Jean-Michel Basquiat Irony of the Negro Policeman 1981
UPDATE: There is a problem with our Paypal widget/account that makes donating hard for some people. What happens is that for some a message pops up that says “This recipient does not accept payments denominated in USD”. This is nonsense, we do.
We have no idea how many people have simply given up on donating, but we can suggest a workaround (works like a charm):
Through Paypal.com, you can simply donate to an email address. In our case that is recedinghorizons *at* gmail *com*. Use that, and your donations will arrive where they belong. Sorry for the inconvenience.

The Automatic Earth and its readers have been supporting refugees and homeless in Greece since June 2015. It has been an at times difficult and at all times expensive endeavor. Not at least because the problems do not just not get solved, they actually get worse. Because the people of Greece and the refugees that land on their shores increasingly find themselves pawns in political games.
Therefore, even if the generosity of our readership has been nothing short of miraculous, we must continue to humbly ask you for more support. Because our work is not done. Our latest essay on this is here: The Automatic Earth for Athens Fund – Christmas and 2018 . It contains links to all 14 previous articles on the situation.
Here’s how you can help:

For donations to Konstantinos and O Allos Anthropos, the Automatic Earth has a Paypal widget on our front page, top left hand corner. On our Sales and Donations page, there is an address to send money orders and checks if you don’t like Paypal. Our Bitcoin address is 1HYLLUR2JFs24X1zTS4XbNJidGo2XNHiTT. For other forms of payment, drop us a line at Contact • at • TheAutomaticEarth • com.
To tell donations for Kostantinos apart from those for the Automatic Earth (which badly needs them too!), any amounts that come in ending in either $0.99 or $0.37, will go to O Allos Anthropos.


Over 50% chance of melt up, with over 90% chance of subsequent melt down of 50% (or more).
• Investors Should ‘Brace For Near-Term Melt-Up – Grantham (MW)
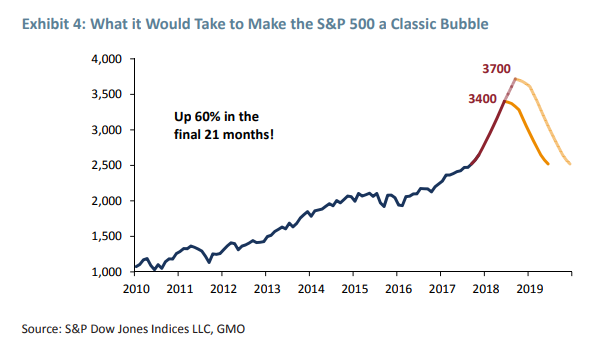
Jeremy Grantham, who is credited with calling the 2000 and 2008 downturns, warned investors Wednesday to be prepared for the possibility of a near-term “melt-up” that would likely set the stage for a burst bubble and a stock-market meltdown. In a 13-page note that he emphasized reflected “a very personal view,” the value investor and co-founder and chief investment strategist of Boston-based asset manager GMO compared the present market setup with the run-up to past bubbles, including the 2000 tech boom and the precursor to the 1929 crash. “I recognize on one hand that this is one of the highest-priced markets in U.S. history. On the other hand, as a historian of the great equity bubbles, I also recognize that we are currently showing signs of entering the blow-off or melt-up phase of this very long bull market,” Grantham said.
He terms the current market run-up the “possible/probable bubble of 2018-19.” In the note, Grantham emphasizes that bubble calls shouldn’t necessarily rely on price alone. Instead, he puts emphasis on price acceleration, which captures “the importance of a true psychological event of momentum increasing to a frenzy.” Read the note here. Grantham favorably cited an academic paper published last year that concluded that the strongest indicator of a bubble in U.S. and almost all global markets was price acceleration. As for the S&P 500 SPX, +0.64% Grantham says that “just recently, say the last six months, we have been showing a modest acceleration, the base camp, perhaps, for a final possible assault on the peak.
“Exhibit 4 (shown below) represents our quick effort at showing what level of acceleration it might take to make 2018 (and possibly 2019) look like a classic bubble,” he wrote. “A range of nine to 18 months from today and a price rise to around 3,400 to 3,700 on the S&P 500 would show the same 60% gain over 21 months as the least of the other classic bubble events.” [..] • “A melt-up or end-phase of a bubble within the next six months to two years is likely, i.e., over 50%.” • ”If there is a melt-up, then the odds of a subsequent bubble break or meltdown are very, very high, i.e., over 90%. • “If there is a market decline following a melt-up, it is quite likely to be a decline of some 50%.”

‘Fat Cat Thursday’. Bad idea if you want a functioning economy.
• Top Bosses Earn More In 3 Days Than Average Worker In Entire Year (G.)
Bosses of top British companies will have made more money by lunchtime on Thursday than the average UK worker will earn in the entire year, according to an independent analysis of the vast gap in pay between chief executives and everyone else. The chief executives of FTSE 100 companies are paid a median average of £3.45m a year, which works out at 120 times the £28,758 collected by full-time UK workers on average. On an hourly basis the bosses will have earned more in less than three working days than the average employee will pick up this year, leading campaigners to dub the day “Fat Cat Thursday”. Frances O’Grady, the TUC general secretary, said it was outrageous that bosses were picking up “salaries that look like telephone numbers” while workers were “suffering the longest pay squeeze since Napoleonic times”.
The analysis by the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) and the High Pay Centre shows chief executives of FTSE 100 companies are paid an average of £898 per hour – 256 times what apprentices earn on the minimum wage. Tim Roache, the general secretary of the GMB union, said the pay gap between bosses and workers was “simply obscene”. “Does anyone really think these fat cats deserve 100 times more than the hard-working people who prop up their business empires?” he said. “Workers who have to scrimp and save to feed their families and put a roof over their head – and like most of Britain’s working population will now be feeling the pinch after the festive period?”

And it’s not just phones and computers either.
• Security Flaws Put Virtually All Phones, Computers At Risk (R.)
One of the bugs is specific to Intel but another affects laptops, desktop computers, smartphones, tablets and internet servers alike. Intel and ARM insisted that the issue was not a design flaw, but it will require users to download a patch and update their operating system to fix. “Phones, PCs, everything are going to have some impact, but it’ll vary from product to product,” Intel CEO Brian Krzanich said in an interview with CNBC Wednesday afternoon. Researchers with Alphabet Inc’s Google Project Zero, in conjunction with academic and industry researchers from several countries, discovered two flaws. The first, called Meltdown, affects Intel chips and lets hackers bypass the hardware barrier between applications run by users and the computer’s memory, potentially letting hackers read a computer’s memory and steal passwords.
The second, called Spectre, affects chips from Intel, AMD and ARM and lets hackers potentially trick otherwise error-free applications into giving up secret information. The researchers said Apple Inc and Microsoft Corp had patches ready for users for desktop computers affected by Meltdown. Microsoft declined to comment and Apple did not immediately return requests for comment. Daniel Gruss, one of the researchers at Graz University of Technology who discovered Meltdown, called it “probably one of the worst CPU bugs ever found” in an interview with Reuters. Gruss said Meltdown was the more serious problem in the short term but could be decisively stopped with software patches. Spectre, the broader bug that applies to nearly all computing devices, is harder for hackers to take advantage of but less easily patched and will be a bigger problem in the long term, he said.
Speaking on CNBC, Intel’s Krzanich said Google researchers told Intel of the flaws “a while ago” and that Intel had been testing fixes that device makers who use its chips will push out next week. Before the problems became public, Google on its blog said Intel and others planned to disclose the issues on Jan. 9. Google said it informed the affected companies about the “Spectre” flaw on June 1, 2017 and reported the “Meltdown” flaw after the first flaw but before July 28, 2017. The flaws were first reported by tech publication The Register. It also reported that the updates to fix the problems could causes Intel chips to operate 5% to 30% more slowly.

They all use these features. They’re not actually flaws. That makes it hard to repair.
• The Microprocessor Security Flaw Explained (BBG)
The weakness uncovered by Google [..] underscores the potential damage wreaked by vulnerabilities in hardware. Complex components, such as microprocessors, can be harder to fix and take longer to design from scratch if flawed. “It’s a big one and it’s a severe one. This gives an attacker capabilities that bypass the common operating system security controls that we’ve relied on for 20 years,” said Jeff Pollard, an analyst at Forrester Research. “There’s big impact on both the consumer and enterprise.” Intel’s stock remained under pressure even after its statement. “We struggle to believe that Intel won’t face some sort of financial liability,” analysts at Sanford C. Bernstein wrote in a note.
[..] Applying the operating system upgrades designed to remedy the flaw could hamper performance, security experts said. The Register reported that slowdowns could be as much as 30% – something Intel said would occur only in extremely unusual circumstances. Computer slowdowns will vary based on the task being performed and for the average user “should not be significant and will be mitigated over time,” Intel said, adding that it has begun providing software to help limit potential exploits. Intel’s efforts to play down the impact resulted in a war of words with AMD. Intel said it’s working with chipmakers including AMD and ARM Holdings, as well as operating system makers to develop an industrywide approach to resolving the issue. AMD was quick to retort, saying, “there is near-zero risk” to its processors because of differences in the way they are designed and built.
The vulnerability doesn’t just affect PCs. All modern microprocessors, including those that run smartphones, are built to essentially guess what functions they’re likely to be asked to run next. By queuing up possible executions in advance, they’re able to crunch data and run software much faster. The problem in this case is that this predictive loading of instructions allows access to data that’s normally cordoned off securely, Intel Vice President Stephen Smith said on a conference call. That means, in theory, that malicious code could find a way to access information that would otherwise be out of reach, such as passwords. “The techniques used to accelerate processors are common to the industry,” said Ian Batten at the University of Birmingham in the U.K. who specializes in computer security. The fix being proposed will definitely result in slower operating times, but reports of slowdowns of 25% to 30% are “worst-case” scenarios, he said.

Foot meet mouth.
• The CEO of Wells Fargo Might Be in Big, Big Trouble (Dayen)
Late last year, Congress scrapped Obama-era rules from the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau that would have banned forced-arbitration clauses in financial contracts. This bill, which President Trump quickly signed, was self-evidently bad for consumers at the time—and if anyone needs further proof of how ridiculous and harmful these clauses are, just look at what Wells Fargo has been up to over the past several months. The mega-bank famously issued at least 3.5 million fake accounts without consumer consent, triggering a $185 million fine to state and federal regulators. The bank aimed to demonstrate sales growth to investors and boost the stock price with bogus numbers, but millions of customers got caught up in the exchange, paying unnecessary fees and taking hits to their credit scores. Scores of defrauded customers sued Wells Fargo in a series of class-action lawsuits.
Wells Fargo then tried to defy metaphysical reality: It moved to block one class-action case in Utah by claiming that the arbitration clause in customer contracts on the real accounts they held at the bank also applied to the fake accounts. By this theory, Wells Fargo customers signed away their legal rights when it came to accounts they didn’t even sign. The Utah plaintiffs fought Wells’s motion to compel arbitration, and rejected a $142 million settlement offer from the bank. While the two sides tangled in court, Wells Fargo CEO Tim Sloan appeared before the Senate Banking Committee on October 3. And when Senator Jon Tester (D-MT) asked Sloan point-blank if Wells Fargo was using arbitration clauses from real accounts and applying them to fake accounts, Sloan said, “There were instances [of that] historically. We’re not doing that today.”
He also committed to not forcing arbitration in fake-accounts cases moving forward. When Senator Chris Van Hollen (D-MD) brought up the Utah case, where Wells Fargo had made motions to compel arbitration just two weeks earlier, Sloan said he wasn’t familiar with it. But lawyers in Utah get C-SPAN. The plaintiffs in the case immediately appealed to the judge and argued that, with his remarks before Congress, Sloan had effectively waived Wells Fargo’s right to compel arbitration. Judge Clark Waddoups promptly scheduled a two-day trial for January 22 on the question. He also allowed the plaintiffs to depose Sloan in conjunction with the trial; that deposition is scheduled for Friday.
This put Sloan in a tight spot. Steven Christensen, attorney for the plaintiffs, told me he had only one question for Sloan: Did he state to Congress that Wells Fargo would waive arbitration claims on fake accounts? If Sloan said yes, the Utah case would go forward; if he said no, Christensen would appeal to Congress to hold him in contempt for lying to the Senate Banking Committee.

End of an era?!
• NYC Apartment Sales Collapse 25% In Q4 As Trump Tax Plan Takes Its Toll (ZH)
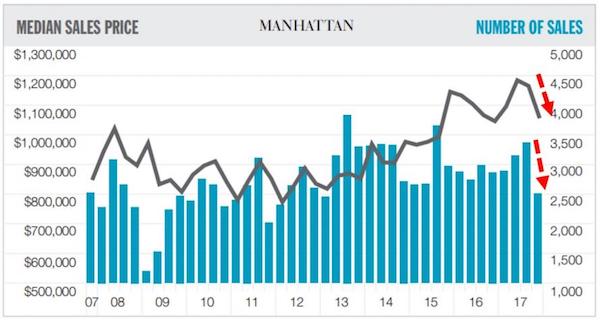
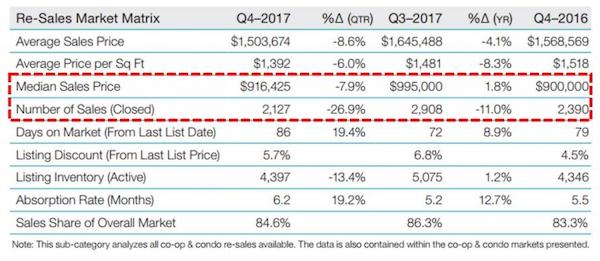
Apparently the combination of a massive flood of excess supply in the form of new luxury developments and a Trump tax plan that penalizes people living in expensive cities by capping SALT, mortgage interest and property tax deductions was simply too much for the Manhattan real estate market to ignore in 4Q 2017. As Douglas Elliman points out in their new Q4 2017 Manhattan Market Report, both prices (-9.4%) and volumes (-25.4%) of New York City apartments collapsed sequentially in Q4 as potential buyers took a pause amid the growing uncertainty.
“Sales activity for the Manhattan housing market was at the lowest fourth quarter total in six years. The pace of the fall market noticeably cooled as market participants awaited the housing-related terms of the new federal tax bill. This translated into a decline in year over year closings for the final quarter of the year, although contract volume showed an uptick. There were 2,514 sales to close in the final quarter of the year, down 12.3% from the prior-year quarter. The decline in sales allowed listing inventory to rise after declining year over year for the past few quarters. There were 5,451 listings at the end of the quarter, up 1.1% from the same period a year ago. As a result, the absorption rate, the number of months to sell all inventory at the current rate of sales slowed, rising to 6.5 months from 5.6 months in the year-ago quarter.
Listing discount, the%age difference between the list price at the date of sale and the sales price, was 5.4% up nominally from 5.3% in the prior year quarter as sellers continued to travel farther to meet the buyer on price. Buyers continued to hold firm, forcing sellers to meet them on price. Days on market, the average number of days to sell all apartments that closed during the quarter rose 3.2% to 97 days from 94 days in than the same period last year. New development active listings and resale listings were up 0.7% and 1.2% respectively over the same period. With the nominal rise in supply, there was also a nominal decline in bidding wars, still accounting for 11.7% of all sales in the quarter, down 0.9% from the same period last year.”

Musk keeps hoping people will forget the last batch of bad data when the newest comes in.
• Tesla Falls Far Short On Model 3 Deliveries (CNBC)
Tesla is apparently still deep in the circles of production hell. On Wednesday, the electric car maker released delivery numbers for the fourth quarter of 2017 that fell short of many expectations on Wall Street, and once again pushed back production targets on its highly anticipated Model 3 sedan. Tesla shares fell roughly 2% in after-hours trading. “As we continue to focus on quality and efficiency rather than simply pushing for the highest possible volume in the shortest period of time, we expect to have a slightly more gradual ramp through Q1, likely ending the quarter at a weekly rate of about 2,500 Model 3 vehicles,” Tesla said in a release. “We intend to achieve the 5,000 per week milestone by the end of Q2.” In 2017, the company had said it planned to reach a production rate of 5,000 cars per week for the Model 3, but later revised back that target to the end of the first quarter.
Now, Tesla expects to reach the target by the end of the second quarter. Tesla said it made “major progress” toward addressing the “production bottlenecks” the company has blamed for falling so far short of its Model 3 targets. The company said that in the last few days of the quarter it reached a production rate that “extrapolates to over 1,000 Model 3’s per week.” CEO Elon Musk had previously said he expected weekly Model 3 production to be “in the thousands” by the end of 2017. Tesla said it delivered 29,870 vehicles in the fourth quarter of 2017, including 1,550 of its anticipated Model 3 sedan. The electric-car maker also delivered 15,200 Model S sedans, and 13,120 Model X SUVs. That represents a 27% increase over the same quarter in 2016 for both models combined, and a 9% increase over Q3 2017, Tesla’s previous best quarter, the company said.

The US has enough cars anyway.
• US Auto Sales Fall for 2nd Year (WS)
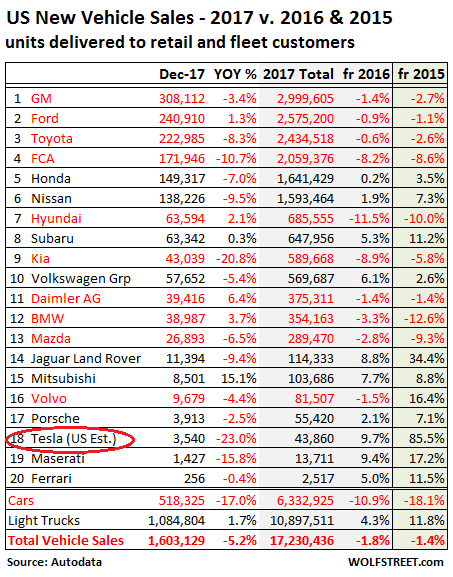
Total new-vehicle sales in the US fell 5.2% year-over-year in December to 1.6 million units. For all of 2017, sales declined by 320,000 vehicles, or 1.8%, to 17.23 million units. It was the first overall decline since the Financial Crisis. Compared to 2015, sales fell by 249,033 vehicles, or 1.4%. These sales are vehicles delivered by dealers to their customers, or delivered by automakers directly to large fleet customers, as reported by Autodata.
For the big three US automakers and some import brands it was the second year in a row of sales declines (two-year percent change from 2015):
GM -2.7%
Ford -1.1%
Fiat Chrysler (FCA) -8.6%
Toyota -2.6%
Hyundai -10.0%
Kia -5.8%
Daimler -1.4%
BMW -12.6%
Mazda -9.3%The table below shows new-vehicle sales by automaker, sorted by total sales in 2017 (gray column). Automakers with declining sales in 2017 are marked in red. The green column shows the two-year %age change from 2015. Turns out that replacement demand for new vehicles after Hurricane Harvey was strong, but not nearly strong enough to pull out the year for total US auto sales, and what demand there has been will peter out going forward. Car sales plunged 17% year-over-year in December, 10.9% in all of 2017, and 18.1% from 2015. They’ve been left behind by consumers who’re switching to crossovers and SUVs which the industry considers trucks. So truck sales – pickups, SUVs, crossovers, and vans – rose 1.7% in December, 4.3% for the year, and 11.8% compared to 2015.

They’re not.
• UK Thinks EU is Bluffing on No Brexit Deal for Banks (BBG)
Prime Minister Theresa May believes Michel Barnier is bluffing when he says there will be no special deal for financial services, officials said, as the U.K. prepares to negotiate its post-Brexit ties with the European Union. Two senior officials familiar with the matter privately think the EU’s chief Brexit negotiator is faking a hard-line stance in ruling out a deal that would allow banks to continue operating freely across the bloc. Talks have yet to start on Britain’s future trade agreement with the EU but Barnier said last month there was no chance of a deal that replicated the easy access that U.K.-based financial services currently enjoy to the single market. The U.K. officials said the French former commissioner was simply setting out an opening position that did not have backing from the 27 other EU member countries.
They said banks based in London will be fine because businesses operating in the EU will need to maintain access to finance after Brexit. The fate of London’s financial district is urgent for May, who last month agreed to pay a £39 billion ($53 billion) bill to start talks on the nuts and bolts of a transition. With Britain’s departure from the bloc just 14 months away, businesses are counting on a two-year adjustment period. [..] Last month, May said U.K. financial services should be optimistic about Britain’s trade talks, which are due to start in March. She cited Polish Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki and Italian Prime Minister Paolo Gentiloni as evidence that other EU leaders are open to Britain carving out a custom-made trading relationship with the bloc that covers services. Yet Barnier insists the U.K. will not be offered anything more than a Canada-style deal, which keeps tariffs to a minimum on goods but does not include trade in services.

Big 2018 story. But it can’t be spoken out loud.
• UK Opposition Party Grassroots Support Second Brexit Vote (R.)
Eight out of 10 grassroots members of Britain’s opposition Labour Party want a referendum on the terms of the country’s exit from the European Union, according to a survey published on Thursday. That is at odds with Labour leader Jeremy Corbyn’s official policy which calls for parliament, not the public, to have the final say on the terms of the deal. It indicates a strong desire among the party’s rank and file members for a chance to demand a rethink on Brexit, or even overturn the outcome of the June 2016 vote to leave the EU. Eighteen months after voting 52 to 48% to withdraw from the EU, Britons remain deeply divided over leaving a bloc which has defined much of the country’s laws, trade policy and international outlook over more than four decades of membership. Theresa May’s Conservative minority government has dismissed the idea of a second referendum.
But ministers have already been forced to give parliament a greater say in the Brexit process than they initially wanted to after members of May’s own party rebelled on the issue in December. Thursday’s survey of attitudes within Britain’s main political parties showed 49% of Labour members definitely wanted a second referendum on the exit deal and a further 29% said they were more in favor of the idea than against it. The poll of more than 4,000 members of political parties was conducted shortly after last June’s national election as part of a three-year academic project by the Mile End Institute at Queen Mary University of London to discover more about people who belong to political parties. It showed even higher demand for a second vote on Brexit among members of the Liberal Democrats and the Scottish National Party. By contrast, only 14% of Conservative Party members wanted a referendum on the exit deal.

Bitcoin is a bad fit in a super-centralized society
• China Communist Party Paper Bashes Bitcoin (SCMP)
China’s ruling Communist Party mouthpiece lashed out at bitcoin on Wednesday, labelling the volatile cryptocurrency a bubble and a modern-day tulip mania. A People’s Daily commentary written under the name “Wei Liang” said it was an established fact that bitcoin was a bubble. “Irrespective of whether it is assessed on price or value, bitcoin is flooded with froth,” it said. “Its so-called advantages – scarcity, authenticity, strong liquidity, transparency and decentralisation – are only covers for speculation and cannot support its volatile price.” It said bitcoin’s bubbles were created by a combination of hype, mystery, decentralisation and possible insider trading, suggesting that a small group of bitcoin owners were speculating on its price and manipulating general investors.
The commentary compared bitcoin to the seventeenth century mania in which prices for tulip bulbs skyrocketed and then collapsed. It also said there would be more “bubble breaking” in bitcoin after governments around the world tightened regulation. The central government sees bitcoin as a source of risk. It banned domestic cryptocurrency exchanges last year after failing to regulate the fast growth of initial coin offerings, the virtual currency equivalent of an initial public offering. [..] Bitcoin investors are on alert to see whether Beijing will take further action against cryptocurrencies, such as shutting down bitcoin “mines”, the energy-hungry operations that create bitcoin by solving mathematical problems using vast banks of computers.

Easy to trace.
• China to Curb Power Supply for Some Bitcoin Miners (BBG)
China plans to limit power use by some bitcoin miners, people familiar with the matter said, a potential challenge to an industry whose energy-intensive computer networks enable transactions in the cryptocurrency. The People’s Bank of China outlined the plan Wednesday at a closed-door meeting, according to the people, who asked not to be identified because it wasn’t public. They didn’t detail how authorities plan to enact the curbs. Chinese officials are concerned that bitcoin miners have taken advantage of low power prices in some areas and affected normal electricity use in some cases, the people said. Local officials have been asked to investigate the high consumption associated with the industry, they said. The curbs will also involve other regulators such as the National Development and Reform Commission, which oversees the power supply.
While the proposed restrictions are unlikely to have a noticeable effect on transaction speeds, they highlight global concerns over the growing energy consumption of bitcoin miners. The industry now uses as much electricity as 3.4 million U.S. households, according to the Digiconomist Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index. China is home to many of the world’s largest miners, some of whom have set up around hydroelectric facilities in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces. “This may have contributed to bitcoin coming off its daily highs,” said Craig Erlam, senior market analyst at online trading firm Oanda in London. “Electricity usage certainly appears to be a significant challenge for the cryptocurrency in the years ahead.” Bitcoin, which surged 15-fold last year, pared gains on Wednesday and traded around $14,900 on Thursday.