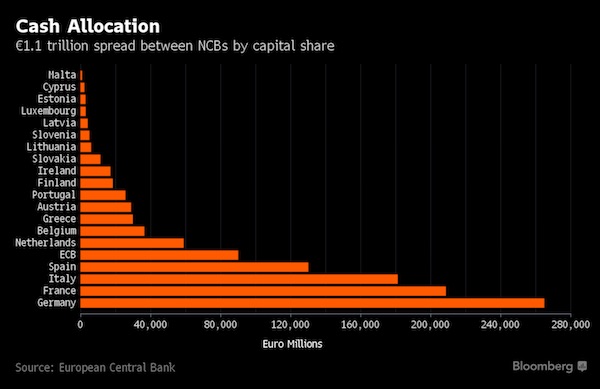
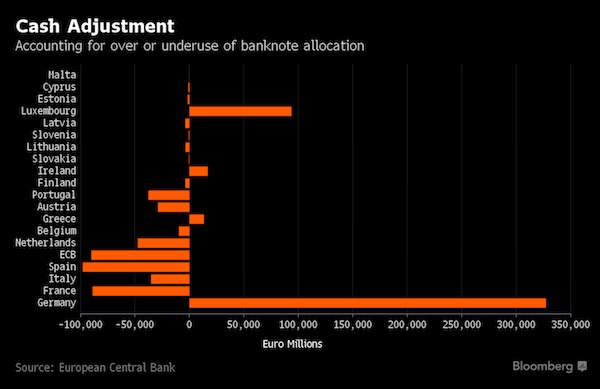
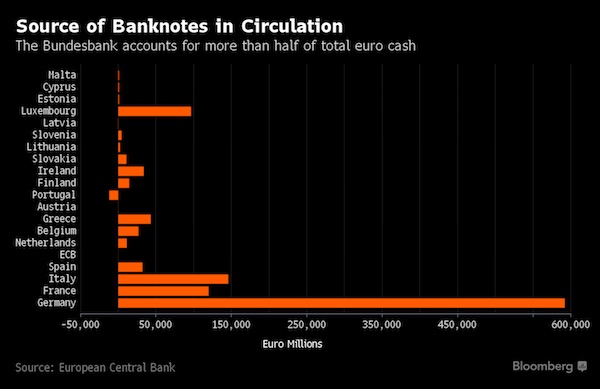
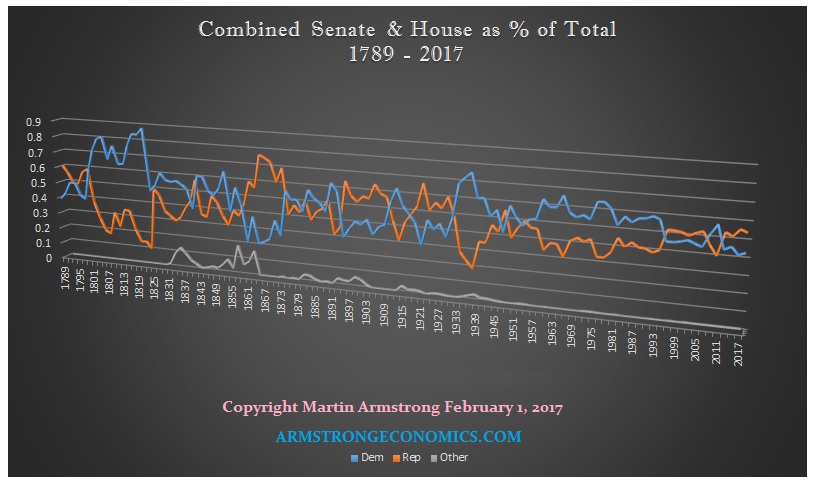
Wassily Kandinsky Free Curve to the Point – Accompanying Sound of Geometric Curves 1925

Is there anyone alive who thinks that the US, EU, global economies are strong enough to withstand large scale liquidity withdrawal?
• This Fed Grows Relentlessly More Hawkish (WS)
“The economy is in great shape,” Fed Chairman Jerome Powell said today at the press conference after the FOMC meeting. Inflation as measured by the Fed’s preferred low-ball measure “core PCE” has hit the Fed’s target of 2%, and the Fed expects it to hit 2.1% by year-end. Inflation as measured by CPI jumped to 2.8%. “Job gains have been strong,” today’s statement said. The “unemployment rate has declined,” while “growth of household spending has picked up,” and “business fixed investment has continued to grow strongly.” This is no longer the crisis economy of yore. But the interest rates are still low and stimulative, befitting for a crisis economy. So something needs to be done, and it’s getting done, if “gradually.”
There were all kinds of intriguing elements in the FOMC’s increasingly hawkish but “gradual” hoopla today. By unanimous vote, the FOMC raised its target for the federal funds rate by a quarter percentage point to a range between 1.75% and 2.0%. This was expected; what’s intriguing is the unanimous vote, unlike prior rate hikes. Four rate hikes in 2018 (two more this year) are now gradually being baked in, according to the median expectation of the 15 members of the FOMC, per the infamous “dot plot” with which the Fed tries to communicate potential rate moves: One member expects 5 rate hikes in 2018; seven members expect 4 hikes; five members expect 3 hikes, and two members expect no more hikes.
At the March meeting, four rate hikes had appeared in the dot plot as a real but more distant possibility. Two more hikes this year would bring the top end of the target range to 2.5% by year-end. This shows the 2018 section of the dot plot:
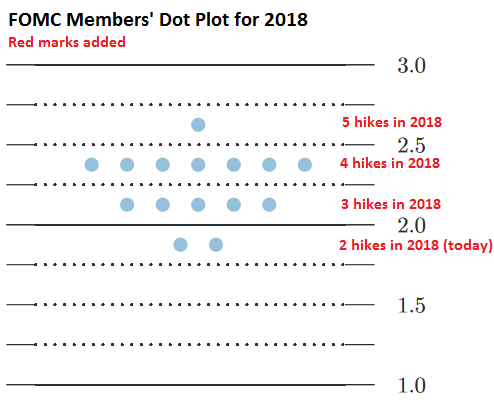
Rates are expected to continue to rise, three times in 2019 and once in 2020, nudging the federal funds rate to nearly 3.5%. A presser after every meeting – oh boy. During the press conference, Powell said that, starting next January, there will be a press conference after every FOMC meeting. This idea has been mentioned a couple of times recently to prepare markets for it. Now it’s official. As in every Fed announcement, it’s no biggie, really, trust us. The move is designed to “explain our actions and answer your questions,” Powell said. It was “only about improving communications.” It didn’t mean at all that the Fed would be speeding up its rate hikes, he said.
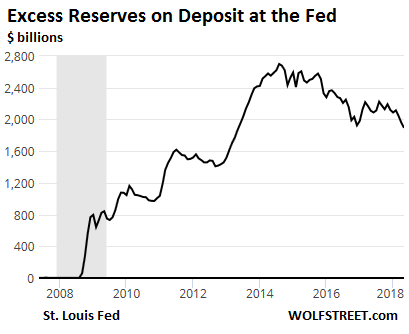
[..] Interest paid to the banks on excess reserves gets a makeover. Banks have about $1.89 trillion in “excess reserves” on deposit at the Fed. The Fed has been paying banks interest on these excess reserves at a rate that was equal to the top of the Fed’s target range – so 1.75% since the last rate hike, which amounts to an annual rate of $33 billion of easy profits for the banks. In theory with today’s rate hike, the FOMC would also have increased the rate it pays on excess reserves to 2.0%.

But the European economy is not ready. What now, accelerate Target2 even more?
• ECB Gets Ready To Pull The Plug On Stimulus Scheme (R.)
The ECB will debate on Thursday whether to end its huge asset purchases by year-end, in what would be its biggest step towards dismantling crisis-era stimulus credited with pulling the euro zone economy out of recession. Financial investors are coming to terms with the end of a decade of easy money from the world’s top central banks, with the Federal Reserve on Wednesday raising interest rates for a seventh time in 3-1/2 years in a further shift from policies used to battle the 2007-2009 financial crisis and recession. Meeting as growth is slowing and political populism threatens to set off market turbulence, the ECB is expected to argue that its 2.55 trillion euro bond-buying scheme has done its job in bringing the 19-member currency bloc back from the brink of collapse.
Whether policymakers take the actual decision at their meeting in Riga on Thursday or hold off until July appears secondary as they have long argued that the scheme, commonly known as quantitative easing (QE), should be concluded and the policy focus shift to the expected path of interest rates. The biggest complication could be the increasingly murky economic outlook, weighed down by a developing trade war with the United States, a populist challenge from Italy’s new government and softening export demand. But these factors could actually hasten the ECB’s decision rather than hold it back as the bank has little policy firepower left and a further weakening of the outlook could make a later exit more difficult.
“We believe the ECB may be in a hurry to close the QE chapter,” Bank of America Merrill Lynch said in a note to clients. “We think this is essentially political, as the ECB would not want its monetary policy to be affected by claims of supporting or conversely impairing the new policy course in Italy.”

Don’t forget the BOJ and China.
• The ECB, Not The Fed, Is The Match That Will Spark Bond Market Volatility (MW)
Rising real interest rates haven’t yet made for a sustained pickup in Treasury volatility, leaving some investors to ask what it would take to spark some turbulence. Danielle DiMartino Booth of Quill Intelligence said the European Central Bank, and not the Federal Reserve, holds the key as it looks to set a timetable for winding down its ultra-accommodative policies. With the Federal Reserve’s shrinking balance sheet unable to offset easy global financial conditions on its own, investors should closely watch the ECB at Thursday’s meeting where the central bank is expected to discuss the end of quantitative easing, though the actual wind-down almost certainly remains several months away at the earliest. “The culmination of ECB QE will remove a bond-volatility governor,” said Booth, in a note published on Tuesday.

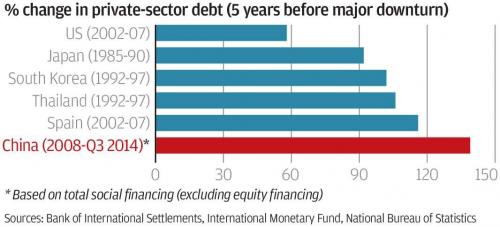
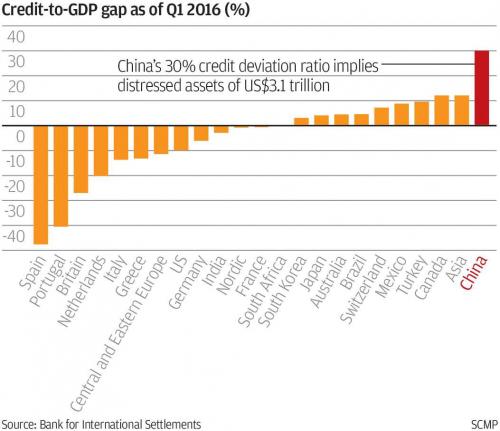
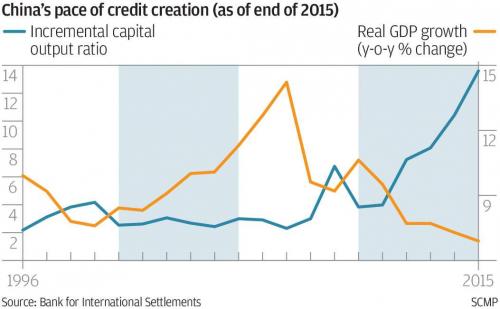
And there comes China. Xi fighting the shadows is like Don Quixote and the windmills.
• China Holds Fire On Rates, Posts ‘Shockingly Weak’ Activity Growth (R.)
China’s economy is finally starting to cool under the weight of a multi-year crackdown on riskier lending that is pushing up borrowing costs for companies and consumers, with data on Thursday pointing to a broad slowdown in activity in May. China’s central bank sparked concerns over the health of the economy earlier in the day when it left short-term interest rates unchanged, surprising markets which had expected it to follow a hike by the Federal Reserve, as it has tended to do. Industrial output, investment and retail sales all grew less than expected, suggesting further weakness ahead if Beijing perseveres with its crackdowns on pollution, questionable local government spending and off-balance sheet “shadow” financing.
The data, which showed the slowest investment growth in over 22 years, “was all shockingly weak by Chinese standards,” economists at Rabobank said, adding that the readings may explain the central bank’s decision to keep rates on hold. “Get ready for headlines talking about Chinese deleveraging hitting the economy – except it isn’t even deleveraging yet! China is walking more of a tightrope than markets believe – and the data underline that issue clearly,” they said. China has been walking a fine line between rolling out measures to curb financial risks and pollution and tapping the brakes so hard that business activity slows sharply.
Much of their effort so far has focused on the banking sector rather than corporate debt reduction or deleveraging – possibly explaining why China’s headline growth has been so surprisingly solid. GDP has expanded at a steady 6.8 percent for three straight quarters. But official and unofficial gauges are now showing the regulatory crackdown is starting to filter through to the broader economy, with companies complaining it is harder to get financing and a growing number of firms defaulting on bonds.

In a world of their own.
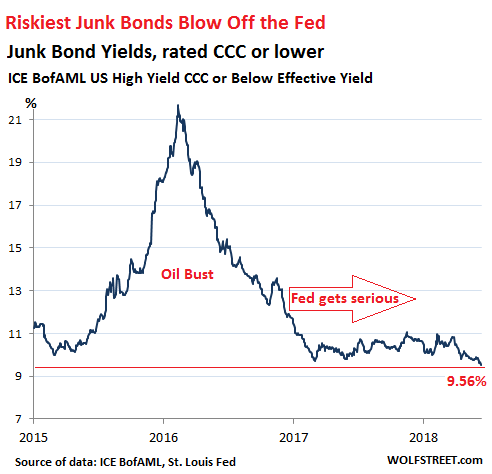
• Riskiest Junk Bonds Completely Blow Off the Fed, Face “Sudden” Reckoning (WS)
High-grade corporate bonds are “gradually” – the key word in everything the Fed says – and reluctantly coming to grips with the new era: Yields are rising and bond prices are falling. The Fed has been laboring to accomplish that. With high-grade debt, the Fed’s plan is working “gradually.” But investors in the riskiest corporate junk debt are totally blowing off the Fed. They’re floating around in their own dream world, facing a very rude awakening. In terms of high-grade corporate bonds, the sell-off has been significant, even if it’s just the beginning. The S&P index for AA-rated bonds is down 2.7% so far this year. As prices have declined, yields have surged, with the average AA yield now at 3.51%, up from around 2.2% in mid to late-2016 (data via ICE BofAML US AA Effective Yield Index):
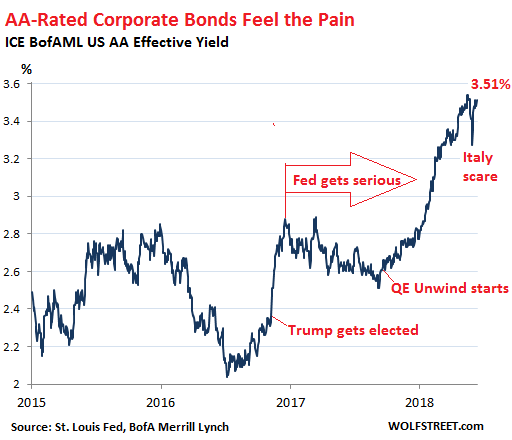
These are the types of bonds that Apple and other large companies hold in their “cash or cash equivalent” accounts that are registered overseas, and that are now being “repatriated” and sold, and the proceeds from the sales are now being plowed into mega-share buyback programs. These corporations, once avid buyers of this high-grade corporate debt, have turned into sellers.
[..] at the riskiest end of the corporate bond spectrum, with bonds rated CCC or below (deep junk), the party that started at the end of the oil bust in February 2016 simply continued. The S&P bond index for CCC-rated bonds has risen 4.5% so far this year (compared to a 2.7% decline for AA-rated index). Since February 2016, when Wall Street decided to plow new money into junk-rated energy companies, the CCC-rated index has skyrocketed 82%. The average yield of bonds rated CCC or lower is now at 9.56%, down from 12.5% in December 2016, when the Fed got serious, and down from 22% during the peak of the oil bust. This is the lowest yield since the bygone era of “QE Infinity” in June 2014:

“Less than 1% of hours with such heavy Tether transactions are associated with 50% of the meteoric rise in bitcoin and 64% of other top cryptocurrencies..”
• Cryptocurrency Bloodbath Continues, Tether Accused Of Manipulating Bitcoin (MW)
The bloodbath in the digital currency market showed no sign of abating, with all major coins trading in the red Wednesday. In the past 24-hours, a further $25 billion has been wiped off the total value of all cryptocurrencies, led by bitcoin, the world’s biggest digital currency, which reached its lowest level since Feb. 5. A single bitcoin traded to an intraday low of $6,133.31 and has since bounced to $6,280.18, down 3.8%, since Tuesday 5 p.m. Eastern Time on the Kraken Exchange. The total value of all cryptocurrencies dipped below $270 billion in late afternoon New York trading, the lowest level since April 11, according to data from CoinMarketCap. The move lower came after a research report found data that it said suggested the price of bitcoin may have been manipulated in late 2017.
In the University of Texas paper, researchers said they uncovered data that they believe shows Tether, a stable coin that is pegged to the U.S. dollar, was used to artificially push up the price of bitcoin during its late 2017 rally towards $20,000. “Less than 1% of hours with such heavy Tether transactions are associated with 50% of the meteoric rise in bitcoin and 64% of other top cryptocurrencies,” wrote John M. Griffin, a finance professor and Amin Shams, a graduate student. Questions have surrounded Tether and crypto exchange Bitfinex, which were both subpoenaed by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission in 2017 seeking data on Tether and its backing of U.S. dollars. Today’s findings will bring the 11th most traded cryptocurrency back into the spotlight.
“Overall, we find that Tether has a significant impact on the cryptocurrency market. Tether seems to be used both to stabilize and manipulate bitcoin prices,” they said.

Losing business support may prove fatal for May.
• The Tories’ Chaotic Brexit Has Lost The Trust Of Business – Jobs Will Go (G.)
[..] away from parliament, and far from the tabloid front pages, a serious breach is opening up in British politics. Last week some of the most senior business leaders in Britain came out of a Brexit meeting at No 10, and promptly tore the prime minister to shreds. “We’re playing economics; [the politicians] are playing politics,” said Paul Drechsler, president of the bosses’ organisation, the Confederation of British Industry. “In the world of business, we’re frustrated. We’re angry.” An extraordinary statement, especially from an executive invited to tea and biscuits with May. If supposedly tame industrialists now talk like this, you have to wonder what sounds come out of the feral lot.
Yet the CBI’s impatience is shared by many. Once the long-haul arm of the Tory movement, the Freight Transport Association lashed out at May last week for “playing chicken with crucial parts of the British economy and the livelihoods of … 7 million Britons”. These are close friends of the Conservative party.As one senior representative of a leading business organisation says: “Over the past two years, most company bosses would never risk saying openly that Brexit is turning out to be a disaster, in case it scared off their best staff.” With fewer than 290 days before Britain formally leaves the EU, their caution is running out.
This is a far bigger story than the one on the front pages about who promised which amendment to which band of Tories. One of the fundamental relationships in the establishment is fracturing – and the consequences for government and economy could prove to be historic.

“Not Trump” is not an identity.
• The North Korea Summit Through the Looking Glass (Jacobin)
On Tuesday, as Donald Trump and Kim Jong-un shook hands for their much-anticipated summit in Singapore, one Korean reporter observed a curious episode. Koreans watching the scene unfold on a TV screen at a railway station in Seoul began applauding. Meanwhile, some nearby Western tourists, perturbed by this development, scratched their heads in confusion. “I am actually baffled to see them clapping here,” said one British tourist. There’s perhaps no better symbol of the gulf in worldwide reactions to the summit than this episode. While South Koreans cautiously celebrated a historic step in the thawing of hostilities that have hung over them for almost seventy years, the Western media seemed to look on with alarm — even anger.
Hostility to the summit, much of it from Democrats and liberals, had been a staple of press coverage in the months leading up to it, often from commentators who just a few months earlier had been panicking about exactly the opposite outcome. But it reached a fever pitch over the last few days. There was, for example, the collective hyperventilation over a symbolic arrangement of North Korean and US flags. There was MSNBC’s Nicole Wallace, who warned that the whole summit was actually a “Trumpian head fake,” a mere artifact of Trump’s “midterm strategy” and his “get out of sitting with Bob Mueller strategy.” Sue Mi Terry of the defense contractor–funded Center for Strategic and International Studies cautioned that “a peace treaty is not okay” and should “come at the end of the process” because it “undermines the justification of our troops staying in South Korea.”

Let’s see what happens when the next ship comes.
• Italy-France Relations Collapse Amid North-African Migrant Spat (ZH)
Italy has postponed high-level discussions with France on Wednesday after French President Emmanuel Macron criticized Rome for refusing to take in a migrant rescue ship full of 629 shipwrecked North Africans – forcing it to divert to Valencia, Spain. After the ship ran out of supplies, the Italian Navy agreed to escort them across the Mediterranean. “Italy’s new Economy Minister Giovanni Tria said he was cancelling a meeting with his French counterpart Bruno le Maire in Paris. The French economy ministry later said the ministers had “agreed that Mr Tria will come to Paris in the coming days”. -AFP
Italy’s decision to refuse the migrants came after their new Interior Minister, Matteo Salvini, said in early June that “the good times for illegals are over” – writing an urgent letter ordering Malta to accept the 629 migrants picked up by the non-governmental organization (NGO) ship MV Aquarius, run by the group SOS Mediterranee. Salvini called Malta the “safest port” for the passengers, advising that Rome would not offer refuge. After Malta refused leading to several days in limbo, Spain agreed to take the passengers. In response to the ordeal, French President Emmanuel Macron accused Italy of “cynicism and irresponsibility,” adding that their EU neighbor is “playing politics” with the refugees.
Meanwhile Gabriel Attal, the spokesman for Macron’s party, called Italy’s actions “nauseating”. Italian Interior Minister Matteo Salvini responded – saying on Tuesday that he would not “accept hypocritical lessons from countries that have preferred to look the other way on immigration,” and adding on Wednesay that unless France issues an “official apology” for Macron’s inflammatory comments, a Friday meeting between Italian Prime Minister Guiseppe Conte and Macron should be canceled.

What will the police do when quantum computing gets involved?
• Apple Steps Up Encrytion To Thwart Police Cracking of iPhones (AFP)
Apple said Wednesday it was strengthening encryption on its iPhones to thwart police efforts to unlock handsets without legitimate authorization. The move by Apple, the latest in an ongoing clash with law enforcement, comes amid reports of growing use of a tool known as GrayKey which can enable police to bypass iPhone security features. Apple said the new features are not designed to frustrate law enforcement but prevent any bypassing of encryption by good or bad actors. “At Apple, we put the customer at the center of everything we design,” the company said in a statement.
“We’re constantly strengthening the security protections in every Apple product to help customers defend against hackers, identity thieves and intrusions into their personal data. We have the greatest respect for law enforcement, and we don’t design our security improvements to frustrate their efforts to do their jobs. Apple said it was working a fix to mitigate the possibility of accessing data from GrayKey or similar tools. Apple said that it has a team that responds to law enforcement and national security requests 24 hours a day. But the company has been a target of some in law enforcement for rejecting efforts to allow easy access to iPhones.
Two years ago, Apple went to court to block an FBI effort to force it to weaken iPhone encryption on the device of a mass shooter in San Bernardino, California, but officials dropped the case after finding a tool to unlock the phone.

As square pegs and round holes go, this one will linger… Greeks don’t want the name Macedonia used in any way, Skopje wants nothing else.
• FYROM and Greece Fail To Resolve Bitter Naming Dispute (G.)
Governments in Skopje and Athens have faced a furious backlash as the challenge of solving one of the world’s most bitter diplomatic feuds hit home just a day after Macedonia announced it was willing to change its name. Hours after the two neighbours declaring they had reached a landmark accord that would see the tiny Balkan state rename itself the Republic of North Macedonia, the nation’s president refused point-blank to sign the deal. “My position is final and I will not yield to any pressure, blackmail or threats,” president Gjorge Ivanov, who is backed by the nationalist opposition, told a news conference in Skopje. The agreement had conceded far too much to Greece – even if its ultimate aim was the country’s future membership of Nato and the EU, he said.
The backlash came despite officials in Brussels, London and Washington reacting with unbridled enthusiasm to the breakthrough. Nato secretary general, Jens Stoltenberg welcomed the accord, saying: “This is really an historical agreement by [politicians] who have shown courage and great political leadership.” Greece has long argued that the state’s name – adopted when it broke away from Yugoslavia in 1991 – conveys thinly disguised irredentist claims on its own northern province of Macedonia. The appropriation of figures associated with ancient Greek history – not least Alexander the Great – had reinforced fears in a region prone to shifting borders.
But opposition to the deal was also pronounced in Greece. As in Skopje – where prime minister Zoran Zaev’s leftist coalition was accused of leading the country to national humiliation – prime minister Alexis Tsipras and his leftist Syriza party was also charged with surrendering cherished national rights. One newspaper ran a front-page graphic showing Tsipras, the Greek foreign minister and president being shot by firing squad for treason.

84 scientists from 44 international organisations..
• Antarctic Ice Melting Faster Than Ever (G.)
Ice in the Antarctic is melting at a record-breaking rate and the subsequent sea rises could have catastrophic consequences for cities around the world, according to two new studies. A report led by scientists in the UK and US found the rate of melting from the Antarctic ice sheet has accelerated threefold in the last five years and is now vanishing faster than at any previously recorded time. A separate study warns that unless urgent action is taken in the next decade the melting ice could contribute more than 25cm to a total global sea level rise of more than a metre by 2070. This could lead eventually to the collapse of the entire west Antarctic ice sheet, and around 3.5m of sea-level rise.
Prof Andrew Shepherd, from Leeds University and a lead author of the study on accelerating ice loss, said: “We have long suspected that changes in Earth’s climate will affect the polar ice sheets. Thanks to our satellites our space agencies have launched, we can now track their ice losses and global sea level contribution with confidence.” He said the rate of melting was “surprising.” “This has to be a cause for concern for the governments we trust to protect our coastal cities and communities,” Shepherd added. The study, published in Nature, involved 84 scientists from 44 international organisations and claims to be the most comprehensive account of the Antarctic ice sheet to date.
It shows that before 2012, the Antarctic lost ice at a steady rate of 76bn tonnes per year – a 0.2mm per year contribution to sea-level rise. However since then there has been a sharp increase, resulting in the loss of 219bn tonnes of ice per year – a 0.6mm per year sea-level contribution. The second study, also published in Nature, warns that time is running out to save the Antarctic and its unique ecosystem – with potentially dire consequences for the world. The scientists assessed the probable state of Antarctica in 2070 under two scenarios. The first in which urgent action on greenhouse gas emissions and environmental protection is taken in the next few years, the second if emissions continue to rise unabated and the Antarctic is exploited for its natural resources.