflation trend. The BOJ’s inflation target is 2%. The BOJ now forecasts core inflation to average 0.2 to 1.2% between April 2016 and March 2017. Boockvar said he believes it’s a fallacy that Japan needs inflation to generate growth. “Inflation readings are a symptom of what underlying growth is,” Boockvar said. “For Kuroda to think ‘I need to generate higher inflation to generate growth’ to me is completely backwards, especially when Japanese wage growth is so anemic. You’re basically penalizing the Japanese consumer, and I don’t know what economic theory is behind that.”

And they will make things worse.
• Negative Rates In The US Are Next (ZH)
When stripping away all the philosophy, the pompous rhetoric, and the jawboning, all central banks do, or are supposed to do, is to influence capital allocations and spending behavior by adjusting the liquidity preference of the population by adjusting interest rates and thus the demand for money. To be sure, over the past 7 years central banks around the globe have gone absolutely overboard when it comes to their primary directive and have engaged every possible legal (and in the case of Europe, illegal) policy at their disposal to force consumers away from a “saving” mindset, and into purchasing risk(free) assets or otherwise burning through savings in hopes of stimulating inflation. Today’s action by the Bank of Japan, which is meant to force banks, and consumers, to spend their cash which will now carry a penalty of -0.1% if “inert” was proof of just that.
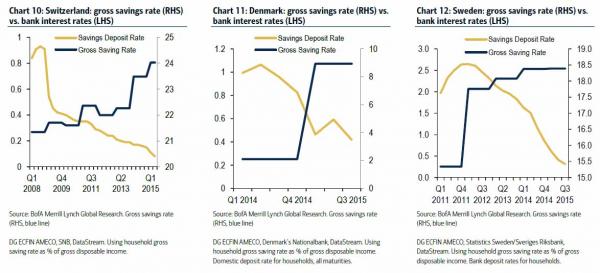
Ironically, and perversely from a classical economic standpoint, as we showed before in the case of Europe’s NIRP bastions, Denmark, Sweden, and Switzerland, the more negative rates are, the higher the amount of household savings! This is what Bank of America said back in October: “Yet, household savings rates have also risen. For Switzerland and Sweden this appears to have happened at the tail end of 2013 (before the oil price decline). As the BIS have highlighted, ultra-low rates may perversely be driving a greater propensity for consumers to save as retirement income becomes more uncertain.” Bingo: that is precisely the fatal flaw in all central planning models, one which not a single tenured economist appears capable of grasping yet which even a child could easily understand.
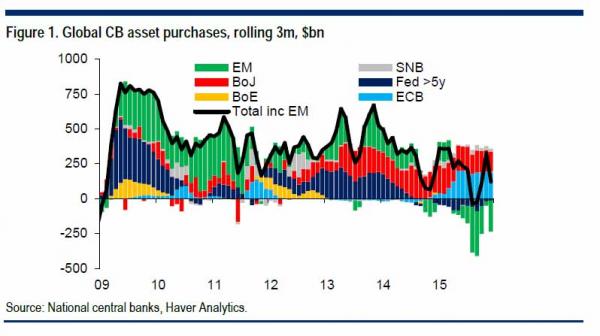
[..] And here is the one chart which in our opinion virtually assures that the Fed will follow in the footsteps of Sweden, Denmark, Europe, Switzerland and now Japan. Since the middle of 2015, US investors have bought a big fat net zero of either bonds or equities (in fact, they have been net sellers of risk) and have parked all incremental cash in money-market funds instead, precisely the inert non-investment that is almost as hated by central banks as gold.
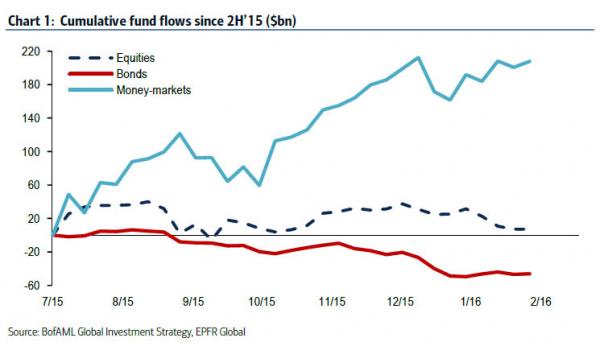

Lots of good graphs. This one must be the scariest.
• The Boxed-In Fed (Tenebrarum)
As we often stress, economics is a social science and therefore simply does not work like physics or other natural sciences. Only economic theory can explain economic laws – while economic history can only be properly interpreted with the aid of sound theory. Here is how we see it: If the authorities had left well enough alone after Hoover’s depression had bottomed out, the economy would have recovered quite nicely on its own. Instead, they decided to intervene all-out. The result was yet another artificial inflationary boom. By 1937 the Fed finally began to worry a bit about the growing risk of run-away inflation, so it took a baby step to make its policy slightly less accommodative.
Once the artificial support propping up an inflationary boom is removed, the underlying economic reality is unmasked. The cause of the 1937 bust was not the Fed’s small step toward tightening. Capital had been malinvested and consumed in the preceding boom, a fact which the bust revealed. Note also that a huge inflow of gold from Europe in the wake of Hitler’s rise to power boosted liquidity in the US enormously in 1935-36, with no offsetting actions taken by the Fed. Moreover, the Supreme Court had just affirmed the legality of several of the worst economic interventions of the crypto-socialist FDR administration, which inter alia led to a collapse in labor productivity as the power of unions was vastly increased, as Jonathan Finegold Catalan points out.
He also notes that bank credit only began to contract after the stock market collapse was already well underway – in other words, the Fed’s tiny hike in the minimum reserve requirement by itself didn’t have any noteworthy effect. On the other hand, if the Fed had implemented the Bernanke doctrine in 1937 and had continued to implement monetary pumping at full blast in order to extend the boom, it would only have succeeded in structurally undermining the economy and currency even more. Inevitably, an even worse bust would eventually have followed.
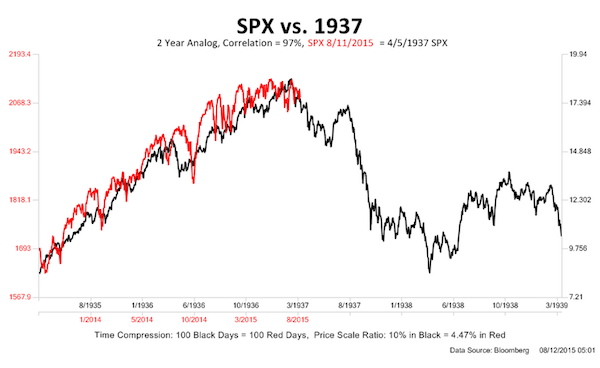

There’s not a number left you can trust.
• Central Banks Go to New Lengths to Boost Economies (WSJ)
Central banks around the world are going to new lengths to boost their economies, underscoring both the importance and limits of monetary policy in a global economy plagued by paltry growth and unsettled markets. The Bank of Japan on Friday joined a host of European peers in setting its key short-term interest rate below zero. The move, long denied as a possible course by the bank s governor, came a week after the ECB president indicated he was ready to launch additional monetary stimulus in March and days after the Fed expressed new worries over market turbulence and sluggish growth overseas. The latest moves by central banks to rescue the global economy capped a volatile month across financial markets, with U.S. stocks finishing strong Friday but nonetheless posting their worst January since 2009, and major currencies lurching lower against the dollar.
The swings highlighted the fragile mood of investors despite hopes that some economies, particularly the U.S., could lead an exit from crisis-era policies. Fresh data Friday that showed the U.S. economy had sputtered in the final months of 2015 could cloud Fed deliberations over the timing of another round of rate increases. U.S. GDP, the broadest measure of economic output, grew by just 0.7% in the fourth quarter, hit hard by shrinking exports and business investment. Despite growth in consumer spending and clear strength in the job market, the weak performance added to concerns that the sagging global economy could hit the U.S.
Markets around the world were buoyed by Japan s move, extending the earlier assurances delivered by the ECB. Japan s Nikkei Stock Average closed up 2.8% in a volatile session, while the yield on Japanese government bonds fell to historically low levels. The Shanghai Composite Index jumped 3.1% and the Stoxx Europe 600 rose 2.2%. U.S. stocks also rose, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average climbing nearly 400 points. Despite the day s surge, some investors remained skeptical about the lasting impact of the central banks efforts. People are starting to feel more and more that central bank action is having less and less fire for effect, said Ian Winer, head of equities at Wedbush Securities.

Lunar New year starts Feb 7. Beijing will be so happy with the week long break.
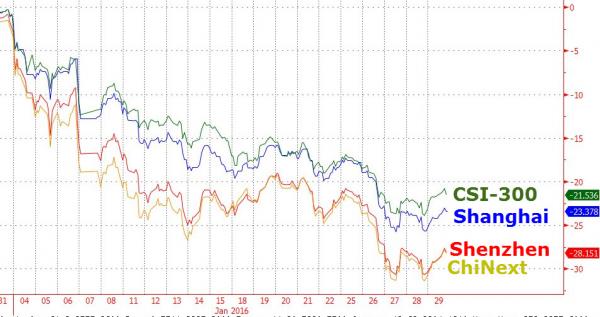
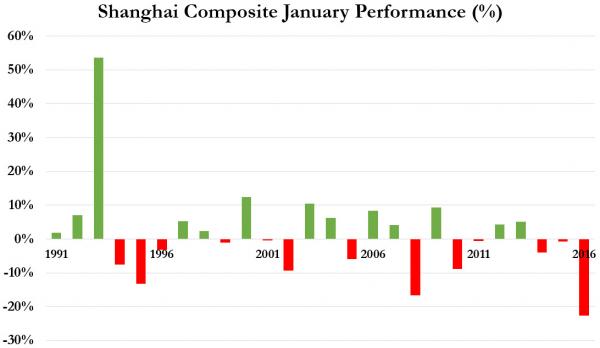
• China Stocks Have Worst.January.Ever (ZH)
Thanks to BoJ’s global “float all boats” NIRP-tard-ness, Chinese stocks avoided the headline of “worst month in 21 years” by rallying above the crucial 2,667 level (for SHCOMP). However, January’s 23% plunge is the worst month since October 2008 and is officially the worst start to a year in the history of Chinese stocks. While Shanghia Composite was ugly, the higher beta Shenzhen and ChiNext indices were a disaster…
Making it the worst January ever…
So February is a buying opportunity?

4% over past 5 years. Could easily be 2% for 2015.
• China’s ‘Hard Landing’ May Have Already Happened (AFR)
It’s the biggest question in the world of finance: how fast is China’s economy growing? And the biggest frustration is: what are the actual numbers? China’s lack of transparency – with murky data releases, opaque policy making and confusing announcements – is notorious among emerging-market watchers. But rarely do research firms or analysts use different figures to the official statistics. Until recently. The Conference Board, a widely respected and often-cited non-profit research group, used an alternate series of Chinese GDP estimates in its latest economic outlook paper. In an effort to adjust for overstated official Chinese data, the Conference Board looked to the work of Harry Wu, an economist at the Institute of Economic Research, Hitotsubashi University in Tokyo, to adjust its calculations.
This was a footnote of the report: “Growth rates of Chinese industrial GDP are adjusted for mis-reporting bias and non-material services GDP are adjusted for biases in price deflators. This adjustment has important implications for our assessment of the growth rate of the global economy in general and that of the emerging markets in particular – both reflecting a downward adjustment in their recent growth rates.” Macquarie Wealth Management analysts picked up on the change, adding: “We are unaware of any other reputable agency adopting anything other than official numbers as a base case, although clearly there has always been a lot of scenario analysis.” Traditionally, China has used the Soviet system of collecting information through a chain of command, where local officials reported on their states, often misrepresenting their figures to meet designated targets.
Over the past 10 years, China has gradually moved towards the internationally recognised System of National Accounts, which relies on statistical surveys to discover what people are spending their money on and where. But as Macquarie points out, that transition is far from complete. The Wu-Maddison estimates are starkly different to those issued by Chinese authorities. Whereas Chinese authorities have claimed average GDP growth of about 7.7% for the past five years, Wu suggests it is much lower, about 4%. These new figures show a much higher degree of volatility than suggested by the official numbers. While the world frets about the possibility of a “hard landing” for the Chinese economy, the Conference Board observed the new estimates “suggest that the economy has already experienced a significant slowdown over the past four years, beginning in 2011.”
Macquarie echoes this sentiment. “In our view, Wu-Maddison numbers explain the current state of commodity markets and fit into the global deflationary narrative much better than official numbers,” the analysts Macquarie said in a note. But, as the bank points out, if the “hard landing” has already occurred, there will be a range of consequences for productivity growth, overcapacity absorption and financial stress. “If Wu estimates are right, the room for stimulus and investment is more limited and the need to drive productivity [structural reforms] much more urgent. Although by the time China retroactively adjusts its GDP, it would be treated as history. “In the absence of stronger productivity rebound, China would be in danger of getting stuck in the ‘middle-income trap’ and would be unable to inject incremental demand into the global economy. Stay safe.”

They can target what they want, and so they do. But it’s meaningless.
• China Set To Adopt 6.5-7% Growth Target Range For 2016 (Reuters)
China’s leaders are expected to target economic growth in a range of 6.5% to 7% this year, sources familiar with their thinking said, setting a range for the first time because policymakers are uncertain on the economy’s prospects. The proposed range, which would follow a 2015 target of “around 7%” growth, was endorsed by top leaders at the closed-door Central Economic Work Conference in mid-December, according to the sources with knowledge of the meeting outcome. The world’s second-largest economy grew 6.9% in 2015, the weakest in 25 years, although some economists believe real growth is even lower. “They are likely to target economic growth of 6.5-7% this year, with 6.5% as the bottom line,” said one of the sources, a policy adviser.
Policymakers, worried by global uncertainties and the impact on growth of their structural economic reforms, struggled to reach a consensus at the December meeting, the sources said. The State Council Information Office, the public relations arm of the government, had no comment on the growth forecast when contacted by Reuters. The floor of 6.5% reflects the minimum average rate of growth needed over the next five years to meet an existing goal of doubling gross domestic product and per capita income by 2020 from 2010. The 2016 growth target and the country’s 13th Five-Year Plan, a blueprint covering 2016-2020, will be announced at the annual meeting of the National People’s Congress, the country’s parliament, in early March.
Although the target range was endorsed by the leadership in December, it could still be adjusted before parliament convenes. “The government will not be too nervous about growth this year and will focus more on structural adjustments,” said a government economist. “Growth may still slow in the first and second quarter and people are divided over the third and fourth quarter. The full-year growth could slow to 6.5-6.6%.” A string of cuts in interest rates and bank reserve requirements since November 2014 have failed to put a floor under the slowing economy. Beijing is expected to put more emphasis on fiscal policy to support growth, including tax cuts and running a bigger budget deficit of about 3% of GDP.
China’s leaders have flagged a “new normal” of slower growth as they look to shift the economy to a more sustainable, consumption-led model. About half of China’s 30 provinces and municipalities have lowered their growth targets for 2016, while nearly a third kept targets unchanged from last year, according to local media. Guangdong and Zhejiang provinces have set a growth target of 7-7.5% this year, while Jiangsu and Shandong are aiming for growth of 7.5-8%. In 2015, growth in Chongqing municipality was 11%, the fastest in the country, while growth in Liaoning province in the rustbelt northeast, was 3%, the country’s lowest. For this year, Chongqing is eyeing 10% growth and Liaoning is aiming for 6%.

Correlation.
• Junk Bonds’ Rare Negative Return In January Is Bad News For Stocks (MW)
The U.S. high-yield, or “junk” bond market, has started the year on the back foot, which history suggests could be a very bad sign for the stock market. The asset class is showing negative returns of almost 2% for the year so far, and negative returns of 7.6% for the last six months, according to The Bank of America Merrill Lynch U.S. High Yield Index. The negative return is especially significant, given that the month of January has recorded positive returns in 25 of the 29 years that the BofA high-yield index has existed, or 86.2% of the time, according to Marty Fridson, chief Investment Officer–Lehmann Livian Fridson, in a report published in LCD. With the S&P 500 index also heading for the biggest monthly decline in nearly six years, stock investors may finally be catching on to the high-yield bond market’s bearish message.
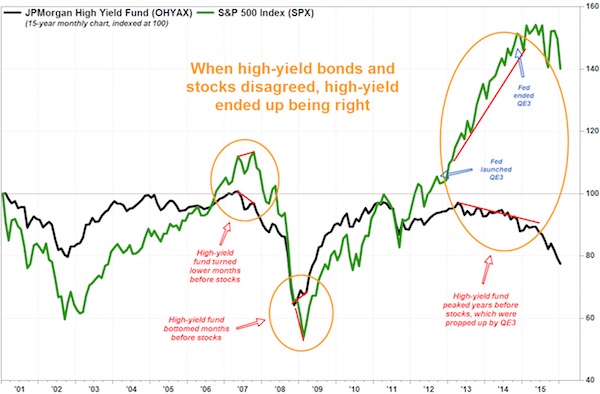
In previous instances in which the high-yield bond market and stocks trended in a different direction, it was the high-yield bond market that proved prescient. The reason stocks have been so late to follow the high-yield market’s bearish trend, may be because of the Federal Reserve’s efforts to prop up asset prices through quantitative easing. The current bearish trend is showing no signs of letting up. The high-yield index’s option-adjusted spread widened to 775 basis points at Thursday’s close from 695 basis points at the end of December, and 526 basis points at the end of July. The OAS is now about 200 basis points wider than its historical average of 576 basis points, according to Fridson. Much of the weakness is still due to the troubled energy sector, which combined with slowing Chinese growth to spark a more than 100 basis-points widening of the BofA US High Yield Index’s option-adjusted spread in the first three weeks of January. That send the spread to a high of 820 basis points on Jan 20.

Condemnation.
• I Worked On Wall Street. I Am Skeptical Hillary Clinton Will Rein It In (Arnade)
I owe almost my entire Wall Street career to the Clintons. I am not alone; most bankers owe their careers, and their wealth, to them. Over the last 25 years they – with the Clintons it is never just Bill or Hillary – implemented policies that placed Wall Street at the center of the Democratic economic agenda, turning it from a party against Wall Street to a party of Wall Street. That is why when I recently went to see Hillary Clinton campaign for president and speak about reforming Wall Street I was skeptical. What I heard hasn’t changed that skepticism. The policies she offers are mid-course corrections. In the Clintons’ world, Wall Street stays at the center, economically and politically. Given Wall Street’s power and influence, that is a dangerous place to leave them.
Salomon Brothers hired me in 1993, seven months after President Bill Clinton’s inauguration. Getting a job had been easy, Wall Street was booming from deregulation that had begun under Reagan and was continuing under Clinton. When Bill Clinton ran for office, he offered up him and Hillary (“Two for the price of one”) as New Democrats, embracing an image of being tough on crime, but not on business. Despite the campaign rhetoric, nobody on the trading floor I joined had voted for the Clintons or trusted them. Few traders on the floor were even Democrats, who as long as anyone could remember were Wall Street’s natural enemy. That view was summarized in the words of my boss: “Republicans let you make money and let you keep it. Democrats don’t let you make money, but if you do, they take it.”
Despite Wall Street’s reticence, key appointments were swinging their way. Robert Rubin, who had been CEO of Goldman Sachs, was appointed to a senior White House job as director of the National Economic Council. The Treasury Department was also being filled with banking friendly economists who saw the markets as a solution, not as a problem. The administration’s economic policy took shape as trickle down, Democratic style. They championed free trade, pushing Nafta. They reformed welfare, buying into the conservative view that poverty was about dependency, not about situation. They threw the old left a few bones, repealing prior tax cuts on the rich, but used the increased revenues mostly on Wall Street’s favorite issue: cutting the debt. Most importantly, when faced with their first financial crisis, they bailed out Wall Street.
That crisis came in January 1995, halfway through the administration’s first term. Mexico, after having boomed from the optimism surrounding Nafta, went bust. It was a huge embarrassment for the administration, given the push they had made for Nafta against a cynical Democratic party. Money was fleeing Mexico, and much of it was coming back through me and my firm. Selling investors’ Mexican bonds was my first job on Wall Street, and now they were trying to sell them back to us. But we hadn’t just sold Mexican bonds to clients, instead we did it using new derivatives product to get around regulatory issues and take advantages of tax rules, and lend the clients money. Given how aggressive we were, and how profitable it was for us, older traders kept expecting to be stopped by regulators from the new administration, but that didn’t happen.
When Mexico started to collapse, the shudders began. Initially our firm lost only tens of millions, a large loss but not catastrophic. The crisis however was worsening, and Mexico was headed towards a default, or closing its border to money flows. We stood to lose hundreds of millions, something we might not have survived. Other Wall Street firms were in worse shape, having done the trade in a much bigger size. The biggest was rumored to be Lehman, which stood to lose billions, a loss they couldn’t have survived. As the crisis unfolded, senior management traveled to DC as part of a group of bankers to meet with Treasury officials. They had hoped to meet with Rubin, who was now Treasury secretary. Instead they met with the undersecretary for international affairs who my boss described as: “Some young egghead academic who likes himself a lot and is wide eyed with a taste of power.” That egghead was Larry Summers who would succeed Rubin as Treasury Secretary.
To the surprise of Wall Street, the administration pushed for a $50bn global bail-out of Mexico, arguing that to not do so would devastate the US and world economy. Unmentioned was that it would have also devastated Wall Street banks.

New twist.
• VW Says Defeat Software Legal In Europe (GCR)
Another week brings more new stories on the diesel-emission cheating scandal that threatens to dig Volkswagen deeper into a ditch of its own making. Following reports in German newspapers late last week suggesting that the “defeat device” software was an “open secret” in VW’s engine group, the company bit back yesterday. VW Group CEO Matthias Müller told reporters at a reception that the sources for the Sueddeutsche Zeitung report “have no idea about the whole matter.” Müller’s statement, as reported by Reuters, “casts doubt” on the newspaper’s report, which it said came from statements by a whistleblower cited in the company’s internal probe of the scandal. The CEO also suggested that the company would not release results of that probe, conducted by U.S. law firm Jones Day, any time before its annual shareholder meeting on April 21.
“Is it really so difficult to accept that we are obliged by stock market law to submit a report to the AGM on April 21,” asked Müller, “and that it is not possible for us to say anything beforehand?” VW Group’s powerful Board of Directors will hold their third meeting in three weeks on the affair this coming Wednesday. Despite PR fallout, VW Group’s German communications unit continues to allege that while the “defeat device” software in its TDI diesels violated U.S. laws, it was entirely legal in Europe. The majority of the 11 million affected vehicles were sold in European countries, helped by policies instituted by some national governments that gave financial advantages to diesel vehicles and their fuel.
In a statement to The New York Times, which published an article on the matter last week, the VW Group wrote that the software “is not a forbidden defeat device” under European rules. As the Times notes, that determination, “which was made by its board, runs counter to regulatory findings in Europe and the United States.” “German regulators said last month that VW did use an illegal defeat device,” the newspaper said, suggesting that the statement reflected VW’s legal approach to the affair. “While it promises to fix affected vehicles wherever they were sold,” it said, “it is prepared to admit wrongdoing only in the United States.” The VW view only underscores the loosely-regulated European emission testing rules, now the subject of a fight in the European Parliament.
Two issues are at stake. The first is the degree to which new and tougher testing rules continue to allow manufacturers to exceed existing emission limits The second is whether European Union authorities can, in some circumstances, overrule the testing bodies of individual countries -namely Germany- which enforce common EU limits within their own borders. And so the saga continues.

I think that as pensions plans crumble to levels where too many elederly go hungry, basic income will come to the forefront.
• Swiss To Vote On Basic Income (DM)
Swiss residents are to vote on a countrywide referendum about a radical plan to pay every single adult a guaranteed income of £425 a week (or £1,700 a month). The plan, proposed by a group of intellectuals, could make the country the first in the world to pay all of its citizens a monthly basic income regardless if they work or not. But the initiative has not gained much traction among politicians from left and right despite the fact that a referendum on it was approved by the federal government for the ballot box on June 5. Under the proposed initiative, each child would also receive 145 francs (£100) a week. The federal government estimates the cost of the proposal at 208 billion francs (£143 billion) a year.
Around 153 billion francs (£105 bn) would have to be levied from taxes, while 55 billion francs (£38 bn) would be transferred from social insurance and social assistance spending. The group proposing the initiative, which includes artists, writers and intellectuals, cited a survey which shows that the majority of Swiss residents would continue working if the guaranteed income proposal was approved. ‘The argument of opponents that a guaranteed income would reduce the incentive of people to work is therefore largely contradicted,’ it said in a statement quoted by The Local. However, a third of the 1,076 people interviewed for the survey by the Demoscope Institute believed that ‘others would stop working’. And more than half of those surveyed (56%) believe the guaranteed income proposal will never see the light of day.

There will be no money to pay for even temporary storage, and there is no solution for permament.
• Radioactive Waste Dogs Germany Despite Abandoning Nuclear Power (NS)
Half a kilometre beneath the forests of northern Germany, in an old salt mine, a nightmare is playing out. A scheme to dig up previously buried nuclear waste is threatening to wreck public support for Germany’s efforts to make a safe transition to a non-nuclear future. Enough plutonium-bearing radioactive waste is stored here to fill 20 Olympic swimming pools. When engineers backfilled the chambers containing 126,000 drums in the 1970s, they thought they had put it out of harm’s way forever. But now, the walls of the Asse mine are collapsing and cracks forming, thanks to pressure from surrounding rocks. So the race is on to dig it all up before radioactive residues are flushed to the surface.
It could take decades to resolve. In the meantime, excavations needed to extract the drums could cause new collapses and make the problem worse. “There were people who said it wasn’t a good idea to put radioactive waste down here, but nobody listened to them,” says Annette Parlitz, spokeswoman for the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS), as we tour the mine. This is just one part of Germany’s nuclear nightmare. The country is also wrestling a growing backlog of spent fuel. And it has to worry about vast volumes of radioactive rubble that will be created as all the country’s 17 nuclear plants are decommissioned by 2022 – a decision taken five years ago, in the aftermath of Japan’s Fukushima disaster. The final bill for decommissioning power plants and getting rid of the waste is estimated to be at least €36 billion.
Some 300,000 cubic metres of low and intermediate-level waste requiring long-term shielding, including what is dug from the Asse mine, is earmarked for final burial at the Konrad iron mine in Lower Saxony. What will happen to the high-level waste, the spent fuel and other highly radioactive waste that must be kept safe for up to a million years is still debated. Later this year, a Final Storage Commission of politicians and scientists will advise on criteria for choosing a site where deep burial or long-term storage should be under way by 2050. But its own chairman, veteran parliamentarian Michael Muller, says that timetable is unlikely to be met. “We all believe deep geology is the best option, but I’m not sure if there is enough [public] trust to get the job done,” he says.

Is it the smugglers or the EU?
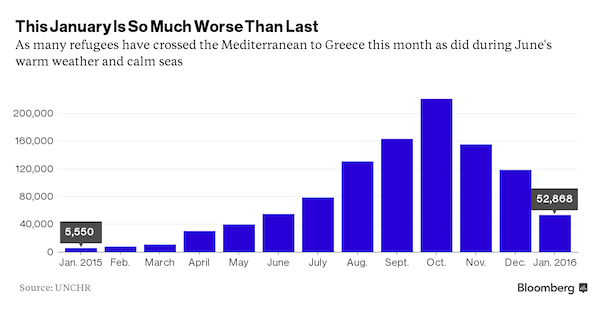
• Mediterranean Deaths Soar As People-Smugglers Get Crueller: IOM (Reuters)
More people died crossing the eastern Mediterranean in January than in the first eight months of last year, the International Organization for Migration said on Friday, blaming increased ruthlessness by people-traffickers. As of Jan. 28, 218 had died in the Aegean Sea – a tally not reached on the Greek route until mid-September in 2015. Another 26 died in the central Mediterranean trying to reach Italy. Smugglers were using smaller, less seaworthy boats, and packing them with even more people than before, the IOM said. IOM spokesman Joel Millman said the more reckless methods might be due to “panic in the market that this is not going to last much longer” as traffickers fear European governments may find ways to stem the unprecedented flow of migrants and refugees.
There also appeared to be new gangs controlling the trafficking trade in North Africa, he said. “There was a very pronounced period at the end of the year when boats were not leaving Libya and we heard from our sources in North Africa that it was because of inter-tribal or inter-gang fighting for control of the market,” Millman said. “And now that it’s picking up again and it seems to be more lethal, we wonder: what is the character of these groups that have taken over the trade?” The switch to smaller, more packed boats had also happened on the route from Turkey to Greece, the IOM said, but was unable to explain why.
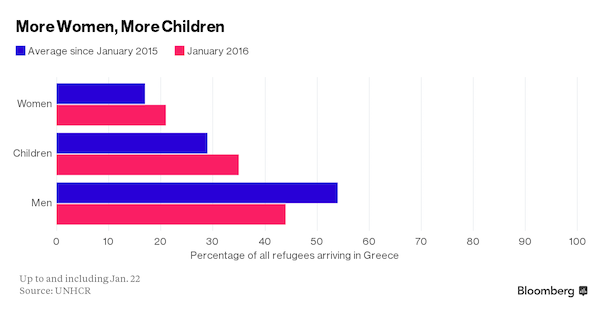
The increase in deaths in January was not due to more traffic overall. The number of arrivals in Greece and Italy was the lowest for any month since June 2015, with a total of 55,528 people landing there between Jan. 1 and Jan. 28, the IOM said. Last year a record 1 million people made the Mediterranean Sea crossing, five times more than in 2014. During the year, the IOM estimates that 805 died in the eastern Mediterranean and 2,892 died in the central Mediterranean. In the past few months the proportion of children among those making the journey has risen from about a quarter to more than a third, and Millman said children often made up more than half of the occupants of the boats.