M. C. Escher Meeting (Encounter) 1940
It’s no surprise that China has its own plunge protection team -but why were they so late?-, nor that Beijing blames its problems on Trump’s tariffs. GDP growth was disappointing at 6.5%, but who’s ever believed those almost always dead on numbers? It would be way more interesting to know what part of that growth has been based on debt and leverage. But that we don’t get to see.
So we turn elsewhere. How about the Shanghai Composite Index? It may not be a perfect reflection of the Chinese economy, no more than the S&P 500 is for the US, but it does raise some valid and curious questions.
Borrowing from Wolf Richter, here are some stats and a graph::
• Lowest since November 27, 2014, nearly four years ago
• Down 30% from its recent peak on January 24, 2018, (3,559.47)
• Down 52% from its last bubble peak on June 12, 2015 (5,166)
• Down 59% from its all-time bubble peak on October 16, 2007 (6,092)
• And back where it had first been on December 27, 2006, nearly 12 years ago.
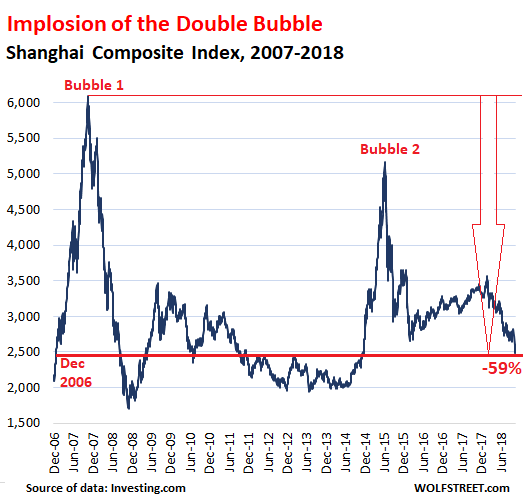
The first thing I thought when I saw that was: how on earth is it possible that in an economy that’s supposedly been growing 6%+ for a decade, stocks have gone nowhere at all? And obviously the role of the Shanghai index is different from that of the S&P, the DAX or the FTSE, but at the alleged Chinese growth rate, the economy would have almost doubled in size in 10 years. And none of that is reflected in stocks?
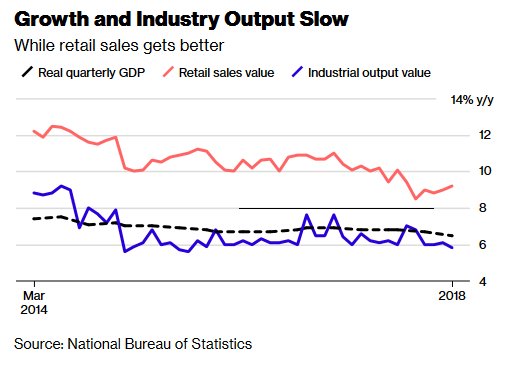
And if you think Shenzhen is a better barometer of ‘real’ China, Tyler Durden had this graph yesterday. Not the same as Shanghai, but similar for sure.
But other aspects of the Chinese economy are perhaps more interesting, I think. China’s mom and pop are not typically in stocks. In the Zero Hedge article I took that graph from, there is also this:
“There’s a liquidity crisis in the stock market, and pledged shares are again starting to sound the alarm,” said Yang Hai, analyst at Kaiyuan Securities. [..] The fear is that if Beijing does nothing, the self-reinforcing liquidation is only set to get worse: with $603 billion of shares pledged as collateral for loans – or 11% of China’s market capitalization, – traders are increasingly concerned that forced sellers will tip the market into a downward spiral.
[..] China in June told brokerages to seek approval before selling large chunks of stock that have been pledged as collateral for loans, while the top financial regulator in August warned the industry that it’s closely watching corporate stock pledges. Neither of those warnings appears to have generated the desired outcome, and the result is that two-thirds of Shenzhen Composite stocks are now at 52-week lows or worse.
[..] what are investors to do in this time of panicked selling? Why demand more bailouts of course, like begging the National Team to step in and rescue them (just like in the housing market): “If there are no real policies to cure the array of problems and ailments in our market, no one will be willing to take the risk,” said Hai. “Authorities keep saying that there is room for more polices, but where are they?”
“It’s high time the state stepped in,” said Dong Baozhen, a fund manager at Beijing Tonglingshengtai Asset Management. “The national funds cannot just sit on the sidelines and watch this atmosphere of extreme pessimism.”
It’s this clamoring for the state to come to the rescue of people who are losing money that would appear to define China today, where there is a stock market and housing market, and many ‘investors’ making lots of money, but where the mentality still seems to lurk back to days of old whenever things don’t only go up in a straight line.
There was another report recently of people demonstrating outside a property developer’s office because the firm had lowered purchase prices by 30%. Those that had paid full price now stood to lose that 30%. This happens frequently, and it can get violent. Mom and pop are not in stocks, they are in real estate:
Property accounts for roughly 70 per cent of urban Chinese families’ total assets – a home is both wealth and status. People don’t want prices to increase too fast, but they don’t want them to fall too quickly either,” said Shao Yu, chief economist at Oriental Securities.
The Chinese are thinking about leaders from Deng Xiao Ping to Xi Jinping that it’s great if they steer the country in a direction where everyone can get rich, but when things go awry, it’s still Beijing’s task to solve the problems if and when they occur. I would expect the same kind of thing in many western countries where people have borrowed heavily into housing bubbles, I don’t see mass foreclosures in Sweden, Denmark, Holland, but bailouts of people who grossly overpaid.
But the Chinese go a step further in their demands from central government. And that is an enormous problem for Xi going forward. One crucial facet of all this is psychological: when people count on being bailed out by their government, they will take much more risk, borrow more, with higher leverage etc. If you allow people things like pledging shares to buy more shares, or homes, and shares fall, you have an issue.
China’s well-known for companies buying each other’s shares to appear viable. It’s also known for local governments borrowing heavily from shadow banks in order for party officials to look as if they’re performing real well.
Now of course, if Beijing keeps on presenting all those growth numbers that look so solid, it’s asking for it. Moreover, the Party has lost control over the shadow banks, and it couldn’t act to regain that control if it wanted. It could initiate a program to forgive debt owed to national banks, but what’s owed to the shadows will have to be paid. We’re talking many trillions.
The Party has let the shadows in, because it made its own debt numbers look so much better. But when this whole debt balloon, on which so much of the GDP growth has rested, and the roads to nowhere and empty apartment blocks and cities, starts to pop, who are the Chinese going to turn to? For that matter, who is Xi going to turn to?
Yes, much of the western wealth has turned into a mirage, but in that respect, too, China has done what we did in a fraction of the time. Trump’s tariffs may play a role in a slowdown, but wait until the western economies deflate their debt bubbles and stop buying much of China’s products.
Bubbles vs balloons, that seems a proper way to phrase this. And for better or for worse, Jerome Powell is hiking interest rates. There’s your Needles and Pins.








