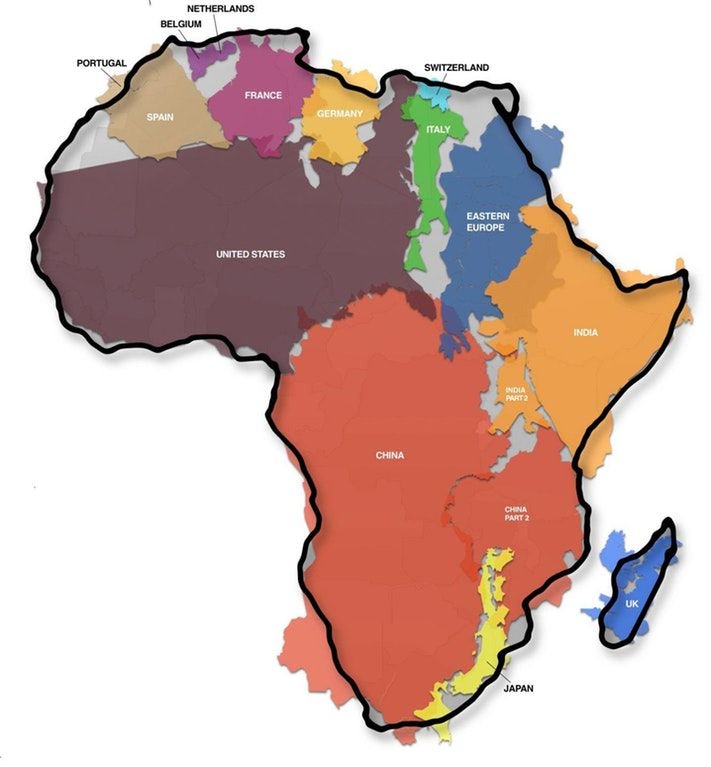
Piet Mondriaan Study for Blue Apple Tree Series 1908

“..trade talks, even the fake kind, is now over, dead and buried..”
• Currency War Begins: China Crashes Yuan Past 7, Halts US Agri Imports (ZH)
Update 2: – China’s central bank has confirmed that it is, indeed, on, saying that it is able to keep the yuan exchange rate at a reasonable and balanced level – whatever that means – while acknowledging that the Yuan plunging beyond 7 per dollar is due to market supply and demand, trade protectionism and expectations on additional tariffs on Chinese goods. Meanwhile, resorting to its old, tired and worn out tricks, Dow Jones reports that the PBOC will crack down on short-term Yuan speculation, and anchor market expectations. Which is great… if only the PBOC didn’t say exactly the same back in May, when it warned currenct traders that those “shorting the yuan will inevitably suffer from a huge loss.” Three months later, it’s currency traders 1 – Beijing 0.
Update 1 – China is firing all the big guns tonight, because just an hour after Beijing effectively devalued the yuan, when it launched the latest currency war with the US, Bloomberg reported that the Chinese government has asked its state-owned enterprises “to suspend imports of U.S. agricultural products after President Donald Trump ratcheted up trade tensions with the Asian nation last week.” China’s state-run agricultural firms have now stopped buying American farm goods, and are waiting to see how trade talks progress. Translation: trade talks, even the fake kind, is now over, dead and buried, and the only question is how Trump will react.
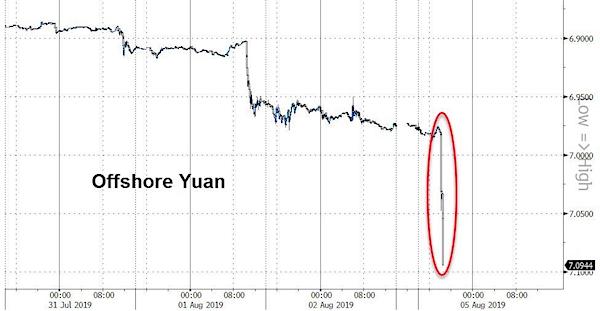
[..] in a dramatically unsettling move for global stability, China’s offshore yuan just collapsed below 7/USD — after the PBOC fixed the onshore yuan below 6.90 for the first time in 2019 — the currency plunging a stunning 12 handles to its weakest on record against the dollar as countless stop losses were triggered and thousands of traders were margined out.
“A break of 7 is quite shocking to the market, and close attention will be paid to how China would deal with this move,” says Tsutomu Soma, general manager of the investment trust and fixed-income securities at SBI Securities Co. in Tokyo in a phone interview. This is the weakest offshore yuan has ever been against the dollar…

Beijing control over the yuan is worrisome. It also prohibits uptake of the currency in global trade.
• China Lets Yuan Slump Past 7 Per Dollar For First Time In Over A Decade (R.)
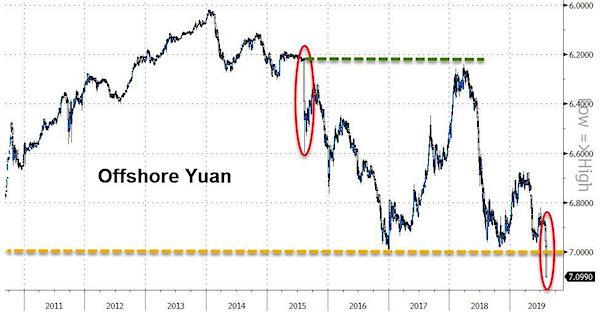
China on Monday let the yuan tumble beyond the key 7-per-dollar level for the first time in more than a decade, in a sign Beijing might be willing to tolerate further currency weakness in the face of an escalating trade row with the United States. The sharp 1.4% drop in the yuan came after the People’s Bank of China set the daily mid-point of the currency’s trading band at 6.9225 per dollar, its weakest level since December 2018. “Today’s fixing was the last line in the sand,” said Ken Cheung, senior Asian FX strategist at Mizuho Bank in Hong Kong. “The PBOC has fully given the green light to yuan depreciation”. The shakeout in the yuan comes days after Trump stunned financial markets by vowing to impose 10% tariffs on the remaining $300 billion of Chinese imports from Sept. 1, abruptly breaking a brief month-long ceasefire in the bruising trade war.
After opening the onshore session at 6.9999 per dollar, the yuan had weakened to 7.0266 per dollar by 0351 GMT, down 1.2% on the day after earlier losing as much as 1.4% of its value. Monday marked the first time the yuan had breached the 7-per-dollar level since May 9, 2008. With the escalating trade war giving Beijing fewer reasons to maintain yuan stability, analysts said they expect the currency to continue to weaken. “In the short-term, the yuan’s strength would be largely determined by the domestic economy. If third-quarter economic growth stabilizes, the yuan could stabilize around 7.2 or 7.3 level,” Zhang Yi, chief economist at Zhonghai Shengrong Capital Management in Beijing.
Capital Economics senior China economist Julian Evans-Pritchard said the PBOC had probably been holding back against allowing a weaker yuan to avoid derailing trade negotiations with the United States. “The fact that they have now stopped defending 7.00 against the dollar suggests that they have all but abandoned hopes for a trade deal with the U.S.,” he said.

Organizers swore peaceful protests. But a few agitators can take care of that.
• Hong Kong Brought To A Standstill As City-Wide Strikes And Protests Hit (G.)
Hong Kong’s embattled leader, Carrie Lam, has warned that mass protests have pushed the region to the brink of a “very dangerous situation” as residents have gone on strike, paralysing the city. Lam, who has disappeared from public view for the past two weeks, gave a media briefing in which she condemned the protests for hurting Hong Kong’s economy and stability. “Such extensive disruptions in the name of certain demands or uncooperative movement have seriously undermined Hong Kong law and order and are pushing our city, the city we all love, and many of us helped to build, to the verge of a very dangerous situation,” she said.
On Monday, transport across Hong Kong was brought to a standstill and more than 150 flights out of the city were cancelled. Almost 100 outbound and 100 inbound flights were cancelled. Protesters also blocked key roads and stopped trains throughout the city. [..] Protesters have shifted tactics beyond only marches and protests in the streets. Civil servants from more than 30 government departments, as well as pilots, teachers, construction workers, engineers, and aviation staff all pledged to strike on Monday.
On Monday morning, several lines of the MTR, the rail network serving Hong Kong, were suspended as protesters, many wearing face masks and black clothing, blocked the doors of trains, preventing them departing the stations. There were also reports of discarded umbrellas being wedged in train doors to prevent them from closing, delaying services. Monday’s planned city-wide protest, which is aimed to disrupt peak-hour travel of commuters, is the fifth consecutive day of mass demonstrations in the city. Simultaneous rallies were planned for seven of Hong Kong’s 18 districts on Monday. Hong Kong has not held a general strike in more than 50 years.

“Rural America is older, sicker, poorer and more dependent upon state aid than it was before.”
• Job Growth In Trump Land Is Dead In The Water (MW)
Since the economy began adding jobs after the Great Recession nine years ago, about 21.5 million jobs have been created in the United States, the second-best stretch of hiring in the nation’s history, second only to the 1990s. But job growth isn’t being spread evenly across the land. Most of the new jobs have been located in a just a few dozen large and dynamic cities, leaving slower-growing cities, small towns and rural areas — where about half of Americans live — far behind. Along with climate change and racial justice, economic development is America’s biggest challenge over the next few decades. Inclusive growth is a must, or else our society will fall apart. The problem: No one — certainly not President Trump — has found the magic wand that will bring back jobs to rural and small-town America.
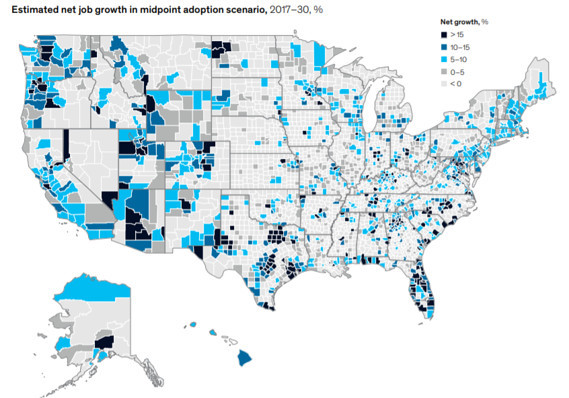
According to a study titled “The Future of Work in America” by the McKinsey Global Institute released in July, 25 cities that are home to about 30% of Americans will capture about 60% of the job growth between 2017 and 2030, just as they did between 2007 and 2017. Twelve are megacities (and their extended suburbs): Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Philadelphia, Phoenix, San Francisco and Washington. Another 13 are high-growth hubs in smaller cities: Austin, Charlotte, Denver, Las Vegas, Minneapolis, Nashville, Orlando, Portland (Ore.), Raleigh, San Antonio, San Jose, Seattle, and Tampa. A few other smaller, fast-growing cities will also add jobs, while vast swaths of the South, Midwest and Plains will lose jobs.
The New York metro area, home to 20 million people, added more jobs over the past year than all the small towns and rural areas — with 46 million people — did combined. Anyone who’s been paying attention to the political map will recognize that the growth is mostly occurring in places that vote for Democrats, while the stagnation is mostly in places that vote for Republicans. Donald Trump has appealed to those who are the most fearful, the most resentful and the most despairing, but the situation hasn’t gotten any better since his election. Rural America is older, sicker, poorer and more dependent upon state aid than it was before.

Feel lucky?
• 10 Alarming Things About The Economy That Politicians Won’t Tell You (MW)
Here are 10 remarkable forecasts and assumptions that Washington is making and isn’t telling you. These are all contained in the Congressional Budget Office’s most recent Long-Term Budget Outlook, the cornerstone document of government financial and economic planning.
1. We’re going to have a lot more immigrants. A lot. They’re expecting a net 22.5 million more immigrants to come to the U.S. over the next 20 years. By 2049, they’re expecting immigration to account for a stunning 87% of annual population growth.
2. We’re going to have a lot more illegal immigrants. Despite the current bluster and the scandals at the border, the CBO expects we’ll have 2.4 million more illegal immigrants (or “undocumented residents,” or whatever) in 20 years’ time than we have today.
3. We’re going to be up to our eyeballs in debt. The national debt is expected to skyrocket to an “unprecedented” 144% of GDP by 2049, or twice the level today. That would put the debt just under $100 trillion. The figure today: Around $18 trillion. As recently as 2000: $4 trillion. Oh, and this isn’t even the worst-case scenario: The national debt could exceed 200% of GDP in 30 years’ time, the CBO acknowledges.
4. We’re going to owe so much money that by 2049 the annual interest on the debt will be about 5% of GDP — roughly the share that we spend today on Social Security. And that’s even if interest rates stay low. Despite rising debt and federal spending, the government is expecting — or hoping — the average rate on federal debt will rise only from today’s lowly 2.4% to 4.2%, still modest by historic standards, by 2049.
5. This debt, and these deficits, will damage the economy. They will crowd private investment out of the debt markets, reducing income and growth, says the CBO. And as we’ll have to borrow more and more from abroad to finance the government, they’ll lead to bigger and bigger interest payments leaving the country.
6. Social Security, Medicare, other health programs and net interest are going to soak up so much of the budget that we’re going to have to slash everything else to the smallest share of the economy in 70 years — just 7%. The average over the past 50 years: 11%.
7. Just to keep the federal deficit to these levels, your taxes will go up. The Obama tax hike on “Cadillac” health-insurance plans will kick in starting in 2022, and the 2017 Trump tax cuts will expire in 2025.
8. Most working stiffs can say goodbye to any other tax cuts. Uncle Sam is explicitly relying on your taxes to go up thanks to “bracket creep,” where income-tax brackets rise only in line with inflation while your income — you hope — rises faster.
9. While tax rates go up for most people, they won’t for those earning the most. That’s because more and more of their income will be above the Social Security “cap,” saving them an effective 12.4% a year. The cap this year is $132,900.
10. Meanwhile, working stiffs will be taxed at twice the marginal rate of those who live on dividends. By 2049, says the CBO, labor income will be taxed at a marginal rate of 32%, compared to just 16% for capital income. Good to know, isn’t it? It would be great to see some of this stuff come up in the presidential race, wouldn’t it?

“The Fed hiked 25bps to 3.25% in Feb 1994. Grown men cried on the trading floor. Salesmen. They were soon laid off. Their clients suffered staggering losses. They too were fired.”
• The Crashes That Cause Grown Men To Cry (Eric Peters)
He started his career in 1989, with Fed Funds at 9.75%. The Fed slashed rates to 8.25% in Dec 1989 as the S&L Crisis unfolded. They continued cutting until Aug 1992, when rates hit a mindboggling low of 3.00%. The Fed kept money that cheap for 1.5 yrs. Investors had recently earned 9.75% for taking no risk and found themselves starved for returns. So banks structured complex products that offered enhanced yields by selling volatility – they were great, provided the Fed neither hiked nor cut rates. They flew off the shelves. Salespeople gouged their clients. The Fed hiked 25bps to 3.25% in Feb 1994. Grown men cried on the trading floor. Salesmen. They were soon laid off. Their clients suffered staggering losses. They too were fired.
And as their bosses and boards discovered the scale of their unbounded risk, they instructed the banks to get them out at the best price. Whenever that happened, the cost was far bigger than expected. And this in turn was reflexive. Those clients who had earlier assured themselves that they could stomach the ride – because they were long-term investors – were forced to vomit. They call that period The Great Bond Massacre. But it seemed like every few years, another great massacre would unfold in one thing or another. So he assumed that this is how the world worked. Of course, he wasn’t alone. Global central bankers also recognized this to be the case. So they strived to avoid new massacres. But their tools only worked when the mechanic applied greater leverage with each use. Massacre after massacre, they cranked away. By 2019, they had produced the longest economic expansion and equity bull market in American history.

Is this enough to end the Fed?
• Inside The Plunge Protection Team: Chaos (ZH)
Now, thanks to Bloomberg, we have a much more detailed look into what transpired at the trading desk of the “Plunge Protection Team”, and what we learn is that the past year said institution which forms the bedrock of support for the US capital market has been gripped by what at times is sheer chaos. Why? Perhaps it will not come as a surprise to anyone, that the reason for said chaos is another career economist, in this case the “new” president of the New York Fed, John Williams (no relation to the Star Wars guy). As Bloomberg details in a “must read” report, “an unusual level of internal tension broke out in recent weeks at the fortress-like Federal Reserve Bank of New York in lower Manhattan.”
This was prompted by the sudden departure of the two longtime officials mentioned above, which “shook staff, sank morale and drew attention to the leadership of the New York Fed under John Williams as he enters his second year at the helm.” And yes, this is the same John Williams who two weeks ago prompted a mini market tantrum following one of the most epic communication fuck ups by a central banker. As Bloomberg writes “the story involves Simon Potter, who ran the all-important markets desk, and Richard Dzina, head of the financial services group. Both were abruptly relieved of their roles in late May by Williams.
Little explanation was given, but according to current and former New York Fed employees, as well as those close to the bank, the nature of the exits, by fault or design, seemed to be a warning: fall in line.” It is not clear exactly what the two titans of US capital markets had to “fall in line” for, but two things are certain – i) Potter did not “resign”, he was fired by Williams, and ii) now that an economist with zero capital markets experience is in charge, and following his termination of Potter and Dzina, the world is one step closer to collapse as a clueless PhD hack is in charge of the most important market in the world.

“Judge Koeltl concluded that, quite simply, the claims made as the basis of Russiagate are insufficient to even warrant a hearing.”
• Russiagate is the New 42 (Craig Murray)
Douglas Adams famously suggested that the answer to life, the universe and everything is 42. In the world of the political elite, the answer is Russiagate. What has caused the electorate to turn on the political elite, to defeat Hillary and to rush to Brexit? Why, the evil Russians, of course, are behind it all. It was the Russians who hacked the DNC and published Hillary’s emails, thus causing her to lose the election because… the Russians, dammit, who cares what was in the emails? It was the Russians. It is the Russians who are behind Wikileaks, and Julian Assange is a Putin agent (as is that evil Craig Murray). It was the Russians who swayed the 1,300,000,000 dollar Presidential election campaign result with 100,000 dollars worth of Facebook advertising.
It was the evil Russians who once did a dodgy trade deal with Aaron Banks then did something improbable with Cambridge Analytica that hypnotised people en masse via Facebook into supporting Brexit. All of this is known to be true by every Blairite, every Clintonite, by the BBC, by CNN, by the Guardian, the New York Times and the Washington Post. “The Russians did it” is the article of faith for the political elite who cannot understand why the electorate rejected the triangulated “consensus” the elite constructed and sold to us, where the filthy rich get ever richer and the rest of us have falling incomes, low employment rights and scanty welfare benefits. You don’t like that system? You have been hypnotised and misled by evil Russian trolls and hackers. [Whether Trump and/or Brexit were worthy beneficiaries of the popular desire to express discontent is an entirely different argument and not one I address here].
Except virtually none of this is true. Mueller’s inability to defend in person his deeply flawed report took a certain amount of steam out of the blame Russia campaign. But what should have killed off “Russiagate” forever is the judgement of Judge John G Koeltl of the Federal District Court of New York. In a lawsuit brought by the Democratic National Committee against Russia and against Wikileaks, and against inter alia Donald Trump Jr, Jared Kushner, Paul Manafort and Julian Assange, for the first time the claims of collusion between Trump and Russia were subjected to actual scrutiny in a court of law. And Judge Koeltl concluded that, quite simply, the claims made as the basis of Russiagate are insufficient to even warrant a hearing. The judgement is 81 pages long, but if you want to understand the truth about the entire “Russiagate” spin it is well worth reading it in full. Otherwise let me walk you through it.

Poverty as a means of getting rid of the unwanted.
In a recent book ostensibly focused on Jeremy Corbyn’s Labour party, but partly about recent British political history, the academics Matt Bolton and Frederick Harry Pitts explain the last decade in terms of “austerity populism”. Cuts, welfare crackdowns and the case for leave, they explain, were all sold to the public via the exclusion of supposedly unproductive undesirables: “scroungers” in the austerity narrative; “migrants” in the stories that swirled around the 2016 referendum. Both traded on a nostalgic idea of national struggle, keeping calm and carrying on, and some strange, latent belief that the country was in need of a purgative spell of pain akin to an imaginary version of the second world war.
In this vision, David Cameron’s election victory in 2015 and the leave side’s win a year later were watershed moments on the same national journey. But if austerity populism has so far been politically successful, it also comes with obvious risks. Trumpeting the wonders of slashing services and kicking around the poor only works for as long as the majority of people are largely untouched by those things – which is why Johnson is now partly changing tack and pledging to spend money (although our nasty, broken benefits system and countless imperilled public services will surely remain untouched).
By the same token, the romance of leaving the EU will only endure while its losers – sheep farmers, car industry workers, people who have come to the UK from central and eastern Europe – form a minority, and enough voters can still be persuaded that they will be winners in a Tory Brexit. Yet, however shambolic the opposition offered by Labour, the lived reality of no deal would surely risk tipping too many people into doubt and fear and away from the Conservatives, which is one reason why Johnson and his allies are in such an obvious hurry. The emotional side of me would simply describe this all as a very English tragedy, centred on a mean-spiritedness that the woman I met in Dover would instantly recognise. And at least until the end of this long, overheated summer and the start of an autumn of nightmares, millions of us will carry on behaving much as we have done for the last decade: not just passing by on the other side, but dancing as we do it.

A weird propaganda tool. That we pay attention to it is a flashing red sign of where our societies are at.
• Bellingcat Unloads 4,000-Word Hit Piece On Tulsi Gabbard (RT)
Running as an anti-war candidate in the US comes with a target painted on your back that draws fire from those rooting for foreign interventions. In case of Tulsi Gabbard, it includes a lengthy piece on chemical attacks in Syria. Gabbard, a Democratic presidential hopeful, became the most-googled candidate during the second primary debate – but the surge of public interest came with renewed attacks against her anti-interventionist agenda. In case you’ve missed it all, Gabbard has been branded a ‘Russian’ spoiler for whichever candidate is eventually picked, and, once again, an apologist for Syrian President Bashar Assad.
Joining the chorus of bashers on Sunday was Elliot Higgins, the founder of the UK-based ‘citizen investigation’ outlet Bellingcat, who wrote a whopping 4,000-word piece attacking Gabbard’s negative attitude toward regime change wars. In particular, Higgins didn’t like her skepticism over chemical weapons attacks in Syria reflected on her campaign website. The attacks were used by Washington to justify missile attacks against the country’s government – and by extension continued illegal US military presence in the country.
The mammoth piece starts with screenshots featuring logos of RT and InfoWars (Russian propaganda, dear readers, conspiracy theories!) and goes on to criticize anyone doubting the US-favored narrative about what happened in Syria. MIT Professor Theodore Postol gets an honorable mention, with whom Higgins no longer debates in person since their encounter in 2018. Back then, Higgins failed to address Postol’s technical criticisms of his investigations and instead resorted to mocking applauses and calling his opponent a tool of Russian propaganda.

Always a sucker for a good history lesson.
• America’s Other Original Sin (Bacevich)
Can there be more than one Original Sin? I’m guessing that may be a theological nonstarter, but as a basis for historical interpretation there is real merit in considering the possibility of multiple exiles from the Garden of Eden. That the arrival of the first African slaves to Jamestown 400 years ago this month qualifies as America’s Original Sin is now widely recognized. While holdouts remain, most agree that slavery and racism together have left an indelible stain on our nation. Many would argue that this awareness has arrived belatedly. I might even cite myself as an example.
As a kid growing up in Northwest Indiana in the middle of the last century, I judged slavery to have been an unfortunate mistake long since corrected. In the de facto segregated Calumet region where my family lived, race obviously remained a sensitive subject, but to my mind one best kept at arm’s length. I had more important things to worry about than the relationship between white people like me and those who were not white—why the Cubs were permanently stuck in or near the National League cellar being but one example. In the decades since, I’ve learned to see matters differently. So have many others.
But let me suggest the possibility of a Second Original Sin, not rising to the level of the first, but at least deserving far more attention than it has received. And that’s the sin committed in December 1898, when the United States laid claim to the Philippines. The history of this transaction, centering on a transfer of sovereign authority from Madrid to Washington, is both well known and almost entirely forgotten. As had been the case with race in East Chicago, Indiana, back in the late 1950s, the incorporation of the Philippines into an increasingly far-flung American empire has been written off. This, I have come to believe, is unfortunate, especially today when the American empire appears increasingly precarious.
The essential facts are these. In April 1898, the United States went to war with Spain. The war’s nominal purpose was to liberate Cuba from oppressive colonial rule. The war’s subsequent conduct found the United States not only invading and occupying Cuba, but also seizing Puerto Rico, completing a deferred annexation of Hawaii, scarfing up various other small properties in the Pacific, and, not least of all, replacing Spain as colonial masters of the Philippine Archipelago, located across the Pacific.

1898 US Political Cartoon: U.S. President William McKinley is shown holding the Philippines, depicted as a savage child, as the world looks on. The implied options for McKinley are to keep the Philippines, or give it back to Spain, which the cartoon compares to throwing a child off a cliff.