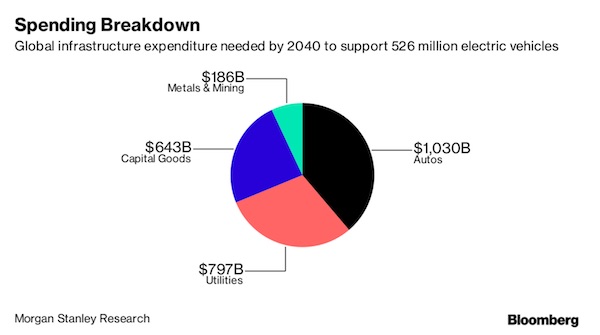
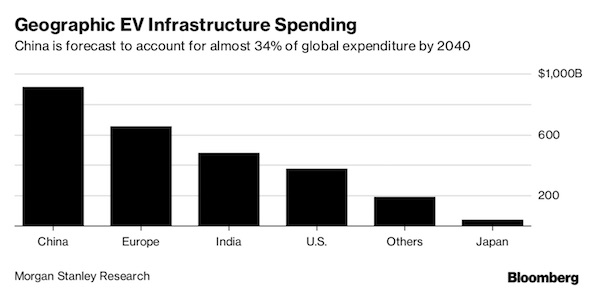
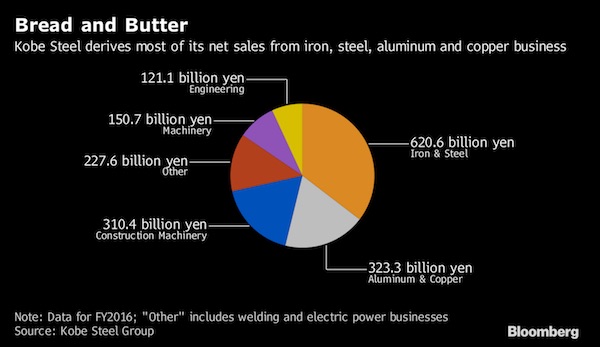
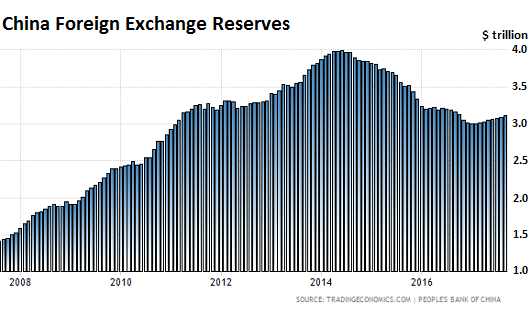
Harris&Ewing Treasury Building, Fifteenth Street, Washington, DC 1918



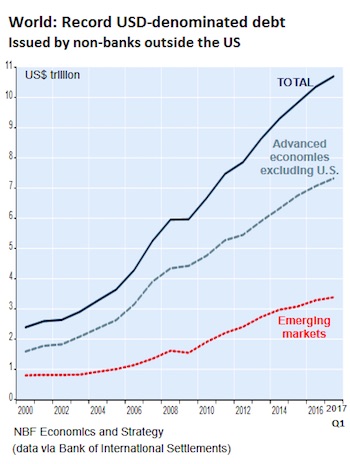
$11 trillion is merely the start.
• Asia’s Two Biggest Stock Markets Have Become An $11 Trillion Headache (BBG)
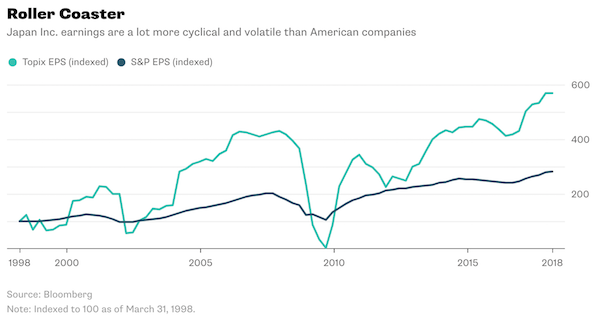
Asia’s two biggest stock markets are jostling for an ignominious prize. Japan’s Topix index and China’s Shanghai Composite Index have tumbled more than 13% in 2016 to rank along Nigerian and Mongolian shares as the world’s worst performers. In the two years through the end of December, the Asian gauges outperformed MSCI’s global measure by at least 20 percentage points. The Bank of Japan stood pat on monetary policy Thursday, sending Tokyo stocks tumbling, while the Shanghai measure fell to a one-month low. The benchmark gauges in two of the world’s largest stock markets, which have a combined value of almost $11 trillion, are declining as investors detect a reduced appetite from policy makers to boost monetary stimulus.
Thursday’s BOJ decision was the first under Governor Haruhiko Kuroda where a majority of economists expected easing that didn’t materialize, while strategists now see China’s central bank keeping its main interest rate on hold until the fourth quarter. “Neither China nor Japan have a solid plan on dealing with their slowing economies,” said Tomomi Yamashita at Shinkin Asset Management. “There is still scope for easing, and as for Japan there are fiscal policies they can carry out. There’s still hope. But today there was just too much hope on the BOJ.”
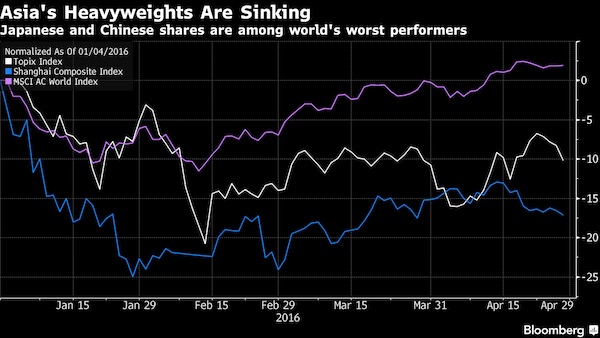
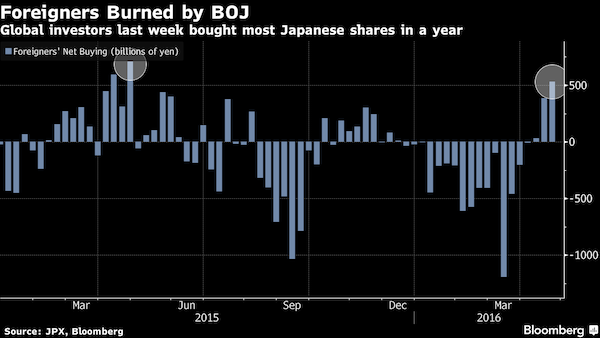
The Topix sank 3.2% on Thursday after the central bank kept bond-buying, interest rates and exchange-traded fund purchases unchanged. The stock gauge has fallen for four straight days, handing losses to foreign investors who piled the equivalent of $4.9 billion into the market last week, the most in a year. Overseas traders were net sellers of Japanese equities for the first 13 weeks of 2016. “I give up,” Ryuta Otsuka at Toyo Securities in Tokyo said. “It’s a really disappointing result and I feel like throwing in the towel. It cuts because we had so much hope.” The Topix posted four straight annual gains through 2015, while even a $5 trillion rout in Chinese shares last summer couldn’t stop the Shanghai Composite from being the world’s top-performing major market over the last two years. The declines for both gauges in 2016 compare with a 2.5% advance by the S&P 500, which is closing in on last year’s record.
Read more …

Sometimes I wonder why it takes people so long to figure things out. I’ve been saying ever since Abenomics was launched that it would fail. Because it was always pie in the sky only, not based on any understanding of what caused spending to plummet.
• Japan’s Abenomics ‘Dead In The Water’ After US Currency Warnings (AEP)
The Bank of Japan has been forced to retreat from further emergency stimulus after a blizzard of criticism at home and abroad, and warnings that extreme measures may now be doing more harm than good. The climb-down by the world’s most radical central bank is the latest sign that the monetary experiments since Lehman crisis may have run their course. The authorities have not exhausted their ammunition but are hitting political and legal constraints. The yen surged 3pc against the US dollar in the biggest one-day move in eight months and equities skidded across Asia after the BOJ failed to take fresh action to stave off deepening deflation, catching markets badly off guard. Governor Haruhiko Kuroda dashed hopes for ‘helicopter money’, warning that direct monetary financing of spending would be “illegal”.
Mr Kuroda insisted that the BoJ still has plenty of firepower and can at any time push interest rates even deeper into negative territory or boost bond purchases beyond the current $74bn a month. “If additional easing is needed, we will do so promptly,” he said. The reality is that negative rates (NIRP) have backfired badly on every front. They have prompted bitter protests from banks and money market funds caught in a squeeze. The yen has appreciated by 10pc since the BoJ first embarked on the policy in January, the exact opposite of what was intended. The rising yen – ‘endaka’ – is pushing Japan deeper into a deflation trap and undercutting the whole purpose of ‘Abenomics’. Core inflation has fallen to minus 0.3pc. The Nikkei has dropped 13pc this year, with contractionary wealth effects that make the BoJ’s task even harder.
“Negative rates have completely failed,” said David Bloom from HSBC. Washington will not tolerate the use of NIRP in any case, deeming it a disguised attempt to drive down exchange rates and export problems to the rest of the world. Jacob Lew, the US Treasury Secretary, warned Japan and the eurozone at the G20 in Shanghai in February that the Obama administration is losing patience with use of beggar-thy-neighbour tactics by countries already running a current account surplus. They are in effect shifting their excess capacity abroad. Germany in particular is coming into the US cross-hairs. Richard Koo from Nomura said the US is now on the warpath against currency manipulators. Mr Lew’s threat effectively renders Abenomics “dead in the water”. The Japanese economy is contracting again, caught in a debt-deflation vice.
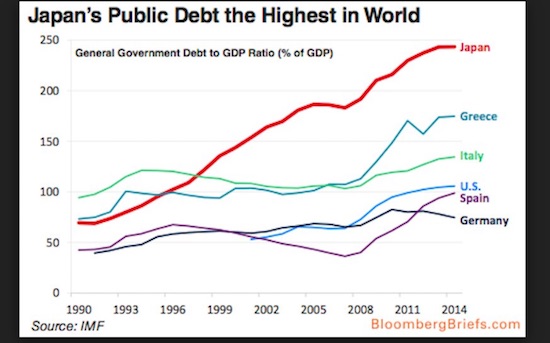
Growth has been negative for four of the last eight quarters. What was once a ‘Lost Decade’ is turning into a “Lost Quarter Century” with no remedy in sight. “Their options are diminishing. I can’t see any way out of the debt-trap, and it is an acid test for the western world,” said Neil Mellor from BNY Mellon. Public debt is rising fast on a shrinking economic base, pushing the public debt ratio to an estimated 250pc of GDP this year. “The debt will never be ‘repaid’ in the normal sense of the word,” said Lord (Adair) Turner from the Institute for New Economic Thinking. Olivier Blanchard, the former chief economist for the International Monetary Fund, warned recently that country is nearing the end-game as the pool of domestic funding for the bond market starts to dry up and the Japanese treasury is forced to rely on much more costly capital from global investors.
Read more …

The predictable culmination of decades of a failed system is a hockeystick.
• Debt Is Growing Faster Than Cash Flow By The Most On Record (ZH)
By now it is a well-known fact that corporations have no real way of generating organic growth in this economy, so they are relying on two things to boost share prices: multiple expansion (courtesy of central banks) and debt-funded buybacks (courtesy of central banks), the latter of which requires the firm to generate excess incremental cash. Incidentally, as SocGen showed last year, all the newly created debt in the 21st century has gone for just one thing: to fund stock buybacks.

The problem with this is that if a firm is going to continue to add debt to its balance sheet in order to fund buybacks (and dividends), then it needs to be able to generate enough operational cash flow in order to service the debt. Even if one makes the argument that debt is cheap right now, which may be true, or that central banks are backstopping it, which is certainly true in Europe as of a month ago, the fact remains that principal balances come due eventually also, and while debt can be rolled over, at some point the inability to generate cash from the operations catches up with them; furthermore even a small increase in rates means the rolling debt strategy is dies a painful death, as early 2016 showed.
In the following chart we can see net debt growth skyrocketing nearly 30% y/y, while EBITDA (cash flow) has been contracting for the past year. In fact, as SocGen shows below, the difference in the growth rate between these two most critical data series is now over 35% – the biggest negative differential in recent history.

Of course, every finance 101 student knows that a firm which has to borrow more cash than it is able to produce from its core operations is not a sustainable business model, and yet today’s CFOs, pundits and central bankers do not. And the next question is: what happens if the Fed does raise rates, what happens to the feasibility of these companies servicing the debt while also spending on R&D and CapEx (assuming there is any), and who can only afford the rising interest expense as a result of ever smaller interest rates? The answer is, first, massive cost cutting, i.e. layoffs, which would be a poetic way for the Fed’s disastrous policies to be reintroduced to the real economy… and then, more to the point, mass defaults.
Read more …

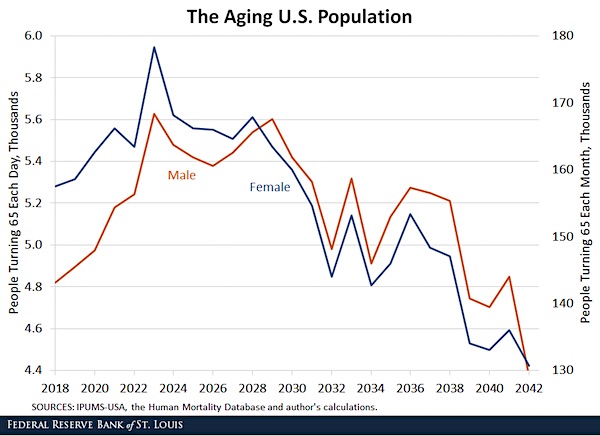
Our entire societies will have to change dramatically because of this. Parents will have to move in with their children again. The children who earn much less than the parents did.
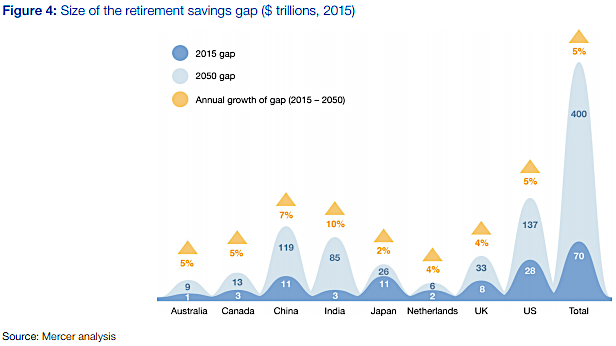
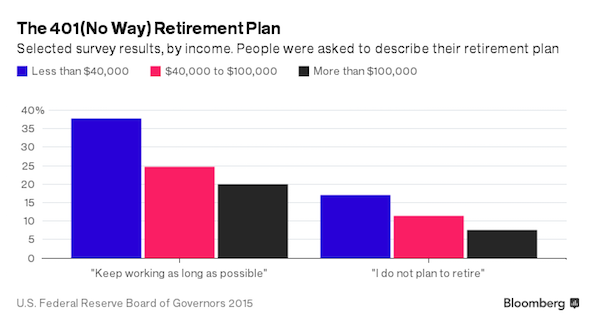
• The Typical American Couple Has Only $5,000 Saved For Retirement (MW)
When American companies began switching from traditional pensions to self-directed 401(k)-like plans in the 1980s and 1990s, it was supposed to lead to a golden age of retirement security. No longer would workers be at the mercy of the company’s generosity or of Social Security’s solvency; workers themselves would be responsible for saving enough for a comfortable retirement. Some 30 years later, the results are in: The median working-age couple has saved only $5,000 for their retirement, according to an analysis of the Federal Reserve’s 2013 Survey of Consumer Finances by economist Monique Morrissey of the Economic Policy Institute. The do-it-yourself pension system is a disaster.
Even as the traditional company-funded pension has nearly disappeared and even as Social Security benefits are being slowly eroded, most workers haven’t saved enough to offset those losses to their retirement income. 70% of couples have less than $50,000 saved. Even those on the cusp of retirement — the median couple in their late 50s or early 60s — has saved only $17,000 in a retirement savings account, such as a defined-contribution 401(k), individual retirement account, Keogh or similar savings account. How long does $5,000, or even $50,000, last? Until the first big medical bill? Morrissey figures that about 43% of working-age families have no retirement savings at all. Among those who are five to 10 years away from retirement, 39% have no retirement savings of their own.
The sad fact is that most Americans are less prepared for retirement than Americans were 30 years ago. Few have enough pension wealth to make much difference in their lives once they stop working. The lack of savings in 401(k) and individual retirement accounts wouldn’t be a such big deal if retirees could rely on other sources of income, such as a traditional defined-benefit pension or Social Security. But those other income sources are declining. Fewer and fewer newly retired people are covered by a regular pension that provides a guaranteed monthly check based on salary and years of service. In addition, Social Security benefits are already being reduced as the normal retirement age is gradually increased from 65 to 67. Further reductions in Social Security benefits — by limiting the cost-of-living adjustment or by increasing the normal retirement age to 70, for example – would be disastrous for tomorrow’s retirees.
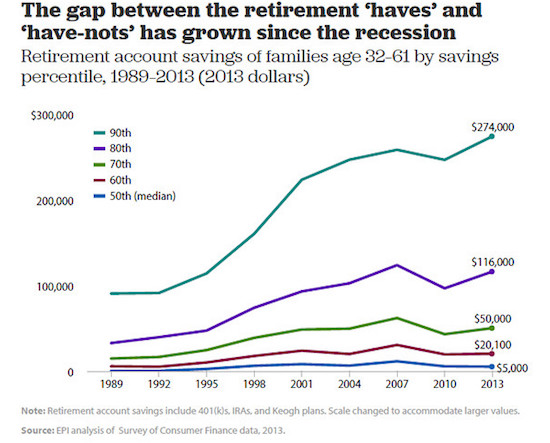
The median working-age couple had $5,000 in a retirement savings account as of the most recent data. The top 10% of savers had accumulated $274,000, according to the Economic Policy Institute analysis of Federal Reserve survey data
Read more …

Forget growth. Think survival.
• US Corporate Profits on Pace for Third Straight Decline (WSJ)
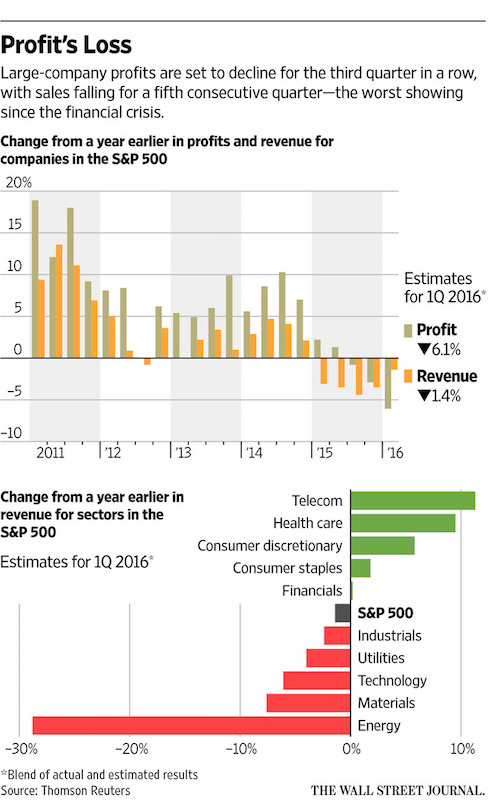
U.S. corporate profits, weighed down by the energy slump and slowing global growth, are set to decline for the third straight quarter in the longest slide in earnings since the financial crisis. Weakness was felt across the board, with executives from Apple to railroad Norfolk Southern and snack giant Mondelez saying the current quarter remains tough. 3M, which makes tapes, filters and insulation for consumer electronics, forecast continued weak demand for that industry. Procter & Gamble reported sales declines in its five business categories despite price increases. “It’s a difficult environment indeed,” said PepsiCo CEO Indra Nooyi. “Most of the developed world outside the United States is grappling with slow growth. GDP growth in developing and emerging markets is also challenged.”
The concerns from company executives echo weak economic data released Thursday morning, which showed U.S. gross domestic product rose just 0.5% in the first quarter. Business investment and consumer spending on goods slowed, while consumer spending on services climbed. “On the one hand, consumer spending continued to be the primary economic driver in the U.S. On the other hand, industrial production has been disappointing,” United Parcel Service Inc. CEO David Abney said Thursday after the delivery company reported a 3.1% revenue increase. Based on the 55% of companies in the S&P 500 index that had already reported results Thursday morning, Thomson Reuters expects overall earnings to decline by 6.1% in the first quarter compared with a year earlier.
Even excluding energy companies, which are expected to have their worst quarter since oil prices began to plunge in 2014, profits are on pace to fall by 0.5%. Revenues are expected to fall 1.4% overall, or rise 1.7% excluding energy, according to Thomson Reuters. This would mark the S&P 500’s third consecutive quarter of declining earnings—the longest streak since the financial crisis. Revenues will have declined for five quarters in a row, outstripping even the four-quarter slide in 2008 and 2009.
Read more …

The US dollar is set to rise like a mushroom cloud and break the global camel’s back.
• Dollar Drops to 11-Month Low as Asian Stocks Fall; Oil Near $46 (BBG)
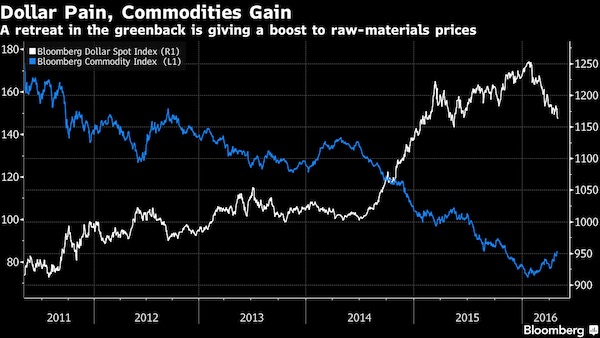
The dollar dropped against all of its G-10 peers after weaker-than-expected U.S. economic growth dimmed prospects for a Federal Reserve interest-rate increase at a time when monetary easing is being put on hold elsewhere. Asian stocks fell and crude oil traded near $46 a barrel. The Bloomberg Dollar Spot Index sank to an 11-month low, while the yen was headed for its biggest weekly jump since 2008 after the Bank of Japan unexpectedly refrained from adding to record stimulus on Thursday. Japanese financial markets are shut for a holiday and an MSCI gauge of shares in the rest of the Asia-Pacific region slid for the third day in a row. The greenback’s decline is proving a plus for commodities, which are poised for their best monthly gain since 2010. Crude has jumped 20% since the end of March, while gold and silver are at 15-month highs.
The BOJ’s surprise decision capped a week of fence-sitting for central banks, with the Fed keeping interest rates steady for a third straight meeting and policy makers from New Zealand to Brazil also holding the line. The slowest pace of American economic expansion in two years reignited some concern over the global outlook, and pushed out bets on the potential timeline for tighter Fed policy. “Central banks look like they have run out of bullets to a degree,” said Mark Lister at Wellington’s Craigs Investment Partners. “We’re getting to that point where there are limits to the results they can get from anything more they do. This points to a fragile outlook with still a lot of risks out there.”
Read more …

Worrying only if it surprises you perhaps?!
• Sluggish US Growth Part Of A Worrying Global Trend (G.)
It would be easy to dismiss the slowdown in the US economy to near-stall speed as a piece of rogue data resulting from the inability of number crunchers at the Department of Commerce in Washington to take account of the fact that large parts of the country are blanketed by snow during the winter. Easy but wrong. Back in spring 2015, the world’s biggest economy was expanding at an annual rate of 3.9%. In the third quarter the growth rate halved to 2%, before falling again to 1.4% in the final three months of the year. Describing the further easing to 0.5% in the first three months of 2016 as a temporary aberration – which was the knee-jerk response of upbeat analysts on Wall Street – is pushing it a bit.
A better explanation is that the sluggishness of US growth is part of a global trend, in which all the major economies are expanding more weakly than they were in the middle of last year. That’s the story for China, the eurozone, Japan and the UK. Each quarter, the data company Markit compiles a global Purchasing Managers’ Index for JP Morgan, with the intention of providing an up-to-date picture of economic conditions. The result for the first three months of 2016 showed activity at its lowest level in more than three years. Nor is there much hint of an improvement in the near future. In the US, firms are hacking back at investment – normally the sign of a looming recession. Consumer confidence has weakened, in part because real incomes are being squeezed.
As export-driven economies, Japan and the eurozone rely on a thriving US to buy their goods, so it is no surprise to find both struggling. The Bank of Japan will be forced to revisit its decision not to provide additional stimulus, since the upshot of its inaction has been a sharp rise in the yen, which will lead to even slower growth. Mario Draghi may again have to lock horns with the Bundesbank president, Jens Weidmann, in order to force through measures aimed at boosting activity in Europe. But the law of diminishing returns is at work. Each cut in interest rates, each fresh dollop of quantitative easing, has less of an impact than the last. The global economy is running out of steam and the conventional weapons are increasingly ineffective. This is not about blizzards shutting factories in Michigan. It goes much deeper than that.
Read more …

Britain is a sad joke.
• Renting In London More Costly Than Living In Most European 4-Star Hotels (Ind.)
It is now cheaper to live in a 4-star hotel in two-thirds of European capitals than it is to rent the average London flat. Latest figures show that the average rent for a London flat is now £1,676 per month – or £55 a night – having increased by 30% in the last four years. For the same amount of money you could live year round in a hotel in Dublin, Rome, Paris or Brussels. Among the hotels that are more affordable than the average London rent include the Mercure Warszawa Grand in Warsaw that boasts a fitness centre, business facilities and two restaurants.
The Best Western Plus Hotel in Paris, the Nordic Hotel Domicil in Berlin and the Relais Castrum Boccea in Rome can also all be booked for less than £55 a night on travel websites for the 5th May this year. The figures were highlighted by Labour’s Mayoral candidate Sadiq Khan. He said: “Renting a home shouldn’t be a luxury, but under the Tories Londoners could live in 4-star luxury in most of Europe for what they pay. “Rents have gone up by 30% with a Tory Mayor and it would be exactly the same under Zac Goldsmith – with rents soaring above £2,000 a month. Mr Khan said he would create a London-wide social letting agency as well as naming and shaming bad landlords and setting up a landlord licensing scheme.”
Read more …

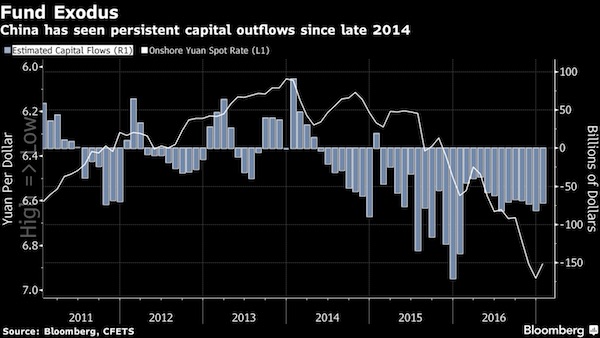
And that’s before the bad debts are properly accounted for, and while the PBoC still issues record amounts of additional debt.
• China Banks’ Profit Growth Stalls As Bad Debts Rise (R.)
Four of China’s five largest state-owned banks barely posted any growth in profit in the first quarter, as widely expected, with rising bad debt and narrower margins hitting their bottom lines. The country’s banks face challenges from both defaulting borrowers, who are struggling amid a slowing economy, and successive cuts in interest rates which have eaten away at margins. Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China’s biggest lender by assets, announced a 0.6% rise in net profit on Thursday. Bank of Communications posted a 0.5% rise in net profit in the first quarter and Agricultural Bank of China a slightly better 1.1% rise in profit. On Tuesday, Bank of China recorded a 1.7% rise in net profit in the fist quarter.
Non-performing loan (NPL) ratios remained flat -or rose- at all four lenders, while bad loan volumes increased, helping to sink loan-loss allowance ratios. At ICBC, the volume of non-performing loans increased 14% in the three-month period to 204.66 billion yuan ($31.60 billion), from 179.52 billion yuan at the end of 2015, sending the bank’s NPL ratio to 1.66% from 1.5%. ICBC’s loan-loss allowance ratio fell to 141.21%, from 156.34% at the end of December. ICBC also pointed to “the continuing impact of five interest rate cuts by the People’s Bank of China” since 2015 as a source of stress. The bank reported its interest margin (NIM) – the difference between its lending rate and the cost of borrowing – fell to 2.28 at the end of the first quarter, from 2.47 at end-December.
At BoC, NIM fell to 1.97 at end-March from 2.12 at end-December. BoCom did not disclose its NIM, but reported a 2.78% decline in net interest income, even as the bank’s net income rose half a% to 19.07 billion yuan for the first quarter. AgBank also did not disclose its NIM. In a bid to relieve banks of the mounting pile of bad debts, China’s central bank is preparing regulations that would allow commercial lenders to swap non-performing loans of companies for stakes in those firms, sources told Reuters in February.
Read more …

Going through the motions.
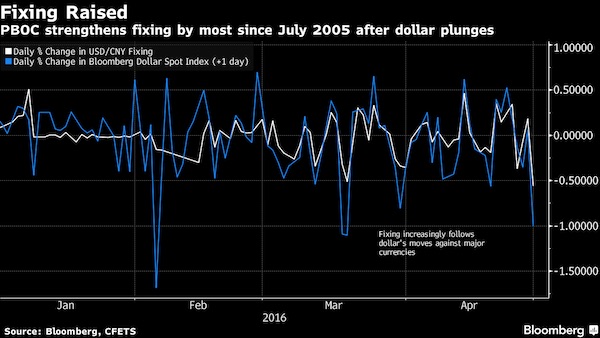
• China’s Central Bank Raises Yuan Fixing by Most Since July 2005 (BBG)
China’s central bank responded to an overnight tumble in the dollar by strengthening its currency fixing the most since a peg was dismantled in July 2005. The reference rate was raised by 0.6% to 6.4589 per dollar. A gauge of the greenback’s strength sank 1% on Thursday after the Bank of Japan’s decision to unexpectedly keep monetary policy unchanged sent the yen surging. The offshore yuan was little changed at 6.4834 after gaining 0.3% in the last session. While the change in the fixing is extreme relative to the small moves of recent years, analysts said it reflects increased volatility in the dollar against other major exchange rates rather than a policy shift by the People’s Bank of China. The yuan weakened against a basket of peers even as it climbed versus the greenback on Friday.
“The offshore yuan’s reaction is muted, so it seems the market was already expecting a much stronger fixing,” said Ken Cheung, a currency strategist at Mizuho Bank in Hong Kong. “This is a reaction to the dollar weakness overnight, and there’s not much in the way of policy intention to read into.” The dollar reached the lowest level since June after the yen jumped the most in almost six years and data showed U.S. gross domestic product expanded in the first quarter at the slowest pace in two years. A Bloomberg replica of the CFETS RMB Index, which measures the yuan against 13 exchange rates, fell 0.2% to a 17-month low. The onshore yuan climbed less than 0.1%.
“The fixing is no surprise, the expectation for a stronger yuan fix was laid by the gains for the yen after the Bank of Japan announcement yesterday,” said Patrick Bennett at Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce in Hong Kong. “The trade weighted basket continues to depreciate, albeit at a modest pace. But the key to the lower trade-weighted rate does not really lie with the PBOC, rather it is the dollar weakness against other major currencies which is the main driver.”
Read more …

May 1 is big, but still just a transfer station. July 1 is much bigger.
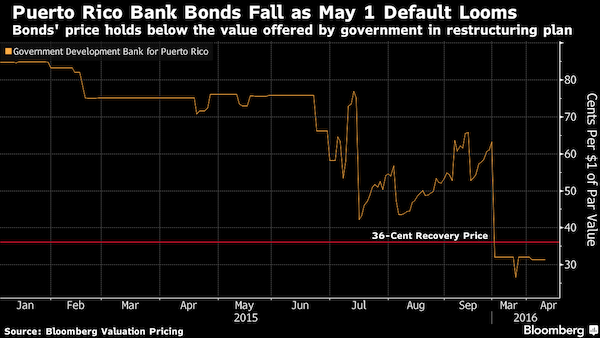
• Puerto Rico Risks Historic Default as Congress Chooses Inaction (BBG)
Even if Puerto Rico manages to strike a last-minute deal to defer bond payments due in three days, the commonwealth’s financial collapse is about to enter an unprecedented phase. Anything short of making the $422 million payment that Puerto Rico says it can’t afford would be considered a technical default. More importantly, it opens the door to larger and more consequential defaults on debt protected by the island’s constitution, and raises the risk of putting efforts to resolve the biggest crisis ever in the $3.7 trillion municipal market into turmoil. Nearly 10 months after Governor Alejandro Garcia Padilla said the commonwealth was unable to repay all its obligations, Puerto Rico has failed to reach an accord on a broad restructuring deal presented to bondholders.
During that time the administration has delayed payments to suppliers, postponed tax refunds, grabbed revenue originally used to repay other bonds and missed payments on smaller agency debt. With its options drying up, no bondholder agreement in sight and Congressional action delayed, defaulting may be the next step for Puerto Rico. “It’s a game changer because it starts an actual legal process with teeth on both sides that can finally advance settlement negotiations,” said Matt Fabian at Municipal Market Analytics. “Pre-default negotiations are really not going anywhere. Post default might have a better chance.” Puerto Rico and its agencies racked up $70 billion in debt after years of borrowing to fill budget deficits and pay bills as its economy shrunk and residents left the island for work on the U.S. mainland.
The island’s Government Development Bank, which lent to the commonwealth and its municipalities, is in talks with creditors to avoid defaulting on the $422 million that’s due May 1. The commonwealth may use a new debt moratorium law if it cannot defer that GDB payment, Jesus Manuel Ortiz, a spokesman for Garcia Padilla, said. While a GDB default would be the largest yet by Puerto Rico, a missed payment on its general obligations would signal to investors that the commonwealth is finally executing on its warnings that it cannot pay its debts. Puerto Rico and its agencies owe $2 billion on July 1, including a $805 million payment on its general-obligation bonds, which are guaranteed under the island’s constitution to be paid before anything else.
Read more …

“..60 million people worldwide requiring “urgent assistance..”..
• El Niño Dries Up Asia As Its Stormy Sister La Niña Looms (AFP)
Withering drought and sizzling temperatures from El Nino have caused food and water shortages and ravaged farming across Asia, and experts warn of a double-whammy of possible flooding from its sibling, La Nina. The current El Nino which began last year has been one of the strongest ever, leaving the Mekong River at its lowest level in decades, causing food-related unrest in the Philippines, and smothering vast regions in a months-long heat wave often topping 40 degrees Celsius (104 Fahrenheit). Economic losses in Southeast Asia could top $10 billion, IHS Global Insight told AFP. The regional fever is expected to break by mid-year but fears are growing that an equally forceful La Nina will follow.
That could bring heavy rain to an already flood-prone region, exacerbating agricultural damage and leaving crops vulnerable to disease and pests. “The situation could become even worse if a La Nina event — which often follows an El Nino — strikes towards the end of this year,” Stephen O’Brien, UN under-secretary-general for humanitarian affairs and relief, said this week. He said El Nino has already left 60 million people worldwide requiring “urgent assistance,” particularly in Africa. Wilhemina Pelegrina, a Greenpeace campaigner on agriculture, said La Nina could be “devastating” for Asia, bringing possible “flooding and landslides which can impact on food production.” El Nino is triggered by periodic oceanic warming in the eastern Pacific Ocean which can trigger drought in some regions, heavy rain in others.
Much of Asia has been punished by a bone-dry heat wave marked by record-high temperatures, threatening the livelihoods of countless millions. Vietnam, one of the world’s top rice exporters, has been particularly hard-hit by its worst drought in a century. In the economically vital Mekong Delta bread basket, the mighty river’s vastly reduced flow has left up to 50% of arable land affected by salt-water intrusion that harms crops and can damage farmland, said Le Anh Tuan, a professor of climate change at Can Tho University. More than 500,000 people are short of drinking water, while hotels, schools and hospitals are struggling to maintain clean-water supplies. Neighbouring Thailand and Cambodia also are suffering, with vast areas short of water and Thai rice output curbed.
Read more …

You would think the reason to continue executing a policy lies in its success rate. Not so, you poor innocent you. In reality, the very failure of a policy is reason to continue it: if the strongest eurozone economy with low unemployment does not show any signs of inflationary pressures, the ECB after all might have a point in continuing its ultra-loose monetary policy
• German Inflation Turns Negative In April (R.)
German consumer prices unexpectedly fell in April, data showed on Thursday, illustrating the scale of the task the ECB faces in trying to propel inflation back to its target range. The eurozone has struggled with little or no inflation for the past year and the ECB expects the bloc-wide figure to turn negative again before slowly ticking up, undershooting its goal of just under 2% for years to come. The ECB unveiled a surprisingly large stimulus package in March but falling inflation expectations have fueled expectations of even more easing, possibly as early as June, when the bank’s staff present new growth and inflation forecasts. “It might be hard for some German ECB critics to digest, but if the strongest eurozone economy with low unemployment does not show any signs of inflationary pressures, the ECB after all might have a point in continuing its ultra-loose monetary policy,” ING Bank economist Carsten Brzeski said.
Separate data on Thursday showed unemployment unexpectedly fell in April, with the jobless rate remaining at its lowest in more than 25 years. German consumer prices, harmonized to compare with other European countries (HICP), fell by 0.1% on the year after a 0.1% rise in March, the Federal Statistics Office said. The Reuters consensus forecast was for a zero reading. On a non-harmonized basis, consumer prices fell 0.2% on the month and inched up 0.1% on the year. A breakdown showed energy remained the main drag while the food, services and rental costs increased at a slower pace. Analysts said the German data suggested that the April inflation rate for the whole eurozone, due out on Friday, would also turn negative again.
Read more …

It’s high time now to see how the Greek debt trap is linked to the article above about German deflation. The link continues with the article below this one: Germany monopolizes the benefits of being in the EU.
• Greece’s Perfect Debt Trap (Kath.)
The longer we spend in the hole the harder it is to get out. As long as the negotiations with the troika are not finished and the economy is starved of cash, as long as businesses cannot plan for the next day and citizens remain wary of returning cash to the banks, recovery becomes even more difficult. The government promises that after a positive evaluation by creditors the economy will bounce back like a spring released. Even if we were to accept this theory – which would also demand huge investments – a positive evaluation is still the prerequisite. Despite the progress made in the talks, the economy is deteriorating. Indicative of this is a growing inability to pay taxes. Today outstanding tax debts exceed €87 billion. At the end of 2012 they were at €55.1 billion.
They have grown by 32 billion euros since then, equaling the amount raised by tax rate increases over the same period (as Kathimerini reports on Friday). In the first quarter of 2016, outstanding debts increased by €3.22 billion and, by the end of the year, may exceed last year’s total of €13.48 billion. Nonperforming bank loans, which were at 8.2% of the total at the start of 2010, were at 36.4% at the end of 2015. Unpaid dues to social security funds came to €15.78 billion at the end of the first quarter, from €13.02 billion last September. The swelling of these debts did not begin under this government. Previous governments and opposition parties, as well as creditors, all played a role in this. From the start of the crisis, citizens/taxpayers have been buffeted by uncertainty, despair and anger.
The expectation of debt relief encouraged delays in payments, while excessive taxation meant that outstanding payments multiplied. Also, the state, unable to meet its own obligations, held back on paying what it owed to taxpayers. With the worsening economy and the lack of trust, capital controls were inevitable and, of course, drove us deeper into trouble. This anxiety is set to continue. The government cannot undertake the burden of what creditors demand, and the creditors, in turn, appear disinclined to help out. As the Federation of Greek Industries noted in its weekly bulletin on Thursday: “The government’s insistence on raising taxes instead of cutting expenses, and the recessionary impact that this will have on the economy, leads to the troika’s shortsighted persistence on contingency measures which, unfortunately, increase further the recessionary wave and will be the final blow to the economy.”
We are caught in the perfect trap. As long as the negotiations drag on, the instability and lack of confidence will increase outstanding debt at all levels, prevent growth and, in turn, demand even harsher measures. The only way out is for both the government and creditors to show good will and trust each other. After the past year this seems a most unlikely leap of faith.
Read more …

Dividing and demolishing the Union brick by brick. Germany wants to be left with the benefits of that union only, and to shed the drawbacks. Not going to work out well.
• German Minister Proposes Law To Limit Social Benefits For EU-Foreigners (DW)
EU foreigners living in Germany may soon have to wait five years before qualifying for social benefits, reported newspapers on Thursday, in reference to a new proposed law from German Labor Minister Andrea Nahles. “We have to stop immigration into the social security system,” Nahles said during an interview in December when she announced plans to restrict social benefits for non-German EU citizens. She added that the restrictions were a matter of “self defense” for Germany. Should the law pass, foreigners from fellow EU member states will be strictly excluded from social assistance if they do not work in Germany or have not acquired social security rights through previous work in Germany. With those same conditions, EU foreigners would also be shut out from Germany’s benefit system for the unemployed, which is known as “Hartz IV.”
EU citizens can eventually gain access to social benefits – but only if they have been living in Germany for five years without state assistance. The draft law, however, provides so-called “transition benefits” for those EU foreigners who no longer qualify for social assistance in Germany. For a maximum of four weeks, those affected will receive assistance to cover the costs of food, housing, and health care. They will also be given a loan to cover costs for a return trip to their home country, where they can then apply for social benefits. The new measures are a direct response to a decision by Germany’s Federal Social Court late last year concerning immigrants from EU countries. In December 2015, the court ruled that EU-foreigners would only acquire entitlement to social benefits after living in the country for at least six months. The decision led to backlash from local authorities, who feared the social system would be overburdened.
Read more …

This is something we’ll see a lot of. It’s over. What’s left is pretense.
• Finland Parliament, Pressured By Weak Economy, Debates Euro Exit (R.)
Finnish lawmakers on Thursday held a rare debate on whether the Nordic country should quit the euro after 53,000 people signed a petition to force the issue into parliament. The petition, although very unlikely to lead to Finland’s exit of the 19-member currency bloc, highlights the growing level of frustration over the country’s economic performance amid rising unemployment, weak outlook and government austerity. The initiative demands a referendum on euro membership, but this would only go ahead if parliament backed such a vote. Although no political group has proposed a euro exit, some euro-sceptic parliamentarians cited lack of independent monetary policy as a problem and said Finland should have held a referendum before adopting the euro in 1998.
Nordic neighbors Sweden and Denmark voted against adopting the euro a few years later. “The euro is too cheap for Germany and too expensive for the rest of Europe, it does not fulfill requirements of an optimal currency union,” said Simon Elo, an MP from the co-ruling euro-sceptic Finns party. The Finnish economy grew by just 0.5% last year after three years of contraction. The stagnation stemmed from a string of problems, including high labor costs, the decline of Nokia’s former phone business and a recession in neighboring Russia. This year, Finland’s economy is expected to grow slower than in any other EU country, except Greece. Some economists say the country’s prospects would improve if it returned to the markka currency which could then devalue against the euro.
Read more …

Union? What union?! Get real.
• Italy Says Austria ‘Wasting Money’ In Migrant Border Row (AFP)
Italy told Austria Thursday it would prove Vienna was “wasting money” on anti-migrant measures and closing the border between the two countries would be “an enormous mistake”. Austrian Interior Minister Wolfgang Sobotka, who has vigorously defended the controversial package which was driven by a surge of the far right, met his counterpart Angelino Alfano over the plans, which have infuriated Italians. Alfano said “the numbers do not support” fears of a mass movement of migrants and refugees across the famous Brenner Pass in the Alps. Sobotka said preparations would continue for the construction of a 370-metre (yard) barrier which would be up to four metres (13 foot) high in places, but Alfano said the feared-for crisis would not materialise and “we will show them it is money wasted”.
Italian Premier Matteo Renzi has warned that closing the pass would be a “flagrant breach of European rules” and is pushing the European Commission to force Austria to hold off on a move many fear could symbolise the death of the continent’s Schengen open border system. On Thursday he described the bid to close the border as being “utterly removed from reality”. A European Commission spokesman said the body had “grave concerns about anything that can compromise our ‘back to Schengen’ roadmap”. Its chairman Jean-Claude Juncker is expected to discuss the issue with Renzi at talks in Rome on May 5. The Vienna government is under intense domestic pressure to stem the volume of asylum seekers and other migrants arriving on its soil with the far-right surging in polls.
UN chief Ban Ki-moon hit out Thursday at what he called “increasingly restrictive” refugee policies in Europe, saying he was “alarmed by the growing xenophobia here” and elsewhere in Europe, in a speech to the Austrian parliament. More than 350,000 people, many of them fleeing conflict and poverty in countries like Syria, Iraq and Eritrea, have reached Italy by boat from Libya since the start of 2014, as Europe battles its biggest migration crisis since World War II. Wedged between the Italian and Balkan routes to northern Europe, Austria received 90,000 asylum requests last year, the second highest in per capita terms of any EU country. Legislation approved Wednesday by the Austrian parliament enables the government to respond to spikes in migrant arrivals by declaring a state of emergency which provides for asylum seekers to be turned away at border points.
Read more …

Portugal sees what Canada sees too. Question is how deliberate is the EU policy of being so slow in relocating refugees to countries asking for them? Portugal wants 10,000. Canada will take a multiple of that.
• One Nation in Europe Wants Refugees But Is Failing to Get Enough (BBG)
Portugal has offered to host 10,000 of the refugees who’ve landed on Europe’s shores from the globe’s war-torn zones. So far, it has taken in 234. Not because it doesn’t want to. Rather, because few have come knocking at its door. “It’s difficult to quickly find refugees that can come to Portugal,” President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa said on Friday as he met migrants in Evora, southern Portugal. As the refugee crisis stretches the struggling Greek government and rattles politics in Germany and beyond, Portugal’s willingness to share the burden isn’t getting a lot of attention. While the country blames a lack of coordination in Europe and administrative roadblocks, the contrast between its economic performance and that of Germany, which admitted more than 1 million migrants in 2015 alone, may also be playing a role.
Although the Portuguese economy recovered in 2014 and accelerated last year after shrinking for three years through 2013, joblessness remains high. Unemployment, which has eased to 12.3% after peaking at 17.5% in 2013, is still almost triple the German rate of 4.3%, and that may continue to dent Portugal’s allure. “It’s not a very appealing destination given the unemployment rate,” said Rui Serra, chief economist at Caixa Economica Montepio Geral in Lisbon. “It’s easier for an immigrant to go to the center of Europe where there is a more concentrated market than in some countries of the periphery like Portugal. In the center of Europe income per capita is higher.” Prime Minister Antonio Costa says there are structural problems in the euro zone that aggravate the disparities.
“That structural problem has to do with the asymmetry between the different economies,” he said in Athens on April 11. “It’s necessary to give a new impulse to the convergence of our economies with the more developed economies of the euro zone.” With the country’s demographics in mind, the Portuguese government has laid out the welcome mat for refugees. Portugal’s population has declined and aged every year from the end of 2011 to about 10.37 million at the end of 2014 as a weak economy has led many working-age residents to leave. Germany’s population, while also aging, still increased overall every year in the same period.
Read more …