
Marjory Collins Window of Jewish religious shop on Broome Street, New York Aug 1942



“..the hundreds of billions of dollars fleeing emerging economies, from Brazil to China, don’t come with images of women and children on capsizing boats. Nor do banks that have lent trillions that will never be repaid post gruesome videos. ”
• The World Economic Order Is Collapsing And There Seems No Way Out (Observer)
Europe has seen nothing like this for 70 years – the visible expression of a world where order is collapsing. The millions of refugees fleeing from ceaseless Middle Eastern war and barbarism are voting with their feet, despairing of their futures. The catalyst for their despair – the shredding of state structures and grip of Islamic fundamentalism on young Muslim minds – shows no sign of disappearing. Yet there is a parallel collapse in the economic order that is less conspicuous: the hundreds of billions of dollars fleeing emerging economies, from Brazil to China, don’t come with images of women and children on capsizing boats. Nor do banks that have lent trillions that will never be repaid post gruesome videos. However, this collapse threatens our liberal universe as much as certain responses to the refugees.
Capital flight and bank fragility are profound dysfunctions in the way the global economy is now organised that will surface as real-world economic dislocation. The IMF is profoundly concerned, warning at last week’s annual meeting in Peru of $3tn (£1.95tn) of excess credit globally and weakening global economic growth. But while it knows there needs to be an international co-ordinated response, no progress is likely. The grip of libertarian, anti-state philosophies on the dominant Anglo-Saxon political right in the US and UK makes such intervention as probable as a Middle East settlement. Order is crumbling all around and the forces that might save it are politically weak and intellectually ineffective. The heart of the economic disorder is a world financial system that has gone rogue.
Global banks now make profits to a extraordinary degree from doing business with each other. As a result, banking’s power to create money out of nothing has been taken to a whole new level. That banks create credit is nothing new; the system depends on the truth that not all depositors will want their money back simultaneously. So there is a tendency for some of the cash banks lend in one month to be redeposited by borrowers the following month: a part of this cash can be re-lent, again, in a third month – on top of existing lending capacity. Each lending cycle creates more credit, which is why lending has always been carefully regulated by national central banks to ensure loans will, in general, be repaid and sufficient capital reserves are held. .
The emergence of a global banking system means central banks are much less able to monitor and control what is going on. And because few countries now limit capital flows, in part because they want access to potential credit, cash generated out of nothing can be lent in countries where the economic prospects look superficially good. This provokes floods of credit, rather like the movements of refugees.

Never could. Only thing they could do was to make things much worse. Mission accomplished.
• Central Bank Cavalry Can No Longer Save The World (Reuters)
In 2008 central banks, led by the Federal Reserve, rode to the rescue of the global financial system. Seven years on and trillions of dollars later they no longer have the answers and may even represent a major risk for the global economy. A report by the Group of 30, an international body led by former ECB chief Jean-Claude Trichet, warned on Saturday that zero rates and money printing were not sufficient to revive economic growth and risked becoming semi-permanent measures. “Central banks have described their actions as ‘buying time’ for governments to finally resolve the crisis… But time is wearing on, and (bond) purchases have had their price,” the report said. In the United States, the Fed ended its bond purchase program in 2014, and had been expected to raise interest rates from zero as early as June 2015.
But it may struggle to implement its first hike in almost 10 years by the end of the year. Market pricing in interest rate futures puts a hike in March 2016. The Bank of England has also delayed, while the ECB looks set to implement another round of quantitative easing, as does the Bank of Japan which has been stuck in some form of quantitative easing since 2001. Reuters calculates that central banks in those four countries alone have spent around $7 trillion in bond purchases. The flow of easy money has inflated asset prices like stocks and housing in many countries even as they failed to stimulate economic growth. With growth estimates trending lower and easy money increasing company leverage, the specter of a debt trap is now haunting advanced economies, the Group of Thirty said.
The Fed has pledged that when it does hike rates, it will be at a slow pace so as not to strangle the U.S. economic recovery, one of the longest, but weakest on record in the post-war period. Yet, forecasts by one regional Fed president shows he expects negative rates in 2016. Most policymakers at the semi-annual IMF meetings this week have presented relatively upbeat forecasts for the world economy and say risks have been largely contained. The G30, however, warned that the 40% decline in commodity prices could presage weaker growth and “debt deflation”. Rates would then have to remain low as central banks would be forced to maintain or extend their bond programs to try and bolster growth and the price of financial assets would fall.

The liquidity squeeze is universal.
• Quantitative Frightening (Economist)
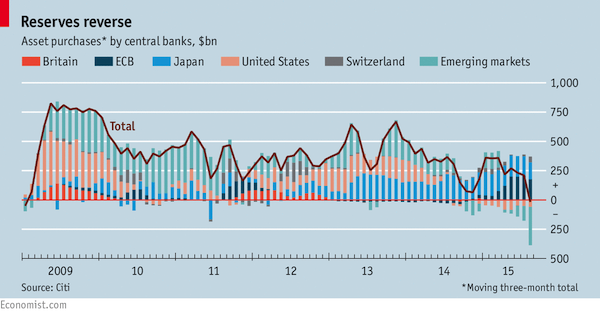
A defining feature of the world economy over the past 15 years was the unprecedented accumulation of foreign-exchange reserves. Central banks, led by those in China and the oil-producing states, built up enormous hoards of other countries’ currencies. Global reserves swelled from $1.8 trillion in 2000 to $12 trillion by mid-2014. That proved to be a high point. Since then reserves have dropped by at least $500 billion. China, whose reserves peaked at around $4 trillion, has burnt through a chunk of its holdings to prop up the yuan, as capital that had once gushed in started to leak out. Other emerging markets, notably Russia and Saudi Arabia, have also called on their rainy-day stashes. This has sparked warnings that the world faces a liquidity squeeze from dwindling reserves.
When central banks in China and elsewhere were buying Treasuries and other prized bonds to add to their reserves, it put downward pressure on rich-world bond yields. Running down reserves will mean selling some of these accumulated assets. That threatens to push up global interest rates at a time when growth is fragile and financial markets are skittish. Analysts at Deutsche Bank have described the effect as “quantitative tightening”. In principle, rich-world central banks can offset the impact of this by, for instance, additional QE, the purchase of their own bonds with central-bank money. In practice there are obstacles to doing so.
That one country’s reserves might influence another’s bond yields was expressed memorably in 2005 by Ben Bernanke, then a governor at the Federal Reserve and later its chairman, in his “global saving glut” hypothesis. Large current-account surpluses among emerging markets were a reflection of excess national saving. The surplus capital had to go somewhere. Much of it was channelled by central banks into rich-world bonds held in their burgeoning reserves. The growing stockpiles of bonds compressed interest rates in the rich world. Controlling for the range of things that influence interest rates, from growth to demography, economists have attempted to gauge the impact of reserve accumulation.
Francis and Veronica Warnock of the University of Virginia concluded that foreign-bond purchases lowered yields on ten-year Treasuries by around 0.8 percentage points in 2005. A recent working paper by researchers at the ECB found a similar effect: increased foreign holdings of euro-area bonds reduced long-term interest rates by about 1.5 percentage points during the mid-2000s. Yet there are doubts about how tightly reserves and bond yields are coupled. Claudio Borio of the Bank for International Settlements and Piti Disyatat of the Bank of Thailand have noted that Treasury yields tended to rise in 2005-07 even as capital flows into America remained strong, and that rates then fell when those inflows slackened. The link has been rather weak this year, too. Reserves have been run down but bond yields in both America and Europe have also fallen.

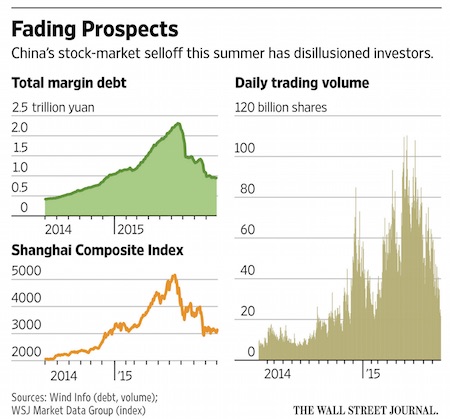
The ‘rescue’ has chased many ‘investors’ out.
• Beijing’s Market Rescue Leaves China Stocks Stuck in the Doldrums (WSJ)
Six weeks after the Chinese stock market hit a floor following a sustained selloff, Beijing can claim credit for halting the decline—but not much else. The Chinese government, which some analysts estimate has spent hundreds of billions of yuan buying stocks to stop the crash, is now left with a market in the doldrums. Shares are languishing near their lows, trading volume is down by about 70% from a peak in June, and volatility has fallen by more than half since July’s record. Valuations in some parts of the market remain among the most expensive anywhere. “Low volume, low volatility and a tight trading range” are hallmarks of a market getting stuck, said Hao Hong, managing director at Bank of Communications Co. If history is a guide, the market could be stuck for some time.
Shanghai’s largest selloff on record, which lasted more than four months during the global financial crisis, knocked 50% off the market’s value. After the benchmark rallied in 2009, it languished for years thereafter. In the heat of this summer’s selloff, Beijing promised that brokerages would buy shares as long as the Shanghai Composite Index remained under the 4500 level. But authorities appear to have given up. After plunging as much as 41% from June to its low point on Aug. 26, the benchmark settled into a tight trading range for more than a month. The Shanghai index rose 4% in the two trading days the past week, after the market reopened on Thursday following a weeklong holiday. It closed up 1.3% on Friday at 3183, still 41% away from the 4500 level.
The weeks of late-day stock surges—indications of intervention by state-backed funds—have been absent recently. Shares of resource-investment company Guangdong Meiyan Jixiang Hydropower surged as much as 153% after disclosing in early August that government agency China Securities Finance Corp. had become its largest shareholder. They have since plummeted 38%. By late September, trading volume for China’s domestic stock market thinned to below 30 billion shares in a single session. That compares with a record of more than 100 billion shares in early June. The average daily volume last month was at its lowest since February.

Give them a shot at making things worse, and they won’t disappoint.
• Fed Officials Seem Ready To Deploy Negative Rates In Next Crisis (MarketWatch)
Fed officials now seem open to deploying negative interest rates to combat the next serious recession even though they rejected that option during the darkest days of the financial crisis in 2009 and 2010. “Some of the experiences [in Europe] suggest maybe can we use negative interest rates and the costs aren’t as great as you anticipate,” said William Dudley, the president of the New York Fed, in an interview on CNBC on Friday. The Fed under former chairman Ben Bernanke considered using negative rates during the financial crisis, but rejected the idea. “We decided – even during the period where the economy was doing the poorest and we were pretty far from our objectives – not to move to negative interest rates because of some concern that the costs might outweigh the benefits,” said Dudley.
Bernanke told Bloomberg Radio last week he didn’t deploy negative rates because he was “afraid” zero interest rates would have adverse effects on money markets funds – a concern they wouldn’t be able to recover management fees – and the federal-funds market might not work. Staff work told him the benefits were not great. But events in Europe over the past few years have changed his mind. In Europe, the European Central Bank, the Swiss National Bank and the central banks of Denmark and Sweden have deployed negative rates to some small degree. “We see now in the past few years that it has been made to work in some European countries,” he said. “So I would think that in a future episode that the Fed would consider it,” he said.
He said it wouldn’t be a “panacea,” but it would be additional support. In fact, Narayana Kocherlakota, the dovish president of the Minneapolis Fed, projected negative rates in his latest forecast of the path of interest rates released last month. Kocherlakota said he was willing to push rates down to give a boost to the labor market, which he said has stagnated after a strong 2014. Although negative rates have a “Dr. Strangelove” feel, pushing rates into negative territory works in many ways just like a regular decline in interest rates that we’re all used to, said Miles Kimball, an economics professor at the University of Michigan and an advocate of negative rates.
But to get a big impact of negative rates, a country would have to cut rates on paper currency, he pointed out, and this would take some getting used to. For instance, $100 in the bank would be worth only $98 after a certain period. Because of this controversial feature, the Fed is not likely to be the first country that tries negative rates in a major way, Kimball said. But the benefits are tantalizing, especially given the low productivity growth path facing the U.S. With negative rates, “aggregate demand is no longer scarce,” Kimball said.


That’s the same as saying a crash is inevitable.
• IMF: Keep Interest Rates Low Or Risk Another Crash (Guardian)
The IMF concluded its annual meeting in Lima with a warning to central bankers that the world economy risks another crash unless they continue to support growth with low interest rates. The Washington-based lender of last resort said in its final communiqué that uncertainty and financial market volatility have increased, and medium-term growth prospects have weakened. “In many advanced economies, the main risk remains a decline of already low growth,” it said, and this needed to be supported with “continued accommodative monetary policies, and improved financial stability”. The IMF’s managing director, Christine Lagarde, said there were risks of “spillovers” into volatile financial markets from central banks in the US and the UK increasing the cost of credit.
The IMF has also urged Japan and the eurozone to maintain their plans to stimulate their ailing economies with an increase in quantitative easing. But she urged policymakers in Japan and the eurozone to boost their economies with an expansion of lending banks and businesses via extra quantitative easing. But the policy of cheap credit and the $7 trillion of quantitative easing poured into the world economy since 2009 has become increasingly controversial. A quartet of former central bank governors responded to the IMF’s message with a warning to current policymakers that they risked sowing the seeds of the next financial crisis by prolonging the period of ultra-low interest.
In a study launched in Lima to coincide with the IMF’s annual meeting, the G30 group of experts said keeping the cost of borrowing too low for too long was leading to a dangerous buildup in debt. The study was written by four ex-central bank governors, including Jean-Claude Trichet, former president of the European Central Bank, and Axel Weber, previously president of the German Bundesbank, and now chairman of UBS.

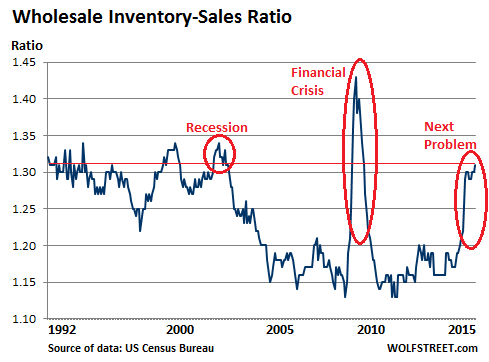
The inventory-to-sales ratio.
• Last Time This Ratio Soared Like This Was After Lehman Moment (WolfStreet)
This was a data set we didn’t need. Not one bit. It mauled our hopes. But the US Census Bureau dished it up anyway: wholesales declined again, inventories rose again, and the inventory-to-sales ratio reached Lehman-moment levels. In August, wholesales dropped to $445.4 billion, seasonally adjusted. Down 1.0% from July and down 4.7% from August last year. It was ugly all around. Wholesales of durable goods dropped 1.2% for the month, and 1.9% year over year. The standouts: Computer and computer peripheral equipment and software plunged 5.1% for the month and 6.2% year-over-year. Machinery sales dropped 2.7% from July and 3.5% year-over-year. Both are the signature of our ongoing phenomenal white-hot high-tech investment boom in corporate America, focused more on financial engineering than actual engineering.
Wholesales of non-durable goods fell 0.7% for the month and plunged 7.2% year-over year! Standouts: petroleum products (-36.6% year-over-year) and farm products (-12.4% year-over-year). They’ve gotten hammered by the commodities rout. But the pharmaceutical industry is where resourcefulness shines. At $52 billion in wholesales, drugs are the largest category, durable or non-durable. And sales rose another 0.9% for the month and jumped 14% from a year ago! Price increases in an often monopolistic market can perform stunning miracles. Without them, wholesales would have looked a lot worse! Falling sales are bad enough. But ominously, inventories continued to rise from already high levels to $583.8 billion and are now 4.1% higher than a year ago.
Durable goods inventories rose 0.3% for the month and 4.2% year-over-year, with automotive inventories jumping 13.5% year-over-year. Non-durable goods inventories are now 4.0% higher than a year ago, with drugs (+5.4%), apparel (+11.6%), and chemicals (+7.9%) leading the way. But petroleum products inventories dropped 21.9% year-over-year. The crucial inventory-to-sales ratio, which shows how long merchandise gets hung up before it is finally sold, has been getting worse and worse. In July last year, it was 1.17. It hit 1.22 in December. Then it spiked. In August, it rose to 1.31, the level it had reached just after the Lehman moment in 2008:

What future do we have left?
• Why We Shouldn’t Borrow Money From The Future (John Kay)
More than a half-century ago, John Kenneth Galbraith presented a definitive depiction of the Wall Street Crash of 1929 in a slim, elegantly written volume. Embezzlement, Galbraith observed, has the property that “weeks, months, or years elapse between the commission of the crime and its discovery. This is the period, incidentally, when the embezzler has his gain and the man who has been embezzled feels no loss. There is a net increase in psychic wealth.” Galbraith described that increase in wealth as “the bezzle.” In a delightful essay, Warren Buffett’s business partner, Charlie Munger, pointed out that the concept can be extended much more widely. This psychic wealth can be created without illegality: mistake or self-delusion is enough. Munger coined the term “febezzle,” or “functionally equivalent bezzle,” to describe the wealth that exists in the interval between the creation and the destruction of the illusion.
From this perspective, the critic who exposes a fake Rembrandt does the world no favor: The owner of the picture suffers a loss, as perhaps do potential viewers, and the owners of genuine Rembrandts gain little. The finance sector did not look kindly on those who pointed out that the New Economy bubble of the late 1990s, or the credit expansion that preceded the 2008 global financial crisis, had created a large febezzle. It is easier for both regulators and market participants to follow the crowd. Only a brave person would stand in the way of those expecting to become rich by trading Internet stocks with one another, or would deny people the opportunity to own their own homes because they could not afford them.
The joy of the bezzle is that two people – each ignorant of the other’s existence and role – can enjoy the same wealth. The champagne that Enron’s Jeff Skilling drank when the US Securities and Exchange Commission allowed him to mark long-term energy contracts to market was paid for by the company’s shareholders and creditors, but they would not know that until ten years later. Households in US cities received mortgages in 2006 that they could never hope to repay, while taxpayers never dreamed that they would be called on to bail out the lenders. Shareholders in banks could not have understood that the dividends they received before 2007 were actually money that they had borrowed from themselves.

Right. It won’t help, but it should be done anyway?!
• Euro Superstate Won’t Save Dysfunctional Single Currency: Ex-IMF Chief (Telegraph)
The euro will be consigned to a permanent state of malaise as deeper integration will bring no prosperity to the crisis-hit bloc, according to the former chief economist of the IMF. In a stark warning, Olivier Blanchard – who spent eight years firefighting the worst global financial crisis in history – said transferring sovereignty from member states to Brussels would be no “panacea” for the ills of the euro. The comments – from one of the foremost western economists of the last decade – pour cold water on grandiose visions for an “EU superstate” being hailed as the next step towards integration in the currency bloc Following this summer’s turmoil in Greece, leaders from France’s Francois Hollande, the European Commission’s Jean-Claude Juncker, and ECB chief Mario Draghi, have spearheaded the drive to create new supra-national institutions such as a eurozone treasury and parliament.
The plans are seen as essential in finally “completing” economic and monetary union 15 years after its inception. But Mr Blanchard, who departed the IMF two weeks ago, said radical visions for a full-blown “fiscal union” would not solve fundamental tensions at the heart of the euro. “[Fiscal union] is not a panacea”, Mr Blanchard told The Telegraph. “It should be done, but we should not think once it is done, the euro will work perfectly, and things will be forever fine.” Although pooling common funds, giving Brussels tax and spending powers, and creating a banking union were “essential” reforms, they would still not make the “euro function smoothly even in the best of cases”, said the Frenchman.
Any mechanism to transfer funds from strong to weak nations – which has been fiercely resisted by Germany – would only mask the fundamental competitiveness problems that will always plague struggling member states, he said. “Fiscal transfers will help you go through the tough spot, but at the same time, it will decrease the urge to do the required competitiveness adjustment.” The creation of a “United States of Europe” has been seen as a necessary step to insulate the eurozone from the financial contagion that bought it to its knees after 2010. It is a view shared by Mr Blanchard’s successor at the IMF, American Maurice Obstfeld, who has championed deeper eurozone integration as the best way to plug the institutional gaps in EMU. Mr Blanchard, however, said no institutional fixes would bring back prosperity back to the single currency.
Without the power to devalue their currency, peripheral economies would forever be forced to endure “tough adjustment”, such as slashing their wages, to keep up with stronger member states, he said. In this vein, Mr Blanchard dismissed any talk of a growth “miracle” in Spain – which has been hailed as a poster child for Brussels’ austerity diktats. He added he was “surprised” that sluggish eurozone economies were not doing better in the face of a cocktail of favourable economic conditions. “When people talk about the Spanish miracle, I react. When you have 23pc unemployment and 3pc growth, I don’t call this a miracle yet.” “I thought that the zero interest rate, the decrease in the price of oil, the depreciation of the euro, the pause in fiscal consolidation, would help more than they have”, he said.

It makes no difference what IMF and World Bank say. Or do.
• The Real Fight To Win The International Currency Wars (Telegraph)
The IMF and World Bank are divided over the question of currency depreciations as a tool of economic warfare. So who is really right? China’s decision to tweak its exchange rate peg with the dollar in August provoked reactionary howls of derision – from the US to India – that Beijing was gearing up for a new wave of international currency warfare. But do currency wars really work? Ahead of its bi-annual World Economic Outlook in Peru this week, the IMF has waded into the debate. It published a comprehensive set of findings confirming that weaker currencies are still an effective tool for economies to grow their way out of trouble. An exchange rate depreciation of around 10pc, said the IMF, results on average, in a rise in exports that will add 1.5pc to an economy’s output. But both the research and the timing are not uncontroversial.
China’s renminbi revaluation was nowhere near this 10pc magnitude, but its 3pc weakening was still the single biggest move in the exchange rate for more than twenty years. The intervention was seen by some as the opening gambit in another global “race to the bottom”. It sparked concern that China’s neighbouring economies would respond with retaliatory action in a desperate bid to boost flagging growth. The Fund’s research also seemed to confirm an intuitive principle of economics. Weaker currencies mean a country’s export goods are more attractive to external markets by making them cheaper for foreign buyers. Thus, devaluations have a direct and substantial impact in boosting GDP. History also shows that weakening exchange rates are a tried and tested resort for struggling nations trying to artificially boost their competitiveness, protect export shares, and undercut rivals.
But for all its apparent effectiveness, “competitive easing” runs counter to the IMF’s recommendation’s for the world’s economic policymakers. Exchange rate manipulation is a “cheat’s method”. It allows government’s to bypass painful “structural reforms” such as freeing up labour markets, reforming tax policies, and boosting investment – the holy grail of economic policy, long championed by the IMF. The Fund’s findings also put its research department at odds with its sister organisation – the World Bank. Three months before the IMF analysis, the Bank produced its own set of findings which trashed the notion that currency wars still work. Studying 46 countries over 16 years, researchers found that in the wake of the financial crisis, episodes of “large depreciation appeared to have had little impact on exports.”
Instead, the move towards more complex and inter-connected supply chains – spanning countries, continents and currencies – has muddied the relationship between lower exchange rates and cheaper goods. Over a third of all global trade is now made up of export goods whose components are are no longer solely produced in a single economy – or “global value chains” in economist speak. Currency depreciation, in this analysis, is a dud tool for policymakers. The benefits of devaluation in one country can be offset by currency strength in partner economies who make up the chain.

Big problems for big funds. Just starting.
• When Pension Funds Go Empty, All Bets Are Off (NY Post)
Some 407,000 Teamsters are learning a painful lesson: Their private-sector pensions aren’t as safe as they once thought. Pay attention, government workers -and taxpayers- in New York and New Jersey. Last week, letters informed these Teamsters they’re facing cuts in benefits of up to 60%. Why? Because their pension fund is going broke. The Central States Pension Fund covers workers from more than 1,500 trucking, construction and other companies in 37 states. Thanks to trucking deregulation, declining union rolls, aging workers and weak stock-market returns, the fund is now paying out $3.46 in benefits for every $1 it takes in. That’s $2 billion a year in red ink.
At that rate, doom arrives in 2026, sinking Central States and maybe even the federal fund that’s supposed to insure such private-sector pensions. Retirees would get even lower benefits — or maybe nothing at all. Which is why Congress and President Obama last year gave “multi-employer” funds like Central States the green light to restructure if necessary — and slice benefits. At least a few big pension systems are sure to follow Central States. And so the retirement security countless workers have long counted on went poof. Government pensions aren’t immune. Yes, many state constitutions bar pension cuts — and if the funds sink, politicians would find it easier to hit up taxpayers in a crunch than anger unions and their members by trimming benefits.
Easier at first, anyway. But when the well runs dry, what’ll happen? That’s the nut New Jersey governments have been grappling with in recent years. New York’s situation is better — but it, too, faces a reckoning. That’s even though Jersey’s funds need a whopping $200 billion to make good on their pension promises, while Empire State funds need $308 billion. Driving the shortfalls: Too many retirees for each current worker, as with Central States; overly generous pension promises pols made to please unions — and governments’ habit of not paying what they should into the funds.

Ouch. The plot thickens and deepens. They still didn’t come clean. “Investors are traumatized by past events, they will be paralyzed if VW’s current diesel line-up has questionable software on board..”
• US Probes A Second VW Emissions Control Device, Failure To Disclose (BBG)
The EPA is investigating a second emissions-control software program in Volkswagen AG cars that were rigged to pass pollution tests, one that the automaker may have failed to properly disclose. The computer program is on the EA 189 diesel engines used since 2009 that are also fitted with software that the automaker has admitted was designed to fool emissions tests, according to a person familiar with the matter who asked not to be named because the information is private. “VW did very recently provide EPA with very preliminary information on an auxiliary emissions control device that VW said was included in one or more model years,” EPA spokesman Nick Conger said. The agency, as well as its California counterpart, “are investigating the nature and purpose of this recently identified device.”
The possibility of a second device under scrutiny will make it harder for Volkswagen to emerge from the crisis. Already, VW faces criminal and civil liability as a company, including more than 250 class-action lawsuits. Some of its executives also face individual charges, and investigators and prosecutors are trying to figure out just how widespread the cheating was. The device was disclosed in applications to regulators for the 2.0 liter turbo diesel engine models to be sold next year, the company said Saturday in an e-mailed statement from Wolfsburg, Germany. The EPA and the California Air Resources Board are reviewing the device, which VW said serves to warm up the engine, and additional information is being submitted, according to the statement.
Automakers are required to point out if engines have special operating modes that can affect the way pollution-control equipment works. Such programs aren’t necessarily prohibited, and don’t by themselves indicate an attempt to cheat, though carmakers are supposed to disclose them so regulators can adjust their tests to be sure the vehicles still meet standards. Volkswagen has withdrawn applications for EPA certification of diesel vehicles for the 2016 model year. The company decided the newly disclosed technology qualified as an emissions-control device that the EPA needed to review, Michael Horn, the president and chief executive officer of Volkswagen of America, told Congress Thursday.

The crumbling walls of Berlin.
• Germany Readies For More Woe As Scandal And Slowdown Hit Economy (Observer)
When the German football team lost 1-0 to the Republic of Ireland on Thursday night in a European championship qualifying match, it capped a grim week for national pride. The shock defeat on the football field followed the ritual grilling of Michael Horn, the US boss of disgraced car-maker Volkswagen, by the US Congress; record losses at the country’s biggest bank, Deutsche Bank; and a clutch of dire economic figures, including the sharpest drop in exports since 2009. Suddenly, the health of Germany’s economy, powerhouse of the 19-member eurozone, is under question, just as the slowdown in emerging markets, including China, starts to take its toll. Volkswagen, for decades the ultimate symbol of lean, beautifully engineered German industry, is a byword for shoddy corporate practices since it admitted to deceiving regulators over emissions from its diesel cars.
Horn apologised during the bruising congressional hearing, and was forced to concede that it was “very hard to believe” that the scandal was the work of a few rogue engineers. Ben May of consultancy Oxford Economics says it is not yet clear how the Volkswagen scandal will affect the wider German economy, but it could have a considerable impact if it undermines confidence in diesel cars generally. “Diesel cars are the speciality of European manufacturers,” he says. “If you start to see buyers ditch diesel, or policymakers put in place regulations that mean it’s harder to produce cheap, compliant diesel cars, you might see Japanese and American producers gaining a bigger share of the European market.”
Meanwhile Frankfurt-based Deutsche Bank, which is being reshaped by its new boss, John Cryan, announced its largest-ever loss, more than €6bn, in the third quarter. Shareholders welcomed the announcement as a signal that Cryan was taking an aggressive approach to turning Deutsche Bank around, and would not be asking them to contribute more capital. But news that another pillar of the German corporate establishment looked shaky added to the sense of uncertainty. Germany’s economic model is heavily dependent on exports, including to fast-growing emerging economies, a specialism that has served it well in recent years. But analysts say the sharp decline in exports – they fell by more than 5% in August – could be the first solid evidence that the downturn in emerging markets has started to hit home in Europe.

“..charges to be prepared against Drumm on up to 30 different offences.”
• Ex-CEO Of Anglo Irish Bank In US Custody Facing Extradition (Guardian)
US marshals in Massachusetts have arrested David Drumm – the former chief executive of Anglo Irish Bank who is seen as a culprit in Ireland’s banking crisis – on an extradition warrant, according to the US attorney’s office in the state. A spokeswoman for the the US attorney in the District of Massachusetts, Christina DiIorio-Sterling, said: “I can confirm that Mr Drumm was arrested by US Marshals in Massachusetts on an extradition warrant. He will remain in custody until his hearing in federal court in Boston on Tuesday.” It was reported in January that Ireland had sent an extradition file to the US government, outlining charges to be prepared against Drumm on up to 30 different offences.
The Irish office of public prosecutions, which has brought other Anglo Irish Bank executives to trial, requested in July that a parliamentary inquiry into Ireland’s banking crisis not publish a statement Drumm had issued to it. Drumm stepped down from the one-time stock market titan in December 2008, a month before it was nationalised. He filed for bankruptcy in his new home of Boston two years later, owing his former employer more than $11m from loans he had been given. A Boston court dismissed his application as not remotely credible earlier in 2015, saying he had lied and acted in a fraudulent manner in his bid to be declared bankrupt in the United States.
Bailing out the failed bank that Drumm ran from 2005 to 2008 cost taxpayers around €30bn, close to one-fifth of Ireland’s annual output. It was seen as the heart of a banking crisis that forced Ireland itself into a 2010 international bailout. In July an Irish court sentenced three former employees of Anglo Irish Bank to between 18 and 36 months in prison, the first bankers to be jailed since the country’s financial crash.

“..it is doubtful that China can achieve the consumption-driven rebalancing that it seeks. After all, no high-performing East Asian economy has achieved such a rebalancing in the past, and China has a similar growth model…”
• China’s Monetary-Policy Choice (Zhang Jun)
Since assuming office in 2013, Premier Li Keqiang’s government has chosen not to loosen the previous government’s rigorous macro policies, instead hoping that the resulting pressure on existing industries might help to stimulate the authorities’ sought-after structural shift toward household consumption and services. Economists welcomed this ostensibly reasonable approach, which would slow the expansion of credit that had enabled a massive debt build-up in 2008-2010. China’s lower growth trajectory was dubbed the “new normal.” But, for this approach to work, GDP growth would have had to remain steady, rather than decline sharply. And that is not what has happened. Indeed, although structural adjustment continues in China, the economy is facing an increasingly serious contraction in demand and continued deflation.
The consumer price index (CPI) has remained below 2%, and the producer price index (PPI) has been negative, for 44 months. In a country with a huge amount of liquidity – M2 (a common measure of the money supply) amounts to double China’s GDP – and still-rising borrowing costs, this makes little sense. The problem is that the government has maintained a PPI-adjusted benchmark interest rate that exceeds 11%. Interest rates reach a ludicrous 20% in the shadow banking sector, and run even higher for some private lending.
The result is excessively high financing costs, which have made it impossible for firms in many manufacturing industries to maintain marginal profitability. Moreover, the closure of local-government financing platforms, together with the credit ceiling imposed by the central government, has caused local capital spending on investment in infrastructure to drop to a historic low.And tightening financial constraints have weakened growth in the real-estate sector considerably. With local governments and companies struggling to make interest payments, they are forced into a vicious cycle, borrowing from the shadow banking sector to meet their obligations, thereby raising the risk-free interest rate further. If excessively high real interest rates are undermining the domestic demand that China needs to reverse the economic slowdown, one naturally wonders why the government does not take steps to lower them. The apparent answer is the government’s overriding commitment to shifting the economy away from investment- and export-led growth. But it is doubtful that China can achieve the consumption-driven rebalancing that it seeks. After all, no high-performing East Asian economy has achieved such a rebalancing in the past, and China has a similar growth model.

Most western media headlines say “Thousands protest…”. Regardless, you’d need millions to have any effect.
• Hundreds Of Thousands Protest EU-US TTiP Trade Deal in Berlin (Reuters)
At least 150,000 people marched in Berlin on Saturday in protest against a planned free trade deal between Europe and the United States that they say is anti-democratic and will lower food safety, labor and environmental standards. Organizers – an alliance of environmental groups, charities and opposition parties – said 250,000 people had taken part in the rally against free trade deals with both the United States and Canada, far more than they had anticipated. “This is the biggest protest that this country has seen for many, many years,” Christoph Bautz, director of citizens’ movement Campact told protesters in a speech. Police said 150,000 people had taken part in the demonstration which was trouble free. There were 1,000 police officers on duty at the march.
Opposition to the so-called Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) has risen over the past year in Germany, with critics fearing the pact will hand too much power to big multinationals at the expense of consumers and workers. “What bothers me the most is that I don’t want all our consumer laws to be softened,” Oliver Zloty told Reuters TV. “And I don’t want to have a dictatorship by any companies.” Dietmar Bartsch, deputy leader of the parliamentary group for the Left party, who was taking part in the rally said he was concerned about the lack of transparency surrounding the talks. “We definitely need to know what is supposed to be being decided,” he said. Marchers banged drums, blew whistles and held up posters reading “Yes we can – Stop TTIP.”
The level of resistance has taken Chancellor Angela Merkel’s government by surprise and underscores the challenge it faces to turn the tide in favor of the deal which proponents say will create a market of 800 million and serve as a counterweight to China’s economic clout. In a full-page letter published in several German newspapers on Saturday, Economy Minister Sigmar Gabriel warned against “scaremongering”. “We have the chance to set new and goods standards for growing global trade. With ambitious, standards for the environment and consumers and with fair conditions for investment and workers. This must be our aim,” Gabriel wrote.

For the 2020 Olympics?!
• Tepco Expects To Begin Freezing Ice Wall At Fukushima No. 1 By Year-End (BBG)
Tokyo Electric Power Co. expects to begin freezing a soil barrier by the end of the year to stop a torrent of water entering the wrecked Fukushima nuclear facility, moving a step closer to fulfilling a promise the government made to the international community more than two years ago. “In the last half-year we have made significant progress in water treatment,” Akira Ono, chief of the Fukushima No. 1 plant, said Friday during a tour of the facility northeast of Tokyo. The frozen wall, along with other measures, “should be able to resolve the contaminated water issues before the (2020) Olympic Games.” Solving the water management problems will be a major milestone, but Tepco is still faced with a number of challenges at the site.
The company must still remove highly radioactive debris from inside three wrecked reactors, a task for which no applicable technology exists. The entire facility must eventually be dismantled. Currently, about 300 tons of water flow into the reactor building daily from the nearby hills. Tepco has struggled to decommission the reactors while also grappling with the buildup of contaminated water. Even four years after the meltdowns and despite promises from policymakers, water management remains one of Tepco’s biggest challenges in coping with the fallout of Japan’s worst nuclear disaster.
The purpose of the ice wall — a barrier of soil 30 meters (98 feet) deep and 1,500 meters (0.9 mile) long which is frozen to -30 degrees Celsius (-22 Fahrenheit) — is to prevent groundwater from flooding reactor basements and becoming contaminated. “As the radiation levels decrease via natural decay, water management becomes the main issue,” Dale Klein, an independent adviser for Tepco and a former chairman of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, said by e-mail. “It is a very important issue for the public, and good water management is needed for Tepco to restore the public’s trust.”

Yeah, don’t give them TVs or radios. Who knows what they might do.
• UK Home Office Bans ‘Luxury’ Goods For Syrian Refugees (Observer)
The Home Office warned councils against providing Syrian refugees with “luxury” items days before the home secretary, Theresa May, delivered an uncompromising speech limiting the right to claim asylum in Britain. Local authorities were sent new draft guidance on refugee resettlement in the week before May’s anti-immigration speech on Tuesday, rhetoric that critics said articulates the government’s increasingly hostile attitude towards refugees and asylum seekers. The Home Office guidance states that councils should not offer white or brown goods that might be deemed nonessential to resettled Syrians as part of the vulnerable persons resettlement scheme. Items that appear not to be allowed include fridges, cookers, radios, computers, TVs and DVDs.
Charities expressed concern, saying that the government should be concentrating on setting minimum standards for all Syrians seeking sanctuary in the UK instead of stating what they should not be allowed. “Child refugees aren’t coming here for our services, they are coming for our protection. We should give it gladly,” said Kirsty McNeill, campaigns director for charity Save the Children. The head of refugee support at the British Red Cross, Alex Fraser, said that all accommodation provided should afford “dignity and safety”. “People fleeing violence and persecution have been forced to endure the most appalling ordeals, and when they arrive in the UK they should be given the best possible start,” he said. Lisa Doyle, head of advocacy at the Refugee Council, said: “Resettling refugees in Britain shouldn’t just be about basic survival: everyone needs to be given the tools to build a life.”
The government has been accused of an inadequate response to the Syrian refugee crisis in recent months. In early September, under considerable pressure, David Cameron pledged that the UK would accept 20,000 refugees from camps bordering Syria over the next five years, and that the resettlement programme would prioritise vulnerable children and orphans. One local authority, Islington council in north London, confirmed it had received new draft guidance that permitted provision of “food storage, cooking and washing facilities” but it said that accommodation “should not include the provisions of other white goods and brown goods which could be considered luxury items”.

All upcoming attention for the Paris talks will be wasted or worse.
• World Will Pass Crucial 2ºC Global Warming Limit (Observer)
Pledges by nations to cut carbon emissions will fall far short of those needed to prevent global temperatures rising by more than the crucial 2C by the end of the century. This is the stark conclusion of climate experts who have analysed submissions in the runup to the Paris climate talks later this year. A rise of 2C is considered the most the Earth could tolerate without risking catastrophic changes to food production, sea levels, fishing, wildlife, deserts and water reserves. Even if rises are pegged at 2C, scientists say this will still destroy most coral reefs and glaciers and melt significant parts of the Greenland ice cap, bringing major rises in sea levels.
“We have had a global temperature rise of almost 1C since the industrial revolution and have already seen widespread impacts that have had real consequences for people,” said climate expert Professor Chris Field of Stanford University. “We should therefore be striving to limit warming to as far below 2C as possible. However, that will require a level of ambition that we have not yet seen.” In advance of the COP21 United Nations climate talks to be held in Paris from 30 November to 11 December, every country was asked to submit proposals on cutting use of fossil fuels in order to reduce their emissions of greenhouses gases and so tackle global warming. The deadline for these pledges was 1 October.
A total of 147 nations made submissions, and scientists have since been totting up how these would affect climate change. They have concluded they still fall well short of the amount needed to prevent a 2C warming by 2100, a fact that will be underlined later this week when the Grantham Research Institute releases its analysis of the COP21 submissions. This will show that the world’s carbon emissions, currently around 50bn tonnes a year, will still rise over the next 15 years, even if all the national pledges made to the UN are implemented. The institute’s figures suggest they will reach 55bn to 60bn by 2030.








