
Arthur Siegel Zoot suit, business district, Detroit, Michigan Feb 1942



Debt rattle.
• US Stocks Surge, Snapping 6-Day Losing Streak (AP)
The Dow Jones industrial average rocketed more than 600 points Wednesday, its biggest gain in seven years, snapping a six-day losing streak that had Americans nervously checking their investment balances. While the surge came as a relief to many, Wall Street professionals warned that more rough days lie ahead, in part because of weakness in China, where signs of an economic slowdown triggered the sell-off that has shaken global markets over the past week. Heading into Wednesday, the three major U.S. stock indexes had dropped six days in a row, the longest slide in more than three years. The Dow lost about 1,900 points over that period, and more than $2 trillion in corporate value was wiped out. On Tuesday, a daylong rally collapsed in the final minutes of trading.
On Wednesday, the market opened strong again, and the question all day was whether the rally would hold. It did, and picked up speed just before the closing bell. The Dow vaulted 619.07 points, or 4%, to 16,285.51. It was the Dow’s third-biggest point gain of all time and its largest since Oct. 28, 2008, when it soared 889 points. The Standard & Poor’s 500 index, a much broader measure of the stock market, gained 72.90 points, or 3.9%, to 1,940.51. In %age terms, it was the best day for the S&P 500 in nearly four years. The Nasdaq composite rose 191.05 points, or 4.2%, to 4,697.54. Analysts said investors apparently saw the big sell-off as an opportunity to go bargain-hunting and buy low. “That always leads to a bounce or spike in the market,” said Quincy Krosby, market strategist for Prudential Financial.

“Meanwhile, the IMF predicted the world economy would grow 3.5% this year…”
• Worst Decline In World Trade In 6 Years (RT)
The first half of 2015 has seen the worst decline in world trade since the 2009 crisis, according to World Trade Monitor. The data could imply that globalization has reached its peak. In the first quarter of 2015, the volume of world trade declined by 1.5%, while the second quarter saw a 0.5% contraction (1.1% growth in annual terms), which makes the first six months of the year the worst since the 2009 collapse. Global trade won back 2% in June, but the authors of the research, the Netherlands Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis, warned that the monthly numbers were volatile and suggested looking at the long-term figures.
“We have had a miserable first six months of 2015,” chief economist of the WTO Robert Koopman told the FT. The organization had predicted trade would grow 3.3% this year, but is likely to downgrade the estimate in the coming weeks. According to Koopman, the downturn in world trade reflects the delay in the recovery of the European economy and the economic slowdown in China. “There’s an adjustment going on in the global economy and trade is a place where that adjustment becomes pretty visible,” added the economist. However, despite the fact that globalization has indeed reached its peak, there are no signs that it will decline, said Koopman. Meanwhile, the IMF predicted the world economy would grow 3.5% this year.

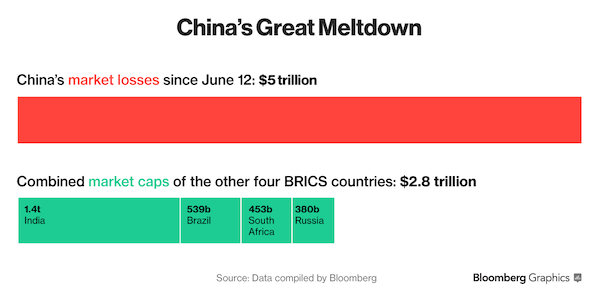
$5 trillion.
• China Meltdown So Large That Losses Eclipsed BRICS Peers, Twice (Bloomberg)
Take the combined size of all stocks traded in Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa, multiply by two, and you’ll get a sense of how much China’s market value has slumped since the meltdown started. Shanghai-listed equities erased $5 trillion since reaching a seven-year high in June, half their value, as margin traders closed out bullish bets and concern deepened that valuations were unjustified by the weak economic outlook. The four other countries in the BRICS universe have a combined market capitalization of $2.8 trillion, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. China has accounted for 41% of equity declines worldwide since mid-June, with the scale of the drop also exceeding the entire size of the Japanese stock market.
Losses accelerated following the shock yuan devaluation on Aug. 11 as investors took the step as a sign the government is more worried about the pace of the economic slowdown than previously thought. That, in turn, sent convulsions through global markets, particularly hurting countries that rely heavily on China as a destination for their exports of vegetables, minerals and fuel, including Brazil, Russia and South Africa. The Shanghai Composite Index remains 33% higher in the past 12 months. “China has been the single most important source of growth in the world for several years, hence such a sharp slowdown has a profound impact on trade,” Nathan Griffiths at NN Investment Partners in The Hague said by e-mail. Stock-market volatility on the “downside is much more important than the move on the upside for broader markets,” he said.

By one metric…
• The Stock Market Hasn’t Had a Selloff Like This One in Over 75 Years (BBG)
By one metric, investors would have to go back 75 years to find the last time the S&P 500’s losses were this abrupt. Bespoke Investment Group observed that the S&P 500 has closed more than four standard deviations below its 50-day moving average for the third consecutive session. That’s only the second time this has happened in the history of the index. May 15, 1940, marked the end of the last three-session period in which this occurred. This string of sizable deviations from the 50-day moving average is a testament to just how severe recent losses have been compared to the index’s recent range. “Not even the crash of 1987 got this oversold relative to trend,” writes Bespoke.
The money management and research firm produced a pair of analogue charts showing what’s in store if the S&P 500 mimics the price action seen in mid-1940. Overlaying the axes gives the impression that the worst of the pain is behind us, and a market bottom isn’t too far off. However, indexing the S&P 500 to five sessions prior to the tumult shows that a replication of the mid-1940 plunge could see equities run much further to the downside and into a bear market. If it tracked the 1940 trajectory, the S&P 500 would hit a low of 1,556 in relatively short order. But Bespoke doesn’t think stocks are fated to repeat that selloff.
“There is nothing, nothing, we have seen – Chinese fears, positioning, valuation, or any other factor – suggests to us that we are headed to 1556,” the analysts write. “More likely, in our view, is something along the lines of the top analogue; we doubt the bottom is in, but see it unlikely we enter a bear market and a true stock market crash.”

Back to the country.
• China’s Workers Abandon The City As Beijing Faces An Economic Storm (Guardian)
Liu Weiqin swapped rural poverty for life on the dusty fringes of China’s capital eight years ago hoping – like millions of other migrants – for a better future. On Thursday she will board a bus with her two young children and abandon her adopted home. “There’s no business,” complained the 36-year-old, who built a thriving junkyard in this dilapidated recycling village only to watch it crumble this year as plummeting scrap prices bankrupted her family. “My husband will stick around a bit longer to see if there is any more work to be found. I’m taking the kids.” Weeks of stock market turmoil have focused the world’s attention on the health of the Chinese economy and raised doubts over Beijing’s ability to avert a potentially disastrous economic crisis, both at home and aboard.
The financial upheaval has been so severe it has even put a question mark over the future of premier Li Keqiang, who took office less than three years ago. Following a stock market rout dubbed China’s “Black Monday”, government-controlled media have rejected the increasingly desolate readings of its economy this week. “The long-term prediction for China’s economy still remains rosy and Beijing has the will and means to avert a financial crisis,” Xinhua, the official news agency, claimed in an editorial. Meanwhile Li told the state TV channel CCTVthat “the overall stability of the Chinese economy has not changed”. The evidence in places such as Nanqijia – a hardscrabble migrant community of recyclers around 45 minutes’ drive from Tiananmen Square – points in the opposite direction.
“It’s the worst we’ve seen it. It’s even worse than 2008,” said Liu Weiqin, who like most of the village’s residents hails from Xinyang in south-eastern Henan province, one of China’s most deprived corners. “When things were good we could earn 10,000 yuan [£1,000] a month. But I’ve lost around 200,000 yuan since last year,” added Liu, who was preparing to leave her cramped redbrick shack for a 10-hour coach journey back to her family home with her eight-year-old son, Hao Hao, and five-year-old daughter, Han Han.

Trouble in Utopia?
• China’s Central Bank Won’t Do Beijing’s Dirty Work (Pesek)
China’s Zhou Xiaochuan is either the smartest or most reckless central banker in the world. Even after its fifth rate cut in nine months on Tuesday, the People’s Bank of China is running a monetary policy that’s too tight for an economy on the brink. The PBOC is grappling with weakening growth, excessive debt and a plunging equity market that’s wreaking havoc on household wealth, corporate profits and business confidence. So why is Zhou still only offering monetary-baby steps over the shock-and-awe recently favored by Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda? It’s partly because he wants to prevent China’s central bank autonomy from being reduced to a hollow cliché.
Zhou’s team – well aware that he has a control-obsessed Communist Party looking over his shoulder – wants to make sure President Xi Jinping does his part to restore China’s economy. We’ll know soon enough whether Zhou is being reckless. Many commentators have argued the PBOC should initiate quantitative easing. After all, China’s overcapacity and debt levels – the country’s local governments alone owe more than Germany’s annual gross domestic product – caution against a new round of fiscal stimulus. If the data on China’s economic fundamentals and Shanghai stocks cascade lower in the months ahead, Zhou might have some explaining to do. But, for now, his show of independence is a silver lining amid the ongoing turmoil.
Zhou is an economic modernizer without peer in today’s Beijing, a disciple of former premier Zhu Rongji, China’s most-important reformer since the pioneering Communist Party chairman Deng Xiaoping. Zhou’s top goal has been to get the yuan added to the International Monetary Fund’s special drawing rights program. But unlike other Chinese policy makers, who want to leverage that status to increase the country’s global clout, he wants to use it to spur further economic reforms. He knows that once the yuan is recognized as a reserve currency, Beijing will have no choice but to adhere to global economic norms.

Ambrose can’t seem to be able to make up his mind these days. Make it a Minsky moment then.
• China Is In A Serious Bind But This Is Not Yet A ‘Lehman’ Moment (AEP)
The European and American economies are at this point like 747 jumbo jets flying smoothly into stiff headwinds at 37,000 ft. Such craft do not normally fall out of the sky just like that. The great unknown is China. Some of us never believed in the first place that the Communist Party can perform miracles, or that China is necessarily destined for economic hegemony this century. We have long argued that the post-2009 credit blitz has been unprecedented in any major country in history. Loans have increased from $9 trillion to $27 trillion in six years. The extra debt alone is greater than the combined banking systems of the US and Japan, and its potency is dying as the output gained from each yuan of fresh credit drops from 80pc to nearer 25pc.
We argued – like premier Li Keqiang, our lonely hero in the Politburo – that the country is hurtling straight into the middle income trap unless it ditches Deng Xiaoping’s obsolete catch-up model in time, both by weaning itself off investment-led growth and by relinquinshing the Party grip on Chinese society. We expected trouble. Yet the crumbling credibility of China’s leaders this year is disturbing to watch. They have made serial errors. They sat on their hands as real one-year borrowing costs rocketed to 5pc. They botched the local government reform plan over the winter, precipitating a four-month fiscal crunch (spending fell 19.9pc in January) that would bring any country to its knees. They deliberately stoked a stock mania in Shanghai and Shenzhen, thinking it would reflate the economy by means of equity rather than debt.
They then mobilized the state’s coercive powers to stop it collapsing, only to fail. Finally, they abandoned China’s dollar peg and switched to a managed float before the economy had pulled out of recession (my term, not theirs), causing much of the world and many of its own citizens to conclude that Beijing is deliberately trying to drive down the yuan. It is this that precipitated the August storm. It is has the potential to turn dangerous. Nomura says capital flight reached almost $200bn in early July. Reports are circulating that it may be much higher. The central bank (PBOC) is burning through foreign reserves to defend the currency. This is causing a liquidity squeeze and lowering the monetary multiplier, yet the PBOC cannot easily slash rates to support the economy without inviting further outflows. Hence the timid 50 point cut in the reserve requirement ratio on Tuesday.
We are already seeing signs of disguised capital controls. Beijing has invoked anti-terror laws to investigate anybody suspected of smuggling money out of the country. Police raids are under way in Macau, the casino centre used to launder capital flight. Beijing has lifted the interest rate cap on long-term deposit accounts to try to entice savings to stay within China. These steps may at least slow the exodus of money. My own view – with low conviction, as they say in the hedge fund world – is that China will weather this immediate storm, though with difficulty.

That is Minsky.
• Capitalism Is Always And Fundamentally Unstable (Steve Keen)
Minsky’s view that capitalism is fundamentally unstable can be derived from a simple, dynamic view of capitalism: without bankruptcy or government intervention, a pure free market capitalist economy will collapse into a private debt black hole. The political implications of this are (a) that capitalism needs debt write-offs to survive, and (b) that government money creation is needed to avoid economic collapse. This is a huge political shift from today’s politics where the rights of creditors are enforced to the detriment of debtors, and where Neoliberalism has attempted to reduce the size of the public sector.

Used all the tricks in the book.
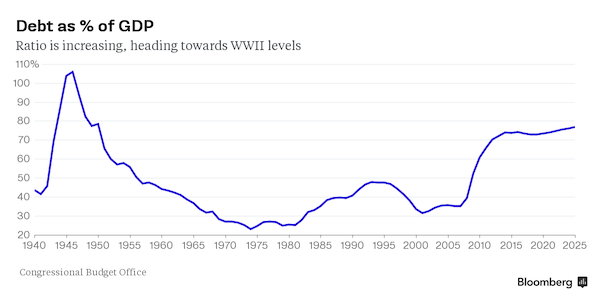
• The US Is Short on Options to Confront Next Crisis (Benchmark)
Stock market and commodity price declines are sweeping the globe, raising a question: If the U.S. economy lands in another hole, what tools does it have to dig itself out? Perhaps not many, or at least not as many as before the 2008 meltdown. U.S. debt stands at 74% of gross domestic product, compared with 35% in 2007, based on a Congressional Budget Office report released Tuesday. That burden is expected to grow further in coming years, limiting government options for additional fiscal stimulus in the form of spending or lower taxes. While the U.S. could follow in the footsteps of Japan, Ireland, Italy or Greece, which have racked up even higher debt-to-GDP levels, heftier deficits would be a hard political sell.
After all, Congress has been loathe to borrow, curbing spending through “sequester” limits and pushing the nation to the brink of default in 2011 amid disputes over a debt-limit extension. In recent years, the Federal Reserve has provided the stimulus that austerity-minded fiscal policy makers didn’t. The central bank has held interest rates near zero since 2008 and carried out three massive asset purchase programs to boost the economy. Now, cutting interest rates wouldn’t be an option in the face of a big downturn. That means the Fed would need to once again turn to unconventional steps such as further asset purchases or increased forward guidance. They’ve done it before, so it’s hard to make the case that they wouldn’t do it again, but it does mean that a crucial option — interest rates — is missing from their toolbox.
Partly for that reason, the Bank for International Settlements has warned that still-low rates around the world pose a looming economic risk. “Restoring more normal conditions will also be essential for facing the next recession, which will no doubt materialise at some point,” according to an annual report from the organization of central banks. “Of what use is a gun with no bullets left?”

“..Monday’s issues are likely to lead to changes in how markets operate at times of uncertainty..” Ha ha, want to bet?
• Stock Market Tumult Exposes Flaws in Modern Markets (WSJ)
Monday’s mayhem exposed significant flaws in the new architecture of Wall Street, where stock-linked funds—as much as shares themselves—now trade en masse on U.S. markets. Many traders reported difficulty buying and selling exchange-traded funds, a popular investment in which baskets of stocks and other assets are packaged to facilitate easy trading. Dozens of ETFs traded at sharp discounts to their net asset value—or their components’ worth—leading to outsize losses for investors who entered sell orders at the depth of the panic. Products built to provide insurance for investors came up short. As a result of trading halts in futures tied to the S&P 500 index, it was difficult for investors to get consistent prices on contracts linked to them that offer insurance against S&P 500 declines.
Elsewhere, the value of the most widely tracked Wall Street gauge of investor anxiety, the CBOE Volatility Index, or VIX, wasn’t published until almost 10 a.m. Monday, half an hour after stock trading began and after the Dow Jones Industrial Average had already posted its largest-ever intraday point decline. That made it difficult for investors to easily gauge the fear in the market. “ETFs have democratized investing,” said David Mazza, head of ETF research at State Street Global Advisors, a major ETF provider. But he and others added that ETFs don’t prevent investors from suffering losses if they buy or sell when the market is under stress. Analysts said that, while losses were inevitable for some investors amid the turmoil, and unruly trading is hardly unheard of on late-summer days, Monday’s issues are likely to lead to changes in how markets operate at times of uncertainty.

The WSJ tries for a positive spin here, but what this really means is commodities are in for foul weather.
• China Remains a Key Commodities Player, Despite Waning Appetites (WSJ)
The fear that China’s appetite for commodities, from copper to coal, is falling after a decade of breakneck growth has sent prices tumbling, but the country’s sheer scale in these markets means that China will continue to shape them in the long term, even if at a slower speed. China now buys about an eighth of the world’s oil, a quarter of its gold, almost a third of its cotton and up to half of all the major base metals. Its buying power has made the country integral to global commodities trading, influencing everything from prices to the hours traders work. While analysts predict a slowdown in the growth of Chinese commodity demand, they believe the country’s clout in the market isn’t likely to wane.
Commodities have fallen sharply in recent days, extending a summer of declines, amid concerns that a slowdown in China’s economic growth will sap the demand that drove markets through more than a decade of gains. China’s voracious consumption amid double-digit annual economic growth also encouraged a glut of new supply, from fertilizers to gold. Earlier this week, oil fell to its lowest levels in over six years. Industrial metals, such as copper and aluminum, have lost about 20% of their value this year, as has iron ore.

ha ha ha
• Oil Industry Needs to Find Half a Trillion Dollars to Survive (Bloomberg)
At a time when the oil price is languishing at its lowest level in six years, producers need to find half a trillion dollars to repay debt. Some might not make it. The number of oil and gas company bonds with yields of 10% or more, a sign of distress, tripled in the past year, leaving 168 firms in North America, Europe and Asia holding this debt, data compiled by Bloomberg show. The ratio of net debt to earnings is the highest in two decades. If oil stays at about $40 a barrel, the shakeout could be profound, according to Kimberley Wood at Norton Rose Fulbright in London. “The look and shape of the oil industry would likely change over the next five to 10 years as companies emerge from this,” Wood said.
“If oil prices stay at these levels, the number of bankruptcies and distress deals will undoubtedly increase.” Debt repayments will increase for the rest of the decade, with $72 billion maturing this year, about $85 billion in 2016 and $129 billion in 2017, according to BMI Research. A total of about $550 billion in bonds and loans are due for repayment over the next five years. U.S. drillers account for 20% of the debt due in 2015, Chinese companies rank second with 12% and U.K. producers represent 9%. In the U.S., the number of bonds yielding greater than 10% has increased more than fourfold to 80 over the past year, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. 26 European oil companies have bonds in that category..

Hamster and treadmill.
• For Oil Producers Cash Is King; That’s Why They Just Can’t Stop Drilling (BBG)
Investors sent a surprising message to U.S. shale producers as crude fell almost 20% in August: keep calm and drill on. While most oil stocks have fallen sharply this month, the least affected by the slump share one thing in common: they don’t plan to slow down, even though a glut of supply is forcing prices down. Cimarex Energy jumped more than 8% in two days after executives said Aug. 5 that their rig count would more than double next year. Pioneer Natural Resources Co. rallied for three days when it disclosed a similar increase. Shareholders continue to favor growth over returns, helping explain why companies that form the engine of U.S. oil – the frackers behind the boom – aren’t slowing down enough to rebalance the market.
U.S. production has remained high, frustrating OPEC’s strategy of maintaining market share and enlarging a glut that has pushed oil below $40 a barrel. “These companies have always been rewarded for growth,” according to Manuj Nikhanj, head of energy research for ITG Investment Research in Calgary. Now though, “the balance sheets of this sector are so challenged that investors are going to have to look at other factors,” he said. Output from 58 shale producers rose 19% in the past year, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Despite cutting spending by $21.7 billion, the group pumped 4% more in the second quarter than in the last three months of 2014.
That’s buoyed overall U.S. output, which has only drifted lower after peaking at a four-decade high in June. The government estimates production will slide 8% from the second quarter of this year to the third quarter of 2016. OPEC has been pumping above its target for more than a year. The oversupply may worsen if Iran is allowed to boost exports should it strike a deal with the U.S. and five other world powers to curb the Islamic Republic’s nuclear program.

“The province’s Wildrose opposition has noted that a barrel of Alberta’s oil is now cheaper than a case of beer.”
• Alberta’s Economy Heading Toward Contraction (Globe and Mail)
Faced with a collapse in energy prices, widespread drought, forest fires and the uncertainty of an untested government, the engine that drove much of Canada’s growth over the past decade has seized. Alberta’s economy is expected to contract this year. “I think it’s inevitable that Alberta will be in a contraction this year,” said Todd Hirsch, the chief economist for ATB Financial. “In 2016, I’m still optimistic we can squeeze out a very modest recovery. But this province won’t feel like it normally does until 2017 at the earliest.” Apart from a devastated energy sector, the provincial government has declared a provincewide agricultural disaster. After weeks of near-record drought, fields of parched grain can be found across much of Alberta.
The Agriculture Financial Services Corp. now expects to pay out as much as $1-billion to struggling farmers. Although most of Alberta’s farmers have crop insurance, the provincial agency will use the money to ensure the speedy compensation of farmers for lost crops and revenue. At the same time, dry weather gave rise to an early fire season in Alberta that has burnt 493,000 hectares across central and northern areas of the province – a burn area nearly twice the five-year average. A final price tag for the 1,646 fires seen across Alberta so far has yet to be determined. The struggling economy will have a huge effect on the government’s finances.
The provincial budget deficit could be the largest in nearly two decades, topping $8-billion if oil prices remain low, according to John Rose, the City of Edmonton’s chief economist. That would complicate Premier Rachel Notley’s campaign promise to increase spending on health and education while balancing the books by 2018. “It’s turning out worse than I expected,” said Mr. Rose, who warned of a significant slowdown in the provincial economy last December. “My forecast for 2015 was predicated on oil holding around $60 a barrel through the year. Things have gone awry.”

Can’t reform EU, Yanis.
• Yanis Varoufakis Pushes For Pan-European Network To Fight Austerity (ABC.au)
As far as Yanis Varoufakis is concerned, the Greek election campaign will be ‘sad and fruitless’. He tells Late Night Live why he won’t be running and why he is instead putting his energy into political action on a European level. When Greek prime minister Alexis Tsipras suddenly resigned last week, calling for fresh elections, his former finance minister Yanis Varoufakis was about to set off for France. His destination was the Fête de la Rose—a political event organised by the French Socialist Party, held annually in the tiny town of Frangy-en-Bresse, not far from the Swiss border. As rain poured down on the gathering, Varoufakis opened his speech with words familiar to any student of Marxist politics: ‘A spectre is haunting Europe.’
In Varoufakis’s adaptation, the spectre is that of democracy, and the powers of old Europe are as opposed to democracy in 2015 as they were to communism in 1848. For Varoufakis, the events of this year are an ‘Athens spring’ that was crushed by the banks after the Greek public’s vote against austerity in July. But as he explained to Late Night Live, he won’t be running for Greek parliament in the September elections, as he no longer believes in what Syriza and its leader, Tsipras, are doing. ‘The party that I served and the leader that I served has decided to change course completely and to espouse an economic policy that makes absolutely no sense, which was imposed upon us,’ he says.
‘I don’t believe that we should have signed up to it, simply because within a few months the ship is going to hit the rocks again. And we don’t have the right to stand in front of our courageous people who voted no against this program, and propose to them that we implement it, given that we know that it cannot be implemented.’ He has sympathy for a grouping of rebel MPs known as Popular Unity, but fundamentally disagrees with their ‘isolationist’ stance of desiring a return to the drachma. Instead, he says, his focus has turned to politics at the European level. ‘I don’t believe this parliament that will emerge from the coming election can ever hope to establish a majority in favour of a rational economic program and a progressive one,’ he says.
‘Instead of becoming engaged in an election campaign which in my mind is quite sad and fruitless, I’m going to be remain politically active—maybe more active than I have been so far—at the European level, trying to establish a European network. ‘National parties forming flimsy alliances within a Europe that operates like a bloc, like a macroeconomy, in its own interests—that model doesn’t work anymore. I think we should try to aim for a European network that at some point evolves into a pan-European party.’

“(Varoufakis) was talking and they paid no attention to him. They had switched off..”
• Tsipras Rules Out Coalition Partners, Says Varoufakis ‘Lost His Credibility’ (AP)
Greece’s prime minister on Wednesday raised the political stakes ahead of next month’s early national election, saying he will not enter a coalition with the main center-right and centrist opposition parties even if he needs their backing to govern. Alexis Tsipras resigned last week, barely seven months into his four-year mandate, when his bailout-dependent country received a new rescue loan that saved it from a looming bankruptcy and exit from the euro currency. He is seeking a stronger mandate, after his radical left-led coalition effectively lost its parliamentary majority when dozens of his own hardline left lawmakers refused to back new austerity measures demanded for the loan — which parliament approved with the backing of pro-European opposition parties.
Tsipras is widely expected to win the snap election, which will most likely be held Sept. 20, but it is unclear whether he will secure enough seats in parliament to govern alone. In an interview with private Alpha TV Wednesday, Tsipras ruled out a coalition with the center-right main opposition New Democracy party, or the smaller centrist Potami and PASOK parties. “I will not become prime minister in a coalition government with (New Democracy, PASOK or Potami),” he said. “I think that all three parties essentially express the old political system.” Before the election date is set, main opposition parties must complete the formal process of trying to form a national unity government. That procedure — doomed due to the parties’ disagreements — is expected to end Thursday.
Tsipras’ disaffected former comrades are angry at his policy U-turn to secure the international loans, as he was elected Jan. 25 on pledges to scrap creditor-demanded income cuts and tax hikes. They have formed the rebel group Popular Unity, now Greece’s third-largest party. Deepening the rift in Syriza, 53 members of the 201-strong central committee — the main party organ — announced their resignations from the party Wednesday, as they are switching to Popular Unity. Tsipras has argued that he was forced to accept creditors’ terms to keep Greece in the euro, and said that if he secures a slender majority in the election he will seek a coalition with his current partner, the small right wing populist Independent Greeks.
[..] In his interview, Tsipras said he accepted the bailout deal to avoid having to deal with a Greek bank collapse “and, possibly, civil strife” if the country was forced out of the euro. Tsipras also explained why, shortly before the agreement, he sacked his flamboyant finance minister, Yanis Varoufakis, who alienated Greece’s creditors with his aggressive talk and delaying tactics. Tsipras said that in a top-level June 25 meeting he and Varoufakis attended with the IMF, ECB and EC heads, “(Varoufakis) was talking and they paid no attention to him. They had switched off,” Tsipras said. “He had lost his credibility with his interlocutors.”

Until the next one.
• Greek Minister Says €5 Billion ATE Bank Scandal Is Biggest Of Its Type (Kath.)
Minister of State for Combating Corruption Panayiotis Nikoloudis on Wednesday described the illegal loans provided by the now-defunct Agricultural Bank of Greece (or ATEbank) between 2000 and 2012, which he is responsible for investigating, as the “biggest scandal since the modern Greek state was founded.” “We are talking about €5 billion at least… which dwarfs the infamous [Giorgos] Koskotas scandal involving the Bank of Crete [in the late 1980s], which ran to the equivalent of €60 million.”
The results of a preliminary investigation, which were made public in July, indicated that ATEbank was used to siphon some €5 billion to supporters of previous governments as part of a patron-client relationship. Prosecutors are investigating more than 1,300 loans that were issued without the necessary guarantees being demanded by the bank. ATEbank was absorbed by Piraeus Bank in 2013. Nikoloudis said that the loans were not given randomly, but to specific people, including “media owners, select businessmen and agricultural cooperatives.”

Shorting Sainsbury.
• Hedge Funds Set To Bank Millions Short Selling In London Share Slump (Guardian)
Hedge funds are set to bank tens of millions of pounds from the slump in share prices in London, having bet almost £18bn that the FTSE 100 would fall. The funds making the bets include Lansdowne Partners, which is run by George Osborne’s best man, Peter Davies, and Odey Asset Management, which is led by Crispin Odey – who made millions by predicting the credit crisis and earlier this year said the world was heading for a downturn “likely to be remembered in 100 years”. Short selling, effectively betting that share prices will fall, involves borrowing shares in a company and selling them with a view to buying them back at a lower price. The hedge fund makes a profit by banking the difference , as long as the shares do in fact fall.
As concerns over the slowing Chinese economy have grown, traders have increasingly bet that the fallout would be felt in blue-chip shares in London. The average%age of FTSE 100 company shares out on loan to short sellers has risen from 1.2% a year ago to 1.75%. The value of the short positions hedge funds have taken in FTSE 100 companies is £17.8bn, according to research by Markit. By the close of trading on Monday the FTSE 100 had fallen for 10 days in a row, sending it 17% down from its record high in April, before bouncing back by 3% on Tuesday. The biggest short positions are in Wm Morrison and J Sainsbury, with 16.4% of Morrisons shares out on loan, and 16.2% of Sainsbury’s shares. Traders have bet on the two supermarkets struggling further in the face of fierce competition from the discounters Aldi and Lidl.

Hopelessness is.
• Mass Migration: What Is Driving the Balkan Exodus? (Spiegel)
When Visar Krasniqi reached Berlin and saw the famous image on Bernauer Strasse – the one of the soldier jumping over barbed wire into the West — he knew he had arrived. He had entered a different world, one that he wanted to become a part of. What he didn’t yet know was that his dream would come to an end 11 months later, on Oct. 5, 2015. By then, he has to leave, as stipulated in the temporary residence permit he received. Krasniqi is not a war refugee, nor was he persecuted back home. In fact, he has nothing to fear in his native Kosovo. He says that he ran away from something he considers to be even worse than rockets and Kalashnikovs: hopelessness. Before he left, he promised his sick mother in Pristina that he would become an architect, and he promised his fiancée that they would have a good life together.
“I’m a nobody where I come from, but I want to be somebody.” But it is difficult to be somebody in Kosovo, unless you have influence or are part of the mafia, which is often the same thing. Taken together, the wealth of all parliamentarians in Kosovo is such that each of them could be a millionaire. But Krasniqi works seven days a week as a bartender, and earns just €200 ($220) a month. But a lack of prospects is not a recognized reason for asylum, which is why Krasniqi’s application was initially denied. The 30,000 Kosovars who have applied for asylum in Germany since the beginning of the year are in similar positions. And the Kosovars are not the only ones. This year, the country has seen the arrival of 5,514 Macedonians, 11,642 Serbians, 29,353 Albanians and 2,425 Montenegrins. Of the 196,000 people who had filed an initial application for asylum in Germany by the end of July, 42% are from the former Yugoslavia, a region now known as the Western Balkans.
The exodus shows the wounds of the Balkan wars have not yet healed. Slovenia and Croatia are now members of the European Union, but Kosovo, which split from Serbia and became prematurely independent in 2008, carves out a pariah existence. Serbia is heavily burdened with the unresolved Kosovo question. The political system in Bosnia-Hercegovina is on the brink of collapse, 20 years after the end of the war there. And Macedonia, long the post-Yugoslavia model nation, has spent two decades in the waiting rooms of the EU and NATO, thanks to Greek pressure in response to a dispute over the country’s name. The consequences are many: a lack of investment, failing social welfare systems, corruption, organized crime, high unemployment, poverty, frustration and rage.

“..helicopters, mounted police and dogs..”
• Hungary Scrambles To Confront Migrant Influx, Merkel Heckled (Reuters)
Hungary made plans on Wednesday to reinforce its southern border with helicopters, mounted police and dogs, and was also considering using the army as record numbers of migrants, many of them Syrian refugees, passed through coils of razor-wire into Europe. In Germany, which expects to receive 800,000 of them this year, Chancellor Angela Merkel was heckled by dozens of protesters as she visited an eastern town where violent anti-refugee protests erupted at the weekend. The surge in migrants seeking refuge from conflict or poverty in the Middle East, Africa and Asia has confronted Europe with its worst refugee crisis since World War Two, stirring social tensions and testing the resources and solidarity of the 28-nation European Union.
A record 2,533 mainly Syrians, Afghans and Pakistanis crossed from Serbia into EU member Hungary on Tuesday, climbing over or squirreling under a razor-wire barrier into the hands of an over-stretched police force that struggled to fingerprint and process them. Authorities said over 140,000 had been caught entering so far this year. Unrest flared briefly at a crowded reception center in the border region of Roszke, with tear gas fired by police. Another 1,300 were detained on Wednesday morning. More will have passed unnoticed, walking through gaps in a border fence being built by Hungary in what critics say is a futile attempt to keep them out. They packed a train station in the capital, Budapest, hundreds of men, women and children sleeping or sitting on the floor in a designated “transit zone” for migrants.
Almost all hope to reach the more affluent countries of northern and western Europe such as Germany and Sweden. Visiting the eastern German town of Heidenau, where violence broke out during weekend protests by far-right militants against the arrival of around 250 refugees, Merkel said xenophobia would not be tolerated. About 50 protesters booed, whistled and waved signs that read “Volksverraeter” (traitor), a slogan adopted by the anti-Islam PEGIDA movement earlier this year. “There is no tolerance for those people who question the dignity of others, no tolerance for those who are not willing to help where legal and human help is required,” Merkel told reporters and local people. “The more people who make that clear … the stronger we will be.”









