Pablo Picasso Tête de femme �1926

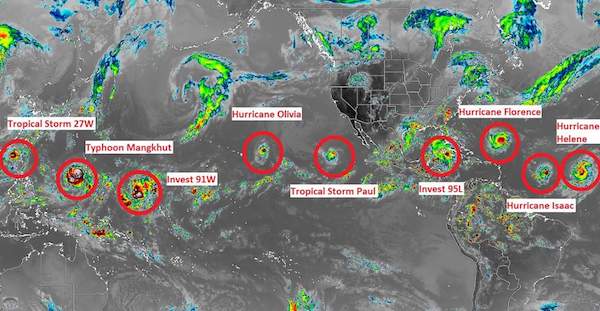
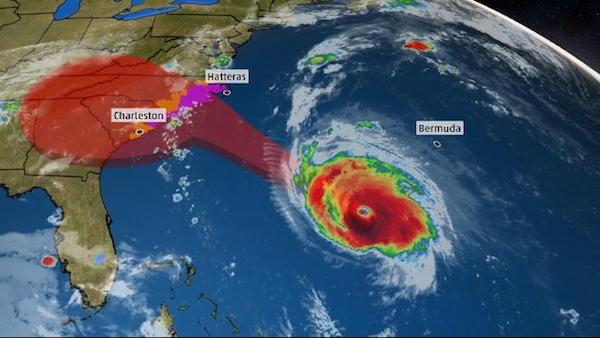
Mangkhut is twize the size of Florence and a lot stronger. Tons of scary videos from Hong Kong.
• Typhoon Mangkhut Heads Towards China As Dozens Killed In Philippines (G.)
Typhoon Mangkhut killed at least 30 people in the Philippines as it obliterated homes and crops and caused massive flooding, and is now on course to plough into China’s southern coast. Presidential adviser Francis Tolentino said the heaviest casualty was recorded in the mountainous Cordillera region in northern Luzon, where heavy rains caused landslides that left 24 people dead and 13 more missing. Four others – including two children – were buried in a landslide in Nueva Ecija, another in Kalinga, and one person was killed by a falling tree in Ilocos Sur, Tolentino said.
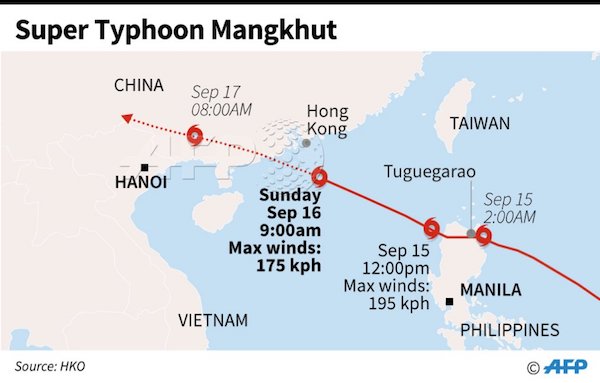
The storm, which was the strongest the region has seen this year, was not as ferocious as feared, though due to the remote areas where the typhoon hit, the full death toll and extent of the destruction is still unknown. By Sunday morning, it was hurtling towards China’s heavily populated southern coast with winds of 177km/h (110mph). In Hong Kong, where the huge storm is expected to skirt just 100km (62 miles) south of the city, officials raised the storm alert to a T10, its highest level. Businesses have been boarded up and most flights cancelled.
Philippines (2018) – Typhoon Mangkhut – Seems like the world's ending
.
.#Hurricane #hurricaneflorence #Florence #NorthCarolina #SouthCarolina #EastCoast #Virginia #NationalHurricaneCenter #landfall #TropicalStorm #Typhoon #TyphoonMangkhut #weather #hurricanes #MangKhut pic.twitter.com/MsGQPiiMrV— Ruivismo (@blogruivismo) September 16, 2018

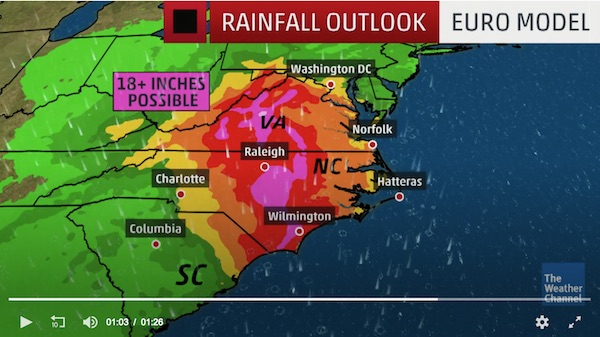
The water has nowhere to go.
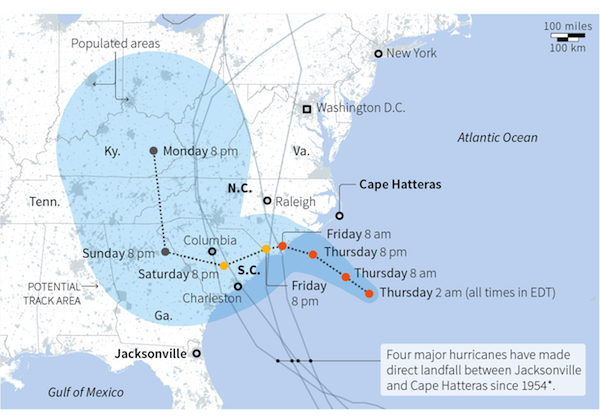
• Florence Dumps ‘Epic’ Amounts Of Rain On Carolinas (BBC)
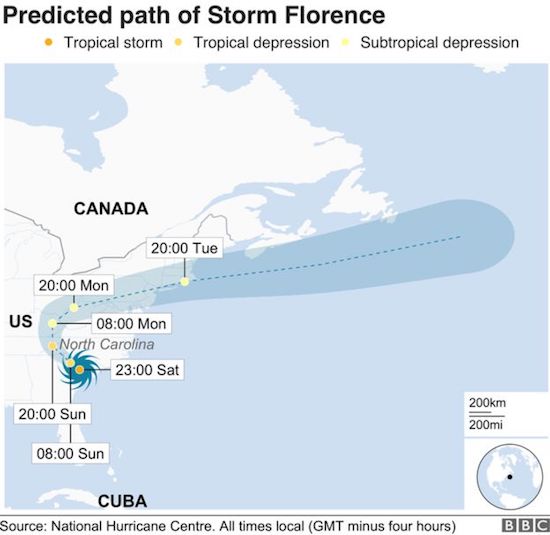
US east coast communities face “epic amounts of rainfall” from tropical storm Florence, which has been linked to at least 12 deaths. It has caused catastrophic flooding since arriving as a category one hurricane on Friday. Some towns have already seen 2ft (60cm) of rain in two days, with totals forecast to top 3.5ft (1m) in places. It is feared that more communities could become deluged as the storm crawls west at only 2mph (3km/h). “This system is unloading epic amounts of rainfall, in some places measured in feet and not inches,” North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper said on Saturday. He urged against residents attempting to return home, warning that “all roads in the state are at risk of floods”.

“There’s no snooze button on the national debt clock..”
• ‘We’re Using the Future for a Fiscal Dumping Ground’ (Barron’s)
There’s no snooze button on the national debt clock, though you wouldn’t know it by the way public alarm has quieted as the situation grows worse. October begins a new fiscal year for the U.S. government—and a faster ballooning of how much it owes. Barring a behavioral miracle in Congress, trillion dollar yearly budget shortfalls will return, perhaps as soon as the coming year. And unlike the ones brought by the financial crisis and Great Recession of 2007-09, these will start during a period of relative plenty, and won’t end. Debt held by the public, a conservative tally of what America owes, will swell from $15.7 trillion at the end of September, or 78% of GDP to $28.7 trillion in a decade, or 96% of GDP.
Those estimates, provided by the Congressional Budget Office, are based on reasonable assumptions about economic growth, inflation, employment, and interest rates, but they leave out some important things. They assume that the nation’s need for increased infrastructure investment, estimated by the American Society of Civil Engineers at $1.4 trillion through 2025, goes unmet. They don’t account for the possibility of another financial crisis, or war, or a rise in the frequency or severity of natural disasters, and they assume that some Trump tax cuts will expire in 2025.
There is no clear milestone that marks the moment a country loses control of its finances, but consider how the bar has already been lowered for what seems possible in Congress. Even debt scolds no longer talk seriously about America paying down what it owes, or holding the dollar amount steady. The new path of fiscal prudence involves containing debt at some manageable percentage of GDP, and the opportunity for that is slipping.

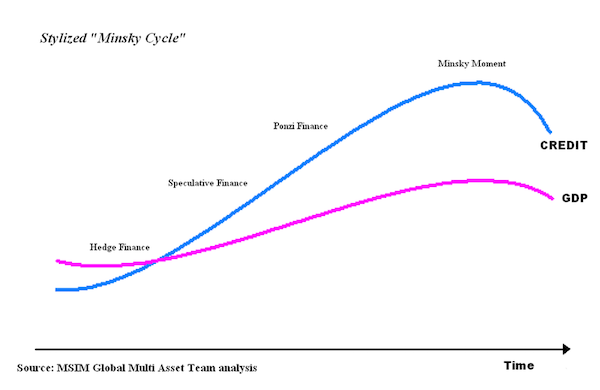
“If I have to blame anybody, I will blame Bernanke..”
• The Lehman Brothers Bankruptcy (ET)
Sept. 15 marks the 10th anniversary of the collapse of Lehman Brothers, which had unprecedented ramifications worldwide. Painful lessons have been learned, but the debate continues among economists about whether the crisis could have been handled better. Lehman was the fourth-largest U.S. investment bank before it filed for bankruptcy. With $639 billion in assets, it was the biggest bankruptcy in U.S. history. It was also the largest victim of the subprime mortgage crisis that swept through global financial markets. And its collapse intensified the market shock, which wiped out nearly $10 trillion from global equity markets in October 2008, the largest monthly decline on record. The policymakers who handled Lehman’s bankruptcy in 2008 argue they did all they could.
However, economist Steve Keen, author of “Can We Avoid Another Financial Crisis?”, believes policymakers had a great deal of responsibility for causing the crisis. Keen is a harsh critic of mainstream economists who ignored mounting private debt in their forecasts and policy recommendations. “They could have prevented the bubble burst in the first place,” he said. He thinks the former chairman of the Federal Reserve, Ben Bernanke, was one of those who failed to recognize the risk created by the private debt explosion. “All these regulators were collecting data on global private debt and not worrying about it because economic theory said it did not matter,” he said. “If I have to blame anybody, I will blame Bernanke,” he said, adding that Bernanke “was the main academic economist saying ‘Don’t worry about the level of private debt.’”

But when? It’ll take a long time still before it becomes an option, and by then Brexit will be much closer.
• Give Britain A New Referendum On Brexit – London Mayor (G.)
The mayor of London has issued a dramatic call for another referendum on EU membership, insisting that the people must be given the chance to reject a Brexit deal that will be bad for the economy, jobs and the NHS. Writing in the Observer, Sadiq Khan says that, with so little time left to negotiate, there are now only two possible outcomes: a bad deal for the UK or “no deal” at all, which will be even worse. “They are both incredibly risky and I don’t believe Theresa May has the mandate to gamble so flagrantly with the British economy and people’s livelihoods,” he writes. Khan says that backing a second referendum was never something he expected to have to do.
But so abject has been the government’s performance, and so great is the threat to living standards and jobs, he says, that he sees no alternative than to give people a chance to stay in the EU. “This means a public vote on any Brexit deal obtained by the government, or a vote on a ‘no-deal’ Brexit if one is not secured, alongside the option of staying in the EU,” he writes. “People didn’t vote to leave the EU to make themselves poorer, to watch their businesses suffer, to have NHS wards understaffed, to see the police preparing for civil unrest or for our national security to be put at risk if our cooperation with the EU in the fight against terrorism is weakened.” The intervention from one of Labour’s most powerful politicians will put yet more pressure on the party leader Jeremy Corbyn to throw his support behind another referendum at Labour’s annual conference, which opens in Liverpool next weekend.

Italy had signed -oil- deals with Gaddafi.
• Italy Faults France for Gaddafi’s Downfall and Migrant Crisis (Sp.)
In Rome, the responsibility for the influx of migrants is laid on France, which persuaded NATO countries to get rid of Gaddafi. As a result, Libya is now torn apart by rival factions and an ongoing conflict between its two governments. “It is clearly now undeniable that this country (Libya) finds itself in this situation because someone, in 2011, put their own interests ahead of those of the Libyan people and of Europe itself,” Italian Defense Minister Elisabetta Trenta wrote on Facebook. “France, from this point of view, is partly to blame,” she added. Italian parliamentary speaker Roberto Fico was even more explicit, pointing to “a serious problem that has come from France.”
Italy’s Deputy Prime Minister Matteo Salvini also chimed in, blaming former French President Nicolas Sarkozy for unleashing the war in Libya and the present government for adding fuel to the flames of the Libyan conflict. Italians are filled with nostalgia each time they recall the time when Rome and Tripoli signed an agreement to allow Italian companies to extract oil in Libya. The Gaddafi government was holding back the flow of migrants to Europe and the country’s GDP was the second biggest in Africa and the first among the Arabic-speaking states of the Maghreb. In Rome, the emphasis is that the decision to overthrow Gaddafi was made without taking into account the views of Italy.
Seven years on, the French look equally unenthusiastic about the so-called “Libyan Revolution,” with President Emmanuel Macron admitting that the intervention was a mistake. “I remember how some people decided to get rid of the Libyan leader without having any action plan for the future. We plunged Libya into a situation of lawlessness without having a chance to rectify the situation,” Macron said when speaking in the Tunisian parliament earlier this year.

Don’t stop talking.
• Trump ‘Likely’ To Announce New China Tariffs As Early As Monday (R.)
U.S. President Donald Trump is likely to announce new tariffs on about $200 billion on Chinese imports as early as Monday, a senior administration official told Reuters on Saturday. The tariff level will probably be about 10 percent, the Wall Street Journal reported, quoting people familiar with the matter. This is below the 25 percent the administration said it was considering for this possible round of tariffs. The upcoming tariffs will be on a list of items that included $200 billion worth of internet technology products and other electronics, printed circuit boards and consumer goods including Chinese seafood, furniture and lighting products, tires, chemicals, plastics, bicycles and car seats for babies.
It was unclear if the administration will exempt any of the products that were on the list, which was announced in July. On Friday, White House spokeswoman Lindsay Walters said Trump “has been clear that he and his administration will continue to take action to address China’s unfair trade practices. We encourage China to address the long-standing concerns raised by the Unites States.” Trump had already directed aides to proceed with tariffs, despite Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin’s attempts to restart trade talks with China.

Do you see it happening?
• Europe’s Meat And Dairy Production Must Halve By 2050 (G.)
Europe’s animal farming sector has exceeded safe bounds for greenhouse gas emissions, nutrient flows and biodiversity loss, and urgently needs to be scaled back, according to a major report. Pressure on livestock farmers is set to intensify this century as global population and income growth raises demand for meat-based products beyond the planet’s capacity to supply it. The paper’s co-author, Professor Allan Buckwell, endorses a Greenpeace call for halving meat and dairy production by 2050, and his report’s broadside is squarely aimed at the heart of the EU’s policy establishment.
Launching the report, the EU’s former environment commissioner Janez Potocnik said: “Unless policymakers face up to this now, livestock farmers will pay the price of their inactivity. ‘Protecting the status quo’ is providing a disservice to the sector.” The study calls for the European commission to urgently set up a formal inquiry mandated to propose measures – including taxes and subsidies – that “discourage livestock products harmful to health, climate or the environment”. Livestock has the world’s largest land footprint and is growing fast, with close to 80% of the planet’s agricultural land now used for grazing and animal feed production, even though meat delivers just 18% of our calories.