Edward Hopper The railroad 1922

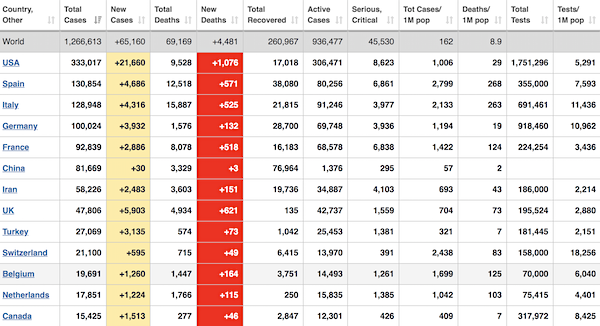
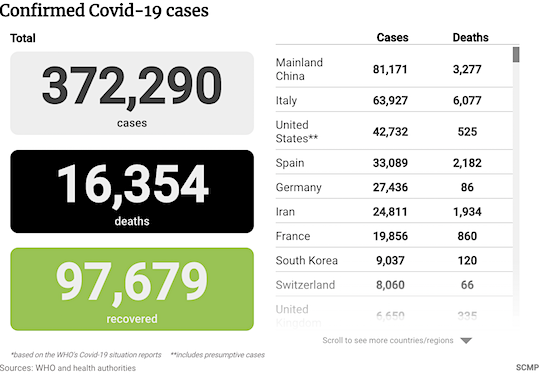
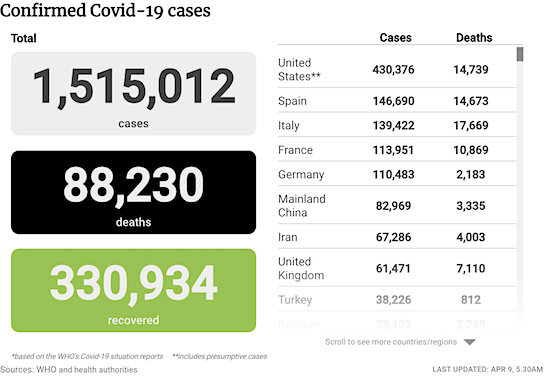
Confirmed coronavirus cases.
• Spain: 148,220
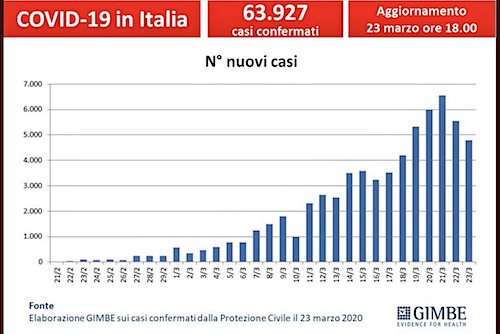
• Italy: 139,422
• Germany: 113,296
• New York State: 151,000
• US records 1,973 #coronavirus deaths on April 8. “The record-breaking figure is slightly higher than the previous day’s toll of 1,939 and brings total US fatalities to 14,695”
• Africa tops 10,000 cases, 500 deaths. Let’s see what the numbers are 3 weeks from now.
Nice discussions about testing and surveillance. But too many people appear to have their minds made up before the discussion starts. It’s not as easy as some may think.
One man’s freedom is another man’s prison, and finding the middle ground takes a lot of effort. However, we do that every day. The internet and smartphones have already brought a lot of added surveillance, but most people still feel free. Even though they don’t have the freedom to rape and murder. There are sliding scales here as far as the eye can see.

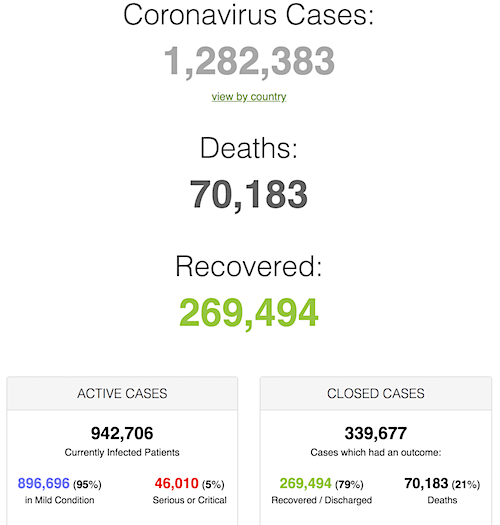
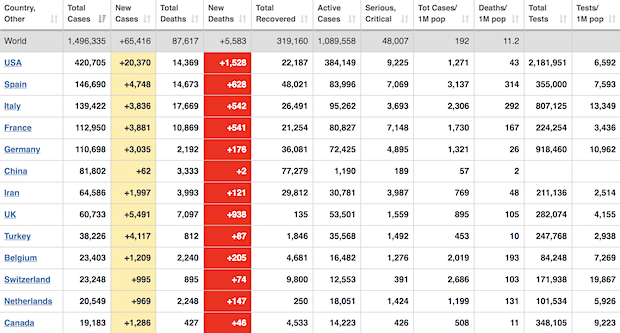
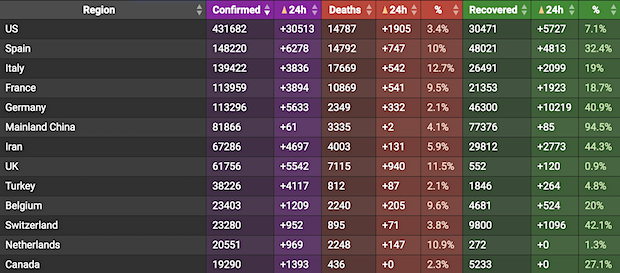
• Cases 1,529,078 (+ 82,097 from yesterday’s 1,446,981)
• Deaths 89,411 (+ 6,321 from yesterday’s 83,090)

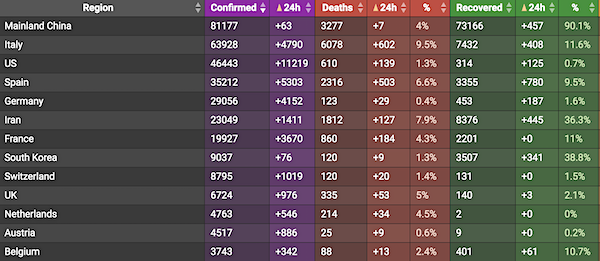
From Worldometer yesterday evening -before their day’s close-
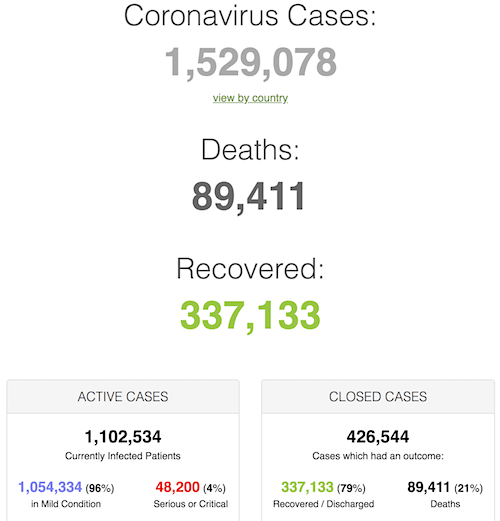
From Worldometer – NOTE: mortality rate for closed cases is at 21% !– NOTE 2: the number of active cases that are critical or severe is going down. 4% now.
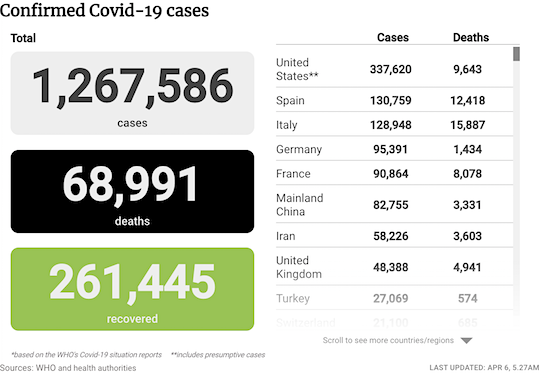
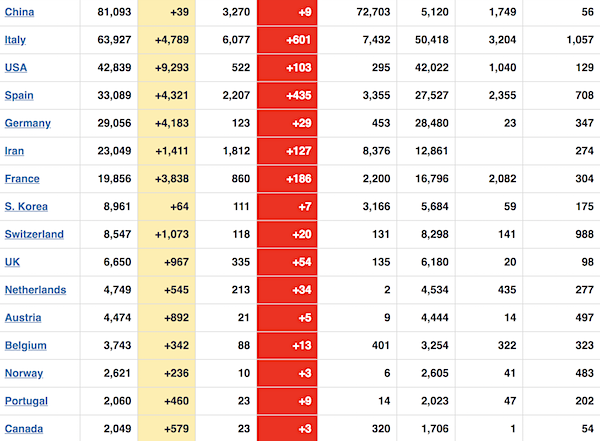
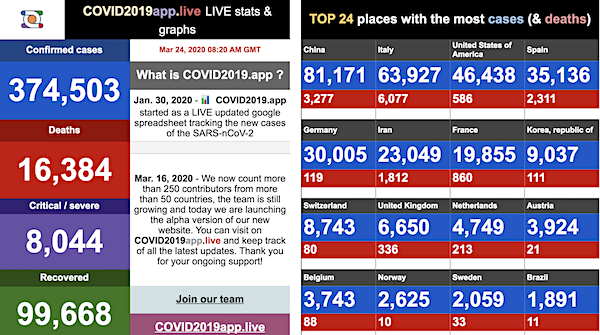
From SCMP:
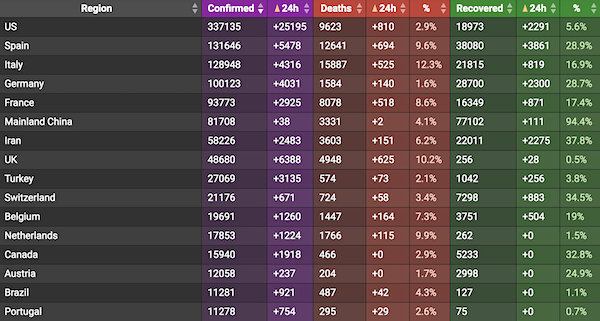
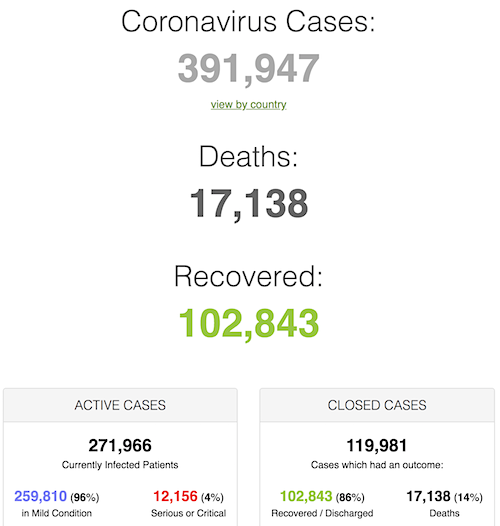
From COVID2019Info.live:

And no dancing either, y’hear?!
• Fauci: I Don’t Think We Should Shake Hands ‘Ever Again’ (Hill)
Anthony Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and a key member of the White House coronavirus task force, on Wednesday suggested that Americans should never shake hands again. “When you gradually come back, you don’t jump into it with both feet. You say, what are the things you could still do and still approach normal? One of them is absolute compulsive hand-washing. The other is you don’t ever shake anybody’s hands,” Fauci told The Wall Street Journal’s podcast.
“I don’t think we should ever shake hands ever again, to be honest with you. Not only would it be good to prevent coronavirus disease; it probably would decrease instances of influenza dramatically in this country,” the doctor added. Fauci also said he hopes to see a “light at the end of the tunnel” by the end of April. The NIAID head said Wednesday morning on Fox News that he thinks the number of U.S. deaths from the virus will be lower than initially predicted. Last week, Fauci and other members of the task force had signaled that anywhere between 100,000 and 240,000 Americans could die from the illness, even if social distancing was successful.

This appears very clumsy.
• The Limits of Location Tracking in an Epidemic (ACLU)
The CDC warns against comingin “close contact” with apersonwho has tested positive for the virus, defining close contactas“being within approximately 6 feet (2 meters), of a person with COVID-19 for a prolonged period of time.” None of the data sources discussed above are accurate enough to identify close contact with sufficient reliability. None are reliably accurate to within 6feet. Using the wrong technology to draw conclusions about who may have become infected might lead to expensive mistakessuch as twoweek isolation from work, friends, and family for someone —perhaps even ahealth care worker or first responder —who was actually not exposed. Israel’suse of location data has already sparked complaintsabout accuracy.
A location tracking system over time can be accurate enough to place a person near a bank, bar, mosque, clinic, or other privacy-sensitive location. But the fact is, commercial location databases are compiled for advertising and other purposes and are simply not accurate enough to reliably determine who was in close contact with whom. The algorithms are not likely to be reliable.Even if we were to imagine a set of location data that had pinpoint accuracy, there would still be problems translating that in any automated way into reliable guesses about whether two people were in danger of transmitting an infection. The Israeli system apparently acts on the basis of nothing more than an automated look at proximity. In Israel, one woman was identified as a “contact” simply because she waved at her infected boyfriend fromoutside his apartment building —and was issued a quarantineorder based on that alone.
Such a system is likely to make many such mistakes; it won’t know that a bank teller is shielded from transmission because they’re behind plexiglass, or that two people close togetherin a building are actually in separate apartments divided by a wall. The alternative is to try to make more educated guessesby taking account of such circumstances as well as such factors as the duration of a contact and the numberof days the positive-testing person has been infected. But those guesses will inevitably be highly unreliable.

All over East Asia.
• Coronavirus and the Future of Surveillance (FA)
Consider the strategies of five East Asian countries—ranging from the democracies of South Korea and Taiwan to the authoritarian Chinese state—that all relied on prominent surveillance methods. South Korea has so far successfully curbed the spread of COVID-19 using classic public health surveillance through large-scale testing. But Seoul has also intrusively tracked down potentially infected individuals by looking at credit card transactions, CCTV footage, and other data. Local authorities have released personal data, sometimes with the consequence that individuals can be identified publicly. Korean officials can enforce self-quarantine through a location-tracking smartphone app.
Taiwan has kept the number of cases very low by employing strict surveillance of people coming into the country and widely distributing that information. In February, for instance, Taiwan announced that all hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies across the country could access their patients’ travel histories. Integrating public- and private-sector databases in such ways would prove difficult in the United Kingdom or the United States or under existing European Union regulations. Just as in South Korea, officials in Taiwan use phone apps to enforce the self-quarantine of suspected infected individuals. Hong Kong issues all new arrivals an electronic wristband that monitors whether they violate quarantine.
Singapore has kept a lid on the pandemic using CCTV footage and the investigative powers of the police: refusal to cooperate with public health requirements is illegal. China’s sheer size makes it the most significant case. Beijing has successfully curbed the spread of the disease. Yes, the pandemic originated in China, but that doesn’t diminish the tangible success of China’s strategy of heavy surveillance. Its “grid management” system divides the country into tiny sections and assigns people to watch over one another. Over a million local monitors log movements, take temperatures, and enforce rules about residents’ activities.
At the same time, China has also harnessed its panoply of digital tools. State-run rail companies, airlines, and the major telecom providers all require customers to present government-issued identity cards to buy SIM cards or tickets, enabling unusually precise mass surveillance of individuals who traveled through certain regions. Color-coded smartphone apps tag people as green (free to travel through city checkpoints) or as orange or red (subject to restrictions on movement). Authorities in Beijing have employed facial recognition algorithms to identify commuters who aren’t wearing a mask or who aren’t wearing one properly.

Not testing grinds economies to a halt. Airlines, restaurants, everyone will want to be safe from infection or they don’t show up. That doesn’t make it an easy or a settled topic, but it’s still true. Can you run London, New York, Tokyo without a subway system? Nope.
• China Seeks To Contain ‘Silent Carriers’ Of Coronavirus (R.)
China released new measures on Wednesday to try and prevent asymptomatic “silent carriers” of coronavirus from causing a second wave of infections, as the country reported another modest rise in new confirmed cases. Mainland China reported 63 new confirmed cases on Wednesday, up from 62 a day earlier, the National Health Commission said. Of those, 61 were travellers arriving from overseas, bringing the total number of confirmed cases in China to 81,865. While new infections have fallen from their peak in February after China locked down several cities and imposed strict travel restrictions, authorities have called for continued vigilance amid fears of a fresh wave of infections.
Aside from curbing an influx of infected travellers from abroad, China’s other concern is managing asymptomatic people, or virus carriers who exhibit no clinical symptoms such as a fever or a cough. China reported 56 new asymptomatic cases on Wednesday, bringing the total number of such cases to 657 since data for such infections were published daily from April 1. The State Council, or Cabinet, on Wednesday published new rules to manage asymptomatic coronavirus carriers, or what some state media described as “silent carriers” of the virus.
Under the regulations, medical institutions must report detection of asymptomatic cases within two hours of their discovery. Local governments must then identify all known close contacts of the case within 24 hours. Asymptomatic patients will be quarantined collectively for 14 days, and will be counted as confirmed cases if they start to show symptoms. People who have had close contact with them must also be quarantined for two weeks. Earlier this week, a new function appeared on Tencent’s ubiquitous (0700.HK) WeChat mobile platform allowing people to check if they have ever sat on trains and planes near an asymptomatic carrier who later became a confirmed case.
https://twitter.com/i/status/1248072025492635648

Sometimes you realize how little we still know about the virus.
• Rapid Health Declines In COVID-19 Patients Jar Doctors, Nurses (R.)
One medical worker called it “insane,” another said it induces paranoia – the speed with which patients are declining and dying from the novel coronavirus is shocking even veteran doctors and nurses as they scramble to determine how to stop such sudden deterioration. Patients “look fine, feel fine, then you turn around and they’re unresponsive,” said Diana Torres, a nurse at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, the epicenter of the pandemic in the United States, where the virus has infected more than 415,000 people. “I’m paranoid, scared to walk out of their room.” It isn’t just elderly or patients with underlying health conditions who can be fine one minute and at death’s door the next. It can happen for the young and healthy, too, health professionals told Reuters.
A young woman died unexpectedly while nurse Laurie Douglas was on duty at Our Lady of the Lake Hospital in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. After 34 years on the job, Douglas said she normally has “an intuition of who is going to fade and who may improve.” “But these people are throwing that out the window,” Douglas said. “Last week, she was planning her wedding. This week, her family is planning her funeral,” she said, referring to the deceased patient. Patients might enter the hospital with strong oxygen levels and be engaged in happy conversation, said a resident emergency doctor at New York-Presbyterian Hospital, only to be “gasping for breath” and intubated a few hours later. “The scary thing is there are no rules to it,” said the resident, who spoke on condition of anonymity.
These scenes are playing out everywhere as COVID-19, the respiratory disease caused by the new coronavirus, has infected more than 1.4 million worldwide and killed more than 83,400 as of Wednesday. The quick turns for the worse are likely products of an “overly exuberant” reaction by the immune system as it fights the virus, said Dr. Otto Yang, an infectious disease specialist at the UCLA Medical Center in Los Angeles. Called a cytokine storm, it occurs when the body overproduces immune cells and their activating compounds – cytokines – causing dangerously high blood pressure, lung damage and organ failure. Emily Muzyka, 25, a nurse in the New York suburbs, said she reached her breaking point last week, when a relatively healthy 44-year-old woman needed sudden intubation.
“I had a meltdown that night,” she said. “I cried to my boyfriend.” In the case of COVID-19 patients, intubation refers to inserting a tube into the mouth and through the airway of a patient struggling to breathe, so they can be hooked to a mechanical ventilator. Associated Press journalist Anick Jesdanun, who was in good health and had run 83 marathons, died last week from COVID-19, according to a post on Facebook by his cousin, Prinda Mulpramook. Jesdanun, who was 51, at first didn’t need hospitalization, according to the post. He had begun to recover and showed clear lungs and strong vital signs during a doctor’s visit in late March. But “a sudden setback” sent him to the emergency room on April 1, and “13 hours later we lost him,” Mulpramook wrote.

Again, we know very little.
• New Projections Show Virus Spreading Twice As Fast As Expected (ZH)
[..] around the world, there are probably dozens of sets of projections, all produced by “credible” researchers, all saying slightly different things. And now, one of those researchers has caught the attention of Bloomberg by announcing that it may have underestimated the virus’s velocity by half, meaning it’s been spreading twice as quickly through China – and will therefore likely follow (or has followed) a similar pattern in the US. This set of projections was produced by researchers at Los Alamos, BBG said. As the CPC lifts travel restrictions on “healthy” residents of Wuhan – sending tens of thousands scrambling to escape the city – the team of researchers has determined that the virus likely spread through the country twice as quickly as initially believed.
New assumptions produced by the team including the average number of people infected in the early days of the epidemic in Wuhan: they have been revised to 5.7, more than twice the number the WHO has projected. Of course, the team’s results are specific to the Chinese outbreak. But although Beijing hesitated during the early days of the outbreak, it’s heavy handed response likely won’t be mimicked by the West, meaning if the virus spread more quickly in China, it’s reasonable to expect that it could travel through the US at around the same speed. At any rate, with this new rate of spread, researchers determined that some 82% of the population would need to be immune, either via a vaccine or because they’d already had the disease, in order to stop the virus from spreading.
Without such protection, high levels of social distancing would be needed, since as many as 1/5 people infected present as asymptomatic, a factor that has terribly complicated the response to the virus. [..] Notably, the Los Alamos report, which was initially published in Emerging Infectious Diseases, relied on anonymized mobile phone travel data and case reports of coronavirus outside the early epicenter in China’s Hubei province to calculate the spread, all things considered, that should be some pretty accurate data, if the authorities haven’t tampered with it. Then again, if they had, the numbers would probably look a lot better than they do.
Death and infection tolls from COVID-19 spreading around the world point to men being more likely than women to contract the disease and to suffer severe or critical complications if they do https://t.co/yOMPMzOjGU pic.twitter.com/U38kp0xiSy
— Reuters (@Reuters) April 9, 2020

They’re Marvel heroes, they don’t need testing.
• US Nurses Who Can’t Get Tested Fear They Are Spreading COVID-19 (R.)
In New York City, an intensive care nurse treated patients for three days after she started displaying symptoms of COVID-19 – but couldn’t get a test from her hospital. In Georgia, a nurse was denied a test after treating an infected patient who died. In Michigan, one of the few hospital systems conducting widespread staff testing found that more than 700 workers were infected with the coronavirus – more than a quarter of those tested. More than a month after the pandemic hit the United States, the persistent test shortages mean that health workers are treating patients while experiencing mild symptoms that could signal they are infected themselves, according to Reuters interviews with 13 nurses and 2 doctors who described testing shortages at their hospitals. Many medical centers are testing only the workers with the most severe symptoms, according to the frontline workers and hospital officials.
As a result, nurses and doctors risk infecting patients, colleagues and their families without knowing they are carrying the virus, medical experts say. The New York City nurse works at Mount Sinai Hospital, a major institution in the national epicenter of the pandemic. Her nausea, upset stomach and low-grade fever did not qualify her to get a test in late March, she told Reuters on condition of anonymity. She continued to work because her fever – at 100.2 degrees Fahrenheit (37.9 Celsius) – was just below the threshold set by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for sending health workers home. But she had the virus, an infection she confirmed when she took it upon herself to get tested at a private clinic, she said.“I knew something wasn’t right,” the nurse said, “but I didn’t really think I had it.”
[..] In Michigan – a leader among states in establishing testing programs that deliver quick results – more than 700 staff in the Henry Ford Health hospital system have tested positive out of some 2,500 employees tested since March 12, chief clinical officer Adnan Munkarah said on April 6. While the infected workers represent just 2% of the system’s overall staff, the high percentage of positive tests in the initial round signals that further testing could reveal many more infections. Until rapid testing is widely available, hospitals face a dilemma: Do they test staff with mild symptoms and keep them home for days as they await results? Or do they keep mildly ill – but desperately needed – staff at work to treat the rush of patients? “It’s a different kind of triage,” said Caplan, the bioethics professor. “It’s precaution versus, ‘I need staff.’”

Not quite sure what’s safer.
• NY Hospital Sends ‘Borderline’ COVID19 Patients Home With Oxygen Monitors (R.)
Some coronavirus patients who would have been admitted into the emergency department at a New York hospital are being sent home with an oxygen-monitoring device as the city’s medical system struggles to reserve resources for only the sickest people. The new program at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital is an example of how doctors are adapting and loosening normal protocols to ease the strain on emergency rooms and intensive care units in New York state, the epicenter of the coronavirus pandemic in the United States. Since last week, more than 200 people with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, the respiratory illness caused by the virus, have been sent home with a pulse oximeter to track their oxygen levels.
A doctor or nurse practitioner follows up with them via video conference. “Some of these patients might have been on the borderline of admission,” Dr. Rahul Sharma, who is overseeing the program as the chief of emergency medicine at Presbyterian’s Weill Cornell Medical Center, said in an interview. An oximeter is a small electronic device that clips onto a fingertip to indirectly measure the oxygen saturation of a patient’s blood. In severe COVID-19 cases, the virus can block up the lungs, hindering their ability to pass oxygen from the air into the bloodstream. While most who contract the virus recover, it has killed at least 4,900 people in the city, according to a Reuters tally.
Some of the NewYork-Presbyterian patients are also being sent home with a 30lb (14 kg) portable oxygen concentrating machine which sends oxygen-rich air through a nasal cannula, a two-pronged tube inserted into the nostrils. The patient is asked to log their oximeter readings to share with a doctor or nurse practitioner at 12-hour and 24-hour consultations. The patient may be re-admitted to the hospital if they take a turn for the worse.

The chloroquine discussion continues. In the meantime, people will continue taking it.
• What The Data Really Shows About Two Treatments For COVID-19 (F.)
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a derivative of chloroquine, and was approved in 1955 as an antimalarial treatment in the United States. More recently, HCQ has been used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, two autoimmune diseases characterized by a damaging inflammatory response. HCQ’s ability to modulate the inflammatory response is one reason why it’s caught the eye of researchers. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to invasion by bacteria, viruses, or other substances. It’s caused by your immune system “attacking” and destroying infected cells or the foreign bodies directly. But sometimes that response can get out of control. In autoimmune disorders, the body mistakenly attacks itself. In COVID-19, the inflammatory response can be so great that it causes severe damage to the lungs, which is why patients with severe cases often need ventilators.
Surprisingly, how HCQ works to diminish the inflammatory response is not fully understood. Current research suggests that it interferes with the normal functioning of two Toll-like receptors, which are “signaling” proteins that your immune system uses to regulate inflammation. This interference may be why HCQ can work to reduce it. Because HCQ has been used for over half a century, its side effects have been well-documented. Most notably, use, especially long-term use, has been associated with an increased risk of retinopathy, or damage to the retina. Some recent studies have also indicated that it may cause toxic side effects in patients taking other common drugs, such as metformin.
Remdesivir (RDV) was designed by the pharmaceutical company Gilead as a possible treatment for hepatitis C virus and respiratory syncytial virus. Some studies have shown that RDV may also inhibit other viruses that possess an RNA genome, including those that cause Ebola, SARS and MERS. Right now, it looks like RDV is effective because it looks very similar to a chemical that viruses need to reproduce. But when the virus errantly uses RDV, the replication stops. When it comes to the safety of RDV, the data are less clear. In limited human trials, elevated liver enzymes were reported, but a full assessment of its side effects have not been determined.
WATCH: Michigan Democrat Rep. Karen Whitsett says hydroxychloroquine “did save my life, and I do credit the President for doing so.”
The media doesn’t get this is about saving people's lives, not politics! pic.twitter.com/4qpfXhPFSp
— Trump War Room – Text TRUMP to 88022 (@TrumpWarRoom) April 8, 2020

Your happy news for the day.
• Miss England Hangs Up Her Crown To Return To Work As A COVID19 Doctor (C24)
Miss England 2019, Bhasha Mukherjee, is hanging up her crown to return to the front-line amid the coronavirus crisis. Last year, while competing in the Miss World pageant, the 24-year-old stepped away from her post as a junior doctor in the medical field, reports People, and shortly after, started doing charity work which was set to go on until later this year. But that all changed when she started receiving messages from her colleagues at the Pilgrim Hospital in Boston in the UK, detailing the extent of the crisis. “When you are doing all this humanitarian work abroad, you’re still expected to put the crown on, get ready… look pretty,” she told CNN, which she said just didn’t feel right anymore.
“I wanted to come back home. I wanted to come and go straight to work,” she said. “I felt a sense of this is what I’d got this degree for and what better time to be part of this particular sector than now.” Bhasha has since returned to the UK from India where she was working as an ambassador for Mercia Lions Club to provide resources to a home for abandoned girls. She will start work in the medical field though after she is done self-isolating in the next two weeks.
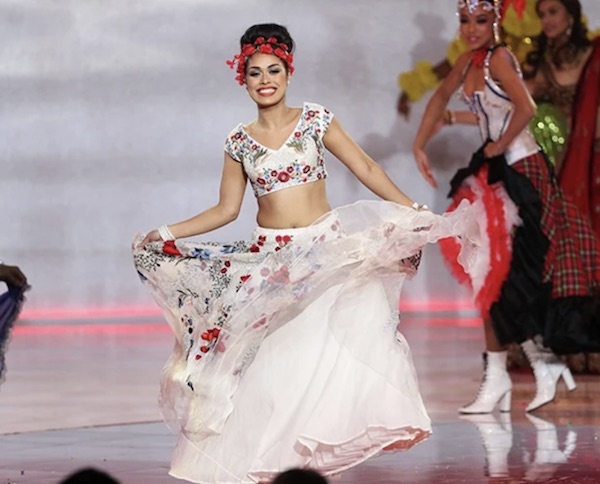

Miss England 2019, Bhasha Mukherjee, during the 69th Miss World pageant. Photo: Getty Images.

If you would have told anyone this on January 1…
• U.S. GDP Will Contract 30% In Second Quarter, 5% In 2020 – PIMCO (R.)
The forced closure of businesses across the United States and surge in unemployment due to the coronavirus pandemic will force U.S. growth to contract by 30% in the second quarter and 5% overall in 2020, Pacific Investment Management Co (PIMCO) wrote on Wednesday. In a blog post, Tiffany Wilding, a North American economist at PIMCO, wrote that evidence from recent jobs reports suggests the unemployment rate may rise as high as 20%. The 30% contraction in growth in the second quarter would likely be followed by two quarters of recovery, Wilding wrote. While two quarters of contraction is shorter than the four recorded in the 2008 financial crisis, the depth of the shock is far greater – quarterly contractions did not rise above 8% during that time.
California-based PIMCO is one of the world’s largest investment firms with $1.91 trillion assets under management as of Dec. 31 2019. “The speed and magnitude of the U.S. labor market disruption has been sharper than any we’ve seen in recent history, suggesting that the decline in overall activity has also likely been much more severe,” wrote Wilding. In spite of the already enormous spate of layoffs, the number of jobs lost is likely to continue to rise as more states close non-essential businesses. The figures are also expected to rise as unemployment offices work through a backlog of claims. Wilding notes that the government’s March employment report showed that layoffs had begun earlier than suggested by weekly unemployment data, and were spread across industries, including healthcare, which PIMCO had expected to remain resilient.

Old ideas for new times.
• Thinking Outside of the “V” Shaped Recovery Box (RIA)
It seems the entirety of the financial media and many on Wall Street believe a “V” shaped economic recovery is in our future. While we hope they are right, we would be foolish to take such analysis and, quite frankly, unwarranted optimism, at face value. If history teaches us one thing, it is that significant, life-altering events are rarely if ever followed by a quick return to normality. In this article, we raise a few considerations that may make you reconsider popular economic narratives. Today, the importance for investors to think outside of the box cannot be overstated.
Or to put it another way, the parameters of “the box” have likely changed and, if so, we should be cognizant of those changes in our decision making. If the future economic recovery does not resemble the “V” shape that the financial markets are depending on, the stock market may be even more over-valued than we think. To that end, consider the following graph showing where the S&P 500 could trade based on a range of historical valuations.
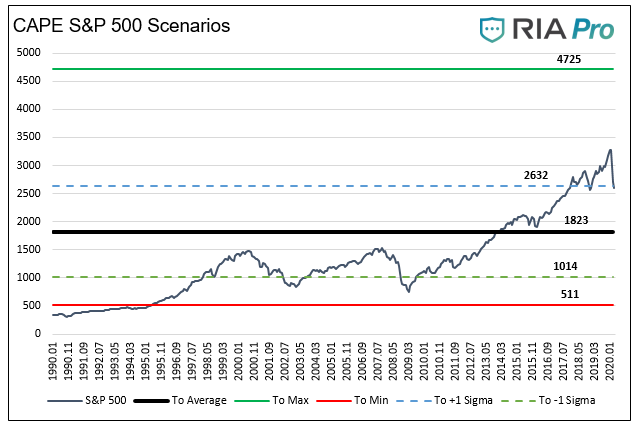
The COVID-19 Crisis may be short-lived or not. Although it seems as though progress is being made, there is nary a sign that a full-fledged cure or vaccine is at hand. Social distancing and mass closures of commercial enterprise appear to slow the exponential spreading of the virus considerably. While very effective in saving lives, these measures come with immense economic costs. The productive output of the global economy has ground to a near-total halt. As the virus appears to have peaked in Asia and is starting to show signs of peaking in Europe, we are hopeful the U.S. will also peak shortly. Then what? From a health standpoint, the answer depends on whether a cure or vaccine is discovered.
If a cure or vaccine is found and can be produced, distributed, and administered quickly, then mandatory and self-regulated social distancing will end, and people will hopefully resume normal activities. This may be the rationale backing a “V” shaped recovery, but as we discuss later in the article, normal may not be the same normal we knew before February 2020. If the spreading of the virus is significantly curtailed, but there is no cure or vaccine developed, the outcome may be very different. Just ask yourself, are you ready to stand in a crowded elevator, hop on a packed train, or stand shoulder to shoulder with other fans at a sporting event or concert? It is quite likely that in the bleaker scenario with no cure or vaccine, there will be some recovery, but most people will dramatically alter their everyday life. Such a change will radically reshape the outlook for human behavior on a vast scale.

How to keep a bubble inflated against all odds.
• Americans Not Making Their Mortgage Payments Soar By 1064% In One Month (ZH)
According to the latest Mortgage Bankers Association Forbearance and Call Volume Survey which highlights the “unprecedented, widespread mortgage forbearance already requested by borrowers affected by the spread of the coronavirus”, the total number of loans in forbearance grew to 2.66% as of April 1; just one month ago, on March 2, the rate was 0.25%, or a 1,064% increase in just one month. For loans backed by Ginnie Mae, which serves low- and moderate-income borrowers, the surge was much greater, with total loans in forbearance soaring to 4.25% from 0.19% one month ago. Overall, the MBA reports that total forbearance requests grew by 1,270% between the week of March 2 and the week of March 16, and another 1,896% between the week of March 16 and the week of March 30.
According to Bloomberg, borrowers with relatively low credit scores, many of whom live paycheck to paycheck, are most likely to seek relief. Over the past two years, Ginnie Mae has guaranteed $583 billion of 30-year mortgages with FICO scores below 715, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. However, the longer the coronavirus shutdown lasts, the higher the FICO cutoff for those borrowers unable (or unwilling) to make mortgage payments. “MBA’s survey highlights the immediate relief consumers are seeking as they navigate the economic hardships brought forth by the mitigation efforts to stop the spread of COVID-19,” said Mike Fratantoni, MBA’s Senior Vice President and Chief Economist. “The mortgage industry is committed to providing this much-needed forbearance as mandated by law under the CARES Act. It is expected that requests will continue to skyrocket at an unsustainable pace in the coming weeks, putting insurmountable cash flow constraints on many servicers – especially IMBs.”
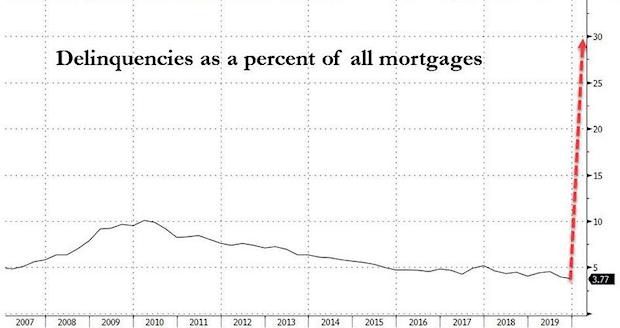
[..] lenders – like everyone else – are operating in the dark, with no way of predicting the scope or duration of the pandemic or the damage it will wreak on the economy. If the virus recedes soon and the economy roars back to life, then the plan will help borrowers get back on track quickly. But the greater the fallout, the harder and more expensive it will be to stave off repossessions. “Nobody has any sense of how long this might last,” said Andrew Jakabovics, a former Department of Housing and Urban Development senior policy adviser who is now at Enterprise Community Partners, a nonprofit affordable housing group. “The forbearance program allows everybody to press pause on their current circumstances and take a deep breath. Then we can look at what the world might look like in six or 12 months from now and plan for that.”
But if the economic turmoil is long-lasting, the government will have to find a way to prevent foreclosures – which could mean forgiving some debt, said Tendayi Kapfidze, Chief Economist at LendingTree. And with the government now stuck in “bailout everyone mode”, the risk of allowing foreclosures to spiral is just too great because it would damage financial markets and that could reinfect the economy, he explained. “I expect policy makers to do whatever they can to hold the line on a financial crisis,” Kapfidze said hinting at just a trace of a conflict of interest as his firm may well be next to fold if its borrowers declare a payment moratorium. “And that means preventing foreclosures by any means necessary.”

The estate is trying to protect Ghislaine.
• Virgin Islands At Odds With Epstein Estate Over ‘Broad’ Liability Releases (R.)
Women who say they were abused by deceased financier Jeffrey Epstein should not be required to sign broad liability waivers in order to get payouts from his estate, the attorney general of the U.S. Virgin Islands said on Wednesday. The office of Attorney General Denise George said in a statement that the estate was demanding the “broad releases,” which would shield not only the estate but potentially other individuals from legal liability, as part of a proposed victim compensation fund. A spokeswoman for George said people covered by the releases could include anyone linked to Epstein who was involved in trafficking or abusing girls. “With this demand still in place, the Fund cannot ensure a fundamentally fair and legally sufficient process for victims who choose to participate,” the attorney general said.
George’s office has asked the Virgin Islands probate court, which is overseeing the estate, to resolve the dispute. The estate was valued at $636.1 million before the recent global market plunge. [..] George sued the estate in January, saying Epstein’s sexual misconduct there stretched from 2001 to 2018 and included raping and trafficking in dozens of women and girls. At least two dozen Epstein accusers have filed civil lawsuits against the estate. Some named Epstein’s friend Ghislaine Maxwell and other alleged enablers of Epstein’s abuses as defendants. Ghislaine, whose whereabouts are currently unknown, has denied the allegations against her.


It’s as simple as that.
• Vindictive Court Rulings Prove British State Wants Assange Dead (WSWS)
In a London court hearing yesterday, District Judge Vanessa Baraitser declared that the extradition show trial of Julian Assange will proceed in May, despite the fact that Britain is under a national lockdown and the coronavirus pandemic is rapidly spreading through the country’s prison system. Baraitser’s ruling was the second in a fortnight that places Assange’s life and safety in jeopardy and underscores the travesty of justice being perpetrated against him. On March 25, she rejected an application for bail made by Assange’s legal team, which detailed the “very real” and potentially “fatal” threat posed to his health by the coronavirus pandemic. Assange is currently held on remand in London’s maximum-security Belmarsh Prison.
[..] In an open letter last month, Doctors for Assange wrote: “Julian Assange’s life and health are at heightened risk due to his arbitrary detention during this global pandemic. That threat will only grow as the coronavirus spreads.” Speaking for the group, Dr. Stephen Frost told the World Socialist Web Site: “Mr. Assange must be assumed by doctors to be severely immunocompromised and therefore at greatly increased risk of contracting and dying from coronavirus in any prison, but especially in a prison such as Belmarsh. Every extra day Mr. Assange is incarcerated in Belmarsh prison constitutes an increased threat to his life.”

I’m thinking the NYT, WaPo, CNN hugely prefer four more years of Trump over four dull Biden years. There’s no money for them in Biden.
• Democrats Salivate Over Obama Coming Off Sidelines (Hill)
The decision by Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) to suspend his campaign means former President Obama is about to get back into the political spotlight. Sources close to Obama and Biden say the two men have spoken “quite frequently,” as one put it, in recent days as Biden pivots to the general election. Obama has also spoken to Sanders in recent days, according to two sources with knowledge of the conversations. The former president has stayed out of the Democratic primary, but sources say he is anxious to endorse his former vice president, Joe Biden, and become an active player in the general election campaign against President Trump. Democrats across the country are also ready for his entry.
“IT IS TIME,” Doug Landry, a former Hillary Clinton aide, wrote Wednesday, tweeting a cartoon image of Obama as superman. “RELEASE THE SUPER SURROGATE.” Sources say the former president is ready but that he and Biden are also conscious of the coronavirus pandemic dominating the country and changing the nature of politics. Biden actually spoke by phone with Trump on Monday to discuss the pandemic, and Sanders made it clear that the spreading virus was one reason he ended his campaign on Wednesday despite the urgings of some supporters to continue. “He’s eager to go,” said one source close to Obama. “He’s been waiting for this election for almost four years.”
The pandemic also affects the basics of campaigning. Large rallies and handshakes are impossible, and Biden has been working for the last several weeks from his basement recreation room. “Like everyone else, Obama is going to have to appear on video or on television, but the biggest question is how?” one source said. “That’s all being ironed out.” Sources on both sides said they expect Obama — and former first lady Michelle Obama — to begin to appear in upcoming virtual fundraisers to help build excitement around Biden’s campaign and activate some bundlers who remained on the sidelines until now. “No one has heard from him in a long time, and people will pay a lot of money to hear from him, even on a computer,” one longtime Obama ally said.
Tucker Carlson:
"Ask yourself, is Joe Biden ready to lead this country? Could he find his car in a three-tiered parking garage? Could he navigate a salad bar? And by the way, what exactly is his position on the Coronavirus pandemic? Those are the mysteries Democrats now face." pic.twitter.com/8jYaRdPRms
— Daily Caller (@DailyCaller) April 9, 2020

It must be possible to run the Automatic Earth on people’s kind donations. These are no longer the times when ads pay for all you read, your donations have become an integral part of the process.
Thanks everyone for your generous donations.

In a park in Ottawa ( Probably Canada, although there’s no ’Sorry’ at the end ) pic.twitter.com/J6Hp48eYzh
— John Cleese (@JohnCleese) April 9, 2020



Support the Automatic Earth in virustime. It’s good for your health.