Dorothea Lange Butter bean vines across the porch, Negro quarter, Memphis, Tennessee 1938



When TBTF starts failing, watch your wallet.
• US Banks’ Dismal First Quarter Spells Trouble For 2016 (Reuters)
It is only April, but some on Wall Street are already predicting a rotten 2016 for U.S. banks. Analysts say it has been the worst start to the year since the financial crisis in 2007-2008 and expect poor first-quarter results when reporting begins this week. Concerns about economic growth in China, the impact of persistently low oil prices on the energy sector, and near-zero interest rates are weighing on capital markets activity as well as loan growth. Analysts forecast a 20% decline on average in earnings from the six biggest U.S. banks, according to Thomson Reuters I/B/E/S data. Some banks, including Goldman Sachs, are expected to report the worst results in over ten years.
This spells trouble for the financial sector more broadly, since banks typically generate at least a third of their annual revenue during the first three months of the year. “What’s concerning people is they’re saying, ‘Is this going to spill over into other quarters?'” Goldman’s Richard Ramsden said in an interview. “If you do have a significant decline in revenues, there is a limit to how much you can cut costs to keep things in equilibrium.” Investors will get some insight on Wednesday, when earnings season kicks off with JPMorgan, the country’s largest bank. That will be followed by Bank of America and Wells Fargo on Thursday, Citigroup on Friday, and Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs on Monday and Tuesday, respectively, in the following week.
Banks have been struggling to generate more revenue for years, while adapting to a panoply of new regulations that have raised the cost of doing business substantially. The biggest challenge has been fixed-income trading, where heavy capital requirements, new derivatives rules, and restrictions on proprietary trading have made it less profitable, leading most banks to simply shrink the business. Bank executives have already warned investors to expect major declines across other areas as well. Citigroup CFO John Gerspach said to expect trading revenue more broadly to drop 15% versus the first quarter of last year. JPMorgan’s Daniel Pinto said to expect a 25% decline in investment banking. Several bank executives have warned about declining quality of energy sector loans.

“California, Illinois, New Jersey, Chicago and Austin, would need to put at least 20% of their revenues into their pension plans to prevent a rise in their deficits, while Nevada would have to contribute almost 40%.”
• US Faces ‘Disastrous’ $3.4 Trillion Pension Funding Hole (FT)
The US public pension system has developed a $3.4tn funding hole that will pile pressure on cities and states to cut spending or raise taxes to avoid Detroit-style bankruptcies. According to academic research shared exclusively with FTfm, the collective funding shortfall of US public pension funds is three times larger than official figures showed, and is getting bigger. Devin Nunes, a US Republican congressman, said: “It has been clear for years that many cities and states are critically underfunding their pension programmes and hiding the fiscal holes with accounting tricks.” Mr Nunes, who put forward a bill to the House of Representatives last month to overhaul how public pension plans report their figures, added: “When these pension funds go insolvent, they will create problems so disastrous that the fund officials assume the federal government will have to bail them out.”
Large pension shortfalls have already played a role in driving several US cities, including Detroit in Michigan and San Bernardino in California, to file for bankruptcy. The fear is other cities will soon become insolvent due to the size of their pension deficits. Joshua Rauh, a senior fellow at the Hoover Institution, a think-tank, and professor of finance at the Stanford Graduate School of Business, who carried out the study, said: “The pension problems are threatening to consume state and local budgets in the absence of some major changes. “It is quite likely that over a five to 10-year horizon we are going to see more bankruptcies of cities where the unfunded pension liabilities will play a large role.” The Stanford study found that the states of Illinois, Arizona, Ohio and Nevada, and the cities of Chicago, Dallas, Houston and El Paso have the largest pension holes compared with their own revenues.
In order to deal with the large funding shortfall, many cities and states will have to increase their contributions to their pension funds, either by raising taxes or cutting spending on vital services. Olivia Mitchell, a professor at the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, told FTfm last month that US public pension plans face “grave difficulties”. “I do believe that US cities and towns will continue to suffer, and there will be additional bankruptcies following the examples of Detroit,” she said. Currently, states and local governments contribute 7.3% of revenues to public pension plans, but this would need to increase to an average of 17.5% of revenues to stop any further rises in the funding gap, the research said. Several cities and states, including California, Illinois, New Jersey, Chicago and Austin, would need to put at least 20% of their revenues into their pension plans to prevent a rise in their deficits, while Nevada would have to contribute almost 40%.

“A lot of people are starting to doubt Abenomics.” Very few have ever believed in it. But there was free money to be had.
• Abenomics Rebuked As BlackRock Joins $46 Billion Japan Pullout (BBG)
For global equity investors and Shinzo Abe, it’s splitsville. Starting in the first days of 2016, foreign traders have been pulling out of Tokyo’s stock market for 13 straight weeks, the longest stretch since 1998. Overseas traders dumped $46 billion of shares as economic reports deteriorated, stimulus from the Bank of Japan backfired and the yen’s surge pressured exporters. The benchmark Topix index is down 17% in 2016, the world’s steepest declines behind Italy. Losing the faith of foreigners would be a blow to the Japanese prime minister – they’re the most active traders in a market Abe has held up as a litmus on his growth strategies. “Japan is back,” and “Buy my Abenomics!” he proclaimed during a visit to the New York Stock Exchange in September 2013, when shares were marching to an eight-year high.
Now about half of those gains are gone and BlackRock, the world’s largest money manager, is among firms ending bullish calls on Japan equities. “Japan has been disappointing,” said Nader Naeimi, Sydney-based head of dynamic markets at AMP Capital Investors, which oversees about $115 billion. He’s a long-time fan of Tokyo equities who says he’s now looking for opportunities to sell. “A lot of people are starting to doubt Abenomics.” While markets elsewhere are climbing back from a global selloff, investors in Japan see fewer reasons for optimism. Growing concern that Abenomics – the three-pronged strategy of fiscal and monetary stimulus and structural reform – is falling flat has spurred speculation the nation will slip into deflation, setting back efforts to end three decades of malaise.
Masahiro Ichikawa, a senior strategist at Sumitomo Mitsui, fears a downward spiral. Foreigners are needed to boost the stock market, and if equities don’t rise the public will lose confidence and curb spending, as he sees it. That could send Japan back into deflation. “If foreigners don’t come back, the future of Abenomics could be jeopardized,” he said.

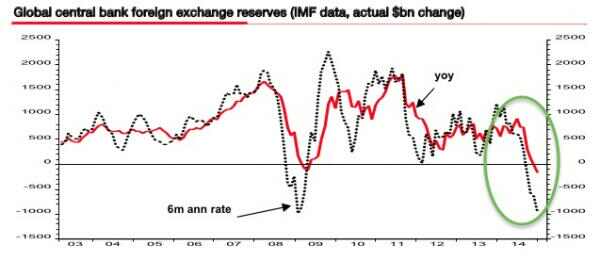
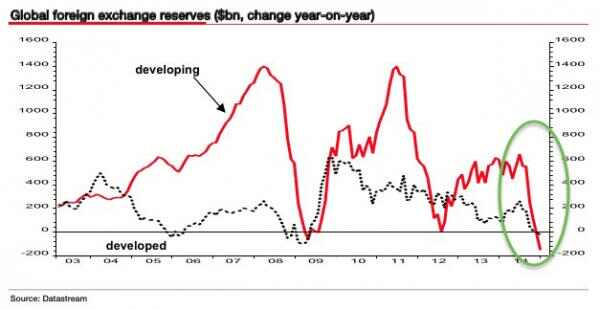
“Reserves will continue to fall until we devalue. Once we get towards $2 trillion the markets will start to panic. They won’t believe that the government can control it any longer..”
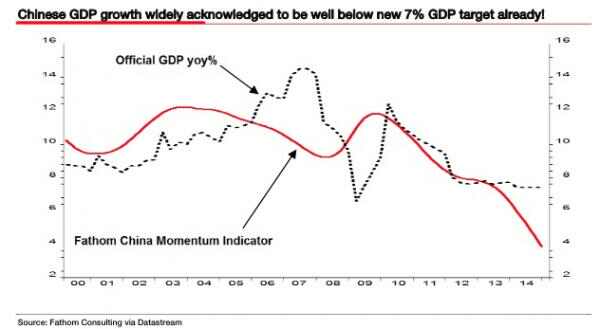
• Beijing Risks ‘Sterling-Style’ Currency Crisis As Deflation Persists (AEP)
A top adviser to the Chinese government has warned that Beijing risks a currency blow-up akin to Britain’s traumatic ordeal in 1992, if it continues trying to defend its exchange rate peg amid a deepening deflation crisis. Yu Hongding, a director of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, said China is caught in two concurrent “deflationary spirals” that are feeding on the other. A major devaluation and a blast of well-targeted fiscal stimulus will be needed to break out of the trap. “They must stop intervening on the exchange market. China needs to devalue by 15pc. They are creating conditions for speculators,” he told the Daily Telegraph, speaking at the Ambrosetti forum of global policymakers on Lake Como.
Prof Yu, a former rate-setter for the PBOC and currently a member of the national planning committee, said the government is making a serious mistake in trying to defend the yuan by burning through foreign exchange reserves, already down to $3.2 trillion from $4 trillion in mid-2014. He warned that the slowdown in capital outlows in March may prove fleeting. “Reserves will continue to fall until we devalue. Once we get towards $2 trillion the markets will start to panic. They won’t believe that the government can control it any longer,” he said. Prof Yu said Beijing had been caught off guard by the relentless slowdown over the last five years. “In 2011 we thought the economy would stabilize, and we thought the same thing in 2012, and again in 2013, and it continued to slide,” he said.
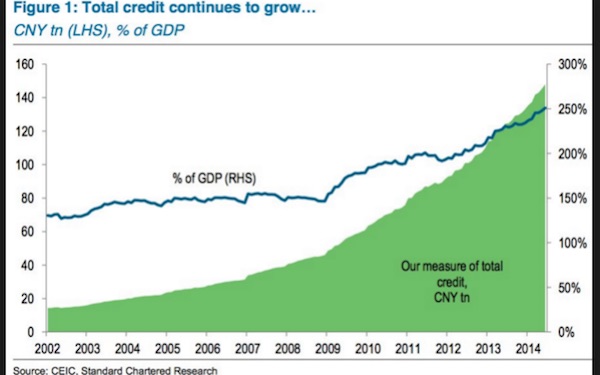
It is far from clear whether the world could handle a 15pc devaluation given the vast scale of Chinese overcapacity, or that the US Treasury and Congress would tolerate such a move. Fears of uncontrollable capital flight and a yuan devaluation were key reasons for the plunge in global equity markets earlier this year, and are clearly what prompted the US Federal Reserve to delay rate rises. The fate of China’s currency has become the most neuralgic issue in global finance. One worry is that a sharp drop in the yuan would set off a second round of ‘currency wars’ across East Asia, transmitting a deflationary shock through the international system as cheap Asian exports flooded into Western markets.
Prof Yu’s life is a remarkable story of achievement in Maoist China. He worked for ten years in a machine factory, wrestling with Marx’s Das Kapital at night before discovering western economics. He devoured Paul Samuelson’s classic text, ‘Foundations of Economic Analysis’, first in a Chinese translation and then in the original after teaching himself English, no easy feat in the Cultural Revolution. He went onto to earn a doctorate at Oxford University, and was still in England when sterling was blown out of the European Exchange Rate Mechanism in September 1992. He still recalls the exact details of the debacle, including the two desperate rate rises by the Bank of England in a single day. “The British experience is very interesting for us,” he said.

Keeps the bubble alive until it doesn’t.
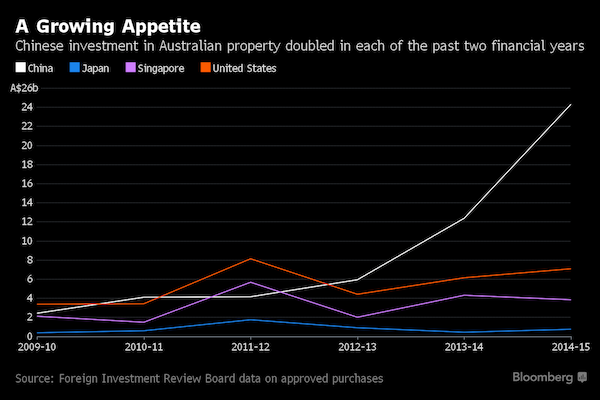
• Chinese Buyers Double Their Aussie Property Investments, Again (BBG)
Chinese appetite for property in Australia shows no sign of waning after buyers doubled investment in the nation’s homes and offices for a second straight year. Spending on Australian residential and commercial real estate rose to A$24.3 billion ($18.4 billion) in the 12 months through June 2015, up from A$12.4 billion a year earlier and A$5.9 billion in 2013, according to the Foreign Investment Review Board’s annual report. All Chinese investors in a survey conducted by KPMG and the University of Sydney want to allocate more money to Australia, a separate report showed on Monday. Real estate is fueling inflows from the world’s second largest economy, which last year overtook the U.S. as Australia’s largest foreign investor.
“Overall we are seeing a strong story of Chinese investment into Australia’s broader economy which is in line with premium products, services and lifestyle-oriented themes,” Doug Ferguson, head of KPMG Australia’s Asia and International Markets and co-author of the report, said in a statement. Purchases by foreigners, many with a connection to China, helped drive an almost 55% jump in home prices across Australia’s capital cities in the past seven years as mortgage rates dropped to five-decade lows. The rising demand has triggered community concern that locals are being priced out of the property market, prompting the government to tighten scrutiny of foreign investment.

Like so many other things these days, perfectly legal.
• In BP’s Final $20 Billion Gulf Settlement, US Taxpayers Pay $15.3 Billion (F.)
Now that a judge has approved BP’s $20 billion settlement over the 2010 gulf oil spill, it is appropriate to look at the overall societal costs, as well as the bottom line to BP. And at tax time, people understandably think about their own taxes, too. The government struck a $20 billion settlement with BP, which is a big number. Yet BP should be able to deduct the vast majority, a whopping $15.3 billion, on its U.S. tax return. That means American taxpayers are contributing quite a lot to this settlement, whether they know it or not. BP can write off the natural resource damages payments, restoration, and reimbursement of government costs. Only $5.5 billion is labeled as a non-tax-deductible Clean Water Act penalty. One big critic of the deal is U.S. Public Interest Research Group, which often rails against tax deductions by corporate wrongdoers.
U.S. Public Interest Research Group has asked the Justice Department to deny tax deductions for BP and other corporate defendants. U.S. PIRG’s has a research report on settling for a lack of accountability that details the tax deductions corporations can claim for legal settlement. However, a change to the tax code may be the only way to get there. The proposed Truth in Settlements Act (S. 1898) would require agencies to report after-tax settlement values. Another bill, S. 1654, would restrict tax deductibility and require agencies to spell out the tax status of settlements. The present tax code allows businesses to deduct damages, even punitive damages. Restitution and other remedial payments are also fully deductible. Only certain fines or penalties are nondeductible. Even then, the rules are murky, and companies routinely deduct payments unless it is completely clear that they cannot.

No bankers have been indicted, and no shareholder has taken them to court.
• British Banks’ ‘Misconduct Bill’ Has Reached Nearly $75 Billion (Reuters)
Lawsuits and misconduct fines have cost Britain’s largest retail banks and customer-owned lenders almost 53 billion pounds ($74.86 billion) over the past 15 years, a new study has found. The scale of the payouts has hampered banks’ efforts to rebuild capital, restricted the amount they are able to lend and reduced dividends for investors. Britain’s banks have been hit by scandals ranging from the manipulation of foreign exchange and benchmark interest rates to the mis-selling of loan insurance and complex interest-rate hedging products. While lenders have struggled to return money to shareholders because of the charges, they have continued to pay billions of pounds in bonuses to staff, the study by the independent think-tank New City Agenda said.
“The profitability of UK retail banks has been imperilled by persistent misconduct,” said John McFall, a director of New City Agenda and former Treasury Committee chairman. “This has made every citizen poorer through our pension funds and our ownership of the bailed out banks.” The report said the mis-selling of payment protection insurance alone cost banks at least 37.3 billion pounds in Britain’s costliest consumer scandal. Lloyds had to set aside 14 billion pounds to cover misconduct between 2010 and 2014, almost twice the amount of any other British lender, the report said.

Yup, that’s how it works.
• The 1% Hide Their Money Offshore – Then Use It To Corrupt Our Democracy (G.)
Over the past 72 hours, you have seen our political establishment operating at a level of panic rarely equalled in postwar history. Britain’s prime minister has had yanked out of him some of his most intimate financial details. Complete strangers now know how much he’s inherited so far from his mum and dad, and the offshore investments from which he’s profited. Yesterday he even took the unprecedented step of revealing the taxes he’d paid over the past six years. Leaders of other parties have responded by summarily publishing their own HMRC returns. In contemporary Britain, where one’s extramarital affairs are more readily discussed in public than one’s tax affairs, this is jaw-dropping stuff. And it will not stop here.
Whatever the lazy shorthand being used by some commentators, David Cameron has not released his tax returns, but merely a summary certified by an accountants’ firm. That halfway house will hardly be enough. If Jeremy Corbyn, other senior politicians and the press keep up this level of attack, then within days more details of the prime minister’s finances will emerge. Nor will the flacks of Downing Street be able to maintain their lockdown on disclosing how many cabinet members have offshore interests: the ministers themselves will break ranks. Indeed, a few are already beginning to do so. But the risk is that all this will descend into a morass of semi-titillating detail: a string of revelations about who gave what to whom, and whether he or she then declared it to the Revenue.
The story will become about “handling” and “narrative” and individual culpability. That will be entertaining for those who like to point fingers, perplexing for those too busy to engage in the detail – and miss the wider truth revealed by the leak which forced all this into public discussion. Because at root, the Panama Papers are not about tax. They’re not even about money. What the Panama Papers really depict is the corruption of our democracy. Following on from LuxLeaks, the Panama Papers confirm that the super-rich have effectively exited the economic system the rest of us have to live in. Thirty years of runaway incomes for those at the top, and the full armoury of expensive financial sophistication, mean they no longer play by the same rules the rest of us have to follow. Tax havens are simply one reflection of that reality.
Discussion of offshore centres can get bogged down in technicalities, but the best definition I’ve found comes from expert Nicholas Shaxson who sums them up as: “You take your money elsewhere, to another country, in order to escape the rules and laws of the society in which you operate.” In so doing, you rob your own society of cash for hospitals, schools, roads… But those who exited our societies are now also exercising their voice to set the rules by which the rest of us live. The 1% are buying political influence as never before. Think of the billionaire Koch brothers, whose fortunes will shape this year’s US presidential elections. In Britain, remember the hedge fund and private equity barons, who in 2010 contributed half of all the Conservative party’s election funds – and so effectively bought the Tories their first taste of government in 18 years.

He will have to reveal a lot more of his own finances, no matter what laws he has lying on the shelf.
• Hit By Panama Row, Cameron Announces New Tax Evasion Law In 2016 (Reuters)
British Prime Minister David Cameron will say on Monday that new legislation making companies criminally liable if employees aid tax evasion will be introduced this year, as he seeks to repair the damage from a week of questions about his personal finances. Cameron published tax records on Sunday to try and defuse criticism over his handling of the fallout from the Panama Papers, in which his late father was mentioned for setting up an offshore fund. After four carefully worded statements in four days, Cameron bowed to pressure and admitted that he had benefited from selling his share in his father’s fund in 2010. He recognized on Saturday that he had mishandled the disclosure. Cameron is leading efforts to persuade British voters to stay in the EU in a June 23 referendum that the polls suggest will be tight, and the tax row has raised concerns among the “in” camp that their cause may have been damaged.
The prime minister will attempt to regain the upper hand when he appears in the House of Commons later on Monday. “This government has done more than any other to take action against corruption in all its forms, but we will go further,” Cameron will say, according to advance excerpts of his statement circulated by his Downing Street office. “That is why we will legislate this year to hold companies who fail to stop their employees facilitating tax evasion criminally liable,” he will say. The plan had already been announced by finance minister George Osborne in March 2015, but previously the commitment was to introduce the legislation by 2020, Downing Street said. The decision to speed up that particular measure is unlikely to satisfy Cameron’s many critics in opposition parties and in some campaign groups that say Britain already has the tools it needs to crack down on tax evasion but lacks the will.

Debt restructuring is still a four letter word in Europe.
• Italy Pushes For ‘Last Resort’ Bank Rescue Fund (FT)
Italy is rushing to cobble together an industry-led rescue to address mounting concerns over the solidity of a banking sector whose woes pose a risk to the wider eurozone economy. Finance minister Pier Carlo Padoan has called a meeting in Rome on Monday with executives from Italy’s largest financial institutions to agree final details of a “last resort” bailout plan. Yet on the eve of that gathering, concerns remain as to whether the plan will be sufficient to ringfence the weakest of Italy’s large banks, Monte dei Paschi di Siena, from contagion, according to people involved in the talks. Italian bank shares have lost almost half their value so far this year amid investor worries over a €360bn pile of non-performing loans — equivalent to about a fifth of GDP. Lenders’ profitability has been hit by a crippling three-year recession.
The plan being worked on, which could be officially announced as soon as Monday evening, recalls the Sareb bad bank created in 2012 by the Spanish government to deal with financial crisis in its smaller cajas banks, say people involved. Although the details remain under discussion, it foresees the establishment of a private vehicle that will include upwards of €5bn in equity contributions – mostly from Italy’s banks, insurers and asset managers – and then a larger debt component. The fund will then mop up shares in distressed lenders. A second vehicle will seek to buy non-performing loans at market prices. “It is a backstop fund,” said one person involved in the talks. The Italian government can provide only limited financial backing because of EU state aid rules and because it is already struggling under a public debt load that amounts to 132.5% of GDP.
The bailout marks the latest and most wide-reaching attempt by Italy to shore up confidence having already sponsored the rescue of four small banks last year and passed a law intended to speed up the sale of bad loans. Both earlier measures failed to eradicate market concerns. [..] people involved in the talks question whether the plan would have the financial scope to provide a buffer of last resort for Monte dei Paschi di Siena. Italy’s third-largest bank was the worst performer in the 2014 European stress tests, with about €170bn in assets and about €50bn in bad loans. It is considered by many bankers to be the major risk to Italian financial stability and regarded as too big to fail. “Monte Paschi is the elephant in the room,” says one of Italy’s top bankers.

Is this an attempt to let Carinthia go broke after all?
• Austria Regulator Imposes 54% Haircut, Long Wait On Heta Bank Creditors (R.)
Austria’s financial markets regulator FMA on Sunday cut the nominal value of “bad bank” Heta Asset Resolution’s senior bonds by more than half, highlighting the long struggle creditors face for repayment if a settlement is not reached. The FMA, which is overseeing the wind-down of Heta, on Sunday announced measures including the bail-in, or haircut, of 54%, the extension of bonds’ maturities to 2023 and the cancellation of coupon payments as of March of last year.The announcement is the latest chapter in a standoff between the province of Carinthia and Heta’s creditors, many of which insist on repayment in full because their bonds were guaranteed by Carinthia, which could push the province into insolvency.
Carinthia guaranteed the bonds of local lender Hypo Alpe Adria before it collapsed and Heta was formed to wind it down. Carinthia says it cannot afford to fully honour the remaining guarantees, which the FMA put at €11.1 billion. Creditors are likely to sue Carinthia to recover the difference between what is paid out to them under Heta’s wind-down and their bonds’ full face value. The FMA put that difference at €6.4 billion, roughly three times the annual budget of Carinthia, a southern province of about 560,000 people that borders Italy and Slovenia and was long the stronghold of far-right politician Joerg Haider. The haircut’s size is based on the amount the FMA expects will be recovered from the sale of Heta’s assets by 2020.
It had said the estimate would be conservative to ensure that, if it is wide of the mark, there is extra revenue to be shared out. Only by the end of 2023 will it be possible to pay out all funds owed, the FMA said, partly in anticipation of many court cases, meaning creditors face a wait of seven years for their repayment of 46% of senior bonds’ face value. Carinthia offered to buy back the bonds it guaranteed, with loans from the Austrian government, for 75% of senior bonds’ face value, plus a last-minute sweetener by the Austrian government that brought the offer to around 82%. Too few creditors accepted the offer when it expired last month, and the question is now whether a compromise can be found or whether the dispute will be settled in court.

Ron Paul doesn’t capture the entire picture, but from a US perspective he’s largely right.
• As Ukraine Collapses, Europeans Tire of Us Interventions (Ron Paul)
On Sunday Ukrainian prime minister Yatsenyuk resigned, just four days after the Dutch voted against Ukraine joining the European Union. Taken together, these two events are clear signals that the US-backed coup in Ukraine has not given that country freedom and democracy. They also suggest a deeper dissatisfaction among Europeans over Washington’s addiction to interventionism. According to US and EU governments – and repeated without question by the mainstream media – the Ukrainian people stood up on their own in 2014 to throw off the chains of a corrupt government in the back pocket of Moscow and finally plant themselves in the pro-west camp. According to these people, US government personnel who handed out cookies and even took the stage in Kiev to urge the people to overthrow their government had nothing at all to do with the coup.
When Assistant Secretary of State Victoria Nuland was videotaped bragging about how the US government spent $5 billion to “promote democracy” in Ukraine, it had nothing to do with the overthrow of the Yanukovich government. When Nuland was recorded telling the US Ambassador in Kiev that Yatsenyuk is the US choice for prime minister, it was not US interference in the internal affairs of Ukraine. In fact, the neocons still consider it a “conspiracy theory” to suggest the US had anything to do with the overthrow. I have no doubt that the previous government was corrupt. Corruption is the stock-in-trade of governments. But according to Transparency International, corruption in the Ukrainian government is about the same after the US-backed coup as it was before.
So the intervention failed to improve anything, and now the US-installed government is falling apart. Is a Ukraine in chaos to be considered a Washington success story? This brings us back to the Dutch vote. The overwhelming rejection of the EU plan for Ukrainian membership demonstrates the deep level of frustration and anger in Europe over EU leadership following Washington’s interventionist foreign policy at the expense of European security and prosperity. The other EU member countries did not even dare hold popular referenda on the matter – their parliaments rubber-stamped the agreement.
Brussels backs US bombing in the Middle East and hundreds of thousands of refugees produced by the bombing overwhelm Europe. The people are told they must be taxed even more to pay for the victims of Washington’s foreign policy. Brussels backs US regime change plans for Ukraine and EU citizens are told they must bear the burden of bringing an economic basket case up to European standards. How much would it cost EU citizens to bring in Ukraine as a member? No one dares mention it. But Europeans are rightly angry with their leaders blindly following Washington and then leaving them holding the bag.

This continues to make my half-Canadian heart bleed. It’s been going on for so long.
• State Of Emergency Over Suicide Epidemic In Canada’s First Nations (G.)
A Canadian First Nation community of 2,000 people has declared a state of emergency after 11 of its members tried to take their own lives, national media reported. CTV News reported on Sunday that the remote northern community of the Attawapiskat First Nation in Ontario experienced an additional 28 suicide attempts last month. More than 100 people in the community have attempted suicide since last September, and one person died, according to CTV. The youngest was 11, the oldest 71. Charlie Angus, the local member of parliament, told the Canadian Press it was part of a “rolling nightmare” of more and more suicide attempts among young people throughout the winter. The Canadian Press said the regional First Nations government was sending a crisis response unit including social workers and mental health nurses to the community following the declaration.
The Health Canada federal agency said in a statement that it had sent two mental health counsellors as part of that unit. Attawapiskat resident Jackie Hookimaw told The Canadian Press that the epidemic started in the autumn when her 13-year-old niece Sheridan killed herself after being bullied at school. “There’s different layers of grief,” she said. “There’s normal grief, when somebody dies from illness or old age. And there’s complicated grief, where there’s severe trauma, like when somebody commits suicide.” Canadian prime minister Justin Trudeau said on Twitter: “The news from Attawapiskat is heartbreaking. We’ll continue to work to improve living conditions for all Indigenous peoples.” Another Canadian First Nation community in the western province of Manitoba appealed for federal aid last month, citing six suicides in two months and 140 suicide attempts in two weeks.

“..three to four times worse than in 1998 or the second great bleaching in 2002.”
• Mass Coral Bleaching Now Affects Half Of Great Barrier Reef (G.)
The mass coral bleaching event smashing the Great Barrier Reef has severely affected more than half its length and caused patches of bleaching in most areas, according to scientists conducting an extensive aerial survey of the damage. “The good news with my last flight is that I found 50 reefs that weren’t bleached, so that may be the southern boundary,” said Terry Hughes from James Cook University. Hughes is the head of the national coral bleaching task force, which has been conducting flights over the length of the reef, mapping bleached areas and recording the severity of the damage. Climate change and a strong El Niño have caused hundreds of kilometres of the reef to bleach, as the higher water temperatures stress the coral, and they expel their symbiotic algae.
If the bleaching is bad enough, or the temperatures remain high for long enough, the corals die, putting the future of reefs at risk. The mass bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef is part of what the US National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration has called the third global bleaching event – the first occurred in 1998. Initial reports suggested only the most northern and remote areas of the Great Barrier Reef were bleaching, but as aerial surveys have continued, scientists have struggled to find a southern boundary. The latest find of a stretch of unaffected reefs around Mackay was a small piece of good news, Hughes said. But he said its significane would be unclear until reefs further south were examined. “It may be a false southern boundary,” Hughes said.
The reefs around Mackay have unusually large tides, which might have pulled in cooler water and saved the coral there. [..] Two weeks ago, the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority reported half the coral in the northern parts of the reef were dead. Hughes said that was consistent with reports from divers north of Port Douglas. Hughes said this was by far the worst bleaching event to have hit the Great Barrier Reef. He said it was three to four times worse than in 1998 or the second great bleaching in 2002. Last year, the Great Barrier Reef narrowly escaped being listed as “in danger” by Unesco, even though environmental groups said it clearly met the criteria. Hughes said the “outstanding universal value” of the reef was now “severely compromised”.
Ariane Wilkinson, a lawyer at Environmental Justice Australia, said the bleaching might cause Unesco to reconsider its decision. “[Unesco] weren’t scheduled to examine the reef this year but in light of the terrible bleaching it is entirely possible that they may decide to look at the reef,” she said. “If the World Heritage system is to have any value, it must address the most serious threats to the most iconic examples of world heritage,” she said. “If any site falls into this category, it is the … Great Barrier Reef.”

Safe third country.
• Fewer Than 0.1% Of Syrians In Turkey In Line For Work Permits (G.)
Fewer than 0.1% of Syrians in Turkey currently stand to gain the right to work under much-vaunted Turkish labour laws, undermining EU claims that the legislation excuses a recent decision to deport Syrian asylum-seekers back to Turkey. Turkish employers have allowed roughly 2,000 – or 0.074% – of Turkey’s 2.7 million Syrians to apply for work permits under new legislation enacted two months ago, according to government figures provided to aid workers at a meeting in late March. The number of permits granted has not yet been disclosed. More applications are expected in the coming months, but the statistic nevertheless highlights how the new law, enacted in January, does not offer blanket access to the labour market for all Syrians in Turkey.
Instead work permits can only be given to those who have the blessing of their employers, many of whom may still be unaware of the law, or unwilling to comply with it since it would require them to pay their employees the minimum wage. The figure was revealed in a speech to aid groups by the head of Turkey’s general directorate for migration management, who said he hoped the number would rise once more people became aware of the law. The news will complicate the new EU-Turkey deal to deport all asylum-seekers arriving to Greece back to Turkey, since the EU has justified the controversial agreement by claiming Turkey was a place that upheld internationally agreed obligations to refugees, including access to legal work. While Turkey is not a full signatory to the 1951 UN refugee convention, EU politicians have sometimes cited the January law as an example of how Turkey maintains the values of the convention by other means.
But in reality the law does not automatically offer most refugees a route out of the black market, several Syrians argued in interviews. Most problematically, the law requires an employer to give his employees a contract before they can apply for a permit. But this is an unattractive proposition for many employers, since they often employ Syrians precisely because they are easily exploited, said Hussam Orfahli, CEO of an Istanbul-based firm that helps Syrians apply for paperwork in Turkey. “If he wants you to have a work permit, then you can get it – but if he doesn’t, then you won’t,” said Orfahli, who has applied for permits on behalf of 60 wealthy clients, but has yet to hear whether any of them have been successful. “The minimum wage is 1,300 Turkish lira [£320] and most employers refuse to give contracts so that they can pay less, and don’t have to pay your health insurance.”

Children injured by (8 hours of!) tear gas. Europe 2016.
• Hundreds Hurt As Refugees Confront FYROM Border Police (AP)
Migrants waged running battles with Macedonian police Sunday after they were stopped from scaling the border fence with Greece near the border town of Idomeni, and aid agencies reported that hundreds of stranded travelers were injured. Macedonian police used tear gas, stun grenades, plastic bullets and a water cannon to repel the migrants, many of whom responded by throwing rocks over the fence at police. Greek police observed from their side of the frontier but did not intervene. More than 50,000 refugees and migrants have been stranded in Greece after Balkan countries closed their borders to the massive flow of refugees pouring into Europe. Around 11,000 remain camped out at the border with Macedonia, ignoring instructions from the government to move to organized shelters as they hold out hope to reach Western Europe.
Clashes continued in the afternoon as migrant groups twice tried to overwhelm Macedonian border security. The increasing use of tear gas reached families in their nearby tents in Idomeni’s makeshift camp. Many camp dwellers, chiefly women and children, fled into farm fields to escape the painful gas. Observers held out hope that evening rainfall, which began about seven hours into the clashes, would dampen hostilities. The aid agency Doctors Without Borders estimated that their medical volunteers on site treated about 300 people for various injuries. Achilleas Tzemos, deputy field coordinator of Doctors Without Borders, told the AP that the injured included about 200 experiencing breathing problems from the gas, 100 others with cuts, bruises and impact injuries from nonlethal plastic bullets.
He said six of the most seriously injured were hospitalized. The clashes began soon after an estimated 500 people gathered at the fence. Many said they were responding to Arabic language fliers distributed Saturday in the camp urging people to attempt to breach the fence Sunday morning and “go to Macedonia on foot.” A five-member migrant delegation approached Macedonian police to ask whether the border was about to open. When Macedonian police replied that this wasn’t happening, more than 100, including several children, tried to scale the fence. Greece criticized the Macedonian police response as excessive. Giorgos Kyritsis, a spokesman for the government’s special commission on refugees, said Macedonian forces had deployed an “indiscriminate use of chemicals, plastic bullets and stun grenades against vulnerable people.”