
Jerome Liebling Butterfly Boy, Harlem, New York City 1949

The last few drops squeezed from a stone-dry stone. Buybacks kill economies.
• US Tax Cuts, Repatriated Cash Used For Record Stock Buybacks (ZH)
While there is still some fringe debate what companies will do with the hundreds of billions in offshore funds repatriated to the US as part of the recently passed Trump tax reform, the discussion is largely over, especially after last week’s Cisco results. The company, which has $68 billion of overseas cash, third after AAPL and MSFT, announced that it would raise its buyback authorization by $25 billion, and revealed plans to repurchase its entire authorization of $31 billion during the next 6-8 quarters, equal to roughly 15% of its current market cap. Call it a partial LBO, courtesy of Donald Trump.
[..] Here’s what Goldman’s David Kostin said in his latest Weekly Kickstart report: “Since December, S&P 500 firms have announced buybacks totaling $171 bn. YTD announcements of $67 bn represent a 22% increase versus the same period in 2017. The buyback window has re-opened and firms are taking advantage of the recent correction; the GS Buyback Desk reported that last week was the most active week in its history.” The $171 billion in YTD stock buyback announcements is the most ever for this early in the year. In fact, it is more than double the prior 10 year average of $77 billion in YTD buyback announcements.
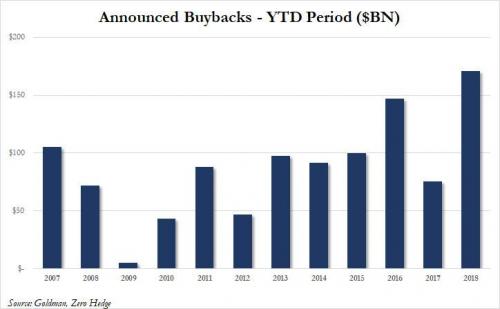
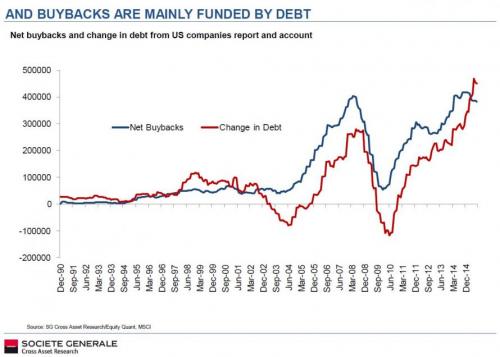
[..] in addition to what we first pointed out over two years ago, namely that all net debt issuance in the 21st century has been used to pay for stock buybacks… here is what John Hussman commented on this record last hurrah in stock buybacks: “Though buybacks are primarily debt-financed, they are also highest at market peaks, and contract sharply at major market troughs. Corporations are still borrowing to buy the dip at peak valuations, within a few percent of extremes associated with prospective 10-12yr market losses.”

There was no need for better design, the Fed has traders’ backs regardless.
• VIX Products Were Extremely Ill-Designed (Eric Peters)
There’s no question that, in an economy and in a financial system where there’s the level of debt that we have and the sensitivity to interest rates, rising rates are kind of a pre-condition to equity market disruptions and selloffs. I think that the level of volatility selling and its integration into risk models across virtually every type of investment strategy are contributors. And, having gone through such a long period with very, very little movement, I’d say that many people’s trading books were robust for relatively small moves. But once you’ve passed a certain move – and I think in this case it was probably the S&P down 3-ish% that triggered a whole series of different adjustments that people needed to make to their books and their option books – that then amplified the move in volatility and led to this blowup in the VIX product.
But you have to remember that these VIX products were extremely ill-designed. And they were very vulnerable to this. They’re a rare thing that you see in our industry, which is they had a predefined stop loss. And markets are pretty good at finding stop losses and triggering them. I started my career in the commodity pits, and I witnessed firsthand how the commodity pit is built around finding stop losses on the top side of the bottom side of markets. So I think the market did a great job of finding the stops – and in this case finding the weakest ones, which were in the VIX complex – and hitting them. But I don’t think that that really explains why this move happened. Why did we get the first leg down, and why are markets starting to move with very little news flow? And, again, that’s something that’s difficult to explain for a lot of people that are trying to do it.
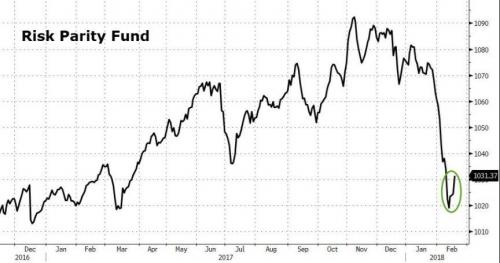
[..] The biggest problem in the investment industry today, the portfolio construct that investors have come to rely on, which is a brilliant construct really pioneered by Ray Dalio – he naturally has done incredibly well from this, and it’s been a fantastic strategy – this risk parity strategy. And, while there’s certainly more complexity to it that just being long equities and leveraged funds, let’s just view it as that strategy for a moment. It’s essentially what the dominant portfolio has become at all the major investors, pensions, endowments, etc. in the industry. And the beauty of that portfolio has been that you’ve been able to own risk assets and then you’ve been able to own a hedge, which is a leveraged bond portfolio, and that hedge has actually paid you a positive return.
The problem is when equity valuations become very high and interest rates get very low it’s difficult for that strategy to continue to perform very well. All else being equal. Now, however, if you add modest inflation into the formula, that portfolio actually becomes pretty toxic. That’s the environment I think we’re entering into. And that’s why, ultimately, I see some of these shocks like this most recent market shock as just being trail markers on this path to a much more difficult investment environment.

Deputy A.G. Rod Rosenstein: “There is no allegation in the indictment that the charged conduct altered the outcome of the 2016 election.”
Virginia State Senator Richard Black: “When you become a special counsel, you have an open checkbook for the US Treasury and you are guaranteed to become a mega-millionaire if you simply can drag out the proceedings,”
• Until There Are Facts On Election Meddling, It’s All Just Blather – Lavrov (RT)
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has again dismissed claims of Russian meddling in the US election, saying that until facts are presented by Washington, they are nothing but “blather.” Speaking at the Munich Security Conference in Germany on Saturday, he said that “Until we see facts, everything else will be just blather.” When asked to comment on the indictment of Russian nationals and companies in the US over alleged meddling in the 2016 US election, the foreign minister answered:“You know, I have no reaction at all because one can publish anything he wants. We see how accusations, statements, statements are multiplying.”
On Friday, a US federal grand jury indicted 13 Russian nationals and three entities accused of interfering in the 2016 election and political processes. According to the indictment, those people were “supporting the presidential campaign of then-candidate Donald J. Trump… and disparaging Hillary Clinton” as they staged political rallies and bought political advertising, while posing as grassroots entities.
[..] Even US Deputy Attorney General Rod Rosenstein had to admit that there were “no allegations” that this “information warfare” yielded any results and affected the outcome of the presidential election. The underwhelming indictment was also slammed in the US. Virginia State Senator Richard Black accused FBI Special Counsel Robert Mueller of deliberately dragging out the Russian meddling probe for his own gain. “To a certain extent, I think, Robert Muller is struggling to keep alive his position of a special counsel. The special counsel has already earned seven million dollars. When you become a special counsel, you have an open checkbook for the US Treasury and you are guaranteed to become a mega-millionaire if you simply can drag out the proceedings,” Black told RT.

Maxed out. Forget the web. Think savings, pensions.
• Apocalypse Now For Britain’s Retailers As Low Wages And The Web Cause Ruin (G.)
“Who’d be a retailer now?” That was the comment from City economist Jeremy Cook when the latest set of grim retail sales data was released by the Office for National Statistics last Friday. “The average Brit,” he added, “has spent the past few years living by the mantra ‘When the going gets tough, the tough go shopping.’” After a grim December, many had been hoping for a bounceback, but the figures showed that consumers were not as hardy as they once were, said Cook, and the retail sector was facing a long-term, continuing slowdown. Shoppers are being hit by declining real wages, record levels of consumer debt and the prospect of higher borrowing costs. But the wider problem is a structural shift in the way consumers spend their money.
This is threatening famous retailers and forcing a rethink about how high streets will look in years to come, and what might be done with retail parks and malls when retailers shut up shop. It is not just about shoppers preferring to buy online – although 20% of fashion sales, where the pressures are perhaps worst, have now moved to the internet. There’s been a seismic shift in the way we spend our time and money. Social media, leisure, travel, eating out, eating in – using takeaways and delivery services – and technology are all taking time and cash that would once have gone straight to shops. In food, increasing numbers of people now prefer to buy local and often. Fewer big weekly shops mean out-of-town superstores are under pressure and the big supermarkets are trying to lure in other retailers to take space they no longer need.
This rapid change in shopping habits is boosting sales at the likes of Amazon, Asos and Boohoo, but forcing radical change on British towns and cities as physical retail space becomes redundant. The past few months have seen a stream of collapses – from fashion store East to shoe chain Shoon and bed specialists Warren Evans and Feather & Black. Toys R Us is teetering on the brink of bankruptcy, while House of Fraser, Debenhams and New Look are all struggling, with all three considering large-scale closures of stores or space.

Almost funny.
• UK Will Need ‘Thousands’ More Customs Officers After Brexit (R.)
The Dutch government plans to hire at least 750 new customs agents in preparation for Britain’s exit from the European Union. The Dutch parliament’s Brexit rapporteur, Pieter Omtzigt, who had recommended the move, said both sides of the English Channel had been slow to wake up to the reality that Britain was on course to leave the EU in 14 months’ time. “If we need hundreds of new customs and agricultural inspectors, the British are going to need thousands,” he said. Omtzigt warned that “for a trading nation like the Netherlands, you just cannot afford for customs not to work, it would be a disaster”.
In a letter to parliament on Friday, the deputy finance minister, Menno Snel, said the cabinet had “decided that the Customs and Food and Wares agencies should immediately begin recruiting and training more workers”. He said the government was working on the basis of two scenarios: that Britain leaves the EU with no deal in place, or that it leaves on similar terms to those of the EU’s recent trade deal with Canada. “The results are that … around 930 or 750 full-time employees are needed,” Snel said. “It speaks for itself that the cabinet is following the negotiations closely in order to be able to react appropriately.”

“The real story of how Britain’s economy has been left high and dry by a doomed economic philosophy..”
• The Big PFI Heist: How Big Banks Launched The Takeover Of UK Plc (Ind.)
Sir Howard Davies, chairman of the Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS), recently made an astonishing admission on BBC1’s Question Time when he stated that private finance initiatives (PFI) had been a “fraud on the people”. Beyond seemingly populist rhetoric, the real story of PFI reveals that RBS alongside other global banks, notably HSBC, were instrumental in what Sir Howard has effectively labelled a great heist. The past month has seen the demise of construction giant Carillion followed by the collapse of Capita’s market value: both firms having built huge empires by providing outsourced services to public authorities. These initial tremors might be the canary in the coal mine. Profit warnings have been issued for other government contractors, such as Interserve. The domino effect has shades of the 2007-08 financial crisis even though it is clearly not of the same magnitude.
All this has thrown up searching questions, not least around staff redundancies and pensions, bailouts, inflated dividends and executive remuneration. Yet even in the throes of this PFI and outsourcing crisis, public-private Partnerships (PPP) are far from dead and buried. On the contrary, the Naylor Review – a report recommending the disposal of NHS land and assets to generate investment – is rehabilitating PPP. Furthermore, the Government is pushing through Accountable Care Organisations (ACO), a form of PPP based on an American model of healthcare. The Government cites too the model of Alzira in Spain where a consortium of private companies not only financed and built facilities but also delivered health services.
Of course, PFI was not always a toxic brand. In 1997 it appeared to be New Labour’s magical solution to chronic underinvestment in public services in the wake of Thatcherism. As Alan Milburn – the former Labour Health Secretary described by Private Eye as an “almost maniacal convert to PFI” – put it: “It’s PFI or bust.” The argument went that Labour had inherited public services in such a diabolical state of neglect that there was no alternative to the private financing of whole swathes of infrastructure. It was a persuasive argument which seduced many. The Blairite Third Way would somehow square the circle by delivering new schools, hospitals, roads, railways and prisons without the debt or inefficiency of the public sector. It seemed too good to be true yet those who dared to question the orthodoxy du jour were swatted away.

“..including one which switched off emissions cleaning after 26 km of driving..”
• Software Helped Daimler Pass US Emissions Tests (R.)
U.S. investigators probing Mercedes maker Daimler have found that its cars were equipped with software which may have help them to pass diesel emissions tests, a German newspaper reported on Sunday, citing confidential documents. There has been growing scrutiny of diesel vehicles since Volkswagen admitted in 2015 to installing secret software on 580,000 U.S. vehicles that allowed them to emit up to 40 times legally allowable emissions while meeting standards when tested by regulators. Daimler, which faces ongoing investigations by U.S. and German authorities into excess diesel emissions, has said investigations could lead to significant penalties and recalls.
The Bild am Sonntag newspaper said that the documents showed that U.S. investigators had found several software functions that helped Daimler cars pass emissions tests, including one which switched off emissions cleaning after 26 km of driving. Another function under scrutiny allowed the emissions cleaning system to recognize whether the car was being tested based on speed or acceleration patterns. Bild am Sonntag also cited emails from Daimler engineers questioning whether these software functions were legal.

We don’t we just shoot the remaining polar bears right now, and move on?!
• Global Sea Ice Hits New Record Low For January (Ind.)
The world’s sea ice shrank to a record January low last month as the annual polar melting period expanded, experts say. The 5.04 million square miles of ice in the Arctic was 525,000 square miles below the 1981-to-2010 ice cover average, making it the lowest January total in satellite records, according to the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Combined with low levels in the Antarctic, global sea ice amounted to a record low for any first month of the year, the organisation concluded. The news comes just days after researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder said the rate at which sea levels are rising was increasing every year, driven mostly by accelerated melting in Greenland and Antarctica.
The NSIDC, a respected authority on the Earth’s frozen regions, which researches and analyses snow, glaciers and ice sheets among other features, said that ice in the Arctic Ocean hit “a new record low” at both the start and end of last month. In an online post, the group said: “January of 2018 began and ended with satellite-era record lows in Arctic sea ice extent, resulting in a new record low for the month. Combined with low ice extent in the Antarctic, global sea ice extent is also at a record low.” It said the Arctic experienced a week of record low daily ice totals at the start of the month, with the January average beating 2017 for a new record low. “Ice grew through the month at near-average rates, and in the middle of the month daily extents were higher than for 2017,” the report went on. “However, by the end of January, extent was again tracking below 2017.”

• Yes, we should. Even if 50% ia an arbitrary number.
• No, we won’t.
• Should We Give Up Half Of The Earth To Wildlife? (O.)
The orangutan is one of our planet’s most distinctive and intelligent creatures. It has been observed using primitive tools, such as the branch of a tree, to hunt food, and is capable of complex social behaviour. Orangutans also played a special role in humanity’s own intellectual history when, in the 19th century, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, co-developers of the theory of natural selection, used observations of them to hone their ideas about evolution. But humanity has not repaid orangutans with kindness. The numbers of these distinctive, red-maned primates are now plummeting thanks to our destruction of their habitats and illegal hunting of the species. Last week, an international study revealed that its population in Borneo, the animal’s last main stronghold, now stands at between 70,000 and 100,000, less than half of what it was in 1995.
“I expected to see a fairly steep decline, but I did not anticipate it would be this large,” said one of the study’s co-authors, Serge Wich of Liverpool John Moores University. For good measure, conservationists say numbers are likely to fall by at least another 45,000 by 2050, thanks to the expansion of palm oil plantations, which are replacing their forest homes. One of Earth’s most spectacular creatures is heading towards oblivion, along with the vaquita dolphin, the Javan rhinoceros, the western lowland gorilla, the Amur leopard and many other species whose numbers are today declining dramatically. All of these are threatened with the fate that has already befallen the Tasmanian tiger, the dodo, the ivory-billed woodpecker and the baiji dolphin – victims of humanity’s urge to kill, exploit and cultivate.
As a result, scientists warn that humanity could soon be left increasingly isolated on a planet bereft of wildlife and inhabited only by ourselves plus domesticated animals and their parasites. This grim scenario will form the background to a key conference – Safeguarding Space for Nature and Securing Our Future – to be held in London on 27-28 February. The aim of the symposium is straightforward: to highlight ways of establishing sufficient reserves and protected areas to halt or seriously limit the major extinction event that humanity now faces. According to one recent report, the number of wild animals on Earth has halved in the past 40 years, as humans kill for food in unsustainable numbers and pollute or destroy habitats, and worse probably lies ahead.
[..] The current focus on protecting what humans are willing to spare for conservation is unscientific, they say. Instead, conservation targets should be determined by what is necessary to protect nature. This point is stressed by Harvey Locke, whose organisation, Nature Needs Half, takes a far bolder approach and campaigns for the preservation of fully 50% of our planet for wildlife by 2050. “That may seem a lot – if you think the world is a just a place for humans to exploit,” Locke told the Observer. “But if you recognise the world as one that we share with wildlife, letting it have half of the Earth does not seem that much.” The idea is supported by E O Wilson, the distinguished Harvard biologist, in his most recent book, Half Earth. “We thrash about, appallingly led, with no particular goal other than economic growth and unfettered consumption,” he writes. “As a result, we’re extinguishing Earth’s biodiversity as though the species of the natural world are no better than weeds and kitchen vermin.”
The solution, he says, is to fill half the planet with conservation zones – though just how this division is to be decided is not made clear in his book. In any case, Hoffman points out, simply setting aside huge chunks of land or marine areas will not, on its own, save the day. “We could earmark the whole of northern Canada as a wildlife reserve but, given the paucity of animals who live in these frozen regions, that would not have a significant effect on a great many species who live elsewhere,” he said.








