‘Daly’ Store, Manning, South Carolina 1941



Deflation.
• What’s Happened To International Bank Lending? (WEF)
The Bank of International Settlements has just released its latest international banking statistics, which run until the end of June 2015, and they make for some pretty horrible reading. Cross-border lending fell by $910 billion (£589 billion), an enormous slump, and the largest since the fourth quarter of 2008, the worst bit of the global financial crisis. BIS is often referred to as the central bank of central banks, collating information on financial flows around the world and trying to make sense of what’s happening on a global scale. According to today’s data, cross-bank lending retreated at the fastest pace in more than six years. The period between Q1 2014 and Q1 2015 was the strongest run since the crash, with a (very small) contraction recorded in only one quarter, and decent growth in the others. Then it fell off a cliff:
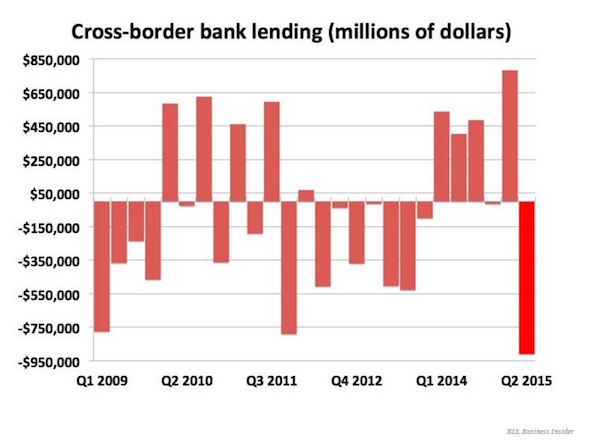
There’s a precise definition of cross-border lending from BIS, which the crucial definition being “when the ultimate obligor or guarantor resides in a country that is different from the residency of the reporting institution.” During the worst quarter of the financial crisis, Q4 2008, cross-border lending shrank more than twice as quickly, plunging by more than $2 trillion, and making Q2 2015’s decline look decidedly less dramatic:
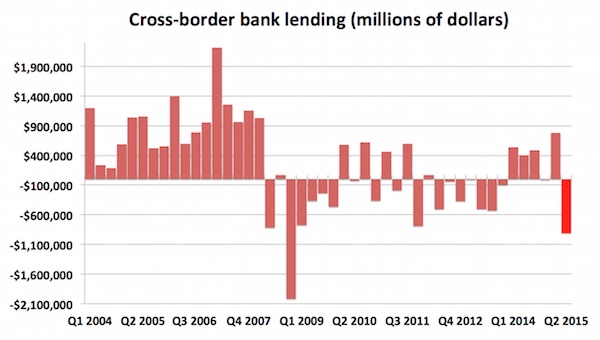
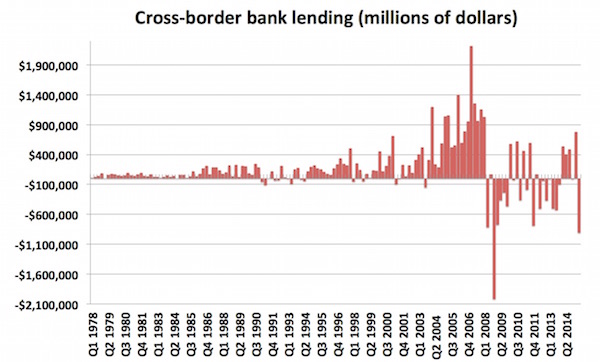
The longer timeframe also offers some perspective on the post-crisis period generally, showing how small the increases in cross-border lending have been, when it’s increased at all. That’s in stark contrast to the years leading up to the crisis, when lending across borders exploded: 10 of the 16 quarters from 2004 to the end of 2007 saw stronger growth than any single quarter since. Taking a look even further back, to 1978, three more things become clear — firstly, cross-border lending has exploded in size over the last 40 years. Secondly, the figures show just how strange the period since the crisis is, interrupting decades of growth (with some interruptions in the early 1990s). And finally, it shows that Q2 2015 was the worst quarter ever, other than Q4 2008. Take a look:

Not surprised.
• Greek Creditors Refuse To Make Next Loan Payment (Zero Hedge)
At first it was cute: when Greece got its first “dramatic” bailout in 2010 sending the global markets and the EUR first plunging then soaring, it was a melodrama of sorts – people still cared. Then, by the time the second and third bailouts rolled around, especially in the aftermath of the most ridiculous referendum in modern history, where a majority of Greeks voted for one thing only to get the other, it became a tragicomedy in what everyone hoped would be its final, “German colonial” season. It wasn’t. Moments ago, Germany’s Suddeutsche Zeitung reported that just two (or is it three, this past summer is one big blur) months after Greece voted through its third bailout, one which will raise its debt/GDP to over 200% on a fleeting promise that someone, somewhere just may grant Greece a debt extension (which will do absolutely nothing about the nominal amount of debt), its creditors have already grown tired with the game and are refusing to pay the next Greek loan tranche of €2 billion.
Specifically, the payment of the first €2b tranche of €3b is now sait to be delayed because Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras failed to implement reforms on schedule, Sueddeutsche Zeitung reports, citing unidentified senior EU official. Wait, you mean the Greeks (over)promised and never delivered? Who could have possibly seen this coming? Not the unidentified EU official who blasts Athens as having implemented only a third of the required projects. As a result, the tranfer probably will only take place in November, if then, since only 14 of the 48 “milestones” linked to payments have been decided on. The report goes on to tell us what we already knew: talks between the government in Athens and the Troika + the ESM (or Quadriga, or whatever it’s called) ended last week without success.
SZ goes into the unpleasant details, noting that there are inconsistencies in how the banks deal with bad loans, estimated that 320,000 apartment owners have mortgage payments in arrears, threatened with foreclosures, evictions, and so on. In other words, the Greek holiday from being held accountable for anything which started in July and lasted until October is over. Yet, there is still hope: in a separate report, Germany’s Bild tabloid cites Deutsche Bank analysts as anticipating a debt reduction for Greece of €200 billion by year-end, and amount which Bild conveniently calculates corresponds to €700 per inhabitant of the Eurozone. It adds that, as noted above, Greek debt would total €340b by year-end, or 200% of Greek GDP, some 140% higher than allowed by European treaties. It concludes by citing Lueder Gerken, Chairman of the Centre for European Policy, as saying that a Greek “haircut is economically inevitable, as well as a fourth rescue package.”

It’s all in the housing market.
• ‘Giant Wave of Money’ Headed for Sweden Creates Policy Nightmare (Bloomberg)
European Central Bank President Mario Draghi said boo last week and the krona jumped. With the ECB signaling a new wave of stimulus to prop up the euro zone, the question is how Sweden’s central bank can fight the monetary expansion coming from the south with its own, much smaller toolbox as it tries to stop the krona appreciating. “The nightmare for the Riksbank board is maybe something like this: they are gathered in the south of Sweden, looking out over the Baltic Sea, when they see a giant wave of money coming in from the euro zone and try to fight it with a hose,” Robert Bergqvist, chief economist at SEB in Stockholm and a former researcher at the Riksbank, said by phone. The Riksbank is due to announce its next rate decision on Oct. 28.
Most economists surveyed by Bloomberg see the bank keeping its repo rate at minus 0.35%, though there’s speculation policy makers will need to expand their quantitative easing program. Failure to do so would lead to the krona strengthening “markedly,” Nordea Bank says. Draghi’s stimulus measures to date have already forced his Swedish counterpart, Stefan Ingves, to resort to unprecedented measures to drive up consumer prices in Scandinavia’s largest economy. He cut Sweden’s main rate below zero for the first time in February and started buying bonds, expanding the QE program several times since. Underlying price growth has stayed below the Riksbank’s 2% target since the beginning of 2011.
The stimulus program marks a departure from the cautious approach Ingves had adopted earlier, as he argued that excessively low rates risked overheating Sweden’s already hot property market. Now, there’s a growing chorus of voices from bank executives to analysts warning of unsustainable housing price developments. But Ingves can’t afford to take his attention away from consumer prices. “The Riksbank is fully focused on the inflation target,” Pierre Carlsson, an analyst at Handelsbanken, said by phone. “They’ve let go of the housing market, at least officially, and it’s not something that should keep them from further action. But they’re hardly happy.”

Consumption vs supply.
• Oil Supply Hits 85-Year High in US (Bloomberg)
Hedge funds placed the most bets on falling oil prices since July as rising piles of crude dashed hopes of a near-term recovery. Money managers’ short position in West Texas Intermediate crude jumped by 18% in the week ended Oct. 20, the largest surge since July 21, according to data from the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. That pulled their net-long position down by more than 16,000 contracts of futures and options. Crude stockpiles in the U.S. rose 22.6 million barrels in the past four weeks to the highest October level since 1930, even as producers have idled more than half their drilling rigs in the past year. A global surplus of crude could last through 2016, according to the International Energy Agency. “The decline in U.S. drilling and production is not enough to rebalance even the U.S. market, let alone the global market,” said Tim Evans at Citi Futures Perspective.
“How much do you really want to pay for the next million barrels of inventory you don’t need?” WTI fell 2.4% in the report week to $45.55 a barrel on the New York Mercantile Exchange. The front-month contract dropped 1.4% to settle at $43.98 a barrel on Monday. Oil inventories in the U.S. have risen 5% in the past four weeks to 477 million barrels, the highest seasonal in 85 years, when massive production in east Texas caused the state to empower its Railroad Commission to regulate output. Supplies have risen as refineries have slowed processing to perform seasonal maintenance. U.S. plants ran at 86.4% of capacity last week, compared with 96.1% at the end of July. “We’re in the middle of refinery maintenance season. Utilization is low, imports are up, and we’re building crude,” said David Pursell at investment bank Tudor Pickering Holt & Co. in Houston, said in a phone interview. “The middle of October is an easy time to be bearish on crude.”

“..the most recent operator in the state to declare bankruptcy, filing in mid-September in hopes of clearing more than $3.25 billion in debt.”
• Bakken Oil Companies Declare Bankruptcy (BT)
As crude oil prices hang low, about $43 per barrel Monday, some North Dakota operators are trying to divest interests in the Bakken. Two debt-heavy operators in the state, Tulsa, Okla.-based Samson Resources and Denver-based American Eagle Energy, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, planning to sell off Bakken assets to pay back what they owe. Samson, with production acres in the Three Forks and Middle Bakken plays, has not yet succeeded in selling off acreage, spokesman Brian Maddox said. “We have not currently entered into agreements to divest other larger packages, including our Bakken, Wamsutter, San Juan and non-core Mid-Con assets, because we perceived the value offered was less than the value of retaining those properties when economic factors and the impact to our credit position were considered,” the company said in first-quarter 2015 filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Even if we are successful at reducing our costs and increasing our liquidity through asset sales, we do not expect to have sufficient liquidity to satisfy our debt service obligations, meet other financial obligations and comply with restrictive covenants contained in our various credit facilities.” The company is the most recent operator in the state to declare bankruptcy, filing in mid-September in hopes of clearing more than $3.25 billion in debt. As part of the company’s restructuring agreement, second lien lenders own all of the equity of the reorganized company in exchange for providing at least $450 million of new capital to increase liquidity.

Stevo!!
• Economists Prove That Capitalism Is Unnecessary (Steve Keen)
Actually they’ve done no such thing. But they do effectively assume that it’s unnecessary all the time. This transcendental truth became apparent to me in the reactions I have had from mainstream economists to a lecture I gave to my Kingston students this month. In it I explained that, at a very basic level, the original “Neoclassical” mathematical model of a market economy is mathematically unstable: it doesn’t converge to a stable pattern of relative prices and a stable growth path for the economy, as its developer Leon Walras thought it did. Mainstream economists reacted to my lecture by saying that, while the argument, which was first made in the 1960s by Jorgenson (who was applying a mathematical theorem from the early 1900s) was mathematically correct, all one had to do was assume that “economic agents” would then notice the instability and change their behavior. The model would then converge to equilibrium—problem solved.
And how would “economic agents” notice this instability? They would realize that a pattern of relative prices that had occurred once before in the past happened again. Hmmm. O.K.A.Y… I’ve read this sort of nonsense in dozens of mainstream academic papers over the years, and railed against it in an academic sort of way. But maybe because I’d just been reading and teaching Hayek to the same class, the true absurdity of this standard mainstream riposte stood out clearly to me. It’s an assumption that individuals in a market economy are so all-knowing that, in effect, they don’t need markets at all: they can just work it all out in their heads. Yet if anything defines a capitalist economy, it’s the dominance of markets. So effectively the mainstream reaction to anything which disturbs their preferred way of modeling a market economy is to make assumptions that, if they were true, would make a market economy itself unnecessary in the first place.
I know I’m not being original in saying this, by the way: this is the same point that Hayek made, in many different ways, when pointing out that the strength of a market economy was how it let people combine fragmented and incomplete knowledge in a way that no centralized system could do. As he put it:
“The fact that much more knowledge contributes to form the order of a market economy than can be known to any one mind … is the decisive reason why a market economy is more effective than any known type of economic order”.
Hayek’s main target here were socialists who believed that a complex economy could be centrally planned—thus doing away with markets institutionally. But he also criticized his mainstream rivals for assuming the existence of all-seeing, all-knowing “economic agents” to overcome mathematical problems in their equilibrium-obsessed models of the economy. Here he was actually in agreement with his great rival Keynes, since they both said that the only way equilibrium could be achieved would be if people’s expectations about the future were both shared and correct. Quoting Hayek:
“It appears that the concept of equilibrium merely means that the foresight of the different members of the society is in a special sense correct.”
And quoting Keynes:
“I accuse the classical economic theory of being itself one of these pretty, polite techniques which tries to deal with the present by abstracting from the fact that we know very little about the future.”
If the mainstream fantasies about the knowledge levels of individual agents were to be taken seriously, they’d need a convincing model to explain how such a state of mutual wisdom might come about. But as Hayek noted, rather than doing so, mainstream economists simply assumed that everyone was Nostradamus:
“instead of showing what bits of information the different persons must possess in order to bring about that result, we fall in effect back on the assumption that everybody knows everything and so evade any real solution of the problem.”

Mish’s reaction to Steve’s piece above.
• Keen vs. Keen: Will the Real Steve Keen Please Stand Up? (Mish)
In his Debtwatch Manifesto Keen proposes three mechanisms for dealing with the debt crisis. The first is a debt jubilee. The second is a mechanism that would act to restrict share prices. In his third proposal, Keen states “Lenders would only be able to lend up to a fixed multiple of the income-earning capacity of the property being purchased—regardless of the income of the borrower. A useful multiple would be 10, so that if a property rented for $30,000 p.a., the maximum amount of money that could be borrowed to purchase it would be $300,000.”
Hmm. How can Keen, me, or anyone else discern the correct “useful multiple”? Shouldn’t this be left to the free market? Keen also discusses full reserve proposals, one by Irving Fisher, the other HR2990 a bill Proposed by Congressman Dennis Kucinich in 2011.
Keen: Technically, both these [full reserve] proposals would work. I won’t go into great detail on them here, other than to note my reservation about them, which is that I don’t see the banking system’s capacity to create money as the causa causans of crises, so much as the uses to which that money is put. The problem comes when that money is created instead for Ponzi Finance reasons, and inflates asset prices rather than enabling the creation of new assets.
Mish: I propose, the system’s capacity to create money at will is the very problem. The fact of the matter is central banks can create money but not dictate where it goes. Curiously, Keen is willing to let bureaucrats decide what constitutes Ponzi financing, even though history shows government bodies and central banks have a 100% failure rate at identifying bubbles. Keen is concerned about “where the money goes”, yet is willing to trust bureaucrats more than the free market. To quote Keen directly … “And how would economic agents notice this instability? They would realize that a pattern of relative prices that had occurred once before in the past happened again. Hmmm. O.K.A.Y.”

“..what better excuse to override every principle of free market economics, financial discipline and public policy fairness than stopping a reenactment of the 1930s – putative soup-lines and all?”
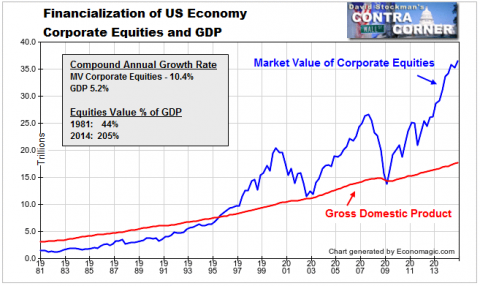
• Bernanke’s Bogus Contra-Factual, 1: The Myth Of Great Depression 2.0 (Stockman)
It took no “courage” whatsoever to inflate the Fed’s balance sheet from $900 billion to $2.3 trillion during just 17 weeks in September-December 2008. What it actually took was an epochal con job by a naïve Keynesian academic whose single idea about economics was primitive, self-serving, borrowed and wrong. The claim that the Great Depression was caused by the Fed’s failure to go on a bond buying spree in 1930-1933 was Milton Friedman’s monumental error. Professor Bernanke’s scholarship amounted to little more than xeroxing Friedman’s flawed work, and then shouting loudly in the Eccles Building boardroom at the time of the Lehman bankruptcy that Great Depression 2.0 was lurking just around the corner. That was just plain hysterical malarkey.
But at the time, it served the interests of the Wall Street/Washington Corridor perfectly. As Wall Street’s decade long spree of leveraged speculation was being liquidated in September 2008, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley and their posse of hedge fund speculators desperately needed rescue from their own reckless gambles – especially their funding of giant balance sheets swollen by long-dated, illiquid, risky assets with cheap hot funds in the wholesale money market. So what better excuse to override every principle of free market economics, financial discipline and public policy fairness than stopping a reenactment of the 1930s – putative soup-lines and all? At the same time, beltway politicians and fiscal authorities were tickled pink.
They would be able to unleash a monumental $800 billion potpourri of K-street pork and tax and entitlement giveaways to “fight” the recession, knowing that Bernanke & Co would finance it with an eruption of public debt monetization that was theretofore unimaginable. In short, no public official has ever committed an economic folly greater than the horrific misdeed of Ben S. Bernanke when he provided the Great Depression 2.0 cover story for the lunatic outbreak of central bank money printing shown below. It destroyed the last vestige of Wall Street discipline in a financialized economy that had already been bloated and deformed by two decades of Greenspan era Bubble Finance.
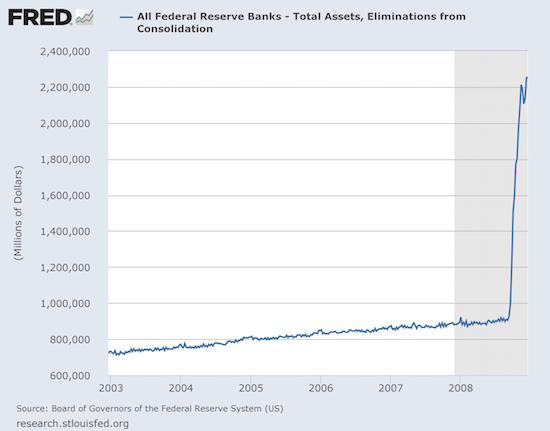

Bernanke on tour.
• Something Happened (Jim Kunstler)
Ben Bernanke’s memoir is out and the chatter about it inevitably turns to the sickening moments in September 2008 when “the world economy came very close to collapse.” Easy to say, but how many people know what that means? It’s every bit as opaque as the operations of the Federal Reserve itself. There were many ugly facets to the problem but they all boiled down to global insolvency — too many promises to pay that could not be met. The promises, of course, were quite hollow. They accumulated over the decades-long process, largely self-organized and emergent, of the so-called global economy arranging itself. All the financial arrangements depended on trust and good faith, especially of the authorities who managed the world’s “reserve currency,” the US dollar.
By the fall of 2008, it was clear that these authorities, in particular the US Federal Reserve, had failed spectacularly in regulating the operations of capital markets. With events such as the collapse of Lehman and the rescue of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, it also became clear that much of the collateral ostensibly backing up the US banking system was worthless, especially instruments based on mortgages. Hence, the trust and good faith vested in the issuer of the world’s reserve currency was revealed as worthless. The great triumph of Ben Bernanke was to engineer a fix that rendered trust and good faith irrelevant.
That was largely accomplished, in concert with the executive branch of the government, by failing to prosecute banking crime, in particular the issuance of fraudulent securities built out of worthless mortgages. In effect, Mr. Bernanke (and Barack Obama’s Department of Justice), decided that the rule of law was no longer needed for the system to operate. In fact, the rule of law only hampered it. Mr. Bernanke now says he “regrets” that nobody went to jail. That’s interesting. More to the point perhaps he might explain why the Federal Reserve and the Securities and Exchange Commission did not make any criminal referrals to the US Attorney General in such cases as, for instance, Goldman Sachs (and others) peddling bonds deliberately constructed to fail, on which they had placed bets favoring that very failure.

“Rajoy’s party has the support of about 27% of voters compared with almost 45% in the previous general election..”
• Rajoy Calls Election for Spain Against Backdrop of Party Unrest (Bloomberg)
Spanish Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy called a general election for Dec. 20, insisting he is the best candidate to win the ballot despite unrest within his party. Speaking in Madrid, the 60-year-old premier said his government has turned the economy around and honored its pledge to bring down unemployment after it reached a record high on his watch. Rajoy urged Spaniards to vote for continuity and stability, arguing that he’s best placed to safeguard the recovery and create more jobs. “If I didn’t think I was the best candidate I wouldn’t be running,” he said at a televised press conference Monday. Asked about potential coalitions, Rajoy avoided going into detail about what his preferred options would be, but insisted that he wouldn’t try to form a government if his party didn’t win the most votes.
He batted away speculation that he would be prepared to step down to facilitate a coalition government if a junior partner “called for his head.” “My head is well placed and I’m not letting anyone change that place,” he said. Rajoy’s party has the support of about 27% of voters compared with almost 45% in the previous general election, when it secured its best result ever. With the prime minister’s party dogged by corruption allegations, many of its traditional voters have been drawn to pro-market party Ciudadanos, led by 35-year-old former lawyer Albert Rivera. Rajoy denies any wrongdoing. For a party that prides itself on internal discipline, Rajoy has had to suffer a raft of dissent in recent weeks. His predecessor Jose Maria Aznar criticized the party’s performance, Budget Minister Cristobal Montoro launched an attack on his cabinet colleagues and lawmaker Cayetana Alvarez de Toledo announced in a newspaper column that she wouldn’t run again on a list led by the prime minister.
Spaniards will go to the polls with the economy growing at the fastest pace since 2007 and unemployment at the lowest in almost four years. Still, opinion polls suggest about 40% of PP voters are considering other options. “The economic recovery is helping Rajoy recover moderate voters,” said Narciso Michavila, chairman of pollster GAD3. “The question is whether that’s enough.” The PP is outpacing Socialists, the other Spanish incumbent party, by about four%age points, according to the average of 10 polls publicly released since Oct. 5. Ciudadanos is running third with an average support of 18.2%, while Syriza’s ally Podemos is on 13.6%.

Lots of different views on this, coup or no coup. Wonder how it’ll play out. President plays strange role, but he’s out in January.
• Portugal’s Constitutional Crisis Threatens All European Democracies (Telegraph)
On October 4, the ruling conservative coalition that has governed Portugal for four years lost its parliamentary majority. The centre-right alliance, led by Prime Minister Pedro Passos Coelho, had overseen the implementation of one of the toughest austerity packages in the euro following a €78bn bail-out in 2011. The incumbents still emerged as the biggest party with 36.8pc of the vote share, but lost 17 seats and their parliamentary majority in the process. In second place was the main opposition Socialists (PS) led by Antonio Costa. Mr Costa – a moderate who supports Portugal’s euro membership – gained 32.4pc of the vote share. The result was disappointing but not catastrophic for the former mayor of Lisbon, who had been narrowly leading the polls in the electoral run up. But Portugal’s more stridently anti-austerity, eurosceptic parties on the Left – the radical Left Bloc and the anti-euro Communists, saw a surprising surge in support.
Combined, they gained 18.5pc of the vote. Despite the inconclusive result, the election indicated an overall dissatisfaction with Portugal’s dominant pro-austerity, pro-bail-out forces (including the Socialists). The electoral result pointed to the likely continuation of a minority centre-right government led by Mr Passos Coelho. However, for any new government to carry out painful economic reforms demanded by the EU, the PM would require opposition support in parliament. Mr Costa, however, vowed never to back the conservatives. Instead, after a few weeks of political horsetrading, he brokered a historic coalition deal with the radical Left Bloc and Communists in order to clump together a workable political majority of just under 51pc.
Hailed as a “Berlin Wall moment” for the country, the three main parties on the Left managed to put aside internecine squabbles to present themselves as the only government that could secure political stability for Portugal. Despite getting into bed with hardened eurosceptic Communists, Mr Costa promised not to jettison his pro-European principles and to notionally abide by the stringent fiscal targets imposed by Portugal’s former creditors in Brussels. However, the Leftist alliance is of a decidedly anti-austerity bent. Its policies would likely jeopardise the fiscal consolidation of the centre-right, and poison Portugal’s relationship with Brussels, say analysts. “The minimum wage would probably be raised, further tweaks to the social security system would probably be off the table, as would a further liberalisation of the labour market, or a reduction in the tax-burden,” notes Federico Santi at Eurasia Group.

Goat.
• Goldman Sachs Banker Likely To Face Jail Amid Rare Criminal Charges (Guardian)
A Goldman Sachs banker is expected to be jailed over the leaking of confidential information from the New York Fed, the investment banker’s former employer. Federal prosecutors are preparing to this week announce criminal charges against the banker, Rohit Bansal, and an employee of the regulator, according to the New York Times. Lawyers for the men, who were both fired in the wake of the leak, are said to be hammering out a deal with prosecutors. Even if they agree on the plea deal, they are likely to face up to a year in jail. It is rare for criminal charges to be brought directly against bankers in the US, but the attorney general, Loretta Lynch, has set out new guidelines designed to ensure that more executives, bankers and other businesspeople are held personally accountable for their actions.
Under the planned deal, Goldman would not face criminal charges but would pay a fine of as much as $50m and would be forced to admit that it failed to properly supervise Bansal. A spokesman for Goldman said: “Upon discovering that a new junior employee had obtained confidential supervisory information from his former employer, the New York Fed, we immediately began an investigation and notified the appropriate regulators, including the Fed. “That employee and a more senior employee who failed to escalate the issue, were terminated shortly thereafter. We have zero tolerance for improper handling of confidential information. We have reviewed our policies regarding hiring from governmental institutions and have implemented changes to make them appropriately robust.” The case highlights the dangers of a revolving door between banks and regulators. Bansal had spent seven years at the New York Fed before joining Goldman, where he advised one of the same banks he had previously regulated.

It’s completely unclear to me what, if any, funds the EU has sent to date to Athens to deal with the refugee crisis. Can’t find a single report on the topic. This, too, has been approved, but not paid yet.
• EC Approves Aid As Greece Prepares To Host More Migrants (Kath.)
A day after a crisis summit on the refugee problem, where Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras agreed to increase Greece’s reception capacity for migrants to 50,000 by the end of the year, the European Commission approved the release of emergency aid to Athens. Confirming the approval of €5.9 million to help Greece cope with the large numbers of migrants and refugees arriving in the country daily from Turkey, European Commissioner for Migration Dimitris Avramopoulos said on Monday that the aid was aimed at enabling authorities to “cover the transportation costs for a significant number of these persons from the eastern Aegean islands to reception centers in mainland Greece once they have been properly registered, identified and fingerprinted.” A statement issued by the EC indicated that the sum was aimed at paying for the transport of 60,000 people. It remained unclear, however, where those people would stay as Greek authorities are still seeking venues.
Sources in Brussels indicated that Tsipras came under huge pressure at the Sunday summit to set up a large facility for migrants in Athens. In comments after the meeting, Tsipras said the creation of such a facility, “the size of a small city,” was among a series of “unacceptable demands” that he rejected. On Monday, government spokeswoman Olga Gerovasili also presented the outcome of the summit as a minor victory for Greece. “What was asked of us, to place 20,000 people in a giant camp, was rejected,” she said, adding that “there will be no concentration camps in our country.” She added that authorities were preparing a housing program to help up to 20,000 migrants, indicating that this too would require European funding.

Blackwater looms.
• Slovenia To Hire Private Security Firms To Manage Migrant Flows (Reuters)
Slovenia is planning to employ private security firms to help manage the flow of thousands of migrants and refugees travelling through the country toward northern Europe, a senior official has said. Bostjan Sefic, state secretary at the interior ministry, said 50-60 private security guards would assist the police where necessary. More than 76,000 people have arrived in Slovenia from Croatia in the past 10 days. More than 9,000 were in Slovenia on Monday, hoping to reach Austria by the end of the day, while many more were on their way to Slovenia from Croatia and Serbia. The emergency measure was announced by the prime minister, who described the migrant crisis as the biggest challenge yet to the EU.
If a joint solution is not found, [the trade bloc] will start breaking up, Miro Cerar warned. About 2,000 migrants waited in a field in Rigonce on the Croatian border on Monday for buses to take them to a nearby camp to be registered before they are allowed to proceed north. [..] Slovenia, the smallest country on the Balkan migration route, has brought in the army to help police. Other EU states have pledged to send a total of 400 police officers this week to help manage the flow of people. Over the past 24 hours, 8,000 people arrived in Serbia en route to northern Europe, the UN refugee agency, UNHCR, said.

“The idea that EU border countries should solve 80% of the problem is completely out of touch with reality.”
• Italy Says EU’s Response ‘Inadequate’ as Refugee Numbers Surge (Bloomberg)
European Union agreements on the free movement of people may be at risk of collapse unless the bloc eases the burden for border countries forced to handle asylum-seekers, Italian Foreign Minister Paolo Gentiloni said. Gentiloni, whose country has borne the brunt of the influx from Africa and the Middle East, said that common policies to share the burden would leave the EU much better placed to help people fleeing conflict. He also called for clear criteria to define so-called safe countries that migrants could be sent back to. “Europe – with hundreds of millions of people – can accept hundreds of thousands of migrants” so long as there is a common policy, Gentiloni said. “The idea that EU border countries should solve 80% of the problem is completely out of touch with reality.”
Europe’s worst refugee crisis since World War II intensified at the end of summer after German Chancellor Angela Merkel said there could be no limit on granting asylum to those who legitimately met the criteria. Migrants also began shifting from a route that once led mainly through Libya to southern Europe to one winding from Turkey to Greece, through the Balkan states, and then further north. With winter approaching and more than a million migrants set to reach the EU this year, the bloc’s leaders are struggling to present a united front as national authorities have tightened their borders and waved asylum seekers through to neighboring countries. Slovenia said at a Sunday meeting in Brussels that Croatia is causing chaos by sending migrants across its frontier with little warning.
In yet another sign of the divisions, Dutch Finance Minister Jeroen Dijsselbloem on Monday said it was a concern that Poland wasn’t accepting more refugees. “Poland is taking only a limited number of people and I find that disturbing,” he said at an event in The Hague. “Poland gets a lot of subsidies. We help to build Poland – they should take up asylum seekers in return.” Gentiloni’s warning came as the United Nations said the influx on the region’s southeastern fringe is growing. As many as 49,000 migrants entered the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, which isn’t an EU member, last week, Mirjana Milenkovski of the UNHCR, said on Monday. The daily average number of people entering Serbia increased to 7,000 from 5,000 a week earlier, she said. “Nothing has been done really adequately,” Gentiloni said. “We are still perhaps not adequate to the dimension and the perspective of these flows.”

“They are using the refugee crisis as another way to apply pressure on Athens, to demand even more asphyxiating measures. Is this opportunism? Cynicism? Crudeness? Whatever term we choose, none is a synonym for solidarity.”
• Using The Refugee Crisis (Boukalas)
Splitting the refugee crisis into three or more parts does not make any political sense nor is it morally acceptable. You can’t say that it’s a Balkan problem or an Italian problem or a French problem. The alliance of 28 states is still called the European Union even though it is blatantly dominated by Germany and even though we see countries expecting to better serve their own interests by gravitating toward Berlin. Therefore, a summit on the refugee crisis organized by the EU is from the onset incomplete when it does not include Italy and France, if, of course, the objective is to find a way to help the refugees and not to solve the refugee “problem” challenging individual states and leaders.
Yet even if we were to accept that the priority is to meet the challenges faced by the so-called Balkan corridor, then it is incomprehensible why Turkey was not invited to attend, given its key role in this avenue of arrival into the European Union. Of course, it is also very understandable given that Angela Merkel’s recent visit to Turkey was as the head of the EU rather than the chancellor of Germany. She’s already taken care of business so discussions with and the participation of the other parties involved, even those which are at the vanguard, is unnecessary. Greece’s position is particularly delicate. There have been many times in history when being at the crossroads of three continents was a problem rather than advantage.
The reality of the refugee crisis in this country is symbolized by a recent photograph showing a girl on the island of Lesvos giving a doll to another little girl, a refugee in her father’s arms, and in the father’s smile, which is full of gratitude and trust. Because of the crisis, which has thrown the welfare state and all of its institutions into complete disarray, what Greece can offer these people is about as much as that offered by the Lesvos girl: a gesture of kindness and whatever has been scraped together. So far, Greece has managed to do this, mainly thanks to the excellent work and dedication of volunteers, both Greek and foreign. Of course there is no shortage of scumbags who charge refugees €20 for access to a plug to charge their cell phones or €5 for a piece of plastic to keep the rain off.
The contribution of the European Union to Greece’s refugee management is extremely small and in many respects restricted to promises. It is also becoming clearer that the problems Greece faces in dealing with the influx does not constitute an important reason for foreign creditors to relax their control of finances but an opportunity to become even stricter. They are using the refugee crisis as another way to apply pressure on Athens, to demand even more asphyxiating measures. Is this opportunism? Cynicism? Crudeness? Whatever term we choose, none is a synonym for solidarity.

Death penalty.
• Big-Game Hunters Are Killing African Lions In Record Numbers (Bloomberg)
Big-game hunters are killing African lions in record numbers as U.S. regulators threaten to curtail one of world’s most exclusive, expensive and controversial pursuits. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has an Oct. 29 deadline to make a final determination on the status of the African lion, which it has proposed to list as threatened under the Endangered Species Act. The agency has also recommended requiring a special permit to import lion trophies. Those findings could curtail the number of slain lions entering the U.S., while also driving up safari costs that are often more than $100,000.
That’s leading to a rush of Americans taking their guns to Africa in pursuit of the king of the jungle. Last year, Americans imported a record 745 African lions as trophies, up 70% since 2011 and more than double the total in 2000, according to data from the Fish and Wildlife Service. “Guys fearing that I’ll never get my opportunity to get a lion, they’re getting it while the getting’s good,” said Aaron Neilson, an African safari broker based in Colorado whose exploits, including lion hunts, are featured on a Sportsman Channel television show. “The overall consensus among everybody selling lion hunts has been, ‘Man, get it now.”’

Palm oil.
• Indonesia’s Forest Fires Labelled A ‘Crime Against Humanity’
Raging forest fires across Indonesia are thought to be responsible for up to half a million cases of respiratory infections, with the resultant haze covering parts of Malaysia and Singapore now being described as a “crime against humanity”. Tens of thousands of hectares of forest have been alight for more than two months as a result of slash and burn – the fastest and quickest way to clear land for new plantations. Indonesia is the world’s largest producer of palm oil and fires are frequently intentionally lit to clear the land with the resulting haze an annual headache. But this year a prolonged dry season and the impact of El Niño have made the situation far worse, with one estimate that daily emissions from the fires have surpassed the average daily emissions of the entire US economy.
The fires have caused the air to turn a toxic sepia colour in the worst hit areas of Sumatra and Kalimantan, where levels of the Pollutant Standard Index (PSI) have pushed toward 2,000. Anything above 300 is considered hazardous. Endangered wildlife such as orangutans have also been forced to flee the forests because of the fires. Six Indonesian provinces have declared a state of emergency. Across the region Indonesia’s haze crisis has been causing havoc – schools in neighbouring Singapore and Malaysia have been shut down, flights have been grounded, events cancelled and Indonesian products boycotted, as millions try to avoid the intense smoke. In the worst affected parts, on Sumatra and Kalimantan, ten people have died from haze-related illnesses and more than 500,000 cases of acute respiratory tract infections have been reported since July 1.