Pablo Picasso Bust of woman with arms raised 1922

Picked up these numbers last week on Twitter. Chavez announced cancer in late 2012, died early 2013. Oil prices only explain a smal part of it. Economic warfare does the rest.
@spectatorindex – Venezuela GDP growth.
2012: 5.6%
2013: 1.3%
2014: -3.9%
2015: -6.2%
2016: -17%
2017: -15%
2018: -16%
• US Sanctions On Venezuela Are Killing Citizens – Former UN Rapporteur (Ind.)
The first UN rapporteur to visit Venezuela for 21 years has told The Independent the US sanctions on the country are illegal and could amount to “crimes against humanity” under international law. Former special rapporteur Alfred de Zayas, who finished his term at the UN in March, has criticized the US for engaging in “economic warfare” against Venezuela which he said is hurting the economy and killing Venezuelans. The comments come amid worsening tensions in the country after the US and UK have backed Juan Guaido, who appointed himself “interim president” of Venezuela as hundreds of thousands marched to support him. European leaders are calling for “free and fair” elections. Russia and Turkey remain Nicolas Maduro’s key supporters.
Mr De Zayas, a former secretary of the UN Human Rights Council (HRC) and an expert in international law, spoke to The Independent following the presentation of his Venezuela report to the HRC in September. He said that since its presentation the report has been ignored by the UN and has not sparked the public debate he believes it deserves. “Sanctions kill,” he told The Independent, adding that they fall most heavily on the poorest people in society, demonstrably cause death through food and medicine shortages, lead to violations of human rights and are aimed at coercing economic change in a “sister democracy”. On his fact-finding mission to the country in late 2017, he found internal overdependence on oil, poor governance and corruption had hit the Venezuelan economy hard, but said “economic warfare” practised by the US, EU and Canada are significant factors in the economic crisis.
In the report, Mr de Zayas recommended, among other actions, that the International Criminal Court investigate economic sanctions against Venezuela as possible crimes against humanity under Article 7 of the Rome Statute. The US sanctions are illegal under international law because they were not endorsed by the UN Security Council, Mr de Zayas, an expert on international law and a former senior lawyer with the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, said. “Modern-day economic sanctions and blockades are comparable with medieval sieges of towns. “Twenty-first century sanctions attempt to bring not just a town, but sovereign countries to their knees,” Mr de Zayas said in his report.

Xi remains nervous.
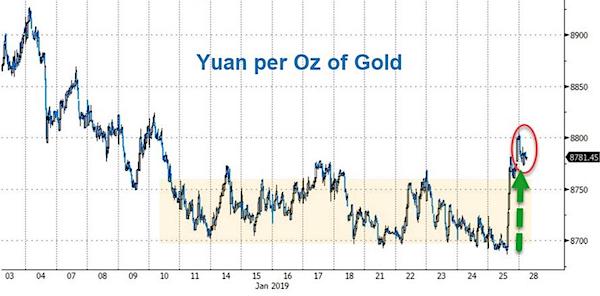
• PBOC Fixes Yuan Dramatically Stronger Following Gold Spike (ZH)
PBOC fixed the yuan dramatically stronger against the dollar overnight, sending offshore yuan surging to its strongest against the dollar in six months. While the Chinese currency is reportedly strengthening on the heels of trade talks optimism (which is entirely the opposite of the rhetoric coming out of Washington), we note that this was the biggest positive shift in the yuan fix in 19 months…
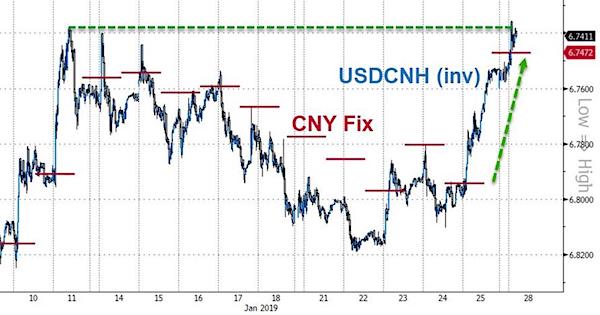
Notably, the yuan is strengthening considerably more against the dollar than it is against the broad basket of trade partner currencies…Shanghai Accord 2.0? And coincidentally, the surge in yuan comes the day after gold prices broke out higher… Perhaps the PBOC’s aggressive action was prompted to manage the Yuan peg against gold back into balance?

If you look closer, nothing seems very dramatic. But real estate has become such a huge part of the economy that Beijing must weigh curbing risks vs continued growth.
It’s also the speed with which this has happened. 10 years ago Chinese didn’t borrow for homes. It’s literally been used to mitigate the financial crisis.
• China’s Real Estate Loan Growth Slows Further In 2018 (CNBC)
Loans to China’s property sector grew at a slower pace in 2018 as Beijing tightened home-purchase rules to curb bubble risk, but lending to property developers expanded slightly faster than the year before, central bank data showed on Friday. Outstanding yuan property loans grew 20% from a year earlier to 38.7 trillion yuan ($5.72 trillion) by end-December, compared with 20.9% growth in 2017, the PBOC said in a quarterly financial report. Outstanding mortgage lending climbed 17.8% year-on-year to 25.75 trillion yuan by the end of 2018, below a 22.2% rise in 2017, central bank data showed.
Policymakers have vowed to ensure “stable and healthy” development of the property market, repeatedly emphasizing that homes are for living in, not speculative investment. The government’s sustained drive to reduce debt risks in the economy has cooled the property market but a continued downturn in credit growth in the sector could add to growing pressures on the world’s second-largest economy. The real estate sector is a key driver of economic growth, so any further weakness could influence the pace and scope of fresh stimulus steps expected from Beijing this year.
Property investment is also looking wobbly, with analysts waiting to see if the government will risk loosening restrictions on home buyers that have kept speculation in check. Real estate investment in December rose 8.2% from a year earlier, down from 9.3% in November, according to Reuters calculations based on data released by the National Bureau of Statistics. That was just ahead of the slowest pace of growth last year at 7.7% recorded for October. Developers raised their borrowings last year though, with loans extended for property development up 22.6% in 2018 versus growth of 21.7% in 2017, the report showed. The central bank also said outstanding household loans jumped 18.2% to 47.9 trillion yuan by end-2018.

How much can Brexit hurt the British? A lot, we must assume. Then again, if you fall for this stuff at this moment in time, maybe you deserve what’s coming. How about a crisis worse than the 1930s?
• Britain’s Biggest Lender To Offer 100% Mortgages To First-Time Buyers (G.)
Britain’s biggest lender is to offer 100% mortgages to first-time buyers in a return to lending last seen before the financial crash – but only if the buyer has family that can stand behind the loan. Under the new Lloyds Bank “Lend A Hand” deal, a first-time buyer will be able to borrow up to £500,000 for a new home, without putting down a penny of deposit. The Lloyds move marks a major expansion into the first-time buyer market, as most other mainstream lenders demand a minimum deposit worth 5% of the property purchase price, although Barclays has offered a similar “family springboard” deal. Lloyds has priced the mortgages to undercut the Barclays offer.
The deal – part of what Lloyds said is a £30bn commitment to help first-time buyers – will reopen concern about a two-tier market where buyers with well-off families can elbow aside those without. Saving for a deposit is usually cited by first-time buyers as the biggest hurdle to home ownership. Lloyds said the average deposit put down by first-time buyers has climbed to £33,211, and a staggering £110,182 in London. The Lloyds deal requires that a member of the family – such as parent, grandparent or close relative – helps out. The bank will only grant the 100% mortgage if the family member puts a sum equal to 10% of the value of the property into a Lloyds savings account.

“The anticipated recession will be worse than the 1930s, let alone 2008.”
• UK Cannot Simply Trade On WTO Terms After No-Deal Brexit (G.)
The UK will be unable to have frictionless, tariff-free trade under World Trade Organization rules for up to seven years in the event of a no-deal Brexit, according to two leading European Union law specialists. The ensuing chaos could double food prices and plunge Britain into a recession that could last up to 30 years, claim the lawyers who acted for Gina Miller in the historic case that forced the government to seek parliament’s approval to leave the EU. It has been claimed that the UK could simply move to WTO terms if there is no deal with the EU. But Anneli Howard, a specialist in EU and competition law at Monckton Chambers and a member of the bar’s Brexit working group, believes this isn’t true. “No deal means leaving with nothing,” she said. “The anticipated recession will be worse than the 1930s, let alone 2008.
It is impossible to say how long it would go on for. Some economists say 10 years, others say the effects could be felt for 20 or even 30 years: even ardent Brexiters agree it could be decades.” The government’s own statistics have estimated that under the worst case no-deal scenario, GDP would be 10.7% lower than if the UK stays in the EU, in 15 years. There are two apparently insurmountable hurdles to the UK trading on current WTO tariffs in the event of Britain crashing out in March, said Howard. Firstly, the UK must produce its own schedule covering both services and each of the 5,000-plus product lines covered in the WTO agreement and get it agreed by all the 163 WTO states in the 32 remaining parliamentary sitting days until 29 March 2019. A number of states have already raised objections to the UK’s draft schedule: 20 over goods and three over services.
To make it more complicated, there are no “default terms” Britain can crash out on, Howard said, while at the same time, the UK has been blocked by WTO members from simply relying on the EU’s “schedule” – its existing tariffs and tariff-free trade quotas. The second hurdle is the sheer volume of domestic legislation that would need to be passed before being able to trade under WTO rules: there are nine statutes and 600 statutory instruments that would need to be adopted. The government cannot simply cut and paste the 120,000 EU statutes into UK law and then make changes to them gradually, Howard said. “The UK will need to set up new enforcement bodies and transfer new powers to regulators to create our own domestic regimes,” she said.

Fast and loose with Good Friday.
• May To Seek Binding Changes To Irish Backstop – Boris Johnson
Prime Minister Theresa May will seek legally binding changes to the Irish backstop from the European Union in an attempt to break the deadlock over Brexit, lawmaker Boris Johnson wrote in The Telegraph on Sunday, citing senior government sources. The PM is looking to change the text of the agreement to insert either a sunset clause or a mechanism for the UK to escape without reference to the EU, Boris Johnson said in The Telegraph. The contentious backstop arrangement is designed to prevent a hard border between Ireland and the UK province of Northern Ireland by requiring Britain to keep some EU rules if it was unable to agree a trade deal with the bloc. Ireland said earlier on Sunday it would not accept any changes to the backstop agreement.

The backstop will be May’s major point of contention this week. Stop her! There’s already talk of reinserting issues in the deal that have already been thrown out.
• Ireland Stresses It Will Not Yield On Brexit Backstop (G.)
Ireland has launched a last-minute effort to warn Theresa May off any attempt to unravel the backstop, two days before a crucial Commons debate that may decide the next move for the UK’s rudderless Brexit policy. Simon Coveney, the Irish foreign minister and deputy prime minister, insisted the backstop – the mechanism to ensure there will be no hard border between the Irish Republic and Northern Ireland if Britain and the EU fail to strike a free trade deal – was “part of a balanced package that isn’t going to change”. In a forceful interview, he insisted it was only part of the withdrawal agreement because of the UK’s red lines.
On Tuesday Tory Brexiters may get the chance to vote for amendments that would signal their willingness to back May’s Brexit deal subject to the backstop’s either being removed or time-limited. Ministers have not formally backed any of the anti-backstop amendments, which are incompatible with the deal that May agreed with UK leaders, but if one were to pass by a majority, she would be able to present the EU with a firm idea of what changes might get her deal through parliament – something that as yet remains unclear to Brussels. In an interview with BBC One’s The Andrew Marr Show, Coveney said he did not see the need for further compromise because “the backstop is already a compromise”.
Although originally Northern Ireland-specific, it was made UK-wide at the request of May, he said. “And the very need for the backstop in the first place was because of British red lines that they wanted to leave the customs union and single market,” he said.

Many Brits are so poor they can’t even think of stockpiling.
• UK Military Bases Stockpiling To Prepare For No-Deal Brexit (Sky)
Britain has begun stockpiling food, fuel, spare parts and ammunition at military bases in Gibraltar, Cyprus and the Falklands in case of a no-deal Brexit, Sky News has learnt. Extra supplies are also being built up at bases in the UK to reduce the risk of the armed forces running short and being unable to operate if it suddenly becomes much harder to import and export day-to-day goods after 29 March. Military chiefs have spent at least £23m on what is being described as “forward-purchased” goods, Sky News understands. The move is part of contingency planning by the government – codenamed Operation Yellowhammer – to reduce disruption if Britain departs from the European Union without an agreement, according to three defence sources.
“An army marches on its stomach. If supply lines breakdown they struggle,” one source said. Any blockage in the flow of food and other vital items to Britain’s military bases overseas could impact on operations and affect thousands of soldiers, sailors and airmen. There is a concern that supplies delivered to British troops in the rest of Europe – the UK has a permanent presence in Cyprus and a base on the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, which shares a border with Spain – could be impacted, according to the sources.

We haven’t seen any of it yet.
• Brexit Exposes Growing Fractures In UK Society (G.)
Britons have become angrier since the referendum to leave the EU, according to a survey which suggests there is widespread unhappiness about the direction in which the country is heading. 69 per cent of respondents said they felt their fellow citizens had become “angrier about politics and society” since the Brexit vote in 2016, according to the Edelman Trust Barometer, a long-established, annual survey of trust carried out across the globe. 40 per cent of people think others are now more likely to take part in violent protests, the UK results from the survey show, even though violent political protest in Britain is rare.
One person in six said they had fallen out with friends or relatives over the vote to leave the bloc, the survey found. Edelman, which said the findings exposed a “disUnited Kingdom”, found widespread concern about where the government was heading, particularly among those who voted remain, and those who backed Labour. Overall, about 65% of Britons think the country is “on the wrong track”, the survey suggests. Amongst remain voters the figure is 82%, but even among leave voters the figure is 43%. Some 60% of people who identify with the Conservatives think the country is heading in the right direction, but among Labour identifiers, the figure is just 20%.

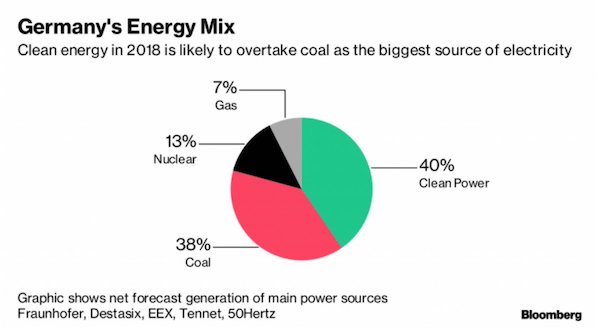
The coal phase-out is part of a 500 billion-euro switch away from fossil fuels and toward renewables..
Compensating coal-mining regions & consumers for higher electricity prices expected to cost German taxpayer up to €78bn.
But across the border lies Italy, and next to it Greece. How are they going to pay for such a switch? And if they don’t, what’s the use of Germany doing it?
• In Germany’s Plan To Phase Out Coal, A Big Polluter Will Benefit (BBG)
A proposal to stop Germany from using coal for power generation within two decades may leave an unexpected beneficiary: The company that burns the most of the fuel. While RWE AG was quick to say it’s “too soon” to shed all fossil fuel plants by 2038, the recommendations outlined this weekend by a panel advising Chancellor Angela Merkel called for compensation for the utilities and 40 billion euros ($45.6 billion) for regions coping with the transition. Together, the measures would significantly soften the blow on industry from Merkel’s vow to scale back greenhouse gases. They show how far the government has moved away from a quick clampdown on the most polluting fossil fuel and give more certainty for the future of some of RWE’s most valuable assets.
And while the proposals could yet be watered down by politicians, they signal a longer life for many of the utility’s plants than environmentalists had hoped for. “We believe that clarity, compensation payments, and a relatively long phase-out period should trigger a re-rating for the company’s conventional power generation,” said Guido Hoymann, an analyst at the private bank B. Metzler Seel. Sohn & Co. KGaA who added RWE to a list of top 10 German stocks.
Germany’s 120 or so remaining coal and lignite plants have a combined capacity of about 45 gigawatts. That’s enough to feed 40 percent of the nation’s power demand or about 32 million homes. Germany is already falling short on its targets to slash greenhouse gas emissions and sees closing coal plants as one of the most important ways to make the reductions needed. The coal commission includes members from the main political parties, environmental groups and industry charged with developing a consensus that Germany can live with for years to come.