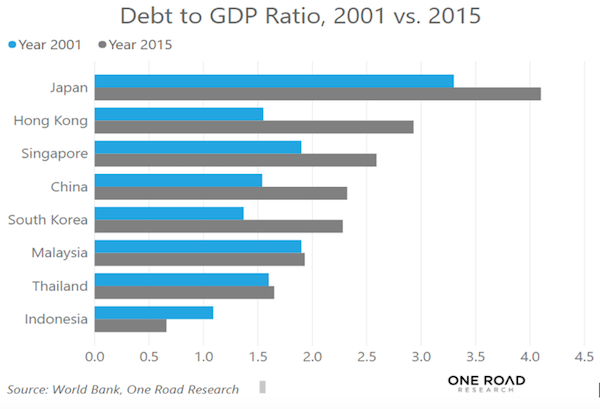
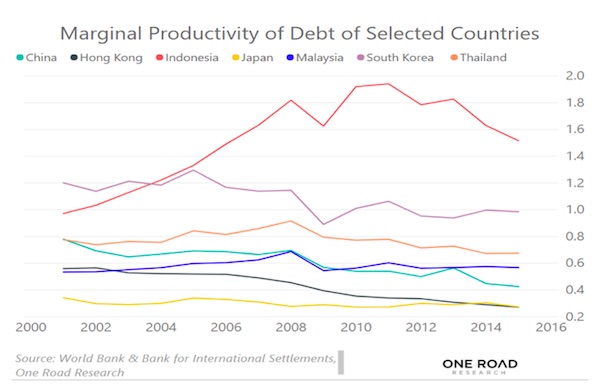
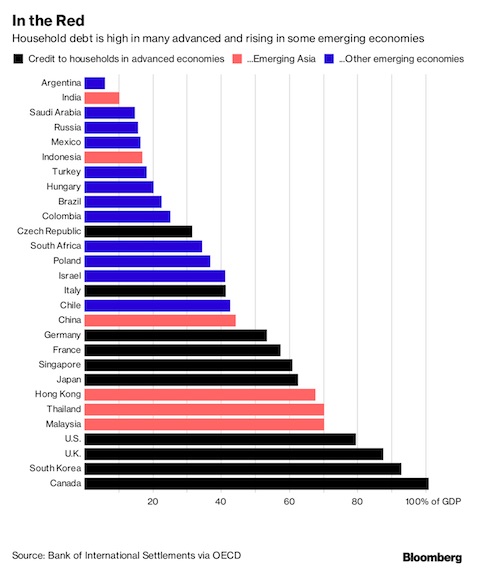
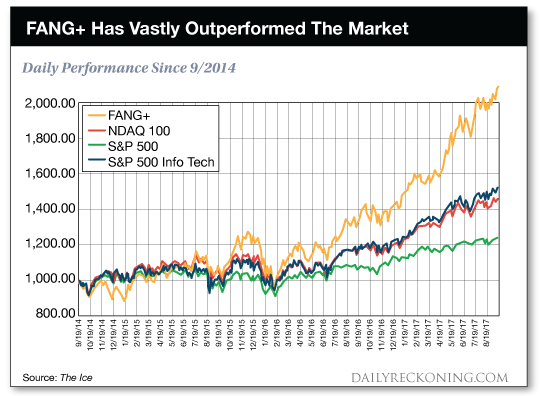
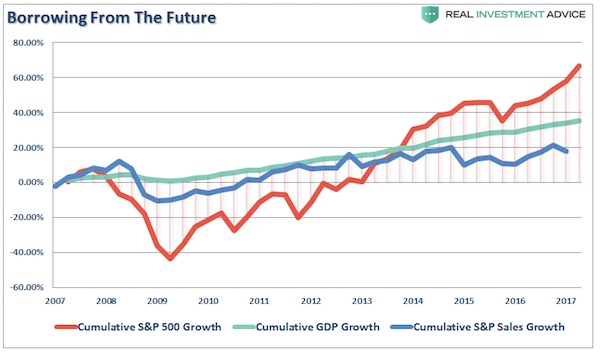
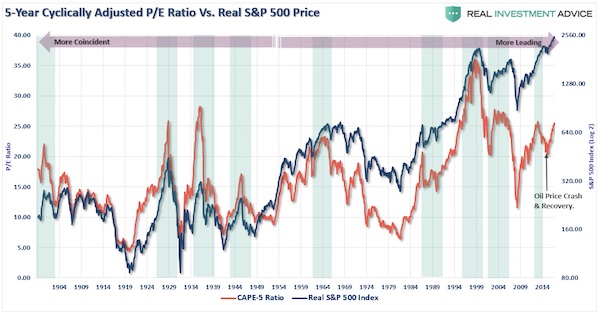
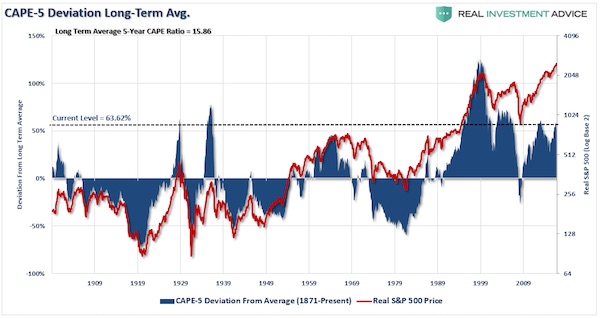
Cy Twombly Fifty Days at Iliam: Like a Fire that Consumes All before It 1978

https://twitter.com/EricLDaugh/status/1962678023959761031
JUST IN: Ilhan Omar reported a negative net worth of -$45,000 when she was first elected to Congress in 2019.
Her latest financial disclosure from May 2025 shows a net worth of up to $30 Million.
That’s a 66,676% increase in 6 years. pic.twitter.com/hDhyMCVt0K
— Bad Hombre (@joma_gc) September 2, 2025
NAVARRO: “Trump got lied to … not just by Fauci but by Pfizer … They didn't disclose the side effects of that [COVID vaccine] and they weren't clear with him. They made him think that it was a true vaccine, when it's not. It's mRNA technology.” pic.twitter.com/AsFqAy1FuR
— Chief Nerd (@TheChiefNerd) September 2, 2025
Siberia2
https://twitter.com/mog_russEN/status/1962775725402136920
France
https://twitter.com/Megatron_ron/status/1962810022586466400
AfD
The death count of opposition party AfD politicians standing for local elections in the German state of North-Rhine Westfalia has risen to 6. What's the probability that this happens by chance? https://t.co/itdgwWPLke
— Richard Werner (@scientificecon) September 2, 2025
A total of SIX AfD politicians died in the lead-up to elections in North Rhine-Westphalia.
Not saying I know what is happening here, but usually I subscribe to the general thought that there is no such thing as a coincidence in this world, but that evil is very much real. pic.twitter.com/hfTgiWHrco
— Eva Vlaardingerbroek (@EvaVlaar) September 2, 2025
Elon
ELON: CHINA’S TALENT AND INFRASTRUCTURE OUTPACE THE U.S.
“The sheer number of smart, hardworking people in China is incredible – far more than here, in my opinion.
They’ve got a lot of energy, and their architecture is far more impressive than the US.
The train stations, the… pic.twitter.com/nCrcVjrWBA
— Mario Nawfal (@MarioNawfal) September 1, 2025

Nap Scott


i wonder how many Westerners recognize themselves in this.
“Russia is determined to preserve the memory of WWII, as well as defend international law and “the true values that our world is built on.”
• ‘Western Liberal Dictatorships’ Spreading Hate In The World – Moscow (RT)
Moscow is committed to countering the xenophobia promoted by the West, Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova told RT. She made the remarks as President Vladimir Putin concluded his four-day visit to China by attending a military parade in Beijing on Wednesday, marking the 80th anniversary of Japan’s defeat in World War II. She argued that efforts by some politicians and media outlets to downplay or “distort” the victory of Russia and China in World War II show that “fascism, Nazism, racism, and xenophobia have not been completely eradicated.”
“These were the views our country fought against 80 years ago, and we are still confronting them on the international stage today,” she said. Zakharova added that Russia is determined to preserve the memory of WWII, as well as defend international law and “the true values that our world is built on.” “They haven’t yet been crippled by the Western liberal dictatorships that try to sway us towards a distorted understanding of people,” she said.

Europe built its entire existence on this for 50+ years. Now they’ve given it all away, “inspired” by some weird kind of Russophobia, or Putinphobia perhaps. And it’s not coming back, if they have second thoughts. It was sold to China in a binding agreement. They will have to replace it with US LNG at 4-5 times the price.
“Self-deindustrializing” is an apt term. When the current grossly unpopular leaders have been chased out of their plush seats, their successors will be left with a third world continent. You want me to believe this was NOT done intentionally? I find that hard.
• Did You Notice The EU Just Lost Its Gas Lifeline? (RT)
The EU’s cheap-gas lifeline just got handed to Beijing instead. With three signatures, Russia, China and Mongolia rerouted half a century of energy history eastward. On Tuesday, the three countries signed a legally binding memorandum for the Power of Siberia 2 pipeline – a roughly 2,600-km line, at an estimated cost of around $13.6 bn, that will carry 50 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas every year through Mongolia into northern China’s industrial heartland. While the pricing structure has yet to be fixed, the signatories have effectively redrawn the European energy map. For decades, this gas was the bedrock of German and Western European industry, piped from Russia’s Yamal fields in the Arctic through Nord Stream 1 directly into Germany. Now, that same supply is being redirected east.
Isn’t there already a pipeline? Yes. Power of Siberia 1, which came online in 2019, snakes east from Yakutia into northeastern China. What makes this deal different? Power of Siberia 2 is different: it will run a more direct route through Mongolia, which will gain access to the gas, tapping the very Yamal fields in western Siberia that once connected to Germany through the Nord Stream and Yamal-Europe pipelines, as well as transit revenues. Unlike POS1, which sources Russia’s Asian-facing fields, POS2 will draw gas from Arctic reserves that once fed Europe’s factories.
In other words, it closes the chapter of Europe as the main customer for Russian gas and hard-wires China as the new anchor market. What’s the timeline? The memorandum is binding but still vague. Key details such as pricing formulas, financing structures, and construction deadlines have not been finalized. One thing is clear though: once the backbone of EU’s growth, the gas will instead be sent into pipelines running east through Mongolia to China. For Brussels and Berlin, it’s not just a loss of supply but a structural break: the age of cheap Siberian gas for Europe is over.
Europe's fate sealed. China gets low-cost, dependable Russian pipeline gas that once upon a time powered Europe/Germany. Mongolia benefits via transit. Ukraine used to benefit via transit.
"Russia’s gas giant Gazprom PJSC has signed a legally binding agreement to build the Power… pic.twitter.com/20QYlZf3Y0
— Alex Christoforou (@AXChristoforou) September 2, 2025
As well as as the Power of Siberia 2 signing, Moscow also pledged to boost flows on existing lines. POS1 volumes will rise from 38 to 44 billion cubic meters a year – roughly a quarter of what the EU once bought from Russia. Russia’s Far Eastern route, piping gas in from the Sakhalin mega-projects, will rise from 10 to 12 billion cubic meters – about a tenth of what Europe used to purchase from Moscow annually. But the big figure is Power of Siberia 2: 50 billion cubic meters annually, slightly less than the Nord Stream 1 pipeline once carried into Germany before it was blown up. Add it all together and China will be importing over 100 billion cubic meters of Russian gas every year – volumes comparable to the flows that for decades underpinned Europe’s industrial base.
For the EU, the symbolism is brutal. The same Arctic molecules that drove the post-war boom and kept German factories competitive are now earmarked for China. The EU attempted to cut itself off from Russian supply after 2022, in a rupture that was allegedly tacitly backed by NATO. Since then, the bloc has been forced to buy US LNG at much higher prices than Russian pipeline gas, triggering an energy price crisis across the bloc and helping drive Germany into recession. With Power of Siberia 2 signed, the option of reversing course and reconnecting Europe to Russian gas has effectively vanished.

“..it will amplify and cement a massive shift in the flow of affordable Russian energy, away from lustily self-deindustrializing NATO-EU Europe to dynamic China and Asia.”
• The West Has Just Been Given A Rude Awakening (Amar)
Oswald Spengler, eccentric German arch-conservative, brilliant author of “The Decline of the West,” and proud pessimist extraordinaire (“optimism is cowardice”), could also be rather woke: You will find no more disdainful scorn or biting derision for the West’s navel-gazing than his. Skewering the Occident’s “provincial presuppositions,” naïve vanity, and self-crippling narrow-mindedness, Spengler dismissed its compulsive solipsism as producing a “prodigious optical illusion” of self-importance. Today, a little over a hundred years after these observations, Spengler would feel grimly vindicated. The string of international events – on a scale from “remarkable” to “game-changing” – that has just unfolded first at the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summit in Tianjin, then around Beijing’s massive 80th-anniversary World War II victory parade, should bring home to even the most somnambulant inhabitant of the Western mainstream media bubble two key facts about our world as it really is.
First, a new global order centered on Eurasia (minus a small, odd, and dismal peninsula, compulsively fixated on the Atlantic and masochistically obedient to the US) and the Global South is emerging unstoppably. China’s President Xi Jinping made clear in Tianjin that its custodians will relegate the West’s farcical “rules-based international order,” this ugly aberration that has facilitated the Gaza genocide and other mass crimes, to the rubbish heap of history. And second, the West is missing its chance to play a role in shaping what is coming after its half-delusional and entirely brutal “unipolar moment.” Stuck in self-defeating complacency, as illustrated by US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent’s bigoted dismissal of the SCO meeting as a “performative” get-together of “bad actors,” current Western establishments are determined to keep self-marginalizing.
In Slovak leader’s Robert Fico’s apt terms, most of the Western leadership will go on playing “frog at the bottom of the well,” all too happy to live without a clue. Maybe that’s all for the better: It is hard to see them make a sincere contribution to a world built on “sovereign equality,” “international rule of law,” and “multilateralism” (Xi Jinping), “valid and unshakable” UN principles (Russia’s Vladimir Putin), and a type of “connectivity” that respects “sovereignty and territorial integrity” (Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi).
In this regard, one of the two most spectacular developments in Beijing has been that China and Russia are now getting close to constructing one of the most ambitious pipeline projects in history: The Power of Siberia 2, connecting Russian gas fields to China via Mongolia, “could,” Bloomberg admits, “redefine the global gas trade,” including, the Financial Times points out, that of the LNG-trading US, Australia, and Qatar. That is an understatement. At a projected capacity of 50 billion cubic meters per year for at least 30 years, Power of Siberia 2 will affect all of the above. In essence, it will amplify and cement a massive shift in the flow of affordable Russian energy, away from lustily self-deindustrializing NATO-EU Europe to dynamic China and Asia.

“The Power of Siberia 2 project, which transits Mongolia, moved forward after the participants signed a “legally binding memorandum..”
• Gazprom Chief Reports Progress On ‘World’s Biggest Project’ With China (RT)
Russia and China have advanced plans for the construction of the Power of Siberia 2 natural gas pipeline, which will transit Russian gas from Siberia to the Asian powerhouse, Gazprom CEO Aleksey Miller said Tuesday. Miller is in China this week as part of a Russian delegation led by President Vladimir Putin, who on Tuesday met with Chinese President Xi Jinping and Mongolian President Ukhnaagiin Khurelsukh for trilateral talks in Beijing. At the meeting Xi highlighted the importance of “hard connectivity” through cross-border infrastructure for shared development. The Power of Siberia 2 project, which transits Mongolia, moved forward after the participants signed a “legally binding memorandum,” Miller told reporters. The project will be the “biggest, largest-scale and capital-intensive project in the world’s gas industry,” Miller said.
Power of Siberia 2 is intended to connect gas fields of western Siberia with consumers in western China. The section passing through Mongolia, known as the Soyuz Vostok pipeline, would also allow supplies to be sold to Mongolian buyers. Talks on the pipeline have been underway since at least 2006, with route options and pricing terms repeatedly debated. Officials said the project is expected to deliver 50 billion cubic meters of gas annually for at least 30 years. China has become the leading buyer of Russian pipeline gas after the European Union declared reliance on Russian energy a threat to its member states and moved to cut imports. The EU’s policy shift – promoted as a response to Moscow’s role in the Ukraine conflict – aligned with long-time US efforts to boost American liquefied natural gas exports to Europe.
The Power of Siberia 1 pipeline, which was launched in 2019, has already delivered over 100 billion cubic metres of gas to China from eastern Siberia. Miller said Moscow and Beijing have agreed to significantly increase the supplies. Gas presently being delivered to China – and to Mongolia in the future – is objectively cheaper than supplies previously sent to Europe thanks to shorter transportation routes, Miller noted.

But I thought Little Rocket Man was your friend?!
• Russia, China and North Korea ‘Conspiring’ Against US – Trump (RT)
President Donald Trump has accused China, Russia and North Korea of conspiring against the United States. He made the remarks on his Truth Social platform during a military parade in Beijing on Wednesday marking the victory over Japan in World War II. “Many Americans died in China’s quest for Victory and Glory. I hope they are rightfully honored and remembered for their bravery and sacrifice!” Trump wrote. He also wished Chinese President Xi Jinping “a great and lasting day of celebration.” “Please give my warmest regards to Vladimir Putin and Kim Jong-un, as you conspire against the United States of America,” he added.
Trump did not attend the celebrations in Beijing, which are said to be the largest in decades. US relations with both China and Russia remain strained by his trade war, sanctions, and the Ukraine conflict. Trump met with Putin in Alaska last month as part of his push to mediate a ceasefire in Ukraine. Although there were no breakthroughs, both sides hailed the summit as a positive step.China and Russia have repeatedly accused the US of trying to impose its will on the global stage and denounced what they call “unilateral” sanctions. At the Shanghai Cooperation Organization summit on Monday, Xi renewed his call to end the “Cold War mentality” and to work toward building an “equitable” system of international relations.

“Far-right politician Andrey Paribuy was killed not by a Russian agent, but by a grieving father desperate for justice..”
• Are Ukrainian Vigilantes Rising Up Against The Kiev Regime? (Romanenko)
When the news broke that a suspect had been arrested in the assassination of former Rada speaker, far-right Maidan figure Andrey Parubiy, much of the initial discussion revolved around Russia. Ukrainian authorities are predictably looking for a “Russian footprint.” But the suspect’s own words tell a very different story – a story of a grieving father who turned his despair into violence, and in doing so, revealed a deeper crisis within Ukrainian society itself.The man accused of murdering Parubiy, one Mikhail Stselnikov, is not a shadowy foreign agent, but a Ukrainian whose son went missing in the war against Russia. His confession was blunt: his act was driven by personal revenge against the Ukrainian authorities. He says he chose Parubiy because he lived nearby, and he would’ve chosen former president Petro Poroshenko if that were more convenient.
This choice of target is not random: these are men who, since the 2014 Maidan revolution, took Ukraine down the path the path toward confrontation with Russia, NATO aspirations, and ultimately, a devastating war.For this father, the tragedy is bitterly ironic. His son died fighting the Russians, yet he places blame not on Moscow, but on his own government. His child became a casualty not of “Putin’s aggression,” but of decisions made by Kiev’s political elite a decade earlier. In killing Parubiy, a key figure of the Maidan, he struck at the heart of the establishment that, in his view, had condemned his son to die.,This crime cannot be brushed aside as the madness of one man. It speaks to a growing disillusionment among Ukrainians, who have borne the brunt of the war’s human cost. Forced conscriptions, brutalized bystanders dragged from streets into military vans, families torn apart by mobilization – such practices have deepened anger at the government.
Even more painful is the perception that Kiev drags its feet on prisoner exchanges and the recovery of fallen soldiers’ remains. For parents like Stselnikov, this adds a layer of cruelty to an already unbearable loss. It is not only that their children die; it is that the state remains indifferent to their suffering.Polling data backs up this mood. According to a survey by Rating Group in August 2025, a staggering 82% of Ukrainians now favor negotiations with Russia, while only 11% support continuing the war. Ukrainian leader Vladimir Zelensky commands just 35% support. Ukrainians are exhausted, embittered, and increasingly view their leaders not as protectors but as obstacles to peace.Answering reporters’ questions in the courtroom, Stselnikov said: “I want to be judged quickly, exchanged as a prisoner of war, and go to Russia to look for my son’s body.”
These words should chill anyone who still clings to the narrative of a united Ukraine standing firm against Russia. Here is a man who fought no battles but lost everything – and he trusts Russia, the supposed enemy, more than his own government. He admitted to having been in contact with Russians while searching for his son, but he insisted they did not influence his crime. His grievance was not geopolitical but deeply personal: a loss compounded by his own state’s callousness. In the absence of hard evidence, Ukrainian officials defaulted to the familiar refrain of Russian involvement. Police chief Ivan Vyhivskyi hinted at it, but the very vagueness of the accusation betrays its weakness. If there was any clear indication the Kremlin had orchestrated this assassination, one would expect Ukraine’s leadership to loudly seize upon it. Instead, the rhetoric has been strangely subdued.
This muted response suggests what many Ukrainians already suspect: blaming Russia here is a fig leaf. It deflects attention from the uncomfortable truth that this killing was a homegrown act of despair. The system created by Ukraine’s post-Maidan elites is now cracking from within.The death of Andrey Parubiy at the hands of an ordinary Ukrainian grieving father points to the alienation of the people from their government. The legitimacy of Zelensky’s administration, already battered by polling numbers and public resentment, is further eroded when citizens believe Moscow to be is more trustworthy than Kiev. A regime that forces its sons to die, fails to return their bodies, and silences the grief of their families cannot endure such wounds forever. Ukraine’s leaders would do well to heed this message – before more fathers decide that revenge is the only way left to be heard.

“GPS navigation is based on receiving radio signals from satellites. There is no way to selectively block or disturb these for just a single receiver..”
• Von der Leyen Is Lying About Russian GPS Interference (MoA)
There is reason why the name of the President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen is often mangled into von der Lying. She is notoriously negligent with facts. Here she is caught outright lying to spread fake anti-Russian propaganda. When I read the headline below, first published by the Financial Times, I immediately thought that something was very wrong with it. Ursula von der Leyen’s plane hit by suspected Russian GPS interference (archived) – FT, Sep 1 2025 “A suspected Russian interference attack targeting Ursula von der Leyen disabled GPS navigation services at a Bulgarian airport and forced the European Commission president’s plane to land using paper maps. A jet carrying von der Leyen to Plovdiv on Sunday afternoon was deprived of electronic navigational aids while on approach to the city’s airport, in what three officials briefed on the incident said was being treated as a Russian interference operation.”GPS navigation is based on receiving radio signals from satellites. There is no way to selectively block or disturb these for just a single receiver. If someone would have manipulated GPS in that area it would effected every GPS receiver in the same geography. But I could not find any reports from Bulgaria that taxi drivers or other people using GPS navigation had any trouble with it. There was not a single tweet on X complaining about it. “The whole airport area GPS went dark,” said one of the officials. After circling the airport for an hour, the plane’s pilot took the decision to land the plane manually using analogue maps, they added. “It was undeniable interference.” The Bulgarian Air Traffic Services Authority confirmed the incident in a statement to the Financial Times. “Since February 2022, there has been a notable increase in [GPS] jamming and recently spoofing occurrences,” it said.
“These interferences disrupt the accurate reception of [GPS] signals, leading to various operational challenges for aircraft and ground systems.” The three anonymous “officials” the FT is quoting (which likely include von der Leyen) are lying. The statement by the Bulgarian Air Traffic Services Authority is just a general one. It does not say anything about the alleged incident. GPS failure does not mean that one has to use “paper maps”. (There are by the way no longer any “paper maps” on professional airliners. Maps are stored digitally.) Modern planes do not depend on GPS. They mainly use their Inertial Reference System. They can also navigate by following ground radar signals. Airports for regular landing of jets have Instrument Landing Systems installed. Short range radio signals from the ground will guide the plane onto the runway. There is no need to wait “for an hour”.
As Simple Flying summarizes:
• The IRS, or Inertial Reference System, is the main navigational system in aircraft, independent of outside signals or input.
• GPS is crucial for navigation in modern aircraft, with other aids like VOR and NDB used for backup.
• Aircraft navigational systems are highly independent, with [Flight Management Systems] processing multiple positional data for precise navigation.The claims of “paper maps” and “an hour” on hold, just like the whole story, did not make any sense to me.It has now been confirmed that the story is wrong. It is a lie, made up out of whole cloth.

Was it Michael Moore who said ‘you can’t declare war on a noun’?
• Why Can’t We End the War on Drugs? (Pinsker)
After the GOP obliterated President Clinton in the 1994 midterms, his party put the liberal wing to pasture. For the final six years of his presidency, the Clinton administration “triangulated” its way through various legislative, budgetary (and, ahem, “personal”) entanglements. Never again would a leading Democrat dare say, “The era of big government is over.” Today, it’d be utterly unfathomable! Next came eight years of President George W. Bush. His failures in Iraq and the economic crisis gave the radical leftists the opening they coveted. And on Election Day 2008, they took control of everything. Meanwhile, the GOP embraced the banner of conservatism under Sen. Barry Goldwater (R-Ariz.) in the 1960s and President Ronald Reagan in the 1980s. We’ve been operating under these ideals for most of the last 100 years: The Republican Party is the conservative party. We believe in limited government, personal liberty, and rugged individualism.
At this point, it’s hardwired into our DNA. Like many of you, I became a conservative because I believe these values will maximize peace, prosperity, and opportunity for my countrymen — it’s how we safeguard our God-given rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. I firmly, wholeheartedly believe that conservatism is our best defense against tyranny. (Probably our last defense, too.) But as a conservative, I’ve always struggled with the War on Drugs. For purely ideological reasons, I’m troubled by the government banning adults from living how they want or having the freedom to make their own decisions — especially in the privacy of their own homes. We ought to have the right to make our own choices, even if those choices are destructive and unhealthy. Look, if you wanna eat Twinkies, smoke pot, scroll Instagram, and drink Jack Daniels all day, you should have the right. (Just don’t ask the rest of us to subsidize your lifestyle.) Freedom of choice necessarily implies the freedom to make bad decisions, too.
Such is the horror — and the curse — of free will. But do you really have free will if you’re a drug addict? By definition, an addict is addicted, so probably not: Your brain, body, and soul are enslaved in chemical bondage, which makes it absolutely antithetical to free will! And I’m unsure how to reconcile this contradiction. There’s also more pragmatic concerns: The two most heavily abused drugs in America are alcohol and nicotine, and their commonality is obvious: They’re both legal. Seems reasonable to assume that if you make more drugs legal, there’d be more Americans using (and abusing) drugs. We already see this with the pro-marijuana movement: As more states legalized marijuana, its usage skyrocketed. There are now more daily pot-smokers in America than daily alcohol drinkers. By some metrics, the number of cannabis-involved ailments and emergency room visits has jumped by nearly 50%. It’d be stupid to assume that’s purely coincidental.
Should we suspend the War on Drugs, we’d better double down on rehab centers and medical facilities, because the number of U.S. drug users will grow considerably. The social cost will be in the billions. Maybe even trillions! Then again, the Drug War has ALREADY cost taxpayers over a trillion dollars. Damned if you do, damned if you don’t. There really aren’t any good options, alas; it’s a choice between what’s bad and what’s (likely) worse.Full disclosure: I used to serve on the board of directors of Drug Free America. Despite my misgivings, I liked ‘em and (mostly) supported their efforts. (I was also very honest about my own background when they recruited me: I’ve done PR for liquor brands, alcohol products, gambling, and other “sins.” They told me that was fine — they needed help with their messaging.)
So if you want to call me a hypocrite, you’d have a point. I’m far more passionate about expanding personal liberty than curtailing it. So, in the immortal words of Axl Rose, “Where do we go? Where do we go now?” What, if anything, should we change about our Drug War? Post-Obama, conservatism and liberalism are both North Stars — ideologies that push their adherents in a specific direction. And because they’re both North Stars, they also share the same weakness: Some ideas work far better as theories than as “real-world” policies, because the social cost is simply too great. And my suspicion is that’s why we can’t end the War on Drugs. Not today, not tomorrow, not next week. Probably not ever. Too many people would be hurt. And, paradoxically, too much freedom would be lost.

“Gavin Newsom likes to boast that his state is the world’s fourth-largest economy.”
• CNBC Just Spilled the Awful Truth About California (Green)
Question: What do you call “key sectors” of the world’s fourth-largest economy when they rely on illegal alien labor working for substandard wages, fewer benefits, and at greater risk of exploitation? I’d call it a crime. But in California, they call it “putting billions of dollars at risk” when President Donald Trump actually enforces the law. You know, like the chief executive takes an oath to do. With California’s $4 trillion gross domestic production, Gov. Gavin Newsom likes to boast that his state is the world’s fourth-largest economy. But a new CNBC report by Kate Rogers reveals more than it meant to about how “Trump’s immigration policy threatens key sectors” of Newsom’s state.One in four Californians is an immigrant, and, according to the Bay Area Economic Institute and the University of California-Merced, one in five of those is here illegally. In other words, California is home to around two million or more illegal aliens.
“As the Trump administration continues to ramp up immigration enforcement, industries key to the state’s $4 trillion economy like agriculture, construction and hospitality could be among those hardest hit by the loss of California’s immigrant workforce,” Rogers reported. “These are the workers that are keeping our economy afloat. They’re keeping businesses open,” Abby Raisz, research director at the Institute, told CNBC. Joe Garcia, president of the California Farmworker Association and CEO of Jaguar Labor Contracting, said in the report, “The lettuce, the strawberries, all the wine we drink on a daily basis, fruit juices– everything that a farmworker picks, packs, pre-harvest– they do the jobs all year round that put food on your table.”
Did he mean to repeat the “Who will pick our cotton?” trope? Regardless, CNBC said that Garcia’s firm “connects farmworkers to growers,” which I guess makes Jaguar Labor a profitable middleman in the market for illegal workers. “Sectors like construction and farming are staring down worker shortages that predate any change to immigration policy. In California, more than sixty percent of construction workers are immigrants and a quarter of them are undocumented,” according to the story. California’s unemployment rate is among the highest in the nation, and according to a Public Policy Institute last June, “about 10% of Californians — almost 2 million — are un- or underemployed as of the last quarter.” Two million illegals. Two million unemployed citizens. Does anybody else see the problem here?
Can anyone else taste the crocodile tears when Los Angeles restaurant owner (and illegal alien employer, apparently) Courtney Kaplan complained, “The biggest challenge for us, aside from the lost revenue and the decrease in business, has been the uncertainty of every day.” Overregulation and overtaxation jack up the price of everything in California, including labor. Now, business and political leaders swear to God the state’s economy can’t function without the underpaid workers they euphemistically call “undocumented.”Could we not use “undocumented,” please? The correct legal term — as in, it’s written into our immigration laws — is “illegal alien.” “Alien” because they’re foreign to this country. “Illegal” because they entered illegally. Here’s the exit question — not for you or me, dear reader, but for California. If your four-trillion-dollar behemoth is built on the backs of illegal aliens, is it really worth that much?

“By giving Biden’s “portrait” in the Rose Garden to a machine, Trump is doing more than just mocking his former opponent..”
• Trump Epically Trolls Biden Again (Margolis)
President Donald Trump has never been one to miss an opportunity for humor at the expense of his political rivals, and his latest idea may be his boldest act of trolling yet. In a conversation with Reagan Reese in the Oval Office, Trump revealed his vision for the redesigned Rose Garden, where presidential portraits will line the walkways in ornate gold frames. But when it came to Joe Biden, Trump had something very different in mind. As he showed Reese the new portraits, she remarked, “I love the frames, I love the gold.” Trump explained, “So that was done for very high-end paintings. I’m looking at frames and saying, ‘what about that one?’” Then, Reese pressed him on whether Biden would also get a spot in the display. Trump paused, then grinned. “Isn’t that an interesting question,” he said. “And I’ll listen to you too, because it’s a decision I have to make. We put up a picture of the autopen.”
The room erupted in laughter. “Oh, that’s hilarious,” Reese told him. Trump didn’t miss a beat. “He didn’t win the race. He lost badly. He was a horrible president.” To prove he was serious, Trump even showed Reese a mock-up of what the so-called “Biden Autopen” portrait would look like hanging in the Rose Garden alongside the greats. “So what do you think?” he asked her. “I think you got to,” Reese responded. “I gotta do it,” Trump said. The autopen has been around since the 1950s, but its constitutional legitimacy has always been questionable. Barack Obama tested the limits in 2013, signing a bill into law from a Hawaiian vacation with cover from a Bush-era legal memo. But the Biden administration took things much further, routinely using the device in ways that raise doubts about whether the president himself even approved pardons or executive orders issued in his name.
https://twitter.com/nicksortor/status/1962668061128863812?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw%7Ctwcamp%5Etweetembed%7Ctwterm%5E1962668061128863812%7Ctwgr%5Eaa928af76cfb59d98c6436ee59841090050b7320%7Ctwcon%5Es1_c10&ref_url=https%3A%2F%2Fpjmedia.com%2Fmatt-margolis%2F2025%2F09%2F02%2Fthis-might-be-trumps-most-epic-trolling-of-joe-biden-ever-n4943251
No president had ever relied on the autopen so often — or under such a veil of secrecy. The revelation was especially troubling given that it happened during a presidency already clouded by widespread doubts about the commander-in-chief’s mental capacity.In June, it emerged that the Biden administration used the autopen for pardons and executive orders even while Biden was physically present in Washington, a glaring inconsistency that suggests he may not have known, or consented to, what was being done in his name. The crisis deepened in July when the New York Times revealed that Biden had not personally approved every pardon or act of clemency attributed to him.
That exposé left the most chilling question unanswered: during Biden’s presidency, was the constitutional power of the executive branch quietly transferred from the elected president to a machine and to unelected aides who controlled it? By giving Biden’s “portrait” in the Rose Garden to a machine, Trump is doing more than just mocking his former opponent; he’s cementing Biden’s legacy as a president defined by absence, detachment, and failure. Future generations walking through the Rose Garden would see Washington, Lincoln, and Reagan staring proudly from gilded frames and then, in Biden’s place, a cold mechanical autopen.

She has 3 properties. One listed as secondary residence, that in reality is rented out. Which is illegal -1. The other two are listed as primary residence. You can’t have two. Illegal 2. Moreover, one of those is also rented out. Illegal 3.
• This Explosive Revelation Could Bury Lisa Cook (Jeff Charles)
Federal Reserve Governor Lisa Cook is going to have some ‘splainin’ to do after it was revealed that she is renting out a home she listed as her “primary residence” when filling out mortgage applications. Charlie LeDuff of the Michigan Enjoyer in a post and video on X exposed Cook’s alleged misdeeds, noting that she “has a bank loan on a ‘secondary home in Massachusetts, which the Trump administration alleges she rents out full-time.” “A judge might call that mortgage fraud,” LeDuff added. Cook also owns a condo in Atlanta, which she claims is her primary residence on banking and government documents. The Trump administration alleges there is evidence that she rents that one out too. And that also could be mortgage fraud. But Cook also has a THIRD home in Ann Arbor, which she also lists as her primary residence on banking and government papers.
Lisa must be living in Ann Arbor in the tidy brick house with a columned portico on Jackson Avenue, right? LeDuff, who visited the third home, indicated it was not exactly in tip-top condition. “The glass in the storm door was filthy with neglect,” he wrote. “A metal lockbox—the kind used by realtors—hung on the door knob. From the porch, I could see a figure sitting at the dining room table. When I knocked, the door slightly cracked open, only to reveal a white man partially visible behind the filthy glass.”One of the individuals LeDuff spoke to at the home indicated he was renting the home. The author wrote, It’s hard to believe Cook got confused over her mortgage paperwork” because she “is a financial sophisticate, a member of the board of governors of the world’s most powerful central bank.” Cook allegedly listed two of her properties as primary residences in her 2025 government ethics filings.
Fed Gov. Lisa Cook’s Ann Arbor Pad Is a Rental, Too
The recently fired financial sophisticate has been playing by different rules than the rest of usBy Charlie LeDuff (@Charlieleduff)
Ann Arbor — Lisa Cook’s financial house is on fire. Naturally, there is a Michigan angle to… pic.twitter.com/i7mEDXDa4y
— Michigan Enjoyer (@mich_enjoyer) September 2, 2025
Cook is facing allegations of mortgage fraud involving properties she owns in Massachusetts, Georgia, and Michigan. Federal Housing Finance Agency Director Bill Pulte said she misrepresented her properties to obtain more favorable mortgage rates. President Donald Trump fired Cook “for cause” last month after demanding that she resign. Cook responded by filing a lawsuit against the president, the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, and Fed Chair Jerome Powell. The suit alleges that the president does not have the authority to fire her.
This isn’t looking good for Cook. Yes, it is likely that many Americans make these types of mistakes when filling out paperwork. But, as LeDuff pointed out, Cook is definitely not one of those people. A person in her position would know better than to list a rental property as a primary residence. However, it appears many like Cook get away with this because they are in powerful positions. New York Attorney General Letitia James is facing similar allegations, and there are likely plenty more who have done the same. Perhaps at least some of these people might face accountability.

Is this just trying to make us think things have improved? Because we sure don’t seem to see proof of that.
• Israel Had ‘Total Control’ Over Congress – Trump (RT)
Israel previously had “total control” over the US Congress, and it was impossible for someone speaking “badly” of the Jewish state to be in politics, US President Donald Trump has said. Trump said that in an exclusive interview with the Daily Caller published on Monday, repeatedly stating that Israel used to have the “strongest lobby I’ve ever seen” in the US. “If you go back 20 years. I mean, I will tell you, Israel had the strongest lobby in Congress of anything or body, or of any company or corporation or state that I’ve ever seen. Israel was the strongest. Today, it doesn’t have that strong a lobby. It’s amazing,” Trump explained.
There was a time where you couldn’t speak bad, if you wanted to be a politician, you couldn’t speak badly [of Israel]. Times have changed, and US politics now has all sorts of critics of Israel, namely “AOC plus three” and “all these lunatics,” Trump added. The US president referred to the so-called ‘Squad’, an informal progressive left-wing faction of the Democratic Caucus in the US House, originally composed of Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, Ilhan Omar, Ayanna Pressley, and Rashida Tlaib, known for their strong anti-Israel stance.
The conflict between Israel and Hamas in Gaza, prompted by a surprise assault on southern Israel mounted by the Palestinian group on October 7, 2023, has further eroded West Jerusalem’s influence in the US, Trump suggested. “They may be winning the war, but they’re not winning the world of public relations, you know, and it is hurting them,” he said. At the same time, Trump praised himself for what he had done for Israel, claiming that “nobody has done more” for the country. The US president said Israel was “amazing” since he has been enjoying “good support” from them in return as well.

Next, he’ll send them to Chicago and Baltimore. Saying it’s his job as a president to keep people safe. It’ll all end up at SCOTUS.
• Democrat Judge Rules Trump Deployment of National Guard To LA Was Illegal (ZH)
A federal judge in California ruled on Tuesday that President Donald Trump violated a 19th century law when he mobilized 4,000 National Guard troops and 700 marines to Los Angeles in June. “The evidence at trial established that Defendants systematically used armed soldiers (whose identity was often obscured by protective armor) and military vehicles to set up protective perimeters and traffic blockades, engage in crowd control, and otherwise demonstrate a military presence in and around Los Angeles,” wrote US District Court Judge Charles Breyer (Clinton) in a 52-page ruling. “In short, Defendants violated the Posse Comitatus Act,” he continued. Breyer’s ruling follows a three-day trial last month, in which lawyers for the state of California argued that Trump had exceeded his authority when he deployed the federal troops to deal with thousands of protesters who took to the streets of downtown LA against his immigration policies.
California asked Breyer to order the Trump administration to return control of the remaining troops to Gov. Gavin Newsom, and to halt the use of the military “to execute or assist in the execution of federal law.” Of note, Breyer’s order is limited to California, and Trump doesn’t have to withdraw the 300 National Guard troops currently on the ground in LA. Those troops can continue to protect federal property under the Posse Comitatus Act – an 1878 law that prevents a president from using the military as a domestic police force without Congressional approval. According to Breyer, Trump “deployed the National Guard and Marines to Los Angeles, ostensibly to quell a rebellion and ensure that federal immigration law was enforced,” adding “There were indeed protests in Los Angeles, and some individuals engaged in violence,” but that “there was no rebellion, nor was civilian law enforcement unable to respond to the protests and enforce the law.”
The Trump administration is now prevented from using military troops in the Golden State “to execute the laws, including but not limited to engaging in arrests, apprehensions, searches, seizures, security patrols, traffic control, crowd control, riot control, evidence collection, interrogation, or acting as informants,” unless the situation falls under the Posse Comitatus Act. And while the order only applies to California, Breyer wrote that Trump’s intention to deploy National Guard troops in other cities would be “creating a national police force with the President as its chief.”
While the judge’s decision may have minimal impact on the ground in California, the case could still have nationwide implications as Trump and Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth deploy National Guard members in Washington, D.C., and threaten to do so in other blue cities to address street crime. The Trump administration is likely to appeal Breyer’s decision, which could result in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit and even the Supreme Court weighing in on the administration’s unconventional use of the National Guard. -Fox News. Breyer’s decision comes shortly after the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit halted one of his emergency orders issued in June in which he ordered Trump and Hegseth to hand the National Guard back to Newsom.

What a rathole. How is it possible?
• Woke Rats Jump Ship As Trump Puts CDC Under A Microscope (ZH)
The covid pandemic was an exceptional example of the abuse of government power and the classic error of putting blind faith in scientific institutions that are vulnerable to political and corporate manipulation. To put it simply, the hysteria over covid was entirely fabricated and the CDC played a primary role in perpetuating the fear. The CDC knew as early as October of 2020 that the median Infection Fatality Rate (IFR) of covid was a tiny 0.23% (meaning 99.8% of the population was not under threat). The death rate was far below the 3% initially predicted by the World Health Organization. The data also didn’t take into account the fact that the majority of deaths were people with comorbidities – Meaning many of them likely died of a different illness or long term health problems, but covid was officially assumed to be the cause.
The CDC response should have been focused on caring for the older subset of the American population which was at greater risk. Instead, the organization tried to terrorize the public with tales of hospitals “packed to capacity with the unvaccinated” while suffering on respirators (no evidence has ever been produced to support this claim). The CDC joined with Democrats to fear monger over “mass deaths in the streets”. They initially lied about the effectiveness of the shot (it is now well known that the covid vaccine does not prevent transmission). They lied about the effectiveness of natural immunity. They lied about the effectiveness of the masks. They lied about the effectiveness of social distancing. They defended the lockdowns (which were an abject failure). Almost every aspect of the pandemic response ended up being a farce.
The CDC and many of its employees act as a political propaganda mechanism, not as an objective scientific guardian of the public good. The organization functions like a cult that worships far-left bureaucratic leadership instead of adhering to the scientific method. This has become even more apparent in recent months as the agency faces scrutiny. After the firing of CDC Director Susan Monarez for refusing to institute Trump’s policy changes, the rush for the exits has begun. The woke creatures are now slithering out of the weeds to escape RFK Jr’s lawnmower.
A glaring example is the resignation of Dr. Demetre Daskalakis, a CDC director who has attacked Trump’s policies as dangerous and “unscientific”. It is perhaps no coincidence that Daskalakis is a LGBT activist that promotes transgender treatments for children (a highly unscientific practice). This is the kind of person that rises through the ranks at the CDC:
CDC … "Why doesn't anyone believe us anymore."
Hell, I don't know … let's ask your new spokesmen Dr. Demetre Daskalakis who was pushing 3 different vaccines on your official website, Friday. pic.twitter.com/QbxDgIWw2n
— Catturd ™ (@catturd2) January 23, 2023
Because of the CDCs behavior during the pandemic as well as the woke agenda of their staff, the American populace has demanded accountability and reform. Trump’s decision to make RFK Jr the Secretary of the Department of Health was widely applauded because of the trespasses of the CDC and affiliated agencies during covid. Only Democrats and Big Pharma are opposed to an audit of CDC policies. It’s no surprise that the agency is facing a wave of mass firings and a wave of mass walkouts. Democrats seem to believe that the Trump Administration has no say in underlying federal operations. After all, the system has functioned this way for generations. Presidents come and go; the real power is among the unelected armies of bureaucrats. The moment these people are faced with actual oversight, they become enraged.

The entire man looks calcified, not just the brain.
• The Penguin Quits – Fast Action Needed (CTH)
New York Representative Jerry “The Penguin” Nadler has announced he is not going to seek reelection in 2026. 78-year-old Nadler was going to face a significant primary threat from the far-left.
NEW YORK – “Watching the Biden thing really said something about the necessity for generational change in the party, and I think I want to respect that,” Mr. Nadler said, adding that a younger successor “can maybe do better, can maybe help us more.” Rep. Jerry Nadler, was the former chair of the House Judiciary Committee who joined forces with Adam Schiff and spearheaded President Donald Trump’s impeachment effort. Nadler and Schiff formed a joint House impeachment committee and then hired Mary McCord as the lead staff for the effort. Mary McCord previously worked as DOJ-National Security Division head with Michael Atkinson as her office lawyer.When McCord quit the DOJ and went to work for Schiff and Nadler, Atkinson was moved to Intelligence Community Inspector General (ICIG). As the ICIG, Michael Atkinson then changed the rules for whistleblowers within the CIA permitting a false assertion by Eric Ciaramella, who subsequently told a fictional story presented by Alexander Vindman. The fake “Ukraine Impeachment” effort stemmed from this political scheme. Vindman lied, Eric Ciaramella advanced the lie to ICIG Michael Atkinson who then spun the false allegation back to his colleague Mary McCord. That’s the origin of the fraud behind the first impeachment effort.
1/ Who told President Trump to appoint Michael Atkinson as ICIG? The appointment of Michael Atkinson was not a mistake. The impeachment was pre-planned. Find the person who put his name in front of President Trump, and you find one of the internal operatives within the Trump administration specifically working to hurt President Trump in his first term. Is that person around in term #2?
2/ Where is Michael Atkinson’s transcript? ICIG Michael Atkinson testified to the joint House subcommittee on impeachment about why he changed the rules for CIA whistleblowers. Atkinson testified about his activity to the Schiff/Nadler committee, IN FRONT OF MARY McCORD.Adam Schiff promptly classified and sealed the Atkinson deposition transcript in an attempt to forever bury it. The equity stakeholders are: (1) the House of Representatives, and (2) the CIA.NEEDED ACTION – House Speaker Mike Johnson should be able to find that Atkinson transcript, declassify and make it public. However, the CIA is likely also the equity stakeholder. So, give it to Director John Ratcliffe who then declassifies it and gives it to DNI Tulsi Gabbard for release.

That was one weird accident.
• Trump to Give Giuliani Presidential Medal of Freedom (Salgado)
After a car crash hospitalized Rudy Giuliani just after he stopped to help a crime victim, Donald Trump announced he would be giving his long-time ally a very great honor.The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest honor that an American civilian can receive, and Giuliani, famous for his successful tenure as New York mayor and his years of providing legal support to Donald Trump, will receive it.Trump posted on Truth Social Monday, “As President of the United States of America, I am pleased to announce that Rudy Giuliani, the greatest Mayor in the history of New York City, and an equally great American Patriot, will receive THE PRESIDENTIAL MEDAL OF FREEDOM, our Country’s highest civilian honor. Details as to time and place to follow. Thank you for your attention to this matter. MAKE AMERICA GREAT AGAIN!!!”
BREAKING: President Trump says he will award former New York City Mayor Rudy Giuliani the Presidential Medal of Freedom. The announcement comes after Giuliani was seriously injured in a car crash over the weekend. pic.twitter.com/qhXI8ClU71
— Fox News (@FoxNews) September 1, 2025
State Department Ambassador and Chief of Protocol Monica Crowley responded to the news, “Congratulations to America’s Mayor and a truly great patriot @RudyGiuliani! This is so well deserved and the best news, my friend.”Article III Project founder Mike Davis celebrated, “Well-deserved recognition for an iconic American leader. Every mayor in America should follow the broken-windows strategy @RudyGiuliani, the greatest mayor ever, developed and deployed to Make New York City Great Again in the 1990s.”Michael Ragusa, head of Giuliani’s security, released a statement on X Sunday, stating, “On the evening of August 30, 2025, in New Hampshire, Mayor Giuliani was involved in a motor vehicle accident. Prior to the incident, he was flagged down by a woman who was the victim of a domestic violence incident. Mayor Giuliani immediately rendered assistance and contacted 911. He remained on scene until responding officers arrived to ensure her safety.”
I’m at the Staten Island Richmond County Fair and just heard about Rudy Giuliani’s injury.
On Staten Island Rudy is a beloved figure. A few of us paused to say a prayer for his swift and pain-free recovery.
We’re pulling for you Mayor! https://t.co/PNoz41eqSY
— Curtis Sliwa (@CurtisSliwa) August 31, 2025
Then, Giuliani resumed his journey, and “while traveling on the highway, Mayor Giuliani’s vehicle was struck from behind at high speed. He was transported to a nearby trauma center, where he was diagnosed with a fractured thoracic vertebrae, multiple lacerations and contusions, as well as injuries to his left arm and lower leg.” Ragusa said Giuliani was recovering well, but his injuries sound pretty severe.Giuliani’s account subsequently posted an update, reporting that the woman Giuliani tried to help was actually the aggressor in the situation, and her boyfriend was the person who needed aid and medical attention. Also, as of today, Giuliani is still in the trauma center because of the severe injuries he sustained. It is unclear when he will be enough recovered to receive his award from Trump.




Bloom
30,000 hours of footage, equivalent to 3 years and 7 months, were filmed to capture the blooming of 77 types of flowers, and the result is spectacular.pic.twitter.com/GdXbqmJBo2
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) September 2, 2025
Horns
This is one of the best images of all time! pic.twitter.com/uHENQP1EiG
— The Figen (@TheFigen_) September 1, 2025
Trees
Cell towers may be quietly damaging the trees around them.
As wireless networks spread through cities and suburbs, scientists are starting to notice a troubling pattern: trees closest to cell towers often show unusual signs of stress.
In one 9-year study in Germany, researchers… pic.twitter.com/7f4dzBpcSE
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) September 2, 2025

Support the Automatic Earth in wartime with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.