Times Square NYC ca. 1909

What’s kept us alive will kill us off.
• Higher Interest Rates To Spell Private Debt Trouble in Many Countries (BBG)
Hong Kong, Sweden, China and Australia could all find themselves in hot water over private-sector debt if borrowing costs rise, according to research by Oxford Economics. That’s because those countries all have a particularly high share of floating-rate debt in relation to economic output. If interest rates increase, households and companies are likely to feel the pinch, the study of 16 economies found. With global economic momentum picking up, several major central banks are weighing steps to tighten policy, though the pace of movement varies significantly. The Federal Reserve is expected to raise interest rates again next week and economists also predict that Sweden’s Riksbank will tighten policy later this year.
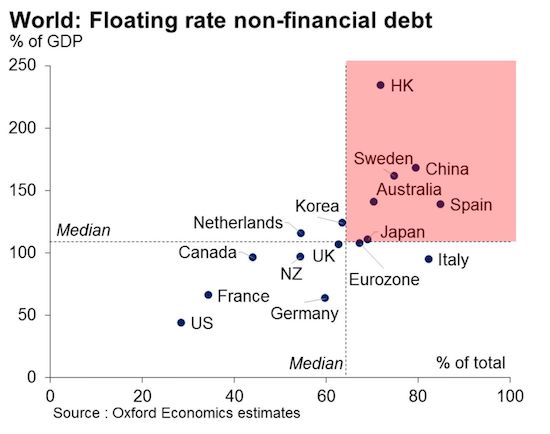
Oxford Economics estimated that an interest rate rise of 100 basis points would raise Hong Kong’s debt service ratio by around 2.5% of GDP after a year, while Sweden, China and Australia would experience increases of between 1.5% and 1.7% of GDP. By contrast, Germany, where debt levels are moderate, as well as France and the U.S. are less likely to suffer. For the latter two, that’s because mortgages are typically of fixed rate.

It’s embarrassing that we need this to be pointed out.
• The US Economy Is Not Really Growing (RIA)
Most people are aware that GDP growth has been lower than expected in the aftermath of the Global Financial Crisis of 2008 (GFC). For example, real GDP growth for the past decade has been closer to 1.5% than the 3% experienced in the 50 years prior to 2008. As a result of the combination of slow economic growth and deficit spending, most people are also aware that the debt/GDP ratio has been rising. However, what most people don’t know is that, over the past ten years, the dollar amount of cumulative government deficit spending exceeded the dollar amount of GDP growth. Put another way, in the absence of deficit spending, GDP growth would have been less than zero for the past decade. Could that be true?
Let’s begin with a shocking chart that confirms the statements above, and begins to answer the question. The black line shows the difference between quarterly GDP growth and the quarterly increase in Treasury debt outstanding (TDO). When the black line is above zero (red dotted line), the dollar amount is GDP is growing faster than the increase in TDO. From 1971 to 2008, the amount of GDP typically grew at a faster rate than the increase in TDO, which is why the black line is generally above the red dotted line.
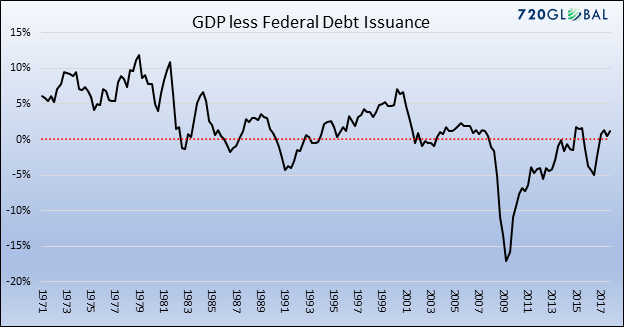
Most people are aware that GDP growth has been lower than expected in the aftermath of the Global Financial Crisis of 2008 (GFC). For example, real GDP growth for the past decade has been closer to 1.5% than the 3% During the 1971-2008 period, inflation, budget deficits, and trade deficits varied widely, meaning that the relationship between GDP growth and TDO was stable even in the face of changes in other economic variables. Regardless of those changing economic variables, the US economy tended to grow at a pace faster than TDO for four decades. The only interruptions to the pattern occurred during recessions of the early 1980s, early 1990s, and early 2000s when GDP fell while budget deficits did not.
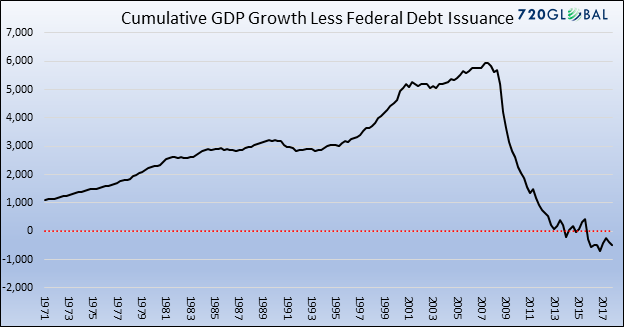
[..] From 2008-2017, GDP grew by $5.051 trillion, from $14.55 trillion to $19.74 trillion. During that same period, the increase in TDO totaled $11.26 trillion. In other words, for each dollar of deficit spending, the economy grew by less than 50 cents. Or, put another way, had the federal government not borrowed and spent the $11.263 trillion, GDP today would be significantly smaller than it is. It is possible to transform Chart 1, which shows annual changes in TDO and GDP from 1970-2017, into Chart 3 below, which shows the cumulative difference between the growth of TDO and GDP over the entire period from 1970-2017. The graph below clearly shows the abrupt regime change that occurred in the aftermath of the GFC. A period in which growth in GDP growth exceeded increases in TDO has been replaced by a period in which increases in TDO exceeded GDP growth.

“These dang trillions are flying by so fast, they’re hard to see.”
• US Gross National Debt Spikes $1.2 Trillion in 6 Months, Hits $21 Trillion (WS)
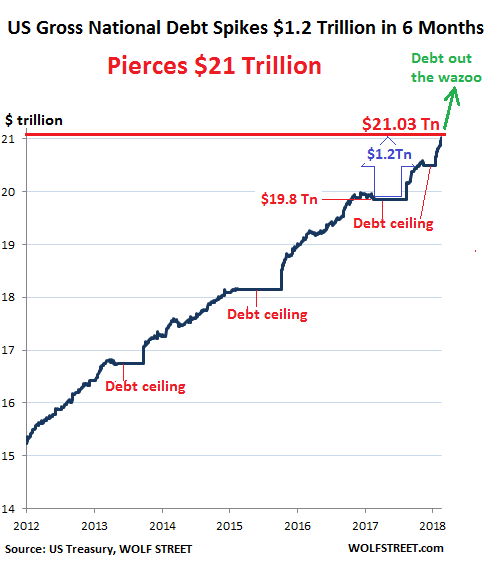
The US gross national debt jumped by $72.8 billion in one day, on Thursday, the Treasury Department reported Friday afternoon. This March 16 is a historic date of gloomy proportions, because on this date, the US gross national debt punched through the $21 trillion mark and reached $21.03 trillion. Here’s the thing: On September 7, 2017, a little over six months ago, just before Congress suspended the debt ceiling, the gross national debt stood at $19.84 trillion. In those six-plus months – 132 reporting days, to be precise – the gross national debt spiked by $1.186 trillion. I tell you, these dang trillions are flying by so fast, they’re hard to see. And we wonder: What was that? Where did it go?
Whatever it was and wherever it went, it added 6% to the gross national debt in just 6 months. And with 2017 GDP at $19.74 trillion in current dollars, the gross national debt now amounts to 106.4% of GDP. In the chart below, the flat spots are the various debt-ceiling periods. This is a uniquely American phenomenon when Congress forbids the Administration to borrow the money that it needs to borrow in order to spend it on the things that Congress told the Administration to spend it on via the appropriation bills. So that’s where we are, on this glorious day of March 16, 2018:

So many holes have been pointed out in ‘the official story’ that not much of it remains standing.
• Russia Expels 23 British Diplomats In Retaliation (Ind.)
Russia has announced it will expel 23 British diplomats in response to the expulsion of 23 Russian diplomats from Britain. The move marks the latest development in the diplomatic spat over the poisoning of former Russian spy Sergei Skripal in Salisbury on 4 March. The Russian Foreign Ministry announced on Saturday morning that the 23 diplomatic representatives of the British Embassy in Moscow should leave Russia within a week. The ministry also said all activities by the British Council, the UK’s international organisation for cultural relations, would cease in Russia and that the planned reopening of the British consulate in St Petersburg would no longer go ahead. The ministry warned that Russia could take further measures if Britain takes any more “unfriendly actions” against the country.
Shortly before the announcement, British ambassador to Russia, Laurie Bristow, was summoned to the foreign ministry for talks, where he learned of the retaliation measures. As he left the ministry, Mr Bristow said: “This crisis has arisen as a result of an appalling attack in the UK, the attempted murder of two people using a chemical weapon developed in Russia and not declared by Russia to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) as Russia is obliged to do under the Chemical Weapons Act.” The retaliation from Russia comes four days after Theresa May announced that 23 Russian diplomats would be expelled from Britain after Russia missed a deadline to provide an explanation for the poisoning of Skripal and his daughter Yulia. Both remain critically ill in hospital.
Russia has continued to dismiss accusations of Russian culpability for the attack and to deny possessing Novichok, the nerve agent used in the incident. On Friday, UK Foreign Secretary Boris Johnson directly accused Russian President Vladimir Putin of ordering the poisoning, saying it was “overwhelmingly likely” Mr Putin personally ordered the assassination attempt. Dmitry Peskov, Russian presidential press secretary, responded to the verbal escalation with a further denial of the state’s involvement. “Any reference or mention of our President in this connection is nothing but a shocking and unforgivable violation of the diplomatic rules of propriety,” Mr Peskov said.

Once Europe does this, will other ‘entities’ follow?
• EU Ready To Hit Big US Tech Firms With 3% Turnover Tax (R.)
Large companies with significant digital revenues in the European Union such as Google and Facebook could face a 3% tax on their turnover under a draft proposal by the European Commission seen by Reuters. The proposal, expected to be adopted next week and still subject to changes, updates an earlier draft which envisaged a tax rate of between 1 and 5%. The tax, if backed by EU states and lawmakers, would only apply to large firms with annual worldwide revenues above 750 million euros (£662.2 million) and annual “taxable” revenues above 50 million euros in the EU. The threshold for EU revenues has been raised from 10 million euros initially foreseen to exempt smaller companies and emerging start-ups from the tax.
Large U.S. firms such as Uber, Airbnb and Amazon could also be hit by the new levy, which would apply across the 28 EU countries. Big tech firms have been accused by large EU states of paying too little tax in the bloc by re-routing some of their profits to low-tax member states like Ireland and Luxembourg. Services that will be taxed are digital advertising, which would capture both providers of users’ data like Google, and companies offering ad space on their websites, like popular social media such as Facebook. The tax would be also be levied on online platforms offering “intermediation services,” a concept under which the Commission includes gig economy firms such as Airbnb and Uber. Digital market places, including Amazon, would also be within the scope of the levy.

True enough: Kudlow was by no means the only one to get it all awfully wrong.
• Goldilocks, R. I. P. – Part 2 (Stockman)
Goldilocks is a conceit of monetary central planning and its erroneous predicate that falsifying financial asset prices is the route to prosperity. In fact, it only leads to immense and unstable financial bubbles which eventually crash – monkey-hammering the purported Goldilocks Economy as they do. It also leads to a complete corruption of the economic and financial narrative on both ends of the Acela Corridor. To wit, the Fed’s serial financial bubbles on Wall Street are falsely celebrated as arising from a booming main street economy. In fact, they are an economic dagger that bleeds it of investment and cash and exposes it to “restructuring” mayhem from the C-suites when the egregious inflation of share prices and stock option values finally gets crushed by another financial meltdown.
In this context, the Washington Post (WaPo) is out this morning with brutal takedown of our friend Larry Kudlow for his ebullient whistling past the graveyard on the eve of the financial crisis and Great Recession. It would be an understatement to say he didn’t see it coming, but it’s also completely unfair not to acknowledge that 95% of Wall Street and 100% of the FOMC were equally bubble-blind. In fact, when Larry Kudlow waxed eloquently in a piece in the National Review about the awesome economy the George Bush Administration had produced in December 2007, he was just delivering the Wall Street consensus forecast for the coming year:
“There’s no recession coming. The pessimistas were wrong. It’s not going to happen. At a bare minimum, we are looking at Goldilocks 2.0. (And that’s a minimum). Goldilocks is alive and well. The Bush boom is alive and well. It’s finishing up its sixth consecutive year with more to come. Yes, it’s still the greatest story never told…….In fact, we are about to enter the seventh consecutive year of the Bush boom.”
Well, not exactly. The worst recession since the 1930s actually incepted that very month and 10 months latter came Washington’s hair-on-fire moment when the monetary and fiscal spigots were opened far wider than ever before – bailing out everything that was collapsing, tottering, moving or even standing still.

Our education system serves uniquely to create pawns in games.
Sunday night was Secretary of Education Betsy DeVos’s turn through the CBS 60-Minutes wringer of censure with a visibly frustrated inquisitor Lesley Stahl trying to hector her into self-incrimination. The sad truth about American schools is that they’re a mirror for the painful collapse of the society they supposedly serve — a process ongoing for decades before Ms. DeVos came on the scene. The expectation that some uber-regent can or ought to fix public education is bound to disappoint a news media searching for saviors. The further we leave the 20th century behind, the more anomalous its organizing principles look, especially the idea of preparing masses of young people for mass, regimented work at the giant corporate scale.
There’s a big divergence underway between the promises of schooling and the kind of future that the 21st century is actually presenting — of no plausible careers or vocations besides providing “therapy” and policing for the discontented masses stewing in anomie and compensatory pleasure-seeking, with all its nasty side effects. In the meantime, we’re stuck with wildly expensive, out-of-scale, giant centralized schools where the worst tendencies of human status competition are amplified by smart phones and social media to all but eclipse classroom learning.
Education in the years to come is destined to become more of a privilege than a right, and it will probably depend more on how much an individual young person really desires an education than just compelling masses of uninterested or indisposed kids to show up everyday for an elaborate and rather poorly supervised form of day-care. But it’s difficult to let go of old habits and obsolete arrangements, especially when we’ve spent countless billions of dollars on them. I call the future a World Made By Hand because it is going to be entirely unlike the sci-fi robotic fantasy that currently preoccupies the thought-leaders in this culture. A lot of what will be required in this time-to-come will be physical labor and small-scale skilled work in traditional crafts. There never were that many job openings for astronauts, not even in the 1960s, but in the decades ahead there will be none — notwithstanding Elon Musk’s wish to colonize Mars.

In New York, 111,000 students in the public school system are homeless.
• ‘America’s New Vietnam’: The Homelessness Crisis Seems Unsolvable (G.)
In Los Angeles, the more the politicians push to solve the city’s festering homelessness crisis, the worse it seems to get. The city leadership has taken one bold step after another: restructuring the budget to free more than $100m a year in homelessness funding, sponsoring one voter-approved initiative to raise more than $1bn for housing and backing another regional proposal to raise the sales tax and generate an estimated $3.5bn for support services over the next decade. And yet the tent cities continue to proliferate, in rich neighborhoods and poor, by the beach, the airport, the Hollywood Walk of Fame and within view of City Hall itself. It’s the sorriest urban scene anywhere in America, and the same voters who not so long ago opened their hearts and their wallets to put an end to it are growing increasingly impatient.
As the numbers of homeless people continue to rise – the latest figures put the countywide number at 58,000, up more than 20% in a single year – and new encampments spring up on sidewalks, under freeways, and along stretches of river and rail lines, the politicians who not so long ago were earning praise for their courage are facing the beginnings of an angry backlash. “How many people have we housed?” the Los Angeles Times asked impatiently in a blistering series of editorials late last month. “How many are we on track toward housing? Is Los Angeles setting the national standard for rapid and effective response to a vexing problem? Or are its leaders merely mastering the art of appearances while passing the buck and hoping things turn around? … Who’s in charge here?”

Sorry, but that apocalypse is already very much here. ‘Ordinary people’ already have no idea what’s true or real or not.
• An Information Apocalypse Is Coming. How Can We Protect Ourselves? (G.)
John F Kennedy’s last speech reads like a warning from history, as relevant today as it was when it was delivered in 1963 at the Dallas Trade Mart. His rich, Boston Brahmin accent reassures us even as he delivers the uncomfortable message. The contrast between his eloquence and the swagger of Donald Trump is almost painful to hear. The problem is, Kennedy never spoke these words. He was killed before he made it to the Trade Mart. You can only hear them now thanks to audio technology developed by a British company, CereProc. Fragments of his voice have been taken from other speeches and public appearances, spliced and put back together, with neural networks employed to mimic his natural intonation.
[..] “Dual use” of technology is not a new problem. Nuclear physics gave us both energy and bombs. What is new is the democratisation of advanced IT, the fact that anyone with a computer can now engage in the weaponisation of information; 2016 was the year we woke up to the power of fake news, with internet conspiracy theories and lies used to bolster the case for both Brexit and Donald Trump. We may, however, look back on it as a kind of phoney war, when photoshopping and video manipulation were still easily detectable. That window is closing fast. A program developed at Stanford University allows users to convincingly put words into politicians’ mouths. Celebrities can be inserted into porn videos. Quite soon it will be all but impossible for ordinary people to tell what’s real and what’s not.
What will the effects of this be? When a public figure claims the racist or sexist audio of them is simply fake, will we believe them? How will political campaigns work when millions of voters have the power to engage in dirty tricks? What about health messages on the dangers of diesel or the safety of vaccines? Will vested interests or conspiracy theorists attempt to manipulate them? Unable to trust what they see or hear, will people retreat into lives of non-engagement, ceding the public sphere to the already powerful or the unscrupulous? The potential for an “information apocalypse” is beginning to be taken seriously. The problem is we have no idea what a world in which all words and images are suspect will look like, so it’s hard to come up with solutions.
Perhaps not very much will change – perhaps we will develop a sixth sense for bullshit and propaganda, in the same way that it has become easy to distinguish sales calls from genuine inquiries, and scam emails with fake bank logos from the real thing. But there’s no guarantee we’ll be able to defend ourselves from the onslaught, and society could start to change in unpredictable ways as a result. Like the generation JFK was addressing in his speech, we are on the cusp of a new and scary age. Rhetoric and reality, the plausible and the possible, are becoming difficult to separate. We await a figure of Kennedy’s stature to help us find a way through. Until then, we must at the very least face up to the scale of the coming challenge.

Would have been nice to see Orwell comment on this.
• China To Bar People With Bad ‘Social Credit’ From Planes, Trains (R.)
China said it will begin applying its so-called social credit system to flights and trains and stop people who have committed misdeeds from taking such transport for up to a year. People who would be put on the restricted lists included those found to have committed acts like spreading false information about terrorism and causing trouble on flights, as well as those who used expired tickets or smoked on trains, according to two statements issued on the National Development and Reform Commission’s website on Friday. Those found to have committed financial wrongdoings, such as employers who failed to pay social insurance or people who have failed to pay fines, would also face these restrictions, said the statements which were dated March 2.
It added that the rules would come into effect on May 1. The move is in line with President’s Xi Jinping’s plan to construct a social credit system based on the principle of “once untrustworthy, always restricted”, said one of the notices which was signed by eight ministries, including the country’s aviation regulator and the Supreme People’s Court. China has flagged plans to roll out a system that will allow government bodies to share information on its citizens’ trustworthiness and issue penalties based on a so-called social credit score.

We’re going to figure this one out way too late. The time to stop this is now, not at some future point down the line. But we’re not doing anything at all. We blindly parrot claims about clean energy and electric cars that will allegedly ‘save’ us, because we want to do the saving without paying a price for it that makes our lives one iota less comfy.
• Global Biodiversity Crisis Puts Mankind At Risk (AFP)
Earth is enduring a mass species extinction, scientists say – the first since the demise of the dinosaurs and only the sixth in half-a-billion years. The reason? Humanity’s voracious consumption, and wanton destruction, of the very gifts of nature that keep us alive. Starting Saturday, a comprehensive, global appraisal of the damage, and what can be done to reverse it, will be conducted in Colombia. “The science is clear: biodiversity is in crisis globally,” WWF director general Marco Lambertini told AFP ahead of a crucial meeting of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). “We depend on biodiversity for the food we eat, the water we drink, the clean air we breathe, the stability of weather patterns, and yet our actions are pushing nature’s ability to sustain us to the brink.”
Scientists and government envoys will gather as the 128-member IPBES to dot the i’s and cross the t’s on five monumental assessment reports designed to inform global policymaking into the future. Compiled over the last three years, the reports will provide the most up-to-date picture of the health of the world’s plants, animals and soil. [..] Meeting host Colombia claims to boast the world’s largest variety of birds and orchids and is second only to Brazil in terms of overall species diversity. Paradoxically, decades of conflict have preserved fragile habitats in no-go zones in the country, whose mountainous topography supports 311 different ecosystems.