Ernest R. Ashton Evening near the Pyramids 1898

Facebook knows more about you than your friends and family do. No, really. But it can’t figure out -for years- that its data are being downloaded and used?! Yeah, I’ll buy that.
The real issue here should be what Facebook itself uses its -or should that be ‘your’- data for, and what intelligence services do with it.
• Facebook And Cambridge Analytica Face Mounting Pressure Over Data Scandal (G.)
Facebook and that worked with Donald Trump’s election team have come under mounting pressure, with calls for investigations and hearings to explain a vast data breach that affected tens of millions of people. In Britain, the head of the parliamentary committee investigating fake news accused Cambridge Analytica and Facebook of misleading MPs after revelations in the Observer that more than 50m Facebook profiles were harvested and used to build a system that may have influenced voters in the 2016 presidential campaign. The Conservative MP Damian Collins said he would call the heads of both companies, Alexander Nix and Mark Zuckerberg, to give further testimony.
His intervention came after a whistleblower spoke to the Observer and described how the profiles, mostly of US voters, were harvested for Cambridge Analytica, in one of Facebook’s biggest ever data breaches. The disclosures caused outrage on both sides of the Atlantic; in the US, a state attorney general has called for investigations and greater accountability and regulation. There have been reports that Cambridge Analytica is trying to stop the broadcast of a Channel 4 News exposé in which Nix is said to talk unguardedly about the company’s practices. According to the Financial Times, reporters posed as prospective clients and secretly filmed a series of meetings, including one with the chief executive. The report is due to air this week.

Very little credibility so far. From descriptions of the nerve agent, it would seem impossible that “..at least 38 people in Salisbury had been identified as having been affected by it..” and all lived to tell it. Is the whole Novichok story a fabrication? Know what, Boris? Why not show the proof you claim to have?!
• Boris Johnson Ramps Up Anti-Russia Rhetoric (G.)
Boris Johnson will today seek to convince the EU foreign affairs council to join him in fresh condemnation of Russia after his explosive claims that Moscow has been creating and stockpiling nerve agent novichok and working out how to use it for assassinations. Scientists from the UN-backed Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons arrive today to analyse samples of the agent used to poison the former spy Sergei Skripal and his daughter Yulia. The foreign secretary made his claims after Russian EU ambassador Vladimir Chizhov issued blanket denials and said British agents might have used their stockpiles at Porton Down.
As the row enters its third week, Johnson dismissed Chizhov’s comments, saying they were “not the response of a country that really believes it’s innocent”. On Sunday, Vladimir Putin, fresh from a profoundly unsurprising electoral victory, denied any such nerve agents existed and said the idea of carrying out such a killing during an election campaign would be “rubbish, drivel, nonsense”. The latest theory to gain prominence is that the Skripals were poisoned via his car’s ventilation system. The report, from ABC news in the US, came as counter-terrorism police renewed their appeal for sightings of Skripal’s burgundy BMW 320D saloon car on 4 March. ABC also reported that at least 38 people in Salisbury had been identified as having been affected by the nerve agent.

Zero interest rates?!
• Why Default Rates Are Subdued Even As Corporate Debt Levels Hit Records (MW)
U.S. corporate debt levels stand above crisis highs even as default rates among the most leveraged firms remain subdued. With an economy hitting its stride, it’s perhaps no surprise that the high-yield bond market is placid. The extent of the divergence between debt levels and defaults, however, is worrying to some analysts who feel rising corporate indebtedness will eventually catch out unwary investors and deflate the junk-bond market. But beyond complacency John Lonski at Moody’s Capital Market Research, argued that globalization and the tendency of U.S. businesses to hoard cash as reasons why corporate debt levels may no longer move in sync with default rates and credit spreads.
The high-yield default rate in the fourth-quarter of 2017 fell to 3.3%, even as U.S. nonfinancial-corporate debt ended in 2017 at 45.4% of GDP. This compares with a much higher default rate of 11.1% in the second quarter of 2009, with corporate debt levels at 45% of GDP. Granted, the current levels come with the economy in the eighth year of an expansion, while the second quarter of 2009 marked the final quarter of the longest and deepest U.S. recession since the Great Depression. The yield spread between high-yield bonds and safe government paper, as represented by the 10-year Treasury note narrowed to an average 3.63 percentage points in the fourth quarter of 2017, from an average 12.02 percentage points in the second quarter of 2009.
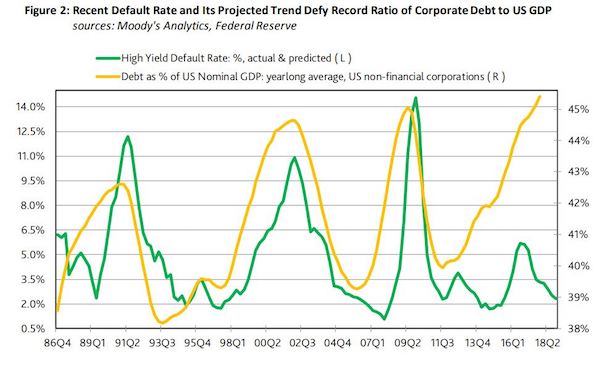
The tight credit spreads reflects that borrowing costs are still close to historic lows, and that investors are demanding minimum compensation for holding arguably the riskiest debt in the bond market. One answer “might be supplied by the ever increasing globalization of U.S. businesses where the more relevant denominator is not U.S. GDP, but world GDP” said Lonski. The fortunes of U.S. companies are now wove into the broader global economy. When commodity prices took a hit in 2015 and early 2016, crimping growth in China and other emerging markets, high-yield bonds were also slammed.

If they keep up the forward guidance, everyone will sleep on. But will the yield spread sleep too?
• How Seriously is the Treasury Market Taking the Fed? (WS)
Back in October 2015, the three-month Treasury yield was 0%. Many on Wall Street said that the Fed could never raise interest rates, that the zero-interest-rate policy had become a permanent fixture, like in Japan, and that the Fed could never unload the securities it had acquired during QE. How things have changed! On Friday, the three-month Treasury yield closed at 1.78%, the highest since August 19, 2008. When yields rise, by definition bond prices fall:
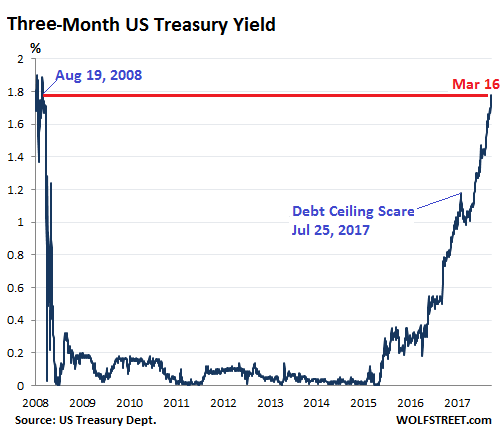
Back in October 2015, the three-month Treasury yield was 0%. Many on Wall Street said that the Fed could never raise interest rates, that the zero-interest-rate policy had become a permanent fixture, like in Japan, and that The Fed’s target range for the federal funds rate has been 1.25% to 1.50% since its last rate hike at the December FOMC meeting. In other words, the three-month yield is already above the upper limit of the Fed’s target range after the next rate hike. So the market has fully priced in a rate hike at the FOMC meeting ending March 21. And it’s also starting to price in another rate hike in June. In this rate-hike cycle, the Fed has engaged in policy action only at meetings that are followed by a press conference.
There are four of these press-conference meetings per year. The next two are this week and June. If, in this cycle, the Fed hike rates at an FOMC meeting that is not followed by a press conference – there are also four of them this year – it would be considered a “monetary shock” that the Fed decided to administer to the markets. It would be like a rate hike of 50 basis points instead of the expected 25 basis points. There would be a hue and cry in the markets around the world. But I think the Fed isn’t ready to spring that on the markets just yet. Maybe later. The two-year yield rose to 2.31% on Friday, the highest since August 29, 2008:
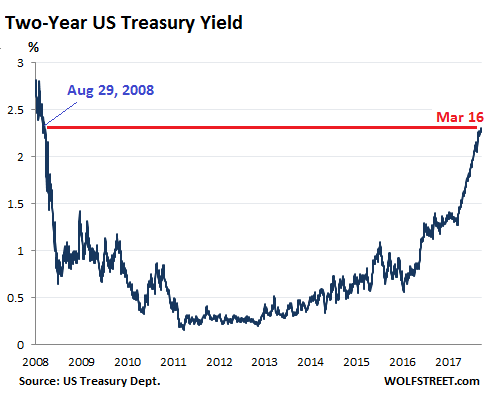
Back in October 2015, the three-month Treasury yield was 0%. Many on Wall Street said that the Fed could never raise interest rates, that the zero-interest-rate policy had become a permanent fixture, like in Japan, and that In past rate hike cycles, the two-year yield reacted faster to rate-hike expectations than the 10-year yield. This is happening now as well. The 10-year yield has its own dynamics that are not in lockstep with the Fed’s rate-hike scenario. On Friday, the 10-year yield closed at 2.85%, within the same range where it had been since late February, tantalizingly close to 3%:
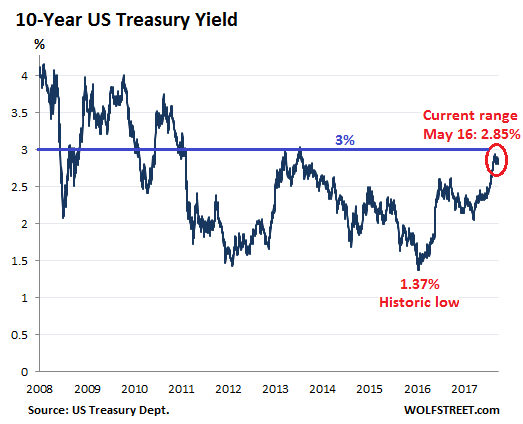
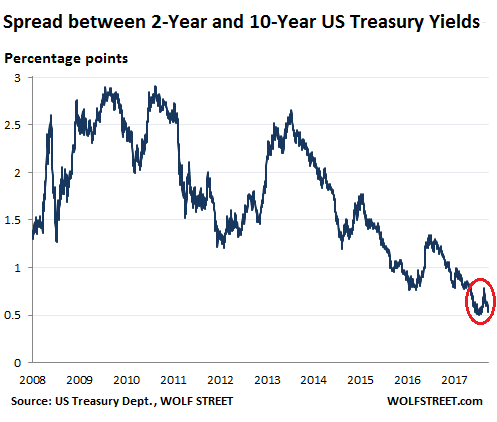
Back in October 2015, the three-month Treasury yield was 0%. Many on Wall Street said that the Fed could never raise interest rates, that the zero-interest-rate policy had become a permanent fixture, like in Japan, and that [..] After the surge of the two-year yield, the difference between the two-year and the 10-year yield – the “two-10 spread” – has narrowed again. On Friday, it was at 54 basis points. In the chart below, note the narrowing at the end of last year to 50 basis points, then the mini-spike, as the 10-year yield surged faster than the two-year yield, and the recent fallback:

Always the same braindead question: “What’s keeping Americans from saving?” We still don’t know?!
• 65% of Americans Save Little or Nothing (CNBC)
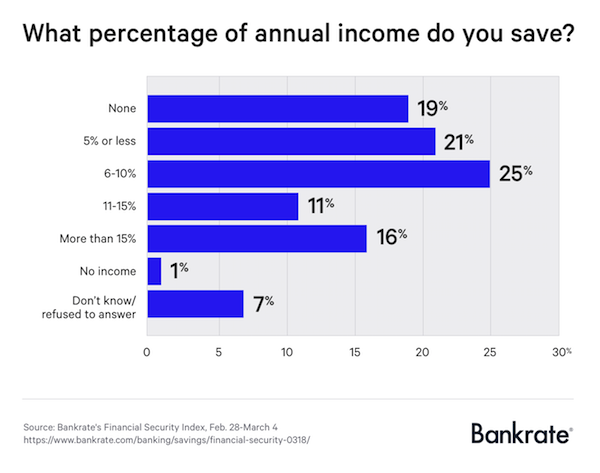
Despite a low unemployment rate and increasing wage growth, Americans still aren’t saving much. That’s according to a new survey from Bankrate.com, which found that 20% of Americans don’t save any of their annual income at all and even those who do save aren’t putting away a lot. Only 16% of survey respondents say that they save more than 15% of what they make, which is what experts generally recommend. A quarter of respondents report saving between 6 and 10% of their income and 21% say they sock away 5% or less.
At this rate, many people could be setting themselves up to fall short in retirement, Bankrate warns. “With a steady, significant share of the working population saving nothing or relatively little, it’s virtually guaranteed that they’ll be unable to afford a modest emergency expense or finance retirement,” says Mark Hamrick, senior economic analyst at Bankrate. “That amounts to a financial fail.” The economy might be prospering now, but that won’t last forever: “The party has to stop sometime, and when it does, employers will lay off workers,” the study says. In fact, Bankrate estimates that half of the American population won’t be able to maintain their standard of living once they stop working.
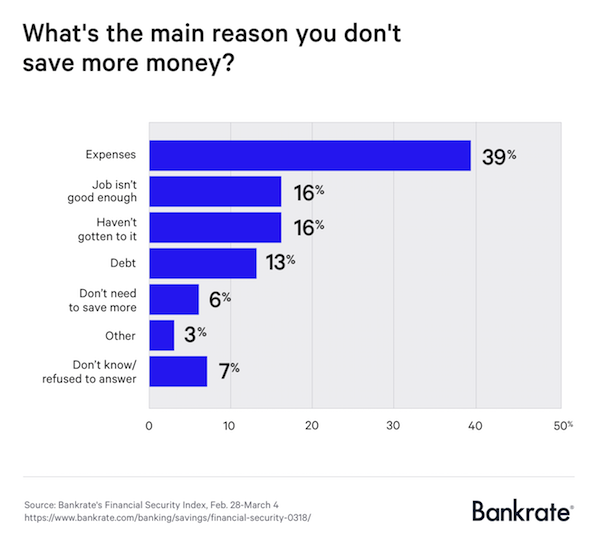
A report from GoBankingRates found similar results: Over 40% of Americans have less than $10,000 saved for when they retire. What’s keeping Americans from saving? “Expenses” was the No. 1 answer of 39% of respondents. Another 16% say they don’t have a “good enough job” to be able to save, which presumably means they aren’t earning enough. “The average American has less than $5,000 in a financial account, a quarter to a fifth of what you should have, and those aged 55 to 64 who have retirement savings only carry $120,000 — which won’t last long in the absence of paychecks,” the survey reports.

How strong will this make the dollar?
• Developing Countries At Risk From US Rate Rise, Debt Charity Warns (G.)
The expected rise in US interest rates will increase financial pressures on developing countries already struggling with a 60% jump in their debt repayments since 2014, a leading charity has warned. The Jubilee Debt Campaign said a study of 126 developing nations showed that they were devoting more than 10% of their revenues on average to paying the interest on money borrowed – the highest level since before the G7 agreement to write off the debts of the world’s poorest nations at Gleneagles, Scotland, in 2005. Five of the countries on the charity’s list – Angola, Lebanon, Ghana, Chad and Bhutan – were spending more than a third of government revenues on servicing debts.
Developing country debt moved down the international agenda following the Gleneagles agreement in which the G7 industrial countries agreed to spend £30bn writing off the debts owed to the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank by the 18 poor countries. But developing country debt is now once again being closely monitored by the IMF, which says 30 of the 67 poor countries it assesses are in debt distress or at risk of being so. Lending to developing countries almost doubled between 2008 and 2014 as low interest rates in the west led to a search for higher-yielding investments. A boom in commodity prices meant many poor countries borrowed in anticipation of tax receipts that have not materialised.
But the Jubilee Debt Campaign said the boom–bust in commodity prices was only one factor behind rising debt, pointing out that some countries were paying back money owed by former dictators, while others had been struggling with high debts for many years but had not been eligible for help. The campaign said developing countries were also vulnerable to a rise in global interest rates as central banks withdrew the support they have been providing since 2008. [..] The US Federal Reserve is expected to raise interest rates this week – with the financial markets expecting two or three further upward moves during 2018.
Tim Jones, an economist at the Jubilee Debt Campaign, said: “Debt payments for many countries have risen rapidly as a result of a lending boom and fall in commodity prices. The situation may worsen further as US dollar interest rates rise, and as other central banks reduce monetary stimulus. Debt payments are reducing government budgets when more spending is needed to meet the sustainable development goals.”
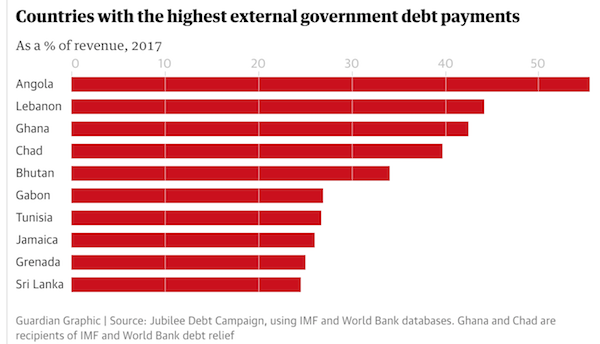

A few economies that have not done well.
• Rising US Interest Rates May Damage Gulf Economies (MEE)
[..]The latest available data shows that Oman, for instance, has a debt equivalent to 31.4% of their GDP for 2016, which is up from 4.9% in 2014, according to TradingEconomics.com. That jump in debt coincided with a fall in oil prices from more than $100 a barrel in mid-2014 to a low of $26 in early 2016. Rising rates also tend to increase costs for businesses, says Rosso. And the higher costs of borrowing ultimately means that fewer businesses that request loans from banks will receive the money they need. In short, growth in the available credit in the economy will slow. If we learned nothing else from the financial crisis of 2008-2009, it is that the world of business runs on credit. Slower credit growth usually means slower economic growth.
The base case is that among the countries with the dollar peg such as Saudi Arabia, UAE and Oman, the increased interest rates will likely drag on growth for their economies. The timing is really pretty bad for some of the countries involved. For instance, the Saudi economy shrank by 0.43% in the quarter ending September 2017, according to TradingEconomics.com. The prior quarter was worse; the economy sank 1.03%. Two quarters of negative growth is generally seen as a recession. Will the impact of rising rates push Saudi’s economy back into another recession? It’s hard to tell so far, but there is a risk. Similar problems seem likely for some other countries in the dollar-peg group.
The latest data from Oman is awful as well, although not as recent as that on Saudi Arabia. That economy contracted 14.1% in 2015, followed by another 5.1% decline in 2016. Likewise, the UAE has seen its growth steadily decline in each of the five years through 2016 from 6.9% to 3% most recently. That would not be bad for economic growth, but it is going in the wrong direction.

That’s quite the statement.
• Kim Jong-Un Has Committed To Denuclearisation, Says South Korea (G.)
South Korea’s foreign minister has said that North Korea’s leader has “given his word” that he is committed to denuclearization, a prime condition for a potential summit with President Donald Trump in May. Trump has agreed to what would be historic talks after South Korean officials relayed that Kim Jong-un was committed to ridding the Korean Peninsula of nuclear weapons and was willing to halt nuclear and missile tests. North Korea hasn’t publicly confirmed the summit plans, and a meeting place isn’t known. South Korea’s Kang Kyung-wha said Seoul has asked the North “to indicate in clear terms the commitment to denuclearization” and she says Kim’s “conveyed that commitment.” She told the CBS programme Face the Nation that “he’s given his word” and it’s “the first time that the words came directly” from the North’s leader.

Only include this because it’s exactly what I said last week. Kim still hasn’t publicly agreed to meet.
• Kim Jong-Un Caught Off Guard by Trump’s Quick Agreement to Meet (BBG)
U.S. President Donald Trump’s immediate willingness to meet Kim Jong Un for nuclear talks likely caught the North Korean leader by surprise, forcing him to consider his position before responding publicly, the South Korean foreign minister said. “We were all quite surprised by the readiness of that decision,” South Korea’s Kang Kyung-wha said on CBS’s “Face the Nation” Sunday. “It was an extremely courageous decision on the part of President Trump. We believe the North Korean leader is now taking stock.” Trump agreed to meet with Kim on March 8 after a briefing from South Korean officials.
The summit, expected to take place in a few months, would represent the first time a U.S. president has met a North Korean leader – either Kim or his father or grandfather – and is part of an overall strategy to dismantle that nation’s rapidly advancing nuclear weapons program. Pyongyang has already detonated what it described as a hydrogen bomb capable of riding an intercontinental ballistic missile to cities across the U.S., and Kim has threatened to use nuclear arms against Americans. The summit, if it occurs, will likely follow an already-scheduled meeting between Kim and South Korean President Moon Jae-in to take place in South Korea, at which denuclearization will also be discussed, Kang said.

Yeah, Shinzo, the Russians did it.
Tyler earlier: “82% of Asahi poll respondents said Abe bears responsibility for the doctored documents relating to the Moritomo scandal”
• Japan: Embattled Shinzo Abe Blames Staff Over Land Sale Scandal (AFP)
Japan’s embattled prime minister has hit back at critics over a favouritism and cover-up scandal that has seen his popularity plunge and loosened his grip on power. In a statement in parliament, Shinzo Abe stressed he had not ordered bureaucrats to alter documents relating to a controversial land sale. “I have never ordered changes,” he said. The scandal surrounds the 2016 sale of state-owned land to a nationalist operator of schools who claims ties to Abe and his wife Akie. The sale was clinched at a price well below market value amid allegations that the high-level connections helped grease the deal. The affair first emerged early last year, but resurfaced after the revelation that official documents related to the sale had been changed.
Versions of the original and doctored documents made public by opposition lawmakers appeared to show passing references to Abe were scrubbed, along with several references to his wife Akie and Finance Minister Taro Aso. Aso has blamed the alterations on “some staff members” at the ministry. But Jiro Yamaguchi, a politics professor at Hosei University in Tokyo, said the public was “not at all convinced” by this explanation. “Why was the land sold at a discount price? Without any political pressure, this could never happen, and voters are angry about it,” said Yamaguchi. The prime minister repeated an apology, saying he “keenly felt” his responsibility over the scandal that has “shaken people’s confidence in government administration.”
The affair is hitting Abe’s ratings hard, with a new poll in the Asahi Shimbun showing public support nosediving by 13 percentage points from the previous month to 31%. The figure is the lowest approval rating for Abe in the poll since his return to power at the end of 2012.

A different kind of protectionism.
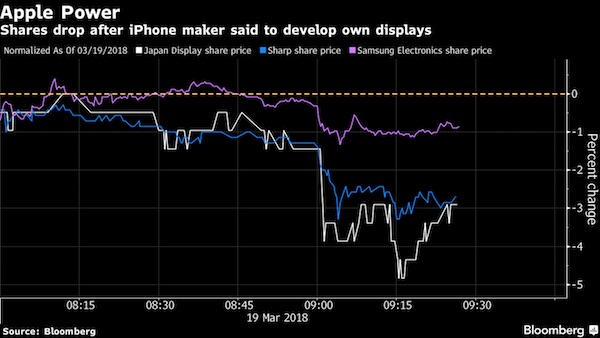
• Apple Is Secretly Developing Its Own Screens for the First Time (BBG)
Apple is designing and producing its own device displays for the first time, using a secret manufacturing facility near its California headquarters to make small numbers of the screens for testing purposes, according to people familiar with the situation. The technology giant is making a significant investment in the development of next-generation MicroLED screens, say the people, who requested anonymity to discuss internal planning. MicroLED screens use different light-emitting compounds than the current OLED displays and promise to make future gadgets slimmer, brighter and less power-hungry. The screens are far more difficult to produce than OLED displays, and the company almost killed the project a year or so ago, the people say.
Engineers have since been making progress and the technology is now at an advanced stage, they say, though consumers will probably have to wait a few years before seeing the results. The ambitious undertaking is the latest example of Apple bringing the design of key components in-house. The company has designed chips powering its mobile devices for several years. Its move into displays has the long-term potential to hurt a range of suppliers, from screen makers like Samsung, Japan Display, Sharp and LG to companies like Synaptics that produce chip-screen interfaces. It may also hurt Universal Display, a leading developer of OLED technology. Display makers in Asia fell after Bloomberg News reported the plans. Japan Display dropped as much as 4.4%, Sharp tumbled as much as 3.3% and Samsung slid 1.4%.

“$22,837 per person, not including mortgages…”
• Canadian Household Debt Hits Record $1.8 Trillion (CP)
Canadians’ collective household debt has climbed to $1.8 trillion as an international financial group sounds an early warning that the country’s banking system is at risk from rising debt levels. Equifax Canada says consumers now owe $1.821 trillion including mortgages as of the fourth-quarter of 2017, marking a 6% increase from a year earlier. Although nearly half of Canadians reduced their personal liabilities, roughly 37% added to their debt to push the average amount up 3.3% to $22,837 per person, not including mortgages.
The fresh numbers come as an international financial group owned by the world’s central banks says Canada’s credit-to-GDP and debt-service ratios show early warning signs of potential risk to the banking system in the coming years. The latest report by the Bank for International Settlements says Canada’s credit-to-GDP gap and debt-service ratios have surpassed critical thresholds and are signalling red, pointing to vulnerabilities. The group, however, cautions that these indicators should not be treated as a formal stress test, but as a first step in a broader analysis.

From Merkel’s own camp.
• German Interior Minister Wants More Internal EU Border Controls (DW)
Germany should consider stepping up its border controls, German Interior Minister Horst Seehofer said on Sunday. “Not that many border points in Germany are permanently occupied,” Seehofer told German weekly newspaper Die Welt am Sonntag, adding: “We will now discuss whether that needs to change.” Seehofer also appealed for the suspension of the Schengen Agreement, which allows free movement within the EU bloc. “Internal border checks [between EU member states] must be in place so long as the EU fails to effectively control the external border,” he said, adding: “I don’t see it being able to do this in the near future.” The reintroduction of border controls is a prerogative of EU member states. Under EU rules they must remain an exception and respect the principle of proportionality.
Germany’s temporarily reintroduced border controls continue until May 12 and have been imposed on the land border with Austria and on flight connections from Greece because of the “security situation in Europe and threats resulting from the continuous secondary movements,” according to the European Commission. Seehofer’s comments follow EU demands in February that Germany and four other Schengen members – Austria, Denmark, Sweden and Norway – lift their border controls when the current agreed terms run out in May. [..] Seehofer is a member of the Christian Social Union (CSU), the Bavarian sister party of German Chancellor Angela Merkel’s conservative Christian Democrats (CDU).

Waterwars in waterworld.
• Water Shortages Could Affect 5 Billion People By 2050 – UN (G.)
More than 5 billion people could suffer water shortages by 2050 due to climate change, increased demand and polluted supplies, according to a UN report on the state of the world’s water. The comprehensive annual study warns of conflict and civilisational threats unless actions are taken to reduce the stress on rivers, lakes, aquifers, wetlands and reservoirs. The World Water Development Report – released in drought-hit Brasília – says positive change is possible, particularly in the key agricultural sector, but only if there is a move towards nature-based solutions that rely more on soil and trees than steel and concrete.
“For too long, the world has turned first to human-built, or ‘grey’, infrastructure to improve water management. In doing so, it has often brushed aside traditional and indigenous knowledge that embraces greener approaches,” says Gilbert Houngbo, the chair of UN Water, in the preface of the 100-page assessment. “In the face of accelerated consumption, increasing environmental degradation and the multi-faceted impacts of climate change, we clearly need new ways of manage competing demands on our freshwater resources.” Humans use about 4,600 cubic km of water every year, of which 70% goes to agriculture, 20% to industry and 10% to households, says the report, which was launched at the start of the triennial World Water Forum.
Global demand has increased sixfold over the past 100 years and continues to grow at the rate of 1% each year. This is already creating strains that will grow by 2050, when the world population is forecast to reach between 9.4 billion and 10.2 billion (up from 7.7 billion today), with two in every three people living in cities. [..] By 2050, the report predicts, between 4.8 billion and 5.7 billion people will live in areas that are water-scarce for at least one month each year, up from 3.6 billion today, while the number of people at risk of floods will increase to 1.6 billion, from 1.2 billion.