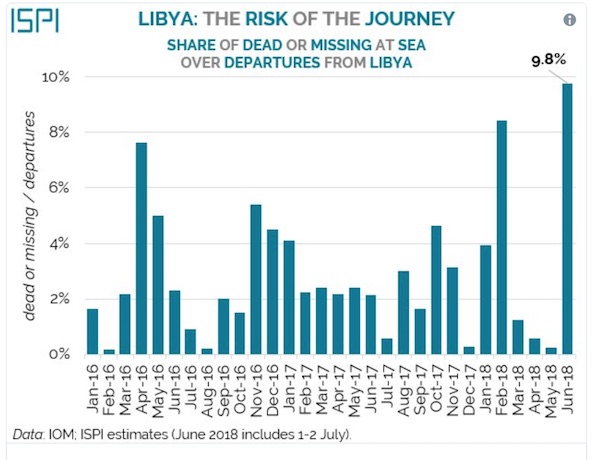
Berthe Morisot Julie and her boat 1884

$1.2 trillion will have to be rolled over this year. There are $90 billion of offshore renminbi deposits in Hong Kong available to buy dollars. Good luck.
• China Has a Dangerous Dollar Debt Addiction (Balding)
China’s foreign debt has been rising rapidly, and that’s becoming an increasingly big problem — for the country and, potentially, the world. Officially, China lists its outstanding external debt at $1.9 trillion. For a $13 trillion economy, that’s not a major amount. But focusing on the headline number significantly understates the underlying risks. Short-term debt accounted for 62% of the total as of September, according to official data, meaning that $1.2 trillion will have to be rolled over this year. Just as worrying is the speed of increase: Total external debt has increased 14% in the past year and 35% since the beginning of 2017. External debt is no longer a trivial slice of China’s foreign-exchange reserves, which stood at just over $3 trillion at the end of November, little changed from two years earlier. Short-term foreign debt increased to 39% of reserves in September, from 26% in March 2016.
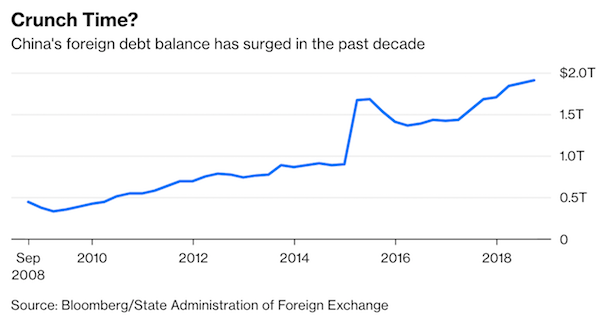
The true picture may be more precarious. China’s external debt was estimated at between $3 trillion and $3.5 trillion by Daiwa Capital Markets in an August report. In other words, total foreign liabilities could be understated by as much as $1.5 trillion after accounting for borrowing in financial centers such as Hong Kong, New York and the Caribbean islands that isn’t included in the official tally. Circumstances aren’t moving in China’s favor. The nation’s companies rushed to borrow in dollars when there was a 3% to 5% spread between Chinese and U.S. interest rates and the yuan was expected to strengthen. Borrowing offshore was cheaper and offered the additional bonus of likely currency gains. Now, the spread in official short-term yields has shrunk to near zero and the yuan has been depreciating for most of the past year. Refinancing debt in dollars has become harder, and more risky.
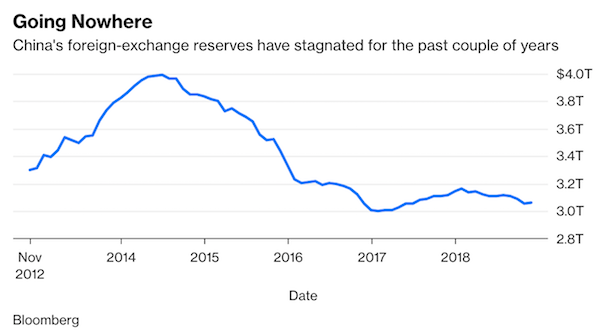
Beijing’s policies have exacerbated the buildup of foreign debt. To promote Xi Jinping’s Belt and Road Initiative, the president’s landmark foreign policy endeavor, China has been borrowing dollars on international markets and lending around the world for everything from Kenyan railways to Pakistani business parks. With this year and 2020 being the peak years for repayments, China faces dollar funding pressure. To repay their dollar debts, Chinese firms will either have to draw from the central bank’s foreign-exchange reserves (a prospect Beijing is unlikely to allow) or buy dollars on international markets. This creates a new set of problems. There are only 617 billion yuan ($90 billion) of offshore renminbi deposits in Hong Kong available to buy dollars. If China was to push firms to bring debt back onshore, this would necessitate significant outflows that would push down the yuan’s value against the dollar.

More trickle down fails.
• China Drops Hints Of Trade Pain Ahead (BV)
While a cut in the reserve requirement ratio, China’s fifth in a year, was not surprising, the 100-basis point shift that started off 2019 was larger than anticipated. Of course, demand for cash tends to spike around this time of year, due to both the Chinese New Year holiday and tax deadlines, but the economy is cooling uncomfortably fast. Official figures may show growth slowed to 6.3% in the fourth quarter, Standard Chartered reckons. Friday’s announcement adds to other easing measures: People’s Bank of China officials last month announced a new policy tool to encourage lenders to disburse their cash more widely. The “targeted medium-term lending facility” will make cheaper funding available to banks that the PBOC judges to be doing their part by lending more to small companies.
It’s certainly not full-blown monetary stimulus yet; the central bank has not fired its heavier artillery, such as a benchmark rate cut. The market has also been kept waiting for reductions to cost of borrowing from the PBOC’s more important channel, its regular medium-term lending facility. But the overall direction of travel is clear, and both recent moves point to structural issues that worry pessimists: the extra liquidity pumped into the system does not seem to be translating into more loans for smaller companies, which may signal deeper problems with capital allocation, not to mention the private sector’s nervousness about politics in 2019.
All of this is bad news for Beijing’s trade negotiators, when they hold talks with U.S. counterparts face-to-face this week. As the pain mounts, they may be pushed to yield more in order to gain relief. They could, for example, agree to formally drop the controversial “Made in China 2025” plan, or to announce concrete measures to beef up enforcement of intellectual property rights. Trump said on Sunday that weakness in China’s economy will push officials to negotiate. He may be right.

Tariffs rose Jan 1. It’s getting urgent.
• US and China To Resume Trade Talks With Both Eager For Compromise (G.)
US officials arrived in China for the first face-to-face negotiations since a 90-day truce was declared in a trade war between Washington and Beijing, in the hope of ending a bruising confrontation between the world’s two largest economies. Hopes that the sixth round of negotiations between the two sides could yield a breakthrough helped Asian shares rise on Monday, combined with optimism about the state of the global economy on the back of strong US jobs figures on Friday. In Tokyo, the Nikkei soared more than 3% and there were also strong positive moves in Shanghai, Hong Kong and Sydney. US and Chinese trade representatives were set to hold talks on Monday and Tuesday.
After failing to reach an agreement in December when Donald Trump and Xi Jinping met, both sides agreed to suspend tariff increases while holding discussions on technology transfers, as well as intellectual property theft and cybersecurity. If no agreement is reached, US tariffs on $200bn of Chinese goods will increase in March to 25% from the current 10%. Trump said on Sunday that China was under pressure to do a deal amid signs of a slowdown in its economy. “I think China wants to get it resolved. Their economy’s not doing well. I think that gives them a great incentive to negotiate,” he said. “China’s slowdown is occurring across the board, affecting almost every industry and region,” said Scott Kennedy, a trade expert focused on China at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “Resolving the trade war or at least finding some common ground with Washington will be needed to fully restore confidence,” he said.

Whatever the outcome, chaos guaranteed. You can jot down next Tuesday night in your agenda for that.
• May To Hold Parliamentary Brexit Vote On January 15 (R.)
Prime Minister Theresa May will hold a delayed parliamentary vote on her Brexit deal on Tuesday, January 15, the BBC reported on Monday, citing government sources. May was forced to pull the vote on her deal in December after she said it would be defeated by a large majority. The government had previously said the vote would be held in the week of January 14. May said on Sunday that Britain would be in uncharted territory if her Brexit deal is rejected by parliament, despite little sign that she has won over sceptical lawmakers.

In case you were still wondering who will be blamed.
• Theresa May Pleads For EU To Give Ground And Rescue Brexit Deal (G.)
Theresa May is preparing to make another desperate plea to EU leaders to offer a concession on the Irish backstop as she attempts to win over Brexiters who have vowed to vote down the government’s deal. The prime minister on Sunday promised to hold the meaningful vote in parliament in the week beginning 14 January despite growing opposition from Conservative backbenchers and the Democratic Unionist party, whose votes are required to push the deal through parliament. As MPs prepare to return to Westminster with the crucial Commons vote looming on the withdrawal agreement, Downing Street insisted that new compromises could still be won from Europe that would ensure the safe passage of May’s plan.
The hope of new developments came as opposition to the prime minister’s deal hardened. The hurdles facing May include: • Brexiters say the government faces a disaster if it fails to ditch the current deal, with DUP deputy leader Nigel Dodds describing the Irish backstop as “toxic”. • EU sources say talks to be held in Dublin on Tuesday between Leo Varadkar and Germany’s foreign minister, Heiko Maas, will not seek to reopen negotiations over the 585-page withdrawal agreement. • Senior MPs including Yvette Cooper and Nicky Morgan are launching a parliamentary campaign to rewrite government legislation to block a no-deal Brexit. • Chris Patten, the former Conservative Party chairman, called for a second referendum on the UK’s decision to leave the EU. • More than 200 MPs have signed a letter calling for Theresa May to rule out a no-deal Brexit. Tory ex-minister Dame Caroline Spelman, who organised the letter with Labour’s Jack Dromey, said the group had been invited to see the prime minister on Tuesday.
In an interview on Sunday, May said the vote, which was due to be held last month and postponed, would go ahead next week, as she sought further clarification from the EU to address MPs’ concerns. She also said she would look at giving parliament a greater say in how the UK’s future relationship would be negotiated, but refused to say exactly what that might be. Asked if there had been any changes she could offer to backbenchers who were expected to vote down her deal, she told BBC1’s Andrew Marr Show: “What we will be setting out over the next few days are assurances in three areas: first are measures specific to Northern Ireland; the second is a greater role for parliament as we take these negotiations forward into the next stage for our future relationship; and third – and we are still working on this – is further assurances from the European Union to address the issues that have been raised.”
Whitehall sources insisted that a compromise could still be found with the EU and that further planned announcements will be made this week that would win over MPs opposed to the deal. “We will be working flat out. There will be further contacts with the EU leaders. The issue of the backstop is not yet over,” the source said.

“The EU cannot now give another concession ahead of the vote because if the deal isn’t ratified, it means any new concessions will simply be banked again to no benefit at all. It would be pointless.”
• Germany and Ireland Step Up Efforts To Find Brexit Border ‘Fix’ (G.)
Germany’s foreign affairs minister is to fly to Dublin on Tuesday for Brexit talks as relations with Ireland intensify in an attempt to find a “fix” that will help Theresa May get the EU withdrawal agreement ratified. Heiko Maas will address an annual gathering of Ireland’s global diplomatic corps and take part in an unofficial fourth round of talks between Ireland and German leaders since Thursday. He will make the address in English, with a large German media contingent accredited, a reflection of how significant his speech is deemed back in Berlin. Last week the taoiseach, Leo Varadkar, had a lengthy telephone call with Angela Merkel. He then flew to Munich to address a meeting of her coalition partners, the CSU, and on Friday met the Germany chancellor’s successor as CDU leader, Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer, for discussions on Brexit and the future of Europe.
The emerging Irish-German nexus on the Irish border backstop “fix” is being seen as significant in Irish political circles, where people also point to the fact that Varadkar speaks German and has a good working relationship with Merkel. They point out it was Merkel, not the taoiseach, who requested the phone call with Varadkar last Thursday. The talks lasted 40 minutes and were, according to Varadkar, “an opportunity to kind of brainstorm a bit as to what we could do to assist prime minister Theresa May in securing ratification of the withdrawal agreement”. But informed EU sources say Brexiters should not raise their hopes of a reopening of negotiations. The “fix” will be further details in the political declaration on the future relationship and not the 585-page withdrawal agreement. “That is locked,” said one EU source.
There is deep frustration that the British cannot see how far the EU went to break the impasse on the Irish border talks, yielding to May’s demands for a UK-wide customs arrangement. One EU source said: “The EU was totally opposed to this in 2017 and again in March and June in 2018. It then emerged out of the tunnel in the autumn as the solution, but the Brexiters did not see it for what it was – a major concession. [..] “They are now looking for more concessions, but they just can’t be given. The Brits banked this major concession and just did nothing with it. People can’t understand why it wasn’t sold as a victory for May. “The EU cannot now give another concession ahead of the vote because if the deal isn’t ratified, it means any new concessions will simply be banked again to no benefit at all. It would be pointless.”

That’s about $20,000. Not including mortgages and student loans.
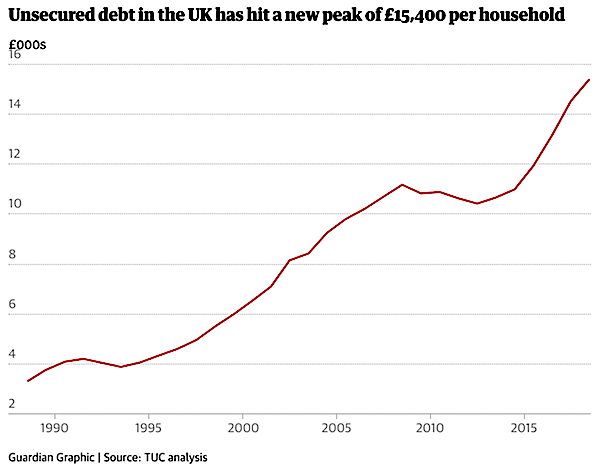
• Average UK Unsecured Household Debt Hits Record £15,400 (G.)
Britain’s household debt mountain has reached a new peak, with UK homes now owing an average of £15,385 to credit card firms, banks and other lenders, according to the TUC. The trade union body said household debt rose sharply in 2018 as years of austerity and wage stagnation forced households to increase their borrowing. The TUC said in its annual report on the nation’s finances that the amounts owed by British households rose to a combined £428bn in the third quarter of 2018. Each household owed £886 more than it did 12 months previously, it said. The figures do not include outstanding mortgage debts but do include student loans.
The level of unsecured debt as a share of household income is now 30.4%, the highest level it has ever been at. It is well above the £286bn peak in 2008 before the financial crisis, the TUC said. That figure also included student loans, but tuition fees then were £3,000 a year compared with up to £9,250 now. [..] The TUC general secretary, Frances O’Grady, said: “Household debt is at crisis level. Years of austerity and wage stagnation has pushed millions of families deep into the red. The government is skating on thin ice by relying on household debt to drive growth. A strong economy needs people spending wages, not credit cards and loans.”

They’re going to stay home?!
• UK Car Sales Record Biggest Fall Since Financial Crisis (R.)
British new car sales in 2018 fell at their fastest rate since the global financial crisis a decade ago, hit by a slump in demand for diesel, stricter emissions rules and waning consumer confidence due to Brexit, according to an industry body. Demand dropped by nearly 7% last year to 2.37 million vehicles, the largest fall since registrations nosedived 11.3% in 2008, preliminary data from the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) showed. A nearly 30% drop in demand for diesel was the most significant factor in the decline. Diesel has been pummelled since the Volkswagen emissions cheating scandal of 2015, prompting a crackdown and higher levies.
But the industry also warned that Britain’s departure from the European Union due at the end of March risks the future of a sector which employs over 850,000 people and has been one of Britain’s few manufacturing success stories since the 1980s. “It’s still hard to see any upside to Brexit,” said SMMT Chief Executive Mike Hawes. “Everyone recognises that Brexit is an existential threat to the UK automotive industry and we hope a practical solution will prevail,” he said, calling for lawmakers to back Prime Minister Theresa May’s deal to guarantee a transition period. [..] After record highs in 2015 and 2016, demand fell in 2017 and some analysts see car demand as a leading indicator which could be a harbinger for future economic performance. Britain’s economy slowed to a crawl at the end of 2018, the housing market is stalling and lending to consumers growing at its slowest pace in nearly four years, according to data released on Friday.

Macron is not just a fool himself, he’s surrounded by them as well. His spokesman after fleeing his office out of a back door as protesters invaded the courtyard and smashed up several cars said: “It wasn’t me who was attacked.” “It was the Republic.”.
Because the government is the Republic. The population is not.
• France’s Macron Reeling As Tough Stance Against ‘Yellow Vests’ Backfires (R.)
Emmanuel Macron intended to start the new year on the offensive against the ‘yellow vest’ protesters. Instead, the French president is reeling from more violent street demonstrations. What began as a grassroots rebellion against diesel taxes and the high cost of living has morphed into something more perilous for Macron – an assault on his presidency and French institutions. The anti-government protesters on Saturday used a forklift truck to force their way into a government ministry compound, torched cars near the Champs Elysees and in one violent skirmish on a bridge over the Seine punched and kicked riot police officers to the ground.
The French authorities’ struggle to maintain order during the weekend protests raises questions not just over policing tactics but also over how Macron responds, as he prepares to bring in stricter rules for unemployment benefits and cut thousands of public sector jobs. On Sunday evening, Macron wrote on Twitter: “Once again, the Republic was attacked with extreme violence – its guardians, its representatives, its symbols.” His administration had hardened its stance against the yellow vests after the protest movement appeared to have lost momentum over the Christmas holidays.
The government would not relent in its pursuit of reforms to reshape the economy, government spokesman Benjamin Griveaux said on Friday, branding the remaining protesters agitators seeking to overthrow the government. Twenty-four hours later, he was fleeing his office out of a back door as protesters invaded the courtyard and smashed up several cars. “It wasn’t me who was attacked,” he later said. “It was the Republic.”

“There is a Euro, which is a single currency in an incomplete monetary union, with a set of fiscal rules that are evidently economically illiterate..”
• The Euro: A Mindless Idea – Ashoka Mody (Spiked)
[..] most serious of all is the notion of common economic development as a basis for Europe. It was briefly true after the Treaty of Rome in 1957, which opened up the borders, but the momentum ran out within two decades. You open borders, but once they’re open, there’s not a lot more you can do. Even the gains from the so-called Single Market are very limited beyond a certain point. Every economist understands that. On the Euro, there was never any question that it was a bad idea. Nicholas Kaldor, an economist at Cambridge University, wrote in March 1971 that a single currency was a terrible idea, both as economics and as politics. And Kaldor has been proven right time and again.
But the entire European establishment just ignores every subsequent warning from well-regarded economists, and produces defensive counternarratives. For example, I often hear that Europe needs fixed exchange rates in order to have a Single Market. Why? Germany is trading a lot with Poland, Hungary and the Czech Republic, which are in the Single Market, but have different currencies. These fluctuate, but the trade continues apace. You don’t need a single currency for a Single Market.
spiked: When did your critique of the European project emerge? Was it during your involvement in the Irish bailout? Mody: When I finished at the IMF I planned to write a book on the Euro crisis. And I began writing it as an IMF economist would – what happened before the crash, the bubble, the bubble bursting, the panic, the fact it wasn’t well managed, and so on. But I soon realised that something wasn’t right here. And so I spent two years tracing the history of the Euro, and asking the question: what brought the Euro into existence in its current form? You see, it is not just that there is a Euro. There is a Euro, which is a single currency in an incomplete monetary union, with a set of fiscal rules that are evidently economically illiterate – and nobody questions the fact that they are economically illiterate, that they lack a necessary fiscal backstop and the necessary fiscal union. So why does it exist?