
Marc Riboud Paris 1953

Endlessly ironic that publications like the Hill write on this. They are more responsible for all the nonsense than any politicians are.
• Dems Push Leaders To Talk Less About Russia (Hill)
Frustrated Democrats hoping to elevate their election fortunes have a resounding message for party leaders: Stop talking so much about Russia. Democratic leaders have been beating the drum this year over the ongoing probes into the Trump administration’s potential ties to Moscow, taking every opportunity to highlight the saga and forcing floor votes designed to uncover any business dealings the president might have with Russian figures. But rank-and-file Democrats say the Russia-Trump narrative is simply a non-issue with district voters, who are much more worried about bread-and-butter economic concerns like jobs, wages and the cost of education and healthcare.
In the wake of a string of special-election defeats, an increasing number of Democrats are calling for an adjustment in party messaging, one that swings the focus from Russia to the economy. The outcome of the 2018 elections, they say, hinges on how well the Democrats manage that shift. “We can’t just talk about Russia because people back in Ohio aren’t really talking that much about Russia, about Putin, about Michael Flynn,” Rep. Tim Ryan (D-Ohio) told MSNBC Thursday. “They’re trying to figure out how they’re going to make the mortgage payment, how they’re going to pay for their kids to go to college, what their energy bill looks like. “And if we don’t talk more about their interest than we do about how we’re so angry with Donald Trump and everything that’s going on,” he added, “then we’re never going to be able to win elections.”
Ryan is among the small group of Democrats who are sounding calls for a changing of the guard atop the party’s leadership hierarchy following Tuesday’s special election defeat in Georgia — the Democrats’ fourth loss since Trump took office. But Ryan is hardly alone in urging party leaders to hone their 2018 message. Rep. Tim Walz (D-Minn.) has been paying particularly close attention to voters’ concerns because he’s running for governor in 2018. The Russia-Trump investigation, he said, isn’t on their radar. “I did a 22-county tour. … Nobody’s focusing on that,” Walz said. “That’s not to say that they don’t think Russia and those things are important, [but] it’s certainly not top on their minds.”

Elections it is then. A rudderless society.
• UK Housing Crisis Threatens A Million Families With Eviction By 2020 (G.)
More than a million households living in private rented accommodation are at risk of becoming homeless by 2020 because of rising rents, benefit freezes and a lack of social housing, according to a devastating new report into the UK’s escalating housing crisis. The study by the homelessness charity Shelter shows that rising numbers of families on low incomes are not only unable to afford to buy their own home but are also struggling to pay even the lowest available rents in the private sector, leading to ever higher levels of eviction and homelessness. The findings will place greater pressure on the government over housing policy following the Grenfell Tower fire disaster in west London, which exposed the neglect and disregard for people living in council-owned properties in one of the wealthiest areas of the capital.
The Shelter report highlights how a crisis of affordability and provision is gripping millions with no option but to look for homes in the private rented sector due to a shortage of social housing. Shelter says that in 83% of areas of England, people in the private rented sector now face a substantial monthly shortfall between the housing benefit they receive and the cheapest rents, and that this will rise as austerity bites and the lack of properties tilts the balance more in favour of landlords. Across the UK the charity has calculated that, if the housing benefit freeze remains in place as planned until 2020, more than a million households, including 375,000 with at least one person in work, could be forced out of their homes. It estimates that 211,000 households in which no one works because of disability could be forced to go.
Graeme Brown, the interim chief executive at Shelter, said: “The current freeze on housing benefit is pushing hundreds of thousands of private renters dangerously close to breaking point at a time when homelessness is rising.” A total of 14,420 households were accepted by local authorities as homeless between October and December 2016, up by more than half since 2009 – with 78% of the increase since 2011 being the result of people losing their previous private tenancy. Local authorities are under a legal obligation to find emergency accommodation, such as in bed and breakfasts.

A kernel of truth does not a good reasoning make.,
• The Answer Is Wages, Not Capital (Angusto)
As in any other religion, faith lies behind capitalism. Faith that capital is a panacea always and in any situation: to push economic growth or to help less developed countries to catch up. Yet the fact is that the EU countries that were the main receivers of cohesion funds, before the extension to the East, later became rescued countries – and we have never before had as much capital on tap along with current low growth.
Both these facts should be enough to break the faith in capital or, at least, to recognise its limits. Let’s see those limits in the above-mentioned causes. The virtue of capital transfers to help low developed countries is based in old Marshall Plan history, which attributes the successful German recovery after WW2 to USA loans. Sure, those loans helped, but the necessary knowledge was already there and the capital transfers allowed the Germans to rebuild their supply capacity. Conversely, in the EU rescued countries, entering the EU came with a local supply capacity destruction, in Schumpeterian terms, for which cohesion funds were unable to compensate. As a result, their domestic demand outstripped internal supply and trade deficits became recurrent until the financial crash.
The key element was not capital but knowledge and its absence or availability in both situations; something very obvious but all too often forgotten. If capital has any virtue it comes from its origin: the capacity to produce output sufficient to recover the inputs used, to satisfy consumption needs and to save a part to be invested as new inputs for raising future output. It means that the virtue is not in the savings/capital itself but in the capacity to generate it. That’s why capital transfers that simply increased the receivers’ inputs provision, without increasing the output/input ratio –or system efficiency–, were in the end wasted money. To avoid this, it would have been necessary to increase the receivers’ efficiency, which is much more correlated with parameters like educational levels than with capitalization! Again, knowledge is the key question.
Furthermore, capital on its own is not only unable to help less developed countries catch up on their wealthier peers but it’s also unable to propel economic growth on its own, as we are now seeing. After years of letting profits grow at the cost of wages, hoping that greater capital would bring greater growth, now we hear companies claiming that they do not invest because they do not have sufficient demand to justify the investment. The clear solution would be to increase wages, but no single company will do it out of fear that the others won’t follow suit. In fact, what any company hopes is that the others increase wages and salaries but not itself. That’s why a global agent is needed: trade unions and the public administration! The latter to increase its spending to guarantee full employment and the former profiting from full employment to bargain higher salaries.

Bloomberg’s valiant attempt to make you see it doesn’t understand energy. Well done!
• Not All Fossil Fuels Are Going Extinct (BBG)
Bloomberg New Energy Finance’s latest New Energy Outlook points the way to a sunny, windy future for the global electric power industry. That doesn’t mean that fossil fuels (or nuclear power) will vanish. It also doesn’t mean that all fossil fuels are the same. The future of natural gas and coal is a tale of two resources — one a story of rising fortunes, the other of slow decline. The latest outlook on natural gas is brighter than ever: BNEF’s forecast for gas shows a higher estimate for consumption in 2040 than in previous years, with a short decline at the end of this decade.
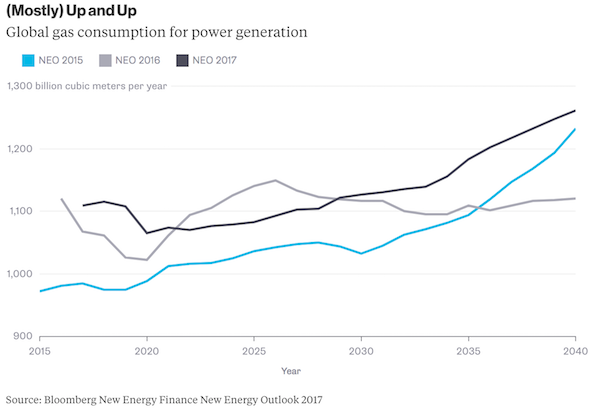
Coal is a different matter. Coal demand is expected to peak late next decade, then decline almost every year to reach a low of 3.1 billion metric tons in 2040, about 25% lower than at its peak.
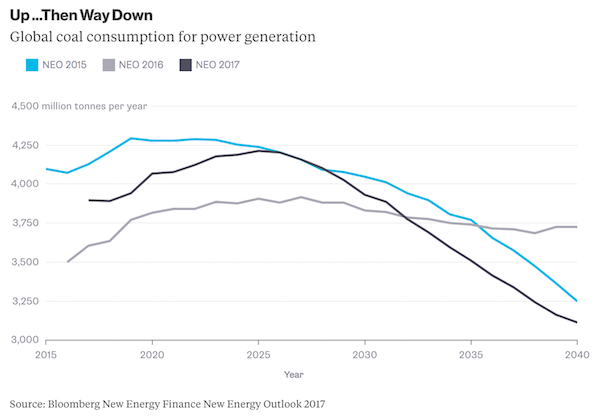
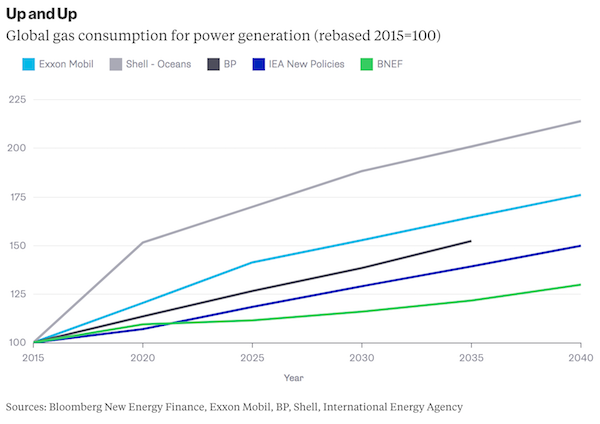
This long-term outlook is nuanced, as it should be. The aggregated demand for each fuel from 2020 to 2040 has not changed much in three successive New Energy Outlook reports. Total gas consumption has only increased 6% since the 2015 report, while coal consumption from 2020 to 2040 – despite the plunge that is now expected, as noted above – has only changed 3.5%, and was exactly the same in 2016. However, the shape of that coal curve is still important, even if the volume hasn’t changed much. A coal mine that opens today could have a 60-year life, but it is likely to be one fraught with oversupply and competition from other coal producers, as well as other technologies. So how does the 2017 New Energy Outlook for gas and coal compare to how major oil companies and the International Energy Agency see it? For gas, everyone agrees: Consumption grows. Shell expects gas consumption to more than double and, perhaps not surprisingly, Exxon Mobil and BP also expect consumption to increase at least 50%. BNEF’s expectations are a bit more muted.

Looks a tad hippyish, but as I’ve said a million times, no society should ever sell its basics to anyone. It’s lethal.
• Reclaiming Public Services (TNI)
Reclaiming Public Services is vital reading for anyone interested in the future of local, democratic services like energy, water and health care. This is an in-depth world tour of new initiatives in public ownership and the variety of approaches to deprivatisation. From New Delhi to Barcelona, from Argentina to Germany, thousands of politicians, public officials, workers, unions and social movements are reclaiming or creating public services to address people’s basic needs and respond to environmental challenges. They do this most often at the local level. Our research shows that there have been at least 835 examples of (re)municipalisation of public services worldwide since 2000, involving more than 1,600 municipalities in 45 countries.
Why are people around the world reclaiming essential services from private operators and bringing their delivery back into the public sphere? There are many motivations behind (re)municipalisation initiatives: a goal to end private sector abuse or labour violations; a desire to regain control over the local economy and resources; a wish to provide people with affordable services; or an intention to implement ambitious climate strategies. Remunicipalisation is taking place in small towns and in capital cities, following different models of public ownership and with various levels of involvement by citizens and workers. Out of this diversity a coherent picture is nevertheless emerging: it is possible to build efficient, democratic and affordable public services. Ever declining service quality and ever increasing prices are not inevitable. More and more people and cities are closing the chapter on privatisation, and putting essential services back into public hands.
Ulli Sima, Vienna City Councilor for the Environment and Wiener Stadtwerke: “As early as 2001, Vienna protected drinking water with a constitutional decision. Municipal services must remain public and should not be sacrificed to private profit. We want to ally with other cities for strong municipal servicest.” Eloi Badia, the Barcelona Councilor for presidency, water and energy: “It is important to demystify the process of privatisation that has been launched in recent years by several governments, because it’s a model that has not proved its efficiency, failing to offer a better service or a better price.”
Célia Blauel, President of Eau de Paris and Deputy Mayor of Paris in charge of the environment, sustainable development, water and the energy-climate plan: “Bringing local public services under public control is a major democratic issue, especially for such essential services as energy or water. It means greater transparency and better citizen supervision. In the context of climate change, it can contribute to leading our cities toward energy efficiency, the development of renewables, the conservation of our natural resources, and the right to water. ”

Yesterday I wrote: “To paraphrase Juncker: “When things get serious in Europe, no rules or laws are immune to lies.”
Today, Don Quijones says: “..when things get serious in the EU, laws get bent.”
That ends to the Cyprus model before it was even truly inaugurated.
• Contagion from the 2 Friday-Night Bank Collapses in Italy? (DQ)
When things get serious in the EU, laws get bent and loopholes get exploited. That is what is happening right now in Italy, where the banking crisis has reached tipping point. The ECB, together with the Italian government, have just this weekend to resolve Banca Popolare di Vicenza and Veneto Banca, two zombie banks that the ECB, on Friday night, ordered to be liquidated. Unlike Monte dei Pachi di Siena, they will not be bailed out primarily with public funds. Senior bondholders and depositors will be protected while shareholders and subordinate bondholders will lose their shirts. However, as the German daily Welt points out, subordinate bondholders at Monte dei Pachi di Siena had billions of euros at stake, much of it owned by its own retail customers who’d been sold these bonds instead of savings products such as CDs. So for political reasons, they were bailed out.
Junior bonds play a smaller role at the two Veneto-based banks. According to the Welt, the two banks combined have €1.33 billion (at face value) in junior bonds outstanding. They last traded between 1 cent and 3 cents on the euro. So worthless. Only about €100 million were sold to their own customers, not enough to cause a political ruckus in Italy. So they will be crushed. The good assets and the liabilities, such as the deposits, will be transferred to a competing bank. According to a rescue plan apparently drawn up by investment bank Rothschild that surfaced a few days ago, Intesa Sao Paolo, Italy’s second largest bank, would get these good assets and the deposits (liabilities), for the token sum of €1, while all the toxic assets (non-performing loans) would be shuffled off to a state-owned “bad bank” – and thus, the taxpayer.
According to the Italian daily Il Sole 24 Ore, the bad bank would be left holding over €20 billion of festering assets. “Intesa gets a free gift, the state takes on all the bad stuff and the taxpayer pays,” said at the time Renato Brunetta, parliamentary leader for former prime minister Silvio Berlusconi’s Forza Italia party. It is testament to just how desperate the situation has become in Italy’s banking crisis. The country’s largest lender, Unicredit, is in no position to help out: it had to raise €13 billion of new capital earlier this year just to keep itself afloat. Whether the deal with Intesa is still possible after the ECB’s decision to liquidate the banks, and what form this deal, if any, will take, and how much the taxpayer will have to fork over, and how to sugarcoat this in the most palatable terms is what the Italian government is currently trying to hammer out in its emergency meeting.

How anyone can label this anything but ‘criminal’ is beyond me.
• Health Spending In Greece Down 40% In 2009-2015 (Amna)
Health spending in Greece plunged 40% in the 2009-2015 period, Deloitte said in a survey released on Thursday. According to the survey, health spending fell to €14.1 billion in 2014, hit by a significant shrinking in medical/pharmaceutical coverage by the state and the social insurance system. It also stressed that this sharp decline mostly hit pharmacies and other professionals in the health sector and less the country’s hospitals. Hospital spending fell to €6.2 billion in 2015, from €9.0 billion in 2009, for an average annual decline of 6.0%, while average annual decline in the retail sector reached 7.0% and 9.0%, respectively. Deloitte said the state social insurance system covers 59.1% of total health spending in Greece, with patients covering 35.5% -a %age significantly higher compared with other European countries (UK 9.5%, France 6.7%, Italy 21.7%).
3.7% of total health spending is covered by private insurance contracts. Private hospitals were also hit during the 2009-2015 period, leading to more consolidation as the number of private hospitals fell by 6.0% and their size grew by around 1.0%. The total number of private and state hospitals in Greece was 283, mostly in Attica, offering 45,900 beds. The survey said that the number of beds surpassed demand by at least 18%. The survey noted that health spending recovered slightly to €14.7 billion in 2015 and stressed that international investors were showing strong interest for business deals in Greece.

Want Moody’s to be nice to you? Slash your health system by 40%.
• Moody’s Raises Greece’s Sovereign Bond Rating After Bailout (AFP)
Credit ratings agency Moody’s late Friday raised Greece’s long-term issuer rating to “Caa2” from “Caa3” after eurozone governments extended a credit lifeline to the country. Moody’s also changed its outlook to “positive”, up from “stable” previously, saying it saw signs that the heavily indebted country’s economy was stabilising. It pointed to a mid-June agreement reached by Greece’s creditors to relaunch an aid plan to the country, which had been blocked for months due to disagreements between eurozone countries – especially Germany – and the IMF. The move reduces the spectre of a short-term crisis, after eurozone governments agreed to give Greece a new credit lifeline of some €8.5 billion ($9.5 billion). Moody’s said it expected Greece’s debt ratio to stabilise this year at 179% of GDP, adding that growth should return to the economy this year and next.
Greece returned to growth in the first quarter of 2017, with a 0.4% increase in GDP, according to figures revised upwards in early June. “It is too early to conclude that economic growth will be durable,” Moody’s said. The IMF, which links financial aid to debt relief, has also signed an “agreement in principle” to allow immediate assistance that avoids a payment crisis in Athens this summer. It said Thursday that negotiations with creditors for debt reduction had “made progress”. “If we did not think there was a good chance of reaching a debt deal, we would not have chosen that route,” an IMF spokesman said. Moody’s also raised the long-term country ceilings for foreign-currency and local-currency bonds to B3 from Caa2.

Another kernel of truth that proves writing articles is not that easy.
• Greece, A Guinea Pig For A Cashless And Controlled Society (MPN)
The IMF, which day after day is busy “saving” economically suffering countries such as Greece, also happens to agree with this brave new worldview. In a working paper titled “The Macroeconomics of De-Cashing,” which the IMF claims does not necessarily represent its official views, the fund nevertheless provides a blueprint with which governments around the world could begin to phase out cash. This process would commence with “initial and largely uncontested steps” (such as the phasing out of large-denomination bills or the placement of upper limits on cash transactions). This process would then be furthered largely by the private sector, providing cashless payment options for people’s “convenience,” rather than risk popular objections to policy-led decashing.
The IMF, which certainly has a sterling track record of sticking up for the poor and vulnerable in society, comforts us by saying that these policies should be implemented in ways that would augment “economic and social benefits.” These suggestions, which of course the IMF does not necessarily officially agree with, have already begun to be implemented to a significant extent in the IMF debt colony known officially as Greece, where the IMF has been implementing “socially fair and just” austerity policies since 2010, which have resulted, during this period, in a GDP decline of over 25%, unemployment levels exceeding 28%, repeated cuts to what are now poverty-level salaries and pensions, and a “brain drain” of over 500,000 people—largely young and university-educated—migrating out of Greece.
Indeed, it could be said that Greece is being used as a guinea pig not just for a grand neoliberal experiment in both austerity, but de-cashing as well. The examples are many, and they have found fertile ground in a country whose populace remains shell-shocked by eight years of economic depression. A new law that came into effect on January 1 incentivizes going cashless by setting a minimum threshold of spending at least 10% of one’s income via credit, debit, or prepaid card in order to attain a somewhat higher tax-free threshold. Beginning July 27, dozens of categories of businesses in Greece will be required to install aptly-acronymized “POS” (point-of-sale) card readers and to accept payments by card.
usinesses are also required to post a notice, typically by the entrance or point of sale, stating whether card payments are accepted or not. Another new piece of legislation, in effect as of June 1, requires salaries to be paid via direct electronic transfers to bank accounts. Furthermore, cash transactions of over €500 have been outlawed. In Greece, where in the eyes of the state citizens are guilty even if proven innocent, capital controls have been implemented preventing ATM cash withdrawals of over €840 every two weeks. These capital controls, in varying forms, have been in place for two years with no end in sight, choking small businesses that are already suffering.

Inevitable. Chemists go where they smell money.
• Monsanto And Bayer Are Maneuvering To Take Over The Cannabis Industry (WT)
You may remember hearing back in September that Bayer, the largest pharmaceutical company in the world, made a deal to buy out Monsanto for $66 billion. Although Monsanto was voted the most evil company in the world in 2013 and its reputation has continued to fall since, Bayer still went ahead with the buyout. A merger between these two companies is unsurprising, as though they both have long histories of involvement with Nazism and chemical weapons like agent orange which have devastated Vietnam since the war. In fact, Bayer began as a break-off company of the infamous IG Farben, which produced the chemical weapons used on the Jews during the Nazi reign. After the war, Farben was forced to break up into several companies, including BASF, Hoeschst, and Bayer.
Soon after at the Nuremberg trials, 24 Farben executives were sent to prison for crimes against humanity. However, in a matter of just 7 years each of them was released and began filling high positions in each of the former Farben companies, and many of them began working for the Russian, British, and American governments through a joint intelligence venture called “Operation Paperclip”: (“IG (Interessengemeinschaft) stands for “Association of Common Interests”: The IG Farben cartel included BASF, Bayer, Hoechst, and other German chemical and pharmaceutical companies. As documents show, IG Farben was intimately involved with the human experimental atrocities committed by Mengele at Auschwitz. A German watchdog organization, the GBG Network, maintains copious documents and tracks Bayer Pharmaceutical activities.” – Alliance for Human Research Protection)
After all these years, Bayer is now richer and more powerful than their predecessor company I.G. Farben ever was. According to Big Buds Magazine, Monsanto and Scotts Miracle-Gro have a “deep business partnership” and plan on taking over the cannabis industry. Hawthorne, a front group for Scotts, has already purchased three of the major cannabis growing companies: General Hydroponics, Botanicare, and Gavita. Many other hydroponics companies have also reported attempted buyouts by Hawthorne. (“They want to bypass hydroponics retail stores…When we said we won’t get in bed with them they said, ‘Well, we could just buy your whole company like we did with Gavita and do whatever we want.’” – Hydroponics Lighting Representative) Jim Hagedorn, CEO of Scotts Miracle-Gro, has even said that he plans to “invest, like, half a billion in [taking over] the pot business… It is the biggest thing I’ve ever seen in lawn and garden.”
He has also invested in companies such as Leaf, which grows cannabis in an electronically regulated indoor terrarium accessible via smartphone. It is logical that Bayer, being the parent company, would work together with Monsanto in order to share secrets which would advance mutual business. Many people in the cannabis industry have been warning about this, including Michael Straumietis, founder and owner of Advanced Nutrients. (“Monsanto and Bayer share information about genetically modifying crops,” Straumietis notes. “Bayer partners with GW Pharmaceuticals, which grows its own proprietary marijuana genetics. It’s logical to conclude that Monsanto and Bayer want to create GMO marijuana.” – Michael Straumietis)








