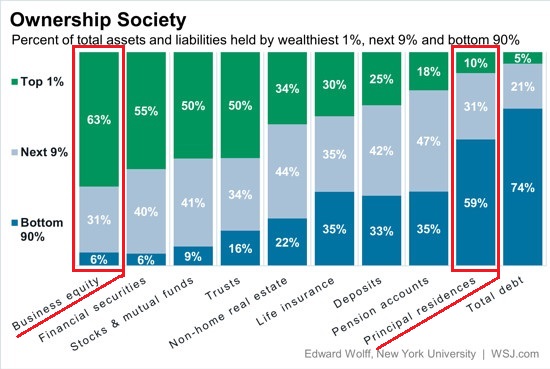
DPC Bromfield Street in Boston 1908



Too many kinds of bonds carry too much risk going forward.
• Bond Funds Stock Up On Treasuries In Prep For Market Shock (Reuters)
U.S. corporate bond funds this year are adding Treasuries to their holdings at more than twice the rate of corporate debt amid concern that the struggling European economy and potential changes in Federal Reserve policy will drag down profits at U.S. corporations. Through September, corporate bond portfolios boosted their holdings of U.S. government debt by 15%, compared with a 6.5% increase in corporate bonds during the same period, according to Lipper Inc data. The funds now hold about $13 billion in Treasuries, 15% more than the $11.3 billion they held at the end of 2013. Corporate bond funds typically invest in a range of debt that includes mortgage-backed securities, U.S. Treasuries and bonds backed by student loans, credit cards and auto loans. Some corporate junk bond funds have guidelines that allow them to buy individual stocks. The move to buy Treasuries, which are more easily traded than most corporate bonds, show that managers anticipate market turmoil that could lead to redemption demands from investors.
Matt Toms, head of fixed income at New York-based Voya Investment Management, said he has cut exposure to corporate bonds in favor of mortgage-backed securities, for example. In particular, he has reduced corporate debt issued by U.S. financial companies because of their exposure to the weak European economy. He sees mortgage-backed bonds as more U.S.-centric because they are backed by the ability of American homeowners to make good on their monthly mortgage payments. “The volatility in Europe could translate more quickly through the corporate debt issued by U.S. banks,” Toms said. A year ago, the Voya Intermediate Bond Fund’s top 10 holdings included debt issued by Morgan Stanley, JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs. But more recently, none of those banks’ debt cracked the top 10 holdings of the fund, disclosures show. Toms, who runs the $1.9 billion Voya Intermediate Bond Fund, said nearly two-thirds of the portfolio’s assets are in government bonds or government-related securities. “That’s a highly liquid pool,” he said.
Read more …

“The drop wiped $158.6 billion off the market value of 75 shale producers since the end of August.” Most of it borrowed money. That’s a lot of mullah.
• Investors Pull Shale Money, Put Brakes on Wall Street-Funded Boom (Bloomberg)
Falling oil prices are testing investors’ commitment to the Wall Street-funded shale boom. Energy stocks led the plunge earlier this month in U.S. equities and the cost of borrowing rose. The Energy Select Sector Index is down 14% since the end of August, compared with 3.8% for the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index. The yield for 190 bonds issued by U.S. shale companies increased by an average of 1.16 percentage points. Investors’ sentiment toward the oil and gas industry has “certainly changed in the last 30 days,” said Ron Ormand, managing director of investment banking for New York-based MLV & Co. with more than 30 years of experience in energy. “I don’t think the boom is over but I do think we’re in a period now where people are going to start evaluating their budgets.” What distinguishes this U.S. energy boom from the way the industry operated in the past is the involvement of outside investors. In 1994, drillers funded 42% of their own capital spending, according to an Independent Petroleum Association of America member survey.
Today, shale companies are outspending their cash flow by 50% thanks to borrowed money, according to the IPAA. They’re selling more than twice as much equity to the public as they did 10 years ago, according to Tudor Pickering Holt, a Houston investment bank. “After the tech bubble and then the real estate bubble, Wall Street had to put its money somewhere, and it looks like they put a lot of it into domestic onshore oil and gas production,” said Michael Webber, the deputy director of the Energy Institute at the University of Texas at Austin, who advises private investors. West Texas Intermediate, the benchmark U.S. oil price, has fallen 25% since its recent peak on June 20. Between the S&P 500’s record high on Sept. 18 and its five-month low on Oct. 15, energy companies led the index down 14%, more than any other industry, data compiled by Bloomberg show. When the market rebounded on Oct. 16, energy again took the lead, gaining 1.7%. The drop wiped $158.6 billion off the market value of 75 shale producers since the end of August.
Read more …

“Such an environment would tend to favor Republicans, but their advantage is limited by the fact that people don’t like them, either.”
• Solid Majority In US Says Country ‘Out Of Control’ (CNBC)
With just two weeks to go until Election Day, a clear picture of the American electorate is emerging, and it is not pretty, for either party. The country is anxious about the economy, Ebola and Islamic extremists, and does not really feel Republicans or Democrats have solutions to any of these vexing problems. The latest Politico Battleground Poll of likely voters in key House and Senate races finds that 50% say the nation is “off on the wrong track” while just 20% say things are “generally headed in the right direction.” A remarkable 64% say things in the U.S. are “out of control” while just 36% say the U.S. is in “good position to meet its economic and national security challenges.” The economy continues to dominant the issue landscape with 40% rating it the top issue, to 20% for national security. President Barack Obama remains mired in negative territory, with 47% approving of his job performance and 53% disapproving.
Such an environment would tend to favor Republicans, but their advantage is limited by the fact that people don’t like them, either. In total, 38% approve of Democrats in Congress, while just 30% approve of Republicans. On the generic ballot questions, Democrats enjoy 41% support (including the independent Senate candidate in Kansas) while Republicans get 36%. That’s hardly the backdrop for a massive GOP wave, though the polls suggest Republicans are still significant favorites to pick up the six seats they need to control the Senate next year. The Ebola outbreak has clearly helped shape the final weeks in several Senate races, emerging as a significant wild card issue. In the Politico poll, only 22% of respondents said they had “a lot of confidence” that the federal government is doing all it can to contain the deadly disease. And the poll finished on Oct. 11, before the hospitalization of a second Dallas nurse.
Read more …

Work-years, that is. Not a bad concept.
• It Will Take 398,879,561 Years To Pay Off The US Government Debt (Black)
The US government’s debt is getting close to reaching another round number – $18 trillion. It currently stands at more than $17.9 trillion. But what does that really mean? It’s such an abstract number that it’s hard to imagine it. Can you genuinely understand it beyond just being a ridiculously large number? Just like humans find it really hard to comprehend the vastness of the universe. We know it’s huge, but what does that mean? It’s so many times greater than anything we know or have experienced. German astronomer and mathematician Friedrich Bessel managed to successfully measure the distance from Earth to a star other than our sun in the 19th century. But he realized that his measurements meant nothing to people as they were. They were too abstract. So he came up with the idea of a “light-year” to help people get a better understanding of just how far it really is. And rather than using a measurement of distance, he chose to use one of time.
The idea was that since we—or at least scientists—know what the speed of light is, by representing the distance in terms of how long it would take for light to travel that distance, we might be able to comprehend that distance. Ultimately using a metric we are familiar with to understand one with which we aren’t. Why don’t we try to do the same with another thing in the universe that’s incomprehensibly large today—the debt of the US government? Even more incredible than the debt owed right now is what’s owed down the line from all the promises politicians have been making decade after decade. These unfunded liabilities come to an astonishing $116.2 trillion. These numbers are so big in fact, I think we might need to follow Bessel’s lead and come up with an entire new measurement to grasp them. Like light-years, we could try to understand these amounts in terms of how long it would take to pay them off. We can even call them “work-years”.
So let’s see—the Social Security Administration just released data for the average yearly salary in the US in fiscal year that just ended. It stands at $44,888.16. The current debt level of over $17.9 trillion would thus take more than 398 million years of working at the average wage to pay off. This means that even if every man, woman and child in the United States would work for one year just to help pay off the debt the government has piled on in their name, it still wouldn’t be enough. Mind you that this means contributing everything you earn, without taking anything for your basic needs—which equates to slavery.
Read more …

The numbers get scary.
• Don’t Be Distracted by the Pass Rate in ECB’s Bank Exams (Bloomberg)
For investors, the European Central Bank’s yearlong evaluation of the region’s banks isn’t just about who passes and who fails. The bigger question will be how much the ECB marks down lenders’ capital during its balance sheet inspection known as the asset quality review. The central bank and national regulators will publish their findings on Oct. 26. “The focus will be on how the asset quality review influences the development of capital ratios and non-performing loans,” said Michael Huenseler at Assenagon Asset Management SA in Munich. The largest impact may be on Italian lenders led by Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena, Unione di Banche Italiane and Banco Popolare, according to a report last month from Mediobanca analysts. They foresee a gap of more than 3 percentage points between the capital ratios published by the companies and the results of the ECB’s asset quality review. Deutsche Bankmay see its capital fall by €6.7 billion, cutting its ratio by 1.9 percentage points, the analysts said.
The biggest lenders may see their combined capital eroded by about €85 billion in the asset quality review because of extra provisioning requirements, according to the Mediobanca analysts, led by Antonio Guglielmi. That’s equivalent to a reduction of 1.05 percentage points in their average common equity Tier 1 ratio, the capital measure the ECB is using to gauge the health of the banks under study, the analysts said. The AQR evaluates lenders’ health by scrutinizing the value of their loan books, provisioning and collateral, using standardized definitions set by European regulators. To pass, a bank must have capital amounting to at least 8% of its assets, when weighted by risk. The bigger the hit to their capital, the more likely lenders will need to take steps to increase it. Banks the ECB will supervise directly already bolstered their balance sheets by almost €203 billion since mid-2013, ECB President Mario Draghi said this month, by selling stock, holding onto earnings, disposing of assets, and issuing bonds that turn into equity when capital falls too low, among other measures.
Read more …

It was always just a mirage.
• Why It’s Now Too Late For Germany To Rescue The Eurozone Alone (Telegraph)
The eurozone is yet again in a nasty state. As it suffers from low growth and low inflation, the two combine to make a nasty cocktail. Without much of either, unemployment remains stuck at an eye wateringly high 11.5pc, and government debt burdens are likely to feel increasingly heavy. The European Central Bank (ECB) has announced a variety of acronyms – CBPP3, TLTROs, and an ABS purchase scheme – all stimulus measures designed to combat the euro area’s low inflation crisis. Yet so far, they’ve been insufficient to raise expectations of future inflation, implying that the firepower just isn’t strong enough. Economists are hoping that the ECB will deploy outright quantitative easing, and start buying up the sovereign bonds of eurozone governments. Without it, analysts have warned that both the eurozone as a whole, and even Germany – its former powerhouse economy – could now enter their third technical recession since 2008. Yet hopes of a monetary bazooka have so far been quashed by political concerns.
Some corners are hoping for Germany to launch its own form of stimulus. But a new report from ratings agency Standard & Poor’s suggests that such a move would be too little, too late, and “alone would have little effect on the rest of the eurozone”. “On the fiscal side … the margin for manoeuvre available to most eurozone members is still very limited”, the report states. “This is why the focus has unavoidably turned to Germany, the only large eurozone country with both a current surplus and a balanced budget”. According to S&P’s analysis, a stimulus package worth as much as 1pc of German GDP would provide just a 0.3pc boost to eurozone GDP, while creating 210,000 new jobs. The report states that the numbers: “put Germany’s potential contribution to higher growth in the eurozone into perspective, with the conclusion being that a stimulus package in that country alone would have a modest effect on its neighbours”.
Read more …

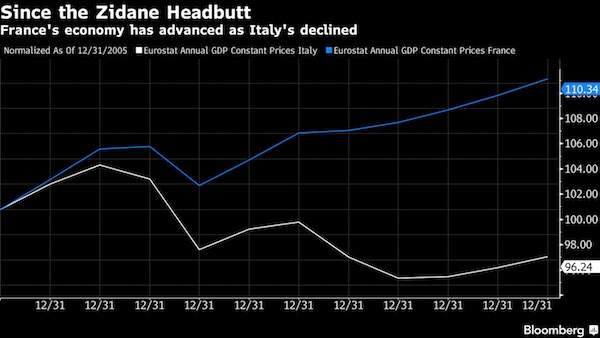
In any case, it shouldn’t. But Italy’s debt is so high (133% of GDP) that the only way out leads out of the EU.
• Why ‘Italy Doesn’t Need Germany’s Help’ (CNBC)
Despite Italy slipping back into recession amid a stagnant economic environment, the president of one of the country’s richest regions said the country doesn’t need Germany — or anybody else’s — help to recover. “I don’t want to be helped by the Germans or by anybody else, I want to be strong enough to grow and to sort my own problems. Can we do this as Italians? Yes, we can. We just have to work harder and do the right things,” Roberto Maroni, the President of the Lombardy region in northern Italy, told CNBC on Tuesday. “In Italy, it’s more difficult than elsewhere in the world because we are Italians. It’s a good thing to be Italian but it’s more difficult to do the same thing in Italy than in Germany or in France. But I think that we will have to do it.” Maroni’s comments come at a time of economic woe for Italy. The country slipped back into recession in the second quarter of 2014, according to data released by Italy’s statistics agency ISTAT, in August.
In an attempt to boost growth, Prime Minister Matteo Renzi unveiled a budget-busting program of tax cuts and additional borrowing in order to resuscitate the economy. He has also proposed sweeping reforms to the labor market to encourage hiring as the unemployment rate topped 12.3% in August. The 2015 budget has put Italy on a collision course with Europe, however, as it pushes the country’s public deficit right up to the 3% limit set by the European Commission. Maroni, a senior member and former leader of the opposition right-wing party Northern League, said the proposals were not enough on their own. “I think that he is doing maybe the right things but in the wrong way. He wants to reform the labor market but…it only works if you have economic growth. That is the way you can create new jobs, not simply changing the laws.” “We’re in a moment when economic growth is far away from coming to Italy,” he added. “Before making these reforms you need to boost economic growth and that’s not what Matteo Renzi is doing now.”
Read more …

Perhaps true, but certainly too late.
• Europe Can Learn From US And Make Each State Liable For Its Own Debt (Sinn)
The French prime minister, Manuel Valls, and his Italian counterpart, Matteo Renzi, have declared – or at least insinuated – that they will not comply with the fiscal compact to which all of the eurozone’s member countries agreed in 2012; instead, they intend to run up fresh debts. Their stance highlights a fundamental flaw in the structure of the European Monetary Union – one that Europe’s leaders must recognise and address before it is too late. The fiscal compact – formally the Treaty on Stability, Coordination, and Governance in the Economic and Monetary Union [PDF] – was the quid pro quo for Germany to approve the European Stability Mechanism (ESM), which was essentially a collective bailout package. The compact sets a strict ceiling for a country’s structural budget deficit and stipulates that public-debt ratios in excess of 60% of GDP must be reduced yearly by one-twentieth of the difference between the current ratio and the target.
Yet France’s debt/GDP ratio will rise to 96% by the end of this year, from 91% in 2012, while Italy’s will reach 135%, up from 127% in 2012. The effective renunciation of the fiscal compact by Valls and Renzi suggests that these ratios will rise even further in the coming years. In this context, eurozone leaders must ask themselves tough questions about the sustainability of the current system for managing debt in the EMU. They should begin by considering the two possible models for ensuring stability and debt sustainability in a monetary union: the mutualization model and the liability model.
Europe has so far stuck to the mutualisation model, in which individual states’ debts are underwritten by a common central bank or fiscal bailout system, ensuring security for investors and largely eliminating interest-rate spreads among countries, regardless of their level of indebtedness. In order to prevent the artificial reduction of interest rates from encouraging countries to borrow excessively, political debt brakes are instituted. In the eurozone, mutualisation was realised through generous ESM bailouts and €1tn ($1.27tn) worth of TARGET2 credit from national printing presses for the crisis-stricken countries. Moreover, the European Central Bank pledged to protect these countries from default free of charge through its “outright monetary transactions” (OMT) scheme – that is, by promising to purchase their sovereign debt on secondary markets – which functions roughly as Eurobonds would. The supposed hardening of the debt ceiling in 2012 adhered to this model.
Read more …

” … as German Chancellor Angela Merkel herself has told confidants, the real test will come when a major member state is forced to submit to the EU corset. That time is now.”
• ‘Poets and Alchemists’: Berlin and Paris Undermine Euro Stability (Spiegel)
Market uncertainty over the future of the euro has returned, but that hasn’t stopped France from flouting European Union deficit rules. Berlin is already busy hashing out a dubious compromise. Following three hours of questioning at European Parliament, a visibly exhausted Pierre Moscovici switched to German in a final effort to assuage skepticism from certain members of European Parliament. “As commisioner, I will fully respect the pact,” he said. Moscovici was French finance minister from 2012 until this April and will become European commissioner for economic and financial affairs when the new Commission takes office next month. But can he be taken at his word? There is room for doubt. In response to the unprecedented euro-zone debt crisis, the European Union agreed to strengthen its Stability and Growth Pact in recent years. Member states gave the European Commission in Brussels greater leeway to monitor national budgets and also bestowed it with rights to levy stiffer fines for countries that violate those rules.
Smaller member states have already been forced to comply. Still, as German Chancellor Angela Merkel herself has told confidants, the real test will come when a major member state is forced to submit to the EU corset. That time is now. And the big EU member state in question is France. The development is creating a dilemma for Merkel. The issue is far greater than a few tenths of a percentage point in the French budget deficit. At stake are France’s national pride and sovereignty — and the question as to whether the lessons of the crisis can actually be applied in practice. Also at stake is the euro-zone’s trustworthiness, and whether member states will once again fritter away global faith in the common currency by not abiding by their own internal rules. “The markets are watching us,” says one member of the German government — and he doesn’t sound particularly confident that the world will be impressed.
The markets are indeed jittery. The German economy is growing more sluggishly than expected and is no longer strong enough to buoy the rest of the euro zone. Interest rates for Greek government bonds have suddenly surged, likely because of domestic political instability, rising close to the levels that threatened to push the country into bankruptcy in early 2010. Meanwhile, the European Central Bank has already used up a good deal of the instruments it might have used to combat a new crisis.
Read more …

What, did anyone suggest the crisis was over?
• S&P Warns Crisis Not Over As France Output Tumbles (CNBC)
Ratings agency Standard & Poor’s warned on Thursday that the euro zone crisis was entering a “stubborn phase of subdued growth” in what it says is a new stage in the region’s economic crisis. The warning comes as new data showed a deepening downturn in France’s private sector economy during October. Markit’s Flash Composite Output Index (PMI) for France slipped to 48.0, from 48.4 in September. That was its lowest reading since February. A reading below 50 marks a contraction in private sector activity. “We believe that the euro zone’s problems are still unresolved,” said Standard & Poor’s credit analyst Moritz Kraemer in a statement. Further data released by Markit showed the private sector in Germany grew, offering some hope after a series of disappointing data for the euro zone’s largest economy. The flash composite PMI for October climbed to 54.3 from 54.1 last month.
Read more …

Well, obviously. That’s the whole idea.
• Central Banker Admits QE Leads To Wealth Inequality (Zero Hedge)
Six years after QE started, and just about the time when we for the first time said that the primary consequence of QE would be unprecedented wealth and class inequality (in addition to fiat collapse, even if that particular bridge has not yet been crossed), even the central banks themselves – the very institutions that unleashed QE – are now admitting that the record wealth disparity in the world – surpassing that of the Great Depression and even pre-French revolution France – is caused by “monetary policy”, i.e., QE. Case in point, during the Keynote speech by Yves Mersch, ECB executive board member, in Zurich on 17 October 2014 titled “Monetary policy and economic inequality” he said:
More generally, inequality is of interest to central banking discussions because monetary policy itself has distributional consequences which in turn influence the monetary transmission mechanism. For example, the impact of changes in interest rates on the consumer spending of an individual household depend crucially on that household’s overall financial position – whether it is a net debtor or a net creditor; and whether the interest rates on its assets and liabilities are fixed or variable.
Such differences have macroeconomic implications, as the economy’s overall response to policy changes will depend on the distribution of assets, debt and income across households – especially in times of crisis, when economic shocks are large and unevenly distributed. For example, by boosting – first – aggregate demand and – second – employment, monetary easing could reduce economic disparities; at the same time, if low interest rates boost the prices of financial assets while punishing savings deposits, they could lead to widening inequality.
Alas, in the past 6 years, low interest rates have not only boosted financial asset prices but have resulted in the biggest artificial asset bubble ever conceived. As for reducing unemployment, don’t ask Europe – and its unprecedented record unemployment, especially among the youth – how that is going. As for the US where unemployment is “dropping”, ask the 93.5 million Americans who have dropped out of the labor force, those whose real wages haven’t risen in the past 20 years, or the soaring part-time workers just how effective monetary policy has been in the US.
Read more …

Weird ideas some people have. But I’m sure they go down well at a Bloomberg Government breakfast in Washington.
• French Envoy To US Says ‘Poker Player’ Putin Bluffed and Won (Bloomberg)
Vladimir Putin has outmaneuvered his opponents and humiliated Ukraine by continuing to back pro-Russian separatists and flouting a cease-fire, making it crucial that sanctions on Russia remain firm, France’s ambassador to the U.S. said. The Russian president “has won because we were not ready to die for Ukraine, while apparently he was,” Ambassador Gerard Araud said yesterday at a Bloomberg Government breakfast in Washington, in remarks he said represented his personal opinion. Echoing the view of other European envoys in Washington, Araud expressed concern that the Ukraine conflict has hit an impasse, leaving Putin the winner by default.
While many observers have called Putin a geopolitical chess player, he said, the Russian leader is more a “poker player really, putting all the money on the table, saying, ‘Do the same,’ and of course we blink. We don’t do the same.” The economic sanctions against Russia must stay in place to prevent Putin from going further, said Araud, who moved to Washington in September after serving as the French ambassador to the United Nations. “The question is there on the table: When is Putin going to stop?” Araud said. “That’s the reason that we need to keep the sanctions” because, “let’s be frank, it’s more or less the only weapon that we have. We are not going to send our soldiers in Ukraine. It does not make sense to send weapons to the Ukrainians, because the Ukrainians would be defeated real easily, so it will only prolong the war” and lead to a “still bigger Russian victory.”
Read more …

And for them. And for Canadians.
• Canada’s Biggest Banks Say Worst to Come for Loonie (Bloomberg)
The oil boom that powered Canada’s recovery from its 2009 recession is turning into a bust for the nation’s dollar. Canada’s currency tumbled this month to a five-year low of C$1.1385 per U.S. dollar as the price of oil, the country’s biggest export, fell 30% from a June peak. Without a sustained increase in crude, the local dollar will weaken at least another 4% to C$1.18, according to Toronto-Dominion Bank and Royal Bank of Canada, the nation’s two biggest lenders. “The risk is, a sustained push lower in oil prices cuts Canadian growth,” Shaun Osborne, the chief currency strategist at Toronto-Dominion, Canada’s largest bank, said by phone on Oct. 15. “Any sort of setback for growth and investment in the energy sector is likely to have a fairly significant knock-on effect for the rest of the economy.”
The slide in oil, caused by a combination of oversupply and falling global demand, is a setback for Canada. Since the recession, most new business investment and jobs have come from the oil-rich province of Alberta. The nation’s trade surplus turned into a deficit in August, and economic growth stalled the previous month. Money managers are boosting bets the Canadian dollar will keep weakening. Hedge funds and other large speculators pushed net-bearish wagers on the currency to 16,167 contracts in the week ending Oct. 17, the most since June, according to the Commodity Futures Trading Commission in Washington. Investors held net-long positions as recently as Sept. 26.
Read more …

Interesting view.
• The Financialization of Life (Real News Network)
Costas Lapavitsas, Economics Professor, Univ. of London: I will present to you some ideas that I have dealt with in my new book, Profiting without Producing, which has just come out, which discuss finance and the rise of finance. I can’t tell you very much about Baltimore because I don’t know about it, but I will tell you quite a few things about what I call the financialization of capitalism, which impacts on Baltimore and on many other places. So, getting on with it, and very quickly because time is short, I think it’s fair to say and all of us would agree that finance has an extraordinary presence in contemporary mature economies. It’s very clear in the case of the U.S., but equally clear in the case of the United Kingdom, where I live, Japan, about which I know quite a bit, Germany, and so on. There’s no question at all about it.
Finance is a sector of the economy in mature countries which has grown enormously in terms of size relative to the rest of the economy, in terms of penetration into everyday lives of ordinary people, but also small and medium businesses and just about everybody. And in terms of policy influence, finance clearly influences economic policy on a national level in country after country. The interests of finance are paramount in forming economic policy. So that is clear. Finance has become extraordinarily powerful. And that, in a sense, is the first immediate way in which we can understand financialization. Something has happened there, and modern mature capitalism appears to have financialized. Now, what is this financialization? The best I can do right now is to give you the gist of this argument of mine in my book. And I will come clean immediately and tell you that I think financialization is basically a profound historical transformation of modern capitalism.
Read more …

Ambrose has it in for Russia.
• Oil Slump Leaves Russia Even Weaker Than Decaying Soviet Union (AEP)
It took two years for crumbling oil prices to bring the Soviet Union to its knees in the mid-1980s, and another two years of stagnation to break the Bolshevik empire altogether. Russian ex-premier Yegor Gaidar famously dated the moment to September 1985, when Saudi Arabia stopped trying to defend the crude market, cranking up output instead. “The Soviet Union lost $20bn per year, money without which the country simply could not survive,” he wrote. The Soviet economy had run out of cash for food imports. Unwilling to impose war-time rationing, its leaders sold gold, down to the pre-1917 imperial bars in the vaults. They then had to beg for “political credits” from the West. That made it unthinkable for Moscow to hold down eastern Europe’s captive nations by force, and the Poles, Czechs and Hungarians knew it. “The collapse of the USSR should serve as a lesson to those who construct policy based on the assumption that oil prices will remain perpetually high. A seemingly stable superpower disintegrated in only a few short years,” he wrote.
Lest we engage in false historicism, it is worth remembering just how strong the USSR still seemed. It knew how to make things. It had an industrial core, with formidable scientists and engineers. Vladimir Putin’s Russia is a weaker animal in key respects, a remarkable indictment of his 15-year reign. He presides over a rentier economy, addicted to oil, gas and metals, a textbook case of the Dutch Disease. The IMF says the real effective exchange rate (REER) rose 130pc from 2000 to 2013 during the commodity super-cycle, smothering everything else. Non-oil exports fell from 21pc to 8pc of GDP. “Russia is already in a perfect storm,” said Lubomir Mitov, Moscow chief for the Institute of International Finance. “Rich Russians are converting as many roubles as they can into foreign currencies and storing the money in vaults. There is chronic capital flight of 4pc to 5pc of GDP each year but this is no longer covered by the current account surplus, and now sanctions have caused foreign capital to turn negative, too.”
“The financing gap has reached 3pc of GDP, and they have to repay $150bn in principal to foreign creditors over the next 12 months. It will be very dangerous if reserves fall below $330bn,” he said. “The benign outcome is a return to the stagnation of the Brezhnev era in the early 1980s, without a financial collapse. The bad outcome could be a lot worse,” he said. Mr Mitov said Russia is fundamentally crippled. “They have outsourced their brains and lost their technology. The best Russian engineers go to work for Boeing. The Russian railways are run on German technology. It looked as if Russia was strong during the oil boom but it was an illusion and now they are in an even worse position than the Soviet Union,” he said.
Read more …

The TTIP is a real evil, that’s why it’s being discussed in secret.
• Big Tobacco Puts Countries On Trial As Concerns Over TTIP Mount (Independent)
Tiny Uruguay may not seem a likely front line in the war of the quit smoking brigade against Big Tobacco. But the Latin American country has unwittingly found itself not just in the thick of that battle, but in the middle of an even bigger fight – that of the rising opposition to international free trade deals. Philip Morris is suing Uruguay for increasing the size of the health warnings on cigarette packs, and for clamping down on tobacco companies’ use of sub-brands like Malboro Red, Gold, Blue or Green which could give the impression some cigarettes are safe to smoke. The tobacco behemoth is taking its legal action under the terms of a bilateral trade agreement between Switzerland – where it relatively recently moved from the US – and Uruguay. The trade deal has at its heart a provision allowing Swiss multinationals the right to sue the Uruguayan people if they bring in legislation that will damage their profits.
The litigation is allowed to be done in tribunals known as international-state dispute settlements (ISDS), ruled upon by lawyers under the auspices of the World Trade Organisation. Such an ISDS agreement is also core to the EU’s planned Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) treaty being negotiated with the US. The critics of TTIP fear the tribunals will see US multinationals sue European governments in such areas as regulating tobacco, health and safety, and quality controls. In the UK, critics have been particularly vocal about fears US healthcare companies now running parts of the NHS might use ISDS tribunals to sue future British governments wanting to reverse the accelerating privatisation of parts of the health service. The British Government argues that such worries are “misguided” and says TTIP will create jobs and be good for the economy. ISDS agreements are necessary to give companies the confidence to invest, it says, particularly in more politically unstable countries.
Read more …

Getting worse all the time.
• Tesco’s Profits Black Hole Bigger Than Expected (Guardian)
Tesco has revealed that the hole in its first half profits is bigger than previously thought and runs back into previous financial years, plunging the embattled supermarket into fresh turmoil. Confidence in what was once one of the most respected companies in the FTSE 100 was also dealt a fresh blow by the admission that it was unable to provide any guidance on full-year profits because of a number of uncertainties, sending its shares down 6% to 170p.25p when the stock market opened. The company’s shares have almost halved in value since the start of this year. It also revealed that its under fire chairman Sir Richard Broadbent is to be replaced, after a disastrous three year tenure. Tesco said the month-long investigation by forensic accountants from Deloitte had established that its first half profits had been artificially inflated by £263m rather than the £250m the company had originally estimated.
The problem relates to when the retailer books payments received from suppliers who pay the big grocery chains to run in-store promotions on their behalf. Deloitte said £118m of the figure related to the first six months of the current financial year but that £145m related to previous years. Chief executive Dave Lewis said the Deloitte report would be passed to the FCA and that from the company’s perspective this “drew a line” under the issue. With that out of the way he outlined three immediate priorities: to restore the competitiveness of the core UK business, to protect and strengthen its balance sheet and to begin “the long journey of rebuilding trust and transparency in the business and the brand”. The investigation, prompted by information from a whistleblower, has resulted in the suspension of eight senior executives, including Chris Bush, the head of the UK food business.
Read more …

The costs of cleaner energy, or the cost of political incompetence?
• EU Braces for Battle to Set Energy, CO2 Goals for Next Decade (Bloomberg)
European Union leaders face heated negotiations today on a deal to toughen emission-reduction policies in the next decade and boost the security of energy supplies amid a natural-gas dispute between Russia and Ukraine. The main challenge for the 28 heads of government will be to iron out differences on a strategy that ensures cheaper and safer energy while stepping up climate-protection measures. The agenda of the two-day Brussels summit, the final one to be chaired by EU President Herman Van Rompuy, also features a debate on the European economy and on measures to prevent the spread of the Ebola virus. Countries including Poland, Portugal, Spain, France and the U.K. have signaled that the outstanding issues that leaders will need to resolve at the gathering include sharing the burden of carbon cuts, the nature of energy targets and plans for power and gas interconnectors.
“It will not be easy to reach an accord, many countries have energy problems, and some have re-opened coal mines,” French energy minister Segolene Royale told lawmakers in Paris yesterday. “But I think we will have the wisdom, the strength, and the sense of responsibility to reach an accord.” EU leaders plan to back a binding target to cut greenhouse gases by 40% by 2030 from 1990 levels, accelerating the pace of reduction from 20% set for 2020, according to draft conclusions for the meeting obtained by Bloomberg News. An agreement would ensure the bloc remains the leader in the fight against global warming before a United Nations climate summit in Lima in December and a worldwide deal expected to be clinched in 2015 in Paris, according to the European Commission, the EU’s executive arm. While differences among member states on the carbon target are narrowing down, leaders still need to resolve issues including emissions burden-sharing, which pits richer countries in western Europe against mostly ex-communist east and central European nations led by Poland.
Read more …

“Coal is at a crossroads in Europe. For some, the fuel is too polluting to keep burning in such high quantities. But for others, it is too cheap, too abundant and too politically strategic to abandon.” Germany invests heavily in brown coal.
• Several Factors Conspire To Increase Fossil Fuel Use (FT)
Under slate-grey skies one chilly October morning in Warsaw, Ewa Kopacz, Poland’s new prime minister, saw first-hand the front line in Europe’s high-stakes battle over the future of coal. Outside parliament, where she was to make her maiden speech as the country’s leader, hundreds of helmeted miners sounded foghorns, chanted slogans and waved banners in a protest calling for action to save their industry. Coal is at a crossroads in Europe. For some, the fuel is too polluting to keep burning in such high quantities. But for others, it is too cheap, too abundant and too politically strategic to abandon. The midterm future of Europe’s energy mix, and that of coal, may well be decided in Poland, the EU’s second-largest producer and consumer of the black stuff. Coal is the dirtiest of all fossil fuels. Historically, its use in environmentally aware Europe has been falling. But consumption has ticked up since the US shale gas boom sent coal prices tumbling, and countries such as Poland are resisting calls to switch to lower-emission alternatives.
“It will be extremely difficult politically and economically for us just to end our dependence on coal,” says Oktawian Zajac, head of the coal practice at Boston Consulting Group in Warsaw. “In the medium term, the top priority is not to switch away from coal, but to produce coal that is economically justifiable.” That is not the view in Brussels, where diplomats are trying to hammer out an EU deal to curb the bloc’s carbon emissions by 2030. That deal is likely to revolve around whether countries are willing to pay for the environmental benefits of reducing their fossil fuel usage given the costlier alternatives. The biggest impediment to agreement is coal-hungry Poland, and the angry miners who won support in Ms Kopacz’s speech. “I realise how important environmental concerns are … but my government will not accept increases in the costs of energy in Poland and the impact on the economy,” the prime minister said, adding that the fuel was of strategic national importance.
Read more …

Sao Paulois sinking into disaster.
• Water Crisis Seen Worsening as Sao Paulo Nears ‘Collapse’ (Bloomberg)
Sao Paulo residents were warned by a top government regulator today to brace for more severe water shortages as President Dilma Rousseff makes the crisis a key campaign issue ahead of this weekend’s runoff vote. “If the drought continues, residents will face more dramatic water shortages in the short term,” Vicente Andreu, president of Brazil’s National Water Agency and a member of Rousseff’s Workers’ Party, told reporters in Sao Paulo. “If it doesn’t rain, we run the risk that the region will have a collapse like we’ve never seen before,” he later told state lawmakers. The worst drought in eight decades is threatening drinking supplies in South America’s biggest metropolis, with 60% of respondents in a Datafolha poll published yesterday saying their water supplies were restricted at least once in the past 30 days. Three-quarters of those people said the cut lasted at least six hours.
Rousseff, who is seeking re-election in the Oct. 26 election against opposition candidate Aecio Neves, is stepping up her attacks of Sao Paulo state’s handling of the water crisis, saying in a radio campaign ad yesterday that Governor Geraldo Alckmin was offered federal support and refused. Neves, who polls show is statistically tied with Rousseff, and Alckmin are both members of the Social Democracy Party, known as PSDB. Neves said yesterday on his website that ANA is being used by the PT for it’s own purposes. “The agency could have been a much better partner to Governor Alckmin,” he said.
Read more …

How about some solid policies?
• Some US Hospitals Weigh Withholding Care To Ebola Patients (Reuters)
The Ebola crisis is forcing the American healthcare system to consider the previously unthinkable: withholding some medical interventions because they are too dangerous to doctors and nurses and unlikely to help a patient. U.S. hospitals have over the years come under criticism for undertaking measures that prolong dying rather than improve patients’ quality of life. But the care of the first Ebola patient diagnosed in the United States, who received dialysis and intubation and infected two nurses caring for him, is spurring hospitals and medical associations to develop the first guidelines for what can reasonably be done and what should be withheld. Officials from at least three hospital systems interviewed by Reuters said they were considering whether to withhold individual procedures or leave it up to individual doctors to determine whether an intervention would be performed. Ethics experts say they are also fielding more calls from doctors asking what their professional obligations are to patients if healthcare workers could be at risk.
U.S. health officials meanwhile are trying to establish a network of about 20 hospitals nationwide that would be fully equipped to handle all aspects of Ebola care. Their concern is that poorly trained or poorly equipped hospitals that perform invasive procedures will expose staff to bodily fluids of a patient when they are most infectious. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is working with kidney specialists on clinical guidelines for delivering dialysis to Ebola patients. The recommendations could come as early as this week. The possibility of withholding care represents a departure from the “do everything” philosophy in most American hospitals and a return to a view that held sway a century ago, when doctors were at greater risk of becoming infected by treating dying patients. “This is another example of how this 21st century viral threat has pulled us back into the 19th century,” said medical historian Dr. Howard Markel of the University of Michigan.
Read more …