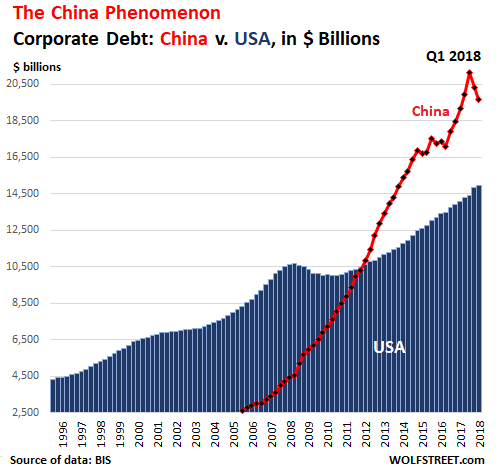
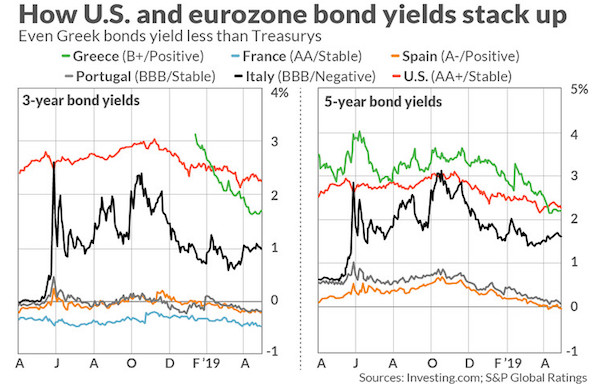
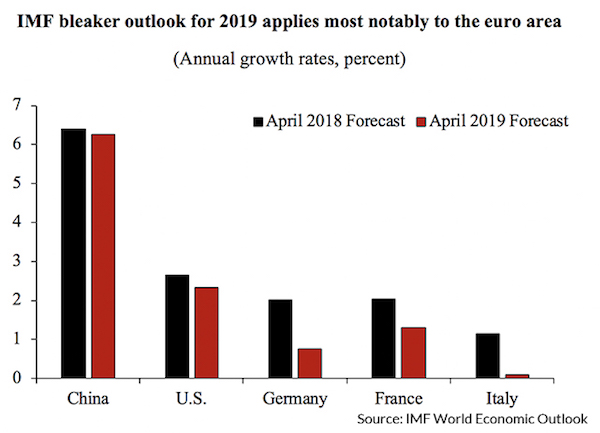
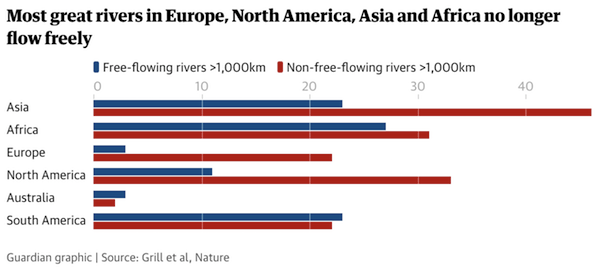
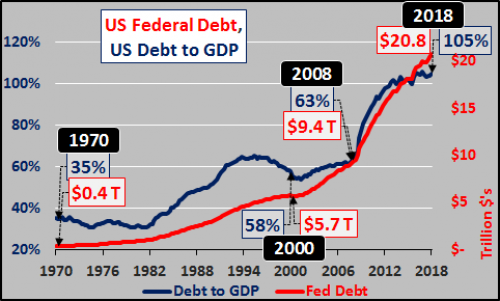
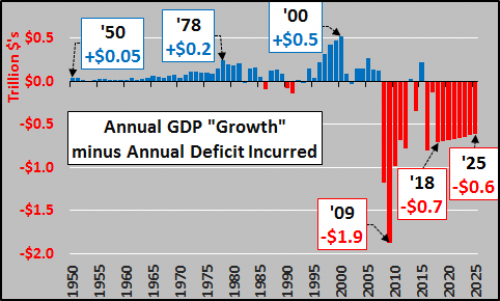
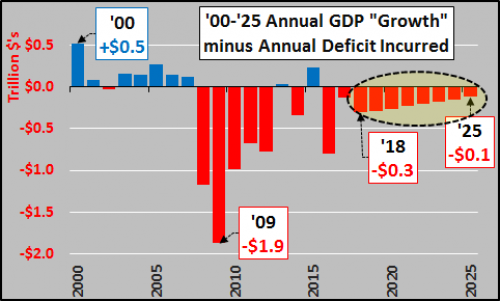
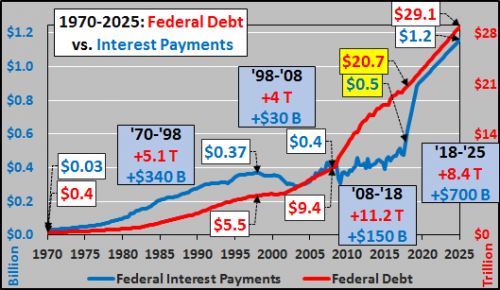
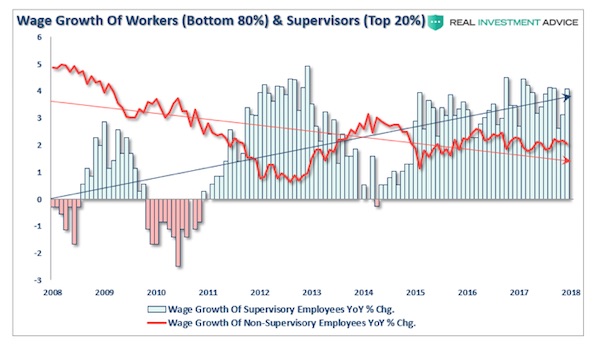
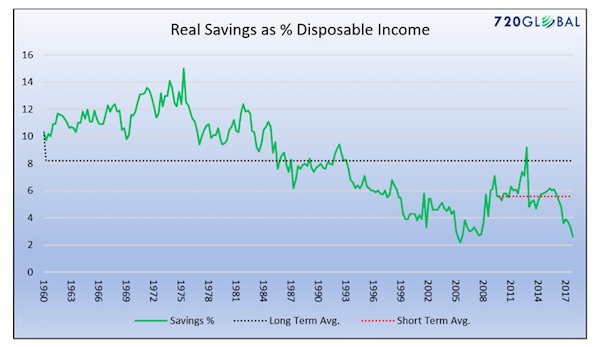
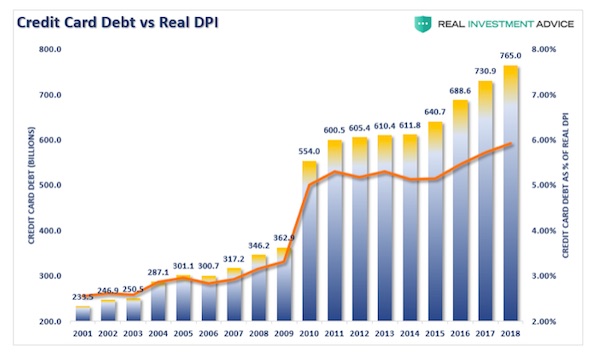
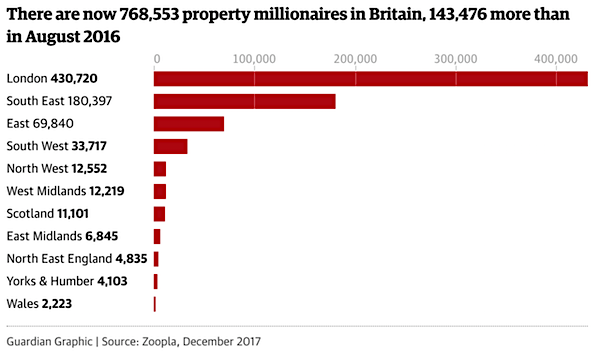
Vincent van Gogh Peach trees in blossom 1888

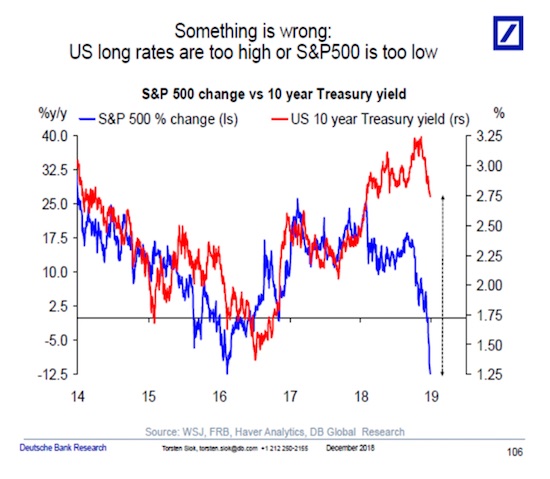
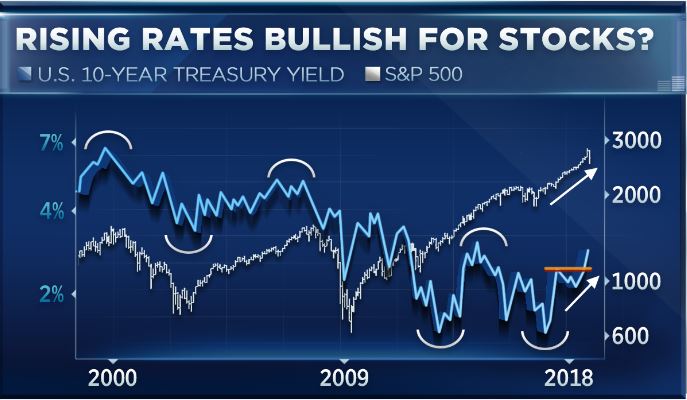
Bond markets are 10x stock markets?!
• What Crushed Stocks? (WS)
On Friday at around 1:40 p.m., during whiplash-inducing market moves, the S&P 500 index was down 1.9%, bringing the total loss for the week to 8.3%, which would have been the biggest weekly loss since November 2008, after the Lehman bankruptcy. But dip-buyers jumped in courageously and saved the day. The S&P 500 ended up 1.5%, bringing to the total loss for the week to 5.2%, the worst week since, well, the selloff in January 2016. Everyone has their own reasons why stocks plunged last week. Some blamed algorithmic trading. Others blamed the short-volatility financial complex that blew up.
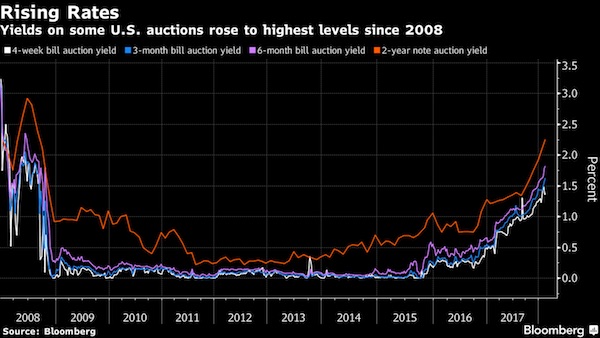
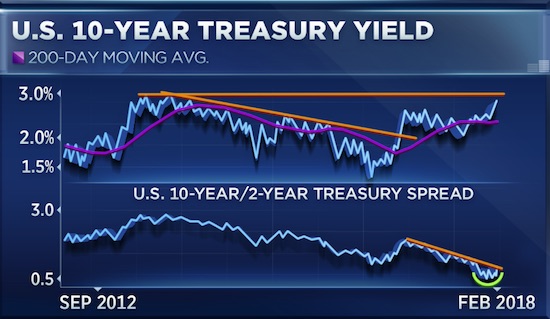
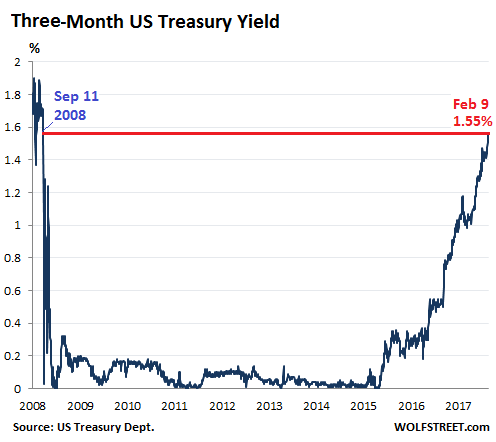
More specifically, Jim Cramer blamed “a group of complete morons” who traded in this space. Others blamed the stratospheric valuations of stocks that had been rallying for eight years with only a few dimples in between, and it’s simply time to unwind some of those gains. Whatever the factors might have been, rising bond yields certainly had something to do with it. They tend to hit stocks, eventually. Last week, prices of short-dated Treasuries edged down and prices of long-dated Treasuries edged down, and their yields edged up, but there was some turmoil in the middle, with some interesting consequences.The three-month Treasury yield rose to 1.55% on Friday, the highest since September 11, 2008. Investors are beginning to price in a rate hike in March:
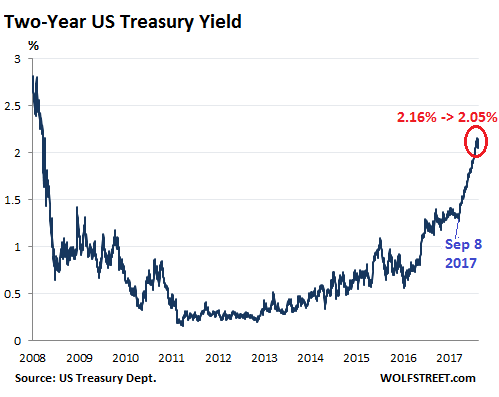
But the two-year yield, after having surged to 2.16% on February 1, got very nervous, dropping and bouncing during the week, and fell sharply on Friday, ending the week at 2.05%:
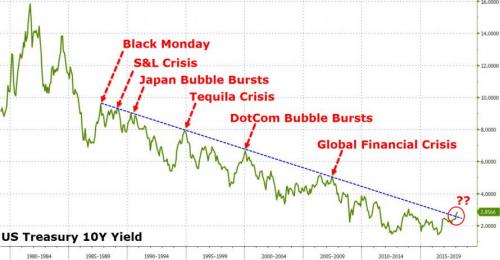
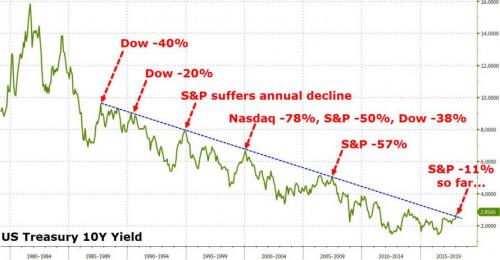
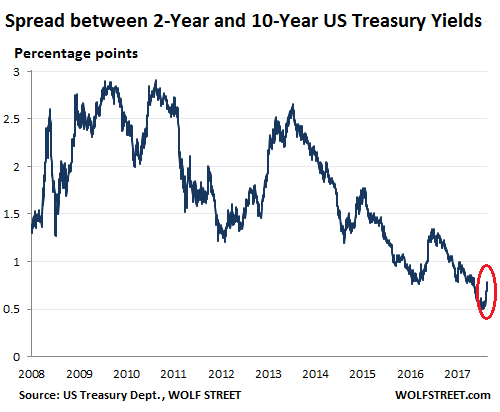
The 10-year yield closed on Friday at 2.83% and in late trading went on to 2.85%. The interesting thing about this is the difference (the “spread”) between the two-year yield and the 10-year yield. It surged. This spread is one of the indications of the slope of the yield curve and was one of the most watched bond-data points during the scare last year over an “inverted” yield curve. This is a phenomenon where the two-year yield would be higher than the 10-year yield. The last time this happened was before the Financial Crisis. By early January, the spread between the two-year yield and the 10-year yield had dropped as low as 50 basis points (0.5 percentage points), the lowest since October 2007. As the two-year yield kept spiking, the 10-year yield had started rising, but not fast enough. All this has changed, and the 10-year yield has been rising faster than the two-year yield and the spread has widened to 78 basis points on Friday:
The 30-year yield rose to 3.14% on Friday. For the first time, it is now back where it had been on December 14, 2016, when the Fed stopped flip-flopping and started getting serious about raising its target range for the federal funds rate. The market responded to each rate hike with increases in short-term yields but defied the Fed on longer-term yields, which fell until September 2017. So what happened last week was that the two-year yield fell, while the yields of most longer maturities stayed put or rose, steepening the yield curve from the two-year yield on up.
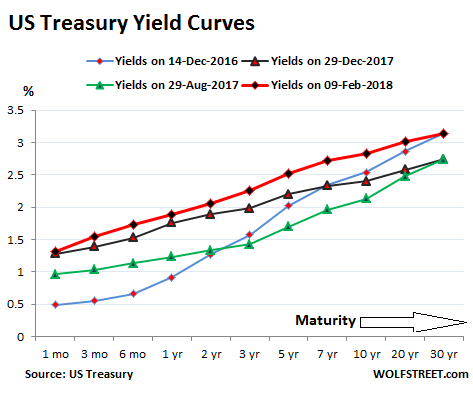
The chart below shows the “yield curves” as they occurred on these four dates: • Yields on Friday, February 9, 2018 (red line) • Yields on December 29, 2017 (black line) • Yields on August 29, 2017 (green line) two weeks before the QE unwind was detailed. • Yields on December 14, 2016 (blue line) when the Fed stopped flip-flopping, raised its rates, and became a clockwork. Note how the spread has widened at the longer-dated ends between the black line (December 29, 2017) and the red line (Friday), and how the slope of the red line has steepened, with the 30-year yield surging 40 basis points over those six weeks. That’s a big move:
Read more …

The cheap money has BEEN the entire market.
• Test Of Nerve For Markets As 10 Years Of Cheap Money Come To An End (G.)
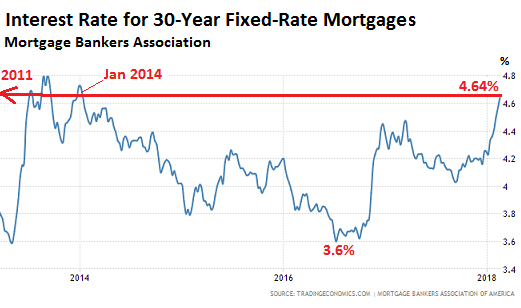
Stock markets are heading for a wild ride this year as central bankers strap on their bullet-proof vests and test investors’ willingness to accept higher interest rates. Last week’s share price crashes, which in two days wiped $4 trillion off the value of markets around the world, was just a foretaste of the battle to come. In the days following Monday’s crash, share values have recovered strongly only to dive again as competing theories about the path of interest rates and the likely impact on economic growth fight for attention. Most investors want the era of cheap borrowing to continue and many are willing to sell their shareholdings if it looks like coming to an end. Without low interest rates, they cannot borrow and invest cheaply, especially in the assets that for the past decade have gone up every year by much more than their salary – property and shares.
Countless businesses have also come to rely on low borrowing costs to keep going, and investors fear they might go bust should their bank raise loan rates. Weaning companies and investors off their addiction was never going to be easy, even 10 years after central banks first put their stimulus packages in place, and despite warnings that these measures need to end. For some time, the US Federal Reserve has taken on the role of the advance guard, forging a path towards higher rates for others to follow. But its campaign got off to a faltering start. Back in 2013 it was forced to retreat when it signalled in the mildest terms that it would begin withdrawing its quantitative easing programme. The main effect of QE was to drive down long-term interest rates, allowing investors to borrow cheaply not just over one or five years, but for 30 years.
And so its withdrawal was as much of a blow for some fund managers as an immediate rate rise. Wall Street and markets in Europe and Asia, where heavy selling turned into a rout, forced Fed officials to retreat. The Fed adopted a more incremental approach. It gave markets more warning and spaced out the policy decisions. As it entered 2017, US interest rates had trebled, but only from 0.25% to 0.75%. Yet the economy was booming more than ever. The Fed appeared ready to get tougher, and with justification, according to Karen Ward at JP Morgan Asset Management. After the heavy lifting needed to get the industrialised world back from bankruptcy, she said, “economies are now rested”. Ward, who until recently was an adviser to the chancellor, Philip Hammond, said: “Households and businesses are feeling better about the future. They do not need a boost in quite the same way. Central banks can ease off the accelerator without troubling either growth or markets.”
Read more …

The problem is not that they’ve never seen a crash, the problem is they’ve never seen a functioning market.
• Market Tests Millennial Traders Who’ve Never Seen A Crash (BBG)
In his career in finance—all seven years of it—Ben Kumar has seen some tough days. There was 2013, when traders worried about the Federal Reserve, and 2016, with the Brexit vote. But, at 29, Kumar and many millennials like him on Wall Street and the City of London have never endured a full-blown crash. For them, markets have always bounced back—fast—and gone on to heights. Now, with world stocks sinking and central banks withdrawing stimulus that’s supported markets for years, elders worry Kumar’s generation isn’t ready for its trial. Kumar is chill. “Find me someone who worked in the era of 15% inflation and I’ll talk to them about Bitcoin and the Internet,” said the 29-year-old, a fund manager at Seven Investment Management in London .
After $3 trillion was erased from global stocks in a week, he’s weighing whether to buy on the dip now—or wait a bit longer. “I don’t even think that this move is a wake-up call,” he said on Tuesday. Many bankers older than 40 shudder at the thought of what will happen if – or when – some unforeseen trigger sparks a crash that drags down not just stocks, but also bonds and currencies together. Etched in their memories is the Lehman Brothers collapse in 2008. In its wake, stock market valuations alone were cut in half. By contrast, most millennial investors have only worked in an era where central banks printed trillions of dollars to prop up their economies and markets. Since starting their careers, average interest rates in the developed world have barely nudged above 1%, inflation all but vanished, the S&P 500 Index more than doubled and bonds rallied so high that more than $7 trillion of debt is negative yielding.
“You have to have had that stage where you’re looking at the screen through your fingers to really appreciate risk-reward in this industry,” said Paul McNamara at GAM in London. “Not just seeing things go wrong, but going so much more wrong than you imagined was possible.”
Read more …

Why own stocks when bond yields rise? Still, inflation is a ludicrous fear.
• Bond-Stock Clash Has Just Begun as Inflation Looms (BBG)
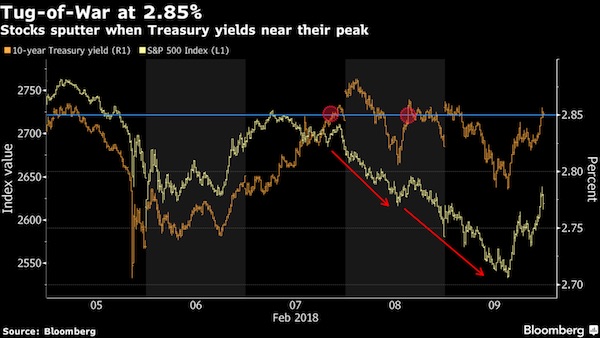
The tug-of-war between stocks and bonds is at the heart of the shakeout roiling financial markets. This week’s U.S. inflation report could hold the key to the next phase. Seemingly every time 10-year Treasury yields approached a four-year high last week, equities investors panicked, fearing the specter of higher inflation and a more aggressive pace of Federal Reserve rate hikes. Whether you want to say Treasuries are in a bear market or not, the surge in yields to start 2018 has left investors reassessing the value of equities and corporate bonds. Profits were easy when the 10-year yield traded in its narrowest range in a half-century, inflation stayed subdued and volatility across financial markets plumbed record lows. Gains are harder when low rates, a linchpin of the post-crisis recovery, start to disappear.
“What’s happening now is just price discovery between bonds and equities – how far can the bond market push yields up before the equity market cracks?” said Stephen Bartolini, portfolio manager at T. Rowe Price, which manages more than $10 billion in inflation-protected strategies. “The big fear in risk markets is that we get a big CPI print and it validates the narrative that inflation is coming back and the Fed is going to have to move faster.” The focus on inflation is nothing new, but it became even more critical after a Feb. 2 report showed average hourly earnings jumped in January at the fastest pace since 2009. That contributed to the dive in stocks. (It also led President Donald Trump to tweet about the “old days” when stocks would go up on good economic news.)
Read more …

Should be filed under Famous Last Words, but won’t be.
• IMF Chief Lagarde Says Market Swings Aren’t Worrying (R.)
Sharp swings in global financial markets in the past few days are not worrying since economic growth is strong but reforms are still needed to avert future crises, the managing director of the International Monetary Fund said on Sunday. Christine Lagarde, speaking at a conference on global business and social trends in Dubai, said economies were also supported by plenty of financing available. “I‘m reasonably optimistic because of the landscape we have at the moment. But we cannot sit back and wait for growth to continue as normal,” she said in her first public comments on market movements since the latest round of turmoil at the end of last week.
“I‘m ringing not the alarm signal, but the strong encouragement and warning signal.” Global stock markets were hit by wild fluctuations, with the U.S. benchmark S&P 500 tumbling 5.2% last week, its biggest weekly percentage drop since January 2016. The volatility was fuelled by investor worries about rising interest rates and potential inflation. Lagarde repeated an IMF forecast, originally issued last month, that the global economy would growth 3.9% this year and at the same pace in 2019, which she said was a good backdrop for needed reforms.
Read more …

No society should ever relinquish control over its essentials.
• UK Labour Vows Renationalisation Of Water, Energy And Rail (G.)
Labour launched a full-frontal attack on the privatised water industry last night, accusing companies of paying out the “scandalous” sum of £13.5bn in dividends to shareholders since 2010, while claiming huge tax breaks and forcing up prices for millions of customers. The assault by shadow chancellor John McDonnell came as he pledged total, “permanent” and cost-free renationalisation of water, energy and rail if Labour won power at the next election. The three privatisations in the 1980s and 1990s became hallmarks of the Tory governments of Margaret Thatcher and John Major. The dramatic intervention – which stunned the companies involved – was the strongest denunciation yet by Jeremy Corbyn’s Labour of the privatisation programme that has become part of the British political landscape of the last 40 years.
The Conservative party and the Confederation of British Industry both condemned McDonnell’s comments. The CBI said Labour’s renationalisation agenda would “wind the clock back on our economy” while chief secretary to the Treasury Liz Truss warned that placing politicians in charge of public utilities “didn’t work last time and won’t work this time”. McDonnell told the Observer that water companies could not even claim to offer choice to customers but instead operated regional monopolies, and were therefore able to increase prices without the risk of losing out to competitors, as well as “load up debt” while paying out huge dividends to shareholders. “It is a national scandal that since 2010 these companies have paid billions to their shareholders, almost all their profits, whilst receiving more in tax credits than they paid in tax,” he said.
“These companies operate regional monopolies which have profited at the expense of consumers who have no choice in who supplies their water. “The next Labour government will call an end to the privatisation of our public sector, and call time on the water companies, who have a stranglehold over working households. Instead, Labour will replace this dysfunctional system with a network of regional, publicly owned water companies.” Citing figures from the National Audit Office, the shadow chancellor said water bills had risen by 40% in real terms since privatisation of the industry in 1989. In 2016-17, the forecast average for water bills was £389 per household. McDonnell claimed that in 2017, privatised water companies paid out a total £1.6bn to their shareholders. Since 2010, the total was £13.5bn.
[..] Corbyn said that Labour would back a “great wave of change across the world in favour of public, democratic ownership and control of our services and utilities. “We can put Britain at the forefront of the wave of change across the world in favour of public, democratic ownership and control of our services and utilities,” he said. “From India to Canada, countries across the world are waking up to the fact that privatisation has failed, and taking back control of their public services,” he added.
Read more …

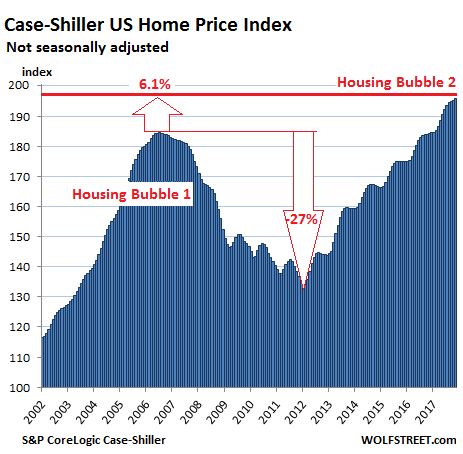
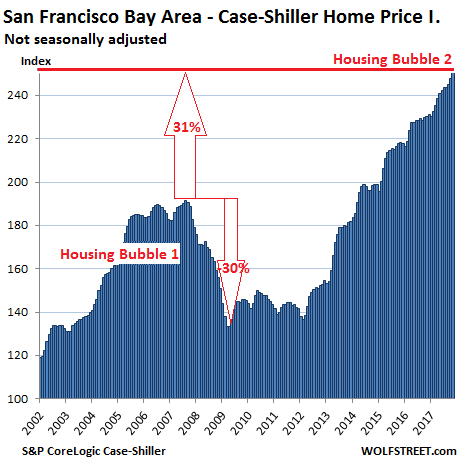
Banks and governments are accomplices in blowing this bubble.
• Australia’s Big Banks Focus On Job Cuts As Inquiry Looms (R.)
Australia’s big banks are responding to a revenue crunch by cutting jobs and other costs, prompting fears on the eve of an inquiry into their businesses that the industry’s tarnished reputation is about to take another hit. Regulators’ demands that banks hold more capital and their scrutiny into internal operations have made cost-cuts the in-vogue metric at the so-called Big Four banks, Australia and New Zealand Bank, Commonwealth Bank of Australia, National Australia Bank and Westpac, to boost profits. But the strategic change will come at a cost for the banks. “If you can be the most successful at bringing your staff numbers down the quickest, that’s going to give you the quickest cost advantage,” said one senior bank insider with direct knowledge of the cost-cutting strategy.
But, added the insider, as jobs cuts mount, “society and the community will push back, won’t accept it.” Cost cuts are not limited to jobs, with banks preparing to make use of improved technology to reengineer back office functions, and reduce the number and physical size of their branches. But the insider said he expected the Big Four to shed up to 40,000 jobs over five years as part of that overhaul, making a reduced wages bill the primary saving. The focus on costs coincides with the start of a royal commission looking into misconduct in the financial sector starting Monday. Scandals that have shaken public confidence include allegations of interest rate rigging, claims of a toxic trading room culture within some banks, and accusations that some institutions withheld legitimate health insurance payouts and gave misleading financial advice.
The inquiry, expected to last a year and which can recommend criminal charges and legislative changes, could potentially result in restrictions that affect bank profits, similar to a government-imposed bank tax levied last year. According to the government, Australia’s big four are still among the most profitable banks in the world, earning net profit margins of 36.4% in the June quarter of 2017. Years of economic growth and a booming property market had encouraged executives to focus on lifting sales rather than trimming operations. “Top line revenue growth is going to be a struggle, so they need to look closely at their cost lines really seriously,” said Brad Potter, head of Australian equities at Nikko Asset Management, which owns shares in the major banks.
Read more …

It’s the economy that causes much of the illness. Putting dollar numbers on it is not the way to go.
• Treating Mental Illness Could Save Global Economy Billions (CNBC)
Reducing mental illness is one of the key ways to increase happiness worldwide, according to a study by the Global Happiness Council (GHC). The report, published Saturday, said that while mental illness was one of the main causes of unhappiness in the world, the net cost of treating it was actually negative. “This is because people who are mentally ill become seriously unproductive. So when they are successfully treated, there are substantial gains in output. And these gains exceed the cost of therapy and medication,” GHC researchers said. The most common conditions associated with mental illness are depression and anxiety disorders, the study said. And at least a quarter of the global population were thought to experience these conditions over the course of their lifetime.
Researchers at the GHC also said that mental illness was a “major block” on the global economy as it was found to be the main illness among people of a working age. Therefore, treating the conditions, it said, would save national income per head by 5% — that equates to billions worldwide. The study estimated that for every $1 spent on treating depression, production would be restored by the equivalent of $2.5. And while physical healthcare costs were thought to balance out, the GHC claimed net savings when treating anxiety disorders was greatest of all — with production restored by the equivalent of $3 for every $1 spent. In the U.K., the National Health Service (NHS) estimates that around 10 to 15% of people are considered to have had a mental illness at some stage of their lives. There are many types of mental illness but most conditions fit into either a neurotic or psychotic category, according to the NHS.
Read more …

Any individuals will escape persecution.
• Pain Pill Giant Purdue to Stop Promotion of Opioids to Doctors (BBG)
Pain-pill giant Purdue Pharma will stop promoting its opioid drugs to doctors, a retreat after years of criticism that the company’s aggressive sales efforts helped lay the foundation of the U.S. addiction crisis. The company told employees this week that it would cut its sales force by more than half, to 200 workers. It plans to send a letter Monday to doctors saying that its salespeople will no longer come to their clinics to talk about the company’s pain products. “We have restructured and significantly reduced our commercial operation and will no longer be promoting opioids to prescribers,” the company said in a statement. Instead, any questions doctors have will be directed to the company’s medical affairs department. OxyContin, approved in 1995, is the closely held company’s biggest-selling drug, though sales of the pain pill have declined in recent years amid competition from generics.
It generated $1.8 billion in 2017, down from $2.8 billion five years earlier, according to data compiled by Symphony Health Solutions. It also sells the painkiller Hysingla. Purdue is credited with helping develop many modern tactics of aggressive pharmaceutical promotion. Its efforts to push OxyContin included OxyContin music, fishing hats and stuffed plush toys. More recently, it has positioned itself as an advocate for fighting the opioid addiction crisis, as overdoses from prescription drugs claim thousands of American lives each year. Purdue and other opioid makers and distributors face dozens of lawsuits in which they’re accused of creating a public-health crisis through their marketing of the painkillers. Purdue officials confirmed in November that they are in settlement talks with a group of state attorneys general and trying to come up with a global resolution of the government opioid claims.
Read more …

At least there are still some truly pan-European values left.
• Asylum Seekers In UK Living In ‘Disgraceful, Unsafe’ Housing (G.)
Asylum seekers are being placed in appalling housing conditions where they are at risk from abuse and violence, according to a survey published on Sunday documenting the lives of new arrivals. A year after the home affairs select committee found asylum seekers were being held in “disgraceful” conditions and called for a major overhaul of the system, new research suggests the situation remains poor. In-depth interviews with 33 individuals inside a north London Home Office asylum accommodation centre found that 82% had found mice in their rooms. The survey, by the human rights charity Refugee Rights Europe, also found that two-thirds of asylum seekers interviewed felt “unsafe” or “very unsafe”.
Others, some of whom have been diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder after fleeing violence and persecution from war zones, described how non-residents would enter the building and threaten residents, or simply use the kitchens and hallways to sleep. Of those interviewed, 30% alleged they had experienced verbal abuse in the accommodation from fellow residents or from staff, with 21% claiming they had experienced physical violence. “A number of respondents were under the impression that the cleaning staff may hold racist views. Sometimes this was expressed through abusive or hostile language in English, and, at other times, the respondents were shouted at in a foreign European language which they couldn’t understand,” said the study.
Marta Welander, head of Refugee Rights Europe, said: “An entire year has passed since the home affairs select committee released its alarming report on asylum accommodation in the UK, yet it seems as though little to nothing has changed. Our research revealed terrible hygiene standards and widespread problems with vermin. “Many of the [interviewees] said they felt unsafe in their accommodation, in particular the younger ones or those diagnosed with PTSD. Others explained they’re experiencing health problems, which they attributed to the unsanitary conditions in their bedrooms and communal areas.”
Read more …

C’mon, it’s funny.
• Russia Might Sell S-400 Systems To US If Americans Feel Insecure (RT)
The head of Russia’s strategic defense industry corporation Rostec says Moscow is ready to sell S-400 air defense systems to any nation that feels insecure and wants to seal its airspace, including the US if it wants to. Just before the end of the year, Moscow agreed to supply S-400 surface-to-air missile batteries to Ankara, making Turkey the first NATO member state that will integrate Russian technology into the North Atlantic defense structure once the $2.5 billion order is delivered. On Wednesday, Sergey Chemezov, head of the Russian state conglomerate Rostec, extended the offer to purchase S-400 Triumf, or the SA-21 Growler as it is known by NATO, to the Pentagon. “The S-400 is not an offensive system; it is a defensive system. We can sell it to Americans if they want to,” Chemizov told the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) when asked about the strategic reasoning behind the S-400 sale to Turkey.
The S-400, developed by Russia’s Almaz Central Design Bureau, has been in service with the Russian Armed Forces since 2007. The mobile surface-to-air missile system which uses four projectiles can strike down targets 40-400 km away. The deployment of S-400 batteries to Syria served as one of the pillars to the successful Russian anti-Islamic State (IS, formerly ISIS/ISIL) campaign. While the Almaz Bureau is currently developing S-500 systems, foreign orders to purchase the S-400 have skyrocketed. Besides China and Turkey, who are awaiting order deliveries, India, Qatar and Saudi Arabia are currently negotiating to purchase the Russian military hardware. The growing demand can be attributed to the high reliability and long history of the S missile defense system family. The S-200, designed by Almaz in the 1960s, still serves many nations today. On Saturday, a Syrian S-200 Vega medium-to-high altitude surface-to-air missile was allegedly used to intercept an Israeli F-16.
Read more …

The humanitarian industrial complex in all its glory.
• Oxfam Staff Partied With Prostitutes In Chad, Haiti, (G.)
Oxfam was hit with new allegations of staff involvement with prostitution on Saturday, after claims that employees at a second country mission had used sex workers while living at the organisation’s premises. Former staff who worked for the charity in Chad alleged that women believed to be prostitutes were repeatedly invited to the Oxfam team house there, with one adding that a senior member of staff had been fired for his behaviour in 2006. Roland van Hauwermeiren, who has since been embroiled in a sexual misconduct scandal in Haiti, was head of Oxfam in Chad at the time. Van Hauwermeiren resigned from Oxfam in 2011, after admitting that prostitutes had visited his villa in Haiti. One former Chad aid worker said on Saturday: “They would invite the women for parties. We knew they weren’t just friends but something else. “I have so much respect for Oxfam. They do great work, but this is a sector-wide problem,” the former staffer told the Observer.
[..] Oxfam said it could not confirm whether it had any records about a Chad staff member dismissed in 2006. Its staff in Chad at the time lived under a strict curfew due to security concerns: employees could not walk around freely and were confined to the guest house from early evening. Some employees had raised the issue of prostitutes with Van Hauwermeiren. Oxfam’s beleaguered chief executive, Mark Goldring, denied suggestions the charity had covered up revelations that staff had hired prostitutes in Haiti during a 2011 relief effort on the earthquake-hit island. His defence of Oxfam’s handling of the scandal came as Britain’s charity regulator said Oxfam had failed to mention allegations of abuse of aid beneficiaries in Haiti and potential sexual crimes involving minors in a report to it in 2011. It took no further action at the time.
[..] The scandal broke on Friday when the Times revealed that senior Oxfam staff had paid earthquake survivors for sex and that a confidential Oxfam report had referred to a “culture of impunity” among aid workers in Haiti. The Times on Saturday said Oxfam did not tell other aid agencies about the behaviour of staff involved after they had left to work elsewhere. Goldring told BBC Radio 4’s Today programme on Saturday: “With hindsight, I would much prefer that we had talked about sexual misconduct, but I don’t think it was in anyone’s best interest to be describing the details of the behaviour in a way that was actually going to draw extreme attention to it.”
Read more …

And what about next week?
• Maclean’s Is Asking Men To Pay 26% More For Latest Issue (Maclean’s)
This month, Maclean’s has created two covers with two different prices—one at $8.81, the other at our regular price of $6.99—to reflect the 26% gap between full-time wages paid to men and women in Canada.It’s a cheeky way to draw attention to a gap that has barely budged in decades, but we’re not the first to do this. In 2016, a group of students at the University of Queensland in Australia put on a bake sale. They called it the Gender Pay Gap Bake Sale, and they priced their cupcakes higher for men than women to illustrate Australia’s pay equity gap. The fierce social media backlash (“Kill all women” and “Females are f–king scum, they should be put down as babies” and “I want to rape these feminist c–ts with their f–king baked goods”) was so horrific it made international headlines.

When we discussed the story during our Maclean’s news meeting at the time, we wondered what would happen if we tried it here in Canada. So let’s see, shall we? After years of stasis, pay equity is having its moment as the next beat in the cadence of the #MeToo movement. Our hope is that these dual covers stir the kind of urgent conversation here that is already happening elsewhere around the world. In England, Carrie Gracie, the BBC’s China editor, resigned earlier this year when her pay was revealed to be at least 50 per cent less than her two male counterparts, saying, “My managers had yet again judged that women’s work was worth much less than men’s.” #istandwithcarrie trended on Twitter. In Iceland, after women walked out of work at precisely 2:38 p.m.—a full workday minus 30%, to illustrate the pay gap there—the country enacted a new law that makes it mandatory for companies with 25 or more employees to show they provide equal pay.
Read more …

Surprised? Me neither.
• US Professor Fired After Telling Student ‘Australia Isn’t A Country’ (RT)
Southern New Hampshire University has fired a lecturer who insisted that Australia was a continent – but not a country – and took some time to conduct “independent research” into the issue before reviewing a student’s paper. Ashley Arnold, 27, who is studying toward an online sociology degree at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), was “shocked” to learn she had failed an assignment, part of which required students to compare social norms between the United States and any other country – in her case Australia. Arnold was downgraded because her professor believed “Australia is a continent; not a country.” At first I thought it was a joke; this can’t be real. Then as I continued to read I realized she was for real,” she told BuzzFeed News. “With her education levels, her expertise, who wouldn’t know Australia is a country? If she’s hesitating or questioning that, why wouldn’t she just Google that herself?”
To address the professor’s apparent ignorance, Arnold sent a series of emails containing references from the school’s library which clearly stated Australia is both a continent and a country. Arnold even referred her to a section of the Australian government’s webpage called “About Australia” that said “Australia is an island continent and the world’s sixth largest country (7,682,300 sq km).” The female professor with PhD in philosophy, whose name is being kept private, was still not convinced, however, and said she needed to conduct “some independent research on the continent/country issue.” After reviewing Arnold’s paper the professor gave her a new grade of a B+, but never apologized, merely acknowledging that she had a “misunderstanding about the difference between Australia as a country and a continent.”
Read more …