Pablo Picasso Les femmes d’Alger 1955

Prof Appel Dominion
Professor Appel's 2017 Congressional Testimony Regarding How Easy It Is To Change and Manipulate Votes And #Election Outcomes Using The Dominion #VotingMachines Which Were Used By 30 States In The #Election2020 pic.twitter.com/5bEq8tt9Sb
— Planet Ponzi (@PlanetPonzi) November 13, 2020


Limited impact.
• PA Court: Secretary Of State Lacked Authority To Change Voting Deadline (Fox)
A Pennsylvania judge ruled in favor of the Trump campaign Thursday, ordering that the state may not count ballots where the voters needed to provide proof of identification and failed to do so by Nov. 9. State law said that voters have until six days after the election — this year that was Nov. 9 — to cure problems regarding a lack of proof of identification. After the Pennsylvania Supreme Court ruled that mail-in ballots could be accepted three days after Election Day, Pennsylvania Secretary of State Kathy Boockvar submitted guidance that said proof of identification could be provided up until Nov. 12, which is six days from the ballot acceptance deadline. That guidance was issued two days before Election Day.
“[T]he Court concludes that Respondent Kathy Boockvar, in her official capacity as Secretary of the Commonwealth, lacked statutory authority to issue the November 1, 2020, guidance to Respondents County Boards of Elections insofar as that guidance purported to change the deadline … for certain electors to verify proof of identification,” Judge Mary Hannah Leavitt said in a court order. This was in line with the Trump campaign’s argument, which was that there was no basis in the state’s law to extend the identification deadline, and that Boockvar did not have the power to unilaterally change it. The court had previously ordered that all ballots where voters provided proof of identification between Nov. 10 and 12 should be segregated until a ruling was issued determining what should be done with them.
Matt Gaetz: Dead people don’t always vote. But when they do, they prefer to vote by mail.
Dead people don't always vote.
But when they do, they prefer to vote by mail. pic.twitter.com/cCLSrBpcvZ
— Rep. Matt Gaetz (@RepMattGaetz) November 13, 2020

“Every citizen deserves to have faith in the integrity of the election process and its outcome..”
• Michigan State Senators Request Full Election Audit (ET)
At least two Michigan Republican state senators have requested a full election audit, asking the Michigan secretary of state’s office for a full recount before the election results are certified, according to a letter they sent to her office on Thursday. State senators Lana Theis and Tom Barrett wrote that Michigan Secretary of State Jocelyn Benson and canvassers that are reviewing allegations of irregularities and voter fraud made in lawsuits filed by President Donald Trump’s campaign. They are requesting a “full audit” of the election, saying it needs to be done before the state certifies the election results. “Every citizen deserves to have faith in the integrity of the election process and its outcome,” they said in letters.
“It is our responsibility, as elected public servants, to assure the people of Michigan of the process’s integrity through complete transparency and the faithful investigation of any allegations of wrongdoing, fraud, or abuse.” Their letters made reference to allegations made by Trump’s legal team, claims of witnesses about irregularities at polls, and a glitch that switched 6,000 votes from a Republican official to a Democratic official in Antrim County that was later corrected and acknowledged by the secretary of state’s office, although the Michigan GOP said the same software – Dominion Voting Systems – was used in dozens of other counties.
“The erroneous reporting of unofficial results from Antrim county was a result of accidental error on the part of the Antrim County Clerk. The equipment and software did not malfunction and all ballots were properly tabulated. However, the clerk accidentally did not update the software used to collect voting machine data and report unofficial results,” Benson said in a statement last week about Antrim County’s election results. Other allegations from the two lawmakers include ineligible ballots being counted, poll workers being told to backdate ballots, counting the same ballots several times, and other claims.


The shameless backlash against bringing the troops home is stunning.
• Trump’s New Pentagon Sets Up Clash Over Afghanistan Pullout (Pol.)
President Donald Trump’s decapitation strike on the Pentagon this week is raising fears that the U.S. will accelerate the withdrawal of troops from Afghanistan, putting newly installed leaders on a collision course with top generals and others who are urging a more deliberate drawdown. Current and former administration officials say Trump fired Defense Secretary Mark Esper Monday in part over his opposition to accelerating troop drawdowns worldwide, and especially in Afghanistan. The upheaval accelerated on Tuesday with the resignation of three high-level civilians and the installation of loyalists who are expected to ram through Trump’s agenda, and continued on Wednesday when retired Army Col. Douglas Macgregor, an outspoken critic of the war in Afghanistan, was brought on as senior adviser to new acting Defense Secretary Chris Miller.
Any move to accelerate withdrawals would set up a clash with the nation’s top generals and other civilians, who have argued publicly against leaving Afghanistan too quickly while the security situation remains volatile. It would also complicate President-elect Joe Biden’s pledge to leave a small number of troops in the country to guard against terror attacks.
“A precipitous and what appears to be near total withdrawal of U.S. forces from Afghanistan — not on a conditions-based approach advocated by our military, political and intelligence leadership but rather on an old campaign promise by President Trump now carried out by hyperpartisan Trump loyalists installed in a last-minute purge of DoD — is both reckless and will not make America safer,” said Marc Polymeropoulos, a retired CIA senior operations officer. Concerns are also growing within the national security community that the personnel churn portends other major policy shifts, such as military actions abroad and in the U.S. Yet current and former administration officials believe the moves were more about rewarding allies and punishing those who resisted the president’s agenda than they were about major changes in direction.

And the New York Times will stop writing about him?
• Trump Could Be Banned From Twitter After He Leaves Office (Ind.)
Donald Trump will no longer be protected by Twitter’s public interest guidelines when he leaves office in January, meaning he will be suspended or banned if he continues to break the platform’s rules. Twitter’s policy regarding public figures, which was formalised last year, means only “current or potential member of a local, state, national, or supra-national governmental or legislative body” receive special treatment . The US President’s Twitter account was flagged more than a dozen times in the days following the election for posting misinformation and misleading claims about the election. Several prominent Democrats called for Twitter to suspend Mr Trump’s account until all states finish counting the votes, however the platform’s public interest guidelines prevent it from being suspended or removed.
After his lead in several key states began to dwindle to challenger Joe Biden, Mr Trump attempted to undermine the electoral process by calling for a halt to the counting of mail-in ballots. “They are trying to STEAL the Election,” he tweeted. Democratic Congressman David Cicilline described Mr Trump’s tweets as a “threat to democracy”, while fellow congressman Gerry Connolly tweeted, “This is pure disinformation.” Warnings placed on Mr Trump’s tweets meant they were not immediately visible on his timeline and engagement with the tweets was restricted. One warning explained: “Some or all of the content shared in this tweet is disputed and might be misleading about how to participate in an election or another civic process.” The rate of violations would typically lead to an account suspension, either temporarily or permanently. However, public figures are protected by a “public-interest exception” policy.

Not by his politics?
Oh well, Barry has a new book out.
• Obama: ‘Americans Spooked By Black Man In White House’ (JTN)
Just before President George W. Bush left the White House after two terms, he declared he wouldn’t be weighing in with thoughts on his successor, following the model of his father, George H.W. Bush. But Barack Obama made no such pledge. And now, just days after the 2020 election, the 44th president is hawking a new book so get ready to hear a lot more from him. Obama, the first biracial man to be elected president, makes an incendiary charge in his book, “A Promise Land,” which comes out Tuesday. President Trump, he claims, “promised an elixir for the racial anxiety” of “millions of Americans spooked by a black man in the White House.”
Those Americans – whom Obama implies appear racist – were prey to “the dark spirits that had long been lurking on the edges of the modern Republican party – xenophobia, anti-intellectualism, paranoid conspiracy theories, an antipathy toward black and brown folks.” Obama continues: “It was as if my very presence in the White House had triggered a deep-seated panic, a sense that the natural order had been disrupted. Which is exactly what Donald Trump understood when he started peddling assertions that I had not been born in the United States and was thus an illegitimate president.” Obama writes that “he came to regard Trump’s media ubiquity and characteristic shamelessness as merely an exaggerated version of the Republican Party’s attempts to appeal to White Americans’ anxieties about the first Black president – a sentiment he said ‘had migrated from the fringe of GOP politics to the center – an emotional, almost visceral, reaction to my presidency, distinct from any differences in policy or ideology,'” CNN reported.
The 768-page memoir is reportedly just volume one of his latest memoirs. Obama also writes about his shortcomings, like his failure to pass immigration reform, which he called “a bitter pill to swallow.” But he said his agenda was always correct, though voters swept out a slew of Democrats in the 2010 midterm election, two years into his presidency. “As far as I was concerned, the election didn’t prove our agenda had been wrong,” Obama writes of 2010. “It just proved that … I’d failed to rally the nation, as FDR had once done, behind what I knew to be right. Which to me was just as damning.”

“..we have created so much debt and this is a worldwide phenomenon, so we can’t have normal interest rates anymore”
• This Is What Happens To Us When The Great Global Reset Comes (Kitco)
We’re in the end game of a dollar-based system, and a new monetary system will emerge with gold as the anchor, said Willem Middelkoop, founder of the the Commodity Discovery Fund. “We’re in a rough period. It doesn’t matter which president will be next, he can only avoid a deep depression by printing trillions and trillions. As an investor, we concentrate on that part of the story,” he said. Fixing the fundamental problems in our economy, including excessive debt, will require more than just a continuation of past policies. “I think we have created so much debt and this is a worldwide phenomenon, so we can’t have normal interest rates anymore. We have seen the IMF coming out with a statement last week saying that we need a new Bretton Woods moment,” he said.
“We had a cover on Time magazine calling for the Great Reset. We had the World Economic Forum calling for a Great Reset. I wrote a book on the topic, published in 2014, it was called The Big Reset.” A new global system will require an overhaul of many monetary pillars that we currently have, Middelkoop noted. “We need a debt restructuring. IMF and the United Nations have been quite clear about that; we need debt restructuring first for the poor countries but later for the rich countries, we all have too much debt on our books. We need to find a new anchor for the world monetary system,” he said. Until then, trillions more in stimulus will be issued by governments around the world to avoid a global depression like that of the 1930’s, Middelkoop said.


Without COVID, this would have gotten zero attention.
• Three-Quarters Of England’s Care Workers Earn Below ‘Real’ Living Wage (G.)
Almost three-quarters of frontline care workers in England are earning below the “real” living wage, which experts say is the bare minimum to allow families basics such as a secondhand car and a week’s annual UK self-catering holiday, research has revealed. The proportion of care workers below the threshold is even higher in northern areas, where care homes have been hit hardest by Covid-19. In the north-east, 82% of care staff earned less than the England-wide real living wage of £9.50 per hour, while the proportion was 78% in the north-west. One care worker in Lancashire earning £8.72 per hour who recently had her pay cut told the Guardian some colleagues have been using food banks.
The figures apply to more than 832,000 frontline care workers, more than 600,000 of whom are earning below the minimum thresholds. In Hillingdon, the borough that contains Boris Johnson’s Uxbridge and South Ruislip parliamentary constituency, more than 3,000 care workers earn so little that if they are the main breadwinner in a family of four with their partner on similar wages, they could not afford the £112 a week they require for food, according to analysis by Loughborough University that underpins real living wage calculation. When Johnson was London mayor he supported the London living wage campaign as “making economic sense”.
The figures were calculated by the Living Wage Foundation and come amid growing calls for reform of the social care sector to create parity with the NHS, where all nurses earn above the threshold. On Thursday, Jeremy Hunt, the chairman of the Commons health and social care committee, called for a 10-year funding plan for social care akin to the national consensus that established the NHS in 1948. New polling revealed 82% of the public now back government investment in social care to fund a pay rise for care workers according to new polling by Survation for Citizens UK.

But what are the true rates?
• Unemployment Fiasco in Europe Is Kept out of Official Rates (WS)
In Europe, people who are furloughed are paid under government programs via their employers. Many of these programs have been created during the Pandemic. In theory, these people still have jobs. In practice, they’re not working, or are working heavily reduced hours. But they do not count as “unemployed” and are not reflected in the “unemployment” numbers. So throughout the Pandemic, the official unemployment rates barely ticked up, compared to the last crisis, and remain low for the EU era, despite tens of millions of people who’d stopped working due to the lockdowns (chart via Eurostat):
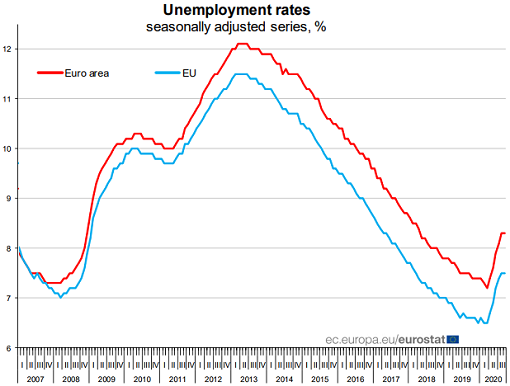
The UK adopted a sweeping job retention program at the beginning of its last lockdown. Each government pays companies, who in turn pay employees between 60% and 84% of their monthly wage. In some cases, the workers work fewer hours for less pay; in others, they don’t work at all. The workers take a hit to their income but their jobs remain intact, at least for the duration of the program. Under the UK program, businesses can claim 80% of a staff member’s regular monthly salary, up to a maximum of £2,500. The money must be passed on to the employee and can also be topped up by the employer.
But the unemployment rate has begun to rise as people come off furlough, and those whose jobs disappeared entered official unemployment. The unemployment rate ticked up to 4.8% in the three months to September, from 4.5% in Q2 and from 3.9% a year earlier, according to the Office for National Statistics (ONS). In London, the unemployment rate surged by 1.2 percentage points from the previous quarter, to 6%. It was the largest quarterly increase in unemployment since the ONS started tracking the data in 1992.

“I’m writing a book for Polity Press entitled The New Economics: A Manifesto. It has a long way to go, but this is the reasonably complete first chapter.”
• Introduction to The New Economics: A Manifesto (Steve Keen)
Even before the Covid-19 crisis began, the global economy was not in good shape, and nor was economic theory. The biggest economic crisis since the Great Depression began late in first decade of the 21st century. Called the “Global Financial Crisis” (GFC) in most of the world and the “Great Recession” in the USA, it saw unemployment explode from 4.6% of the US workforce in early 2007 to 10% in late 2009. Inflation turn into deflation— inflation of 5.6% in mid-2008 fell to minus 2% per year in mid-2009—and the stock market collapsed, with the S&P500 Index falling from 1500 in mid-2007 to under 750 in early 2009. The economy recovered very slowly after then, under the influence of an unprecedented range of government interventions, from the “cash for clunkers” scheme that encouraged consumers to dump old cars and buy new ones, to “Quantitative Easing”, where the Federal Reserve purchased a trillion-dollars-worth of bonds from the financial sector every year, in an attempt to stimulate the economy by making the wealthy wealthier.
This crisis surprised both the policy economists who advise governments on economic policy, and the academic who develop the theories and write the textbooks that train the vast majority of new economists. They had expected a continuation of the boom conditions that had preceded the crisis, and they in fact believed that crises could not occur. In his Presidential Address to the American Economic Association in January 2003, Nobel Prize winner Robert Lucas declared that crises like the Great Depression could never occur again because “Macroeconomics … has succeeded: Its central problem of depression prevention has been solved, for all practical purposes, and has in fact been solved for many decades. (Lucas 2003 , p. 1 ; emphasis added). Just two months before the crisis began, the Chief Economist of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the world’s premier economic policy body, declared that “the current economic situation is in many ways better than what we have experienced in years”, and predicted that “sustained growth in OECD economies would be underpinned by strong job creation and falling unemployment.” (Cotis 2007 , p. 7; emphases added)
How could they be so wrong? Economists could be excused for this failure to see the Great Recession coming if the crisis were something like Covid-19, when a new pathogen suddenly emerged out of China. That such a plague would occur was predicted as long ago as 1995 (Garrett 1995). But predicting when the pathogen would emerge, let alone what its characteristics would be, was clearly impossible. However, the epicentre of the Great Recession was the US financial system itself: the crisis came from inside the economy, rather than from outside. Surely there were warning signs? As Queen Elizabeth herself put it when she attended a briefing at the London School of Economics in 2008, “If these things were so large, how come everyone missed them?”

Good to see Dmitry!
I first realized that the USA was going to follow the general trajectory of the USSR back in 1995. I also immediately realized that the USSR was rather well prepared for collapse whereas the USA was about to be blindsided by it, and so, as a public service, I thought I should warn people. “And a fat lot of good that did!” some of you might immediately exclaim. [..] And so I had my “Eureka!” moment in 1995, and a decade later, in 2005, I went public with my observations. I got a surprisingly sympathetic response from some particularly enlightened people (even if they said so themselves). And now, a quarter of a century after my initial insight, as the US enters national bankruptcy and institutional collapse, the whole world is being treated to an end-of-empire spectacular election extravaganza starring none other than the consummate showman and impresario extraordinaire Donald Trump.
He used to run beauty pageants, while this one is more of an ugliness pageant, but then beauty is rare and always fades while ugliness is commonplace and usually just gets uglier, making it a much safer bet. And so let’s accept it as a parting present to the world from a vanishing nation that gave us horror flicks, reality television and three-ring circuses with sideshow freaks. Within the sweeping panoramic tableau of the 2020 election, Trump (our hero) appears bathed in a golden sunset glow of nostalgia for lost American greatness which he forever promises to rekindle. Rest assured, Trump or no Trump, America will never be great again. But Trump’s magic halo extends out from his resplendent orange cranial plumage and enfolds all those who pine for the lost Pax Americana and fear and loathe what America is fast becoming—which is, to put it bluntly, a holding tank for degenerates of every stripe presided over by a freak show.
They pine for a time when men were manly and women womanly, when secretaries were flattered when their bosses took time away from their busy schedules to rub up against them, and when everyone was either a WASP, or worked hard on trying to look and act like one, or kept to their assigned station in life and knew better than to get too uppity. Arrayed against our fearless orange-hued leader, who at 74 is no spring chicken himself, is a ghoulish gaggle of geriatric gerontocrats. There is Joe Biden, 77, whose brain ran away and joined a circus some years ago but who imagines himself to be president-elect, or senator, or vice-president, or something. Having spent eight years lurking in the shadows as Obama’s VP, Biden is as fit to lead as a pig is kosher after rubbing its side against a corner of a synagogue. To assist Biden in his dodderings there is his party-appointed nanny, Kamala Harris, a mere slip of a girl at 56.
Also haunting the balcony of the American mausoleum is Nancy Pelosi, 80, who still runs the House of Representatives even though proper employment for her at this point would be up on a pole keeping the birds off the corn. There is also Bernie Sanders, 79, a sad pagliaccio whose permanent role in the political Commedia dell’Arte that the Democratic Party stages every four years is to simulate democracy by cheerleading crowds of young imbeciles in Act I, to feign death after falling off his pogo stick in Act II, and to stagger to his feet, wave and smile for the curtain call. Last but not least, there is the horrid harpy Hillary Clinton, who is relatively young at 73 but whose putrid smell and cadaverous, ghastly visage are not longer fit for public display except in most delicately contrived circumstances. Hidden even further backstage is the suppurating cadaver of George Soros who, at 90, is still pulling the strings and wreaking havoc in the US and around the world.

We try to run the Automatic Earth on donations. Since ad revenue has collapsed, you are now not just a reader, but an integral part of the process that builds this site.
Click at the top of the sidebars for Paypal and Patreon donations. Thank you for your support.

What makes us fragile is that institutions cannot have the same virtues (honor, truthfulness, courage, loyalty, tenacity) as individuals.
– Nassim Nicholas Taleb in The Bed of Procrustes

COVID Tracking Project
Cases nationwide are trending up more quickly than at any point in the pandemic. Today’s 7-day average—nearly 130k—is 54k more than two weeks ago, a growth of 71%. pic.twitter.com/S4LUBzWW66
— The COVID Tracking Project (@COVID19Tracking) November 13, 2020

Support the Automatic Earth in virustime, election time, all the time. Click at the top of the sidebars to donate with Paypal and Patreon.