DPC Chamber of Commerce, Boston MA 1904



That is a big number. Add losses in commodities, and you’re talking destruction, of money, credit, virtual wealth, it doesn’t matter anymore what you call it..
• $100 Trillion Up in Smoke (Mauldin)
If energy powers the world, then whoever owns that energy must have power over the world. That’s certainly been the case for the last century or two. Ownership of our primary energy source, crude oil, is what made billionaires of John D. Rockefeller, H.L. Hunt, and assorted Middle Eastern kings, emirs, and sheikhs. Oil in the ground is wealth only on paper – you may own that oil, but it earns you nothing until you recover and sell it. Yet paper wealth is still wealth. It goes on your balance sheet as an asset that you can sell. You can use it as collateral to borrow cash and buy other assets. The ongoing oil price collapse is having a severely negative impact on the wealth of those who own oil reserves. The numbers, as you will see below, are almost incomprehensibly big.
They are so big, in fact, that many analysts have simply tuned out. The attitude seems to be, “These numbers blow up my models, so I will ignore them.” Today we’ll stop dancing around the truth and call the oil collapse what it is: global wealth destruction of epic proportions. In mid-2014, crude oil prices were about $100, depending on which grade you wanted to buy. Now prices hover near $30 – roughly a 70% decline in 18 months. That’s well-known, but we usually discuss the price collapse in terms of particular countries or companies: we don’t look at the bigger picture. Last week someone showed me this from Twitter. I almost fell out of my chair.
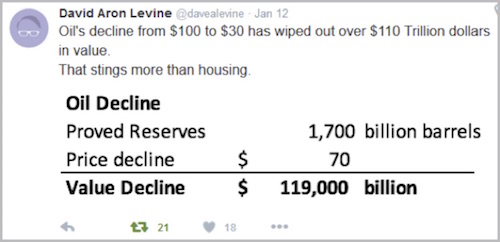
Stop for a minute. Let that sink in. The total value of all the world’s oil reserves is over $100 trillion less than it was just a year and a half ago.
(By the way, I verified Mr. Levine’s reserve total by consulting the CIA’s World Fact Book. It says total world “proved” oil reserves were 1.656 trillion barrels as of January 1, 2015.) To put these figures in perspective, consider that Google’s parent company, Alphabet, briefly surpassed Apple last week as the planet’s largest publicly traded company. Both are worth around $500 billion, depending on the day. The lost value in crude oil is equivalent to a couple of hundred Googles and Apples going up in smoke. If stock values were crashing to that degree, we would call the losses earth-shattering. Yet otherwise intelligent people are saying the oil collapse is a minor issue.

They’re all fully unprepared. Deer and headlights.
• As Big Oil Shrinks, Boards Plot Different Paths Out Of Crisis (Reuters)
As oil and gas companies cut ever-deeper into the bone to weather their worst downturn in decades, boards have adopted contrasting strategies to lead them out of the crisis. Crude prices have tumbled around 70 percent over the past 18 months to around $35 a barrel, leading to five of the world’s top oil companies reporting sharp declines in profits in recent days. Executives at energy firms face a tough balancing act: they must cut spending to stay financially afloat while preserving the production infrastructure and capacity that will allow them to compete and grow when the market recovers. Companies have opted for differing approaches to secure future growth, often choosing to narrow focus to their areas of expertise and the geographic location of their main assets.
American firms Chevron, ConocoPhillips and Hess are withdrawing from more costly deepwater projects to focus on shale oil fields on their home turf, for example. Britain’s BP is betting on offshore gas in Egypt, while Royal Dutch Shell has opted for an alternative route as it seeks to safeguard its future: the $50 billion takeover of BG Group. In the five years before the downturn began in mid-2014, when crude prices held above $100 a barrel, big energy firms had raced to expand production capacity, including buying stakes in vast, costly fields sometimes located thousands of meters under the sea, and miles from land.
Over the past year however, companies have slashed their overall capital expenditure, scrapping plans for mega projects that cost billions to develop and take up to a decade to bring online. “Companies want to strike a balance between long and short-cycle investments while maintaining a robust balance sheet to fund their way through the down cycle,” said BMO Capital analyst Brendan Warn. Focusing on a specific set of expertise and geographies allowed them to offer investors a “unique value proposition”, he added.

Quick, before somone figures out what you’ve lost.
• Exxon Ends Share Buybacks – It Must Be Acquisition Time (Forbes)
If the company was happy buying its own stock in 2014, it should be all the more eager to buy now that shares are down 25%. Unless it sees a better bargain elsewhere. In its fourth-quarter financial release Tuesday, Exxon Mobil announced a halt to share buybacks. The company purchased $4 billion of its own shares in 2015, and has averaged about $20 billion a year in buybacks over the past decade, according to Reuters. The peak buyback year was 2008, when oil prices hit a record high and Exxon bought in $35 billion worth. At first glance, halting buybacks might seem reasonable. Perhaps amid this oil industry depression Exxon just wants to conserve cash — it also expects to reduce capital spending by $8 billion this year.
But think about it. The key to good investing is to buy low and sell high. If Exxon was happy buying back shares in 2014, when its stock price hit $103, it should be all the more eager to continue buying now that shares are down to $74.50. If Exxon didn’t think its own shares weren’t a great investment it wouldn’t have bought $200 billion of them over the past decade. Don’t take my word for it. As CEO Rex Tillerson said in a statement Tuesday, “The scale and diversity of our cash flows, along with our financial strength, provide us with the confidence to invest through the cycle to create long-term shareholder value.” It’s a hallmark of Exxon’s discipline that it continues to invest whether oil prices are low or high. In 2015 it brought on six big projects with 300,000 barrels per day of new production.
Exxon is not worried about running out of cash. Cash flows were on the order of $30 billion for the year. Even in the fourth quarter it generated net income of $2.8 billion (and $16 billion for the year). And don’t think for a second that Exxon intends to cut its dividend payouts, which totaled $12 billion last year. A more plausible reason Exxon is ending buybacks: it’s preparing to acquire another company whose shares are even more deeply discounted than Exxon’s. And with “just” $3.7 billion in cash on hand at the end of the fourth quarter, its likely that Exxon would use its shares as currency for a buyout. Who would they buy? The options abound for a company still sporting an equity market cap of $318 billion. Anadarko Petroleum has long been rumored to be a prime Exxon target; its shares are down about 65% to a market cap of $19 billion.
Occidental Petroleum float is $51 billion, ConocoPhillips $47 billion and Apache is at $15 billion. Deeper in the discount bin, Marathon Oil shares could be had for $6.5 billion, or Devon Energy for $11 billion. Of course Exxon would also need to assume any debt carried by an acquisition target. But that wouldn’t be a problem — compared with the averaged overleveraged oil company, Exxon has modest gearing with $38 billion in debt outstanding. Other than Royal Dutch Shell ’s $52 billion takeover of BG Group , we haven’t seen a landmark merger during this downturn. The last time things got this bad for the industry, back in 1998, BP bought Amoco for $48 billion and Exxon bought Mobil for $75 billion. Ending buybacks is just Exxon’s way of telling the market it’s ready to make a deal.

Hess oil is the case study. “..Hess just sold 25 million shares at a price of $39 after purchasing 63 million shares through 2015 at an average price that was more than double, or $83 a share..”
• Hess Oil: A “Folly For The Ages” (ZH)
[..] back in 2013, when it was trading at a discount to its peers, Hess became the target of an activist campaign led by Paul Singer’s Elliott Management who demanded a quick boost in the stock price, as a result of which the energy producer decided to exit its refining business (arguably the only line of business that would have benefited from the current depressed oil price) while not only raising its dividend but also authorizing a $4 billion share buyback. The company then boosted its buyback further with proceeds from the sale of its retail gas stations (for $2.9 billion) while growing its debt by $1 billion from 2013 to 2015, leading to the repurchase of a total of 62.7 million shares through the end of 2014 at an average price of $83. The stock price reacted as expected: it soared past $100 from below $60 before Elliott turned up. It then continued to spend more billions under additional buyback all the way through the third quarter of 2015, which however took place just as the worst oil downturn in history was taking place.
And then the stock crashed, as investors finally realized that plunging oil, sliding cash flow and surging debt meant the company found itself in a life and death fight for survival. Which brings us to yesterday, when in an attempt to shore up liquidity and avoid halting its dividend, Hess sold 25 million shares at a price of $39/share: a 10% discount to the prior closing price. As Reuters puts it, the “Hess folly is one for the ages.” The silver lining? Unlike before, when Hess’ weak management team was kicked around by a hedge fund, at least it is being proactive now and scrambling to preserve its business even it means huge pain and dilution for shareholders. The company ended 2015 with $2.7 billion in cash and a big revolving line of credit it hasn’t dipped into yet. Capital just raised will push net debt from 5.4x EBITDA to below four times, according to Cowen estimates.
That should allow Hess to keep investing in future production and pay dividends. If oil remains at $30, however, it has just bought itself a few quarters of time. Still, that does not absolve management of pandering to a vocal shareholder: if instead of spending billions on buybacks Hess had done the right thing and saved the cash, it would not only have avoided the wild swings in the stock price which rewarded just activist investors while punishing long-term holders, and have a far bigger war chest to defend itself from $30 oil. The bottom line: Hess just sold 25 million shares at a price of $39 after purchasing 63 million shares through 2015 at an average price that was more than double, or $83 share. As Reuters concludes, “this modern Hess era is a case study that should be required reading in boardrooms everywhere.”

The right wing is getting concerned.
• Debt, Defaults, And Devaluations: A Crash Like Nothing Before (Telegraph)
A global recession is on the way. This truism of economics holds at any point in which the world is not in the grips of a contraction. The real question is always when and how deep the upcoming downturn will be. “The crash will come, but it would be nice if it came two years from now”, Thomas Thygesen, head of economics at SEB told over 200 commodity investors and analysts in London last month. His audience was rapt with unusual attention. They could be forgiven for thinking the slump had not already arrived. Commodity prices have crashed by two thirds since their peaks in 2014. Oil has borne the brunt of the sell-off, suffering the worst price collapse in modern history. Brent crude has fallen from $115 a barrel in the summer of 2014, to just $27.70 in mid-January.
Plenty of investors sitting in the blue-lit, cavernous surrounds of Bloomberg’s London HQ would have had their fingers burnt by the price capitulation. “They tell you should start your presentations with a joke, but making jokes at a commodities seminar is hardly appropriate these days,” Thygesen told his nervous audience. Major oil price falls have a number of historical precedents. Today’s glutted oil market is often compared to the crash of 1986, the last major episode over global over-supply. Back in the late 90s, a barrel of Brent crude fell to as low as $10 in the wake of the Asian financial crisis. But is the current oil price collapse really like anything the world economy has ever experienced?
For many market watchers, a confluence of factors – led by oil, but encompassing China, the emerging world, and financial markets – are all brewing to create a perfect storm in a global economy that has barely come to terms with the Great Recession. “We are in a very unusual situation where market sentiment is of a different nature to anything we’ve seen before,” says Thygesen. Unlike previous pre-recessionary eras, the current sell-off has seen commodity prices, equities and credit conditions all move in dangerous lockstep. Although a 75pc oil price collapse should represent an unmitigated positive for the world’s fuel thirsty consumers, the sheer scale of the price rout is already imperiling the finances of producer nations from Nigeria to Azerbaijan, and is now threatening to unleash a wave of bankruptcies across corporate America.
It is the prospect of this vicious feedback loop – where low oil prices create financial tail risks that spill over into the real economy – which could now propel the world into a “full blown crisis” adds Thygesen. So will it materialise? The world economy is throwing up reasons to worry, as the globe’s largest emerging markets have shown signs of deterioration over the last six months, says Olivier Blanchard, the former long-serving chief economist of the IMF. “China’s growth is probably less than officially reported. Russia and Brazil are doing very badly. South Africa is flirting with recession. Even India may not be doing as well as was forecast,” says Blanchard, who left the Fund after seven years late last year. As it stands however, he says market ructions still represent a classic case of “herd” behaviour. “Investors worry that other investors know something bad, and so just sell, although they themselves have no new information.”
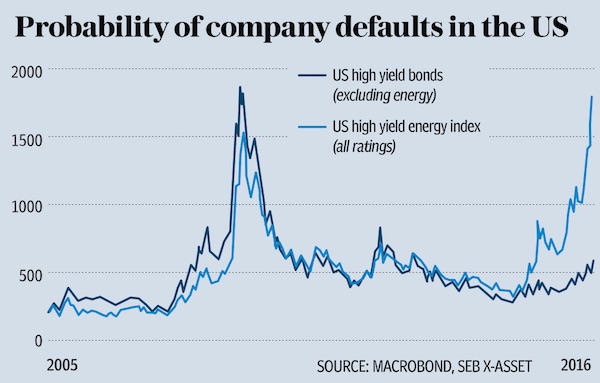
But a tipping point may well be approaching. According to Blanchard’s calculations, a 20pc decline in stock markets that persists for more than six months, will translate into a decline in consumption of between 0.5pc to 1.0pc. “This would be a serious shock. My biggest fear is precisely that the dramatic shift in mood becomes self-fulfilling”. For now, oil-induced financial stress is concentrated in the energy sector. With Brent set to languish around $30-35 barrel for the rest of the year, prices will persist below the $40-60 barrel break-even point that renders the bulk of US oil and gas companies profitable. Spreads on high yield US energy corporates have soared to unprecedented highs. “They make Lehman look like a walk in the park” says Thygesen. More than a third of the entire US high yield bond index is now vulnerable to crude prices remaining low or falling even further, according to calculations from Oxford Economics.

My friend Steve is losing his cool, and high time too. Is he really the only economist who undertands this, and can explain it? Y’all better listen closely, then.
“As someone who spent 2 years warning about this crisis before it happened, and another 8 years diagnosing it (and proposing remedies that would, I believe, be effective, if only banks and governments together would implement them), I find this dual idiocy incredibly frustrating. Rather than understanding the real cause of the crisis, we’ve seen the symptom—rising public debt—paraded as its cause. Rather than effective remedies, we’ve had inane policies like QE, which purport to solve the crisis by inflating asset prices when inflated asset prices were one of the symptoms of the bubble that caused the crisis.”
• Our Dysfunctional Monetary System (Steve Keen)
The great tragedy of the global economic malaise is that it is caused by a shortage of something that is essentially costless to produce: money. Both banks and governments can produce money at physically trivial costs. Banks create money by creating a loan, and the establishment costs of a loan are miniscule compared to the value of the money created by it—of the order of $3 for every $100 created. Governments create money by running a deficit—by spending more on the public than they get back from the public in taxes. As inefficient as government might be, that process too costs a tiny amount, compared to the amount of money generated by the deficit itself. But despite how easy the money creation process is, in the aftermath to the 2008 crisis, both banks and governments are doing a lousy job of producing the money the public needs, for two very different reasons.
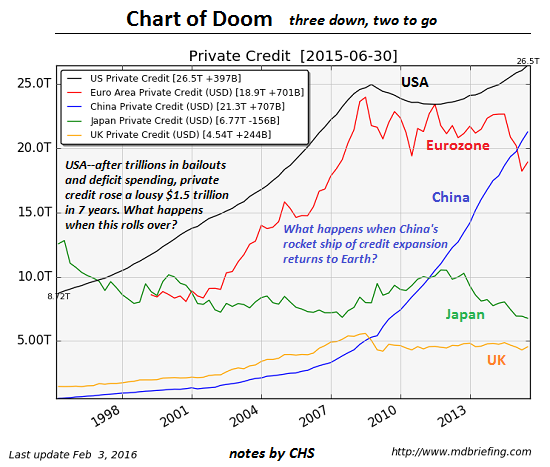
Banks aren’t creating money now because they created too much of it in the past. The booms that preceded the crisis were fuelled by a wave of bank-debt-financed speculation on some useful products (the telecommunications infrastructure of the internet, the DotCom firms that survived the DotCom bubble) and much rubbish (the Liar Loans that are the focus of The Big Short). That lending drove private debt levels to an all-time high across the OECD: the average private debt level is now of the order of 150% of GDP, whereas it was around 60% of GDP in the “Golden Age of Capitalism” during the 1950s and 1960s—see Figure 1.
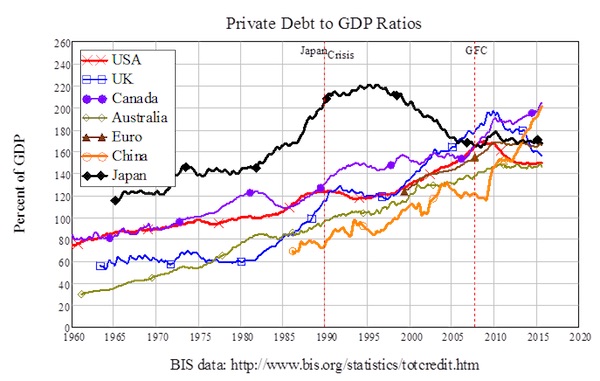
Figure 1: The private debt mountain that has submerged commerce
In the aftermath of the Subprime bubble, credit-money creation has come to a standstill across the OECD. In the period from 1955 till 1975, credit grew at 8.7% per year in the United States; from 1975 till 2008, it grew at 8% per year; since 2008, it has grown at an average of just 1.5% per year. The same pattern is repeated across the OECD—see Figure 2. Globally, China is the only major country with booming credit growth right now, but that will come crashing down (this probably has already started), and for the same reason as in the West: too much credit-based money has been created already in a speculative bubble.
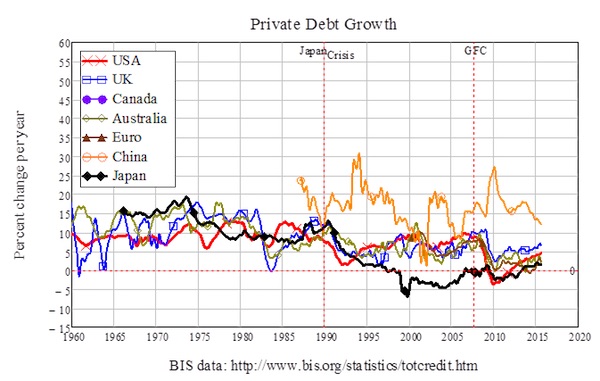
Figure 2: Credit growth is anaemic now, and will remains so as it has in Japan for 25 years
Japan, of course, got mired in this private debt trap long before the rest of the world succumbed. As Figure 1 shows, its private debt bubble peaked in 1995, and since then it’s had either weak or negative credit growth, so that its private debt to GDP level is now in the middle of the global pack. Economic growth there has come to a standstill since: Japan’s economy grew at an average of 5.4% a year in real terms from 1965 till 1990, when its crisis began; since then, it has grown at a mere 0.4% a year. That gives us a simple way to perform a “what if?”. What if the rest of the OECD is as ineffective at escaping from the private debt trap as Japan has been? Then the best case scenario for global credit growth is that it will match what has happened since Japan “hit the credit wall” in 1990

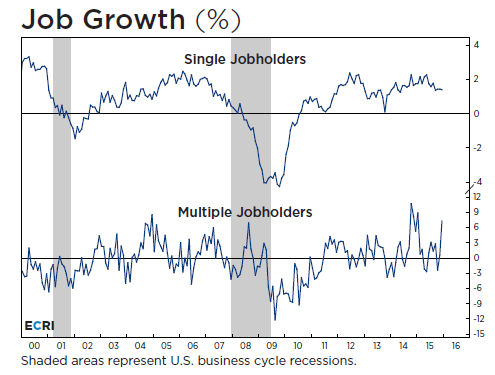
Seasonally adjusted slaughter, that is.
• Why The Bulls Will Get Slaughtered (Stockman)
Needless to say, none of that stink was detected by Steve Liesman and his band of Jobs Friday half-wits who bloviate on bubblevision after each release. This time the BLS report actually showed the US economy lost 2.989 million jobs between December and January. Yet Moody’s Keynesian pitchman, Mark Zandi described it as “perfect” Yes, the BLS always uses a big seasonal adjustment (SA) in January——so that’s how they got the positive headline number. But the point is that the seasonal adjustment factor for the month is so huge that the resulting month-over-month delta is inherently just plain noise. To wit, the seasonal adjustment factor for the month was 2.165 million. That means the headline jobs gain of 151k reported on Friday amounted to only 7% of the adjustment amount!
Any economist with a modicum of common sense would recognize that even a tiny change in the seasonal adjustment factor would mean a giant variance in the headline figure. So the January SA jobs number cannot possibly reveal any kind of trend whatsoever – good, bad or indifferent. But that didn’t stop Beth Ann Bovino, US chief economist at Standard & Poor’s Rating Services, from dispatching the usual all is swell hopium: “Today’s numbers are about momentum, so while 151,000 new jobs in January is below expectations and off pace from prior months, the data shows America’s recovery is continuing. Amid all the global economic turmoil and domestic market gyrations, positive job growth, the drop in the unemployment rate to 4.9%, and the uptick in wages show the U.S. is heading in the right direction.” Actually, it proves none of those things.
For one thing, the January NSA (non-seasonally adjusted) job loss this year of just under 3 million was 173,000 bigger than last January – suggesting that things are getting worse, not better. In fact, this was the largest January job decline since the 3.69 million job loss in January 2009 during the very bottom months of the Great Recession. So are we really “heading in the right direction” as claimed by Bovino, Zandi and the rest of the Cool-Aid crowd? Well, just consider two alternative seasonal adjustment factors for January that have been used by the BLS in the last five years. Had they used the January 2013 adjustment factor this time, the headline gain would have been 171,000 jobs; and had they used the 2010 adjustment factor there would have been a headline loss of 183,000 jobs. We could say in a variant of the Fox News motto – we report, you decide. But believe me, you can look at years of seasonal adjustment factors for January (or any other month) and not find any consistent, objective formula. They make it up, as needed.

“..to help bring Chinese companies to U.S. markets..” Which is not that easy on most exchanges.
• Obscure Chinese Firm Dives Into $22 Trillion US Market (BBG)
When Cromwell Coulson heard that an obscure Chinese real estate firm had agreed to buy the Chicago Stock Exchange, he was shocked. “My first reaction was, ‘Wow, that’s who they’re selling to?”’ said Coulson, CEO of OTC Markets in New York. “These new buyers have no connection to Chicago’s existing business. They’re completely disconnected from the current business of supporting the Chicago trading community. So wow, that’s out of left field.” While the world has gotten used to seeing Chinese companies snap up overseas businesses, the purchase of a 134-year-old U.S. stock market by Chongqing Casin Enterprise – a little-known property and investment firm from southwestern China – raises a whole host of questions. For starters, why does a provincial Chinese business with no apparent ties to the securities industry have any interest in buying one of America’s smallest equity exchanges? And will U.S. regulators sign off?
So far, Casin Group’s intentions are unclear, with calls to the company’s Chongqing headquarters going unanswered on Friday. If the deal does pass muster with American regulators, it would mark the first-ever Chinese purchase of a U.S. equity exchange, giving Casin Group a foothold in a $22 trillion market where even the smallest bourses have room to grow if they can provide the best price for a stock at any given moment. The Chicago Stock Exchange – a subsidiary of CHX Holdings – is minority-owned by a group including E*Trade, Bank of America, Goldman Sachs and JPMorgan, according to the company. The minority shareholders are also selling their stake, Chicago Stock Exchange CEO John Kerin said. The deal values the exchange at less than $100 million, according to a person familiar with the matter.
Casin Group’s offer, announced on Friday in a statement from the Chicago exchange, comes amid an unprecedented overseas shopping spree by Chinese companies. Businesses from Asia’s largest economy have announced $70 billion of cross-border acquisitions and investments this year, on track to break last year’s record of $123 billion, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. While many of those deals had obvious business rationales, the reasons for Casin Group’s bid are less clear. The company, founded in the 1990s through a privatization of state-owned assets, initially focused on developing real estate projects in Chongqing, before expanding into the environmental and financial industries. While the firm owns stakes in banks and insurers, it has no previous experience owning an exchange. Lu Shengju, the majority owner and chairman of Casin Group, wants to help bring Chinese companies to U.S. markets, according to the statement from Chicago’s bourse.

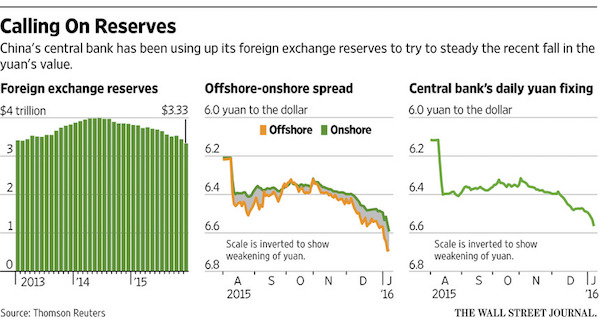
Another $100 billion spent. That leaves about 2 months at this pace till alarm bells will start going off.
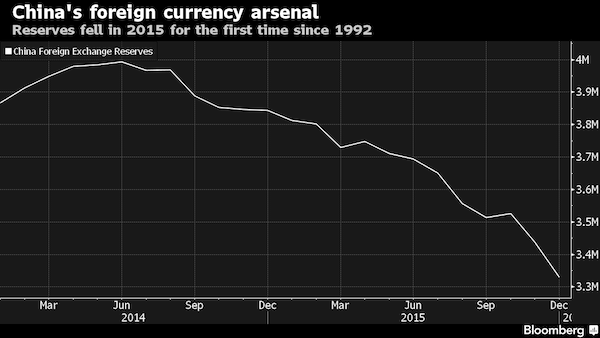
• China’s FX Reserves Decline to $3.23 Trillion (BBG)
China’s foreign-exchange reserves shrank to the smallest since 2012, indicating that the central bank sold dollars as the yuan’s retreat to a five-year low exacerbated depreciation pressure. The world’s largest currency hoard declined by $99.5 billion in January to $3.23 trillion, according to a People’s Bank of China statement released on Sunday. The stockpile fell by more than half a trillion dollars in 2015, the first-ever annual decline. Policy makers fighting to hold up the weakening yuan amid slower economic growth, plunging stocks and increasing outflows have been burning through the reserves. The draw-down has continued since the central bank’s surprise devaluation of the currency in August, when the stockpile tumbled $94 billion, a monthly record at the time.
“While the remaining reserves represent a substantial war chest, the rapid pace of depletion in recent months is simply unsustainable,” said Rajiv Biswas at IHS Global Insight in Singapore. “Domestic private investors and global currency traders see a one-way bet against the currency. This has resulted in large-scale private capital outflows since early 2015 as expectations mount that the PBOC will eventually be forced to capitulate once its reserves are sufficiently depleted.” Capital outflows increased to $158.7 billion in December, the most since September and were $1 trillion last year, according to estimates from Bloomberg Intelligence. That’s more than seven times the amount of cash that left in 2014. The PBOC has stepped up efforts to stem the exodus, warning speculators that they will be punished.
It intervened in the Hong Kong market last month after the yuan’s offshore exchange rate sank to a record 2.9% discount to the onshore rate. Apart from selling dollars, the monetary authority also gave guidance to some Chinese lenders in the city to suspend yuan lending to curb short selling, a move that contributed to the overnight interbank lending rate surging to an all-time high of 66.8% on Jan. 12.

“Now that Chinese firms have bought up so many US and European companies, money laundering can even be done in-house. ”
• The Great Escape from China (Rogoff)
Since 2016 began, the prospect of a major devaluation of China’s renminbi has been hanging over global markets like the Sword of Damocles. No other source of policy uncertainty has been as destabilizing. Few observers doubt that China will have to let the renminbi exchange rate float freely sometime over the next decade. The question is how much drama will take place in the interim, as political and economic imperatives collide. It might seem odd that a country running a $600 billion trade surplus in 2015 should be worried about currency weakness. But a combination of factors, including slowing economic growth and a gradual relaxation of restrictions on investing abroad, has unleashed a torrent of capital outflows. Private citizens are now allowed to take up to $50,000 per year out of the country.
If just one of every 20 Chinese citizens exercised this option, China’s foreign-exchange reserves would be wiped out. At the same time, China’s cash-rich companies have been employing all sorts of devices to get money out. A perfectly legal approach is to lend in renminbi and be repaid in foreign currency. A not-so-legal approach is to issue false or inflated trade invoices – essentially a form of money laundering. For example, a Chinese exporter might report a lower sale price to an American importer than it actually receives, with the difference secretly deposited in dollars into a US bank account (which might in turn be used to purchase a Picasso). Now that Chinese firms have bought up so many US and European companies, money laundering can even be done in-house.
The Chinese hardly invented this idea. After World War II, when a ruined Europe was smothered in foreign-exchange controls, illegal capital flows out of the continent often averaged 10% of the value of trade or more. As one of the world’s largest trading countries, it is virtually impossible for China to keep a tight lid on capital outflows when the incentives to leave become large enough. Indeed, despite the giant trade surplus, the People’s Bank of China has been forced to intervene heavily to prop up the exchange rate – so much so that foreign-currency reserves actually fell by $500 billion in 2015. With such leaky capital controls, China’s war chest of $3 trillion won’t be enough to hold down the fort indefinitely. In fact, the more people worry that the exchange rate is going down, the more they want to get their money out of the country immediately.
That fear, in turn, has been an important factor driving down the Chinese stock market. There is a lot of market speculation that the Chinese will undertake a sizable one-time devaluation, say 10%, to weaken the renminbi enough to ease downward pressure on the exchange rate. But, aside from providing fodder for the likes of Donald Trump, who believes that China is an unfair trader, this would be a very dangerous choice of strategy for a government that financial markets do not really trust. The main risk is that a big devaluation would be interpreted as indicating that China’s economic slowdown is far more severe than people think, in which case money would continue to flee.

But they can’t afford to wait that long.
• Albert Edwards: China Has Only “Months Left” To Stop Collapse (VW)
In this week’s issue of Société Générale’s Global Strategy research note, Edwards writes that “China has burned through almost $800bn of its FX reserves mountain since it peaked at almost $4 trillion in mid-2014. January’s FX data to be released this weekend is set to register another sharp drop of $120bn (consensus estimate).” He goes on: “But at $3.2bn the market remains content that massive firepower remains to support the renminbi. It does not. Our economists estimate that when FX reserves reach $2.8 trillion – which should only take a few more months at this rate – FX reserves will fall below the IMF’s recommended lower bound. If that occurs in the next few months, expect to see a tidal wave of speculative selling, forcing the PBoC to throw in the towel and let the market decide the level of the renminbi exchange rate.”
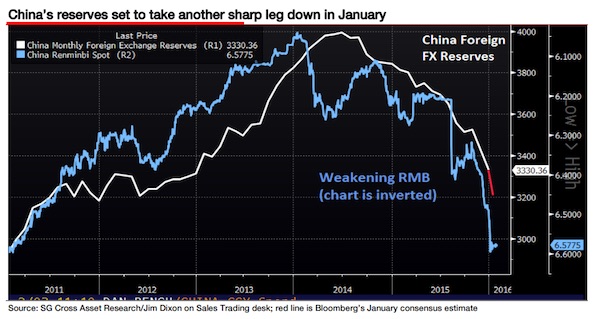
Edwards’ view is based on the predictions of Société Générale’s China economist Wei Yao. Wei Yao has written that in her view, the PBoC might, “move to a free-float within six months, after burning through a significant amount of FX reserves.” Both Yao and Edwards’ doom-mongering is based on the level of China’s FX reserves. China has been depleting its FX reserves in an effort to slow the pace of currency depreciation. However, if the country continues to spend its reserves at the current rate, FX reserves will fall through the $2.8 trillion level that the IMF believes is the lowest acceptable level. The IMF’s ‘lowest acceptable’ reserves level is based on four specific elements that reflect potential drains on the balance of payments: (1) exports, (2) broad money, (3) short-term external debt, and (4) other liabilities (long-term external debt and portfolio liabilities).
Société Générale’s analysts believe that (assuming the level of short-term external debt at remaining maturity was unchanged from year-end 2014) China’s reserves are at 118% of the recommended level (estimated to be $2.8 trillion). If China’s reserves fall below the key $2.8 trillion level, the market could lose confidence in the PBoC’s ability to resist currency depreciation and manage future balance of payments shocks. Only two major emerging market countries (Malaysia and South Africa) have reserves that are below the IMF’s recommended range and many EM countries now have a more robust reserve balance than China in terms of the percentage above the IMF’s recommended minimum.

Because it’s just a narrative. More right wing worry signs.
• Why Doesn’t 4.9% Unemployment Feel Great? (CNN)
The U.S. unemployment rate just fell below 5% for the first time since 2008. Normally, this would merit a celebration. But these aren’t normal times. The economy is better than it was in the Great Recession, but not even President Obama is ready to declare it’s booming. In a special speech Friday touting the job gains during his presidency, Obama admitted there’s more “to tackle.” “We should be proud of the progress we’ve made…we’ve recovered from the worst economic crisis since the 1930s,” Obama said. He doesn’t believe he gets enough credit for creating over 14 million jobs. People as diverse as Democrat Bernie Sanders and Republican Donald Trump don’t put it gently. They claim the “real” unemployment rate is much higher. Sanders calls the economy “rigged,” and Trump says the U.S. never wins anymore. There are three key reasons why everyone from Main Street to Wall Street isn’t cheering 4.9% unemployment.
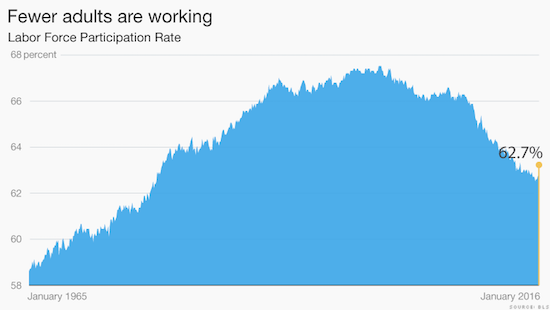
1. Fewer adults are working Only 62.7% of adult Americans are working. The so-called Labor Force Participation rate hasn’t been this low since the late 1970s. The rate measures how many people over age 16 are working or actively seeking work. Back in the ’70s, it was low because fewer women worked outside the home. That’s not the story today. Now, three factors are driving the decrease in workers. The first is that a huge part of the adult population, Baby Boomers, are retiring. That’s expected and healthy. It explains about half of the decline in the workforce. The second is more young people are going to college and graduate school. They are studying more, which should be a positive for the nation. But the third one is alarming: some people have just given up on finding work. It’s hard to quantify how many people fall into this dropout category, but it’s large enough to matter. Politicians like Trump talk about it in stump speeches.The WSJ estimates that about 2.6 million of the roughly 92 million American adults who don’t work want a job but aren’t looking for one.
2. Long-term unemployment is still high Another reason why the jobs picture still looks gloomy is that an unusually high number of people can’t find jobs even though they have been looking for a long time. About 2.1 million Americans have been unable to get a job for over half a year. The government calls these people the “long-term unemployed.” During the worst of the Great Recession, 6.8 million people were long-term unemployed. So there’s been improvement, but there are still roughly double the number of long-term unemployed than in normal times.
3. Wage growth is anemic The last big issue is that wages aren’t going up for many Americans. The typical take home pay (often called “median income” by the Census Bureau) is about the same today as it was 20 years ago, once you adjust for inflation. In other words, middle class families aren’t really getting ahead. They’re just getting by. To be fair, this was a problem even before the Great Recession came along, but experts keep predicting wages will go up and it’s not happening. On Friday, Obama tried to celebrate the small gains that have been made in recent months. “This progress is finally starting to translate into bigger paychecks,” he said. But the reality is wage growth is only 2.5% a year. As Sharon Stark of D.A. Davidson notes, normally when unemployment is this low, wage growth should be humming along at about 4% a year.

So many crazies. Trying to provoke Russia by sending Ukraine’s fascist troops into Syria.
• Risk of WWIII as Saudi Arabia, Turkey –and Ukraine– Wade Into Syria (Trayner)
A terrifying array of rival superpowers are wading into the chaotic conflict on opposing sides. Analysts now fear the bloodbath – already longer than World War One – is mutating into a full-scale regional war. Saudi Arabia has threatened to send in ground troops and intelligence reports suggest Turkey is preparing to invade. Ukraine is also weighing up sending in soldiers. If their forces clashed with Russians or Iranians already on the ground, NATO – including Britain – could be dragged into an apocalyptic World War 3. Most military experts see the conflict as a proxy war between Sunni Muslim Saudi Arabia – supported by the US – on one side and Shia Muslim Iran – backed by Russia – on the other. The civil war in Yemen is also a victim of the new power struggle for control of the Middle East – which dates back to the death of Muhammed in 632 AD.
But the new Cold War – which some claim involved Saudi Arabia arming ISIS and Iran backing militants such as the Houthi rebels in Yemen – would turn searing hot if Saudi troops met the Iranian Army on the battlefield. The US fears Saudi Arabia may have obtained – or tried to obtain – nuclear weapons for an final battle with its centuries-old enemy. Tom Wilson, a research fellow for think tank the Henry Jackson Society, said: “The proxy war between Saudi Arabia and Iran is now in a rapid state of escalation. “Saudi talk of sending troops to Syria may be a bluff to try and force the West to take more decisive action in that country instead. “But if the Saudis do put troops on the ground in Syria then this would represent the opening of a major new front in what is increasingly a full scale regional conflict.”
Russia claims aerial photographs reveal Turkey is preparing to invade Syria, its neighbour. Turkish Islamic extremists are already fighting in Syria – some on the side of ISIS – with well-attended funerals for “martyrs” held back home in Turkey. Ultra-nationalist “Grey Wolves” – who want to protect Turkmen living in northern Syria and restore the Ottoman Empire – are also battling the Syrian army and Russian forces. Enmity between Black Sea rivals Russia and Turkey dates back so long a Jewish “oracle” prophesied an apocalyptic war between Russia and Turkey would usher in the End of Days 200 years ago. Turkey is now a member of NATO and if the old enemies came to blows again – as almost happened when Turkey shot down a Russian jet last year – the US and UK would be compelled to back Turkey. Britain has already been dragged into war with Russia by Turkey once: the Crimean War.


Everything they can do wrong, they do.
• EU Ministers Want To Buttress Borders To Stem Refugee Flow (AP)
European Union nations anxious to stem the flow of asylum-seekers coming through the Balkans are increasingly considering sending more help to non-member Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM) as a better way to protect European borders instead of relying on EU member Greece. With Athens unable to halt the tens of thousands of people making the sea crossing from Turkey, EU nations fear that Europe’s Schengen border-free travel zone could collapse, taking with it one of the cornerstones on which the 28-nation bloc is built. “If Greece is not ready or able to protect the Schengen zone and doesn’t accept any assistance from the EU, then we need another defense line, which is obviously Macedonia and Bulgaria,” Hungarian Foreign Affairs Minister Peter Szijjarto said at Saturday’s meeting of EU foreign ministers in Amsterdam.
An estimated 850,000 migrants arrived in Greece in 2015, overwhelming its coast guard and reception facilities. Aid groups say cash-strapped Greece has shelter for only about 10,000 people, just over 1% of those who have entered. Most of the asylum-seekers then travel on across the Balkans and into the EUs heartland of Germany and beyond. Szijjarto said EU nations are “defenseless from the south. There are thousands of irregular migrants entering the territory of the EU on a daily basis.” Austrian Foreign Minister Sebastian Kurz said the cash-strapped government in Athens still underestimates the crisis. “I still don’t have the feeling that it has dawned on Greece how serious the situation is” for receiving nations like Austria, he said.
The situation has pushed some EU nations to send bilateral aid to FYROM, a non-EU nation, to control its border with EU member Greece. There has been even talk of sending military troops to FYROM to beef up the Greek border. FYROM Foreign Minister Nikola Poposki said after the meeting it did not matter what the aid was technically called. “The essential thing is that we have people and equipment to control the border and do registration where legal crossing should happen,” he said. He said FYROM has already put its own military on the job. “They’re making sure that we have decreased the illegal crossings through our border and were going to continue to make these efforts,” he said.

There certainly is no such thing as an EU policy.
• Austria Threatens To Extend Border Controls (Reuters)
Austria will extend its border controls if Turkey does not take back refugees picked up at sea on their way to Greece, Chancellor Werner Faymann said in an interview with the daily Oesterreich, being published on Sunday. He had earlier said that migrants picked up at the Greek external EU border should be sent back directly to Turkey because this was the only measure that would make a radical enough impact. Austria is set to introduce a new border management system at Spielfeld, a key crossing point on its south-eastern border with Slovenia, which aims at speeding up applications and making the country less attractive to asylum seekers. More such border management facilities on other routes may be needed if Turkey does not respond to his proposal, the chancellor was quoted as saying.
Faymann said Turkey must make a decision by Feb. 18, when EU leaders meet for a summit. It would not be a solution if Turkish border controls led to 10,000 refugees arriving at EU borders instead of 20,000, Faymann was quoted as saying in the interview. “Then we must secure our borders even more,” Faymann said. “To protect internal borders is a makeshift solution. But we have to be prepared.” Ankara and Brussels agreed to slow down the flow of migrants in a Nov. 29 deal, but refugees continue to stream into Greece. Austria, which has a population of 8.4 million and last year received 90,000 applications for asylum, has said that the number of refugees it will accept this year will be limited to 37,500.

And let me guess, Greece should pay its share?!
• Austria Wants EU To Cover Costs Of Additional Migrants (Reuters)
Austria’s Finance Minister Hans-Joerg Schelling has asked the European Commission to provide €600 million to cover the costs of taking in additional refugees, a ministry spokesman said on Saturday. Austria budgeted for 35,000 asylum seekers annually at a cost of €11,000 per person but took in some 90,000 people in 2015, the spokesman quoted the minister as saying in a letter to the head of the EU executive, Jean-Claude Juncker. “Concerning the migration crisis it is high time the Commission returned to its normal function as an independent institution representing the general Community interest and start acting as such,” Schelling said in the letter, part of which was published by the daily Kurier.
Austria and neighboring Germany threw open their borders last year to hundreds of thousands of people pouring into Europe, many of them fleeing conflicts in Syria and elsewhere. Despite an initial outpouring of sympathy for the migrants, public concern about the influx has fueled a rise in support for the far right in Austria. Last week Vienna said it would step up deportations of migrants to countries it deems safe.