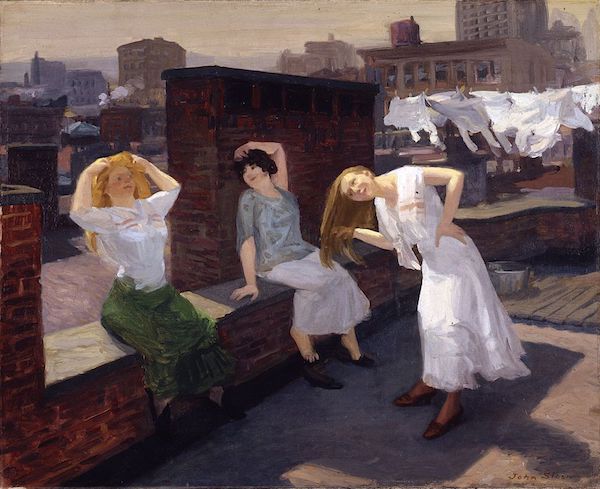
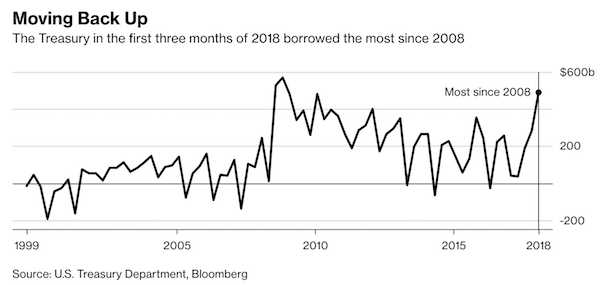
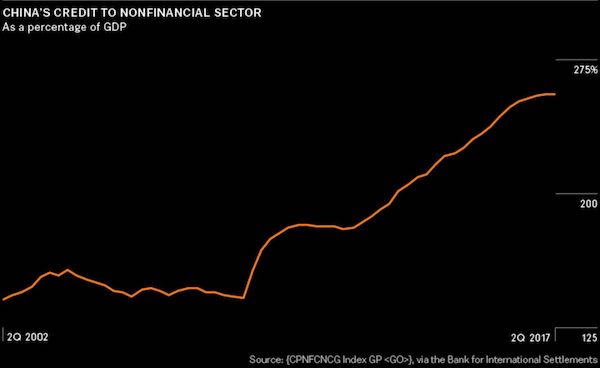
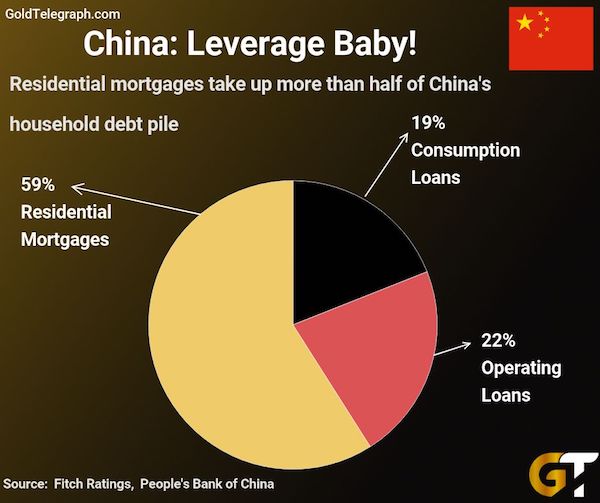
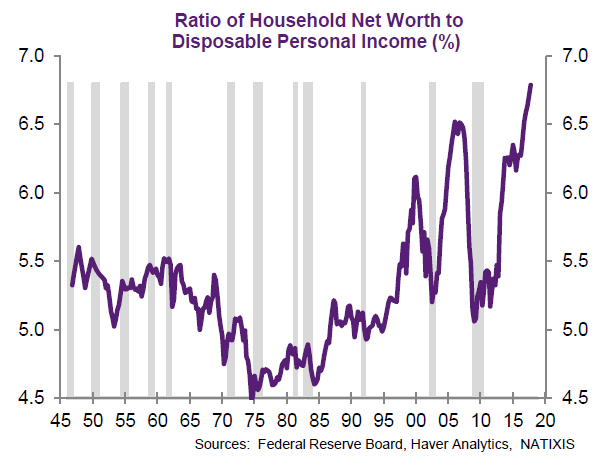
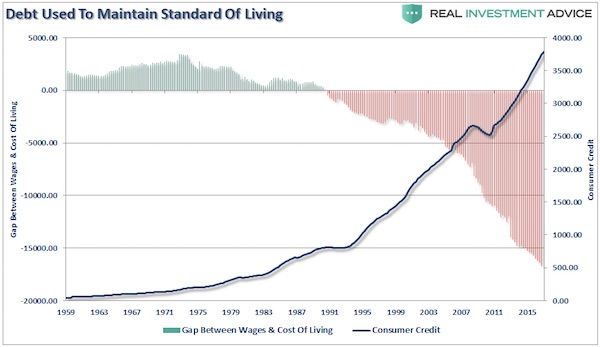
John French Sloan Sunday, Women Drying Their Hair 1912

Argentina, Turkey, Indonesia. Brazil in a bit. The list will grow. As the dollar rises, emerging countries need more dollars to pay their debt, pushing the dollar up even more. And investors pull their money out of these countries. Vicious circles everywhere.
• Behold The Sudden Stop. Risk of Emerging Markets Collapse (Lacalle)
Argentina even issued a one-hundred-year bond at a spectacularly low rate (8.25%) with a very high demand, more than 3.5 times bid-to-cover. That $ 2.5 billion issuance seemed crazy. A one-hundred-year bond from a nation that has defaulted at least six times in the previous hundred years! Worse of all, those funds were used to finance current expenditure in local currency. The extraordinary demand for bonds and other assets in Argentina or Turkey was justified by expectations of reforms and a change that, as time passed, simply did not happen. Countries failed to control inflation, deliver lower than expected growth and imbalances soared just as the U.S. started to see some inflation, rates started to rise.
Suddenly, the yield spread between the U.S. 10-year bond and emerging markets debt was unattractive, and liquidity dried up faster than the speed of light even with a modest decrease of the Federal Reserve balance sheet. Liquidity disappears because of extremely leveraged bets on one single trade – a weaker dollar, higher global growth- unwind. However, another problem exacerbates the reaction. An aggressive increase in the monetary base by the Argentine central bank made inflation rise above 23%. With an increase in the monetary base of 28% per year, and seeking to finance excess spending by printing money and raising debt to “buy time”, the seeds of the disaster were planted. Excess liquidity and the US dollar weakness stopped. Local currencies and external funding face risk of collapse.
The Sudden Stop. When most of the emerging economies entered into twin deficits -trade and fiscal deficits- and consensus praised “synchronized growth”, they were sealing their destiny: When the US dollar regains some strength, US rates rise due to an increase in inflation, the flow of cheap money to emerging markets is reversed. Synchronized indebted growth created the risk of synchronized collapse.

Is this really the end of cheap debt? It’s dangerous too: if Turkey gets into real trouble, Erdogan will seek a scapegoat.
• Dollar Surge Bringing Emerging Market Rate Cut Cycle To A Halt (R.)
A resurgent dollar and higher borrowing costs are smashing through Argentina and Turkey’s currencies like a wrecking ball and raising the likelihood more broadly that emerging markets’ three-year long interest rate cutting cycle is at an end. Emerging markets came into the year flying, riding on the back of a healthy global economy and rising commodity prices alongside tame inflation and a weak dollar. It looked more than likely that a wave of rate cuts would keep rolling, allowing a bond rally to continue. From Brazil and Russia to Armenia and Zambia, developing countries, big and small, have been on a rate cutting spree. With hundreds of rate cuts since Jan. 2015, the average emerging market borrowing cost fell under 6% earlier this year from over 7% at the time.
Fund managers’ profits too have soared in this time, with emerging local currency debt among the best performing asset classes, with dollar-based returns of 14% last year. Even in the first quarter of 2018, returns were a buoyant 4.3% Now though, almost exactly five years since the so-called taper tantrum shook an emerging market rally, these gains appear to be on the cusp of reversal. Argentina has jacked up its interest rates to 40% in response to a rout in its peso currency, while Turkey was also forced into a rate rise as its lira hit record lows against the dollar. Indonesia, after heavy interventions to stem rupiah bleeding, has also said it could resort to policy tightening.

Déja vu.
• WTF Just Happened to Argentina’s Peso? (Fernet)
If you’re watching Argentina’s economy, it hasn’t been a banner week. This week, Argentina had to raise its key interest rate three times to keep the Argentine peso from losing even more value against the dollar. Three interest rate hikes in one week is a lot – it implies the first two didn’t work, and the Central Bank is not in control. The interest rate currently sits at 40%. That means the Central Bank pays 40% per year on peso-denominated debt, which can imply that they expect the value of the peso to fall somewhere in the ballpark of 40% over a one year period. A year ago in April, the rate was closer to 26%. Yikes. And the exchange rate kicked off the week at around 20.5 ARS/USD. It jumped almost to 23 ARS/USD, and is currently hovering around 21.8 ARS/USD.
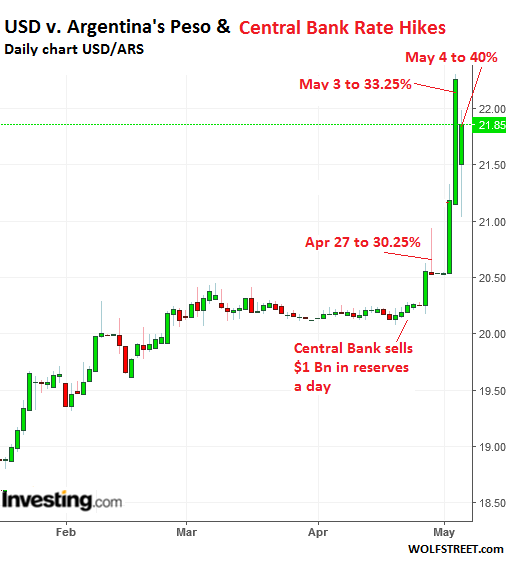
[..] When the US dollar increases in value, emerging market currencies decrease, meaning in Argentina’s case it will take increasingly more pesos to buy dollars. This then amplifies the risk that emerging markets will be unable to make payments on dollar denominated debt, causing investors to sell their emerging market investments, further amplifying the currency stress. The timing specifically in the case of Argentina is uncannily bad. Until this week, non-residents investing in Argentina were exempt from paying the equivalent of capital gains taxes across the board, including local-currency peso-denominated central bank notes, or LEBACs. This Tuesday, this exemption on LEBACs officially no longer applied, meaning foreign holders of these notes now incur a tax equal to 5% on profits.

“Increased American consumption born of an overstimulated economy..”
• Remedies Trump Prescribes For Trade Problems Harm US (Xinhua)
Remedies the Trump administration is prescribing for U.S. trade problems won’t work, and forays in trade disputes with China will harm the United States, a veteran China expert with decades of experience in bilateral relations said [in Silicon Valley] on Saturday. “I believe that Washington has misdiagnosed our trade problems, that its remedies for them won’t work, and that what it is doing will harm the United States and other countries as much or more than it does China,” said Chas Freeman, senior fellow at Brown University’s Watson Institute, when addressing the annual conference of a prominent Chinese American group, the Committee of 100 (C100).
“The United States and China are each too globalized and dynamic to contain, too big and influential to ignore, and too successful and entangled with each other to divorce without bankrupting ourselves and all associated with us,” Freeman, also former U.S. assistant secretary of defense, said in an opening keynote speech. Pointing out that there are many reasons for the United States to seek cooperative relations with a rising China, Freeman added that the Trump administration has decided “to pick a fight — to confront China both militarily and economically.” “The fact that we Americans consume more than we save means that we import more than we produce. That creates an overall trade deficit. Ironically, the Trump administration has just taken steps guaranteed to increase this deficit,” he said.
“It has reduced tax revenues and boosted deficit spending, mostly on military research, development, and procurement. These actions take the national savings rate even lower while inflating domestic demand for goods and services. They cause imports to surge,” he added. “Increased American consumption born of an overstimulated economy explains why China’s trade surplus with the United States is again rising even as its surplus with the rest of the world falls,” he said. “Unless Americans boost our national savings rate by hiking taxes or cut our consumption by falling into recession, our overall trade deficit is sure to bloat,” he said.

The Market Will Plummet if Global Central Banks Pull Plug
“..the reality is when a financial crisis happens, banks close their doors to depositors..”
• In the Coming Crash We’ll be Falling from a Higher Height – Nomi Prins (USAW)
Join Greg Hunter as he goes One-on-One with two-time, best-selling author Nomi Prins, who just released “Collusion: How Central Bankers Rigged The World.” Will the next crash be worse than the last one? Prins says, “Yes, it will because we will be falling from a higher height. The idea here is you are sinking on the Titanic as opposed to sinking on a canoe somewhere. All of this artificial conjured money is puffing up the system, along with money that is borrowed cheaply is also puffing up the system and creating asset bubbles everywhere. So, when things pop, there is more leakage to happen. The air in all these bubbles has created larger bubbles than we have had before.”
How does the common man protect himself? Prins says, “They have to own things, and by that I mean real assets, hard assets like silver and gold. That’s not as liquid, so taking cash out of banks and sort of keeping it in real things and keeping it on site . . . keeping cash physically. You need to extract it from the system because the reality is when a financial crisis happens, banks close their doors to depositors. . . . Also, basically try to decrease your debt.”


Did Flynn plead guilty because he couldn’t pay the legal bills?
How much longer until Mueller is whistled back by his superiors? Can Rosenstein keep silent as one judge after another slams the Special Counsel?
• Mueller Investigation In Jeopardy (ZH)
A funny thing happened on the way to impeaching Donald Trump. After two-years of investigations by a highly politicized FBI and a Special Counsel stacked with Clinton supporters, Robert Mueller’s probe has resulted in the resignation of National Security Advisor Michael Flynn, the arrests of Paul Manafort and Rick Gates, and the indictment of 13 Russian nationals on allegations of hacking the 2016 election – along with the raid of Trump’s personal attorney, Michael Cohen.
The nation has been on the edge of insanity waiting for that much-promised and long awaited link tying President Trump to Vladimir Putin we were all promised, only to find out that there is no link, the deck appears to have been heavily stacked against Donald Trump by bad actors operating at the highest levels of the FBI, DOJ, Obama admin and Clinton camp, and the real Russian conspiracy in the 2016 election was the participation of high level Kremlin sources used in the anti-Trump dossier that Hillary Clinton paid for. Now, as the out-of-control investigation moves from the headlines and into court, the all-encompassing “witch hunt,” as Trump calls it, may be in serious jeopardy.
As of Friday, three separate Judges have rendered harsh setbacks to the Mueller investigation – demanding, if you can believe it, facts and evidence to back up the Special Counsel’s claims – in unredacted format as one Judge demands, or risk having the cases tossed out altogether. [..] And as we noted yesterday, some have suggested that Flynn pleaded guilty due to the fact that federal investigations tend to bankrupt people who aren’t filthy rich – as was the case with former Trump campaign aide Michael Caputo, who told the Senate Intelligence Committee “God damn you to hell” after having to sell his home due to mounting legal fees over the inquiry. “Your investigation and others into the allegations of Trump campaign collusion with Russia are costing my family a great deal of money — more than $125,000 — and making a visceral impact on my children.”

Quite strong for the Wall Street Journal: “Mr. Comey, Peter Strzok, Lisa Page, Andrew McCabe – they have already shattered the FBI’s reputation and public trust.”
• Why The Justice Department Defies Congress (WSJ)
Until this week, Deputy Attorney General Rod Rosenstein and fellow institutionalists at the department had fought Congress’s demands for information with the tools of banal bureaucracy – resist, delay, ignore, negotiate. But Mr. Rosenstein took things to a new level on Tuesday, accusing House Republicans of “threats,” extortion and wanting to “rummage” through department documents. A Wednesday New York Times story then dropped a new slur, claiming “Mr. Rosenstein and top FBI officials have come to suspect that some lawmakers were using their oversight authority to gain intelligence about [Special Counsel Bob Mueller’s ] investigation so that it could be shared with the White House.”
Mr. Rosenstein isn’t worried about rummaging. That’s a diversion from the department’s opposite concern: that it is being asked to comply with very specific – potentially very revealing – demands. Two House sources confirm for me that the Justice Department was recently delivered first a classified House Intelligence Committee letter and then a subpoena (which arrived Monday) demanding documents related to a new line of inquiry about the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Trump investigation. The deadline for complying with the subpoena was Thursday afternoon, and the Justice Department flouted it. As the White House is undoubtedly monitoring any new congressional demands for information, it is likely that President Trump’s tweet Wednesday ripping the department for not turning over documents was in part a reference to this latest demand.
Republicans also demand the FBI drop any objections to declassifying a section of the recently issued House Intelligence Committee report that deals with a briefing former FBI Director James Comey provided about former national security adviser Mike Flynn. House Republicans say Mr. Comey told them his own agents did not believe Mr. Flynn lied to them. On his book tour, Mr. Comey has said that isn’t true. Someone isn’t being honest. Is the FBI more interested in protecting the reputations of two former directors (the other being Mr. Mueller, who dragged Mr. Flynn into court on lying grounds) than in telling the public the truth?
We can’t know the precise motivations behind the Justice Department’s and FBI’s refusal to make key information public. But whether it is out of real concern over declassification or a desire to protect the institutions from embarrassment, the current leadership is about 20 steps behind this narrative. Mr. Comey, Peter Strzok, Lisa Page, Andrew McCabe – they have already shattered the FBI’s reputation and public trust. There is nothing to be gained from pretending this is business as usual, or attempting to stem continued fallout by hiding further details.

And debt pooling. So much for closer integration.
• Merkel Allies Reject Idea Of European Finance Minister (R.)
Leading politicians from Chancellor Angela Merkel’s conservatives want to pass a resolution at a meeting this week to reject any pooling of debts in Europe and any fiscal policy without national parliamentary controls, Handelsblatt reported. The daily business newspaper, citing sources from the conservative bloc’s parliamentary leadership, said the senior politicians also oppose European Commission plans for a European finance minister. The group includes the parliamentary leaders of the conservative bloc in the Bundestag, the European Parliament as well as from Germany’s 16 states, Handelsblatt reported.
Merkel will join them on Monday for a meeting in Frankfurt. The report highlights the resistance among Merkel’s conservatives to any euro zone reforms that could see more German taxpayers’ money being used to fund other member states. The conservatives are nervous about European Union reform after bleeding support to the anti-euro Alternative for Germany (AfD) party at national elections last September. Last month, Merkel called for a spirit of compromise on reforming the euro zone at a meeting with French President Emmanuel Macron, who pressed for solidarity among members of the currency union.

No smooth sailing.
• Weak Foreign Demand Pushes Down German Industrial Orders (R.)
German industrial orders unexpectedly dropped for the third month running in March due to weak foreign demand, data showed on Monday, suggesting factories in Europe’s largest economy are shifting into a lower gear. Contracts for German goods fell 0.9% after a downwardly revised drop of 0.2% the previous month, data from the Federal Statistics Office showed. Analysts polled by Reuters had on average predicted a 0.5% rise in orders. “The economy is slowing down, that’s the sure take-away from today’s industrial orders data,” VP Bank Group analyst Thomas Gitzel said, adding that some growth forecasts would soon have to be revised down.
The government last month cut its 2018 growth forecast to 2.3% from 2.4% and expressed concern about international trade tensions. “The debate about tariffs has probably created great uncertainty in Europe’s export-driven industry,” Gitzel added. As Europe’s biggest exporter to the United States, Germany is desperate to avoid an EU trade war with the United States. In the run-up to a June 1 deadline for U.S. President Donald Trump to decide on whether to impose steel and aluminum tariffs on the EU, Berlin is urging its European partners to be flexible and pursue a broad deal that benefits both sides. The drop in industrial orders was led by foreign orders which fell by 2.6%, while domestic orders rose 1.5%, the data showed.

But the government says there a million LESS people in poverty.
• A Million More UK Children In Poverty Than In 2010 (G.)
The number of children growing up in poverty in working households will be a million higher than in 2010, a new study has found. Research for the TUC estimates that 3.1 million children with working parents will be below the official breadline this year. About 600,000 children with working parents have been pushed into poverty because of the government’s benefit cuts and public sector pay restrictions, according to the report by the consultancy Landman Economics. The east Midlands will have the biggest increase in child poverty among working families, followed by the West Midlands and Northern Ireland, the research found. Frances O’Grady, the TUC general secretary, said child poverty in working households had shot up since 2010.
“Years of falling incomes and benefit cuts have had a terrible human cost. Millions of parents are struggling to feed and clothe their kids,” she said. “The government is in denial about how many working families just can’t make ends meet. We need ministers to boost the minimum wage now, and use the social security system to make sure no child grows up in a family struggling to get by.” [..] A government spokeswoman said it did not recognise the TUC’s figures. She said: “The reality is there are now 1 million fewer people living in absolute poverty compared with 2010, including 300,000 fewer children. “We want every child to get the very best chances in life. We know the best route out of poverty is through work, which is why it’s really encouraging that both the employment rate and household incomes have never been higher.”

Shares down 13% this morning.
• Air France Survival In Doubt Over Strikes (BBC)
The survival of strike-hit Air France is in the balance, according to the country’s economy minister. Bruno Le Maire’s warning that Air France could “disappear” comes as staff begin another round of industrial action over a pay dispute. Despite the French state owning 14.3% of the Air France-KLM parent group, the loss-making airline would not be bailed out, he said. On Friday Air France-KLM’s chief executive quit over the crisis. Air France-KLM is one of Europe’s biggest airlines, but has seen a series of strikes in recent weeks. Monday’s walk-out is the 14th day of action, as staff press for a 5.1% salary increase this year. The government’s response is seen as a test of labour reforms launched by French President Emmanuel Macron. There have also been strikes at the state-owned SNCF rail company.
On Sunday, Mr Le Maire told French news channel BFM: “I call on everyone to be responsible: crew, ground staff, and pilots who are asking for unjustified pay hikes. “The survival of Air France is in the balance,” he said, adding that the state would not serve as a backstop for the airline’s debts. “Air France will disappear if it does not make the necessary efforts to be competitive,” he warned. Despite the strike, the airline insisted that it would be able to maintain 99% of long-haul flights on Monday, 80% of medium-haul services and 87% of short-haul flights. On Friday, Jean-Marc Janaillac, chief executive of parent company Air France-KLM, resigned after staff rejected a final pay offer from him, which would have raised wages by 7% over four years.

That’s about 1 in 20: “From the 8.8 million individual taxpayers who submitted a declaration last year, no more than 450,000 showed a net annual income of 18,000 euros or more..”
• Greece’s Incredibly Shrinking Middle Class (K.)
For salaried workers to bring home 1,500 euros per month net on a 12-month basis, or 18,000 euros per year not including holiday bonuses, their employers need to pay 2,610 euros a month or over 31,300 euros a year, given Greece’s particularly high taxes and social security contributions. For a self-employed professional to pocket the same amount , about 18,000 euros per annum, he or she would have to earn at least 50,000 euros on a yearly basis so as to cover professional expenses, taxes and contributions. As for new pensioners, a net income of 1,500 euros/month or 18,000 euros/year can only be achieved if they worked without pause for 40 years at an average monthly salary of 2,400 euros over that entire period.
The framework that has emerged in the last three years with tax and contribution hikes, in particular, as well as the new way pensions are being calculated are drastically reducing the chances of any worker or pensioner to have a decent monthly salary or pension. Official figures already highlight the shrinking of the so-called middle class: From the 8.8 million individual taxpayers who submitted a declaration last year, no more than 450,000 showed a net annual income of 18,000 euros or more, down from 840,000 in 2010. The shrinking trend of the middle class is expected to continue both for taxation and for practical reasons.
An employer will face the same cost hiring five or six part-timers offering a total of 20-24 working hours per day as in hiring one full-timer offering eight hours of work. Particularly in sectors where there is no need for highly skilled workers, such as retail commerce or tourism, the trend to replace well paid positions has already become dominant. Among the self-employed, overtaxation is this year anticipated to reduce the number of those declaring a taxable income of over 30,000 euros per year. As for pensioners, already the first pensions issues on the basis of the new system of calculation prove that the chances for anyone to secure a benefit of 1,500 euros after retirement are next to zero, and will shrink further in the years to come.

Curious. Bonaire and St. Eustatius are part of the Dutch Kingdom. Conoco can’t move without their permission.
• Conoco Moves To Take Over Venezuelan PDVSA’s Caribbean Assets (R.)
U.S. oil firm ConocoPhillips has moved to take Caribbean assets of Venezuela’s state-run PDVSA to enforce a $2 billion arbitration award over a decade-oil nationalization of its projects in the South American country, according to two sources familiar with its actions. The U.S. firm targeted Caribbean facilities on the islands of Bonaire and St. Eustatius that play critical roles in PDVSA’s oil exports, the country’s main source of revenue. PDVSA relies on the terminals to process, store and blend its oil. “We will work with the community and local authorities to address issues that may arise as a result of enforcement actions,” ConocoPhillips said in a statement to Reuters.