Piet Mondriaan Broadway boogie wooogie 1943

“In today’s bubble, central bankers and governments are fools. They can mobilise more resources to become bigger fools.”
“In addition to taking nearly half of the business labour outlay, China has invented the unique model of taxing the household sector through asset bubbles. The stock market was started with the explicit intention to subsidise state-owned enterprises.”
“China’s residential property value may have surpassed the total in the rest of the world combined.”
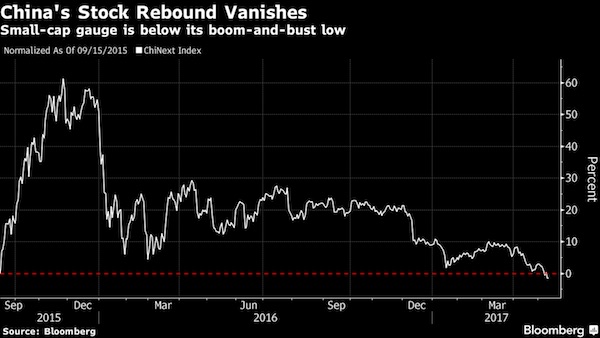
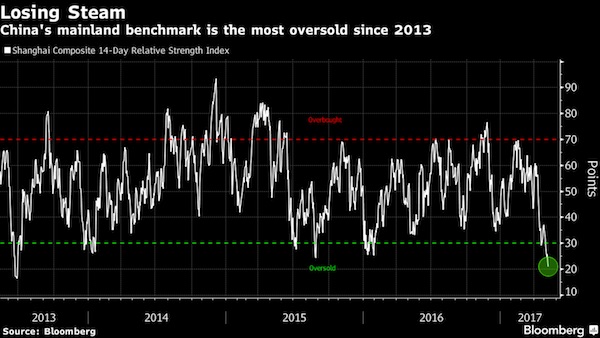
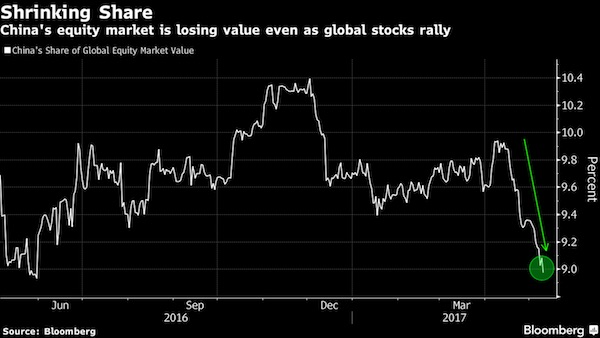
• The Bubble Economy Is Set To Burst, US Elections Be The Trigger (Andy Xie)
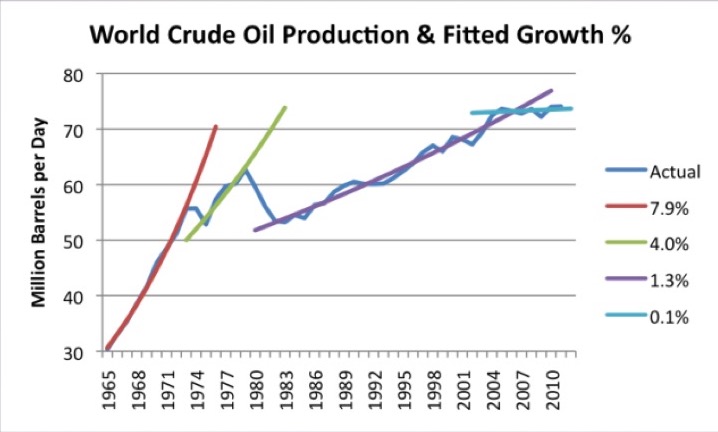
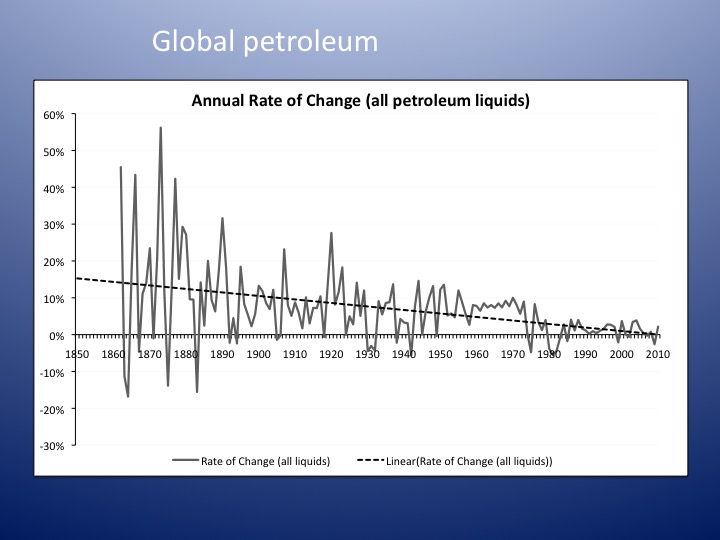
While Western central bankers can stop making things worse, only China can restore stability in the global economy. Consider that 800 million Chinese workers have become as productive as their Western counterparts, but are not even close in terms of consumption. This is the fundamental reason for the global imbalance. China’s most important asset bubble is the property market China’s model is to subsidise investment. The resulting overcapacity inevitably devalues whatever its workers produce. That slows down wage rises and prolongs the deflationary pull. This is the reason that the Chinese currency has had a tendency to depreciate during its four decades of rapid growth, while other East Asian economies experienced currency appreciation during a similar period. Overinvestment means destroying capital. The model can only be sustained through taxing the household sector to fill the gap.
In addition to taking nearly half of the business labour outlay, China has invented the unique model of taxing the household sector through asset bubbles. The stock market was started with the explicit intention to subsidise state-owned enterprises. The most important asset bubble is the property market. It redistributes about 10% of GDP to the government sector from the household sector. The levies for subsidising investment keep consumption down and make the economy more dependent on investment and export. The government finds an ever-increasing need to raise levies and, hence, make the property bubble bigger. In tier-one cities, property costs are likely to be between 50 and 100 years of household income. At the peak of Japan’s property bubble, it was about 20 in Tokyo. China’s residential property value may have surpassed the total in the rest of the world combined.
In 1929, Joseph Kennedy thought that, when a shoeshine boy was giving stock tips, the market had run out of fools. Today, that shoeshine boy would be a genius How is this all going to end? Rising interest rates are usually the trigger. But we know the current bubble economy tends to keep inflation low through suppressing mass consumption and increasing overcapacity. It gives central bankers the excuse to keep the printing press on. In 1929, Joseph Kennedy thought that, when a shoeshine boy was giving stock tips, the market had run out of fools. Today, that shoeshine boy would be a genius. In today’s bubble, central bankers and governments are fools. They can mobilise more resources to become bigger fools. In 2000, the dotcom bubble burst because some firms were caught making up numbers. Today, you don’t need to make up numbers. What one needs is stories.
Hot stocks or property are sold like Hollywood stars. Rumour and innuendo will do the job. Nothing real is necessary. In 2007, structured mortgage products exposed cash-short borrowers. The defaults snowballed. But, in China, leverage is always rolled over. Default is usually considered a political act. And it never snowballs: the government makes sure of it. In the US, the leverage is mostly in the government. It won t default, because it can print money. The most likely cause for the bubble to burst would be the rising political tension in the West. The bubble economy keeps squeezing the middle class, with more debt and less wages. The festering political tension could boil over. Radical politicians aiming for class struggle may rise to the top. The US midterm elections in 2018 and presidential election in 2020 are the events that could upend the applecart.

Time to acknowledge these people really don’t have a clue. They are stuck in models that have long since failed, and they have no others.
• Fed Divide On Inflation Intensified At September Policy Meeting (R.)
Federal Reserve policymakers had a prolonged debate about the prospects of a pickup in inflation and slowing the path of future interest rate rises if it did not, according to the minutes of the U.S. central bank’s last policy meeting on Sept. 19-20 released on Wednesday. The readout of the meeting, at which the Fed announced it would begin this month to reduce its large bond portfolio mostly amassed following the financial crisis and unanimously voted to hold rates steady, also showed that officials remained mostly sanguine about the economic impact of recent hurricanes. “Many participants expressed concern that the low inflation readings this year might reflect… the influence of developments that could prove more persistent, and it was noted that some patience in removing policy accommodation while assessing trends in inflation was warranted,” the Fed said in the minutes.
As such several said that they would focus on incoming inflation data over the next few months when deciding on future interest rate moves. Nevertheless, many policymakers still felt that another rate increase this year “was likely to be warranted,” the Fed said. U.S. stocks and yields on U.S. Treasuries were little changed following the release of the minutes. Fed Chair Janet Yellen has repeatedly acknowledged since the meeting that there is rising uncertainty on the path of inflation, which has been retreating from the Fed’s 2% target rate over the past few months. However, Yellen and a number of other key policymakers have made plain they expect to continue to gradually raise interest rates given the strength of the overall economy and continued tightening of the labor market.
“The majority of Fed officials are worried that core inflation might not rebound quickly, but that isn’t going to stop them from continuing to normalize interest rates, particularly not when the unemployment rate is getting so low,” said Paul Ashworth, an economist at Capital Economics.

More clueless hacks. On Twitter, Tropical Traderhas this: “UK is a f**king leveraged real estate hedge fund Ponzi scheme run by and for spivs and chancers. Of course productivity is going nowhere… ”
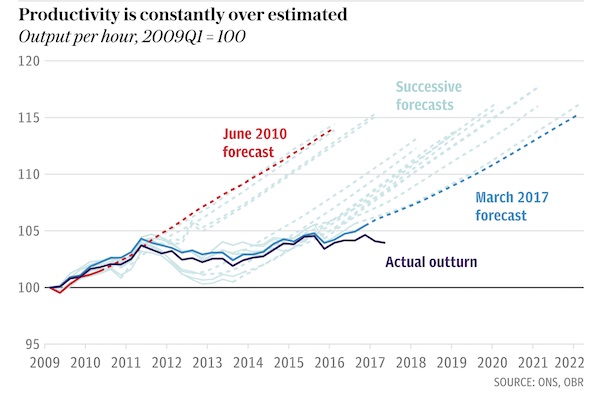
• UK Resigned To Endless Productivity Gloom (Tel.)
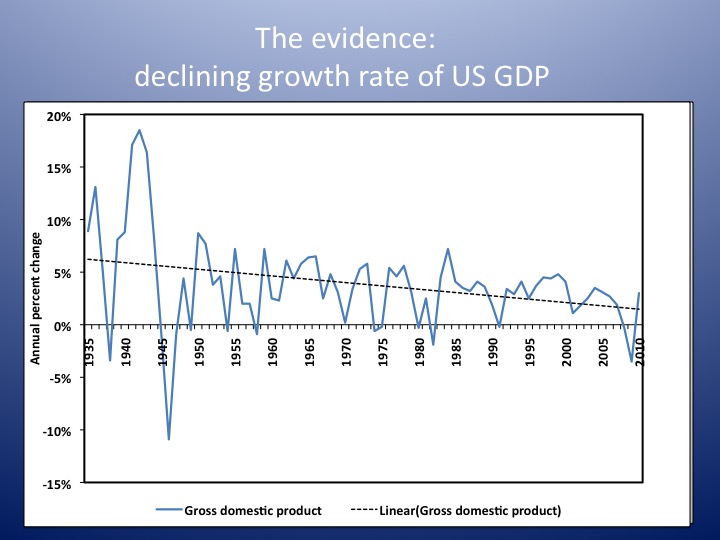
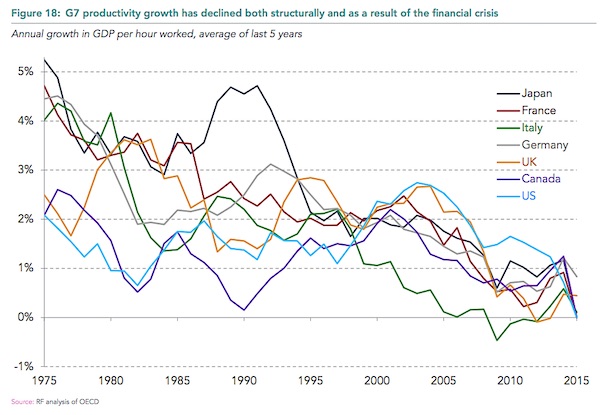
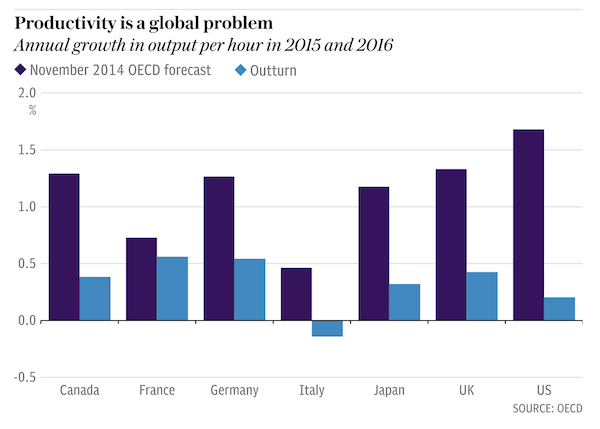
Britain’s productivity crisis is not going to come to an end any time soon. That is the verdict of the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR), the official watchdog of Britain’s government finances, which monitors the economy closely. Productivity is crucial to economic growth and to living standards – workers can be paid more and work less if they produce more output for every hour worked. But since the financial crisis productivity has barely budged. Back in 2010 the OBR predicted productivity would resume its pre-crash trend, rising by about 15pc from 2009 to 2016. That did not happen. Each time the OBR made a forecast – at the Budget or the Autumn Statement – it thought the strong old trend rate would pick up. But it did not. Productivity remained stubbornly low.
After seven years of persisting with this forecast, the OBR has thrown in the towel. “As the period of historically weak productivity growth lengthens, it seems less plausible to assume that potential and actual productivity growth will recover over the medium term to the extent assumed in our most recent forecasts,” the watchdog said. “Over the past five years, growth in output per hour has averaged 0.2%. This looks set to be a better guide to productivity growth in 2017 than our March forecast.” That paints a gloomy picture for future economic growth, pay rises and the government’s finances. The report notes that “some commentators have argued that advanced economies have entered an era of permanently subdued productivity growth for structural reasons”. However, the OBR does not quite go that far.
This puzzle is a global one. Productivity growth has been disappointing across much of the rich world. But that is barely a silver lining, particularly when the underlying causes are hard to establish. At least the global nature of the problem allows for more ‘cures’ to be attempted. The US is currently engaged in monetary tightening. Interest rates are rising and quantitative easing will soon start to be wound back – gently, but still significantly. The move by Janet Yellen and her colleagues at the Federal Reserve should begin to test the idea that low interest rates are in part to blame for low productivity. At some point the theory around employment will surely have to be tested.

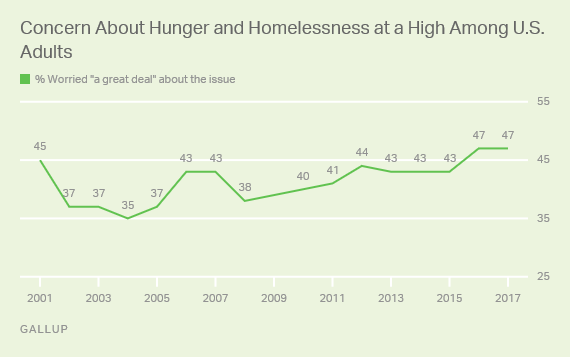
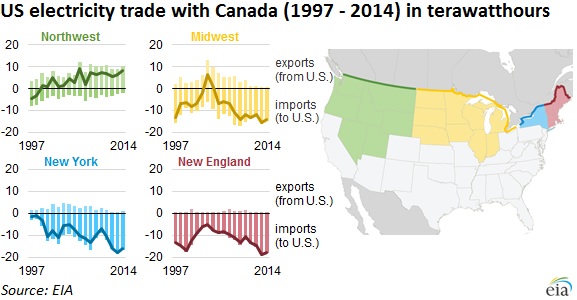
That’s a lot of green.
• The World Must Spend $2.7 Trillion on Charging Stations for Tesla to Fly (BBG)
A $2.7 trillion chasm stands between electric vehicles and the infrastructure needed to make them popular. That’s how much Morgan Stanley says must be spent on building the supporting ecosystem for EVs to reach its forecast of 526 million units by 2040. The estimate, projected by scaling up Tesla Inc.’s current network of charging stations to assembly plants, shows how infrastructure can be the biggest bottleneck for the industry’s expansion, Morgan Stanley said in a Oct. 9 report. To support half a billion EVs, the projected investment will require a mix of private and public funding across regions and sectors, and any auto company or government with aggressive targets will be at risk without the necessary infrastructure, the report said.
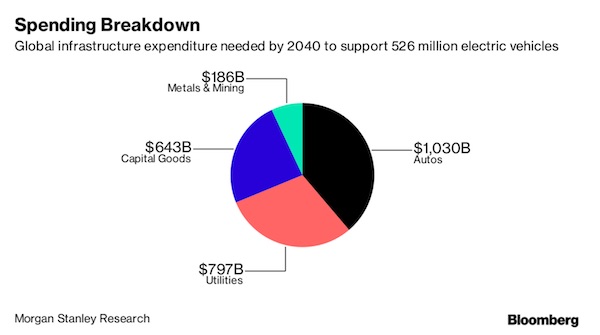
The industry shift to battery-powered cars is being helped by government efforts to reduce air pollution by phasing out fossil fuel-powered engines. China, which has vowed to cap its carbon emissions by 2030 and improve air quality, recently joined the U.K. and France in seeking a timetable for the elimination of vehicles using gasoline and diesel. China will become the largest EV market, accounting for about a third of global infrastructure spending by 2040, according to Morgan Stanley.

Just wait for the dominoes to drop. “In Central Japan Railway’s bullet trains, 310 of the tested parts were found to be sub-standard..”
• Bullet Train Wheel Parts Made By Kobe Steel Failed Quality Tests (BBG)
Kobe Steel’s fake data scandal penetrated deeper into the most hallowed corners of Japanese industry as iconic bullet trains were found with sub-standard parts supplied by the steelmaker. While they don’t pose any safety risks, aluminum components connecting wheels to train cars failed Japanese industry standards, according to Central Japan Railway, which operates the high-speed trains between Tokyo and Osaka. West Japan Railway, which runs services from Osaka to Fukuoka, also found sub-standard parts made by Kobe Steel. The latest scandal to hit Japan’s manufacturing industry erupted on Sunday after the country’s third-largest steel producer admitted it faked data about the strength and durability of some aluminum and copper.
As scores of clients from Toyota to General Motors scrambled to determine if they used the suspect materials and whether safety was compromised in their cars, trains and planes, the company said two more products were affected and further cases could come to light. “I deeply apologize for causing concern to many people, including all users and consumers,” Kobe Steel CEO Hiroya Kawasaki said at a meeting with a senior official from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry on Thursday. He said trust in the company has fallen to “zero” and he will work to restore its reputation. “Safety is the top priority.” Shares in the company rebounded 1% Thursday, after plunging 36% over the previous two days. About $1.6 billion of the company’s market value has been wiped out since the revelations were made.
Figures were systematically fabricated at all four of Kobe Steel’s local aluminum plants, with the practice dating back as long as 10 years for some products, the company said Sunday. Data was also faked for iron ore powder and target materials that are used in DVDs and LCD screens, it said three days later. In Central Japan Railway’s bullet trains, 310 of the tested parts were found to be sub-standard and will be replaced at the next regular inspection, spokesman Haruhiko Tomikubo said. They were produced by Kobe Steel over the past five years, he said.

I suggest mass recalls before Kobe is bankrupt. Or GM will have to pay up.
• General Motors Checking Impact Of Kobe Steel Data Cheating (R.)
General Motors is checking whether its cars contain falsely certified parts or components sourced from Japan’s Kobe Steel, the latest major automaker to be dragged into the cheating scandal. “General Motors is aware of the reports of material deviation in Kobe Steel copper and aluminum products,” spokesman Nick Richards told Reuters, confirming a Kyodo News report. “We are investigating any potential impact and do not have any additional comments at this time” GM joins automakers including Toyota and as many as 200 other companies that have received parts sourced from Kobe Steel as the scandal reverberates through global supply chains. On Wednesday fresh revelations showed data fabrication at the steelmaker was more widespread than it initially said, as the company joins a list of Japanese manufacturers that have admitted to similar misconduct in recent years.
Investors, worried about the financial impact and potential legal fallout, again dumped Kobe Steel stock, wiping about $1.6 billion off its market value in two days. On Thursday in Tokyo, the shares stabilized and were up 1.1% [..] Kobe Steel President Hiroya Kawasaki said on Thursday his company would do the utmost to investigate the reason for the tampering and take measures to prevent further occurrences. He was speaking before meeting an industry ministry official to discuss the matter. The steelmaker admitted at the weekend it had falsified data about the quality of aluminum and copper products used in cars, aircraft, space rockets and defense equipment, a further hit to Japanese manufacturers’ reputation for quality products. Kobe Steel said late on Wednesday it found 70 cases of tampering with data on materials used in optical disks and liquid crystal displays at its Kobelco Research Institute Inc, which makes and tests products for the company.

“Dollar denominated debt owed by governments and non-bank corporations in advanced economies with currencies other than the dollar has reached 26% of their GDP, nearly three times the level of the year 2000.”
And now raise rates….
• De-dollarization Not Now (WS)
China announced today that it would sell $2 billion in government bonds denominated in US dollars. The offering will be China’s largest dollar-bond sale ever. The last time China sold dollar-bonds was in 2004. Investors around the globe are eager to hand China their US dollars, in exchange for a somewhat higher yield. The 10-year US Treasury yield is currently 2.34%. The 10-year yield on similar Chinese sovereign debt is 3.67%. Credit downgrade, no problem. In September, Standard & Poor’s downgraded China’s debt (to A+) for the first time in 19 years, on worries that the borrowing binge in China will continue, and that this growing mountain of debt will make it harder for China to handle a financial shock, such as a banking crisis.
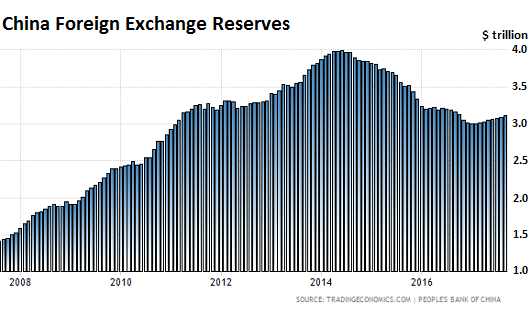
Moody’s had already downgraded China in May (to A1) for the first time in 30 years. “The downgrade reflects Moody’s expectation that China’s financial strength will erode somewhat over the coming years, with economy-wide debt continuing to rise as potential growth slows,” it said. These downgrades put Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s on the same page with Fitch, which had downgraded China in 2013. But the Chinese Government doesn’t exactly need dollars. On October 9th, it reported that foreign exchange reserves – including $1.15 trillion in US Treasuries, according the US Treasury Department – rose to $3.11 trillion at the end of September, an 11-month high, as its crackdown on capital flight is bearing fruit (via Trading Economics):
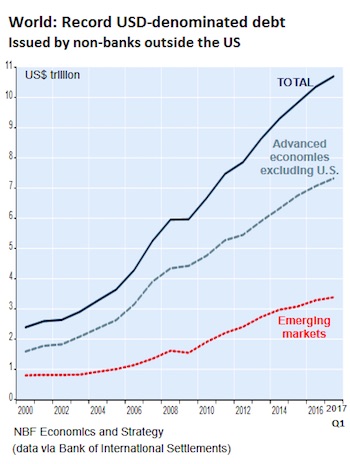
[..] In total, emerging market governments and companies have issued $509 billion in dollar-denominated bonds so far this year, a new record. Dollar-denominated junk bond issuance in the developing world has hit a record $221 billion so far this year, up 60% from the total for the entire year 2016. [..] Dollar denominated debt owed by governments and non-bank corporations in advanced economies with currencies other than the dollar has reached 26% of their GDP, nearly three times the level of the year 2000. Borrowing in foreign currencies increases the default risks.
When the dollar rises against the currency that the borrower uses – which is a constant issue with many emerging market currencies that have much higher inflation rates than the US – borrowers can find it impossible to service their dollar-denominated debts. And when these economies or corporate cash flows slow down, central banks in these countries cannot print dollars to bail out their governments and largest companies. Financial crises have been made of this material, including the Asian Financial Crisis and the Tequila Crisis in Mexico. But today, none of this matters. What matters are yield-chasing investors that, after years of zero-interest-rate-policy brainwashing by central banks, can no longer see any risks at all. And the dollar remains the foreign currency of choice.

The new Silk Road isn’t a Chinese idea. The US toyed with it. Xi has realized it’s the way to export China’s Ponzi. They will insist on having countries use Chinese products, and paying for them. Often with Chinese loans.
• Xi’s Legacy May Rest on the World’s Biggest Infrastructure Project (BBG)
There’s one ambitious scheme of Xi’s about whose importance we may already be certain, one that will leave a big mark one way or another. It’s fundamentally geopolitical in nature, though it may ultimately maintain China’s historical sense of empire. The project is the Belt and Road Initiative, which aims to be nothing less than the biggest infrastructure program the world has ever seen. Sometimes known as One Belt One Road, or OBOR, it will attempt to integrate China’s markets with those on three continents, Asia, Europe, and Africa. The idea is to build an integrated rail network crisscrossing Central and Southeast Asia and reaching far into Europe, while constructing large, modern deep-water ports to link shipping from China and the surrounding western Pacific to South Asia, Kenya, Tanzania, and beyond.
So far, more than 60 countries have signed on or appear inclined to participate. Together they account for about 70% of the Earth’s population and 75% of its known energy supplies. Finding reasonably accurate statistics about Chinese geopolitical initiatives has long been a challenge, but under Xi, OBOR appears to have amassed well over $100 billion in commitments from various Chinese or Chinese-derived institutions, including the recently formed Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, which some already see as a rival to the World Bank. Backed by Xi’s personal prestige, heft on this scale has turned OBOR into a kind of organizing motif for China’s politics and economy. The clear hope is that it will cement the country’s place as a leading, and, perhaps someday soon, the preeminent center of gravity in the world.
[..] Although downplayed in boosterish Chinese discussions, Beijing’s desire for markets to help soak up some of its overcapacity in steel and cement is an important motive behind OBOR’s focus on infrastructure—especially railroad lines. In 2015, China’s steel surplus was equivalent to the total output of the next four producers, Japan, India, the U.S., and Russia. Much the same is true for other key industrial materials. This push to develop outlets for China’s badly unbalanced economy has led many to skip over basic questions about the economic rationale for a vast rail network in the first place. If the ultimate idea is to link East and West with rapid, modern freight trains, as is often suggested, what’s the category of products that will benefit enough from these connections to make them profitable? Perishable and highly time-sensitive goods will almost always be transported by air. Meanwhile, no train, no matter how modern, will beat ocean freight for capacity or price per mile.

Sobering.
• Retirement in Australia is Unrealisable For Most Workers (Satyajit Das)
Australians make up barely 0.3% of the globe’s population and yet hold $2.1 trillion in pension savings – the world’s fourth-largest such pool. Those assets are viewed as a measure of the country’s wealth and economic resilience, and seem to guarantee a high standard of living for Australians well into the future. Other developed nations, aging even faster than Australia and subject to fraying safety nets, have held up the system as a world-class model to fund retirement. In fact, its future looks nowhere near so bright. Australia’s so-called superannuation scheme is a defined contribution pension plan funded by mandatory employer contributions (currently 9.5%, scheduled to rise gradually to 12% by 2025). Employees can supplement those savings and are encouraged to do so with tax breaks, pension fund earnings and generous benefits.
The gaudy size of the investment pool, however, masks serious vulnerabilities. First, the focus on assets ignores liabilities, especially Australia’s $1.8 trillion in household debt as well as total non-financial debt of around $3.5 trillion. It also overlooks Australia’s foreign debt, which has reached over 50% of GDP – the result of the substantial capital imports needed to finance current account deficits that have persisted despite the recent commodity boom, strong terms of trade and record exports. Second, the savings must stretch further than ever before, covering not just the income needs of retirees but their rapidly increasing healthcare costs. In the current low-income environment, investment earnings have shrunk to the point where they alone can’t cover expenses. That’s reducing the capital amount left to pass on as a legacy.
Third, the financial assets held in the system (equities, real estate, etc.) have to be converted into cash at current values when they’re redeemed, not at today’s inflated values. Those values are quite likely to decline, especially as a large cohort of Australians retires around the same time, driving up supply. Meanwhile, weak public finances mean that government funding for healthcare is likely to drop, forcing retirees to liquidate their investments faster and further suppressing values. Fourth, the substantial size of these savings and the large annual inflow (more than $100 billion per year) into asset managers has artificially inflated values of domestic financial assets, given the modest size of the Australian capital markets. As retirees increasingly draw down their savings, withdrawals may be greater than new inflows, reducing demand for these financial assets.
[..] The real lesson of Australia’s experience may be that the idea of retirement is unrealisable for most workers, who will almost certainly have to work beyond their expected retirement dates if they want to sustain their lifestyles. Governments have implicitly recognised this fact by abandoning mandatory retirement requirements, increasing the minimum retirement age, tightening eligibility criteria for benefits and reducing tax concessions for this form of saving. If the world’s best pension system can’t succeed, we’re going to have to rethink retirement itself.

I must admit, the circus continues to amaze. By now, everyone involved on the UK side is just trying to save their political careers. But the Tories want to hold on to power too, and those two things will conflict. They’ll need to make a choice.
• With Brexit Talks Stuck, Britain Is Preparing For The Worst (BBG)
With Brexit talks stuck, the U.K. is preparing for the worst. As the fifth round of negotiations draws to a close on Thursday, progress is so scant that the European side is stepping back from concessions it was said to be considering last month. The Commission won’t talk about trade before getting assurances that the U.K. will pay its dues, and with less than 18 months to go until the country tumbles out of the bloc, the focus in London has turned to contingency planning. Philip Hammond, the pro-EU chancellor of the exchequer, says he’s reluctant to spend cash on a Plan B just to score negotiating points. But he’ll start releasing money as soon as January if progress hasn’t been made in talks. Judging by the latest EU rhetoric, the chances of that happening are growing.
The goodwill that Prime Minister Theresa May generated in her speech in Florence, where she promised to pay into the EU budget for two years after Brexit and asked in return for a transition period so businesses can prepare for the split, hasn’t translated into progress in talks. Meanwhile May’s Conservatives remain deeply divided on the shape of Brexit, with the premier struggling each week to tread a careful line between rival camps. The political establishment is so conflicted that late on Wednesday two politicians from opposing parties joined forces to try and effectively bind May’s hands by tabling an amendment that would enshrine a two-year transition in law. Pound investors are expecting swings in the currency to get more dramatic over the next three months, options show, as political uncertainty unnerves traders.

The torture never stops. And in the end the Germans win.
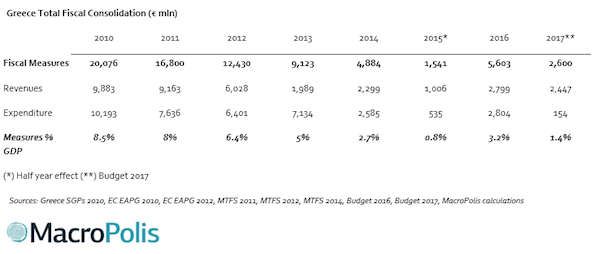
• IMF Report Suggests New Greek Debt Measures Necessary (K.)
The third review of Greece’s third bailout could hit a snag after the International Monetary Fund’s forecast Thursday that the country’s primary surplus in 2018 will be at 2.2% of GDP– significantly lower than the 3.5% predicted by European insititutions and stipulated in the government’s draft budget and the bailout agreement. The latest forecast included in the IMF’s Fiscal Monitor report released Wednesday could, analysts believe, be a source of misery not just for Athens, which may once again be forced to look down the barrel of fresh measures next year to the tune of €2.3 billion – 1.3% of GDP – but for its European Union partners as well, who will have to decide whether to go along with the IMF’s forecast or not.
If they do not, then the risk of the IMF leaving the Greek program will be higher. If, however, European lenders go along with IMF’s forecast, which it first made in July, then Athens is concerned that they may revise their own predictions downward in order to placate the organization – as was the case during the second review – in order to ensure that it remains on board with the Greek program. The latter outcome could, analysts reckon, be the more likely one given that Germany’s Free Democrats (FDP), expected to form part of Chancellor Angela Merkel’s governing coalition, have stated that they will agree to an aid program for Greece on the condition that the IMF takes part in the Greek bailout.