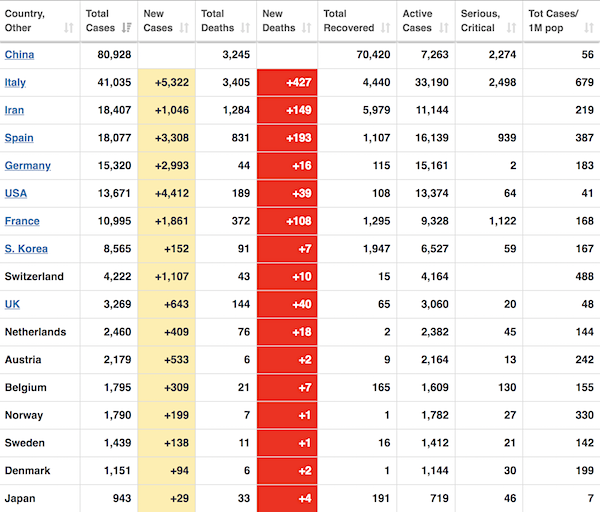
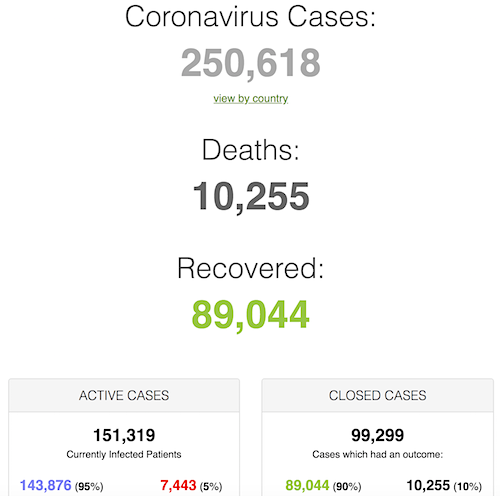
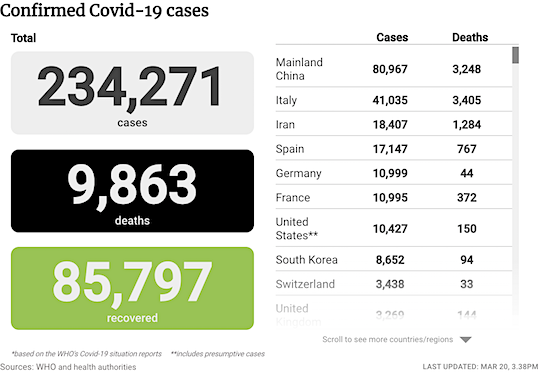
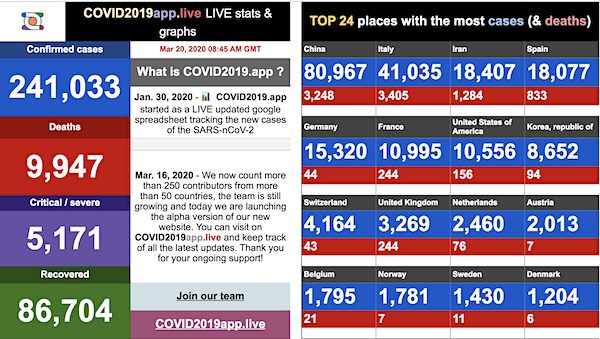
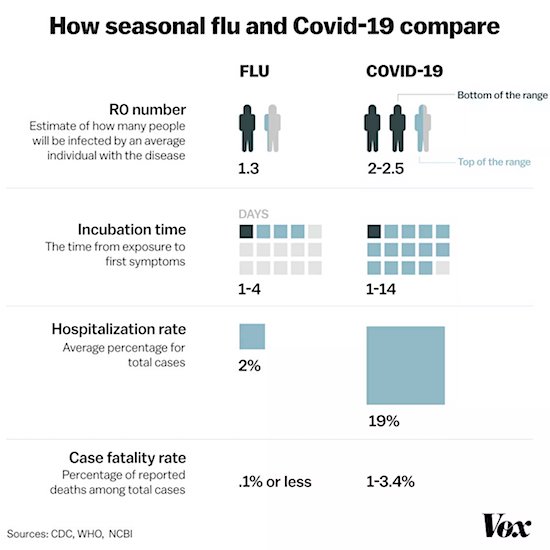
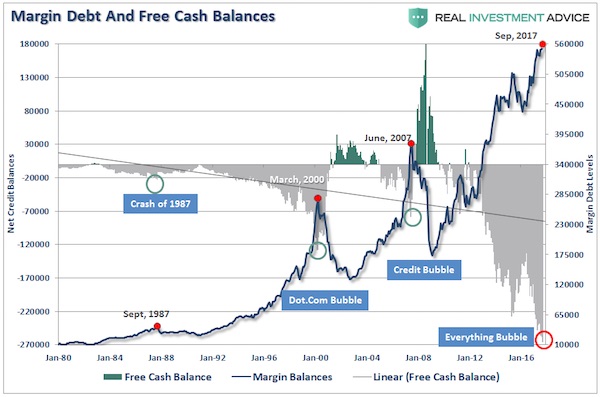
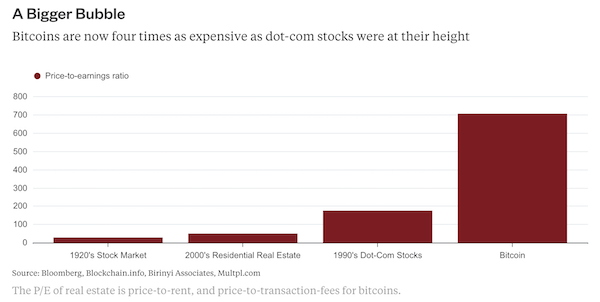
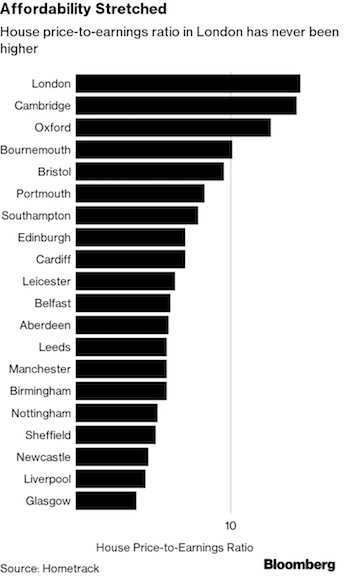
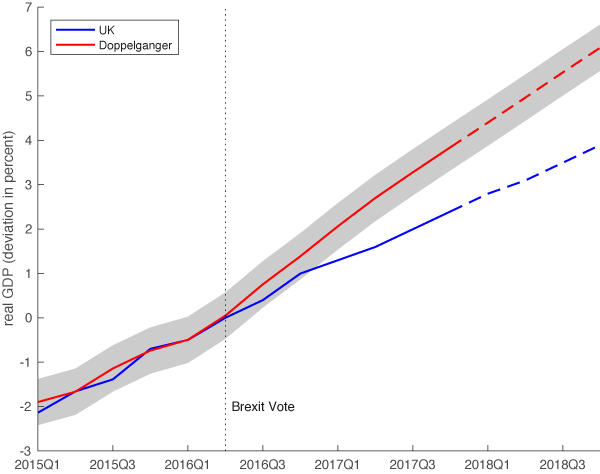
George N. Barnard Nashville, Tennessee. Rail yard and depot. 1864



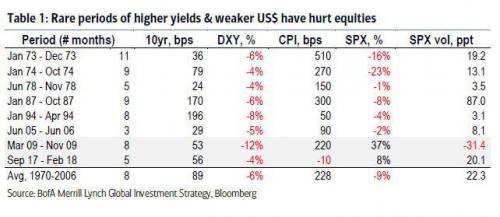
15% is a devastating number. But they’re just going to announce 7% GDP growth no matter what.
• China’s March Exports Shrink 15% Year-on-Year In Shock Fall (Reuters)
China’s export sales contracted 15% in March while import shipments fell at their sharpest rate since the 2009 global financial crisis, a shock outcome that deepens concern about sputtering Chinese economic growth. The tumble in exports – the worst in about a year – compared with expectations for a 12% rise and could heighten worries about how a rising yuan CNY=CFXS has hurt demand for Chinese goods and services abroad, analysts said. In a sign that domestic demand was also tepid, imports into the world’s second-biggest economy shrunk 12.7% last month from a year ago, the General Administration of Customs said on Monday. That was the biggest slump in imports since May 2009, and compared with a Reuters poll forecast for a 11.7% drop.
“It’s a very bad number that was much worse than expectations,” Louis Kuijs, an economist at RBS in Hong Kong, said in reference to the export data. “It leads to warning flags both on global demand and China’s competitiveness.” Buffeted by lukewarm foreign and domestic demand, China’s trade sector has wobbled in the past year on the back of the country’s cooling economy, unsettling policymakers. Chinese Vice Premier Wang Yang was quoted by Xinhua state news agency as saying earlier this month that authorities must act to arrest China’s export slowdown lest it further dampens economic growth.
Read more …

“The fall defied the expectations of economists who said exports usually rebound after the Lunar New Year..”
• China’s March Exports Come In Far Worse Than Expected (WSJ)
China’s exports fell sharply in March while imports slumped once again, suggesting to economists that the world’s second largest economy is being hit with sluggish demand at home and abroad. The nation’s exports slid 15% from a year earlier in March while imports dropped 12.7%, according to data released Monday by the General Administration of Customs. “Domestic demand is still sluggish,” said Kevin Lai, economist at Daiwa Capital. “Other than the U.S., the export situation isn’t looking very strong.” The fall defied the expectations of economists who said exports usually rebound after the Lunar New Year, which fell in February this year. In February, customs data showed exports up 48.3% from a year earlier while imports were down 20.5%.
Exports are no longer the big engine for the Chinese economy that they once were but the absence of growth in that once-critical area is a further drag on already weak growth. China’s economy posted growth of 7.4% last year, its slowest pace in 24 years, and the government has set an even lower target of about 7% growth for this year. Beijing has used a host of targeted measures to boost the economy, ranging from increased infrastructure spending and reductions in electricity tariffs to two cuts in interest rates to lower the cost of borrowing for domestic companies.
Data for the first quarter are due to be released Wednesday, and many economists project growth at less than 7% from a year earlier. Economists expected an increase of about 10% for exports in March and a drop of 12% for imports, according to a poll of analysts by The Wall Street Journal. China posted a trade surplus of 18.16 billion yuan in March, or about $2.93 billion, well below the $60.6 billion surplus in February.
Read more …

“..concerns about the state of the global recovery..” No kidding.
• China’s Trade Collapse Raises Fears Of Growth Slowdown (Telegraph)
China’s exports fell by a spectacular 15pc in March reviving fears of a slowdown in the world’s second largest economy. Trade data showed imports also fell by 12pc year-on-year, resulting in a sharp drop in the country’s trade surplus and leading to concerns economic growth will register a significant slowdown when figures are released on Wednesday. China’s economy has been in the throes of a managed slowdown in the last few years. Beijing has set a target of 7pc GDP growth in 2015 as the country seeks to move towards a more sustainble rate of growth. GDP expanded by 7.4pc in 2014, its slowest rate of output growth in nearly a quarter of a century.
The Australian dollar, which is closely linked to the trade fortunes of the Chinese economy, fell to a six-year low on the back of the news. A significant brake on Chinese growth could now “ripple out across the globe,” said Michael Hewson of CMC Markets. “These data misses raise concerns that not only is the Chinese economy failing to rebalance with demand remaining low, but also the global economy’s demand for Chinese exports is also falling back raising concerns about the state of the global recovery as well,” said Mr Hewson. The sluggish numbers come despite stimulative action from China’s central bank to cut interest rates, and ease bank reserve targets.
Read more …

Australia already knows.
• World Bank Warns Of Hit To Australia As Chinese Growth Falters (AAP)
A Chinese economic slowdown will hit Australia as iron ore prices tumble, the World Bank has said. The bank said Australia’s growth pace had deteriorated sharply since the first quarter of 2014 as declining prices for export commodities depressed mining investment and weakened the Australian dollar. The warning came as poor Chinese trade figures underlined the continued slowdown in the world’s second-largest economy. Exports were down 14.6% in March from a year ago while imports fell 12.3% on the same measure. The Australian dollar fell more than half a US cent to hover around the US76c mark. The World Bank predicted that a further slowdown in China, Australia’s biggest trading partner, would affect Australia and its neighbours.
The bank’s east Asia and Pacific economic update said: “The significant negative impact on Australia and New Zealand, among the world’s largest commodity suppliers, would lead to indirect spillovers on the Pacific Island countries, given their tight links through trade, investment and aid.”. China’s growth pace in 2014 was the weakest since 1990 but the World Bank said things were set to get worse – just a month after the Chinese government cut its growth target to 7%. Chinese growth would ease from 7.4% in 2014, to 7.1% in 2015, 7% in 2016 and 6.9% in 2017.
China is a major buyer of Australian iron ore, which is used to make steel. The World Bank said: “In China, as it shifts to a consumption-led, rather than an investment-led, growth model, the main challenge is to implement reforms that will ensure sustainable growth in the long run.” Sudhir Shetty, the World Bank’s chief economist for east Asia and the Pacific region, said many risks remained for east Asia Pacific region “both in the short and long run”. The gloomy prediction comes as the treasurer, Joe Hockey, forecast the iron ore price dropping to $35 a tonne, which could see commonwealth revenue fall $25bn over four years.
Read more …

Again: they’re just going to say 7% growth no matter what.
• China Growth Last Quarter Seen Worst Since Global Recession
While the central bank has cut interest rates twice in the last six months to cushion a slowdown, rising bad debts and a crackdown on shadow lending are making banks reluctant to lend to smaller firms. “It’s a structural problem that can’t be quickly addressed,” said Zhao Yang, the Hong Kong-based chief China economist at Nomura. “China’s financial system is not friendly to private businesses, and for the central bank, it has few short-term options but to cut required reserve ratios or benchmark interest rates further.” The benchmark one-year lending rate in China is now 5.35%, versus near-zero levels in the U.S., euro zone and Japan. The Wenzhou Private Finance Index, a measure of non-bank lending rates among private companies, is around 20%. State-owned enterprises, traditionally with easier access to credit, have seen output weighed by a restructuring drive and crackdown on corruption and pollution.
That leaves People’s Bank of China Governor Zhou Xiaochuan juggling financial reforms to try to steer toward a more market-driven economy with the need to ensure growth doesn’t slow too fast. GDP data scheduled for Wednesday will probably show the economy expanded 7% in the first quarter from a year earlier, according to the median estimate of 38 economists in a Bloomberg survey as of April 10. That would be the slowest pace since the first quarter of 2009, when China was hit by the global financial crisis, prompting then Premier Wen Jiabao to unleash a massive stimulus package that featured a record credit boom. To achieve this year’s growth target of about 7%, current Premier Li Keqiang may need to add policy support, something he flagged last month he stood ready to do. The consumer-prices index held steady at a 1.4% increase in March from a year earlier, giving room to act.
Read more …

Fighting in the streets more likely.
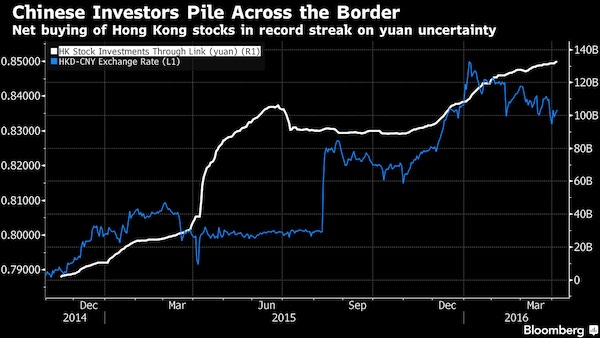
• China’s Stock Surge May Very Well End In Tears (MarketWatch)
Once dismissed as a “ghost train,” the trading scheme — known variously as the “new China through train” or Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect — roared to life last week, helping send the Hang Seng Index HSI, +2.22% to a seven-year high. But this awakening brings not just welcome stock gains, but also fear of a rerun of the euphoric boom and bust of 2007, when a previous through-train plan was announced, only to be later shelved. This time, a possible bust may also challenge the Hong Kong dollar’s currency peg. Unlike the failed 2007 scheme, the new Stock Connect was designed to limit exuberant cross-border money flows, as it operates under a closed loop.
That may be easier said than done. Hong Kong holds a unique position as the first and only stop for mainland Chinese who want to buy foreign equities. This will not be lost on global funds which may want to hitch a ride on this through train, even if it is a roller coaster. All signs suggest the trading scheme will be extended. Hong Kong’s political leader, Chief Executive C.Y. Leung, has been quick to laud the “win-win” of deepening cooperation with Shanghai. Already, it is expected daily trading limits — 10.5 billion yuan ($1.69 billion) going south, and 13 billion yuan going north — will be expanded. Many were caught unaware by the by speed of the post-Easter-holiday surge in southbound investment. As these quotas were filled for the first time, the benchmark Hang Seng Index finished the week up 7.9%.
One explanation for the rush south was a new insurance-investment policy, which allows Chinese mutual funds to participate in the Stock Connect. Another is an inevitable catch-up, with the A-share (Shanghai) rally spilling into H-shares (Hong Kong) as mainland investors come south to pick up bargains. (See previous column on the divergence between the two markets.) Yet turnover figures suggest the Hang Seng Index’s surge past the 27,000 mark cannot be a result of the Stock Connect alone. On Thursday, for instance, volume reached a record 293.9 billion Hong Kong dollars ($37.9 billion), three times normal levels. Analysts are offering different explanations for the surge. Bank of America writes that we are witnessing a “Keynes beauty contest,” in which the jump in money flows is likely driven by some investors anticipating other investors’ reaction to government policy.
Read more …

“Sovereign and corporate borrowers outside America owe a record $9 trillion in the U.S. currency, much of which will need repaying in coming years..”
• The $9 Trillion Short That’s Seen Sending the Dollar Even Higher (Bloomberg)
Investors speculating the dollar rally is fizzling out may be overlooking trillions of reasons why it will keep on going. There’s pent-up demand for the U.S. currency that will underpin years of appreciation because the world is “structurally short” the dollar, according to investor and former International Monetary Fund economist Stephen Jen. Sovereign and corporate borrowers outside America owe a record $9 trillion in the U.S. currency, much of which will need repaying in coming years, data from the Bank for International Settlements show. In addition, central banks that had reduced their holdings of the greenback are starting to reverse course, creating more demand. The dollar’s share of global foreign reserves shrank to a record 60% in 2011 from 73% a decade earlier, though it has since climbed back to 63%.
So, the short-term ebbs and flows caused by changes in Federal Reserve policy or economic data releases may be overwhelmed by these larger forces combining to fuel more appreciation, according to Jen, the London-based co-founder of SLJ Macro Partners LLP and the former head of currency research at Morgan Stanley. “Short-covering will continue to power the dollar higher,” said Jen, who predicts a 10% advance in the next three months to 96 cents per euro. “The dollar’s strength is not just about cyclical factors such as growth. The recent consolidation will likely prove to be temporary.” The U.S. currency was at $1.0593 per euro at 12:09 p.m. in Tokyo. The last time it traded at 96 cents was June 2002.
Most strategists and investors agree on the reasons for the dollar’s advance versus each of its major counterparts during the past year: the prospect of higher U.S. interest rates while other nations are loosening policy. Bloomberg’s Dollar Spot Index, which tracks the U.S. currency against 10 major peers including the euro and yen, has surged 20% since the middle of 2014. The gains stalled recently, sending the index down more than 3% in the three weeks through April 3, as Fed officials tempered investors’ expectations about the pace of rate increases.
Read more …

“Demand will peak way ahead of supply..”
• Saudi Arabia’s Plan to Extend the Age of Oil (Bloomberg)
Last fall, as oil prices crashed, Ali al-Naimi, Saudi Arabia’s petroleum minister and the world’s de facto energy czar, went mum. He still popped up, as is his habit, at industry conferences on three continents. Yet from mid-September to the middle of November, while benchmark crude prices plunged 21% to a four-year low, Naimi didn’t utter a word in public. For 20 years, Bloomberg Markets reports in its May 2015 issue, the world’s $2 trillion oil market has parsed Naimi’s every syllable for signs of where supply and prices are heading. Twice during previous routs—amid the Asian financial crisis in 1998 and again when the global economy melted down 10 years later—Naimi reversed oil’s free fall by orchestrating production cutbacks among members of OPEC. This time, he went to ground.
At the cartel’s semiannual meeting on Nov. 27 in Vienna, Naimi shot down proposed output reductions supported by a majority of the 12 members in favor of a more daring strategy: keep pumping and wait for lower prices to force high-cost suppliers out of the market. Oil prices fell a further 10% by the end of the next day and kept going. Having averaged $110 a barrel from 2011 through the middle of 2014, Brent crude, the global benchmark, dipped below $50 in January. “What they did was historic,” Daniel Yergin, the pre-eminent historian of the oil industry, told Bloomberg in February. “They said: ‘We resign. We quit. We’re no longer going to be the manager of the market. Let the market manage the market.’ That’s when you got this sort of shocked reaction that took prices down to those levels we saw.”
Naimi, 79, dominated the debate at the November meeting, according to officials briefed on the closed-door proceedings. He told his OPEC counterparts they should maintain output to protect market share from rising supplies of U.S. shale oil, which costs more to get out of the ground and thus becomes less viable as prices fall. In December, he said much the same thing in a press interview, arguing that it was “crooked logic” for low-cost producers such as Saudi Arabia to pump less to balance the market. Supply was only half the calculus, though. While the new Saudi stance was being trumpeted as a war on shale, Naimi’s not-so-invisible hand pushing prices lower also addressed an even deeper Saudi fear: flagging long-term demand.
Naimi and other Saudi leaders have worried for years that climate change and high crude prices will boost energy efficiency, encourage renewables, and accelerate a switch to alternative fuels such as natural gas, especially in the emerging markets that they count on for growth. They see how demand for the commodity that’s created the kingdom’s enormous wealth—and is still abundant beneath the desert sands—may be nearing its peak. This isn’t something the petroleum minister discusses in depth in public, given global concern about carbon emissions and efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. But Naimi acknowledges the trend. “Demand will peak way ahead of supply,” he told reporters in Qatar three years ago. If growth in oil consumption flattens out too soon, the transition could be wrenching for Saudi Arabia, which gets almost half its gross domestic product from oil exports.
Read more …

“There’s just no appetite in the euro zone for a grand bargain to take over Greece’s debt to the IMF and the ECB.”
• Greece May Have Blown Best Hope Of Debt Deal (Reuters)
Even if it survives the next three months teetering on the brink of bankruptcy, Greece may have blown its best chance of a long-term debt deal by alienating its euro zone partners when it most needed their support. Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’ leftist-led government has so thoroughly shattered creditors’ trust that solutions which might have been on offer a few weeks ago now seem out of reach. With a public debt equivalent to 175% of economic output and an economy struggling to pull out of a six-year depression, Athens needs all the goodwill it can summon to ease the burden. It owes 80% of that debt to official lenders after private bondholders took a hefty writedown in 2012.
Since outright debt forgiveness is politically impossible, the next best solution would be for Greece to pay off its expensive IMF loans early, redeem bonds held by the ECB and extend the maturity of loans from euro zone governments to secure lower interest rates for years to come. “This step would save Greece’s budget billions of euros, while reforming the Troika arrangement, eliminating the IMF’s and the ECB’s financial exposure to Greece,” said Jacob Funk Kirkegaard, senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics, who advocates such an arrangement. It would lower the effective interest rate on Greek debt to less than 2%, far less than Athens was paying before the euro zone debt crisis began in 2009, and radically reduce the principal amount to be repaid over the next decade, giving Greece fiscal breathing space to revive its economy.
And unlike ideas floated by Greek Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis to swap euro zone loans for GDP-linked bonds and ECB holdings with perpetual bonds, paying out the IMF and the ECB early would be legal and supported by precedent. But if the economics make sense for Greece, the politics no longer add up for its partners. A euro zone official said there had been exploratory talks with the previous conservative-led Greek government about such a plan last year, before then Prime Minister Antonis Samaras chose to bring forward an election he lost rather than complete a bitterly unpopular bailout program. “Now it’s a political non-starter,” said a euro zone official. “There’s just no appetite in the euro zone for a grand bargain to take over Greece’s debt to the IMF and the ECB.”
Read more …

“..the newspaper will have difficulty justifying its headline and the content of its article.”
• Greece Defends Bailout Tactics As Latest Deadline Looms (Guardian)
Greece has denied being intransigent in its dealings with eurozone officials, ahead of another crucial week for the cash-strapped country. Greece’s finance ministry dismissed on Sunday a report by a German newspaper which reported that eurozone officials were “disappointed” by Greece’s failure to come up with plans for economic reforms at last week’s talks in Brussels. The mood between Greece’s leftist government and its eurozone partners has remained tense during negotiations to determine whether or not the country qualifies for further financial aid from international lenders. Frankfurter Allgemeine Sonntagszeitung (FAS) cited officials at last week’s meeting as saying they were shocked by the lack of progress, and that the new Greek representative just asked where the money was – “like a taxi driver” – and insisted his country would soon be bankrupt.
Eurozone officials disagreed with this assessment, saying Athens was still able to meet its international obligations, and regarded its ability to pay public sector wages and pensions as a domestic problem, according to the report. They deplored Greece’s unwillingness to discuss cuts to public sector pensions. The finance ministry in Athens hit back on Sunday, saying: “When the readers of FAS read the minutes … the newspaper will have difficulty justifying its headline and the content of its article. Such reports undermine the negotiation and Europe.” Greece made a €450m loan repayment to the International Monetary Fund last week. A further €747m payment is due on 12 May. There are fears that Athens could run out of cash in coming weeks. It needs to pay out more than €1.5bn of social security payments for April this week.
IMF managing director Christine Lagarde said last week that talks between Greece and its creditors had been “difficult on almost a daily basis”. She added: “What really matters now is for Greece and the three institutions to get on with the work so we can identify together the measures that will take Greece out of the very bad economic situation it could be in if those measures are not taken.” A meeting of deputy finance ministers – called the Euro Working Group – last Thursday gave Athens six working days to come up with a convincing economic reform plan before eurozone finance ministers meet on 24 April to decide whether to unlock €7.2bn of bailout funds. Greece has been on the verge of bankruptcy since 2009 and has depended on rescue loans totalling €240bn from the EU and IMF to stay afloat.
Read more …

“..describing the falling oil price as “unambiguously good” for the economy…”
• UK Economy Poised To Welcome ‘Deflation’ For First Time Since 1960 (Guardian)
Britain could fall into deflation this week for the first time in more than half a century, the result of an escalating supermarket price war and falling energy prices. Inflation, as measured by the consumer prices index, fell to zero in February for the first time since comparable records began in 1989. Estimates from the Office for National Statistics suggested that it was the lowest reading since 1960. The statistics office will release the latest inflation figures, for March, on Tuesday morning. City economists say it is going to be a close call between a zero reading and a 0.1% dip. Petrol prices rose 3.6% last month, reflecting a rebound in global oil prices, which is expected to push up the inflation rate by 0.1 %age points.
This will be offset, however, by the 5% cut in gas prices by British Gas, Britain’s largest energy supplier, and low food price inflation. Fierce competition from discount chains has forced the major supermarket groups to slash prices on basic items such as bread, with the discounter Aldi overtaking Waitrose to become the UK’s sixth-largest grocer recently. Alan Clarke, an economist at Scotiabank, said: “While food price deflation of close to 4% year on year may sound extreme, this represents something of a relief after years of rapid price increases. More specifically, over the seven years between 2007 and 2013, the average annual pace of increase in food price inflation was 5% per year. Enjoy the cheap food and fuel while it lasts!”
Even if the UK avoids deflation in March, it will probably enter a period of falling prices at some point soon – following in the footsteps of other countries. Eurozone inflation has been negative since December, and the US rate turned negative in January before recovering to zero in February. There is no reason to panic, according to the Bank of England and City analysts. They claim any period of UK deflation is likely to prove temporary, unlike the deflationary spiral in Japan, where people have lived with falling prices for two decades. Bank of England governor Mark Carne, has sought to allay fears that Britain faces a 1930s-style deflationary spiral, describing the falling oil price as “unambiguously good” for the economy. An oil glut pushed the price of Brent crude, the international benchmark, down by more than 50% from last summer to a six-year low earlier this year.
Read more …

“It is like the 1970s again, when waves of wealthy people left Britain and it was a disaster..”
• Sales Of London Luxury Homes Drop 80% In One Year (FT)
Wealthy foreigners are shunning London’s luxury housing market following Labour’s announcement that it will end their “non-dom” status if it wins the UK’s general election, according to estate agents. Property deals have begun to fall through in the days since Ed Miliband laid out his plans, they revealed, with some foreign residents also putting their homes up for sale and fleeing the UK. The announcement, combined with Labour’s plan to introduce a mansion tax on high-value homes, has led many foreigners to conclude that the UK is no longer an attractive and reliable home for the rich, agents said. During the past two years Conservative chancellor George Osborne has also made tax changes that have increased the burden on the affluent.
The introduction of capital gains tax on the proceeds of property sales came into force on April 6 and is believed by agents to have contributed to owners’ jitters. Ed Mead, a director of Douglas & Gordon estate agents, said his company had carried out 37 valuations in the past month for owners of high-end homes who were thinking of selling up, when the normal level is about six. “It is like the 1970s again, when waves of wealthy people left Britain and it was a disaster,” Mr Mead said. Sales of homes worth more than £2m have dropped by 80% in the past year, according to Douglas & Gordon.
Read more …

Commodities are a disaster across the board.
• Quarter Of World’s Copper Mines Operating At A Loss (Reuters)
Nearly a quarter of the world’s major copper mines are running in the red, even after producers including Codelco and BHP Billiton engage in their deepest cost-cutting in years, according to a Reuters analysis. A 17% slump since last July has pushed copper futures on the London Metals Exchange to under $6,000 a ton, the lowest since 2009, is the first major test of producers’ margins since the global economic crisis, forcing a new reckoning after five years of relatively consistent profitability. Codelco, the Chilean state miner that produces about 8% of the world’s copper, will review the cost reduction plan at its Salvador mine as it prepares to restart operations there after torrential rains shuttered the complex in March, said a source close to the state-run miner.
The company has an ambitious target to slash total costs by as much as $1 billion this year. Salvador produced copper at a cost of some $11,439 per tonne in the fourth quarter last year, the highest out of 91 mines analyzed by Thomson Reuters unit GFMS as part of its Copper Mine Economics database. The mines account for more than two-thirds of global output, and almost a quarter of them had production costs late last year above current prices. The GFMS analysis, which is based on quarterly and semi-annual filings by 26 mining companies, gives the deepest insight yet into the voracious pace of cost-cutting by miners late last year as the sell-off in copper quickened, a hot topic at CRU Copper’s conference in Santiago this week.
Read more …

Austria’s pulling off quite a feat. In almost total silence.
• Bundesbank Tells German Heta Creditors To Expect 50% Loss (Bloomberg)
German banks should expect to lose at least half of their investments in bonds of Austrian bad bank Heta Asset Resolution and make the appropriate provisions, the Bundesbank director responsible for bank supervision said. “I think this situation has to be taken seriously by the German banks,” Andreas Dombret, also a member of the board of the ECB’s Single Supervisory Mechanism, said in an interview in Johannesburg on Friday. “It’s advisable and recommendable to take provisions on this, and if I were to put a number on this I would say it should be a minimum of a 50% provision for potential losses.” German lenders and insurers have emerged as the biggest creditors of the bad bank set up after the collapse of Hypo Alpe-Adria-Bank, with about €7.1 billion at risk.
Heta was taken over last month by Austrian regulators, who ordered a debt moratorium and said they will impose losses on creditors to fund the bank’s wind-down. Bayerische Landesbank, a former owner of Hypo Alpe, has the biggest exposure among German banks, as around €2.4 billion of loans to the former subsidiary weren’t repaid. Commerzbank, Deutsche Pfandbriefbank, NordLB, and a German unit of Dexia all own Heta debt. While BayernLB has said it will set aside provisions equal to about half of what Heta owes it, Dombret’s recommendation goes further than some of the disclosed provisions other banks have made. Deutsche Pfandbriefbank said it wrote down its €395 million investment by €120 million, or 30%. Austria’s Hypo NOE Gruppe Bank said it provisioned its €225 million holding by “about a quarter.”
Read more …

“The massive hunt was used by the Swedish Defense Ministry to justify a six billion kronor ($696 million) hike in defense spending..”
• Sweden Confirms Mystery ‘Russian Sub’…Was In Fact A Workboat (RT)
The unknown foreign vessel the Swedish Navy searched for near Stockholm last autumn was actually a “workboat,” a senior navy official says. Local media had alleged a hunt was on to try and find a Russian submarine, which was believed to be in the area. Swedish Rear Admiral Anders Grenstad told the Swedish TT news agency on Saturday that what was thought to be a vessel or a foreign submarine was actually just a “workboat.” The Swedish Navy changed the wording from “probable submarine” to “non-submarine” when referring to the reconnaissance mission connected to the unidentified vessel spotted in the Stockholm archipelago. The massive hunt was used by the Swedish Defense Ministry to justify a six billion kronor ($696 million) hike in defense spending between 2016 and 2020.
The drama started after an amateur photograph of an alleged underwater vessel of unidentified origin was sent to the ministry. The man who took the photo raised the alarm because he thought he saw the object surface and disappear again. Sweden undertook an intense one-week search in late October, looking for possible “foreign underwater activity” near Stockholm. During the operation, the Swedish Navy reportedly used over 200 troops, helicopters, stealth ships and minesweepers to search the waters of the Baltic Sea. During the search, the Swedish media exaggerated the story, claiming country’s navy was looking for a submarine in the Baltic Sea, which allegedly belonged to Russia.
Meanwhile, naval officials from Sweden and Russia maintained there was no substance to the reports, which was confirmed by Grenstad. “From the information we have, we cannot draw the same conclusion as the media that there is a damaged U-boat. We have no information about an emergency signal or the use of an emergency channel,” the navy official said. A full report of the search operations will be published later this spring, the Swedish newspaper Svenska Dagbladet reported.
Read more …

“Ukraine’s total debt is estimated at $50 billion, and it has to service about $10 billion of that debt this year..”
• Default In Ukraine ‘Virtual Certainty’: S&P Cuts Rating To ‘CC’ (RT)
Standard & Poor’s has downgraded Ukraine’s long-term foreign currency sovereign credit rating to CC, a notch lower than the previous CCC- level. A default on Ukraine’s foreign-currency debt is a “a virtual certainty,” according to the agency. The ratings agency has said that the outlook remains negative. Ukraine’s foreign currency rating is the world’s second worst, behind Argentina which has a rating of ‘SD’. It is still ahead of Venezuela, which S&P has assigned a ‘CCC’ rating. “The negative outlook reflects the deteriorating macroeconomic environment and growing pressure on the financial sector, as well as our view that default on Ukraine’s foreign currency debt is virtually inevitable,” the ratings agency said in a statement.
Ukraine’s total debt is estimated at $50 billion, and it has to service about $10 billion of that debt this year, including corporate and sovereign loans and bonds. It will receive about $40 billion in IMF loans in the next four years, as well as separate loan guarantees from the US, Europe, and other allies. Public sector debt rose to 71% of Ukraine’s gross domestic product, and is due to rise to 94% of GDP in 2015, according to the National Bank of Ukraine.
Paying back debt is becoming more difficult for Ukraine as the national currency, the hryvnia, continues to plummet in value. It was the worst performing currency in 2014, and lost more than 34% on February 5, when the Central bank said it could no longer support the beleaguered currency. On February 5 the currency hit a historic low of 24.5 per 1 USD, and at the time of publication has only recovered slightly, to 23.4 versus the US dollar. Officially, foreign currency reserves stood at $5.6 billion at the end of March, compared to the $36 billion level in 2011.
Read more …

Rousseff had better wisen up and leave. But that would open her up to prosecution.
• Protests Across Brazil Seek Ouster Of President (AP)
Nationwide demonstrations calling for the impeachment of President Dilma Rousseff swept Brazil for the second day in less than a month, though turnout at Sunday’s protests appeared down, prompting questions about the future of the movement. A poll published over the weekend suggested the majority of Brazilians support opening impeachment proceedings against Rousseff, whose second term in office has been buffeted by a corruption scandal at Brazil’s largest company, oil giant Petrobras, as well as a stalled economy, a sliding currency and political infighting. Only 13% of survey respondents evaluated Rousseff’s administration positively.
Sunday’s protests, which took place in cities from Belem, in the northern Amazonian rainforest region, to Curitiba in the south, were organized mostly via social media by an assortment of groups. Most were calling for Rousseff’s impeachment, but others’ demands ranged for urging looser gun control laws to a military coup. While last month’s protests drew substantial crowds in several large cities, Sunday’s turnout was lackluster. In Rio, several thousand people marched along the golden sands of Copacabana beach, many dressed in the yellow and green of the Brazilian flag. The March 15 protest, by contrast, drew tens of thousands. In the opposition stronghold of Sao Paulo, about 100,000 people marched on the city’s main thoroughfare, according to an estimate by the respected Datafolha polling agency.
The crowd was less than half the size of last month’s demonstration here, when more than 200,000 people turned out, making it the biggest demonstration in Sao Paulo since 1984 rallies demanding the end of the military dictatorship. “I was on the avenue on March 15 and without a doubt, today’s demonstration was much smaller,” said Antonio Guglielmi, a 61-year-old sales representative for construction materials company, vowing, “I will keep coming back to demonstrations like this one — big or small — because it is the best way for us to make our voices heard and demand an end to the Dilma government and the PT and end to corruption. The country cannot go on like this.”
Read more …

New Zealand’s set to land very hard.
• Auckland Housing Bubble ‘Floats Off Into Its Own Orbit’ (Hickey)
If you are reading this and you don’t own Auckland property, then it would be a good idea not to read any further because it will probably ruin your Sunday. Figures released this week by Barfoot & Thompson, Auckland’s biggest real estate agency group, confirmed everyone’s worst fears (or biggest hopes if they owned property in the city). Auckland’s housing market has officially floated off its New Zealand moorings into its own orbit. The Reserve Bank can now have no doubts or caveats around the seasonality or size of the trend — the housing market in New Zealand’s biggest city is booming. The average three bedroom house price on the isthmus of Auckland that used to be the old Auckland Council rose over NZ$1 million for the first time in March.
The average house price in West Auckland rose 20.5% over the last year to NZ$632,032. Barfoot sold 420 homes worth more than NZ$1 million each in the 31 days of March, while selling just 300 homes for less than NZ$500,000. Barfoot’s agents would have collected almost NZ$1 million of commissions each day in March as they sold over NZ$1.2 billion worth of houses over the month. Auckland house prices are now rising at double digit rates on an annual basis, while the rest of the country is growing at less than 5%, or not at all. Even in Christchurch, house price inflation is subdued as a wall of new houses hits the market to soak up demand and replace quake-damaged buildings. Prices are still falling in some regional cities where populations and work are drying up.
Unfortunately for the Reserve Bank, taxpayers outside of Auckland and Auckland’s renters, there is no relief in sight. Net migration is rollicking along at record highs and at least half of new migrants end up in Auckland, or just as importantly, aren’t leaving Auckland. Longer term fixed mortgage rates are low and falling. Employment growth is strong and rental property investors are stocked up with plenty of fresh equity to gear up with much bigger and often interest-only mortgages. New mortgage lending is growing at over 20% per year.
Read more …

Bubbles have their own dynamics. Politicians won’t touch them.
• 40% Of Houses In Auckland Are Bought By Investors (Interest.co.nz)
All we are hearing is about supply and what’s being done there, through such strategies as the Auckland Housing Accord. In his Radio NZ interview the PM banged on and on about what the Government is doing to help supply. There’s two issues here: One, it will take years not months to ramp up the supply of Auckland housing. Two, the Government and other politicians can happily talk and talk and talk about supply because it’s essentially a positive thing to talk about. We’ll build houses, and we’ll create jobs and people will have places to live. Marvellous. But, dear politicians, there’s another side to this and it’s the side you don’t want a bar of because if you are seen to be doing anything about this, well, then it would be negative. Yes, I’m talking about demand.
Reserve Bank Governor Graeme Wheeler recently suggested that about 40% of houses in Auckland were being bought by investors. Now, whatever you want to say about Auckland’s perceived housing supply shortage, if 40% of the available houses are being bought as investments then clearly there’s a hell of a demand issue as well. But what’s the Government doing about that? They could immediately do something about about the high levels of immigration that have seen a net 55,000 people arrive in New Zealand – about 25,000 of them in Auckland – in the past 12 months. They could do something to limit the numbers of offshore-based investors buying properties by introducing a rule that any overseas buyer of a house has to come and actually live in the house, or alternatively that offshore investors must build new houses.
They could introduce capital gains tax on investment properties. They won’t. Why not? Because these things would be unpopular. It’s much easier to talk about building new houses than any measures that might discourage investors from pumping more and more money into the inflated Auckland market. So, we’ll keep talking and talking and talking about supply. And who knows, if enough people believe the mantra then maybe there really will be a whole lot more houses built in Auckland eventually – possibly just in time to coincide with a global event that sees our 40% of investor-buyers take fright of the housing market and disappear overnight.
Read more …

But of course. With exports plunging, the housing bubble is what keeps up appearances.
• New Zealand PM Denies There Is A Housing Bubble (NZ Herald)
Prime Minister John Key has again denied there is a housing crisis or bubble developing in Auckland, despite figures from Barfoot and Thompson last week showing average prices hitting record highs of over NZ$1 million in the old Auckland Council area of the isthmus and the Government itself seeing a supply shortage in Auckland of more than 20,000 dwellings. Key told Morning Report the current double-digit price rises were not sustainable, but the Government had already taken action to free up land supply in Auckland and that restricting migration would frustrate employers looking for skilled staff. “In the end, it’s not sustainable for house prices to rise 10-12-13% per year. The only answer to that is to do what what we’re doing, which is allocate new land and build more houses,” he said, adding continued inflation “forever” at that level would lead to a “bubble”, although he denied it was currently a bubble.
He said the Government’s moves to introduce Special Housing Areas to circumvent the Metropolitan Urban Limit would add new housing supply to the market and slow that double-digit house price inflation, although this would take time while the necessary infrastructure and housing was built. He would not give a time-frame for the supply-driven slowdown in Auckland house price inflation, but “sooner as opposed to later is my guess.” Key referred to the recent supply-driven slowdown in Christchurch house price inflation and downplayed suggestions of tightening migration rules, saying the Government would have to reduce the numbers coming in for skilled occupations and for construction if it was to use the migration lever.
Read more …

Must read.
• The Shadowy History of the Secret Bank that Runs the World (LeBor)
The world’s most exclusive club has eighteen members. They gather every other month on a Sunday evening at 7 p.m. in conference room E in a circular tower block whose tinted windows overlook the central Basel railway station. Their discussion lasts for one hour, perhaps an hour and a half. Some of those present bring a colleague with them, but the aides rarely speak during this most confidential of conclaves. The meeting closes, the aides leave, and those remaining retire for dinner in the dining room on the eighteenth floor, rightly confident that the food and the wine will be superb. The meal, which continues until 11 p.m. or midnight, is where the real work is done. The protocol and hospitality, honed for more than eight decades, are faultless. Anything said at the dining table, it is understood, is not to be repeated elsewhere.
Few, if any, of those enjoying their haute cuisine and grand cru wines— some of the best Switzerland can offer—would be recognized by passers-by, but they include a good number of the most powerful people in the world. These men—they are almost all men—are central bankers. They have come to Basel to attend the Economic Consultative Committee (ECC) of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), which is the bank for central banks. Its current members [ZH: as of 2013] include Ben Bernanke, the chairman of the US Federal Reserve; Sir Mervyn King, the governor of the Bank of England; Mario Draghi, of the ECB; Zhou Xiaochuan of the Bank of China; and the central bank governors of Germany, France, Italy, Sweden, Canada, India, and Brazil. Jaime Caruana, a former governor of the Bank of Spain, the BIS’s general manager, joins them.
In early 2013, when this book went to press, King, who is due to step down as governor of the Bank of England in June 2013, chaired the ECC. The ECC, which used to be known as the G-10 governors’ meeting, is the most influential of the BIS’s numerous gatherings, open only to a small, select group of central bankers from advanced economies. The ECC makes recommendations on the membership and organization of the three BIS committees that deal with the global financial system, payments systems, and international markets. The committee also prepares proposals for the Global Economy Meeting and guides its agenda.
Read more …