Edward Hopper Christmas card 1928

It’s up to you to refuse plastics. Nothing else will work.
• Shale Gas Fuels 40% Increase In Funding For Plastics Production (G.)
The global plastic binge which is already causing widespread damage to oceans, habitats and food chains, is set to increase dramatically over the next 10 years after multibillion dollar investments in a new generation of plastics plants in the US. Fossil fuel companies are among those who have plooughed more than $180bn since 2010 into new “cracking” facilities that will produce the raw material for everyday plastics from packaging to bottles, trays and cartons. The new facilities – being built by corporations like Exxon Mobile Chemical and Shell Chemical – will help fuel a 40% rise in plastic production in the next decade, according to experts, exacerbating the plastic pollution crisis that scientist warn already risks “near permanent pollution of the earth.”
“We could be locking in decades of expanded plastics production at precisely the time the world is realising we should use far less of it,” said Carroll Muffett, president of the US Center for International Environmental Law, which has analysed the plastic industry. “Around 99% of the feedstock for plastics is fossil fuels, so we are looking at the same companies, like Exxon and Shell, that have helped create the climate crisis. There is a deep and pervasive relationship between oil and gas companies and plastics.” Greenpeace UK’s senior oceans campaigner Louise Edge said any increase in the amount of plastic ending up in the oceans would have a disastrous impact. “We are already producing more disposable plastic than we can deal with, more in the last decade than in the entire twentieth century, and millions of tonnes of it are ending up in our oceans.”
The huge investment in plastic production has been driven by the shale gas boom in the US. This has resulted in one of the raw materials used to produce plastic resin – natural gas liquids – dropping dramatically in price. The American Chemistry Council says that since 2010 this has led to $186bn dollars being invested in 318 new projects. Almost half of them are already under construction or have been completed. The rest are at the planning stage. “I can summarise [the boom in plastics facilities] in two words,” Kevin Swift, chief economist at the ACC, told the Guardian. “Shale gas.”

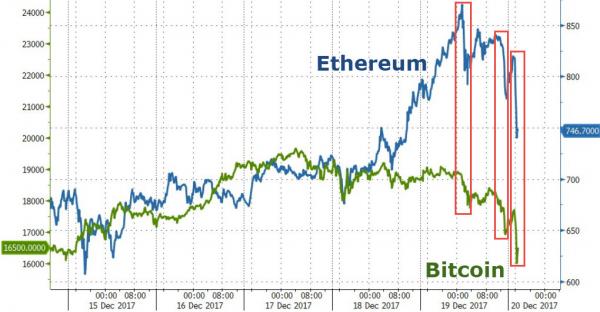
For now, crypto is too small to sink anything at all, but a potential future issue is: If derivatives and leverage play such a big role in crypto, how exactly is it different from all other ‘investments’?
• Bitcoin Could Crash Financial Markets Because Of Massive Borrowing (MW)
Bitcoin mania is starting to look like a religion. I say that because both bitcoin and religion involve faith in the unknowable. Some bitcoin investors believe the cryptocurrency, along with the underlying blockchain technology, will be a vital part of a new, decentralized, post-government society. I can’t prove that won’t happen — nor can bitcoin evangelists prove it will. Like life after death, they can only say it’s out there beyond the horizon. If you believe in bitcoin paradise, fine. It’s your business … until your faith puts everyone else at risk. As of this month, bitcoin is doing it. Is bitcoin in a price bubble? I think so. Asset bubbles usually only hurt the buyers who overpay, but that changes when you add leverage to the equation.
Leverage means “buying with borrowed money.” So when you buy something with borrowed money and can’t repay it, the lender loses too. The problem spreads further when lenders themselves are leveraged. For bitcoin mania to infect the entire financial system, like securitized mortgages did in 2008, buyers would have to use leverage. The bad news is that a growing number do just that. In the U.S., we have a Financial Stability Oversight Council to watch for system-wide vulnerabilities. The FSOC issued its 164-page annual report this month. Here’s its plan on bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies: It is desirable for financial regulators to monitor and analyze their effects on financial stability. Sounds like FSOC is on the case — or at least will be on it, someday. Meanwhile, this month commodity regulators allowed two different U.S. exchanges to launch bitcoin futures contracts.
Oddly, instead of griping about slow regulatory approval, futures industry leaders think the government moved too fast. To get why, you need to understand how futures exchanges work. One key difference between a regulated futures exchange and a private bet between two parties is that the exchange absorbs counterparty risk. When you buy, say, gold futures, you don’t have to worry that whoever sold you the contract will disappear and not pay up. If you close your trade at a profit, the exchange clearinghouse guarantees payment. The clearinghouse consists of the exchange’s member brokerage firms. They all pledge their own capital as a backstop to keep the exchange running. So when the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) gave exchanges the green light to launch bitcoin futures, member firms collectively said (I’ll paraphrase here): “WTF?”

No matter if crypto surges or collapses in 2018, controversies will be much much bigger than this year. Just getting started.
• Was Coinbase’s Bitcoin Cash Rollout A Designed Hit? (Luongo)
[..] if there is a path to harming Bitcoin and the cryptocurrency market available to the money center banks, then they will always opt for it. I’ve been pretty vocal about the need for having a slow, annoying reserve asset in the cryptocurrency space. I’ve talked about it multiple times (here and here). This doesn’t jibe with Bitcoin Cash proponent and Bitcoin.com CEO Roger Ver’s image of Bitcoin. And that is to Roger’s credit, actually. It’s pretty obvious from a cursory glance at Roger’s Twitter feed that he approaches Bitcoin as a radical libertarian/Austrian Economist would — a purely decentralized, trustless money that can wrest control of the world’s monetary system from rentiers in Government and Banking. Music to my ears. On the other hand is the very shady attitude of Blockstream and the Bitcoin Core group who prevailed in the Segwit 2x fight, which, from Roger Ver’s perspective is actually a mop-up operation, not the decisive battle in the war.
“The reason there is so much hostility from Bitcoin Core towards Bitcoin Cash is because Core knows they have stolen the name but are advocating a completely different system than what was originally described by Satoshi. Bitcoin Cash is Bitcoin” — Roger Ver (@rogerkver) December 19, 2017
The real battle for the soul of Bitcoin happened back in August with the fork that created Bitcoin Cash. Complaining about all of these other forks, to Roger, is like closing the barn door after the horses are gone. By keeping Bitcoin slow and expensive they create the need for new solutions to improve it. Why solve a problem when you can artificially create one and then sell everyone the solution? So, I’m ambivalent about this fight for the soul of Bitcoin, because I want a real digital analogue to Gold which only moves the most important transactions. I don’t want all coins to be all things to all people. But, I also know that with this much money at stake there will be pushback from the ‘powers-that-be.’ The Banks and central banks are staring at an existential threat to their future and are doing what they can to stop it from happening. And that, to them, means gaining control over the Bitcoin blockchain. It also means cutting off the means of entry and exit from the cryptocurrency market for average people.

Unemployment in Japan is almost non-existent, but apparently markets don’t work the way they’re supposed to. Tight labor doesn’t lead to higher wages.
• Japan PM Abe Urges Firms To Raise Wages By 3% Or More (R.)
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe on Tuesday urged companies to raise wages by 3% or more next year, keeping up pressure on firms to spend their huge cash pile on wages to broaden the benefits of his “Abenomics” stimulus policies.“We must sustain and strengthen Japan’s positive economic cycle next year to achieve our long-standing goal of beating deflation,” Abe said in a speech at a meeting of Japan’s biggest business lobby Keidanren. “For that, I’d like to ask companies to raise wages by 3% or higher next spring,” he said. Wages at big companies have been rising slightly more than 2% each year since 2014, government data shows, and an increase of 3% or more next year would help the Bank of Japan to reach its elusive 2% inflation target.
BOJ Governor Haruhiko Kuroda told the same meeting that companies remain hesitant to raise wages because they had become accustomed to prioritising job security over wage hikes during 15 years of deflation. “With consumers remaining reluctant to accept price rises, many firms are concerned about losing customers if they raise prices,” he said. “It seems so difficult for many firms to take the first step to raise their prices, that they wait and see what other firms are doing.” Sadayuki Sakakibara, chairman of Keidanren, made no reference to wages at his speech at the meeting, focusing instead on the need for Japan to get its fiscal house in order. “We’d like to strongly call on the need to restore fiscal health,” as worries over the sustainability of Japan’s social welfare system could discourage consumers to spend, he said.

“..due mostly to a boost from rising fuel costs that is seen fading in 2018..”
• Japan’s Household Spending Jumps But BOJ Seen Keeping Stimulus (R.)
Japan’s households spent more than expected in November while consumer inflation ticked up and the jobless rate hit a fresh 24-year low, offering the central bank some hope an economic recovery will drive up inflation to its 2% target. But the increase in prices was due mostly to a boost from rising fuel costs that is seen fading in 2018, keeping the Bank of Japan under pressure to maintain its huge monetary support even as other central banks seek an end to crisis-mode policies. Minutes of the BOJ’s October rate review showed that while most central bank policymakers saw no need to ramp up stimulus, they agreed on the need to sustain “powerful” monetary easing for the time being. “There’s a chance inflation may gradually accelerate toward the fiscal year beginning in April,” as a tightening job market pressures companies to raise wages, said Takeshi Minami, chief economist at Norinchukin Research Institute.
“But inflation remains distant from the BOJ’s 2% target, so the central bank will probably maintain its current policy framework.” Spending was driven by broadbased gains, with households loosening the purse strings for items such as refrigerators, washing machines, and sporting goods and services such as eating-out and travel. Data also showed wage earners’ disposable income rose 1.8% in November from a year earlier, suggesting that higher incomes have encouraged consumers to open their wallets. The nationwide core consumer price index (CPI), which includes oil goods but excludes volatile fresh food prices, rose 0.9% in November from a year earlier, government data showed on Tuesday, marking the 11th straight month of gains. The pace of price growth was just ahead of October’s 0.8% and a median market forecast of the same rate.

Illusions of control. China’s no. 1 threat.
• Shanghai Sets Population At 25 Million To Avoid ‘Big City Disease’ (G./R.)
China’s financial hub of Shanghai will limit its population to 25 million people by 2035 as part of a quest to manage “big city disease”, authorities have said. The State Council said on its website late on Monday the goal to control the size of the city was part of Shanghai’s masterplan for 2017-2035, which the government body had approved. “By 2035, the resident population in Shanghai will be controlled at around 25 million and the total amount of land made available for construction will not exceed 3,200 square kilometres,” it said. State media has defined “big city disease” as arising when a megacity becomes plagued with environmental pollution, traffic congestion and a shortage of public services, including education and medical care.
But some experts doubt the feasibility of the plans, with one researcher at a Chinese government thinktank describing the scheme as “unpractical and against the social development trend”. Migrant workers and the city’s poor would suffer the most, predicted Liang Zhongtang last year in an interview with state media, when Shanghai’s target was being drafted. The government set a similar limit for Beijing in September, declaring the city’s population should not exceed 23 million by 2020. Beijing had a population of 21.5 million in 2014. Officials also want to reduce the population of six core districts by 15% compared with 2014 levels. To help achieve this goal authorities said in April some government agencies, state-owned companies and other “non-core” functions of the Chinese capital would be moved to a newly created city about 100 kilometres south of Beijing.

Well, actually, your data, that is.
• Europe Banks Brace For Huge Overhaul That Opens The Doors To Their Data (CNBC)
From current accounts to credit cards, established lenders have access to vast amounts of information that financial technology (fintech) competitors could only dream of. In Europe, that could all be about to change. On January 8, banks operating in the European Union will be forced to open up their customer data to third party firms — that is, when customers give consent. EU lawmakers hope that the introduction of the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) will give non-banking firms the chance to compete with banks in the payments business and give consumers more choice over financial products and services. Britain’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) has set out similar plans to let customers share their data with other banks and third parties.
With customer consent, U.K. banks will be required to give authorized third-party firms access to current account data. Those regulations form part of a conceptual transition known as “open banking.” Under an open banking framework, proponents say, non-banking firms — from corporations as big as Amazon and IBM to start-ups — would be able create new financial products by utilizing the data of banks. Banks will be required to build application programming interfaces (APIs) — sets of code that give third parties secure access to their back-end data. Those APIs serve as channels for developers to get to the data and build their own products and services around it.
Such information could serve as a tool to understand things such as customers’ spending habits or credit history, and could lead to the creation of new services. “In a world of open banking, the customer can choose a provider in each part of the value chain. And each bank has to participate in the value chain as an earners’ right to be there,” Anne Boden, co-founder and chief executive of U.K. mobile-only bank Starling, told CNBC in an interview earlier this year. [..] Some European lenders are giving early signals as to what a post-PSD2 world will look like. Spain’s BBVA, Denmark’s Saxo Bank, Nordic lender Nordea and Ireland’s Ulster Bank have already published open developer portals ahead of the EU legislation.

UBI experiments that are poorly designed are real threats to the principle.
• Scotland United In Curiosity As Councils Trial Universal Basic Income (G.)
In Scotland, a country wearily familiar with divisions of a constitutional nature, the concept of a basic income is almost unique in enjoying multi-party favour. Across the four areas currently designing basic income pilots – Glasgow, Edinburgh, Fife and North Ayrshire – the projects have variously been championed by Labour, SNP, Green and, in one case, Conservative councillors. Matt Kerr, who has tirelessly lobbied for the idea through Glasgow city council, said: “Reactions to basic income have not split along the usual left/right party lines. Some people to the left of the Labour party think that it undermines the role of trade unions and others take the opposite view. But there should be room for scepticism; you need that to get the right policy.” Advocates are aware such unity of purpose is precious and worth preserving.
“The danger is that this falls into party blocks,” said Kerr. “If people can unite around having a curiosity about [it] then I’m happy with that. But having the first minister on board has done us no harm at all.” Inevitably, Sturgeon’s declared interest has invited criticism from her opponents. A civil service briefing paper on basic income, which expressed concerns that the “conflicting and confusing” policy could be a disincentive to work and costed its national roll-out at £12.3bn a year, was obtained by the Scottish Conservatives through a freedom of information request in October. The party accused her of “pandering to the extreme left of the [independence] movement”. But advocates argue the figures fail to take into account savings the scheme would bring.
The independent thinktank Reform Scotland, which published a briefing earlier this month setting out a suggested basic income of £5,200 for every adult, has calculated that much of the cost could be met through a combination of making work-related benefits obsolete and changes to the tax system, including scrapping the personal allowance and merging national insurance and income tax. [..] Joe Cullinane, the Labour leader of North Ayrshire council, said: “We have high levels of deprivation and high unemployment, so we take the view that the current system is failing us and we need to look at something new to lift people out of poverty. “Basic income has critics and supporters on the left and right, which tells you there are very different ways of shaping it and we need to state at the outset that this is a progressive change, to remove that fear and allow people to have greater control over their lives, to enter the labour market on their own terms.”

“Two whistleblowers claim Home Office departments delay asylum applications for profit..”
• UK Asylum Offices ‘In A Constant State Of Crisis’, Say Whistleblowers (G.)
Staff in the Home Office’s asylum directorate are undertrained, overworked and operating in a “constant state of crisis”, two whistleblowers have claimed, as applicants endure long waits to have their case dealt with due to internal pressures. The Home Office staff have also told the Guardian that asylum case workers are making poor decisions about applications because they are under pressure to focus on more profitable visa applications. Despite a “shocking increase in complaints (from applicants) and MP enquiries questioning delays”, they say caseworkers have been told to brush off all enquires and “just give standard lines” of response when called to account.
A source from the UK Visa and Immigration Unit (UKVI) has alleged that caseworkers have been ordered to kick applications for spousal visas “into the long grass” because they can make more money for the directorate by processing student visas. Spousal visas, also known as settlement visas, cost more than student visas but take much longer to process. The source also claims visa applications are routinely labelled “complex” or ”non-straightforward” by staff – a term which excuses the UKVI from adhering to their standard processing times – it is, the source claimed, “just a euphemism for ‘there’s more profitable stuff we could be doing’”. Paying hundreds of pounds for priority services to try to avoid delays on decisions is a “waste of time”, they warned applicants.
The allegations reflect concerns expressed in a report earlier this year by David Bolt, the Independent Chief Inspector of Borders and Immigration, who said the Home Office is not “in effective control” of its asylum process. [..] Some of the more shocking findings from Bolt’s report included pregnant women being made to wait more than two years for decisions on their immigration applications; an increasing numbers of applicants having their immigration applications registered as “not straightforward” and endlessly delayed; and Home Office employees being “pushed to the limit” by individual targets and threatened with disciplinary action as deadlines approach.

At least one more month of utter despair, with little reason to assume any improvement by then. Mouzalas cannot escape his part of the blame.. That said, he’s not lying when he says “Here in Moria we have a problem with unaccompanied minor refugees. We have asked Europe to take a share of these children. It refuses to do so..”
• ‘Normality’ To Be Restored At Moria By End of January – Greek Minister (K.)
Migration Minister Yiannis Mouzalas said Monday authorities were making huge efforts to improve conditions at the Moria camp on the eastern Aegean island of Lesvos, while accusing European officials of “hypocrisy” for failing to shoulder their share of the burden. Speaking after an unannounced visit at the infamous migrant and refugee processing center, Mouzalas said Greek authorities were hoping to restore “normality” at the facility by the end of January. “It all depends on arrivals,” Mouzalas said. “Today it was good weather and a total of 175 arrivals have been recorded on Lesvos as of this morning,” he said.
Responding to criticism over the scenes of misery and squalor documented by foreign media at Moria last week, the leftist minister said: “Europe must put an end to its hypocrisy.” “Here in Moria we have a problem with unaccompanied minor refugees. We have asked Europe to take a share of these children. It refuses to do so,” Mouzalas said. “It’s very easy to act like a prosecutor. Dealing with the situation in a way that helps refugees and migrants is the hard part. And this is what we are expected to do,” he said. “There is no point in wagging your finger. What you need to do is mobilize the procedures and mechanisms in order to improve conditions and solve problems,” he said.

And the UNHCR is not beyond blame, either. Pointing fingers at others is always easy, but hard to keep up after two whole years.
• UNHCR Calls For Migrant Transfers, Blames Greece For Grim Conditions (K.)
As temperatures drop, the UN refugee agency (UNHCR) once more urged Greek authorities to swiftly transfer thousands of refugees and migrants living in cramped and unsafe island camps to the mainland where better conditions and services are available. “Tension in the reception centers and on the islands has been mounting since the summer when the number of arrivals began rising,” UNHCR spokeswoman Cecile Pouilly told Voice of America. “In some cases, local authorities have opposed efforts to introduce improvements inside the reception centers,” Pouilly was quoted as saying. More than 15,000 people have been transferred to the mainland over the past year.
Meanwhile, speaking to the New Europe news website, the EU’s special envoy on migration, Maarten Verwey, suggested that Greek authorities were to blame for the grim living conditions inside island migrant camps, as recently documented by American news outlet BuzzFeed and Germany’s Deutsche Welle. “The Commission has made the funding available to ensure appropriate accommodation for all. However, the Commission cannot order the creation or expansion of reception capacity, against the opposition of the competent authorities,” Verwey said, according to New Europe.