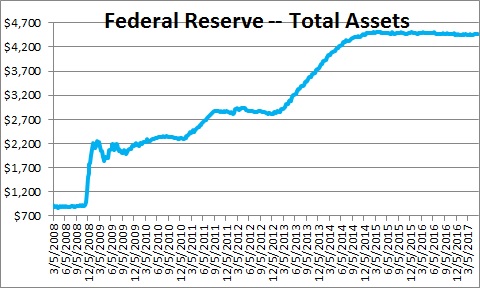
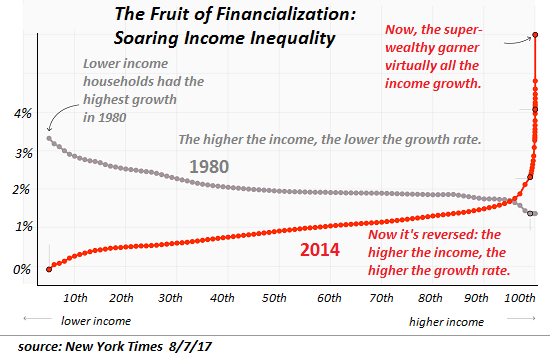
Elliott Erwitt California, USA 1956



Make viruses
VIDEO NOW BLOWING UP THE INTERNET; Pfizer director on camera saying they are “mutating" COVID-19 Virus to increase infectiousness. UNREAL!
"That is Not What We Say to the Public" …
"People Won’t Like That’ … ‘Don’t Tell Anyone"pic.twitter.com/pGP8dCkNNf
— James O'Keefe (@JamesOKeefeIII) January 26, 2023



Pay it forward
https://twitter.com/i/status/1616057896604672003

South Africa Suspended vaccines
https://twitter.com/i/status/1618204753271611394

CJ Hopkins
"The masks were brilliant & pure theatre." (i.e. NOT science).
.@CJHopkins_Z23, Playwright.pic.twitter.com/p4rQBWWb94— Robin Monotti (@robinmonotti) January 25, 2023



Vaxx Street Boys
https://twitter.com/i/status/1618292478150594561


“..NATO’s existence derives its validation from the management of perceived ‘threats’ that in a circular process of thinking precisely were provoked by NATO enlargement – an enlargement done ostensibly to manage such ‘threats’..”
• Is This Western War On Russia Simply Stupidity? (Alastair Crooke)
The US proxy war on Russia is stupid. Professor of Law at the LSE, Peter Ramsay, in a review of Benjamin Abelow’s book, How the West Brought War to Ukraine, outlines how the latter eschews the simplistic ‘Putin invaded Ukraine’ narrative — attributing primary responsibility for the war to less proximate causes: ‘American governmental stupidity and blindness’ and ‘the deference and cowardice’ of Europe’s leaders toward this American governmental ‘stupidity’. “Although Abelow describes the self-deluding arrogance and hypocrisy of Western policy very clearly, he does not attempt to explain how; or why US policy has become so stupid or European leaders so cowardly. He appears dumbfounded by it, describing the level of irrationality involved as ‘almost inconceivable’”.
Nevertheless, we must conceive of it, because it has happened, and it is bringing revolutionary change to a Middle East busily re-configuring itself as an integral part of the BRICS+ bloc; a transition, which in itself, portends a huge shift to the framework of geo-economics. At the bottom, the core “monumental stupidity” — for which Abelow quotes British Academic Richard Sakwa — is not something concealed, but rather, is one of those ‘truths’ that are ‘out there: hiding in the open’. It is that NATO’s existence derives its validation from the management of perceived ‘threats’ that in a circular process of thinking precisely were provoked by NATO enlargement — an enlargement done ostensibly to manage such ‘threats’. In short, it is a circular closed-loop argument.
Not only is there no threat from Russia that is independent of American policy, but it is also the expansion of NATO to ‘meet the threat from Russia’ that creates the very threat that expansion was supposed to meet. Similarly, it is this type of circular reasoning which makes ‘Putin into Hitler’ — a self-fulfilling epithet that is created because NATO expansion is firstly ‘reasonable (a ‘Value’, and a national Right), and therefore that anyone contesting it therefore must be ‘fascist’. Abelow asks simply, “What sane person could believe that putting a Western arsenal on Russia’s border would not produce a powerful response?” At its root, Abelow laments that the insanity that bothers him intensely is that US policy-makers recognize the circularity of their argument (he gives examples), yet will not countenance for a moment any argument against it. They know ‘one thing’, but say ‘another’, he says.
But the charge of insanity, Ramsay opines, “whilst appealing rhetorically, tends to obscure a vital aspect of the narcissism that drives Western policy: the aspect in which the self-regarding sense of virtue is informed by the dominant mindset of our time – ideas which influence not just ‘experts’ – but political leaders and entire populations.” This Narcissism and smug self-regard are indeed a key factor, but we need fully to understand their role by turning to Leo Strauss, whose thinking so shaped a generation of American conservatives (the Straussians).

“This gives us a figure of 1,800 tanks, which must be considered an absolute minimum..” “..the German manufacturer concedes that only 29 of them could be shipped before the summer of 2023..”
• What Heavy Weapons For Ukraine Will Mean On The Battlefield (Khodaryonok)
Another thing to consider is probable Ukrainian losses during offensive operations. The average daily losses of an armored unit in this case stand at 10 to 15%. About 15 to 20% of incapacitated tanks are typically irrecoverable losses, while the rest require repairs (general maintenance for 30 to 50%, medium-level repairs for 15 to 30%, and an overhaul for 10 to 20%). Simply put, at least another 300 tanks are required to offset losses during combat operations. This gives us a figure of 1,800 tanks, which must be considered an absolute minimum. These are very approximate and somewhat simplistic calculations, yet they give us ballpark figures. Great Britain and Poland have officially pledged an armored company each, respectively consisting of up to 14 tanks. Germany will supply a similar amount, while the US is preparing the supply of 31 Abrams heavy weapons.
At a recent meeting of the US-led Defense Contact Group at Ramstein Air Base in Germany, officials from 12 countries discussed sending a total of about 100 tanks to Kiev, if Berlin were to give the green light, which, according to an ABC report, it has done. Rheinmetall could additionally supply a total of 139 tanks to Ukraine, including 88 Leopard 1s and 51 Leopard 2A4s, yet the German manufacturer concedes that only 29 of them could be shipped before the summer of 2023. What impact will NATO’s tanks have? Will all these tanks see combat any time soon? Let’s consider the example of the M1 Abrams, which is seen as one of the symbols of US military power. A small number of these tanks manned by poorly trained crews and lacking full-scale maintenance and supply infrastructure support would most likely yield negative results.
They will fail to change Ukraine’s fortunes on the battlefield, while images of burning American tanks will likely hurt US public opinion. Thus, one of America’s premier weapons, the pride and joy of its defense industry, will be humiliated on the battlefield for a long time. This is something the Pentagon can’t allow to happen under any circumstances. Therefore, before any actual fighting happens, evacuation teams, tank repair units, and spare part supplies must be in place, while crews must receive superior training to handle American tanks. Last but not least, the first deployment of US main battle tanks in Ukraine must be accompanied by a significant Ukrainian army success, at least at the tactical level, which would necessitate no fewer than 200–300 (maybe even 400–500) tanks.
Otherwise, supplying the M1 Abrams to Ukraine makes neither military nor political sense. Transferring them one company (10 to 15 tanks) at a time would only mean that this equipment will burn on the battlefield without making any significant impact or even catching anyone’s attention. So far, Russia has not had any significant trouble dealing with enemy equipment. Since the launch of the military operation, according to Lieutenant General Igor Konashenkov, the Russian Ministry of Defense spokesman, Russian forces have destroyed 376 planes, 203 helicopters, 2,944 UAVs, 402 anti-aircraft missile systems, 988 MLRVs, and 3,898 field artillery guns and mortars. As well as 7,614 tanks and other armored vehicles.

“Right now we are seeing a sharp change in sentiment among the political elites of European countries..”
• Ukraine Demands Jets And Missiles (RT)
Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelensky has called on Western countries to supply fighter jets and long-range munitions, urging for more weapons just hours after the United States and Germany agreed to send heavy battle tanks. Speaking for a video address on Wednesday, Zelensky thanked his German and American counterparts for their decision to send tanks, but quickly shifted to Ukraine’s needs for additional arms. “We must also open deliveries of long-range missiles to Ukraine, it is important – we must expand our cooperation in artillery,” he said, adding that his country also requires fighter jets, and that “speed and volume are key now.”
Washington’s decision to send 31 Abrams tanks broke a stalemate with Berlin, which had refused to send its own Leopard 2 tanks or allow allies to re-export them to Kiev unless the United States followed suit. Ukrainian officials had long pleaded for heavier armor, specifically the M1 Abrams, among other advanced weapon systems from the West. A top advisor to Zelensky, Mikhail Podolyak, told the Telegraph on Wednesday that he expects Ukraine’s patrons to provide long-range missiles eventually, claiming they would be “part of the negotiation process” for the next weapons delivery to Kiev. “Right now we are seeing a sharp change in sentiment among the political elites of European countries, who understand that we need to transfer all equipment, including armored vehicles,” he said. “And we will reach, I am sure, no doubt, an agreement on long-range missiles.”
The advisor added that “Only these missiles will make it possible to destroy almost the entire infrastructure of the Russian rear army.” Citing unnamed sources, the Telegraph reported that the UK government has “not ruled out” longer-range missiles, but currently has no plans to supply them. Washington has previously refused Ukraine’s requests for ATACMS surface-to-surface missiles, which have a range of around 190 miles (305km), though it is unclear whether that, like the M1 Abrams decision, might be subject to change.
Moscow has repeatedly called on Western countries to halt the flow of weapons into Ukraine, saying the arms will only prolong the conflict and make a negotiated settlement impossible. Russia’s ambassador to the US, Anatoly Antonov, condemned the upcoming tank shipments as “another blatant provocation,” insisting the hardware will be “destroyed” by Russian forces.

“Can’t blame the Ukrainians for wanting more and more systems,” Kirby said. “It’s not the first time they’ve talked about fighter jets, but I don’t have any announcements to make on that front.”
• Ukraine Will Now Push For F-16 Fighter Jets (Hill)
With main battle tanks from the U.S. and Germany now headed to Ukraine, Kyiv is now focusing on securing modern fighter jets from Western allies. Yuriy Sak, an adviser to Ukraine’s Defense secretary, told The Hill that he was optimistic about receiving Western fighter jets such as the American F-16s, which Ukrainians have sought since early last year when Russia first invaded. “Every type of weapon we request, we needed yesterday,” Sak said. “We will do everything possible to ensure Ukraine gets fourth-generation fighter jets as soon as possible.” Reuters first reported the news that Ukraine was setting its sights on fighter jets.
Ukraine scored a major win on Wednesday with the announcement from President Biden that the U.S. will donate 31 American-made M1 Abrams main battle tanks to Kyiv. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz on Wednesday also said he would supply Ukraine with the country’s Leopard 2 tanks and approve the transfer of other Leopards from European allies. The tanks were the latest hurdle for Western allies, who have cautiously approved more and more advanced weaponry for Kyiv, from HIMARS launchers to the Western battle tanks. Western fighter jets and longer-range artillery units, which would allow Ukraine to strike Russian forces deeper in occupied territory, will likely be the next debate for NATO.
Ukraine currently uses Soviet-era fighter jets, including MiG-29s, which became a point of controversy last March when the U.S. declined to facilitate the transfer of MiGs from Poland to Kyiv. So far, the U.S. has resisted sending the F-16 fighter jets and does not appear ready to announce their transfer anytime soon. But national security adviser John Kirby told reporters on Wednesday the U.S. was “in constant discussions” with Ukraine and “we evolve those as the conditions change.” “Can’t blame the Ukrainians for wanting more and more systems,” Kirby said. “It’s not the first time they’ve talked about fighter jets, but I don’t have any announcements to make on that front.”
WWIII
According to @JoeBiden WW3 starts with the shipment of “offensive equipment” like “tanks”to Ukraine.
Welcome to WW3!pic.twitter.com/mc7flIH5Ob
— Kim Dotcom (@KimDotcom) January 25, 2023

Focus on China.
• Russia, Now The South And East’s Counterpoint To Israel (Mazaheri)
There is no doubt that were Israel threatened with the forced implementation of even something as fundamentally just and decent as a two-state solution they would resort to using nuclear bombs. They are dead-set on waging war until they get all the Palestinians’ lands, and they have made it clear that there is no place for non-Jews (non-White Jews, actually) inside this land they have stolen as if human mores had not changed since the 19th century. In the blink of a post-corona eye, Russia has become something quite similar. As former Russian ex-president Dmitry Medvedev just reiterated, if the Russian nation is seriously threatened with defeat nuclear weapons will be used in self-defence. Other than North Korea, only Israel feels the need to use such language.
Russia and North Korea are genuine nations, ones whose existence was not entirely contrived by and for Western imperialism, but in many ways Russia has become a new Israel. To be more accurate – Russia is now the counterpoint and antithesis of Israel. Just as Israel, the poisoned blade of Western capitalism and imperialism, faces and constantly thrusts east and south, now Russia is the South and East’s defensive rampart facing West. Russia has gone from post-1991 kowtowing to Western liberal democracy – earnestly trying to join them – to realising that the West has declared total war against them. How can there be a reconciliation? War in the Donbass has been going on for nearly a decade – that’s not the blink of an eye. Anyway, the West simply does not remove sanctions once in place – look at decades of Western policy towards Iran, Cuba, North Korea, etc. – barring total capitulation.
The West only removed sanctions on China because they absurdly thought that China had gone capitalist and that it had all just been Mao’s doing. Sanctions are now back in force, as Xi has reflected the broad persistence of socialism in China. The alleged end of history was based on the idea that only one type of civilisation existed any more, but it’s clear that there is a false idolatry of a West which exists in only in theoretical words and not in practical deeds, and there is a tolerant and truly diverse non-West which insists on national sovereignty and the right to cultural differences. The West’s outpost in Asia is well-known – Israel – and it is not just a rich colonialist’s whim and folly. Israel serves as an imperialist foothold to destabilise the entire Muslim world and Africa – training, funding and supporting all types of awful monarchies and puppet governments – and for these crimes they suffer internally from the awful, unstable Apartheid they have created.
The surprising development is that non-Western bloc’s frontier has shifted West: from 1979 onwards it was clearly Iran. Forty years of war on and around Iran failed to topple the revolution, and drained the West of vital tangible and moral resources. The non-Western frontier has now been pushed back to Russia. Russia is the country that – for reasons which are diametrically and morally the opposite for the reasons of Israel’s existence – will now serve as the non-Western bloc’s frontier, a frontier which will be in long-term combat and instability.
Schlanger
Why NATO is commited to a permanent war against Russia:
— Vera Van Horne (@VeraVanHorne) January 24, 2023

“The open discourse on Ukraine as a testing ground for US weapons and Russia as an example to China suggests that the Americans see the current campaign as a test run for different means of influencing the future..”
• NATO Has Already Destabilized Europe, Asia Is Next (Lukyanov)
Currently, the world’s attention is focused on the European theater of war, but some very interesting events are also unfolding in Asia. Japan is the most illustrative. Until recently, the country was reluctant to peddle a militant attitude either in terms of weaponry or even in using economic pressure. Things are changing, and this is a strong indicator of the transformation of the international arena. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida has just completed a tour of the US and the leading countries in Western Europe. Contrary to usual custom, there was virtually nothing but military rhetoric everywhere. In a policy statement delivered in Paris, Kishida stressed that the security of Europe and the Indo-Pacific region are inextricably linked and must be ensured collectively.
Other statements in Rome, London and Washington confirmed the new trend: In the security field, Japan no longer intends to limit itself exclusively to its relationship with the US, though it forms the basis of its entire defense strategy. Now, Tokyo seeks a much broader engagement with the main Western bloc (NATO), subject to its gradual reorientation towards the Pacific space. This is a new scheme. Since the Cold War, the security system in Asia has been America-centric but not unified, instead based on different groups of countries or bilateral relationships. The US has been the fixed element, the others have varied. Recent innovations such as the “QUAD” involving Japan, India, Australia, and an “Anglo-Saxon club” of the Americans, British and Australians have not disturbed the usual logic. However, something else is emerging – the transfer to greater Asia of the principle of a consolidated alliance, moreover, with European allies to whom the region poses no security threats.
At the heart of the strategy is the logic of Washington, which proceeds from the inevitability of strategic rivalry with China and Beijing’s Asian neighbours, or more precisely, its most bellicose ones. There is no doubt in the US that Beijing will be a major challenge to the American position in the world for years or decades to come. It is discussed in doctrinal documents and it guides the military’s entire posture. Russia is seen as an acute, but short-lived and transient, threat because of what Washington sees as its limited aggregate capabilities. The open discourse on Ukraine as a testing ground for US weapons and Russia as an example to China suggests that the Americans see the current campaign as a test run for different means of influencing the future. In this context, the question of NATO’s status naturally arises.

80 years ago, 25 million Russians were killed by Germans. Baerbock is too young and uneducated to remember that. But every Russian knows. And German tanks are back fighting Russia.
• German Foreign Minister Just Essentially Declared War On Russia (ZH)
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock bluntly stated in fresh remarks that Western allies are fighting a war against Russia. The remarks came during a debate at the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) on Tuesday amid discussions over sending Leopard 2 tanks to Ukraine. While Baerbock’s words were largely ignored in mainstream media, a number of pundits on social media noted with alarm that the German foreign minister just essentially declared war on Russia. Ironically other German officials have long sought to emphasize their country is not a party to the conflict, fearing uncontrollable escalation. Contradicting this official stance, Baerbock said the quiet part out loud, and introduced the comments with: “And therefore I’ve said already in the last days – yes, we have to do more to defend Ukraine. Yes, we have to do more also on tanks.”
And that’s when she asserted: “But the most important and the crucial part is that we do it together and that we do not do the blame game in Europe, because we are fighting a war against Russia and not against each other.” Interestingly, both Chancellor Olaf Scholz and his former defense minister who recently resigned, Christine Lambrecht, have been seen as weak on arming Ukraine – repeatedly declaring an unwillingness to get pulled deeper into the proxy war aspect to the conflict. But now it seems the more hawkish Baerbock is willing to at this point be much more open with the reality of what’s happening. Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova seized on the comments, saying this is yet more proof that the Western allies were planning a war on Russia all along…
“If we add this to Merkel’s revelations that they were strengthening Ukraine and did not count on the Minsk agreements, then we are talking about a war against Russia that was planned in advance. Don’t say later that we didn’t warn you,” Zakharova said. One thing is for sure, things are moving fast…
From Russia
https://twitter.com/i/status/1618014795755839491

“..spend much of the war collaborating closely with the Germans. They had no issues with the Nazi ideology for they too believed that a solution was found in returning to a ‘pure race.’”
• Ukrainian Nationalism as a ‘Cold War Weapon’ (Chung)
The Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN) was founded in 1929 in East Galicia (located in Poland at the time) and called for an independent and ethnically homogenous Ukraine. From the beginning, the OUN had tensions between the young radical Galician students and the older military veteran leadership, who grew up in the more lenient Austro-Hungarian Empire. The younger generation had only known oppression under the new Polish rule and underground warfare. As a result, the younger faction tended to be more impulsive, violent and ruthless. During this period, Polish persecution of Ukrainians increased and many Ukrainians, especially the youth who felt they had no future, lost faith in traditional legal approaches, in their elders and in Western democracies who were seen as turning their backs on Ukraine.
The OUN assassinated Polish Interior Minister Bronislaw Pieracki in 1934. Among those tried and convicted in 1936 for Pieracki’s murder, were OUN’s Stepan Bandera and Mykola Lebed. Both escaped when the Germans invaded Poland in 1939. Support for the OUN increased as Polish persecution of Ukrainians continued. By the beginning of the Second World War, the OUN was estimated to have 20,000 active members and many times that number in sympathizers in Galicia. In 1940 the OUN would split into the OUN-M led by Andriy Melnyk, and OUN-B headed by Stepan Bandera which made up most of the membership in Galicia and consisted mainly of youth.
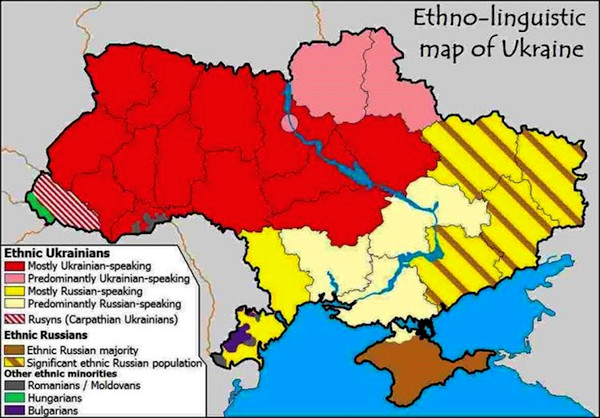
In August 1939, the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany signed the non-aggression pact known as the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, dividing Poland. Eastern Galicia and Volhynia were reunified with Ukraine, under the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. In June 1941, when Nazi Germany invaded Western Ukraine, there were many Western Ukrainians who welcomed the invading Nazis as their ‘liberators.’ It should be noted here that this was not a sentiment predominantly shared by the rest of Ukraine, who fought in or alongside the Russian Red Army against the invading Nazis. Both the OUN-M and OUN-B would spend much of the war collaborating closely with the Germans. They had no issues with the Nazi ideology for they too believed that a solution was found in returning to a ‘pure race.’
In the case of Ukraine, this pure race consisted of a somewhat romanticised concept of ‘ethnic Ukrainian,’ based on the golden age of Kievan Rus’. The OUN believed that the ‘pure ethnic Ukrainian race’ were the only true descendants of the royal bloodline of the Rurik dynasty that ruled Kievan Rus’. And rather than looking at Belarusians and the Russians as their brothers and sisters who shared the same ancestry, the OUN viewed them more so as ‘ethnic impostors’ so to speak of this pure bloodline. This can be seen today with Ukrainian neo-Nazi groups attacking Ukrainian ethnic Russians for the past nine years in Ukraine.[1] An issue that is almost entirely ignored in the West.

“Türkiye is among NATO’s oldest members, and people calling for its exit are “talking about destroying” the bloc..”
• Türkiye To Be Out Of NATO In Months – Erdogan Ally (RT)
Türkiye could leave NATO within months, a politician there has claimed, citing “provocations” by the US-led military bloc against his nation. Ethem Sancak is a Turkish businessman of Arab descent who is active in politics and who local media describe as close to President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. He was commenting on an anti-NATO campaign in Türkiye that the Vatan (Patriotic) Party, where he holds the position of vice chairman for foreign relations, has organized. “NATO forces us to take these actions with their provocations,” he stated, predicting that his party’s goal of getting Türkiye to leave the alliance may come to fruition “in five-to-six months.”
Speaking to the news website enbursa.com on Tuesday, Sancak noted that being part of the bloc puts Türkiye on a collision course with fellow member and longtime rival Greece, and also at risk of being pulled “into a whirlpool in the Middle East.” The recent Koran-burning stunts in some European nations make leaving NATO “a necessity,” he argued. The Danish-Swedish right-wing politician and activist Rasmus Paludan staged a protest last weekend in front of the Turkish embassy in Stockholm, which involved the burning of the holy book of Islam. The incident sparked outrage in the Muslim world, while the Turkish president said Stockholm’s choice to permit the action meant that Ankara would not support Sweden’s request to join NATO.
Sancak said that Turks were increasingly perceiving the US as a nation that pursues “the most hostile and destructive policies.” At the same time they “feel great sympathy towards Russia.” A survey conducted by the Turkish pollster Gezici at the end of last year showed that 72.8% of Turks wanted their nation to have good relations with Russia. Less than a quarter said they believed Moscow to be hostile towards Türkiye. Omer Celik, the spokesman for the ruling Justice and Development Party (AKP), rejected the idea, which he called “mind-blowing.” Türkiye is among NATO’s oldest members, and people calling for its exit are “talking about destroying” the bloc, he told journalists on Wednesday.
The Vatan Party believes that Türkiye would be better off if it dropped its attempts to become a member of the EU and forged good relations with China and Russia instead. It also advocates overcoming differences with Iran and Syria, nations that the US is targeting with crippling sanctions and other forms of pressure. Sancak joined the Vatan Party last year, though his involvement in politics goes back decades to his days as a university student and activist. His business interests include pharmaceuticals and cosmetics as well as media, with the TV channel 360 and the daily newspaper Star among his best-known acquisitions.

“..4000-word New York Times opinion piece titled Nancy Pelosi, Liberated and Loving It by Maureen Dowd.”
• The Worst Article You’ll Ever Read (Space Worm)
It’s not a pretty sight when pols lose power. They wilt, they crumple, they cling to the vestiges, they mourn their vanished entourage and perks. How can their day in the sun be over? One minute they’re running the world and the next, they’re in the room where it doesn’t happen. Donald Trump was so freaked out at losing power that he was willing to destroy the country to keep it. I went to lunch with Nancy Pelosi at the Four Seasons to find out how she was faring, now that she has gone from being one of the most powerful women in the world — second in line to the presidency — and one of the most formidable speakers in American history to a mere House backbencher. I was expecting King Lear, howling at the storm, but I found Gene Kelly, singing in the rain. Pelosi was not crying in her soup.
She was basking as she scarfed down French fries, a truffle-butter roll and chocolate-covered macadamia nuts — all before the main course. She was literally in the pink, ablaze in a hot-pink pantsuit and matching Jimmy Choo stilettos, shooting the breeze about Broadway, music and sports. Showing off her four-inch heels, the 82-year-old said, “I highly recommend suede because it’s like a bedroom slipper.” Fans dropped by our booth to thank Pelosi, and women in the restaurant gave me thumbs-ups, simply because I was sitting with her. “I wonder, Maureen, girl to girl, I keep thinking I should feel a little more, I don’t know,” she hesitated, looking for the right word. Over the course of our conversation, she said the word was “regretful,” and she thought about it in church, and during morning and night prayers, but she just wasn’t feeling it. “It’s just the time, and that’s it. Upward and onward. I’m thrilled with the transition. I think it was beautiful.”
Her daughter Alexandra, a documentary filmmaker, assured me that it’s not an act. “I can tell you, in my 52 years of being alive on this earth, I have never had the kind of weekend I’m having right now,” she said last Sunday. “My mother is at peak happiness. I’ve never seen her like this. It’s like she’s floating through the air. It’s fascinating for my kids because they don’t know this person. “I think you want to enjoy being old. I don’t think you want to spend your final days fighting with Kevin McCarthy about how many seats you get on Appropriations.” Before I could broach the humiliating spectacle of McCarthy abasing himself to the loonies on the far right and being tortured by preposterous Matt Gaetz, Nancy Pelosi brought up her successor. She looked at me, her brown eyes widening, and said: “I’m sad for Kevin that he couldn’t do that in a way that brought a little more dignity to the House of Representatives. It’s strange.” She added, “What happened was inexplicable.”

“..opened the door for US and like-minded investment” in the respective countries’ vast “green” mineral wealth..”
• US Africa Leaders Summit Promises More Exploitation For Africa (GZ)
The US Africa Leaders Summit held this December in Washington DC provided a platform for the Biden administration to advance its agenda across the African continent. With topics ranging from COVID-19 to climate change to “closing the digital divide,” to “strengthening democracy,” Washington’s agenda united around the belief that African collaboration with US multinational corporations would prove mutually beneficial, and advance long-term “progress.” The weekend of discussions was conducted Davos-style, with heads of US industry seated directly beside African heads of state and members of the Biden administration. At the top of the corporate titans’ agenda was the relaxation of regulatory requirements, which they argued would make the continent more “inviting” for outside investment.
One set of regulations that the US would especially like to loosen are those relating to the mining sector. This includes miners’ rights, child labor laws, slavery laws, environmental regulations and mineral tariffs. Deloitte, a US corporate giant and strategic partner of the World Economic Forum, published a paper in 2018, “The Future of Mining in Africa,” which spells out the agenda Washington is advancing across the continent. The paper argued that facilitating the digital transformation known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution would require African nations to loosen mining regulations intended to protect human rights and the environment. The paper lamented that the mining sector “continues to experience scrutiny by regulators in Africa,” which supposedly “creates uncertainty, delayed investment in mining expansion, and stops the development of new mines.”
Deloitte went on to argue that Africa needs “to move away from enforcing [regulatory] compliance for compliance sake and move toward delivering value.” It was clearly implied that that “value” would be determined by corporate America, and not necessarily the African people. The script put forward by Deloitte helped set the stage for the US Africa Leaders Summit this December. There, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken presented a memorandum of understanding to DRC Foreign Minister Christophe Lutundula and Zambian Foreign Minister Stanley Kakubo. The agreement, according to Blinken, “opened the door for US and like-minded investment” in the respective countries’ vast “green” mineral wealth, referring to massive deposits of nickel, cobalt, and copper.
“The DRC produces more than 70 percent of the world’s cobalt. Zambia is the world’s sixth-largest copper producer, second-largest cobalt producer in Africa,” Blinken said. “Global demand for critical minerals is going to skyrocket over the next decades…Electric vehicles help reduce carbon emissions and they support the global response to the climate crisis,” the Secretary of State continued, draping the plundering of Africa’s wealth in friendly green-speak.
Mining
This is what the West’s green, sustainable “Digital Revolution” looks like in Africa. I spoke to Siddharth Kara about the very bottom of the EV supply chain & @BillGates new copper mining project in Zambia — for @TheGrayzoneNews: https://t.co/l6BA2FaQJB
pic.twitter.com/1LA51ZH1TB— Jeremy Loffredo (@loffredojeremy) January 25, 2023

“..the lead researcher said they were not going to publish these findings because it may affect funding from pharma..”
• Breaking The Silence: Do mRNA Vaccine Harms Outweigh Benefits? (Sladden)
‘Double-jabbed’ Malhotra originally supported the program, until a series of events sent him digging into the evidence. What he discovered alarmed him and resulted in the publication of two evidence-based, peer-reviewed papers along with a call for the immediate suspension of the Covid mRNA roll-out. He tells his story: ‘Despite being one of pharma’s biggest critics I could not have expected or conceived of the possibility that these vaccines, these new vaccines, could cause harm. So very early on I was one of the first to have two doses of the Pfizer vaccine, and I helped out at a vaccine centre in January 2021. About a month later I had a conversation with a friend of mine, film director Gurinder Chadha (who was) vaccine hesitant. I said to her, “Listen, traditional vaccines are still one of the safest pharmacological interventions in the history of medicine. That doesn’t mean that all vaccines are completely safe.
No drug is completely safe. But when you compare them to other pharmacological interventions I’ve talked about and campaigned on, for example diabetes drugs, blood pressure pills or statins, they are far, far safer.”’ Malhotra further explains his view during a Good Morning Britain interview. ‘I said, “There are rational concerns for vaccine hesitancy and irrational concerns. The rational concerns are when looking at what the pharmaceutical industry has done for years – they’ve been found guilty of fraud on many occasions – and prescribed medications are the third most common cause of death after heart disease and cancer.” So, I was being open, and I felt compassion for people who were vaccine hesitant. And I said, “In my opinion, as it stands at the moment, traditional vaccines are the safest.”
‘Six months later my father suffered an unexplained … cardiac arrest. The post-mortem didn’t make sense, he was a very fit guy, yet he had very severe narrowings of two of his coronary arteries. I had known his cardiac history inside out, we had done imaging on him a few years earlier. I found myself thinking “hold on a minute, he’s got a rapid progression of coronary artery disease when he’s doing really well during lockdown, walking 10,000 steps a day and eating well. This doesn’t make sense.“ And I could only attribute it at the time to stress, I couldn’t think of any other reason.’ Over following months, emerging data led Malhotra to question whether the vaccine was linked to his father’s death. The first was an abstract published in Circulation (November 8, 2021) by US cardiothoracic surgeon, Dr Steven Gundry, who followed several hundred of his patients after the mRNA (Moderna/Pfizer) jabs.
Gundry found that inflammatory markers correlated with heart disease risk went through the roof. On average, that change increased the risk of those people having a heart attack or stroke within the next five years, from 11 per cent up to 25 per cent. This increase in risk is massive. The next event raised more alarm bells for Malhotra. ‘Within two weeks of that abstract, a whistle-blower contacted me from a prestigious institution in the country, and said that a group of researchers had accidentally found through imaging studies that mRNA vaccines were increasing heart attack risk through inflammation, but the lead researcher said they were not going to publish these findings because it may affect funding from pharma. ‘I then felt a duty and contacted GB News saying, “There is a Circulation abstract but also something else I’ve heard,” and I spoke about it on GB news. That interview went viral … with me raising questions and saying, “We need to investigate this.”’ The push back was strong.

“..most experts would estimate the all-cause mortality death toll from the COVID vaccines to be in the range of 500K to 600K. So the global cost of life from these vaccines is on the order of 10 to 12 million people..”
• 217,000 Americans Killed By The Covid Vaccines In Just The First Year (Kirsch)
A new peer-reviewed paper was just published that finally gets the truth out: Over 217,000 Americans were killed by the vaccine in the first year after rollout The rate of severe adverse events reported in the survey by the survey participants (13.4%) after adjusting by a factor of 2 for categorization error, is still 5X more than was reported by Pfizer in their Phase 3 trial. Since deaths from the vaccine were higher in 2022, most experts would estimate the all-cause mortality death toll from the COVID vaccines to be in the range of 500K to 600K. So the global cost of life from these vaccines is on the order of 10 to 12 million people. But nobody wants to talk about it because that’s the way science works. When you can’t argue with the data, you censor the speaker like the FDA and CDC did to me.
They are actively trying to get the paper retracted because it destroys the narrative. I’m certain they will succeed because journals are under intense pressure to censor any anti-narrative paper. The problem is that Mark’s survey was entirely consistent with my surveys. If they want to have the paper retracted they need to show us THEIR surveys. But of course, they don’t have any surveys because they are too afraid of the results. So they will use hand-waving arguments like “I don’t like the methodology” or some nonsense like that instead of gathering their own data. They will NEVER show us survey data that supports their narrative because it isn’t there. That’s why there are no success anecdotes. NOBODY can give me the name of a US geriatric practice where all-cause deaths plummeted after the vaccines rolled out. In every case, they went the wrong way. The narrative is unraveling at an accelerated pace but the medical community is still fighting the truth.

“FBI has proven itself to be the Deep State’s brownshirts to DOJ’s Gestapo.”
• We Have the Evidence; Time to Hold Government Criminals Accountable (Tom Renz)
How many more young people need to die before doctors and politicians stop pretending that they don’t know what’s going on? Here’s a selection of deaths in just the last two weeks: 16yo High School Flag Football Player 18yo Rugby Player 18yo Baseball Player 18yo Basketball Player 18yo Football Player 18yo MMA phenom 20yo College Tennis Player. But it’s not just young athletes that are literally dropping like flies. Recent “sudden deaths” include a 30yo former WWE and reality TV star, a 31yo American Idol singer, a 33yo TikTok celebrity, a 42yo former football player, a 48yo award-winning Scottish chef, a 54yo Filipino celebrity chef, a 56yo former supermodel, and a beloved 67yo character actor.
These aren’t the aged and infirm (although they’re dying in record numbers too). A 14yo boy has a heart attack. A 16yo girl “dies suddenly” in her sleep…TWO DAYS after her 36yo aunt! Mothers, Fathers-to-be, and toddlers are at risk too. “Vibrant” 33yo women are “dying suddenly.” Even “walking too briskly” to class is now deadly, if you’re a military academy football player that was forced to participate in the experiment. Sometimes people don’t even make it out the door after getting jabbed. And think you’re safe if you ran “vaccine” clinics and dosed thousands with the gene jab? Think again. The data are clear: these injections are killing people at an unprecedented rate. And what has the response been? More gaslighting. Raising money to pay the hospital responsible for losing your child. And urging people to learn CPR.
Maybe we’ll finally get some action now that politicians are dying too. Then again, its curious how it’s never the ones who have been behind this operation nor anyone in their families. It’s time for Republicans to heed calls to start standing up for We the People and demanding an end to this genocide and holding those responsible criminally accountable. If you still need further proof that our government is being run as a criminal enterprise, look no further than the FBI. Between doing its best to take down a sitting president to colluding with Big Tech to censor the Hunter Biden laptop story before the 2020 election and agreeing to cover up Joe’s Top Secret document scandal until after last November’s midterms (while at the same time ginning one up to smear and further harass President Trump), FBI has proven itself to be the Deep State’s brownshirts to DOJ’s Gestapo.
It should be no surprise to anyone, then, that FBI director Christopher Wray was a Davos darling at the annual World Economic Forum gathering, braying about how FBI has embedded itself into Big Tech to expand its surveillance and censorship operations. It’s time to reinstate the Smith-Mundt Act and limit the federal government’s ability to surveil Americans without a court-ordered warrant specific enough to meet the Fourth Amendment standards.

“When the Federal Parliament reconvenes in February, the Government will need to explain – in much more detail – when we can expect to see Mr. Assange return to Australia..”
• Australia Has Not Written to US on Assange For 6 Months (Lauria)
A Freedom of Information request by a member of the Australian parliament has revealed that the Australian government has not engaged in correspondence with the United States regarding the case of imprisoned publisher Julian Assange for at least the last six months. MP Monique Ryan filed the requests with the offices of Prime Minister Anthony Albanese, Attorney General Mark Dreyfus and Foreign Minister Penny Wong and no documents were returned, indicating that there has been no written communication with the U.S. over the fate of Assange since at least last May, reported former Australian Senator Rex Patrick in the Australian publication Michael West Media. The absence of written correspondence does not exclude that Australian officials may have engaged in verbal communications with U.S. counterparts about Assange over the past half year, though written notes are normally made on such meetings.
The freedom of information request asked for all correspondence or other records of communication sent after May 23, 2022 between Albanese and President Joe Biden; Dreyfus and U.S. Attorney General Marrick Garland and Wong and U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken. Albanese raised Assange supporters’ hopes in November when he responded to a question in Parliament from MP Ryan by saying: “The government will continue to act in a diplomatic way, but can I assure the member for Kooyong that I have raised this personally with representatives of the United States government. My position is clear and has been made clear to the US administration that it is time that this matter be brought to a close.”
Hopes for Australian action on Assange were further raised when Australian Broadcasting Corporation journalist John Lyons told an ABC program at the end of December that he understood Assange would be back home in Australia within two months. Ryan told Michael West Media: “If the Albanese Government was serious about working to secure an end to the US prosecution and Mr. Assange’s release, then he and his Ministers would have raised the matter formally, in writing, with their counterparts at the top levels of the US Government. It is now confirmed that they have not done so via any formal means.” Ryan said that she intends to question Albanese about the absence of written communication. “When the Federal Parliament reconvenes in February, the Government will need to explain – in much more detail – when we can expect to see Mr. Assange return to Australia,” she said.




Color change
https://twitter.com/i/status/1618298413338234881



Pendulums
Fifteen uncoupled simple pendulums of monotonically increasing lengths dance together to produce visual traveling waves, standing waves, beating, and (seemingly) random motion
[full video + explanation: https://t.co/sDeFDH1KBc]pic.twitter.com/aO2a5WJ3vL
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) January 25, 2023

Flip-flop
He learned how to do a backflip step by step. The result is amazing…
— Tansu YEĞEN (@TansuYegen) January 24, 2023

Cats are awesome
https://twitter.com/i/status/1617980726502359040
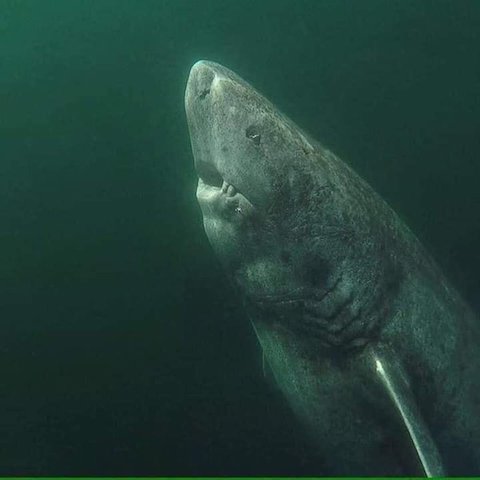


In 2016, a study based on 28 Greenland sharks determined by radiocarbon dating of crystals within the lens of their eyes, that the oldest of the animals that they sampled had lived for 392±120 years and was consequently born between 1504 and 1744


Support the Automatic Earth in virustime with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.