
Arthur Rothstein President Roosevelt tours drought area near Bismarck, ND 1936



“Suddenly, the debate in China has shifted from a perception of too much money sloshing round and too many reserves earning meagre returns, to a concern about the adequacy of reserves given the extent of debt — much of it hidden.”
• Signs Point To Deepening China Distress
China’s foreign exchange reserves fell alarmingly in August, anywhere from $94bn to as much as $150bn according to various calculations. That was just another in a series of dramatic data points that are leading to an increasing sense both within the Middle Kingdom and without that all is not well. For a long time now many hedge funds have been short Macau, once the main beneficiary of both the Chinese propensity to gamble and the rise of China as a market for luxury goods. Then the anti-corruption campaign put a big chill on the junkets to the former Portuguese enclave, as it did on sales of everything from Rolex watches to shark fin soup and abalone in top restaurants. But now there is another strand to the story.
Macau has long been one of the more porous parts of the wall meant to keep capital flows in and out of China under strict control. For example, those who wanted to get significant amounts of money out of China would purchase a dozen watches, using their renminbi credit cards, only to return the time pieces instantly and receive cash refunds, with a discount for the jeweller’s trouble. The currency would then be converted and go straight into bank accounts and investments abroad. Today, the thesis of hedge fund managers putting on the Macau trade is that regulators will tighten up on such practices, causing further damage to Macau’s wounded economy. Suddenly, the debate in China has shifted from a perception of too much money sloshing round and too many reserves earning meagre returns, to a concern about the adequacy of reserves given the extent of debt — much of it hidden.
After all, the downdraft in the stock market was all about the use of borrowed money, invisible to regulators and almost everyone else. Meanwhile, the capital flows out of China continue. It is difficult to calculate what is prudent diversification and what is capital flight. At the same time, more alarmingly, the signs of distress in the real economy are deepening, with ripple effects far beyond the mainland. Greek shipyards, for example, report that the yards in China are desperately discounting the containers they construct. The Chinese shipbuilders have to discount to compensate for the fact they are competing against builders whose currencies have fallen dramatically against the renminbi.

Assessing China without including the shadows is of no use at all.
• Shadow Finance Expansion by Chinese Banks Deepens Credit Mystery (Bloomberg)
China’s riskier banks are investing more customer funds in financing that is kept off their loan books, making it harder for rating companies to gauge their asset quality. There has been a surge in a balance-sheet item known as receivables, which often includes shadow funding such as trusts and wealth products, said Moody’s Investors Service. Fitch Ratings said it is hard to analyze this escalation in activity. Listed banks excluding the Big Four saw short-term investments and other assets – which include receivables – jump 25% in the first half, compared with total asset growth of 12%, data compiled by Bloomberg show. Slower growth in the world’s second-largest economy coupled with “still significant” credit expansion prompted Standard & Poor’s to cut its view of the banking industry’s economic risk to negative from stable this week.
Shadow-finance assets, estimated at 41 trillion yuan ($6.4 trillion) by Moody’s at the end of 2014, have become more attractive as five interest-rate cuts by the central bank since November curbed profits from lending. “Our concern with some of these investment positions is banks are using them as a way to bypass lending restrictions,” said Grace Wu at Fitch in Hong Kong. “Unlike bank loans, they don’t get reported into loan provisions, so it’s more difficult for us to ascertain the asset quality.” The opacity of Chinese banks’ credit exposure helps explain why they are priced as if investors are expecting a nonperforming loan ratio of 10 to 12% next year, which would mark a “sizeable credit crisis” in other countries, according to Wei Hou at Sanford C. Bernstein.
The reported ratio is 1.5%, according to the China Banking Regulatory Commission. The nation’s shadow-banking industry emerged as a way for creditors to circumvent lending restrictions and for savers to attain yields higher than the legally capped deposit rate. It includes trusts, asset-management plans and wealth-management products, which package loans into products for buyers.

As long as Xi is in the US, the homefront will keep things smooth and quiet. But this number points to contraction, even as Xi just reiterated growth is at 7%.
• China Flash PMI Falls To Lowest Since May 2009 (CNBC)
The preliminary Caixin China manufacturing purchasing managers’ index (PMI) fell to a six-and-a-half-year low of 47.0 in September, below the 47.5 forecast in a Reuters poll. This compares with a final reading of 47.3 in August, the lowest since March 2009. A print above 50 indicates an expansion in activity while one below points to a contraction. The closely-watched gauge of nationwide manufacturing activity focuses on smaller and medium-sized companies, filling a niche that isn’t covered by the official data. The decline in the flash PMI was mainly led by the new orders and new export orders sub-indexes, suggesting weak domestic and external demand. The new orders sub-index fell 0.6 percentage points to 46.0 in September, while the new export orders sub-index slipped 0.8percentage points to 45.8.
Wednesday’s data weighed on investor sentiment in Asia, with stock indices in Sydney and Seoul widening losses to more than 1% each in the morning trading session. China stocks, however, trimmed losses to 0.9%, from an over 1% decline at the open. “The principle reason for the weakening of manufacturing is tied to previous changes in factors related to external demand and prices,” said He Fan at Caixin Insight Group. “Fiscal expenditures surged in August, pointing to stronger government efforts on the fiscal policy front. Patience may be needed for policies designed to promote stabilization to demonstrate their effectiveness,” he added. A recent run of disappointing data has raised concerns around the health of China’s economy, leading several banks and international institutions to pare growth forecasts for the country.

“..roughly 55% of China’s 1.37 billion people now live in cities, compared with just under 18% in 1978…”
• China’s Workers Stumble as Factories Stall (WSJ)
For decades, an army of migrant workers drove China’s boom times, flocking to its cities to sew T-shirts, assemble iPhones, or build apartment blocks and Olympic stadiums. The arrangement helped millions of poor, rural Chinese join a new consumer class, though many also paid a heavy price. Now, many migrant workers struggle to find their footing in a downshifting economy. As factories run out of money and construction projects turn idle across China, there has been a rise in the last thing Beijing wants to see: unrest. In Xiguozhuang, a village among cornfields some 155 miles south of Beijing, it had been rare to see working-age men for much of the year. This year, however, many of the men are at home, sidelined by a fading property boom.
“Times are tough now,” said Wang Hongxing, a 39-year-old father of three who has worked at building sites across China’s northeast since his teens, but who has spent the past two months tending his farmland plot. “There are too many workers and wages are dropping.” But for other migrants, especially those of a younger generation who took jobs in factories along China’s coast, a return to farming isn’t an option. Nor do they necessarily want to join the service sector China sees as a cornerstone in its shift to a new economic model. Wang Chao dropped out of school when he was 15 and left his home in Anhui province. After a series of jobs up and down China’s east coast, he felt he had struck gold with a job in a textile factory near his hometown.
The factory closed in July. Mr. Wang, now 19, and other workers gathered recently outside the factory premises to demand back wages. He says he is owed two months’ pay, or about 2,000 yuan, or $320. The owner of the factory, which produces cheap trousers, told workers he is in deep debt and can’t afford to pay them. He couldn’t be reached to comment. Mr. Wang hopes he can find another factory job. In Shanghai, he worked in a restaurant but doesn’t want to do that again. “Factory work is so much more comfortable in comparison, and better paid,” he said. As a result of a rural-to-urban flow that many scholars say is likely the largest in history, roughly 55% of China’s 1.37 billion people now live in cities, compared with just under 18% in 1978.
The migrant workforce now numbers some 274 million but the pace of its expansion has slowed, and many economists believe China now faces a shortage of unskilled labor in urban areas. A mismatch of workers’ skills and aspirations with actual labor demand has exacerbated the problem. “There’s a broad structural imbalance in China’s labor market—a shortage of low-end labor and surfeit of high-end workers,” said Peng Xizhe, professor of population and development at Fudan University in Shanghai. “In China’s job market today, we see university graduates struggling to find work, while employers are finding it hard to fill traditional blue-collar positions.”

“Xi peppered his speech with US cultural references from Sleepless in Seattle and House of Cards to Henry David Thoreau, Walt Whitman, Ernest Hemingway..”
• Xi Jinping Defends China Stock Market Interventions On First US Visit (Guardian)
China’s president, Xi Jinping, has sought to reassure global concern about the world’s second-largest economy, defending his government’s actions in the stock market and saying growth will be maintained. “China’s economy will stay on a steady course with fairly fast growth. It’s still operating in a proper range with a growth rate of 7% … Our economy is under pressure but that is part of the path on the way toward growth,” the Chinese president said in a speech in Seattle on Tuesday, the first day of his state visit to the US. The president defended his government’s intervention into the country’s stock market saying the “recent abnormal ups and downs” in the market had now reached “a phase of self-recovery”.
Xi also reiterated there was no basis for continuing depreciation of the renminbi, saying Beijing was opposed to currency wars and would not devalue yuan to boost exports. World markets experienced more than a month of volatility after China devalued its currency, fuelling concerns about the state of the world’s No 2 economy. Intervention from authorities into the country’s bourses also added to worries Beijing had lost control over the economy. But just minutes after the speech, fresh data showed renewed signs of weakness in the Chinese economy with the Caixin China manufacturing flash PMI coming in at 47, the lowest since March 2009. [..]
Xi peppered his speech with US cultural references from Sleepless in Seattle and House of Cards to Henry David Thoreau, Walt Whitman, Ernest Hemingway – saying he once ordered a Mojito at El Floridita in Havana to better understand Hemingway and Cuba. Dismissing speculation that his sweeping anti-corruption campaign was about factional infighting, Xi said “We have punished tigers and flies. It has nothing to do with power struggles. In this case there is no House of Cards.”

Or they understand it all too well.
• China Has A Message Markets Don’t Understand (CNBC)
China may be compounding its own problems by the way its leaders talk about them. With the country’s growth a concern for global markets, investors are trying to fathom the depth of China’s economic issues and understand what authorities are doing. Analysts say it is difficult to discern what’s really going on there and that the economy has always been difficult to measure. Ahead of his U.S. visit that kicked off Tuesday, Chinese President Xi Jinping said in an interview with The Wall Street Journal that recent intervention in capital markets was necessary or normal and that China is still on track to transform its economy. “I think they are mostly nothing new and simply a repeat of what other officials have said,” Ilya Feygin, managing director at WallachBeth Capital, said of Xi’s comments.
Sticking to policy lines casts doubt for many on whether Chinese leaders have a grip on maneuvering the country’s economic transition in a way that doesn’t shock global markets more than it already has. “I think it’s a combination of missteps that add up to a lot of worries, capacity of the Chinese government to manage its economy through a very challenging environment and not making it worse,” said Scott Kennedy of the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “It begins with their intervention to push up their stock market last year.” Rapid-fire policy changes in the last few months have befuddled outsiders on Chinese leaders’ intentions, which raise real concern on whether the world’s second-largest economy can make a timely transition from a manufacturing hub to a consumer-oriented system.
“The point is to recognize there’s a structural transition going on,” said Arthur Kroeber, head of research at Gavekal Dragonomics. “And the problem we have is the data we have on the bad part of the economy is actually pretty developed. The data on services (is) much better but fuzzier.” Most of the economic reports still focus on manufacturing-related aspects of the economy, such as electricity use and the producer price index. Data such as the Caixin nonmanufacturing PMI provide some light on services, which continued to hold above the 50 expansion/contraction line in August. Manufacturing PMI fell below that line.
Growth in the services sector has outpaced that of the manufacturing sector in the last year and a half, according to the latest National Bureau of Statistics of China data compiled by Wind information. Amid the transition, questions also surround the accuracy of China’s reports on headline GDP growth. The official figure is 7%, the slowest in more than two decades In a report Tuesday, the Asian Development Bank lowered its forecast for Chinese growth in 2015 to 6.8% from 7.2% previously. Other analyst estimates range from 2 to 4 percentage points lower.

“..roughly the same as the UK’s combined emissions for all power stations, vehicles, industry and agriculture..”
• VW Scandal Caused Nearly 1 Million Tonnes Of Extra Pollution (Guardian)
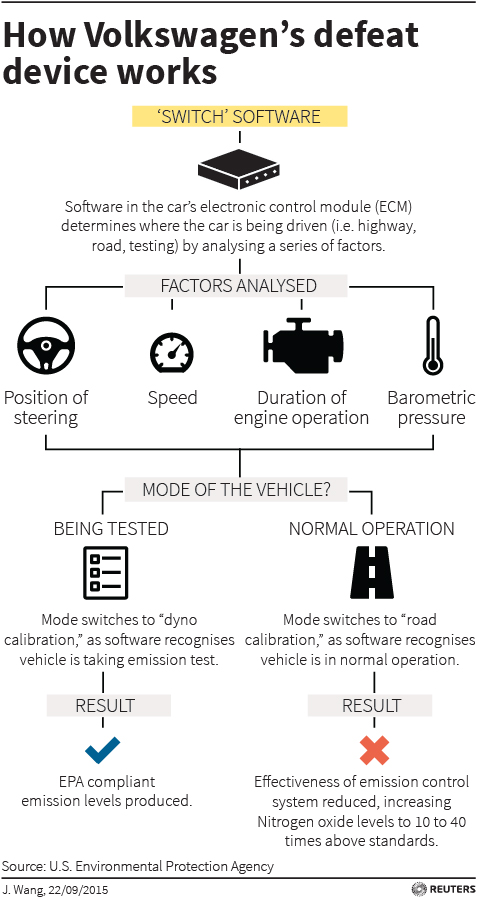
Volkswagen’s rigging of emissions tests for 11m cars means they may be responsible for nearly 1m tonnes of air pollution every year, roughly the same as the UK’s combined emissions for all power stations, vehicles, industry and agriculture, a Guardian analysis suggests. The potential scale of the scandal puts further pressure on Volkswagen’s board and its chief executive, Martin Winterkorn. The company’s executive committee plans to meet on Wednesday to discuss the affair and to agree the agenda of a full board meeting scheduled for Friday, amid reports that Winterkorn could be replaced. The carmaker has recalled 482,000 VW and Audi brand cars in the US after the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) found models with Type EA 189 engines had been fitted with a device designed to reduce emissions of nitrous oxides (NOx) under testing conditions.
A Guardian analysis found those US vehicles would have spewed between 10,392 and 41,571 tonnes of toxic gas into the air each year, if they had covered the average annual US mileage. If they had complied with EPA standards, they would have emitted just 1,039 tonnes of NOx each year in total. The company admitted the device may have been fitted to 11m of its vehicles worldwide. If that proves correct, VW’s defective vehicles could be responsible for between 237,161 and 948,691 tonnes of NOx emissions each year, 10 to 40 times the pollution standard for new models in the US. Western Europe’s biggest power station, Drax in the UK, emits 39,000 tonnes of NOx each year. [..] For years, UK air pollution measurements have failed to show improvements in air quality, even as standards have tightened.
“Since 2003 scientists have been saying things are not right. It’s not just the VW story, this is part of something much bigger,” said Dr Gary Fuller of King’s College. “It has a serious public health impact.” Last week, a report from NGO Transport & Environment found that Europe’s testing regime was allowing nine out of every 10 new diesel vehicles to breach EU limits. Testing regimes in the EU are known to fail to pick up “real world” emissions because cars are not driven in the same way in the laboratory as on the road. Some studies suggest the discrepancy may be up to seven times the legal limit. Williams said being able to mask their NOx emissions would also enable carmakers to pass carbon emissions tests more easily as there was a trade-off between NOx and CO2 in diesel engines.

Bets are open on this one.
• California Tests To Include Larger Diesel Engines From Audi, Porsche (Reuters)
The California Air Resources Board will broaden its testing of Volkswagen cars with diesel engines to include those with 3.0-liter V6 engines sold by two subsidiaries, a spokesman for the state regulator said on Tuesday. The latest models to be examined are the Porsche Cayenne and the Audi A6, Stanley Young, communications director for the Air Resources Board, told Reuters. Volkswagen said on Tuesday that engine software connected with a scandal over falsified U.S. vehicle emission tests could affect 11 million of its cars worldwide as investigations of its diesel models multiplied. The California Air Resources Board’s testing uncovered software in several Volkswagen models that allowed the company to cheat state and federal emissions requirements by switching performance levels between testing and real-world conditions.
“That investigation looked at two-liter four-cylinder engines,” said Young. “Now we’re going to start looking at six-cylinder, three-liter diesel engines.” Young said VW engineers acknowledged the use of a so-called defeat device – in fact, a software algorithm – to circumvent state and federal emissions standards during a Sept. 3 meeting in the board’s El Monte, California testing headquarters, attended by senior engineering executives of the regulator and the car company. It was the 10th meeting between the two sides, called by CARB to resolve the discrepancy between pollution levels measured on the road and those obtained under controlled testing conditions. “They literally ran out of excuses,” Young said, describing the meeting in which the car manufacturer “admitted there was a defeat device.”

It’ll have to be worldwide. Wouldn’t it be funny if test results vary greatly?
• VW Emissions Fallout Spreads To Asia (FT)
South Korea’s environment ministry said it would investigate the emissions compliance of Volkswagen’s diesel cars, as the fallout for the German carmaker after its admission that it rigged US emissions tests spread to Asia. The announcement on Tuesday came a day after Germany called for a probe into the matter, confirming fears Volkswagen’s trouble was unlikely to be confined to the US and that breaches could have occurred in other regions. The US Environmental Protection Agency on Friday ordered the world’s second-biggest carmaker to recall nearly 500,000 cars in the US after it admitted that it had fitted “defeat devices” to bypass environmental standards.
In the first public appearance by a senior executive since the scandal emerged, Michael Horn, VW’s US chief executive, said at an event in New York on Monday that the carmaker had “screwed up”, vowing to fix the vehicles involved and ensure no repetition. Seoul’s environment ministry said it would conduct emissions tests on 4,000-5,000 of VW’s Jetta and Golf models and the Audi A3 sedan that were imported into South Korea since 2014. “We will review if the three car models sold here show the same problems as those in the US, although the carmaker says its cars here have no such problems,” said Park Pan-kyu, the ministry’s deputy director. “We plan to complete the investigation within two months and will come up with punitive measures if any problems are found.
“If South Korean authorities find problems in VW diesel cars, the probe could be expanded to all German diesel cars,” he said. If the cars are found to have breached air pollution standards, the ministry could issue a recall order for vehicles already sold in the country, or order the German carmaker to stop domestic sales of problematic models. It could also impose a maximum Won1bn ($850,000) fine on each model. The ministry said any punitive measures would be levied in consultation with the German government, in keeping with the Korea-EU trade agreement.Volkswagen is one of the best-selling foreign brands in South Korea. VW and Audi accounted for nearly 30% of all foreign cars sold in the country in the first eight months of this year, and more than 90% of the roughly 25,000 vehicles VW sold were diesel models.
Shares in South Korean carmakers Hyundai Motor and affiliate Kia Motors rose more than 3% on Tuesday, on the view that Asian competitors could benefit at VW’s expense. “Volkswagen’s brand value is expected be hit by this issue as its strong diesel engine technology has been the backbone of its brand recognition,” said Yim Eun-young, analyst at Samsung Securities. “This could lead to gains for Hyundai and Kia, which are competing with Volkswagen in the sedan segment.”

As I said yesterday, if VW couldn’t even come close to required emissions, what are the odds others could?
• VW Emissions Investigations To Widen to Entire Auto Industry (WSJ)
Investigations into Volkswagen’s alleged manipulation of U.S. emissions tests should widen to include the entire auto industry, German and French officials said Tuesday, as regulators begin to ponder whether such deception is widespread. Calls for a broader probe came as Italy opened an investigation into the issue and a spokesman for the European Union said its regulators would soon meet with national authorities to discuss how to address the Volkswagen crisis. Concerns that the scandal could lead to broader damage for the industry hit the shares of car companies across Europe on Tuesday and those losses accelerated after Volkswagen warned that 11 million vehicles could be affected.
Shares in Volkswagen dived as much as 23% while those of Daimler AG dropped 5.5% and BMW AG slumped 5.4%. In France, Renault SA dropped 6.3% and PSA Peugeot Citroën was down 8.6%. The state of Lower Saxony, a major Volkswagen shareholder with 20% of the car maker’s voting stock, said the emissions allegations raised doubts about tailpipe data published by all car makers. The French government also called for a broader probe, suggesting a European-wide examination of the auto industry. “We need to do it at the European level,” French Finance Minister Michel Sapin said Tuesday.
In Germany, Olaf Lies, Lower Saxony’s economy minister and a member of the Volkswagen’s supervisory board, called for a wider probe and said investigations into the scandal would have consequences for any executives found guilty of deliberate manipulation. “I am convince that everyone is going to become intensely interested in knowing whether the emissions values that have been measured are the real emissions levels,” he said. “This question will not only affect Volkswagen, but the entire public debate and will certainly play a role at other companies.”

“The only way to change auto company behavior is to put the responsible executives in jail..”
• VW Emissions Cheating Affects 11 Million Cars Worldwide (WaPo)
The deception perpetrated by Volkswagen in the United States reaches around the globe, with about 11 million cars worldwide equipped with software designed to cheat emissions tests, the company said Tuesday. The automaker said it will set aside $7.3 billion to cover fixes and other efforts to win back the trust of our customers. That amount is likely to fall many times short of the actual costs, including car repairs, lawsuits and government penalties around the world. Exactly what alterations are necessary on all of those cars is unknown, and independent engineers said it could be extremely difficult to repair the emissions systems without harming engine efficiency and performance. None could offer what they deemed a reliable estimate of the cost of a potential repair.
“In my German words, we have totally screwed up”, Volkswagen s U.S. chief, Michael Horn, said at an event in Brooklyn late Monday night. The broad scale of the deception suggests that knowledge of the emissions cheating was widespread, and Justice Department investigators are focusing on the actions of executives, according to two people familiar with the inquiry. German news outlets reported Tuesday that the firing of chief executive Martin Winterkorn is imminent, citing unidentified members of the company s board. Also Tuesday, new details of the cat-and-mouse interactions between suspicious regulators and the German car giant showed how far the company was willing to go to assure the government that, contrary to the best evidence, nothing was amiss in its diesel cars.
Last year, Volkswagen informed regulators that it was initiating a 500,000-car recall in the US that would fix the problem. The recall was either a technical failure or, as some U.S. officials said, a ruse. Whether those involved in the emissions cheating software will face more severe penalties is unknown, but anger among customers, who are stuck with cars that violate pollution standards, and dealers, who are left with unsold inventory, has become increasingly evident. Their appeals have been heard in Washington. “It is an outrage that VW would take advantage of its consumers by purposely deceiving them on their mileage on diesel vehicles …There ought to be some prosecutions, and corporate executives that knew this and have done it ought to be going to jail”, Sen. Bill Nelson (D-Fla.) said in a speech on the Senate floor Tuesday, citing the repeated failures of automakers.
“And I lay this not only on the corporate culture, I lay it at the feet of the U.S. regulatory agencies who ought to be doing their job, ought to be doing it in a forceful way”. Noting that Volkswagen had been accused of similar tactics in the United States in the early 1970s, when the company paid fines of $120,000, Clarence Ditlow, director of the Center for Auto Safety, argued that financial penalties are not enough to keep the company honest. “The only way to change auto company behavior is to put the responsible executives in jail,” he said.

In firm denial.
• Europe Stumbles Towards A Migrant Plan (BBC)
There was a sense of grim determination about the crowd of cold and tired refugees and other migrants we met crossing the border one damp and windy night this week from Hungary into Austria. No euphoria. No desperation, such as we’ve seen at so many European borders over the last months, but more a sense of quiet purpose. The young men and families we spoke to were passing through what has become a relatively efficient people’s pipeline established on the ground from southern, into central and onto northern Europe. EU leaders may be in disarray over what to do next but in the meantime – for now – chaos on the ground has given way to an orderly means of transporting migrants from country to country.
One 19-year-old told us it had taken him five days to get from Turkey to Austria, passing through Greece, Macedonia, Serbia, Croatia and Hungary along the way. He still hoped to reach Germany, to join the Syrian community there, which is growing larger by the day. But this is no long-term solution to Europe’s migration conundrum. Europe’s prime ministers and heads of state will discuss that at their emergency meeting in Brussels on Wednesday. A quick or easy fix will be impossible to find and the meeting is likely to be fiery but leaders know they have to stumble towards some sort of plan or risk the unravelling of the EU itself. Look at the anger of Slovakia, Hungary, Romania and the Czech Republic forced on Tuesday at a meeting of European interior ministers to accept their share of 120,000 asylum seekers who will be re-located across the continent. [..]
EU leaders will discuss how to tighten the control of European borders. They’ll also debate a workable EU asylum policy, the more efficient deportation of economic migrants, defining who is a refugee, an asylum seeker or economic migrant, the better integration of refugees and their families already here and sending significant aid abroad to improve living conditions closer to people’s home countries so they shouldn’t be tempted to come to Europe in the first place. Decisions and debates tomorrow and in the months to come will affect all of our lives. Endre Sik is the director of the Centre for Refugee and Migration Studies in Budapest. He told me in 10 years’ time, we will look back and see this as a moment that changed Europe – its general landscape, its politics and its economics. There’s no turning back now from mass migration Europe, he says. This is an unprecedented social phenomenon.

“We would have preferred a consensus but we could not reach that, and it is not for want of trying..”
• EU’s East-West Rift Exposed In Refugee-Sharing Plan (Reuters)
The European Union approved a plan on Tuesday to share out 120,000 refugees across its 28 states, overriding vehement opposition from four ex-communist eastern nations. The European Commission, the EU executive, had proposed the scheme with the backing of Germany and other big powers in order to tackle the continent’s worst refugee crisis since World War Two. But the rift it has caused between older and newer members was glaringly evident as the interior ministers of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Romania and Hungary voted against the plan at a meeting in Brussels, with Finland abstaining. “We would have preferred a consensus but we could not reach that, and it is not for want of trying,” Luxembourg Interior Minister Jean Asselborn, whose country holds the rotating presidency of the EU, told a news conference.
Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico said pushing through the quota system had “nonsensically” caused a deep rift over a highly sensitive issue and that, “as long as I am prime minister”, Slovakia would not implement a quota. And Czech Interior Minister Milan Chovanec tweeted: “We will soon realize that the emperor has no clothes. Common sense lost today.” This year’s influx of nearly half a million people fleeing war and poverty in the Middle East, Asia and Africa has already sparked unseemly disputes over border controls as well as bitter recriminations over how to share out responsibility. Refugees and migrants arriving in Greece and Italy have been streaming north to reach more affluent nations such as Germany, prompting countries in central and eastern Europe alternately to try to block the flow or shunt it on to their neighbors.

How is this Europe? How can Germany and France continue in a Union with Hungary?
• Hungary Mobilizes Troops, Prisoners, Jobless To Fence Out Refugees (Reuters)
Built in a matter of weeks by soldiers, prison laborers and cadres of the unemployed, a vast new wall along Balkan frontiers is a monument to the ruthless efficiency with which Prime Minister Viktor Orban has mobilized Hungary against migrants. Orban describes the arrival of hundreds of thousands of refugees and other migrants in Europe this year from Asia, Africa and the Middle East as an attack on the continent’s Christian welfare model. Until last week, most trekked through Hungary, the main overland entry route into the EU’s border-free Schengen zone from the Balkan peninsula, which they cross after arriving by dinghy in Greece.
While Europe dithered over a collective response, Hungary took matters into its own hands, shutting off the route with a new fence along its entire 175 km (110 mile) border with Serbia, topped with razor wire and guarded by helmeted riot police. It was erected at a cost of 22 billion forints (about $80 million), a rare example of efficiency in a country which built its last underground metro line ten years behind schedule at triple the projected cost. The government says it put the military in charge of the construction so that it could act more quickly. By swiftly mobilizing state resources, the authorities also managed to turn the fence into a national project, immensely popular at home even as it is denounced by European partners.
“It took a while but the government’s campaign to rouse public opinion against the refugees is bearing fruit, and having brought much of the media under control is paying dividends,” said Richard Szentpeteri Nagy, an analysts at Centre for Fair Political Analysis. “By properly filtering the message through public television, what viewers at home see is that this is a mob, throwing stones and attacking police.” In just days since it shut the Serbian frontier, Hungary has already moved even faster to shut the border with Croatia, which is inside the European Union but outside the Schengen zone. A 41-kilometre temporary fence was thrown up within four days. Work is already underway on a permanent barrier, with machines clearing the land, fence posts driven into the ground and razor wire rolled out.

Hollande’s a dunce and a coward. Full stop.
• Hollande Wrongfooted on Refugee Surge, Fearing Le Pen’s Rise (Bloomberg)
As Europe searches for a solution to the migrant crisis, French President Francois Hollande is in his customary position: stuck in the middle and pleasing few. The Socialist leader finds himself playing second fiddle to German Chancellor Angela Merkel in the unfolding drama as European Union leaders meet Wednesday to seek a way out of their impasse on how to cope with thousands of migrants knocking on the region’s gates. France’s acceptance of migrants has been overshadowed by greater generosity shown next door by Germany. “The government is fearful of doing anything that would benefit the anti-immigration right,” said Francois Gemenne , researcher at Sciences Po University.
“At the same time, they have intellectuals in the press and much of their base saying that France, the nation of human rights, looks ridiculous next to Germany. The government doesn’t know what foot to dance on. They’ve ended up with a policy that satisfies no one.” That mirrors much of what Hollande has done in his three years in office. On the economy, his socialist base feels he has sold out by recent moves to liberalize labor markers and ease rules for business, while conservative parties pillory him for raising taxes. Hollande’s approval rating fell one point to 24% in September, according to the most recent Ifop poll. Hollande and Merkel on Sept. 4 jointly urged the EU to agree on a redistribution plan for refugees and to speed up processing in countries where they arrive.
Under a formula proposed by the European Commission, France and Germany agreed to take 30,000 and 44,000 refugees respectively, out of the 160,000 who had made their way to Italy, Greece and Hungary. Those pledges have been overtaken by events as thousands of Syrians a day cross to Greek islands from Turkey, and then try to reach northern Europe. The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development said Tuesday that 700,000 refugees have sought asylum in Europe so far this year and that it’ll be 1 million by year end, a record. That has led Hollande’s opponents to say he’s doing too much or too little.
Marine Le Pen, leader of the anti-immigration National Front and by some measures the most popular presidential candidate in France, has compared the influx of refugees to the barbarian invasions that destroyed the Roman empire. Former President Nicolas Sarkozy said France should reinstall border controls, has blamed Hollande’s handling of the Syrian crisis for the influx, and has called into question automatic citizenship for children born in France. “There are differences of tone between Le Pen and Sarkozy on this issue, but they are basically on the same page,” said Smain Laacher, a sociology professor at the University of Strasbourg.

Damned if you do, doomed if you don’t.
• The Fed Just Made A Gigantic Mess (CNBC)
The Federal Reserve is creating a negative-feedback loop with its mixed messages on interest rates — and it’s messing with the markets. In explaining why the Fed opted to hold rates steady, Fed Chair Janet Yellen said that policy makers remain concerned about slowing economic growth — especially in China — and the impact on global markets and inflation. But then, she added that the Fed could still raise rates in before the year was out — as early as October. What? If slowing global growth and market turbulence was a reason to pause, how likely was it, then, that all of that would be resolved by October? Since Chair Yellen spoke, a number of Fed officials have spoken, reiterating that a rate hike in 2015 remains likely. This is cognitive dissonance at its worst. Investors are now simultaneously worried about incompatible outcomes.
If growth is weak, and inflation continues to fall, the Fed should NOT, and would NOT, raise rates. If this global problem is truly transitory (a word most Fed officials need to look up in the dictionary), then a rate hike should have already occurred. This is a problem of the Fed’s own making. By insisting that interest rate normalization is imminent, the Fed is creating the very problem it is combatting by delaying that very same process. From my vantage point, the Fed more clearly needs to define what it takes to meet its dual mandate — inflation and employment. Clearly, the Fed has reached many of its goals on the employment front, although wage inflation is not accelerating to the point where a rate hike would be justified to cool an overheating economy.
Low inflation, while “transitory,” has persisted for nearly six years and is being pushed even lower by the huge drop in oil prices; the crash in other commodities; slowing growth in China and Japan and Asian emerging markets; recessions in Russia and Brazil and uneven growth in Europe. If the world is not normal, why normalize policy at all? The world affects the U.S. As we have seen in innumerable instances in the past, global instability has altered the course of domestic monetary policy for decades. Factoring that in, does not mean that the Fed has a “third mandate” as some Fed bashers claim. It simply means that the Fed has an obligation to consider how all variables affect its mandate. With an economy only “half-normal,” the normalization of interest rates can wait. But if the Fed continues to convey confusing messages about the timing of normalization, in an abnormal world, it will only serve to exacerbate the very trends it is hoping will abate.

Economics is just politics in disguise.
• Economic Policy Often Seems To Have Little To Do With Economists. Why? (Ind.)
With Jeremy Corbyn as leader of the Labour Party we will hear a great deal from his opponents that his economic policies are not “credible”. At the moment we do not have a clear idea of what these policies will be, but it is worth asking beforehand what exactly a credible economic policy is. A natural way to define a credible economic policy is one that accords with what most economists think. If this was true, you might expect it would be difficult to win an election based on a macroeconomic policy that most economists regard as mistaken. Unfortunately, the last General Election provides a clear counter-example. In that election George Osborne proposed eliminating the overall budget deficit within five years. That contradicted what most economists believe is a sensible fiscal policy, for at least two reasons.
First, it precluded any significant increase in public investment, on things like building schools and flood defences. Every economist I know agrees that now is an excellent time to increase infrastructure investment, because labour is cheap and interest rates are low. Second, another round of austerity is very risky when interest rates are so low. Osborne says we must reduce government borrowing quickly to prepare for the next crisis. That makes little economic or business sense. Firms that cut back on investment when borrowing is cheap and the economy is expanding generally fail. The more significant risk is that the world economy takes a turn for the worse in the next year or two because of events in China or elsewhere. If interest rates are already low because they are having to offset the impact of austerity, the Bank of England has little room to counter these global shocks.
So the prudent policy while interest rates are low is to avoid austerity. The fiscal policy platform on which the Conservatives won was not credible to most academic macroeconomists. The problem is that most people in politics and the media do not get their notion of credibility from this source. So where does their idea of economic credibility come from? Discussion of economic policy in the media is dominated by political rather than economic journalists. They routinely provide comment after major economic policy announcements and interview politicians. They spend most of their time talking to politicians, so the Westminster bubble defines what the media sees as a credible economic policy.

How to turn farmers into serfs.
• English Farmland Prices Double In Five Years (Guardian)
The price of good quality English farmland has doubled over the past five years, making it the most expensive in the world and offering a better return than prime London property, the FTSE 100 or gold. According to agents Knight Frank demand from wealthy private individuals as well as pension funds, has driven up the average price for an acre of “investment grade” English farmland (large plots with economies of scale) to £12,500, up 100% since 2010. In comparison, the price of luxury London homes has risen 42% over the same period, the FTSE 100 has increased 33%, while gold has dropped 10%. Many recent buyers of prime farmland arelifestyle buyers, often London financiers, for whom farming can be more of a hobby than about making the land pay its way.
Even what Knight Frank describes as some of the best land in the world – the pampa west of Buenos Aires in Argentina – sells for just a third of the average price investors are paying for farmland in England. An acre of investment grade land in Argentina sells for £4,510, while in France it fetches about £4,490. On the vast wheat-producing prairies of Canada, quality land fetches just £800 an acre, only 7% of the price achieved in England. Australian farmland values, blighted by drought, have largely flatlined in recent years.
The inflation in English land values is taking place despite a crisis among farmers struggling with falling global prices, particularly for wheat. After peaking at about £214 a tonne in December 2012, feed wheat values have since fallen by more than 50%. Global demand for wheat was 679m tonnes in 2012/13, but only 657m tonnes was produced, pushing prices up sharply. But the situation has now reversed, with global production forecast to hit about 725m tonnes this year but consumption at about 715m tonnes, sending prices spiralling down on commodity markets. UK farm gate milk prices are down by a third since 2013, prompting a wave of closures among English dairy farmers.

And now dinosaurs are literally cool.
• Alaska Fossil Find Points To New ‘Lost World Of Dinosaurs’ (Guardian)
Fossils from a unique plant eating dinosaur found in the high Arctic of Alaska may change how scientists view dinosaur physiology, Alaska and Florida university researchers have said. A paper published on Tuesday concluded that fossilized bones found along Alaska’s Colville river were from a distinct species of hadrosaur, a duck-billed dinosaur not connected to hadrosaurs previously identified in Canada and the Lower 48 states. It’s the fourth species unique to northern Alaska. It supports a theory of Arctic-adapted dinosaurs that lived 69m years ago in temperatures far cooler than the tropical or equatorial temperatures most people associate with dinosaurs, said Gregory Erickson, professor of biological science at Florida State university. “Basically a lost world of dinosaurs that we didn’t realise existed,” he said.
The northern hadrosaurs would have endured months of winter darkness and probably snow. “It was certainly not like the Arctic today up there – probably in the 40s (five to nine degrees ) was the mean annual temperature,” Erickson said. “Probably a good analogy is thinking about British Columbia.” The next step in the research program will be to try to figure out how they survived, he said. Mark Norell, curator of paleontology at the American Museum of Natural History in New York, said by email that it was plausible the animals lived in the high Arctic year-round, just like musk oxen and caribou do now. It’s hard to imagine, he said, that the small, juvenile dinosaurs were physically capable of long-distance seasonal migration. “Furthermore, the climate was much less harsh in the Late Cretaceous than it is today, making sustainability easier,” he said.








