RCA TV test pattern 1939

Anyone would have won against Le Pen.
• Macron Banks On De Gaulle’s ‘Majority Amplifier’ To Govern (R.)
Unknown just three years ago, and with a party only 12 months old, Emmanuel Macron has seized the presidency against all the odds. His challenge now is to govern. To do that he must build a parliamentary majority that supports his election pledges in June legislative elections, when France’s two established parties will put their huge machines to work. Macron has at least one thing in his favor: the “majority amplifier” effect of an electoral system designed by post-war leader Charles de Gaulle specifically to maximize presidential independence from parliament. Last week, the first opinion survey for the legislative elections showed Macron’s new movement “En Marche!” could win between 249 and 286 mainland France seats in the lower house. Even a figure at the bottom of that range would be a good outcome for him.
He only needs 289 for an absolute majority, and the poll excluded 42 seats in Corsica and overseas. It foresaw centrist and conservative parties winning around 200-210 mainland seats, the far-right National Front 15-25 and the Socialists 28-43. “In the lowest-case scenario, En Marche would still be the largest political grouping, which would be enough to try to constitute a majority. The question would then be how and with whom,” said OpinionWay’s Bruno Jeanbart, who directed the poll. En Marche is only a year old and has never fielded candidates before. Only 14 have been named so far, and at first glance a majority looks unlikely. But that reckons without de Gaulle’s amplifier – known as the “fait majoritaire” by French political scientists. [..] The last legislative vote in 2012 also showed the “fait majoritaire” in action.
Socialist Francois Hollande garnered less than 30% in the first rounds of both the presidentials and the legislatives, yet came away with over 40% of the second-round legislative vote and, with help from 17 Green party MPs, governed with a comfortable majority. “Macron can totally have an extremely solid majority of at least 350 MPs,” said Xavier Chinaud, an electoral expert. He added that to reach that number, the president would have to employ tactics like poaching popular MPs from other parties. The old parties will put up a fight, especially the conservative Republicans [..] Now led by Francois Baroin, they hope for enough seats to force Macron into France’s fourth “cohabitation” since 1958. Cohabitation does not have to mean paralysis, but rather that the prime minister and his camp in parliament have the upper hand over the president.

“En Marche doesn’t have the money to finance a full-blown parliamentary run. It must ask its candidates to invest not only their time but also their money in the upcoming blitz campaign.”
• In France, The Run Of Macron’s Life Starts Monday (Pol.)
Winning the presidency now looks like the easy bit. If Emmanuel Macron makes his way to the Élysée Palace, as expected, in the second round of France’s presidential election Sunday, another bruising political battle is looming. To be able to govern and not be sidelined by a hostile parliament, Macron’s nascent political movement En Marche will have to cobble together a majority in the National Assembly in an election beginning on June 11. And unlike in the second round of the presidential ballot — in which parties from across the political spectrum have urged their supporters to vote for him over his far-right opponent Marine Le Pen — Macron’s rivals will be devoting all their energies to defeating him.
The 39-year-old former economy minister will be counting on his army of 250,000 En Marche volunteers, and a crew made up mostly of political novices. And while Macron hopes that a victory in the presidential election will draw others to his banner, for a movement that was launched a little over a year ago, winning control of parliament looks like a tall order. The stakes are high. If Macron can’t clinch a majority, he won’t be able to appoint a prime minister of his liking. He’ll spend his term largely as a figurehead, his dreams of reforming France all but sunk. Macron needs 289 deputies to be ensured of an absolute majority in the lower house of parliament. So far, En Marche, the movement he still refuses to call a party, has endorsed 14.
True to form, Macron exudes a sense of confidence that the momentum of his election will carry over to the parliamentary polls, allowing him to clinch a majority just six weeks later. This may not be out of reach. A survey conducted this week by OpinionWay, although preliminary, indicated that En Marche could well obtain more than half the seats in the National Assembly. By weaving in electoral results from past elections with a recent poll, OpinionWay estimates that the next Parliament would be dominated by En Marche and the conservative Républicains party. The ruling Socialist Party would be decimated, and Le Pen’s National Front would obtain 25 MPs at most – due to France’s electoral system.
Sill, obstacles abound. En Marche will be facing an energized right. Both the mainstream center-right Républicains party and Le Pen’s National Front will emerge from the presidential election feeling that Macron has robbed them of a victory they at some point considered theirs. François Fillon’s failed campaign has left deep wounds in the Républicains, but one way to try to heal them could be to make Macron their common target in June. [..] En Marche doesn’t have the money to finance a full-blown parliamentary run. It must ask its candidates to invest not only their time but also their money in the upcoming blitz campaign. Political parties in France are provided with public funding according to their performance in previous elections. En Marche, founded a little over a year ago, has never put up a candidate for office before.

Not THAT much trust perhaps.
• Euro Gives Up Gains As Investors Look To Post-Election France (G.)
The euro rose to a six-month high in the wake of Emmanuel Macron’s convincing victory in the French election but the upside for the single currency could be short-lived, analysts warned. In Asian trading on Monday, the euro rose as high as $1.1024 , its highest since 9 November, and also jumped to a one-year high of 124.58 yen against its Japanese counterpart. But it had slipped almost 0.3% to $1.096 against the dollar by 5.30am GMT and lost a similar amount to the yen with traders remarking that gains had already been largely priced in thanks to Macron’s strong showing in the first round of voting two weeks ago. “The market already priced in the victory of Macron,” said Masafumi Yamamoto, chief currency strategist for Mizuho Securities in Tokyo.
“We saw some additional rise of the euro this morning, but considering the difficulty for Macron’s party to get a majority in the national assembly election, he may not bring higher growth.” Looking at positioning in the euro, he said, “the market has squared its short positions, but there are no fresh reasons to take long positions, as there will likely be no new positive developments, and limited scope for upside for the euro”. The muted analysis was partly based on an acknowledgment of the problems facing Macron, a 39-year-old former banker who has never held elected office. He was economy minister under outgoing president François Hollande but failed to turn around the fortunes of the beleaguered government. He has pledged to reform the country’s rigid labour laws – long seen by pro-market economists as a hindrance to growth – but such change was beyond the Hollande administration, despite a lengthy struggle.

Reality check.
• US Economy Can’t Even Match the “Sclerotic Statism” of France (CEPR)
The Washington Post has long pushed the view that a dollar (or euro) that is in the pocket of a middle class person is a dollar that should be in the pockets of the rich. (They are okay with crumbs for the poor.) In keeping with this position, in its lead editorial today the Post complained about the “sclerotic statism” of the French economy. It then called for increasing employment, “through reforms of the labor code, not by protectionism or restriction of immigration.” It is worth bringing a little bit of data to the fact free zone of the Washington Post opinion pages. France actually has consistently had a higher employment rate for its prime age workers (ages 25 to 54) than the United States.
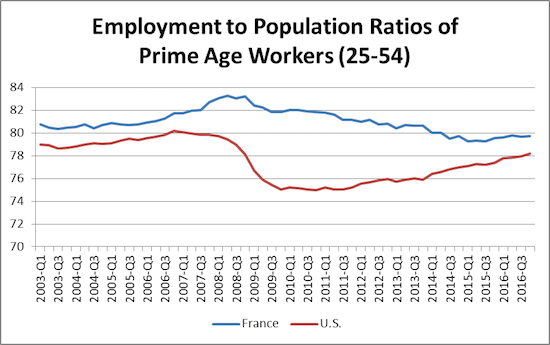
As can be seen, the employment rate for prime age workers in France was roughly 2 percentage points higher in 2003. The gap expanded to almost 7 percentage points following the downturn, but it has in more recent years narrowed again to just under 2 percentage points. France does have much lower employment rates among younger and older workers than the United States, but this is due to policy choices. College is largely free in France and students get stipends from the government. Therefore many fewer young people work. France also makes it much easier for people to retire in their early sixties than in the United States, with largely free health care and earlier pensions. The merits of these policies can be debated, but they are not evidence of a sclerotic economy.
It is also not clear that the Washington Post’s desire to weaken protections for workers (euphemistically described as “reforms of the labor code”) will have a significant effect in reducing unemployment or raising employment. Extensive research has shown there is little relationship between worker protections and employment. It is also worth noting that the Post denounced protectionism in this editorial, but it is fine with protectionism in the form of ever longer and stronger copyright and patent protection, which benefit people it likes.

Expect losses.
• Expect Dramatically Lower Stock Market Returns Over Next Decade (CNBC)
Enjoy the stock indexes riding at record highs for now, but get ready for much stingier markets in the years to come. That’s the message consistently conveyed these days by investment counselors and finance scholars, who argue that with today’s starting equity valuations and low interest rates, the coming decade should produce dramatically lower returns than the historical average. The leaders of Vanguard Group, overseers of some $4 trillion in client assets, have been advising investors to expect a typical 60% stocks/40% bonds portfolio to deliver two- to- three percentage points less in nominal annual returns than its long-term norm. (Since 1926, such an asset mix has returned better than 8.5% annualized.)
Other forecasts are even less generous. Research Affiliates, a quantitative and “smart beta” fund manager, projects that U.S. stocks might only offer one% a year for the next decade, after inflation. This is based largely on the so-called Shiller P/E, a ratio of the S&P 500 index to its trailing ten-year average earnings, which is now above 29 and higher than any period aside from the run-up to the 1929 and 2000 market peaks. Jeremy Grantham of institutional value manager GMO has, by his admission, been wrong for years in assuming that corporate profit margins and equity valuations would revert to their pre-1990s trend levels. Yet even accounting for some more permanent upward shift in these gauges, he sees real (after inflation) returns of 2-3% a year looking out two decades.
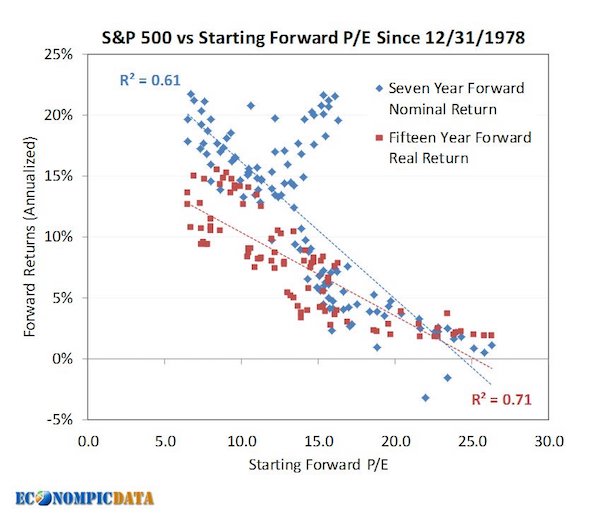
And a simple plot of the market’s forward P/E ratio against subsequent market returns shows that, since 1978, when starting at today’s multiple of around 17.5 forecast earnings, ensuing seven- and 15-year nominal returns (before inflation) have been clustered in the mid- to low-single digits. These forward-return calculations vary in their approach and assumptions, but all are anchored on today’s stock valuations, long-term norms in corporate-profit growth and current interest rates. Stocks, even during the depths of the last bear market, never got dramatically cheap compared to prior cycles and certainly didn’t stay inexpensive for very long. And with risk-free 10-year government debt yielding a skimpy 2.3% in the U.S. and far less elsewhere, all other financial assets have repriced for skimpier future returns as well.

The consumer is toast.
• UK Consumer Spending Weakens With Sharp Slowdown in April (BBG)
U.K. consumer-spending growth slowed in April and is forecast to remain weak in the coming months, according to a report from Visa. Its index showed spending rose an annual 0.5% in April, down from 1% in March and marking one of the slowest rates of growth in the past three years. Weaker household demand is also taking a toll on retailers. A separate report from the Institute for Chartered Accountants in England and Wales showed while there was a jump in business confidence this quarter, retailing was the laggard among nine sectors covered. “The trend of relatively modest expenditure growth is likely to extend in to the coming months, as consumers are squeezed by both rising living costs and relatively lackluster wage growth,” said Annabel Fiddes, an economist at IHS Markit, which compiles the consumer index.
Inflation was at 2.3% last month and is forecast to keep accelerating through this year, outpacing wage increases and leaving workers facing a drop in real incomes. The Bank of England may raise its forecast for consumer-price growth this week, which could indicate an even bigger squeeze on households. The overall business sentiment gauge by the ICAEW jumped the highest in almost a year this quarter. Yet despite firms being more confident, the report showed they are still reluctant to make long-term commitments. While Brexit is dominating the agenda in the buildup to the U.K. election on June 8, the institute said all parties must spell out how they will “address the problem of business investment head-on.”

No wonder consumer spending’s down.
• Brexit Boom Gives Britain More Billionaires, Inequality Than Ever (G.)
Britain has more billionaires than ever in what equality campaigners said was a clear sign the UK economy is only working for the few at the top. There are now 134 billionaires based in the UK according to this year’s Sunday Times Rich List, 14 more than the previous highest total, as the super-rich reap the benefits of a “Brexit boom”. Fifteen years ago, there were 21. The annual rich list showed that the wealthiest 1,000 individuals and families in Britain have combined wealth of £658bn, up from £575bn last year, despite fears that the Brexit vote last June would plunge the economy into a fresh turmoil. The Equality Trust said the £83bn increase in wealth among the richest 1,000 people over the past year could pay the energy bills of all UK households for two and a half years and would be enough for the grocery bills for all food bank users for 56 years.
Wanda Wyporska, the executive director of the trust, said that an elite was sitting on mountains of wealth in the fifth largest economy of the world. “The super-rich continue to streak away from the rest of us, while the poorest see their wealth shrink. This is an economy working for the few, not the many,” she said. “Record numbers of people visited food banks last year, millions are locked out of a decent home and two-thirds of children in poverty are in working households. “We know that inequality damages our economy and society, and makes it harder for ordinary people and their children to get on. With the general election fast approaching, our politicians need to decide the sort of country they want to build. One where we can all prosper or one where we’re picking crumbs from the super-rich’s table.”

China Shadow Banking Assets Estimated at 64.5t Yuan or 87% of GDP: Moody’s.
• China Tycoons Are Setting Up Shop In The US (BBG)
When a new hedge fund opened in Mountainside, New Jersey, a leafy suburb that still holds an annual little-league parade, few would have guessed where much of its funding came from: Chinese billionaire Cai Kui. The credit hedge fund, Westfield Investment, was founded by former Goldman Sachs Managing Director Renyuan Gao and managed $139 million as of January. It’s part of a new crop of asset management firms that are expanding China’s reach on Wall Street as money has poured into the U.S. from the world’s second-biggest economy. China’s marquee names are among those setting up shop in the U.S. Chen Feng, who controls the HNA Group airline and hotel conglomerate, has opened a U.S. money management firm. China Vanke, the mainland’s second-largest residential developer, has indirectly taken a major stake in a manager.
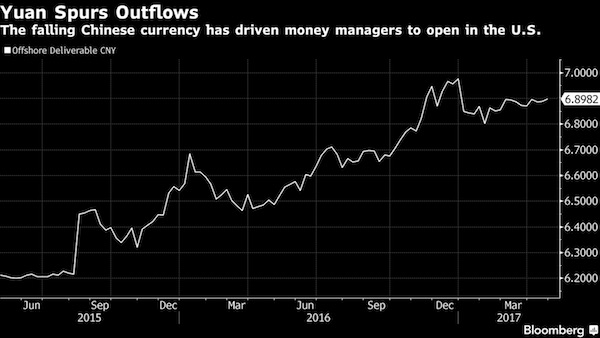
All told, about 324 firms with financial ties to the mainland and Hong Kong had registered with regulators by last year, more than double the number in 2012, filings show. They are riding the wave of capital that left China on concerns about bank debt, a real estate bubble and the yuan, which plummeted about 11% against the dollar in the last two years. The currency flight was reflected in balance of payments data where capital outflows tripled to $220 billion last year from $70 billion in 2014, according to Derek Scissors, a China economist at the American Enterprise Institute. “There is so much Chinese money floating around the U.S. now,” Scissors said. “If you’re a Chinese money manager, why wouldn’t you come here?” The migration comes amid a Chinese shopping spree for an array of U.S. companies, including financial firms like New York’s Cowen Group and the Chicago Stock Exchange.
Chongqing Casin Enterprise led the purchase of the exchange, which was founded in 1882. The deal was reviewed by a U.S. panel on national security grounds and eventually cleared in December. In another deal with political overtones, a subsidiary of Chen’s HNA Group agreed in January to buy a stake in Anthony Scaramucci’s SkyBridge Capital, a New York fund of hedge funds firm. The announcement came after reports that Scaramucci had been tapped for a top job in the White House, stirring speculation that HNA’s motives were partly political. The registration of the China-linked firms with the SEC hasn’t drawn such scrutiny. The SEC began requiring hedge funds and buyout firms to sign up with the agency in 2012 as a result of the Dodd-Frank Act. About 30% of the Chinese firms that registered by 2016 are full-fledged money managers. The rest filed as exempt advisers that operate in the U.S. on a more limited basis.

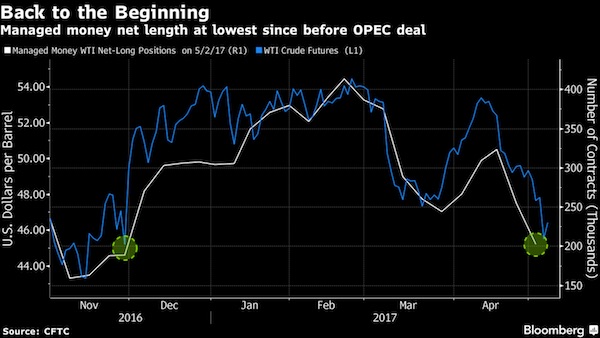
OPEC is fast losing what remained of its credibility.
• Hedge Funds Bail Just Before OPEC-Driven Oil Rally Vanishes (BBG)
Hedge funds jumped out of the oil market just in time. Before West Texas Intermediate crude nosedived on Thursday, wiping out the rally driven by OPEC’s deal, money managers slashed bets on rising prices by 20%, according to U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission data. Now they may soon be well poised to start betting on the next rally. “We are moving toward a positioning where these money managers are no longer over-invested,” Tim Evans at Citi Futures Perspective in New York, said. “This opens up the potential for them to start buying again.” Oil collapsed Thursday amid concerns that OPEC has failed to ease a supply glut as U.S. shale drillers ramp up output. Shares of U.S.-based producers got crushed as investors worry they might be repeating the same pattern that led to the market crash in 2014.
Earlier this year, billionaire wildcatter Harold Hamm urged colleagues to take a “measured” approach to lifting production, or risk a new glut. In a gamble that things could get worse, about $7 million worth of options changed hands Friday that will pay off if WTI falls beneath $39 a barrel by mid-July, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Hedge funds decreased their net-long position, or the difference between bets on a price increase and wagers on a drop, to 203,104 futures and options in the week ended May 2, the CFTC data show. Longs fell about 7%, while shorts surged 37%, following a 26% jump a week earlier. [..] Oil’s tumble to a five-month low was driven purely by technical trading and supply is still getting tighter, according to Citigroup and Goldman Sachs. The current price plunge began when WTI broke through its 200-day moving average. Once that gave way, another key technical indicator called a Fibonacci retracement was breached, paving the way to the low of the year and then $45 a barrel.

Multigenerational households are the model of the past and the future. Come look in Greece.
• Warning For Boomers: Your Gen X Kids Are Coming Back Home – For Good (MW)
Remove the door knockers. Pull down the shutters. Pretend no one’s home. Your adult children are coming back – for good. One-in-nine baby boomer parents said their adult children returned home within the last year, according to a new report from financial services firm Fidelity Investments and Stanford Center on Longevity, which surveyed 9,000 employees.The adult children save money on rent and household goods, but their parents are the ones who appear to be suffering: 68% said they were more stressed, 53% said they were less happy and another 53% said they had less leisure time after the return of their “boomerang kids.” More than three-quarters (76%) said they took on higher expenses, too. Even people who are now in their 40s and 50s are considering mom and dad an option.
Older millennials are 2.7 times more likely to live in their parents’ home than people under 55 years old than in 1999, while Generation-Xers, who are now in their mid-30s to early 50s, were 2.2 times as likely to live with their parents, according to separate data released last week by real estate site Trulia. “No parent is going to want to say no to a child who needs help, but certainly being realistic about the financial situation is important,” said Katie Taylor at Fidelity. More American adults are living with their parents and grandparents than ever before — 19% of the U.S. population (or nearly 61 million people) lived in a multigenerational household, up from 17% (42 million) in 2009 and 12% (27.5 million) in 1980, according to the Pew Research Center, nonprofit think tank based in Washington, D.C.
But not all millennials are as “lazy” or “entitled,” as they are often accused of being. About one in four 25- to 34-year-olds who live at home and are not working or going to school do so because of a health-related reason or because they are acting as caregivers to their family members. And more than a third of Americans, including millennials, expect to financially help their parents within the next few years, another survey found. Some are even making efforts to help their parents save for retirement.

Wow, great timing! We’re coming to you live from the barn, and there’s not a horse in sight.
• Australia To Hold New Inquiry Into ‘Big Four’ Banks (R.)
Australia will hold an inquiry into competition in the country’s financial system, following a series of scandals in the banking sector and public allegations against the “Big Four” banks of abuse of market power. The latest inquiry is part of a number of government measures since last year aimed at alleviating public concerns about the power of the big banks, after revelations of misconduct in the industry. Australia’s four major lenders – Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Westpac, ANZ and National Australia Bank – have come under fire recently following several scams involving misleading financial advice, insurance fraud and interest-rate rigging, as well as for refusing to pass on official interest rate cuts in full. The four together control 80% of Australia’s lending market and have posted record profits for years.
Westpac, NAB and ANZ all reported a rise in half-yearly cash profits this month, taking their total to about A$8.5 billion. CBA will report limited third-quarter figures on Tuesday. “The high concentration and degree of vertical integration in some parts of the Australian financial system has the potential to limit the benefits of competition…and should be proactively monitored over time,” Treasurer Scott Morrison said in a statement on Monday. “The Government is committed to ensuring that Australia’s financial system is competitive and innovative. That is why I have tasked the Productivity Commission to hold an inquiry into competition in Australia’s financial system.” The inquiry will consider the degree of concentration in key segments of the financial system, examine barriers to innovation in the system and look into competition in personal deposits and mortgages for households and small businesses.

The benefits of ZIRP.
• How Zombie Companies Stop Productivity Growth (BBG)
The global economy is picking up steam, but that’s deceptive. The foundations of expansion are soft, marked by weak productivity growth and inequality. The two are related. The productivity problem confronting the world’s advanced economies predates the financial crisis more than a decade ago. When we look beyond the headline statistics, patterns emerge. Advanced economies have become less dynamic and are at risk of becoming sclerotic unless the ambition for reform is revived. It’s essential that we understand three sources of the current productivity slump in particular, and identify the key reforms necessary to address them. First, the productivity slowdown masks a widening performance gap between more productive and less productive firms, as the chart below shows (the picture for service sector firms is even worse).
This divergence is not just driven by firms at the frontiers of their industry, pushing the technological boundaries, but also by stagnating productivity growth at what can be called laggard companies that have failed to adopt the leaders’ best practices. This is also bad news for inclusiveness, since rising wage inequality can be largely traced to the growing differentials in average wages paid across companies, with high-productivity ones paying high wages and low-productivity businesses paying low wages. Second, in well-functioning markets we would expect strong incentives for productive companies to aggressively expand and drive out less productive ones. The opposite has happened. The propensity for high-productivity companies to expand and low-productivity companies to downsize or exit the market has declined over time.
This pattern is evident in the U. S. and is particularly stark in southern Europe, where scarce capital has been increasingly misallocated to low-productivity firms. Third, across the 35 countries in the OECD, we are seeing a drop in the dynamism of the business sector. Not only has the share of recent entrants into the market declined, but marginal companies, which would typically exit or be restructured in a competitive market, are more likely to remain. At the same time, the average productivity of these marginal businesses has fallen. In other words, it has become easier for weak companies that do not adopt the latest technologies to survive. The survival of weak companies drags down average productivity, but the consequences for growth are even worse. Since such firms take up scarce resources, their prolonged survival (or their delayed restructuring) inflates wages relative to productivity, depresses market prices and undermines investment – all of which deters the expansion of productive companies, particularly startups, and amplifies the mismatch of skills.

They’ve known about this for decades.
• German Army To Search All Barracks After Nazi Memorabilia Found (R.)
The head of Germany’s armed forces has called for an inspection of all army barracks after investigators discovered Nazi-era military memorabilia in a garrison, broadening a scandal about right-wing extremism among soldiers. The discovery at a barracks in Donaueschingen, in southwest Germany, was made in an investigation that began after similar Nazi-era items were found in the garrison of an army officer arrested on suspicion of planning a racially motivated attack. As a result, General Inspector Volker Wieker ordered a wider search of barracks. “The General Inspector has instructed that all properties be inspected to see whether rules on dealing with heritage with regard to the Wehrmacht and National Socialism are being observed,” a Defence Ministry spokesman said. Defence Minister Ursula von der Leyen said the military must root out right-wing extremism.
“We must now investigate with all due rigor and with all candor in the armed forces,” the minister told broadcaster ARD on Sunday evening. “The process is starting now, and more is sure to come out. We are not through the worst of it yet.” Displaying Nazi items such as swastikas is punishable under German law, although possession of regular Wehrmacht items is not. Von der Leyen said last week, however, she would not tolerate the veneration of the Wehrmacht in today’s army, the Bundeswehr. Von der Leyen said the arrested officer – who had falsely registered as a Syrian refugee – had likely worked with others to squirrel away 1,000 rounds of ammunition, but the chief federal prosecutor was still investigating the matter. The suspect’s goal, she said, had likely been to carry out an attack and then pin the blame on migrants.

Don’t hold your breath.
• Greek PM Tsipras Rushes To Get Bailout Deal To Parliament With Eye On QE (K.)
After rallying his ministers, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras must now get coalition MPs behind him for a new multi-bill of austerity measures that is set to go to Parliament this coming week. Although some lawmakers have expressed reservations about the deal, which foresees further cuts to pensions and more tax increases, along with changes to the energy and labor markets, it is widely expected that Tsipras will get the support he needs to push the bill into law. A raft of so-called countermeasures – social welfare interventions that will come into effect in 2019 if the government meets budget targets – will be voted on separately and is sure to get the support of coalition MPs. The government has also appealed to the main political opposition New Democracy to back the offsetting measures but ND has refused to oblige.
According to government sources, Tsipras is already looking beyond the vote, expected on May 15 or 16, and beyond a scheduled Eurogroup summit on May 22 where the agreement between Greece and its creditors is expected to be rubber-stumped. Aides to the prime minister said he is considering a cabinet reshuffle to give his government a lift and inspire investors as talks on lightening Greece’s debt and the inclusion of Greek bonds in the ECB’s QE program are next on the agenda. It remains unclear whether Tsipras is considering a “cosmetic” shake-up or a radical overhaul, or whether key cabinet members such as Finance Minister Euclid Tsakalotos would keep their posts. But it appears that the government is keen to send out a message that it is turning a page following the completion of a tough bailout review that dragged on for months.

Our times, and our very selves, are defined by refugees and famine more than anything else. But we don’t like to look at what defines us.
• 1 Million Child Refugees Flee South Sudan’s Civil War (BBG)
More than 1 million children have fled South Sudan’s civil war, two United Nations agencies said Monday, part of the world’s fastest growing refugee crisis. Another 1 million South Sudanese children are displaced within the country, having fled their homes due to the civil war, said the U.N.’s child and refugee agencies in a statement Monday. “The future of a generation is truly on the brink,” said Leila Pakkala, UNICEF’s Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa. “The horrifying fact that nearly one in five children in South Sudan has been forced to flee their home illustrates how devastating this conflict has been for the country’s most vulnerable.”
Roughly 62% of refugees from South Sudan are children, according to the U.N. statement, and more than 75,000 children are alone or without their families. Roughly 1.8 million people have fled South Sudan in total. “No refugee crisis today worries me more than South Sudan,” said Valentin Tapsoba, UNHCR’s Africa Bureau Director. “That refugee children are becoming the defining face of this emergency is incredibly troubling.” For children still living in South Sudan, the situation is still grim. Nearly three quarters of children are out of school, according to the U.N. statement, which is the highest out-of-school population in the world. An official famine was declared in two counties of South Sudan in February, and hundreds of thousands of children are at risk of starvation in the absence of food aid, according to the U.N.

Why Russia’s safety zones make sense.
• Growing Numbers of Refugees In Northern Syria in Urgent Need of Aid (Kom)
The co-chair of the Syrian Democratic Council (SDC), Ilham Ehmed, said that the operations to push out the Islamic State (IS) has resulted in refugee flows into the northern parts of Syria controlled by the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) and that the displaced people are in urgent need of aid. “We have gathered the refugees that came recently in two camps,” Ehmed said to ANF. “In one of the camps, 50 thousand refugees are living. A number of aid organisations are present but there are no serious aid efforts. Many of the organisations receive funding from Europe but they still don’t help,” she said. “One can’t help wondering if they want Syrians to die, if there is a plan to kill them first with war and then with hunger. And if that fails from the heat and the cold. That’s the sad conclusion one draws from the situation.”
The SDC co-chair said they had discussed the urgent needs of food, housing and health with the US-led coalition without any results. “This is not acceptable, they should at least provide support for the refugee camps,” she said, stressing that preparations must be made as the operation to evict IS from Raqqa will give rise to many more refugees. “38 refugees coming from Raqqa have already died, some were children. It’s a tragedy. The European countries and the coalition must take their responsability.” Ehmad stressed the need of mediaction, clinics and doctors in the camps. “This is really urgent. Some will be able to return after the area has been liberated but those who lost their homes will stay, so we must make preparations.”
Ehmad also criticized Europe for giving in to what she called Turkey’s “blackmailing.” “There is an approach to the issue which goes something like this: ‘Let’s give them [Turkey] money so that no refugees will come here’. But everyone knows that the refugees are remaining in our region [Syria] at the moment.” Last year, the United Nations estimated that more than 6 million were internally displaced within Syria, and over 4,8 million were refugees outside of the country.








