Richardson Hope for a New Life: Man passes baby through fence, Serbia/Hungary border 2015



As QE and ZIRP did before them. This started years ago.
• Negative Interest Rates Set The Stage For The Next Crisis (Stephen Roach)
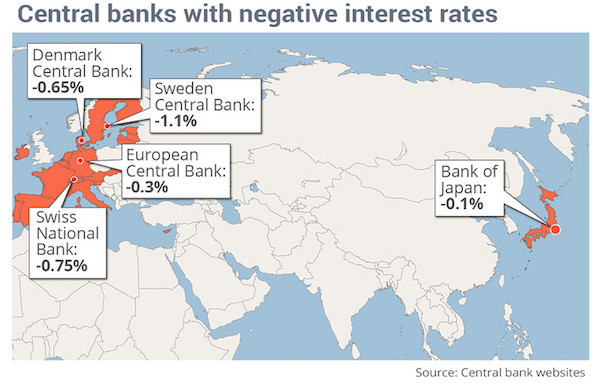
In what could well be a final act of desperation, central banks are abdicating effective control of the economies they have been entrusted to manage. First came zero interest rates, then quantitative easing, and now negative interest rates — one futile attempt begetting another. Just as the first two gambits failed to gain meaningful economic traction in chronically weak recoveries, the shift to negative rates will only compound the risks of financial instability and set the stage for the next crisis. The adoption of negative interest rates — initially launched in Europe in 2014 and now embraced in Japan — represents a major turning point for central banking. Previously, emphasis had been placed on boosting aggregate demand — primarily by lowering the cost of borrowing, but also by spurring wealth effects from appreciating financial assets.
But now, by imposing penalties on excess reserves left on deposit with central banks, negative interest rates drive stimulus through the supply side of the credit equation — in effect, urging banks to make new loans regardless of the demand for such funds. This misses the essence of what is ailing a post-crisis world. As Nomura economist Richard Koo has argued about Japan, the focus should be on the demand side of crisis-battered economies, where growth is impaired by a debt-rejection syndrome that invariably takes hold in the aftermath of a “balance sheet recession.” Such impairment is global in scope. It’s not just Japan, where the purportedly powerful impetus of Abenomics has failed to dislodge a struggling economy from 24 years of 0.8% inflation-adjusted growth in GDP.
It’s also the U.S., where consumer demand — the epicenter of America’s Great Recession — remains stuck in an eight-year quagmire of just 1.5% average real growth. Even worse is the eurozone, where real GDP growth has averaged just 0.1% over the 2008-2015 period. All of this speaks to the impotence of central banks to jump-start aggregate demand in balance-sheet-constrained economies that have fallen into 1930s-style “liquidity traps.” As Paul Krugman noted nearly 20 years ago, Japan exemplifies the modern-day incarnation of this dilemma. When its equity and property bubbles burst in the early 1990s, the keiretsu system — “main banks” and their tightly connected nonbank corporates — imploded under the deadweight of excess leverage.
But the same was true for over-extended, saving-short American consumers — to say nothing of a eurozone that was basically a levered play on overly inflated growth expectations in its peripheral economies — Portugal, Italy, Ireland, Greece, and Spain. In all of these cases, balance-sheet repair pre-empted a resurgence of aggregate demand, and monetary stimulus was largely ineffective in sparking classic cyclical rebounds. This could be the greatest failure of modern central banking. Yet denial runs deep. then-Federal Reserve Chair Alan Greenspan’s “mission accomplished” speech in early 2004 is an important case in point. Greenspan took credit for using super-easy monetary policy to clean up the mess after the dot-com bubble burst in 2000, while insisting that the Fed should feel vindicated for not leaning against the speculative madness of the late 1990s.
Read more …

“When, not if, central banks go completely negative, they will wind up paying banks to borrow money from them. That’s quantitative easing by another name.”
• Why Negative Interest Rates Spell Doom For Capitalism (Romano)
Interest rates in Switzerland, Denmark, Sweden, the European Central Bank and now the Bank Japan have now plunged into negative territory, starting a new phase in the era of central banking that is very much uncharted. Time will tell if it leaves the global economy lost at sea. So far, banks are primarily being charged for keeping excess reserves on account at these central banks, a policy designed to jumpstart lending by making it more expensive for banks to sit on reserves. In some cases, like Sweden, the deposit rates have gone negative, too. Whether it will all work out or not remains to be seen — initiating inflation and economic growth. Maybe it will, but so far it’s not really looking good. So what if it doesn’t work? The longer term implication is that central banks will then feel compelled to move their discount rates and other rates negative, too.
Once that Pandora’s Box is open, it will mean that when financial institutions borrow money from the central bank, they will earn interest instead of owing it. You read that right. When, not if, central banks go completely negative, they will wind up paying banks to borrow money from them. That’s quantitative easing by another name. Say, the interest rate is -1%. For every $1 trillion that is lent, the central bank in theory would owe an additional $10 billion in interest to the borrowing banks. Fast forward 10 or 20 years into the future. Can you imagine a world where commercial banks pay their customers to borrow money? Sure, scoff now. But mark my words. Central banks are so desperate to kick start the economy and credit creation, they will do almost anything. So, if they have to bribe you to borrow money to start acquiring more things, then that’s exactly what they’ll do.
A few problems immediately emerge. If it ends up costing money for banks to lend money, how will they make any profits? The answer might be that the profits will be the difference between the interest earned from that bank borrowing the money from the central bank less the interest owed to the borrowing customer. So, say the bank borrowed from the central bank at -5% and then issued a loan with that money at -1%. The customer still earns 1%age point of negative interest, and the bank still gets to pocket the remaining 4%age points of negative interest from the central bank. But what about savers? Would they be charged just to put money into the bank? If so, why would they keep it there? Since banks depend on deposits to make up their capital requirements, they would have a powerful disincentive against charging customers to keep deposits, lest it provoke a run on the banks. But why invest in bonds? This is where the real rub comes.
Read more …

Chicken and the egg. Central bankers incompetence will drag us all down.
• Central Banking Is In Crisis. Can The World Economy Be Far Behind? (Economist)
A world of helicopter drops is anathema to many: monetary financing is prohibited by the treaties underpinning the euro, for example. Incomes policies are even more problematic, as they reduce flexibility and are hard to reverse. But if the rich world ends up stuck in deflation, the time will come to contemplate extreme action, particularly in the most benighted economies, such as Japan’s. Elsewhere, governments can make use of a less risky tool: fiscal policy. Too many countries with room to borrow more, notably Germany, have held back. Such Swabian frugality is deeply harmful. Borrowing has never been cheaper. Yields on more than $7 trillion of government bonds worldwide are now negative.
Bond markets and ratings agencies will look more kindly on the increase in public debt if there are fresh and productive assets on the other side of the balance-sheet. Above all, such assets should involve infrastructure. The case for locking in long-term funding to finance a multi-year programme to rebuild and improve tatty public roads and buildings has never been more powerful. A fiscal boost would pack more of a punch if it was coupled with structural reforms that work with the grain of the stimulus. European banks’ balance-sheets still need strengthening and, so long as questions swirl about their health, the banks will not lend freely. Write-downs of bad debts are one option, but it might be better to overhaul the rules so that governments can insist that banks either raise capital or have equity forced on them by regulators.
Deregulation is another priority—and no less potent for being familiar. The Council of Economic Advisors says that the share of America’s workforce covered by state-licensing laws has risen to 25%, from 5% in the 1950s. Much of this red tape is unnecessary. Zoning laws are a barrier to new infrastructure. Tax codes remain Byzantine and stuffed with carve-outs that shelter the income of the better-off, who tend to save more. The problem, then, is not that the world has run out of policy options. Politicians have known all along that they can make a difference, but they are weak and too quarrelsome to act. America’s political establishment is riven; Japan’s politicians are too timid to confront lobbies; and the euro area seems institutionally incapable of uniting around new policies.
Read more …

Makes sense, since they have no idea what they’re doing. Then again, since this is a double negative…
• Bank of Japan Baffled by Negative Reaction to Negative-Rate Policy (WSJ)
A clash Thursday between Japan’s central-bank chief and lawmakers highlighted the downside of negative interest rates: They are making the Japanese public feel negative. Bank of Japan Gov. Haruhiko Kuroda, who announced the nation’s first move into minus rates three weeks ago, found himself dodging a concerted attack in Parliament from lawmakers who charged the policy was victimizing consumers and sending a message of despair. Even a ruling-party member, Masahiro Ishida, called the policy hard to grasp. “It could have the opposite effect of confusing the market,” he said. The criticism has come as a surprise to central-bank officials who thought their efforts to spark lending and faster economic growth would gain more public support.
“Those who understand this policy are criticizing us, and those who do not are also criticizing us,” said one official this week. It is a symptom of a global problem. The more central banks move into unconventional policies, the harder it becomes to get their message across. That is a particular problem when the policies are supposed to work in part by inspiring confidence. It also highlights an open question about negative rates: Commercial banks, for the most part, haven’t started charging depositors to hold their cash, despite increasing pressure on margins. But what happens if they do? Under new rules that took effect Tuesday, the Bank of Japan started imposing an interest rate of minus -0.1% on some deposits it holds for commercial banks, meaning the banks have to pay to store their money.
The goal was to bring down interest rates generally, including long-term rates charged for home loans. The move followed years of attempts to defeat deflation and stimulate moribund spending, including by pumping ¥80 trillion ($701 billion) of cash annually into the economy with purchases of government bonds. The immediate impact was muted as global markets swooned and the yen, seen as a haven in times of trouble, rose against the dollar, threatening the profits of Japanese exporters. This week, markets have stabilized, but the central bank is struggling with a different and equally hard-to-control force: public opinion.
Read more …

But if that’s true for all negative rates, who would the yen fall against?
• Nomura Sees Yen Falling More Than 10% on BOJ Negative Rates (BBG)
Nomura is sticking to its forecast for the yen to weaken to 130 per dollar by year-end on the view Japan’s negative interest-rate policy will prompt investors to buy more overseas assets and U.S. borrowing costs will rise. Japan’s biggest brokerage has maintained the projection since December 2014, when the yen completed a six-month slide to 119.78 after the central bank boosted its debt purchases to a record. The yen has rallied 5.5% this year against the dollar, about 14% stronger than Nomura’s target, as a flight to haven assets from tumbling global stocks burnished the currency’s allure. “There is nothing convincing yet to alter the outlook,” said Yunosuke Ikeda at Nomura Securities in Tokyo. “The most important check points for now are a set of U.S. data in early March. If we can confirm recession risks are low, the 130-yen forecast can be maintained.”
The yen’s recent strength was partly driven by the dollar’s weakness as concerns over a slowdown in China and the health of banks in Europe caused traders to pare bets that the Federal Reserve will raise rates again this year after moving in December. There’s a 41% probability the Fed will boost rates by the end of December, according to futures data compiled by Bloomberg. The odds were more than 90% at the end of last year. The yen’s advance is being driven by “low conviction” risk aversion, according to Nomura’s Ikeda, a trend that may lose momentum should the U.S. show signs of strength when economic figures are released next month. “The worst case scenario is the low-conviction risk off will become high-conviction should the U.S. economy become decisively bad,” he said. “ For this, ISM manufacturing and non-manufacturing as well as jobs data due in early March are very significant.”
Read more …

I’ve suggested seppuku before.
• Abenomics? How About Kurodanomics? (BBG)
Despite all Prime Minister Shinzo Abe has done, Japan’s economy contracted an annualized 1.4% in the final three months of 2015, the government announced on Feb. 15. Consumer prices rose just 0.2% year to year, perilously close to deflation. Japanese consumers, hurt by tepid growth in wages and bonuses and a 3%age point rise in the consumption tax in 2014, are holding on to their wallets, with private consumption dropping 0.8% in the quarter. The yen has gained 5.6% against the dollar since the start of the year, eroding profits for exporters such as Toyota Motor and Panasonic. These companies have benefited from the yen’s weakness since the prime minister came to office in late 2012 and began the policy changes known as Abenomics.
“There’s no clear driver to support Japan’s economy,” says Yuichi Kodama at Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance in Tokyo. Yet on the same day the government announced the economy’s contraction, the benchmark Nikkei stock index rose more than 7%. Investors hope that the weak data could spur Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda, who pushed through a negative interest rate last month, to move even deeper into negative territory, or purchase even more bonds. They also hope Abe will postpone another hike in the consumption tax. Handpicked by Abe in 2013, Kuroda has aggressively implemented the monetary policy envisioned by Abenomics. He has championed a quantitative easing program of bond and other asset purchases by the central bank that has left the BOJ with a balance sheet about three-quarters the size of Japan’s $4.6 trillion economy.
Kuroda’s bold and unconventional moves helped drive down the yen, contributing to an increase in corporate earnings and stock prices. In January, the Bank of Japan started charging 0.1% on part of the cash deposited at the central bank by big financial institutions. The idea is to encourage banks to lend instead of watching their cash lose value. “Kuroda is doing everything he can,” says Marcel Thieliant, Japan economist for Capital Economics. Abe’s program has what he calls three “arrows”: an easy-money policy, fiscal stimulus, and structural reforms. Although the BOJ has done its part in terms of interest rates and bond purchases, Abenomics has been a disappointment in the other two areas. The government has moved slowly on reforms of labor laws and other regulations.
As for fiscal stimulus, Abe has increased spending, but also raised the consumption tax to 8%. He wants to raise it to 10%. “Abe and the government have no choice but to depend on Bank of Japan policy,” says Kazuhiko Ogata at Crédit Agricole. But with the BOJ rate negative, Kuroda has little room to maneuver. GDP growth for the fiscal year ending in March will be just 0.8%, according to Bloomberg Intelligence, lower than the central bank’s target of 1.1%. Confidence in Abenomics is falling. In a Yomiuri poll published on Feb. 16, approval of Abe’s economic policies fell to a record low of 39%.
Read more …

Can we talk about timing here, OECD?
• OECD Calls for Urgent Increase in Government Spending (WSJ)
Governments in the U.S., Europe and elsewhere should take “urgent” and “collective” steps to raise their investment spending and deliver a fresh boost to flagging economic growth, the Organization for Economic Growth and Development said on Thursday. In its most forceful call to action since the financial crisis, the OECD said the global economy is suffering from a weakness of demand that can’t be remedied through stimulus from central banks alone. Releasing its first economic forecasts of 2016, it urged governments that can borrow at very low interest rates to boost their spending on infrastructure. The OECD said that if governments work together, fresh borrowing could have such a positive impact on growth that it would reduce rather than increase their debts relative to economic output.
Speaking to The Wall Street Journal, OECD Chief Economist Catherine Mann said that without such action, governments will be unable to honor their pledges to deliver a “better life” for young people, adequate pensions and health care for old people, and the returns anticipated by investors. “The economic performance generated by today’s set of policies is insufficient to make good on these commitments,” said Ms. Mann, who has worked at the U.S. Federal Reserve and the Council of Economic Advisers. “Those commitments will not be met unless there is a change in policy stance.” The Paris-based think tank lowered its forecasts for global growth this year and next. It now expects the U.S. economy to grow by 2.0% in 2016 and 2.2% in 2017, having in November projected expansions of 2.5% and 2.4%, respectively.
The OECD lowered its eurozone growth forecasts to 1.4% and 1.7% from 1.8% and 1.9%, and nudged down its Japanese growth forecast for this year to 0.8% from 1.0%. It left its growth forecasts for China unchanged. Overall, it expects the global economy to grow by 3% this year, the same rate of expansion as in 2015 but slower than the 3.3% it anticipated in November. “The downgrade in forecasts is broadly based, reflecting a wide range of disappointing incoming data for the fourth quarter of 2015 and the recent weakness and volatility in global financial markets,” the OECD said. “These trends have been apparent in both advanced and emerging economies.” Last month, the IMF cut its global growth forecast for this year, but still expected a pickup from 2015.
Ms. Mann said the sharp and varying falls in prices of assets and commodities since the start of the year largely reflect a delayed response to weaker growth prospects around the world, and not just in China. “We should have had a decline starting a year ago,” she said. “We can see in those different rates of decline both investor views of prospects, but some over shooting.” The OECD said that budget policy in a number of major economies -including Japan, the U.K. and the U.S.- is “contractionary,” while some developing economies had also made recent budget decisions that will slow growth. It urged governments to reverse course.
“Governments in many countries are currently able to borrow for long periods at very low interest rates, increasing fiscal space,” the OECD said. “Many countries have room for fiscal expansion to strengthen demand. This should focus on policies with strong short-run benefits and that also contribute to long-term growth. A commitment to raising public investment collectively would boost demand while remaining on a fiscally sustainable path.”
Read more …

Seems obvious.
• China Bears Say the Capital Outflow Is Just Beginning (BBG)
Yuan bears say this month’s rally shouldn’t be taken as a sign China’s great reversal in capital flows has finished. Goldman Sachs warns that any further shock depreciation will only accelerate the exit. Daiwa Capital Markets, which predicted the outflow risks back in 2014, says less than half of the $3 trillion of dollar debt that ended up in China has been repaid. Commerzbank said record new yuan loans in January showed companies are raising money to repay more debt abroad. Corporate bond sales onshore have more than doubled this year, as offshore issuance in the greenback dropped about 30%. Goldman Sachs says there have been $550 billion of outflows in the second half of 2015, and that every 1% yuan weakening risks $100 billion more.
The yuan’s appreciation in the four years through 2013 prompted companies to borrow dollars offshore and use the money to profit from a strong currency and higher interest rates in China. The one-way bets began to fade in 2014 as the exchange rate to the dollar plunged the most since 1994. This month’s 0.9% rally hasn’t dissuaded analysts from forecasting a further 3.4% drop by year-end. “We’re less than halfway done” in terms of carry trade unwinding, said Kevin Lai at Daiwa. “My main focus is not about unwinding, but the reverse carry trade. People are taking fresh positions to sell the yuan. We’re talking about a massive deflationary scenario now, which is very bad for the market, economy, for everything.” Daiwa’s estimate for the carry trade is on the high side because it includes borrowing by companies outside China, such as Hong Kong and Taiwan.
Oversea-Chinese Banking economist Tommy Xie estimates the positions at around $1 trillion, based on data from the Bank of International Settlements and the Hong Kong Monetary Authority. Chinese companies’ total foreign-currency debt dropped by about $140 billion in the second half of 2015 to $1.69 trillion, including corporate borrowing from onshore banks, Goldman estimates. That was dwarfed by the $370 billion outflows by Chinese residents buying foreign currencies, it said. “A risk is that any further shocks to renminbi confidence and the perception of policy uncertainty could sharply compound the outflow pressure and render any subsequent stabilization attempts much less effective,” Goldman wrote in a note released to media on Jan. 26.
Read more …

Much worse now: “As of 2014, according to an estimate by the McKinsey Global Institute, total debt in China stood at 282% of GDP.”
• Red Ink In China (Economist)
This week began with the release of a staggering number. In January, new debt issued in China rose to just over $500 billion, an all-time high. Not all of the “new” debt was actually new; some represented a move out of foreign-currency loans and into local-currency borrowing (in order to reduce foreign-currency risk). But the flow of red ink is not a mirage. China’s government opened the credit taps early in 2016 in order to reduce the odds of a sharp economic slowdown. Private borrowing in China has grown rapidly and steadily since 2008, even as nominal output growth has slowed. As of 2014, according to an estimate by the McKinsey Global Institute, total debt in China stood at 282% of GDP. China is rapidly becoming one of the most indebted countries in the world.
So what? There is a cottage industry of analysts out there gaming out the ways in which a crisis of some sort might unfold within China. But with debts of this magnitude accumulating, you don’t need to posit a looming crisis to draw some reasonably strong, and reasonably gloomy conclusions about the near-term future of the Chinese economy—and the world as a whole. At some point, Chinese corporates will need to deleverage. It is hard to say precisely when or why, but a deleveraging at some point is inevitable. The result of that deleveraging, when it occurs, will be a big drag on demand growth within China. That, in turn, will translate into much slower GDP growth, unless some other source of demand can be found. China could try to boost demand by encouraging more spending and investment by non-corporates.
This probably wouldn’t work especially well, if the history of other economies in such circumstances is any guide. Households have also been adding debt at a good clip. To get them to borrow at an even faster pace, especially at a time when (presumably, given the corporate deleveraging) animal spirits are not at their most spirited, the Chinese government would basically have to force new loans down households’ throats. Certainly, we could expect China to hit the zero lower bound on interest rates and to begin QE. Zero rates and QE would place significant downward pressure on the value of the yuan. That’s just as well, since another thing history tells us is that demand-deficient, deleveraging economies depreciate their currencies and rely on exernal demand to support growth.
Of course, most countries in the situation we’re imagining here aren’t already running big trade surpluses. It is possible, given the importance to China of supply-chain trade, that even a big depreciation wouldn’t boost demand in the economy very much, since it would make imported components more expensive even as it made exports cheaper. If those arguments are right, they suggest that a Chinese adjustment would require either a really big depreciation, or would be slower and more painful, or a bit of both. Conventional wisdom has it, however, that China does not want to depreciate the currency. Depreciation might not boost net exports by much, but it would make dollar-denominated loans more expensive (increasing the pressure on some of those deleveraging corporates), it would squeeze Chinese consumers, and it would represent a big loss of face for the government.
Read more …

Delusional: “The government aims to urbanize 100 million lower-income people within five years to expand a middle class that can afford movies and medicine, and sustain China’s upward trajectory.”
• Overproduction Swamps Smaller Chinese Cities, Revealing Depth of Crisis (WSJ)
Even in China’s remotest places, relentless overproduction—here it is mushrooms and cement trucks—is clouding the country’s path to prosperity and jolting the global economy. When 48-year-old farmer Yang Qun began trading at Suizhou’s bustling morning mushroom market a half decade ago, the fungus industry was expanding, even attracting a rural lending arm of British financial giant HSBC. Ms. Yang saved enough to buy a minivan. When wet snow fell last month, she was settling for closeout prices to unload six bags of dried mushrooms that took a half year to cultivate. For Xu Song, a clanging sound was once a welcome reminder that his 200 colleagues were busy pounding steel into the giant barrels used on cement trucks.
On a recent day, he sat alone watching videos in an unheated office, the only worker left on an abandoned factory floor where dozens of rusting barrels were stacked like multi-ton footballs. “The decline was steep,” says Mr. Xu, standing inside the all-but-defunct Hubei Aoma Special Automobile Co. factory, where he was hired to do quality control. “I don’t know what had really happened to us.” Beyond the glut of steel and apartments that weighed down growth in recent years, China’s economy is also saturated with surplus goods from farms and factories. Numerous small and midsize cities such as Suizhou, which boomed on easy credit and government support for agribusiness and construction, were supposed to provide the second wave in China’s growth story. Instead they are now sputtering, wearing down prices, profits and job opportunities.
The struggles in Suizhou show how China’s slowdown is broad and deep and hard to fix. It has fueled volatile market trading around the world and has contributed to anxiety about potentially stalled U.S. growth. Domestic overproduction means China is now spending less overseas, while businesses that sell to China are bracing for possible protectionist moves aimed at propping up local companies. And with Chinese demand at risk, its industrial giants with idle capacity are looking to capture market share abroad, including construction and railway equipment makers. The government has made a priority of eliminating “zombie companies,” kept alive with loans to produce unneeded goods, to clear the path for more vibrant parts of the economy. The squeeze won’t be easy because in small, remote places such as Suizhou, overbuilt industries are often the economic backbone.
[..] China’s future is dependent on spreading opportunity more widely. While Shanghai and other gleaming metropolises on the coast powered the first decades of market liberalization, Beijing is now counting on smaller cities for the next phase. The government aims to urbanize 100 million lower-income people within five years to expand a middle class that can afford movies and medicine, and sustain China’s upward trajectory.
Read more …

How many times have we said this?!
• You Cannot Print Your Way to Prosperity (Ron Paul)
Last week US stock markets tumbled yet again, leaving the Dow Jones index down almost 1500 points for the year. In fact, most major world markets are in negative territory this year. There are many Wall Street cheerleaders who are trying to say that this is just a technical correction, that the bottom is near, and that everything will be getting better soon. They are ignoring the real message the markets are trying to send: you cannot print your way to prosperity. People throughout history have always sought to acquire wealth. Most of them understand that it takes hard work, sacrifice, savings, and investment. But many are always looking for that “get rich quick” scheme. Monetary cranks throughout history have thought that just printing more money would result in greater wealth and prosperity. Every time this was tried it resulted in failure.
Huge economic booms would be followed by even larger busts. But no matter how many times the cranks were debunked both in theory and practice, the same failed ideas kept coming back. The intellectual descendants of those monetary cranks are now leading the world’s central banks, which is why the last decade has seen an explosion of money creation. And what do the central bankers have to show for it? Lackluster employment numbers that have not kept up with population growth, increasing economic inequality, a rising cost of living, and constant fear and uncertainty about what the future holds. The past decade has been a lot like the 1920s, when prices wanted to drop but the Federal Reserve kept the price level steady through injections of easy money into the economy. The result in the 1920s was the Great Depression.
But in the 1920s prices were dropping because of increased production. More goods being produced meant lower prices, which the Fed then tried to prop up by printing money. Unlike the “Roaring 20s” however, the economy isn’t quite as strong today. It’s more of a gasp than a roar. Production today is barely above 2007 levels, while heavily-indebted households already hurt during the financial crisis don’t want to keep spending. The bad debts and mal-investments from the last Federal Reserve-induced boom were never liquidated, they were merely papered over with more easy money. The underlying economic fundamentals remain weak but the monetary cranks who run the Fed keep trying to pump more and more money into the system. They fail to realize that easy money is the cause, not the cure, of recessions and depressions. [..] The more money the Federal Reserve creates, the more ordinary Americans will end up suffering.
Read more …

What happens when you make it all up.
• The Real Economy Is Talking, but Treasuries Aren’t Listening (BBG)
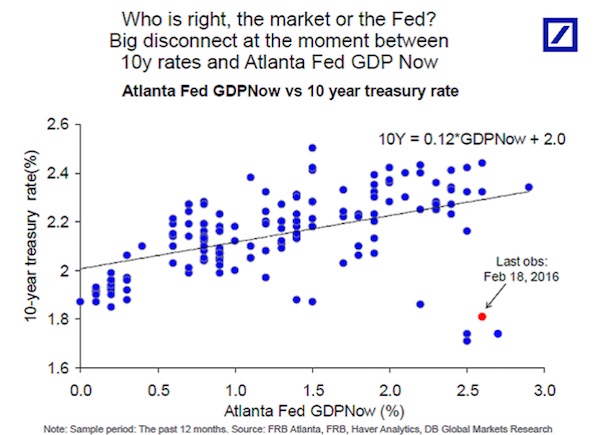
There’s a massive divergence between recent economic data and U.S. Treasury yields. Amid widespread risk aversion, the yield on 10-year debt fell below 1.60% this month before recovering to back over 1.75% on Thursday. According to Deutsche Bank Chief International Economist Torsten Sløk, that’s still far too low. The Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow indicator provides an estimate for quarterly economic growth based on recently released economic data, which currently stands at 2.6% for the first quarter: “Using the historical relationship between the Atlanta Fed GDP Now estimate and 10y rates shows that 10y rates today should not be 1.82% but instead 2.3%,” he wrote. “Put differently, markets are currently pricing a deep recession, but that is simply not what the data is showing.”
Some caveats apply: The sample size depicted here is quite small, so there’s no guarantee the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow will prove accurate, and the composition of growth, not merely the headline rate, is important in assessing economic health. Additionally, while it makes intuitive sense for there to be a relationship between yields on sovereign debt, it’s worth remembering what goes into a bond yield: expectations regarding short-term interest rates, market-based measures of inflation compensation, and the term premium (what investors demand for taking on more duration). At present, market-implied expectations for the federal funds rate and inflation are quite low. Term premiums are also suppressed, due in part to strong demand for U.S. assets that are perceived as a safe haven, particularly in times of market turmoil. Those assets also provide a yield that’s more attractive than most other advanced economies.
Read more …

How the Anglo model of ownership obsession ritually murders itself.
• Number Of UK Homes Worth More Than £1 Million Set To ‘Triple By 2030’ (G.)
The number of properties in Britain worth £1m or more is set to more than triple by 2030, widening the gap between the housing haves and have-nots, according to a report. Less than half a million homes in the UK are currently valued at £1m-plus, but a study by high street lender Santander claims this number will rise to more than 1.6m in the next 15 years. The report also warns that affordability will worsen considerably by the end of the next decade as house price rises far outstrip growth in household incomes. The average property price amounts to 7.9 times the average income at present, but by 2030 this is expected to hit a multiple of 9.7. Santander said: “By 2030 the UK will be even more starkly divided into the housing wealthy and the housing poor than it is now.”
There is a stark geographical divide among the projected members of the £1m club, according to Santander. One in four homes in London will cost £1m-plus by 2030, rising to 70% in two boroughs in the capital – Kensington and Chelsea and the City of Westminster. More than half of homes in three more London boroughs – Camden, the City of London and Hammersmith and Fulham – will also be worth more than £1m. Across the south-east, 7% of homes are expected to be valued at that level. However, many areas of the UK – the north-east, north-west, Yorkshire and Humber, Scotland and the East Midlands – are expected to host a negligible number of such expensive houses (less than 1%). One area, Torfaen in Wales, home to more than 90,000 people, will have none.
The report, carried out in partnership with Paul Cheshire, professor of economic geography at the London School of Economics, predicts that prices in London, which are currently 11.5 times average incomes, will soar to a multiple of 16.5 by 2030. Cheshire said: “By 2030, the divide between housing haves at the top and the have-nots at the bottom will be even wider than it is now. More owners will enjoy millionaire status, as homes that many would consider modest fetch seven figure prices in sought-after areas. “It will make entering the market more difficult still for new buyers, further highlighting the importance of the right timing, advice, support and financial planning; and not just having a mum and dad who bought a house, but a grandparent, too.”
Read more …

Make that the entire western world; pensions are Ponzi’s: “What’s happening to us is a microcosm of what’s going to happen to the rest of the pensions in the United States..”
• 400,000 Americans In Jeopardy As Giant Pension Fund Plans 50% Benefit Cuts (ZH)
Dale Dorsey isn’t happy. After working 33 years, he’s facing a 55% cut to his pension benefits, a blow which he says will “cripple” his family and imperil the livelihood of his two children, one of whom is in the fourth grade and one of whom is just entering high school. Dorsey attended a town hall meeting in Kansas City on Tuesday where retirees turned out for a discussion on “massive” pension cuts proposed by the Central States Pension Fund, which covers 400,000 participants, and which will almost certainly go broke within the next decade. “A controversial 2014 law allowed the pension to propose [deep] cuts, many of them by half or more, as a way to perhaps save the fund,” The Kansas City Star wrote earlier this week adding that “two much smaller pensions also have sought similar relief under the law, and still more pensions are significantly underfunded.”
“What’s happening to us is a microcosm of what’s going to happen to the rest of the pensions in the United States,” said Jay Perry, a longtime Teamsters member. Jay is probably correct. Public sector pension funds are grossly underfunded in places like Chicago and Houston, while private sector funds are struggling to deal with rock bottom interest rates, which put pressure on expected returns and thus drive the present value of funds’ liabilities higher. Illinois’ pension burden has brought the state to its knees financially speaking and in November, Springfield was forced to miss a $560 million payment to its retirement fund. In the private sector, GM said on Thursday that it will sell 20- and 30-year bonds in order to meet its pension obligations.
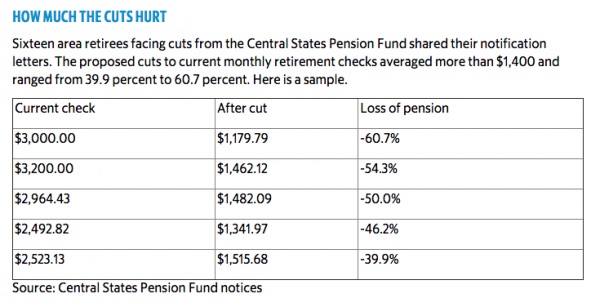
“At the end of last year GM’s U.S. hourly pension plan was underfunded by $10.4 billion,” The New York Times writes. “About $61 billion of the obligations were funded for the plan’s roughly 360,000 pensioners.” Maybe it’s time for tax payers to bail themselves out. Speaking of GM, Kenneth Feinberg – the man who oversaw the distribution of cash compensation to victims who were involved in accidents tied to faulty ignition switches – is now tasked with deciding whether the Central States Pension Fund’s proposal to cut benefits passes legal muster. “Central States’ proposal would allow the retirees to work and still collect their reduced benefits. But some are no longer able to work, and the idea didn’t seem plausible to others,” the Star goes on to note.
“You know anybody hiring a 73-year-old mechanic?” Rod Heelan asked Feinberg. “I’m available.” “I’ll have to go find a job. I don’t know. I’m 68,” Gary Meyer of Concordia, Mo said. “It would probably be a minimum-wage job.” To be sure, retirees’ frustrations are justified. That said, the fund is simply running out of money. “We simply can’t stay afloat if we continue to pay out $3.46 in pension benefits for every $1 paid in from contributing employers,” a letter to retirees reads. The fund is projected to go broke by 2026. Without the proposed cuts, no benefits at all will be paid from that point forward.
Read more …

Not even the WSJ is fooled.
• The Political War on Cash (WSJ)
These are strange monetary times, with negative interest rates and central bankers deemed to be masters of the universe. So maybe we shouldn’t be surprised that politicians and central bankers are now waging a war on cash. That’s right, policy makers in Europe and the U.S. want to make it harder for the hoi polloi to hold actual currency. Mario Draghi fired the latest salvo on Monday when he said the ECB would like to ban €500 notes. A day later Harvard economist and Democratic Party favorite Larry Summers declared that it’s time to kill the $100 bill, which would mean goodbye to Ben Franklin. Alexander Hamilton may soon—and shamefully—be replaced on the $10 bill, but at least the 10-spots would exist for a while longer. Ol’ Ben would be banished from the currency the way dead white males like him are banned from the history books.
Limits on cash transactions have been spreading in Europe since the 2008 financial panic, ostensibly to crack down on crime and tax avoidance. Italy has made it illegal to pay cash for anything worth more than €1,000, while France cut its limit to €1,000 from €3,000 last year. British merchants accepting more than €15,000 in cash per transaction must first register with the tax authorities. Fines for violators can run into the thousands of euros. Germany’s Deputy Finance Minister Michael Meister recently proposed a €5,000 cap on cash transactions. Deutsche Bank CEO John Cryan predicted last month that cash won’t survive another decade. The enemies of cash claim that only crooks and cranks need large-denomination bills. They want large transactions to be made electronically so government can follow them.
Yet these are some of the same European politicians who blew a gasket when they learned that U.S. counterterrorist officials were monitoring money through the Swift global system. Criminals will find a way, large bills or not. The real reason the war on cash is gearing up now is political: Politicians and central bankers fear that holders of currency could undermine their brave new monetary world of negative interest rates. Japan and Europe are already deep into negative territory, and U.S. Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen said last week the U.S. should be prepared for the possibility. Translation: That’s where the Fed is going in the next recession. Negative rates are a tax on deposits with banks, with the goal of prodding depositors to remove their cash and spend it to increase economic demand. But that goal will be undermined if citizens hoard cash. And hoarding cash is easier if you can take your deposits out in large-denomination bills you can stick in a safe. It’s harder to keep cash if you can only hold small bills.
So, presto, ban cash.
Read more …

First Austria, now Switzerland. 5000 francs is well over $5000.
• Swiss MPs Want New 5,000-Franc Banknotes To ‘Save Privacy And Freedom’ (L.)
Two MPs from the canton of Zug’s parliament are calling on the Swiss federal government to create 5,000-franc banknotes to “save the privacy and freedom” of citizens. Philip Brunner and Manuel Brandberg, members of the right-wing Swiss People’s Party, have proposed a motion that they hope Zug will support for a cantonal initiative seeking changes to the federal currency law. They argue that the creation of 5,000-franc notes will ensure that the Swiss franc maintains its status as a safe haven currency. The move goes in the opposite direction of in the European Union, where finance ministers have talked about withdrawing 500-euro bills from circulation to deter their use for financing terrorism, money laundering and other illegal activities.
But Brunner and Brandberg maintain that the tendency in the EU and in OECD member countries is to “weaken individual liberties” and to exercise greater control over citizens. In this context “cash is comparable to the service firearm kept by Swiss citizen soldiers,” the pair argued in their motion, saying they both “guarantee freedom”. “In France and Italy already cash payments of only up to 1,000 euros are allowed and the question of the abolition of cash is being seriously discussed and considered in Europe, “ Brunner said on his Facebook page. The move toward electronic payments allows governments “total surveillance” over individuals, the pair claim. Switzerland already has a 1,000-franc note (worth around $1,008), which is the most valuable banknote in Europe and second in the world only to the Singapore $10,000 note among currencies in general circulation.
Read more …

“You can’t have these conversations when oil is $125 because then you can’t get it out of the ground quickly enough. And you can’t have it at $27 because you’re just trying to survive.”
Hmmm. Looks to me like it’s at $27 that you can’t get it out of the ground quickly enough.
• The Stressed-Out Oil Industry Faces an Existential Crisis (BBG)
The Saudis may go public, OPEC’s in disarray, the U.S. is suddenly a global exporter, and shale drillers are seeking lifelines from investors as banks abandon them. Welcome to oil’s new world order, full of stresses, strains and fractures. For leaders gathering in Houston next week at the IHS CERAWeek conference – often dubbed the Davos of the energy industry – a key question is: what will break first? Will it be the balance sheets of big U.S. shale companies? The treasuries of Venezuela and Nigeria? The resolve of Saudi Arabia, whose recent deal with Russia to freeze output levels offered the first hint of a rethink? After watching prices crash through floor after floor in the worst slump for a generation, the industry is eager for answers.
Insiders say it’s not too hard to visualize what markets might look like after the storm – say five years down the line, when today’s cost-cutting creates a supply vacuum that will push up prices. But it’s what happens in the meantime that’s got them scratching their heads. “This is a weird thing for a market analyst to say because it’s usually the opposite case, but I have more conviction in my five-year outlook than my one-year outlook,” said Mike Wittner at Societe Generale. “Maybe I’m letting my head get turned upside down by the last couple months.” Seeking clarity at closed-door sessions, cocktail hours and water-coolers in Houston will be some of the industry’s biggest players, from Saudi Petroleum Minister Ali al-Naimi to Shell CEO Ben Van Beurden.
In a less volatile year, the long-term viability of fossil fuels might have been high on their agenda after December’s breakthrough climate deal in Paris. But within the industry, that debate has “fallen into the abyss of $27 oil,” said Deborah Gordon, director of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace’s energy and climate program. “It seems like it’s never a good time,” she said. “You can’t have these conversations when oil is $125 because then you can’t get it out of the ground quickly enough. And you can’t have it at $27 because you’re just trying to survive.”
Read more …

Keep watching below.
• Oil Gives Up Gains as Inventories Build (WSJ)
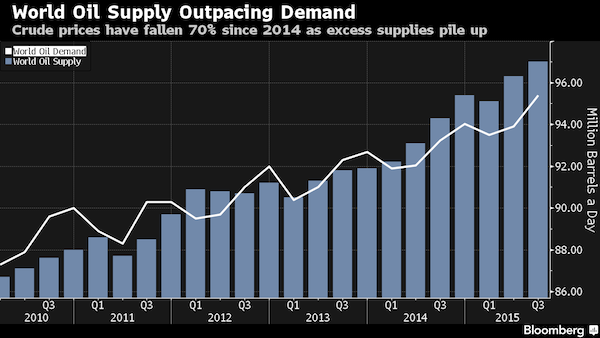
U.S. oil prices eked out a gain Thursday as the U.S. government’s weekly oil-inventory report showed another increase in stockpiles of crude oil. U.S. crude inventories rose by 2.1 million barrels last week to 504.1 million barrels, a new weekly record high, the Energy Information Administration said. In monthly data, which don’t line up exactly with weekly data, inventories last exceeded 500 million barrels in 1930. Light, sweet crude for March delivery settled 0.4%, at $30.77 a barrel on the New York Mercantile Exchange. Brent, the global benchmark, slipped 0.6% to $34.28 a barrel on ICE Futures Europe. Both benchmarks had been up about 3% ahead of the government data, which was delayed one day due to the Presidents Day holiday. Oil prices are down more than 70% since a peak in June 2014, driven lower by a mismatch between ample supplies and tepid demand for crude around the globe.
“U.S. and global inventories are nearing maximums, and global production is showing little sign of slowing,” said Rob Haworth at U.S. Bank Wealth Management in a note. Price moves have been especially volatile in recent weeks amid uncertainty about the pace of global demand growth. The U.S. oil benchmark settled up or down by 1% or more for 23 straight sessions until Thursday, the longest such streak since 2009. U.S. crude stockpiles have climbed since the start of the year as production continued to outpace demand. Inventories fell in the week ended Feb. 5 as imports declined, but imports rose again last week, the EIA data show. ”It’s back to business as usual,” said Bob Yawger at Mizuho. He predicted that prices “will eventually cave under the weight of these storage numbers.”
Read more …

Better come clean before you’re forced to?!
• Anglo American Cut to Junk for Third Time This Week (BBG)
Anglo American’s credit rating was cut to junk by Standard & Poor’s, following similar downgrades by Moody’s Investors Service and Fitch Ratings this week, amid questions about the miner’s ability to sell assets. The company’s rating was reduced to BB from BBB- with a stable outlook, S&P said in a statement Thursday. Moody’s cut Anglo to Ba3, and Fitch lowered the rating to BB+ earlier in the week. The shares slid 4.6% as of 2:25 p.m. in London. Anglo, which became the first major London-based miner to be rated junk, has said it’s looking to speed up sales of coal and iron ore assets after losses bled into a fourth year. It’s trying to engineer a turnaround by focusing on its best mines that produce diamonds, platinum and copper. The company wants to raise $4 billion from mine sales and cut net debt to less than $10 billion this year.
Anglo said on Thursday it will start a tender for a maximum of $1.3 billion of bonds to reduce debt and interest costs. It may purchase $1 billion of notes maturing in 2016, 2017 and 2018 in euros and pounds as well as a maximum of $300 million in dollar-denominated securities, according to company statements.= On Tuesday, Anglo added mines including coal in Australia and nickel in Brazil to an already long list of assets for sale as it seeks to scale back its $12.9 billion debt. CEO Mark Cutifani expects to sell 10 assets by the first half of 2016 and because there are so many up for sale, Anglo wouldn’t be forced to accept any offer, he said.
“Although the program should enable Anglo to lower its debt levels, the depressed market means that we view the proceeds and timeline as very uncertain,” S&P said in the statement. “Because other companies are also seeking to divest assets at this time, we remain very cautious about the timing of any sales and the level of proceeds they will generate.” Goldman Sachs said Tuesday that the miner’s plan to sell off assets was “ambitious” in such a tough environment. Bank of America questioned whether the market trusted the management team to execute sales, while Citigroup said the process was coming too late.
Read more …

Translation: Dump ’em all in Greece. And then dump Greece itself.
• Wary On Turkey, EU Prepares For Refugee Crisis In Greece (Reuters)
The European Union hopes Turkey will prevent as many migrants reaching Greece as last year but is readying “contingency” plans to shelter large numbers who may arrive but can no longer trek north toward Germany. Migration Commissioner Dimitris Avramopoulos told Reuters on Thursday that it was unclear how far Turkey could reduce numbers once the weather improves and, with efforts under way to prevent a repeat of last summer’s chaotic treks through the Balkans, the EU was working with Athens to shelter refugees in Greece. “As long as our cooperation agreement we made with Turkey doesn’t start giving results, the situation will not be easy at all. The flows will continue,” said Avramopoulos. “That is why we have already started working on contingency planning.”
“If this happens, we are going to be confronted with a huge humanitarian crisis and this has to be avoided.” When more than 800,000 people, many Syrian refugees, arrived in Greece last year, most moved north through the Balkans to Germany. Berlin does not want a repeat, leaving states to the south along the route tightening borders and raising a prospect that a large proportion of new arrivals may be halted in Greece. Assessing how far Turkey will help reduce the flow in return for cash and closer ties with the EU is difficult. Avramopoulos noted that arrivals had dropped sharply in the past week or so, despite good sailing weather, but spiked again on Wednesday.
Read more …