Rembrandt van Rijn Study of the Head and Clasped Hands of a Young Man as Christ in Prayer 1655

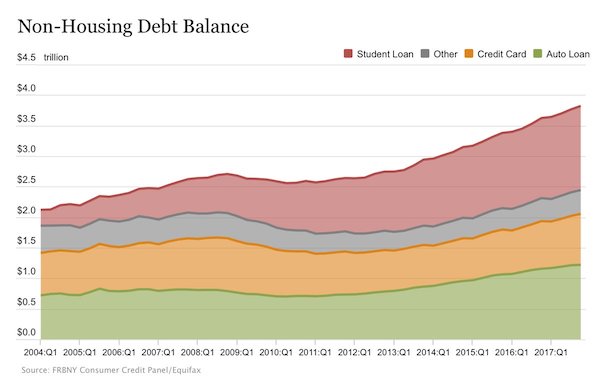
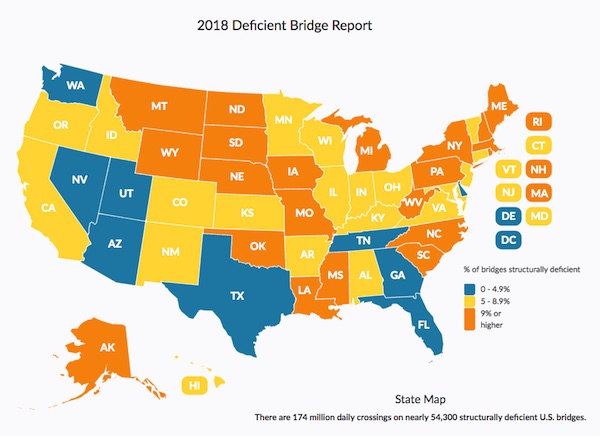
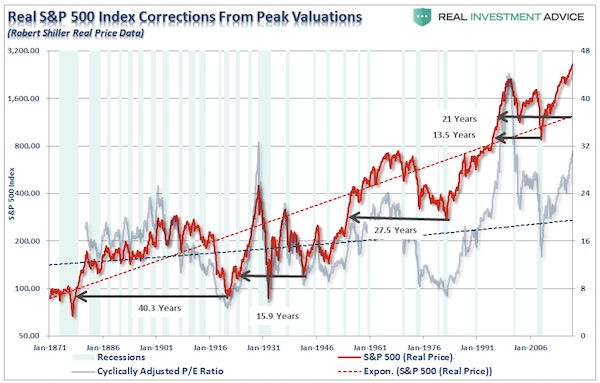
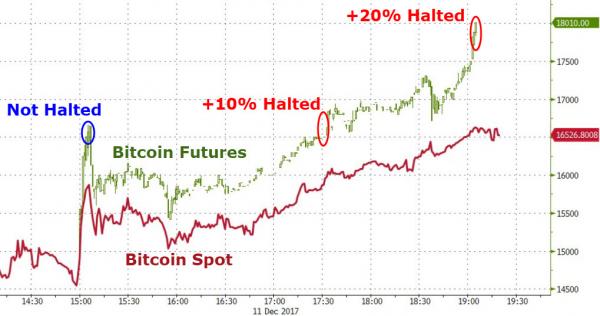
Despite Fed rate hikes, mortgage rates fall. An ominous sign. Maybe we should even say: mortgage rates fall because of Fed rate hikes. Is the pond getting smaller, or are there fewer fish?
• Mortgage Rates Slide May Be Too Late For The Housing Market (MW)
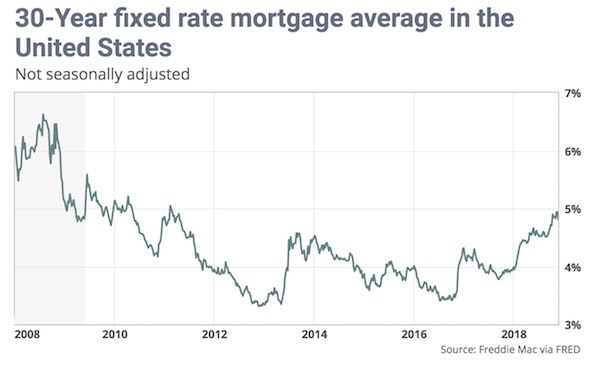
Rates for home loans tumbled as turmoil rocked global financial markets, but any reprieve in rates may come too late for would-be home buyers or refinancers. The 30-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 4.81% in the November 21 week, down 13 basis points, mortgage liquidity provider Freddie Mac said Wednesday. That’s the biggest weekly decline since January 2015 and the lowest level for the popular product since early October. The 15-year fixed-rate mortgage averaged 4.24%, down 12 basis points during the week. The 5-year Treasury-indexed hybrid adjustable-rate mortgage averaged 4.09%, down from 4.15%. Those rates don’t include fees associated with obtaining mortgage loans.
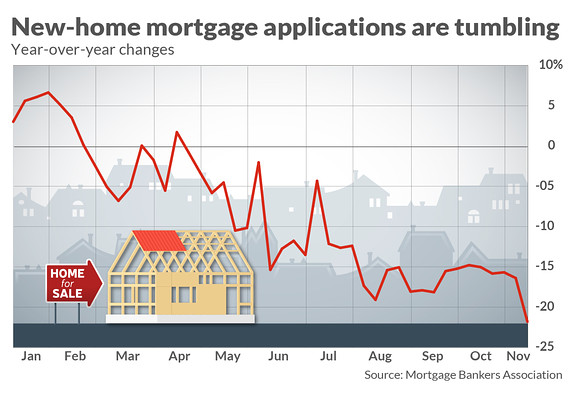
Fixed-rate mortgages follow the U.S. 10-year Treasury note, although with a slight delay. As a global stock sell-off has raged over the past week, bonds have been the best house in a bad neighborhood. The yield on the benchmark 10-year bond touched a six-week low Monday. Bond yields decline as prices rise, and vice versa. Meanwhile, this week has brought a raft of fresh information on the housing market, little of it cheery. Sales of already-owned homes perked up in October, but are still lower than the year-ago selling pace by more than 5%. Home builders broke ground on more — but not enough — homes. And one fresh data point bears watching: mortgage applications for newly-constructed houses are plunging, according to the Mortgage Bankers Association.

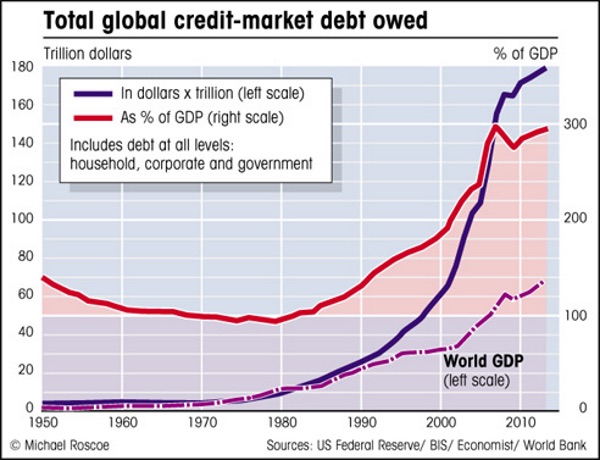
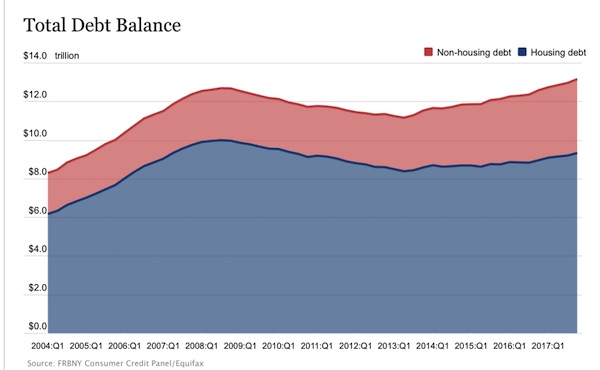
Forgive me for presuming there are several such debt bombs.
• A $9 Trillion Corporate Debt Bomb Is ‘Bubbling’ In The US Economy (CNBC)
At first glance, it looks like a $9 trillion time bomb is ready to detonate, a corporate debt load that has escalated thanks to easy borrowing terms and a seemingly endless thirst from investors. On Wall Street, though, hopes are fairly high that it’s a manageable problem, at least for the next year or two. The resolution is critical for financial markets under fire. Stocks are floundering, credit spreads are blowing out and concern is building that a combination of higher interest rates on all that debt will begin to weigh meaningfully on corporate profit margins. “There is angst in the marketplace. It’s not misplaced at all,” said Michael Temple, director of credit research at asset manager Amundi Pioneer.
“But are we at that moment where this thing blows sky high? I would think that we’re not there yet. That’s not to say that we don’t get there at some point over the next 12 to 18 months as rates continue to move higher.” [..] Over the past decade, companies have taken advantage of low rates both to grow their businesses and reward shareholders. Total corporate debt has swelled from nearly $4.9 trillion in 2007 as the Great Recession was just starting to break out to nearly $9.1 trillion halfway through 2018, quietly surging 86 percent, according to Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association data. Other than a few hiccups and some fairly substantial turbulence in the energy sector in late-2015 and 2016, the market has performed well.
In fact, Fitch Ratings forecasts bond defaults for 2019 at the lowest since 2013, with leveraged loans at the lowest since 2011. Such high debt levels are “certainly something to take notice of,” said Eric Rosenthal, Fitch’s senior director of U.S. leveraged finance. “In terms of the systemic risk, at the moment it’s not there.” One reason markets worry about debt is that there’s not as much cash around to cover it. The cash-to-debt ratio for corporate borrowers fell to 12 percent in 2017, the lowest ever.

It’s starting to feel like a siege.
• Multiple Risks Are Converging on Markets (Rickards)
Warnings of economic collapse are no longer confined to the fringes of economic analysis but are now coming from major financial institutions and prominent economists, academics and wealth managers. Leading financial elites have been warning of coming collapses and dangers. These warnings range from the IMF’s Christine Lagarde, Bridgewater’s Ray Dalio, the Bank for International Settlements and many other highly regarded sources. Just when we think we’ve seen enough of these, another one arrives. This time it’s the legendary Paul Tudor Jones, who manages Tudor Investment. I’ve met Jones; he’s a cerebral yet polite and mild-mannered manager from Tennessee who has not lost his Southern accent despite decades in Connecticut and an estate on Maryland’s Eastern Shore.
What gives Jones’ voice added authority is his longevity in the fund investment world. He’s managed through the 1987 stock crash, the 1994 Mexican crisis, the 1998 Long Term Capital meltdown, the 2000 dot-com crash and, of course, the 2008 financial panic. Jones knows that panics happen, but he also knows they don’t happen all the time. Panics take years to build and usually have specific triggers (even though endpoints can spin wildly out of control). Jones does not treat the possibility of a financial crisis lightly, so his warning deserves close consideration. Jones warns that the next crisis is likely to be triggered by excessive debt, specifically corporate debt, which can be more difficult to manage or bail out than sovereign debt.
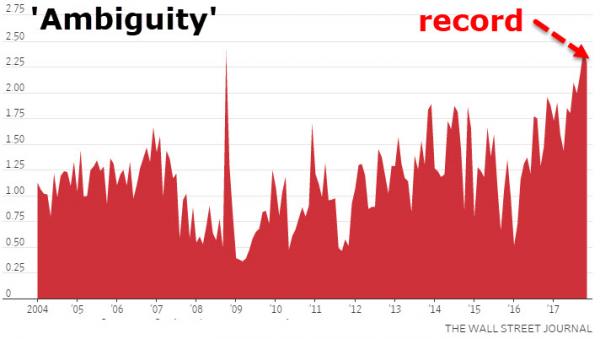
At the same time, other gurus are warning that the next panic will emerge from the foreign exchange market, overvalued equities or commercial real estate. Perhaps the real message is that all of these areas are vulnerable and the next crisis will seem to come from everywhere at once. That’s the danger. We’re looking at another debt crisis and global financial panic. Only this time it won’t come from mortgages alone but from all directions at once.

The original headline talked of 24 hours.
• May In Brussels Dash As Merkel Threatens To Pull The Plug On Brexit Summit (G.)
Theresa May is to make an emergency dash to Brussels on Saturday to complete the Brexit negotiations after the German chancellor, Angela Merkel, threatened to pull the plug on the Sunday leaders’ summit. As she emerged from talks in Brussels lasting nearly two hours with the European commission president, Jean-Claude Juncker, the British prime minister admitted that there were some major issues to resolve. Merkel had let it be known through her diplomats in Brussels that she was unwilling to negotiate with May on Sunday at the extraordinary Brexit summit. She had demanded a finalised agreement to emerge in good time before the leaders’ meeting.
The development threatened to disrupt Downing Street’s plans for agreement among leaders this month in time for a meaningful vote in parliament in early December. After meeting the European commission president on Wednesday, May said: “We have had a very good meeting this evening. We have made further progress and as a result, we have given sufficient direction to our negotiators. “I hope for them to be able to resolve the remaining issues and that work will start immediately. I now plan to return for further meetings, including with President Junker, on Saturday to discuss how we can bring to a conclusion this process and bring it to a conclusion in the interests of all our people.”

Salvini and Di Maio said again this morning that they won’t change a letter in their budget.
• Salvini Ready To ‘Confront EU’ After Italy’s Budget Rejected Again (G.)
Italy’s deputy prime minister Matteo Salvini has said he is prepared to confront EU leaders after the European commission rejected his country’s draft 2019 budget for a second time, while calling on them to “respect the Italian people”. Italy is facing sanctions after the commission said in a report that the government of the far-right League and anti-establishment Five Star Movement had seriously violated fiscal rules. Both parties’ leaders have refused to succumb to pressure to change their deficit target of 2.4% of GDP as they endeavour to push through campaign promises, such as introducing a universal basic income, cutting taxes and lowering the retirement age.
Italy has about €2.3tn (£2tn) of public debt and the Bank of Italy warned this month that the cost of servicing the debt could rise to €5bn in 2019 and €9bn in 2020. The government is convinced that the budget would help the Italian economy grow by 1.5% over the next year. However, the economy stagnated in the third quarter. On Wednesday Italy’s national statistics agency, Istat, revised down its growth forecast for the year to 1.1%; in May it predicted 1.4% for 2018. Salvini, who leads the League, responded sarcastically to news of the commission’s report. “A letter from the EU? I’m also waiting for one from Father Christmas,” he told reporters.
Referring to the commission president and economics commissioner, Salvini said he was ready to “confront [Jean-Claude] Juncker, [Pierre] Moscovici or whoever” over a budget he said responded to the needs of Italians.

But Zuckerberg and Sandberg plead innocent.
• Facebook Admits Targeting George Soros After He Criticized Company (MW)
Facebook Inc. admitted Wednesday that it asked an opposition-research company to investigate billionaire George Soros over his criticism of the social network. In an internal memo released publicly late Wednesday, Elliot Schrage, Facebook’s outgoing head of communications and policy, said he was responsible for hiring the company, Definers Public Affairs, to investigate who was behind the “Freedom From Facebook” campaign. “In January 2018, investor and philanthropist George Soros attacked Facebook in a speech at Davos, calling us a ‘menace to society,’” Schrage wrote in the memo. “We had not heard such criticism from him before and wanted to determine if he had any financial motivation. Definers researched this using public information.
“Later, when the ‘Freedom from Facebook’ campaign emerged as a so-called grassroots coalition, the team asked Definers to help understand the groups behind them. They learned that George Soros was funding several of the coalition members. They prepared documents and distributed these to the press to show that this was not simply a spontaneous grassroots movement.” Definers later distributed a document suggesting Soros, a major donor to liberal causes, bankrolled the anti-Facebook campaign, playing into anti-Semitic conspiracy theories about Soros. Facebook Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg and Chief Operating Officer Sheryl Sandberg have denied knowledge of the Definers efforts until after it was revealed by a New York Times report last week. Facebook has since cut ties with Definers.

A long running but secretive investigation, running concurrently with Mueller’s.
• House GOP To Hold Hearing Into DOJ Probe Of Clinton Foundation (Hill)
Rep. Mark Meadows (R-N.C.) said Tuesday that House Republicans plan to hear testimony on Dec. 5 from the prosecutor appointed by former Attorney General Jeff Sessions to probe alleged wrongdoing by the Clinton Foundation. [..] Meadows, who is also the chairman of the conservative House Freedom Caucus, said the committee plans to delve into a number of Republicans concerns surrounding the foundation, including whether any tax-exempt proceeds were used for personal gain and whether the foundation complied with IRS laws. Sessions appointed Huber last year to work in tandem with the Justice Department to look into conservative claims of misconduct at the FBI and review several issues surrounding the Clintons.
This includes former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton’s ties to a Russian nuclear agency and concerns about the Clinton Foundation. Huber’s work has remained shrouded in mystery. The White House has released little information about Huber’s assignment other than Sessions’s address to Congress saying his appointed successor should address concerns raised by Republicans. But Meadows said the committee thinks it’s time Huber gives an update to Congress about his findings and expects him to be one of the witnesses at the hearing. Meadows also added that his committee is also trying to secure testimonies from whistleblowers who could have more information about potential improprieties surrounding the Clinton Foundation. “We’re just now starting to work with a couple of whistleblowers that would indicate that there is a great probability of significant improper activity that’s happening in and around the Clinton Foundation,” he said.

They must have thought for quite a while that there would never be any scrutiny.
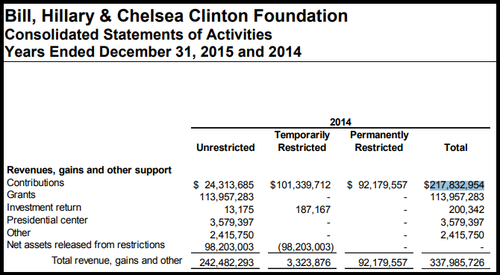
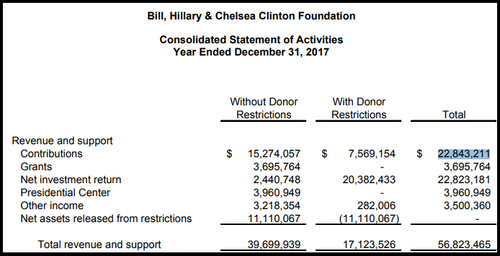
• Clinton Foundation Donations Plummet 90% (ZH)
The Clinton Foundation saw contributions dry up approximately 90% over a three-year period between 2014 and 2017, according to financial statements. The global charity is currently under investigation by the DOJ, FBI and IRS for a variety of allegations – including whether favors were handed out while Hillary Clinton was Secretary of State, also known as “pay for play.” The Clinton-led State Department authorized $151 billion in Pentagon-brokered deals to 16 countries that donated to the Clinton Foundation – a 145% increase in completed sales to those nations over the same time frame during the Bush administration, according to IBTimes.
2014
2017
“American defense contractors also donated to the Clinton Foundation while Hillary Clinton was secretary of state and in some cases made personal payments to Bill Clinton for speaking engagements. Such firms and their subsidiaries were listed as contractors in $163 billion worth of Pentagon-negotiated deals that were authorized by the Clinton State Department between 2009 and 2012.” -IBTimes. Then there was that $1 million check Qatar reportedly gave Bill Clinton for his birthday in 2012, which the charity confirmed it accepted. Coincidentally, we’re sure, Qatar was one of the countries which gained State Department clearance to buy US weapons while Clinton was Secretary of State, “even as the department signaled them out ofr a range of alleged ills,” according to IBTimes.
Then there was the surely unrelated $145 million donated to the Foundation from parties linked to the Uranium One deal prior to its approval through a rubber-stamp committee. “The committee almost never met, and when it deliberated it was usually at a fairly low bureaucratic level,” Richard Perle said. Perle, who has worked for the Reagan, Clinton and both Bush administrations added, “I think it’s a bit of a joke.” –CBS. Meanwhile, according to a November 2016 report by the Dallas Observer, the Clinton Foundation has been under investigation by the IRS since July, 2016, while the Arkansas FBI field office has been investigating allegations of pay-for-play and tax code violations, according to The Hill.

Like that fleece sweater?
• Tyres And Synthetic Clothes ‘Biggest Causes Of Microplastic Pollution’ (G.)
Vehicle tyres and synthetic clothing are the two leading contributors to microplastic pollution from UK households, according to a new report from Friends of the Earth. The report estimates that between 9,000 and 32,000 tonnes of microplastic pollution enter British waterways each year from just four sources. The two leading sources are tyre abrasion, with between 7,000 and 19,000 tonnes entering surface waters each year, and clothing. In the UK an estimated two-thirds of clothing is made from synthetic plastic material, according to analysts from Eunomia, who wrote the report for FoE.
Up to 2,900 tonnes of microplastics from the washing of synthetic clothing such as fleeces could be passing through wastewater treatment into our rivers and estuaries. The scale of plastic pollution from household plastics is of the same magnitude as that from large plastic waste such as bottles and takeaway containers – about 26,000 tonnes of which enters UK waterways each year. The environmental campaign group is calling on the government’s resources and waste strategy – expected next month – to include measures for tackling microplastics as part of a comprehensive action plan. The four key contributors to microplastic pollution in the oceans from UK sources, according to the report, are:
• Vehicle tyres: 68,000 tonnes of microplastics from tyre tread abrasion are generated in the UK every year, with between 7,000 and 19,000 tonnes entering surface waters;
• Clothing: the washing of synthetic clothing could result in the generation of 2,300-5,900 tonnes of fibres annually in the UK – up to 2,900 tonnes of this could be passing through wastewater treatment into our rivers and estuaries;
• Plastic pellets used to manufacture plastic items. Up to 5,900 tonnes are lost to surface waters in the UK every year;
• Paints on buildings and road markings – weather and flake-off results in between 1,400 and 3,700 tonnes ending up in surface water every year.

There’s a disturbing trend emerging that people are fully blind to. In this piece, and I’ve seen it a lot more recently, the topic is the 1st amendment. To make their well-meaning arguments, writers then pose questions like “What if Assange DID get his info from Russia?” or “What if Assange really DOES hate America?” The response of course is that this would make no difference as far as the 1st amendment is concerned.
But in the meantime the possibility that Assange is indeed a Russian agent who hates all Americans has been introduced into the narrative. That makes these articles effectively part of the smear campaign. There is no indication that either allegation is true, but they are posited by those ostensibly defending him. They don’t help. Or rather, they help smear.
• Former New York Times Chief Lawyer: Rally to Support Julian Assange (Timm)
I recently spoke to James Goodale, the famed First Amendment lawyer and former general counsel the New York Times, who led the paper’s legal team in the famed Pentagon Papers case about the dire impact the Justice Department’s move may have on press freedom, regardless of whether people consider Assange himself a “journalist”.
There’s speculation on what Assange could be charged with. There’s a possibility that he could be outright charged under the Espionage Act for the act of publishing classified information. Then there’s the “conspiracy theory” that Assange was engaged in a conspiracy with his sources by asking them or soliciting more information from them that the sources may have gathered illegally. Do you find that type of charge would be just as dangerous as a charge for publishing information?
I do find that that charge would be just as dangerous. As a matter of fact, a charge against Assange for “conspiring” with a source is the most dangerous charge that I can think of with respect to the First Amendment in almost all my years representing media organizations. The reason is that one who is gathering/writing/distributing the news, as the law stands now, is free and clear under the First Amendment. If the government is able to say a person who is exempt under the First Amendment then loses that exemption because that person has “conspired” with a source who is subject to the Espionage Act or other law, then the government has succeeded in applying the standard to all news-gathering.
That will mean that the press ability to get newsworthy classified information from government sources will be severely curtailed, because every story that is based on leaked info will theoretically be subject to legal action by the government. It will be up to the person with the information to prove that they got it without violating the Espionage Act. This would be, in my view, the worst thing to happen to the First Amendment-almost ever.