
Elvis Presley with parents Gladys and Vernon 1937

Cute, funny. But the real cost is much higher. It’s not just the ECB.
• Whatever It Took To Save The Euro (BBG)
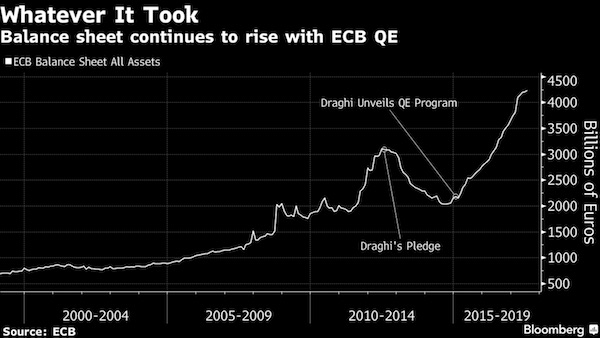
So how much did it end up taking after ECB President Mario Draghi memorably said five years ago he’d do “whatever it takes” to save the euro? About €1.2 trillion ($1.4 trillion). That’s the amount that the ECB’s balance sheet has expanded in the half-decade since Draghi made those remarks at a conference in London (an ironic location from today’s post-Brexit perspective.) Deutsche Bank analysts including Luke Templeman go on to note there’s several things that have changed by that magnitude – €1.2 trillion – in the past five years, in an eerie Da Vinci Code-like confluence:
• The euro region’s gross domestic product has risen about €1.2 trillion
• The Federal Reserve’s balance sheet has also climbed the equivalent of roughly €1.2 trillion
• The combined market cap of the FANG stocks – Facebook, Amazon, Netflix and Alphabet – has jumped about the equivalent of €1.2 trillionTempleman and his colleagues warn against making too much of the symmetry. After all, for the U.S. numbers to be related, it would suggest “every bond the Federal Reserve bought drove people to spend more time on these websites.”

Think uranium.
• US To Cut 755 Us Diplomatic Staff In Russia, Says Putin (AFP)
President Vladimir Putin on Sunday said the United States would have to cut 755 diplomatic staff in Russia and warned of a prolonged gridlock in its ties after the US Congress backed new sanctions against the Kremlin. Putin added bluntly that Russia was able to raise the stakes with America even further, although he hoped this would be unnecessary. A US State Department official denounced the move as a “regrettable and uncalled for act,” adding that Washington was now weighing a potential response. On Friday, the Russian foreign ministry demanded Washington cut its diplomatic presence in Russia by September 1 to 455 people – the same number Moscow has in the US.
“More than a thousand people – diplomats and technical personnel – were working and are still working” at the US embassy and consulates, Putin said in an interview with Rossia-24 television. The US State Department would not confirm the number of US officials serving at the mission. Putin added that an upturn in Russia’s relations with Washington could not be expected “any time soon.” “We have waited long enough, hoping that the situation would perhaps change for the better,” he said. “But it seems that even if the situation is changing, it’s not for any time soon.” Putin warned that Russia could further ratchet up the pressure, but he hoped this would not be needed.

“If you are not busy being born, you are busy buying”.
• Despite Appearances, The Idea Of Social Progress Is A Myth (Satyajit Das)
The undeniable improvement in living standards over the last 150 years is seen as evidence of progress. Improvements in diet, health, safe water, hygiene and education have been central to increased life spans and incomes. The lifting of billions of people globally out of poverty is a considerable achievement. But many of these individuals earn between $2 and $10 dollars a day. Their position is fragile, exposed to the vicissitudes of health, employment, economic conditions and political and societal stability. As William Gibson observed: “The future is already here — it’s just not very evenly distributed”. Economic progress also has come at a cost. Growth and wealth is increasingly based on borrowed money, used to purchase something today against the uncertain promise of paying it back in the future.
Debt levels are now unsustainable. Growth has been at the expense of existentially threatening environmental changes which are difficult to reverse. Higher living standards rely on the profligate use of under-priced, finite resources, especially water and energy, which have been utilised without concern about conservation for future use. Current growth, short-term profits and higher living standards for some are pursued at the expense of costs which are not evident immediately but will emerge later. Society has borrowed from and pushes problems into the future. The acquisition of material goods defines progress. The concept of leisure as shopping and consumption as the primary economic engine now dominate. Altering Bob Dylan’s lyrics, the Angry Brigade, an English anarchist group, described it as: “If you are not being born, you are busy buying”.
[19th-century Thomas Carlyle], who distrusted the “mechanical age”, would have been puzzled at the unalloyed modern worship of technology. Much of our current problems, environmental damage and pollution, are the unintended consequences of technology, especially the internal combustion engine and exploitation of fossil fuels. The invention of the motor vehicle was also the invention of the car crash. Technology applied to war continues to create human suffering. Mankind’s romance with technology increasingly is born of a desperate need for economic growth and a painless, cheap fix to problems such as reducing in greenhouse gas without decreasing living standards.
[..] Pre-occupation with narcissistic self-fulfilment and escapist entertainment is consistent with Carlyle’s concern about the loss of social cohesiveness, spirituality and community. His fear of a pervasive “philosophy of simply looking on, of doing nothing, of laissez-faire … a total disappearance of all general interest, a universal despair of truth and humanity, and in consequence a universal isolation of men in their own ‘brute individuality” … a war of all against all … intolerable oppression and wretchedness” seems modern.

Taxi drivers and shoeshine boys. There’s your peak.
• China Bond Buyers Quiz Taxi Drivers to See If Credit Good (BBG)
In China, taxi rides aren’t just a form of transportation any more. They’ve also become useful for bond buyers doing due diligence. Dining out at restaurants is also helpful. It’s all part of a boom in field trips by market participants coming to grips with a new reality in China: the potential for bond defaults. After decades when authorities effectively provided blanket assistance to keep troubled companies from going under, the Communist leadership’s focus on shuttering unproductive assets has upended the market. A total of 45 onshore corporate bonds have defaulted since the start of last year, a surge from the eight recorded in 2014 and 2015 – which themselves were the first since the market was established in the 1980s. While China has the world’s third-largest bond market, corporate financial transparency can be limited, forcing investors to get creative.
“If you just sit in the office, you would never know if an issuer has actually closed business,” said Xu Hua at Colight Asset Management in Shanghai. “When you go to the local places, be sure to have a chat with taxi drivers or restaurant customers after talking to the issuer – ask them if they have friends working for the company. Has their friends’ pay been cut or raised this year? Has the company delayed paying salaries? What’s the local reputation?” Recent incidents have showcased concerns about corporate governance and disclosure standards. The onshore bonds of two China Hongqiao units slumped in March after the world’s biggest aluminum maker said full-year results may be delayed because of issues raised by its auditor. Bondholders of China Shanshui Cement are still trying to recoup most of their money – at one point the company said it couldn’t repay interest without a company seal.

We really want monopolies? They’re calling it freedom, and beneficial, but…
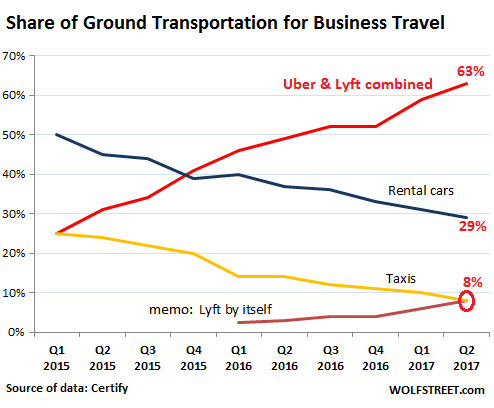
• Uber, Lyft Mangle Rental Cars & Taxis. Other Sectors Next (WS)
Rideshare companies – mostly Uber, but now also Lyft elbowing into the scene – are changing the way business travelers look at ground transportation. In the process, these worker bees, who’re spending their company’s money, are not only crushing the taxi business but also that end of the rental car business. The collapse of business travel spending on taxis and rental cars is just stunning. And there is no turning back. Uber’s and Lyft’s combined share of the ground transportation market in terms of expense account spending in the second quarter has soared to 63%, with Uber hogging 55% and Lyft getting 8%. The share of taxis has plunged to 8%, now equal with Lyft for the first time, according to Certify, which provides cloud-based expense management software.
Uber hit that point in Q1 2015, when expense account spending on Uber matched spending on taxis for the first time, each with 25% of the market; rental cars still dominated with a 50% share. But that was an eternity ago. Note that the share of rental cars and taxis has declined at roughly the same rate. Uber’s growth in the business travel ground transportation market has continued despite its constant drumbeat of intricate debacles in the news, but the rate of growth has slowed. And Lyft’s rate of growth has surged. The chart above shows this surge in the growth rate of Lyft, which caused its share to jump from 3% a year ago to 8% now.

We all know of teh US promise to Russia to not expand NATO.
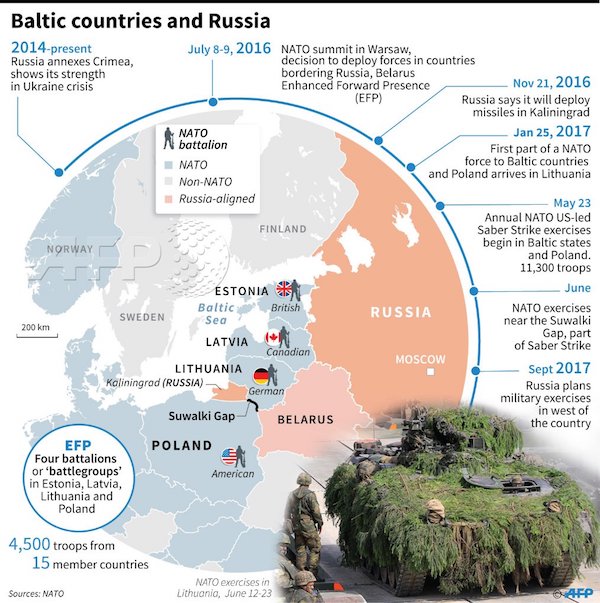
• Pence Sketches Possible Patriot Deployment In Estonia, Vows US Support (AFP)
US Vice President Mike Pence on Sunday raised the possibility of deploying the Patriot anti-missile defence system in Estonia, one of three NATO Baltic states worried by Russian expansionism, Prime Minister Juri Ratas said. “We spoke about it today, but we didn’t talk about a date or time,” Ratas told state broadcaster ERR after Pence began a visit to the tiny frontline state. The Patriot is a mobile, ground-based system designed to intercept incoming missiles and warplanes. “We talked about the upcoming (Russian military) manoeuvres near the Estonian border… and how Estonia, the United States and NATO should monitor them and exchange information,” Ratas said.
Relations between Moscow and Tallinn have been fraught since Estonia broke free from the crumbling Soviet Union in 1991, joining both the EU and NATO in 2004 – a move that Russia says boosted its own fears of encirclement by the West. Concern in Estonia and fellow Baltic states Latvia and Lithuania surged after Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine in 2014 and stepped up military exercises. Pence, in remarks to journalists in the Estonian capital of Tallinn, spoke in strong but general terms about US support for eastern European countries. On Monday, he heads to Georgia – a non-NATO member that is also worried about Russia – and then to Montenegro, which became NATO’s 29th member on June 5. “President (Donald) Trump sent me to Europe with a very simple message. And that is that America first doesn’t mean America alone,” Pence said.

This is not going to be smooth. Throw in a fierce financial crisis and what do you get?
• How Immigration Is Changing Italian and European Demographics (Sp.)
Some European countries, namely Italy, Germany, France and the UK, are facing the so-called “substitution of nations,” where the national ethnical majority is disappearing physically and biologically, and is being substituted by migrants, according to a recent report. Sputnik Italy discussed the issue with Daniele Scalea, the author of the report. The recent report of the Italian-based Machiavelli Center of Political and Strategic Studies, “How immigration is changing Italian demographics” has revealed that a number of European countries are facing the “biological and physical extinction” of their national ethnicities. Ethnic majorities in such countries as Italy, Germany, France and the UK, are gradually turning into ethnic minorities, while being “substituted” by incoming migrants. Sputnik Italy discussed the issue with Daniele Scalea, an analyst at the center and the author of the report.
Migration is drastically changing the habitual course of life in Italy, he told Sputnik. The reason for the influx of African migrants into Europe is not wars or catastrophes, but an explosive demographic increase on the African continent, from 9% to 25% of the global population throughout the last century. While Europe, which accounted for over a fifth of the entire world population in 1950 (22%), is expected to make up just 7% of the world population in the year 2050, the%age of the African population will make a sweeping rise from 9% to 40%. Italy’s fertility rate is less than half of what it was in 1964, the analyst explained in his report. It has dropped from 2.7 children per woman to just 1.5 children per woman currently, a figure well below the replacement level for zero population growth of roughly 2.1 children per woman.
As of the first half of this year, Italy had over 5 million foreigners living as residents, a remarkable 25% growth relative to 2012 and a whopping 270% since 2002. At that time, foreigners made up just 2.38% of the population while 15 years later the figure has nearly trebled to 8.33% of the population. Moreover, even the children being born in Italy are overrepresented by immigrants, whose birthrate is considerably higher than native Italians, the study revealed. It is “unsurprising,” therefore, that Italian regions with the highest fertility rates are no longer in the south, as was usual the case, but in the Italian north and in the Lazio region, where there is a higher concentration of immigrants. If current trends continue, by 2065, first- and second-generation immigrants will exceed 22 million persons, or more than 40% of Italy’s total population.
By comparison, it was only in the not far-off 2001 that the percentage of foreigners living in Italy crossed the low threshold of 1%, which reveals the speed and magnitude of demographic change occurring in Italy, a phenomenon “without precedent” in Italy’s history, the study asserts.

Waterboarding. Disregard all stories of recovery.
• Greece’s Road to Bailout Exit: 140 Reforms Down, Many More to Go (BBG)
Greece’s hard times aren’t over. A return to the bond market last week, the pledge of 8.5 billion euros ($9.5 billion) in new loans from euro-area creditors, the possibility of more money from the International Monetary Fund and a S&P Global Ratings outlook upgrade have coalesced to bolster investor sentiment that Greece has turned a corner. Trouble is, much depends on the country implementing reforms — dozens of the 140 measures agreed to are in various stages of application and more than 100 additional actions are needed to access the remaining 26.9 billion euros in funds before the current bailout program ends in August 2018. While the evidence of belt-tightening is everywhere in Greece, from falling incomes to rising poverty, the country has less to show in terms of structural overhauls.
Creditor demands for more measures threaten to become politically explosive as Greek citizens and businesses count the cost of the financial crisis that has thrown their lives into turmoil over the last seven years. Over the years, creditors have imposed reforms that have affected the daily lives of Greeks, from requiring receipts for tax breaks and e-prescriptions for patients to prevent abuse to pension payout cuts of as much as 50%. While Greece’s record of implementing reforms hasn’t won it any kudos, it is now hitting against even more challenging structural measures aimed at profoundly changing entrenched habits. The real problem is with reforms like fixing the tax system and the judiciary that require “long implementation,” said Gerassimos Moschonas, an associate professor of comparative politics at Panteion University in Athens. Belt-tightening measures have had a dramatic effect on life, making further long-lasting reforms difficult, he said.
“The income of an average household has decreased at least 40% during the crisis, poverty risk has increased 35.6%, pension cuts are enormous and there is over-taxation,” he said. Since Greece became the epicenter of the European debt crisis in 2010, the country has agreed to austerity measures to restructure its economy, which has shrunk by more than a quarter over the period. In exchange, euro-area creditors and the IMF have provided more than 260 billion euros in bailout funds to keep Greece afloat. “Progress with structural reforms has fallen far short of what is needed to allow Greece to succeed in the euro zone, but the program foresees some intensification of efforts,” the IMF said in its report on July 20.
Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s government is struggling to squeeze pensions even more, allow Sunday openings for stores – which could threaten the livelihoods of small mom-and-pop shops that dot the country – consider further taxes and change labor laws that would make it even harder for employees to go on a strike. “There’s no serious implementation,” of difficult structural reforms, said Moschonas. “The Greek state has failed” to put them in place even after they were voted in parliament because of a lack of political will and the absence of technical expertise, he said.

Got them by the balls.
• Greeks Can’t See Any Light At The End Of Any Tunnel (G.)
Athens, like most urban centres, has been hardest hit by a crisis that has seen the country’s economic output contract by a devastating 26%. A study by the DiaNeosis thinktank found that 15% of the population, or 1,647,703 people, in 2015 earned below the extreme poverty threshold. In 2009 that number did not exceed 2.2%. The net wealth of Greek households fell by a precipitous 40% in the same period, according to the Bank of Greece. Unemployment, austerity’s most pernicious effect, hovers around 22%, by far the highest in the EU, despite a 5% drop in the last two years. Although the worst is over in terms of fiscal adjustment, few believe Greece will be able to escape a fourth bailout even if Athens regains market access when its current EU-IMF sponsored programme ends in August next year.
“It is very difficult to see the country being able to make a clean exit [from international stewardship] and raise the sort of money it needs to refinance its debt,” said Kyriakos Pierrakakis, director of research at DiaNeosis. “It will almost certainly need a new financial credit line, a bailout light, and that will come with new conditions.” In such circumstances, faith in government claims that the country has turned the corner – based as much on last week’s market foray as completion of a landmark compliance review and disbursement of €8.5bn in bailout funds – is in short supply. “Greeks can’t see any light at the end of any tunnel,” said Christodoulaki, shaking her head in disbelief. “They won’t believe anything at this point until they see it for real in front of their eyes.”
Across town in the communist party stronghold of Kaisariani, municipal authorities are already preparing for winter. In the giant 1960s concrete town hall, the social services department has lined up fundraising events, including concerts and theatre performances, to finance food donations that local stores and supermarkets can no longer afford to make. “Needs have grown exponentially,” said Marilena Christodoulou, her office wall adorned with the slogan “poverty is not a crime”.

Last bits of a really good piece from a Greek American.
• Greece: A (Basket) Case Study In Savage Globalization (Nevradakis)
Jean-Paul Sartre once famously stated that “a lost battle is a battle one thinks one has lost.” The tragic reality in Greece today, most Greeks, beaten down by the crisis and by the effects of what can be described as savage globalization, are plagued by feelings of collective guilt, self-loathing, hopelessness, feelings of inferiority, and apathy. The “inferiority” of Greece and the Greek people, and their “guilt,” are accepted as “facts of life.” It is, therefore, no surprise to see Greece ranked fourth worldwide in Bloomberg’s misery index for 2017. When one believes they have lost a battle, that means that they also recognize some other entity as the victor. In the case of Greece, that victor could be recognized as the EU and countries considered by average Greeks as “superior” and “civilized.” Writing in 1377, North African historian and historiographer Ibn Khaldun provides us with insights which could help explain Greece’s “xenomania” and nationwide Stockholm Syndrome today:
“The vanquished always want to imitate the victor in his distinctive mark, his dress, his occupation, and all his other conditions and customs. The reason for this is that the soul always sees perfection in the person who is superior to it and to whom it is subservient. It considers him perfect, either because the respect it has for him impresses it, or because it erroneously assumes that its own subservience to him is not due to the nature of defeat but to the perfection of the victor. If that erroneous assumption fixes itself in the soul, it becomes a firm belief. The soul, then, adopts all the manners of the victor and assimilates itself to him. This, then, is imitation.” It is, unfortunately, this very imitation that one observes in crisis-stricken Greece today. A society where the majority whines and complains, or simply gets up and leaves, but does not demand.
A nation that is demoralized; defeated; consumed by hopelessness; devoid of pride, self-respect, and self-confidence; paralyzed by fear; hampered by ignorance; and gripped by feelings of inferiority, cannot deliver change. This situation, of course, suits the powers that be magnificently. A society of self-loathers, a nation that is defeated and demoralized, will not pose a threat to those responsible for that oppression, while other “civilized” countries reap the ancillary benefits of the crisis, as the economic beneficiaries of the mass exodus and “brain drain” from Greece. This is savage globalization in action. In other words, Greece is a prime candidate for, in the words of Oscar López Rivera, the kickstarting of a decolonization process. His words may have been intended for Puerto Rico, but they are similarly applicable to Greece. But will the people of Greece heed Oscar’s words?

21 million slaves. And we talk about Scaramucci’s rants.
• ‘Human Life Is More Expendable’: Why Slavery Has Never Made More Money (G.)
Slave traders today make a return on their investment 25-30 times higher than their 18th- and 19th-century counterparts. Siddharth Kara, a slavery economist and director of the Carr Center for Human Rights Policy at Harvard Business School, has calculated that the average profit a victim generates for their exploiters is $3,978 (£3,030) a year. Sex trafficking is so disproportionately lucrative compared to other forms of slavery that the average profit for each victim is $36,000. In his book Modern Slavery, to be published in October, Kara estimates that sex trafficking accounts for 50% of the total illegal profits of modern slavery, despite sex trafficking victims accounting for only 5% of modern slaves. Kara based his calculations, shared exclusively with the Guardian, on data drawn from 51 countries over a 15-year period, and from detailed interviews with more than 5,000 individuals who have been victims of slavery.
The first move to eradicate slavery was made in 1833, when the British parliament abolished it, 26 years after outlawing the trade in slaves. Nonetheless, at least twice as many people are trapped in some form of slavery today as were traded throughout the 350-plus years of the transatlantic slavery industry. Experts believe roughly 13 million people were captured and sold as slaves by professional traders between the 15th and 19th centuries. Today, the UN’s International Labour Organisation believes at least 21 million people worldwide are in some form of modern slavery. “It turns out that slavery today is more profitable than I could have imagined,” Kara said. “Profits on a per slave basis can range from a few thousand dollars to a few hundred thousand dollars a year, with total annual slavery profits estimated to be as high as $150bn.”








