Dorothea Lange Country filling station, Granville County, NC 1939

Excellent overview of debt-related issues. Steve’s Debt Jubilee warrants serious discussion at high levels. But it’s not happening.
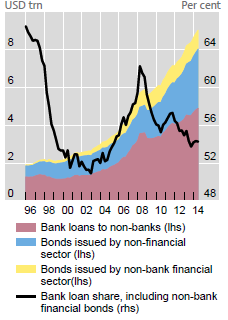
• Debt Nation: The Problem, the Solutions (Valentin Schmid)
There are only two ways to wipe out debt if it cannot be repaid by increases in output. The worst for the economy, even though it may be the fairest, is bankruptcy and debt deflation or destruction. A company or an individual—and sometimes a government—just says it can’t repay its debt. The lender takes control of the assets, if there are any, and tries to recover as much of the loan as possible, making up for the shortfall with its capital provision. This is exactly what happened during the Great Depression, when companies and individuals defaulted in droves, driving thousands of banks into bankruptcy as well. “If you borrowed money to buy a house or a machine, you couldn’t repay the debt, no matter how productive you were. Deflation penalized producers who misjudged the value of their assets at the time,” said Oliver.
Private debt declined 20% from 1930 to 1933 but GDP declined 38%, so the debt-to-GDP ratio actually increased from 175 to 225%, according to data from Debt Economics. “Deflation can increase the level of private debt to GDP, because GDP falls faster than private debt. Paying down the debt, withdrawing money from circulation and reducing its velocity, reduces GDP more than the decline in the debt,” said Keen. So this exercise is best avoided, which is precisely what central banks did during the 2008 crisis with their QE programs and bank bailouts. They managed to avoid a second Great Depression, but they didn’t get rid of the private debt. Despite the evident flaws in a system that has provided incentives for borrowers and lenders to indulge in too much debt for their own good, there are creative ways to reset the system and at least get the economy growing again.
“Every debt collapse in history has had a combination of debt forgiveness and inflation. That is how debt problems are dealt with historically,” said Oliver. Western central banks have tried to create inflation through their QE programs but weren’t successful because of deflationary pressures: overcapacity in China, technological innovation, and the fact that their money printing ended up in the hands of financial actors, who bought a lot of stocks, rather than real people, who would repay debt and buy goods and services. Many economists, including Keen, therefore call for QE for the private sector, rather than the banks, a concept dubbed “helicopter money.” “The creative way to get around it, is use the government’s capacity to create money. You use the same power the central banks did with QE but pay it into private sector accounts rather than commercial bank accounts. Households and companies can use it to pay down debt and those who don’t have debt, can get a cash injection,” he said.


“..America’s putative economic strength might be a mirage [..] the economy may in fact be a lot weaker than all the happy indicators are leading people to believe.”
• American Credit Card Debt Nears All Time Highs (BI)
By most accounts, the American economy seems to be humming along very nicely. Unemployment just hit a nine-year low, the stock market this month climbed to all-time highs, and consumer confidence is as chipper as its been in two years. But at least one indicator suggests that much of the US is actually struggling financially: Americans are piling on credit card debt at record levels that we haven’t seen since the financial crisis. Households added $21.9 billion in credit card debt in the third quarter — the largest increase for that period since 2007 — bringing the amount of outstanding credit card debt to $927.1 billion, according to the latest study from WalletHub. That matches the mark in 2007 before the recession began, and it’s the highest tally since the end of 2008, when the global economy was experiencing a full-on implosion.
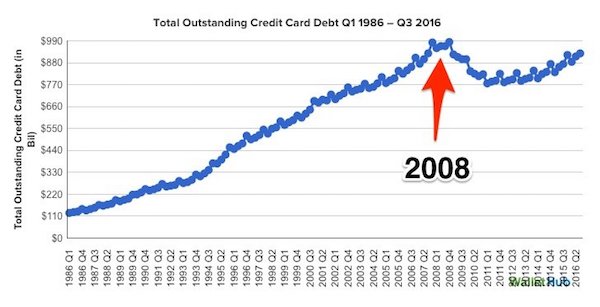
Racking up credit card debt isn’t inherently bad, so long as it’s being paid back. And so far, Americans are defaulting on their credit card debt at near historically low levels. Charge-off rates – the percentage of credit card debt that the companies are unable to collect on — are only at 2.86%, compared with 3.95% in 2007 the quarter before the Great Recession began and in excess of 10% in the years following the crisis, according to WalletHub. But holding a balance is a lousy move from a personal finance perspective — a sign of financial fragility. The fact that the average household with debt now owes $7,941 to credit card companies, according to WalletHub, suggests that America’s putative economic strength might be a mirage – that the economy may in fact be a lot weaker than all the happy indicators are leading people to believe.

Something’s off.
• It’s Been A Nightmare Year For Australian Retail (News.com.au)
It’s been a nightmare year for Australian retail, with a parade of the nation’s best-known brands decimated one after another. And experts say things will only get worse if business leaders and governments do not pick up their game. First it was Dick Smith Electronics, then the Woolworths-owned Masters home improvement chain that went under. Now, thousands more workers will be jobless at Christmas after a fresh slew of corporate collapses rounded out 2016. Payless Shoes this week announced plans to close its doors by the end of February, hot on the heels of Howards Storage World’s demise, and that of children’s fashion label Pumpkin Patch.
While Treasurer Scott Morrison seized on the latest bad news to bolster the Coalition’s tax reform agenda, market watchers say there is far more that needs to be done. Retail analyst Barry Urquhart of Marketing Focus said neither corporate leaders nor government had acknowledged what he called “an attitudinal recession” that was restraining businesses. While the nation was yet to tip into an official recession – despite having just marked its worst quarterly performance since the global financial crisis – Australians remained apprehensive about their futures, he said. And any business that failed to respond to this by recapturing the public imagination with a compelling, value-driven offering would simply fall by the wayside.

JPMorgan’s role is interesting. So is Beppe Grillo’s view of that role: “Italy’s opposition 5-Star Movement has called for JPMorgan’s fees to be voided if taxpayers have to come to the rescue..”
• Italy Prepares To Pump €15 Billion Into Ailing Banks (R.)
Italy’s government is ready to pump €15 billion into Monte dei Paschi di Siena and other ailing banks, sources said, as the country’s third-largest lender pushes ahead with a private rescue plan that is widely expected to fail. The world’s oldest bank has until Dec. 31 to raise €5 billion in equity or face being wound down by the European Central Bank, potentially triggering a wider banking and political crisis in Italy. If needed, the government will pump €15 billion into the Siena-based lender and several other smaller banks to prevent that, two sources close to the matter said on Thursday. One source said unlisted regional banks Banca Popolare di Vicenza and Veneto Banca, which were rescued this year by a state-backed fund, would also get support from the state.
The government would make the €15 billion available in a decree on Dec. 22, La Repubblica newspaper said on Thursday, adding that Banca Carige could also benefit. Italy’s banking sector is saddled with €356 billion of bad loans, around a third of the euro zone’s total and a legacy of the 2008-2009 global financial crisis when, unlike Spain or Ireland, Italy did not act to help its banks. Monte dei Paschi di Siena, advised by investment banks JPMorgan and Mediobanca, plans to raise equity to remove €28 billion in bad loans from its books. Italy’s opposition 5-Star Movement has called for JPMorgan’s fees to be voided if taxpayers have to come to the rescue. “We would have never done a deal like that with JPMorgan. In any case we would not pay the commissions (if the bank had to be nationalized,” Alessio Villarosa, a 5-Star lawmaker, said.

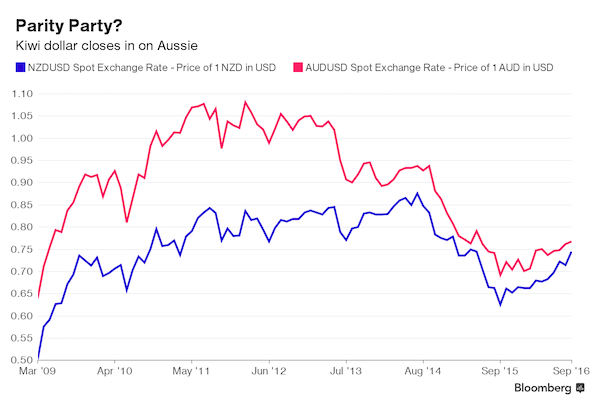
It’s not going to stop at parity.
• Euro Parity With Dollar ‘Only A Matter Of Time’ – ING (CNBC)
Divergence in monetary policy between the United States and Europe will bring parity between the value of the euro and dollar, according to ING. On Thursday the euro hit a low of 1.0364 against the dollar, the lowest level since August 2003 when it traded as low as 1.0357. Dollar strength is the key driver as investors believe the Federal Reserve will adopt a higher rate rise path in 2017 as the U.S. economy gathers momentum. Conversely, the ECB has just announced it will inject a further €540 billion of QE stimulus into the stuttering EU economy.
Analysts at ING wrote Friday that with European inflation struggling to edge higher and yesterday’s dip in to the 1.03 handle, euro/dollar parity is now firmly in view. “With the U.S. economy close to reaching escape velocity (and sustainable 2% inflation), it will only reinforce the downside risks to EUR/USD.” “Expect some consolidation around the 1.0450-1.0500 area, but this week’s fresh EUR/USD low means that the move down to parity is now only a matter of time,” the note reads.

“..either hike the interest rate (as) the U.S. does, or they give up the exchange rate..”
• The Fed Is Pushing China Into A Messy Catch-22 (CNBC)
An interest rate decision in the United States is causing a dilemma for Beijing. The U.S. dollar index surged to a near 14-year high after the Fed’s rate hike on Wednesday and its surprise forecast for three more increases — instead of the two that were expected previously — to come in 2017. Higher interest rates in the United States make it tempting for China to raise its own rates, because Beijing doesn’t want more money to flee the country into higher-yielding U.S. bonds. That flight also hurts China’s currency, the yuan. But Beijing could get its economy into trouble by hiking rates, since its continued economic growth is very heavily driven by borrowing. “You had this pressure that was already building, and the Fed has basically complicated and added to that with a more hawkish message,” said Logan Wright at Rhodium Group.
China’s yuan subsequently fell to its lowest level since 2008, and the country’s 10-year bond yield jumped to its highest level in more than a year. Declines in five-year and 10-year Chinese bond futures were reportedly so drastic Thursday that trade was halted due to a market trading limit. “The bond market itself, it’s raising a lot of attention, and it’s likely reflecting [that] policymakers in China are facing a difficult choice right now,” said Kai Yan, an economist at the IMF. He noted that “the speculation in the market is high because the central bank wants to stand in front of currency pressure to prevent capital outflow.” Chinese policymakers must “either hike the interest rate (as) the U.S. does, or they give up the exchange rate,” Yan said. “It is likely they will do a combination of the two.”
[..] China’s financial and economic challenges have been on the back burner for U.S. markets for much of the past year. The yuan’s depreciation versus the dollar has been largely ignored by global markets, as economic updates out of China have held up thanks largely to a flood of debt that’s propping up the country’s economy. Earlier this year, the Fed was seen as giving China some breathing room to stabilize its currency and economic growth. The U.S. central bank cited international concerns in avoiding a rate hike in the fall of 2015 and reducing its expectations for 2016 rate increases. Those decisions from the Fed helped keep the dollar steady, allowing China to avoid a significant depreciation of its currency. Now, however, some say the Fed may be less concerned about China since the U.S. economy is on firmer footing and can expect big domestic government spending from President-elect Donald Trump’s proposals.

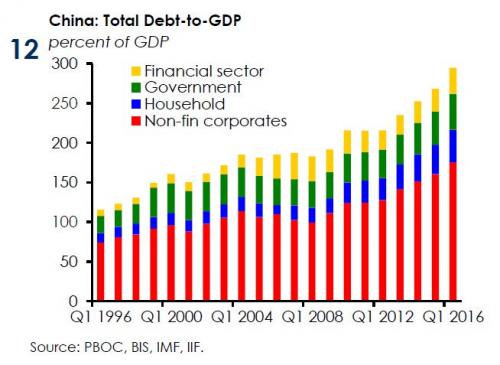
“Houses are for people to live in, not for people to speculate..” Sounds nice, but real estate has been a major contributor to China’s economy and GDP.
• China Vows To Contain Asset Bubbles, Avert Financial Risk In 2017 (R.)
China will stem the growth of asset bubbles in 2017 and place greater importance on the prevention of financial risk, while keeping the economy on a path of stable and healthy growth, media said, citing leaders at an economic planning meeting. China has seen growth stabilize this year, but corporate leverage and credit continue to expand, increasing risks to the world’s second-largest economy as it looks to push forward structural reforms. The annual meeting is attended by China’s top leaders and is closely watched by investors for clues on policy priorities and main economic targets for the year ahead. Monetary policy will be kept “prudent and neutral” in 2017, leaders attending the Central Economic Work Conference said in a statement, as reported by the official Xinhua news agency on Friday.
“Monetary policy will be kept prudent and neutral, adapt to new changes in money supply … and strive to smooth monetary policy transmission channels and improve mechanism to help maintain liquidity basically stable,” they said. The People’s Bank of China has maintained a prudent monetary policy since 2011, raising or cutting interest rates in line with shifts in the economy. The pro-active fiscal policy has been in place since the depths of the global crisis. The property market will be a focus of risk control, as authorities will restrain property bubbles and prevent price volatility, they said. The leaders called for a strict limit on credit flowing into speculative buying in the property market and for a boost in the supply of land for cities where housing prices face stiff upward pressure. “Houses are for people to live in, not for people to speculate,” Xinhua said, citing the statement.

Cohen of course is America’s no. 1 expert on Russia.
• Cold War Hysteria vs. US National Security (Stephen F. Cohen)
Thus far, no actual facts or other evidence have been made publicly to support allegations that the hacking was carried out on the orders of the Russian leadership, that Russian hackers then gave the damaging materials to WikiLeaks, or that the revelations affected the electoral outcome. Nor are Russian President Putin’s alleged motives credible. Why would a leader whose mission has been to rebuild Russia with economic and other partnerships with the West seek to undermine the political systems of those countries, not only in America but also in Europe, as is charged? Judging by the public debate among Russian policy intellectuals close to the Kremlin, nor is it clear that the Kremlin so favored the largely unknown and unpredictable Trump.
But even if Putin was presented with such a possibility, he certainly would have understood that such Russian interference in the US election would become known and thus work in favor of Clinton, not Trump. (Indeed, a major tactic of the Clinton campaign was to allege that Trump was a “Putin puppet,” which seems not to have helped her campaign with voters.) Still worse, since the election these allegations have inspired a growing Cold War hysteria in the American bipartisan political-media establishment, still without any actual evidence to support them. One result is more neo-McCarthyite slurring of people who dissent from this narrative. Thus a New York Times editorial (December 12) alleges that Trump had “surrounded himself with Kremlin lackeys.” And Senator John McCain ominously warned that anyone who disagreed with his political jihadist vendetta against Putin “is lying.”
A kind of witch hunt may be unfolding, not only of the kind The Washington Post tried to instigate with its bogus “report” of scores of American websites said to be “fronts for Russian propaganda,” but at the highest level. Thus, Trump’s nominee for secretary of state is said to be “a friend of Putin” as a result of striking a deal for Exxon-Mobil for Russian oil reserves, something he was obliged to do as the company’s CEO. Several motives seem to be behind this bipartisan American campaign against the President-elect, who is being equated with Russian misdeeds. One is to reverse the Electoral College vote. Another is to exonerate the Clinton campaign from its electoral defeat by blaming that instead on Putin and thereby maintaining the Clinton wing’s grip on the Democratic Party. Yet another is to delegitimate Trump even before he is inaugurated. And certainly no less important, to prevent the détente with Russia that Trump seems to seek.

Obama sounds smaller and weaker here.
• Obama Says Russia Is A Smaller, Weaker Country Than The US (CNBC)
In his final news conference of the year, President Barack Obama emphasized that Russia cannot change or significantly weaken the U.S., adding that Russia is a smaller and weaker country. He said Russia’s economy “doesn’t produce anything that anybody wants to buy,” except oil, gas and arms. The only way Russia can affect the U.S., he said, is “if we lose track of who we are” and “abandon our values.” “Mr. Putin can weaken us just like he’s trying to weaken Europe if we start buying into notions that it’s OK to intimidate the press, or lock up dissidents or discriminate against people,” he said. When asked if he would specifically name Russian President Vladimir Putin as directly responsible for the election hacking, Obama said he wanted to give the intelligence community a chance to gather the information necessary.
He added, however, that “not much happens in Russia without Vladimir Putin,” reaffirming that the hacking happened at the highest levels of the Russian government. “This is a pretty hierarchical operation,” he said. “Last I checked, there’s not a lot of debate and democratic deliberation, particularly when it comes to policies directed at the United States.” Obama reaffirmed his message of political unity and bipartisanship, urging the country to reunite across party lines to defend itself against Russia and others. “Our vulnerability to Russia or any other foreign power is directly related to how divided, partisan, dysfunctional our political process is,” he said. “That’s the thing that makes us vulnerable.”

“His main complaint is that “I don’t think she was treated fairly” by the press corps and the Russian hacks became “an obsession that dominated the news coverage.”
• Obama Goes Off the Clinton Script (WSJ)
Hillary Clinton told her donor base at Manhattan’s Plaza Hotel on Thursday that Russian cyber attacks were both “a personal beef against me” and meant to undermine “the integrity of our democracy,” and Democrats fanned out this week to spread this Kremlin-hacked-the-election narrative. President Obama was asked about all this in his year-end Friday press conference, but even he couldn’t square the contradictions. As liberals assailed the legitimacy of Donald Trump’s victory, Mr. Obama defended “the integrity of our election system,” noting that there is no evidence that ballots weren’t counted fairly. So much for those Jill Stein, Clinton-endorsed recounts, or the conspiracies about compromised voting machines. The President also explained that the emails stolen from John Podesta and the Democratic National Committee were “not some elaborate, complicated espionage scheme.”
He said intelligence and law enforcement were “playing this thing straight” and disclosed sufficient information about the hacks for “the American public to make an assessment as to how to weigh that going into the election.” Mr. Obama conceded that some of the leaked content was “embarrassing or uncomfortable” but all in all “pretty routine stuff.” His main complaint is that “I don’t think she was treated fairly” by the press corps and the Russian hacks became “an obsession that dominated the news coverage.” Really? The Podesta and DNC emails mostly revealed that the Clinton apparat don’t much like conservative Catholics or Bernie Sanders. Mr. Trump’s offenses against beauty queen Alicia Machado in the 1990s and his Billy Bush video were far bigger stories. The emails that really harmed Mrs. Clinton were those she stored on a personal server as Secretary of State, because the arrangement was potentially criminal and underscored doubts about her political character and judgment.

Not could, will. Curious that Dijsselbloem’s solo act in deciding to halt Greek debt relief doesn’t get more attention.
• Schaeuble Could Destroy Eurozone, Not Just Greece (EUO)
The sudden suspension of Greece’s short-term debt relief measures on Wednesday evening (14 December) has sparked fierce criticism by a number of EU officials. EU commissioner Pierre Moscovici, European Parliament president Martin Schultz, French president Hollande and finance minister Michel Sapin, along with many MEPs from the GUE/NGL, S&D and the Greens groups, have echoed support for Greece and prime minister Alexis Tsipras’s decision to give a one-time relief package to low-income pensioners. In essence, there has been no official decision taken by the Eurogroup, the European Stability Mechanism (ESM), or the European Council. Instead, there’s been unilateral action from the head of the Eurogroup without prior coordination with his colleagues.
Creditors should respect their own part of the deal and conclude the second review of the bailout programme, and acknowledge that there are open issues that need be addressed. The Greek government is fully implementing the bailout deal, moving on to needed reforms, providing safety nets for the vulnerable social groups. It’s possible Tsipras’s announcement was brought about by German finance minister Schaeuble and other circles pushing Greece to the limit. But in truth, we need not investigate who has taken the decision but instead focus on substantial issues. These issues include lowering primary surplus targets after 2018 and loosening tax rates so that the economy can become stable and growth can reach sustainable levels.
Even with such strict deadlines, the Greek government has achieved all fiscal targets for 2016, increasing public income and reaching a higher primary surplus than expected. This positive development prompted Tsipras, a few days ago, to announce a one-time relief package for low-income pensioners; a substantive decision after 12 consecutive pension cuts between 2010 and 2014, a loss of more than 30% of national GDP, during the same period, with a considerable part of the population facing poverty and social exclusion. The Greek government’s urgent measures are the least this government can do to temporarily do something for the worse off.
Dimitrios Papadimoulis is vice president of the European Parliament and head of the Syriza party delegation.

Merkel sides with Schaeuble.
• Greek PM Tells Merkel ‘Wounds Of Crisis’ Must Be Healed (R.)
Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras told German Chancellor Angela Merkel on Friday his country was set for strong economic growth and this would help to “heal the wounds of crisis” after years of austerity imposed under international bailouts. On a visit to Berlin, Tsipras was keen to emphasise Greek progress on reforms demanded by Germany as the EU’s most powerful economy and paymaster – a situation that has made Merkel a hate figure for some Greeks. The trip’s timing was also significant, as Greece wrangles with its creditors over terms for its current bailout, the latest of three. On Thursday it snubbed its lenders by passing legislation to give pensioners a one-off Christmas bonus.
Tsipras told reporters before meeting Merkel that he would inform the chancellor of the positive momentum of the Greek economy and his government’s “spectacular overachievement” of revenue targets. “The projections for the Greek economy are extremely positive for next year,” Tsipras said, adding authorities expected 2.7% growth in 2017 and 3.1% in 2018. But Greece’s economic development should not simply be confined to statistics and numbers, he added. “We want it to heal the wounds of crisis and to alleviate all those who have over these difficult years made huge sacrifices in the name of Europe,” Tsipras said.
Merkel showed little willingness to take a position on the disputed question of whether the pre-Christmas payout to pensioners was compatible with bailout obligations. Standing next to Tsipras, she said decisions lay in the hands of the Troika institutions handling negotiations with Greece but “the Greek prime minister’s assessment of the situation will certainly play a role in our discussions.” A German Finance Ministry spokesman said the institutions involved in Greece’s aid programme were critical of Athens in a preliminary report assessing the unilaterally announced measure. “To make the aid programme a success, it’s essential that measures are not decided unilaterally or are not taken back without advance notice,” said spokesman Dennis Kolberg.