
James Ensor The frightful musicians 1891

The entire media left Assange to rot in hell. This is from a longer interview with Maurizi. It captures the essence.
• How Julian Assange Changed Journalism (Stefania Maurizi)
For me it has been really shocking to witness how Julian Assange has declined in the last nine years. I have been able to see changes in Julian’s health and psychology. It was so sad, and no one could do anything. I could report on it and expose it but the other media and public opinion did absolutely nothing to make the government understand how terrible his treatment was. And all this is happening not in Russia, not in North Korea, this is happening in London, in the heart of Europe. I now realize how little we can do in our democracy.
If you look at what has happened to high-profile whistleblowers like Chelsea Manning and Edward Snowden, and an important publisher like Assange, who had the courage to publish these important revelations, what did your democracy do to save them, to treat them in a human way? Chelsea Manning was put in prison for seven years, where she tried to commit suicide twice. Now she is back in prison. Edward Snowden was forced to leave the U.S. Julian Assange has spent nine years in detainment and no one did anything. We were reporting, we were denouncing, we were exposing how seriously his health was declining. Nothing happened.

A great example of how it’s done. I stumbled upon this in the Guardian, “Ask Hadley” by one Hadley Freemen. Yes the kind of thing men won’t read, it’s directed at women. Who in this way get told what to think of Assange. The rape smear against him from MI6 et al has been more successful than anything else in turning especially women against him. This is how. It’s vile and it’s very dirty. And this Hadley person has no qualms about throwing another woman, Pamela Anderson, under the bus to do it. Because, you know, of her reputation.
• Pamela Anderson’s Assange Blanket Conceals The Truth Of His Detention (G.)
Anderson made a long comment to the handily assembled press ranks outside the jail after her visit. She talked about how horrifically unjust it was that Assange was “really cut off from everybody”, to which you can only answer: “Well then, he should be delighted, given he chose to do exactly that for the past seven years when he holed himself up in the Ecuadorean embassy.” Anderson continued: “He does not deserve to be in a supermax prison. He has never committed a violent act. He is an innocent person.”

‘Nothing makes a woman look more credible than writing “Cromwell” on a blanket and then standing outside a prison.’ Photograph: Gareth Fuller/PA
And again, Ms Anderson, one must beg to remind you that, while that may all be true, no one knows that for certain because – and apologies for bringing up this inconvenient truth yet again – he avoided extradition to Sweden to answer to crimes he is accused of by hiding out in an embassy in Knightsbridge for seven flipping years. You remember that, right? You visited him there. That place where your warrior for truth would – according to Ecuador’s UK ambassador, Jaime Marchán – leave half-eaten meals in the sink. As Andrew O’Hagan explained way back in 2014 when describing what it was like spending time with Assange: “If you asked him to do the dishes, he would say he was trying to free economic slaves in China and had no time to wash up.”
Anderson added: “He is a good man, he is an incredible person. I love him.” She clearly rather fancies herself and Assange as the 21st century’s Marilyn Monroe and Arthur Miller (as opposed to what they actually are, which is a real-life Harley Quinn and Joker from Batman: The Animated Series). Still, good for you, Pamela! Love is a wondrous thing. This column sincerely hopes you have many happy years of washing his dishes ahead of you. Anyway, just in case Anderson’s word salad was not sufficiently persuasive, she also wore a blanket emblazoned with writing that included the words “free speech”, “gagged” and “Cromwell”. Because, honestly, nothing makes a woman look more credible than writing “Cromwell” on a blanket and then standing outside a prison. Anderson is just the latest in a long and not especially noble line of people who have decided that the best way to express themselves is by writing words on their clothing.
Pamela Anderson admits to feeling 'sick, nauseous' after visiting Julian Assange at HM Prison Belmarsh. pic.twitter.com/91W8F3SPTx
— RT UK (@RTUKnews) May 7, 2019

“The talks were so bad that the real surprise is that it took Trump until Sunday to blow up,” the source said.”
• China Backtracked On Nearly All Aspects Of US Trade Deal (R.)
The diplomatic cable from Beijing arrived in Washington late on Friday night, with systematic edits to a nearly 150-page draft trade agreement that would blow up months of negotiations between the world’s two largest economies, according to three U.S. government sources and three private sector sources briefed on the talks. The document was riddled with reversals by China that undermined core U.S. demands, the sources told Reuters. In each of the seven chapters of the draft trade deal, China had deleted its commitments to change laws to resolve core complaints that caused the United States to launch a trade war: theft of U.S. intellectual property and trade secrets; forced technology transfers; competition policy; access to financial services; and currency manipulation.
U.S. President Donald Trump responded in a tweet on Sunday vowing to raise tariffs on $200 billion worth of Chinese goods from 10 to 25 percent on Friday – timed to land in the middle of a scheduled visit by China’s Vice Premier Liu He to Washington to continue trade talks. The stripping of binding legal language from the draft struck directly at the highest priority of U.S. Trade Representative Robert Lighthizer – who views changes to Chinese laws as essential to verifying compliance after years of what U.S. officials have called empty reform promises. Lighthizer has pushed hard for an enforcement regime more like those used for punitive economic sanctions – such as those imposed on North Korea or Iran – than a typical trade deal.
“This undermines the core architecture of the deal,” said a Washington-based source with knowledge of the talks. [..] Liu last week told Lighthizer and Mnuchin that they needed to trust China to fulfil its pledges through administrative and regulatory changes, two of the sources said. Both Mnuchin and Lighthizer considered that unacceptable, given China’s history of failing to fulfil reform pledges. One private-sector source briefed on the talks said the last round of negotiations had gone very poorly because “China got greedy”. “China reneged on a dozen things, if not more … The talks were so bad that the real surprise is that it took Trump until Sunday to blow up,” the source said.

If we could get rid of Bolton and Pompeo this way, great! For now though, Trump doesn’t want to start wars, but he won’t fire the warmongers either.
• Trump Blames Bolton For Embroiling Him In Potential Venezuelan Quagmire (Week)
President Trump is having second thoughts about “his administration’s aggressive strategy in Venezuela,” complaining to aides and advisers that “he was misled about how easy it would be to replace the socialist strongman,” President Nicolas Maduro, with opposition leader Juan Guadió, The Washington Post reports. “The president’s dissatisfaction has crystallized around National Security Adviser John Bolton and what Trump has groused is an interventionist stance at odds with his view that the United States should stay out of foreign quagmires.”
Officially, U.S. policy in Venezuela is the same, and last week’s failed effort to oust Maduro has “effectively shelved serious discussion of a heavy U.S. military response,” and “Trump is now not inclined to order any sort of military intervention in Venezuela,” the Post reports, citing current and former officials and outside advisers. Instead, the U.S. is settling in to wait out Maduro on the expectation he will fall on his own, with the help of U.S. sanctions. Russian President Vladimir Putin “is not looking at all to get involved in Venezuela other than he’d like to see something positive happen for Venezuela,” Trump said last week, after a 90-minute phone call with Putin. “And I feel the same way. We want to get some humanitarian aid.” U.S. officials say Russia is deeply involved in backing Maduro.

A constitutional crisis?
• Trump Predicts Dem Investigation Will Drive Him To 2020 Win (Hill)
President Trump, speaking at a rally hours after the White House invoked executive privilege to block the release of special counsel Robert Mueller’s full report, predicted congressional Democrats’ investigations would propel him to a reelection victory in 2020. Trump did not directly address his administration’s decision to defy a subpoena from House Democrats, a move that raised the specter of a constitutional crisis, but he said the party’s desire to probe his administration, campaign and businesses would backfire politically. “They want to do investigations instead of investments,” the president told a crowd of supporters at an outdoor amphitheater just steps from the Gulf of Mexico. “I think it drives us on to victory in 2020.”
Trump said Democrats’ focus on investigations is a “disgrace” and that they should instead work with him on infrastructure, lowering drug prices and improving veterans’ health care. [..] Trump mentioned Barr only in passing during the Wednesday rally but did not address the proceedings. “Now the Democrats — we have a great attorney general — now the Democrats are saying, ‘We want more.’ You know, it was going to be like, ‘We want the Mueller report.’ Now they say, ‘Mueller report? No, we want to start all over again.’”

This will go far. This is very damning.
• Steele’s Stunning Pre-FISA Confession (Solomon)
If ever there were an admission that taints the FBI’s secret warrant to surveil Donald Trump’s campaign, it sat buried for more than 2 1/2 years in the files of a high-ranking State Department official. Deputy Assistant Secretary of State Kathleen Kavalec’s written account of her Oct. 11, 2016, meeting with FBI informant Christopher Steele shows the Hillary Clinton campaign-funded British intelligence operative admitted that his research was political and facing an Election Day deadline. And that confession occurred 10 days before the FBI used Steele’s now-discredited dossier to justify securing a Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) warrant to surveil former Trump campaign adviser Carter Page and the campaign’s ties to Russia.
Steele’s client “is keen to see this information come to light prior to November 8,” the date of the 2016 election, Kavalec wrote in a typed summary of her meeting with Steele and Tatyana Duran, a colleague from Steele’s Orbis Security firm. The memos were unearthed a few days ago through open-records litigation by the conservative group Citizens United. Kavalec’s notes do not appear to have been provided to the House Intelligence Committee during its Russia probe, according to former Chairman Devin Nunes (R-Calif.). “They tried to hide a lot of documents from us during our investigation, and it usually turns out there’s a reason for it,” Nunes told me. Senate and House Judiciary investigators told me they did not know about them, even though they investigated Steele’s behavior in 2017-18.
One member of Congress transmitted the memos this week to the Department of Justice’s inspector general, fearing its investigation of FISA abuses may not have had access to them. Nonetheless, the FBI is doing its best to keep much of Kavalec’s information secret by retroactively claiming it is classified, even though it was originally marked unclassified in 2016. The apparent effort to hide Kavalec’s notes from her contact with Steele has persisted for some time. State officials acknowledged a year ago they received a copy of the Steele dossier in July 2016, and got a more detailed briefing in October 2016 and referred the information to the FBI.

From what I can see, this is quite weak. Jonathan Turley explains why in the next article: “..the contempt action against Barr is long on action and short on contempt ..”
• Democrats Vote To Hold Attorney General Barr In Contempt Of Congress (G.)
House Democrats voted on Wednesday to hold the US attorney general, William Barr, in contempt of Congress, citing his failure to hand over the full, unredacted version of the special counsel Robert Mueller’s report on Russian interference in the 2016 presidential election. The decision came on a day of escalating tensions between Congress and the White House. Earlier on Wednesday, the White House invoked executive privilege to block the House judiciary committee’s request for the full Mueller report and underlying evidence. Later in the day, the House intelligence committee chair, Adam Schiff, subpoenaed Barr for “documents and materials related Special Counsel Robert Mueller’s investigation, including all counterintelligence and foreign intelligence materials produced during the Special Counsel’s investigation, the full unredacted report, and the underlying evidence”.
According to a statement from Schiff’s office, the justice department must produce the documents by 15 May. The Senate intelligence committee, meanwhile, has subpoenaed Donald Trump Jr, two people familiar with the matter told the Associated Press. The panel is calling in the president’s son to answer questions about his 2017 testimony to the panel as part of its investigation into Russian election interference. It is the first known subpoena of a member of Donald Trump‘s immediate family, and a new sign that the Senate panel is continuing with its own Russia investigation even after the release of Mueller’s report on the same subject.

Jonathan Turley is the Shapiro Professor of Public Interest Law at George Washington University and represented the House of Representatives in its successful challenge to executive actions under the Affordable Care Act..
• Democrats Showing Contempt By Holding William Barr In Contempt (Turley)
The House Judiciary Committee is voting to hold Attorney General William Barr in contempt of Congress and to secure a vote of the entire House of Representatives in order to send the matter to federal court. The problem is that the contempt action against Barr is long on action and short on contempt. Indeed, with a superficial charge, the House could seriously undermine its credibility in the ongoing conflicts with the White House. Congress is right on a number of complaints against the White House, including possible cases of contempt, but this is not one of them. As someone who has represented the House of Representatives, my concern is that this one violates a legal version of the Hippocratic oath to “first do no harm.”
This could do great harm, not to Barr, but to the House. It is the weakest possible case to bring against the administration, and likely to be an example of a bad case making bad law for the House. House Judiciary Chairman Jerrold Nadler laid out the case for contempt. He raised three often repeated complaints against Barr in that he failed to release an unredacted report by special counsel Robert Mueller, allegedly lied twice to Congress, and refused to appear before the committee. Yet, notably, the only claim the committee seeks to put before a federal court is the redaction of the report. That seems rather curious since, if Barr lied or refused a subpoena as House leaders claim, it normally would be an easy case of contempt. The reason for this move is that House Democrats know both claims would not withstand even a cursory judicial review.

David Schoen is a civil rights and criminal defense lawyer.
• Democrats Know Mueller Can’t Discuss His Report (Schoen)
When Mueller accepted his appointment as special counsel, he did so fully aware of the federal regulations governing his office. The regulations make it absolutely clear that the special counsel is prohibited from discussing his report publicly. Leading members of Congress now demanding that Mueller testify know he is barred from doing so. The current special counsel regulations were passed while they were members of Congress. In 1978, Congress passed the Ethics in Government Act. It created a process for appointing special prosecutors. This is a different position from special counsels like Mueller. Under the 1978 law, Congress could mandate the appointment of a special prosecutor. Congress could remove the special prosecutor, and the special prosecutor was required to report to Congress. The executive and legislative branches were both a direct part of the process.
However, the law on special prosecutors expired and it was not renewed. In 1999, the special counsel regulations under which Mueller was appointed became law and remain in effect today. These regulations were written and heavily promoted by President Bill Clinton’s administration. They changed the 1978 law in several important ways. Under the current regulations, the special counsel does not report to Congress. Congress cannot require the appointment or removal of a special counsel. These powers and duties lie exclusively with the attorney general. Section 600.9 of the special counsel regulations backed by the Clinton administration places very limited requirements on the attorney general in regard to what he needs to provide to Congress, and he has already exceeded these requirements.

“A strategy of insulting the executioner right before he swings his ax is an odd one but, then, Comey has a long record of odd decisions and questionable judgment.”
• James Comey Is In Trouble And He Knows It (Hill)
James Comey’s planet is getting noticeably warmer. Attorney General William Barr’s emissions are the suspected cause. Barr has made plain that he intends to examine carefully how and why Comey, as FBI director, decided that the bureau should investigate two presidential campaigns and if, in so doing, any rules or laws were broken. In light of this, the fired former FBI director apparently has decided that photos of him on Twitter standing amid tall trees and in the middle of empty country roads, acting all metaphysical, is no longer a sufficient strategy. No, Comey has realized, probably too late, that he has to try to counter, more directly, the narrative being set by the unsparing attorney general whose words in front of the Senate Judiciary Committee last week landed in the Trump-opposition world like holy water on Linda Blair. Shrieking heads haven’t stopped spinning since.
And so we’ve seen Comey get real busy lately. First he penned a curious op-ed in The New York Times. Then a Times reporter, with whom Comey has cooperated in the past, wrote a news article exposing an early, controversial investigative technique against the Trump campaign in an attempt to get out front and excuse it. Next, Comey is scheduled to be encouraged on a friendly cable news “town hall.” In the op-ed, Comey trotted out his now-familiar St. James schtick, freely pronouncing on the morality of others. He sees himself as a kind of Pontiff-of-the-Potomac working his beads, but comes across more like an unraveling Captain Queeg working his ball bearings. Comey adjudged the president as “amoral.” He declared the attorney general to be “formidable” but “lacking inner strength” unlike — the inference is clear — Comey himself. A strategy of insulting the executioner right before he swings his ax is an odd one but, then, Comey has a long record of odd decisions and questionable judgment.

[From 2008 to 2016] “the number of Chinese companies issuing bonds soared from just 68 to a peak of 1,451..”
• Time to Start Worrying About Global Corporate Debt – Bank of England (DQ)
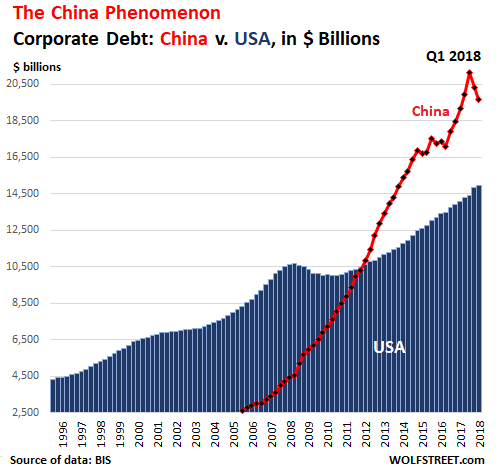
By 2016, emerging market corporations were issuing ten times more money ($711 billion) than before, much of it in hard foreign currencies (mainly euros, dollars and yen) that will prove much harder to pay back if their local currency slides, as is happening in Turkey and Argentina right now. Although bond issuance by emerging market companies declined by 29% in 2017 and remained around the same level in 2018, it is still approximately 7.5 times higher than the pre-crisis level. Much of the increase has been driven by China as it transitioned from a negligible level of issuance of corporate debt prior to the 2008 crisis to a record issuance amount of $590 billion in 2016.
During that time the number of Chinese companies issuing bonds soared from just 68 to a peak of 1,451 and the total amount of corporate debt in China exploded from $4 trillion to almost $17 trillion, according to BIS data. By late 2018 it had reached $19.7 trillion. “There has been a persistent buildup of private debt to record levels in China,” Cunliffe said. Much of this increase took place in the direct aftermath of the financial crisis. The largest increases have been in the corporate sector, mainly in state-owned enterprises. At last count, China’s corporate debt-to-GDP ratio was 153%, enough to earn it seventh place on WOLF STREET’s leaderboard of countries with the most monstrous corporate debt pileups (as a proportion of GDP), 18 places above the US. This chart compares the rise of non-financial corporate debt in China and the US:

“Why would investors expect the euro to appreciate? [..] such a scenario is highly implausible.”
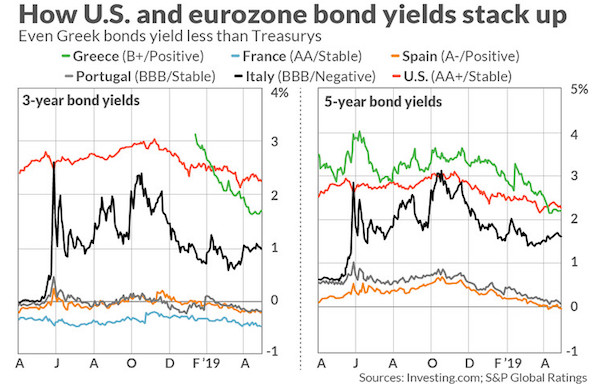
• Greek Bonds Yield Less Than Treasurys – As Irrational As In 2007 (Ashoka Mody)
Yields on five-year Greek government bonds are lower than those of U.S. Treasurys — and have been this way for the past month. Yes, on 3- and 5-year bonds, Greece, with its rating deep in junk territory, pays investors less than the double-A-plus-rated U.S. government does. Italian, Portuguese, Spanish and French government bonds — also lower-rated than the U.S. — offer lower, indeed considerably lower, yields than the U.S. government does, even for 10-year maturities. Even if we stipulate that Greece’s government is, in fact, as creditworthy as the U.S. government, why would investors accept a lower yield on the Greek bond? And why are they willing to accept the even lower yields on the bonds of other eurozone governments?
One possible reason is that they expect the euro to appreciate. Despite the low eurozone bond yields, investors may expect eventually to boost their returns by selling the expensive euros and buying cheaper dollars and other currencies. Indeed, there is some basis for such a strategy. As of late April, the consensus among analysts was that the euro will appreciate significantly over the next couple of years, and more modestly thereafter; forward markets (where buyers and sellers settle the price of a future transaction in advance) support this consensus view.
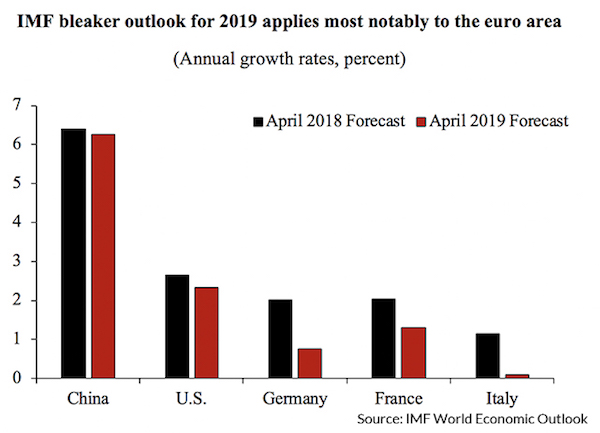
But if expectations of an appreciating euro solve the low-bond-yield puzzle, they raise another, deeper puzzle. Why would investors expect the euro to appreciate? [..] such a scenario is highly implausible. Current growth forecasts point worryingly in the opposite direction. The IMF projects world economic growth to slow more markedly than it already did a year ago. Crucially, of all major economies, those in the eurozone appear to be decelerating particularly quickly.

Fish farms kill.
• Have We Reached The End Of Wild? (G.)
In salmon’s case, we have interrupted one of the most dramatic cycles of nature, the wild fish’s journey from the rivers where they spawn to the oceans where they grow and back again. The result is that fish have died, species that eat them have died, communities that depend on them have faded, the food supply has been polluted and a lot of tax dollars have been wasted. [..] In an inspired gambit, Artifishal takes a swerve into the metaphyscial, framing the salmon emergency as a question about the human soul, about what it needs – about what we need – to survive.
The contention of the film-makers is that while it may be human nature to seek dominion and control over the rest of nature, the very thing we need to survive is precisely that which defies our control, that thing which, when we seek to subjugate it, instead either slips through our nets, or is caught and dies. If we drive the wild to extinction, the film suggests, we will bring our own that much closer. “I really hope the film leaves the viewer with this disquieting question, which is, have we reached the end of wild?” said Murphy in a phone conversation near the end of a tour to promote the movie, which debuted at the Tribeca film festival after a tour of screenings in Patagonia stores. “At the outset we kept wondering if we would find a bad guy. And we didn’t. In fact, I kept feeling that the force of antagonism was us – we’re the bad guy. Because humans just are always looking out for themselves.”

More damage from renewables. There’s no free lunch. The sooner we get that straight, the better.
• Only A Third Of World’s Great Rivers Remain Free Flowing (G.)
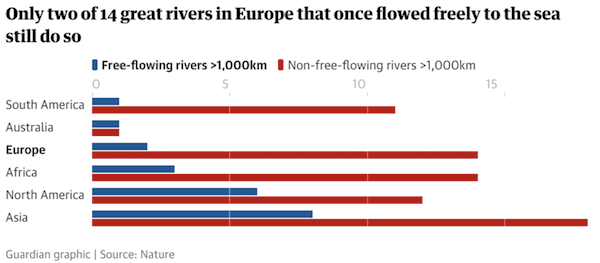
Only a third of the world’s great rivers remain free flowing, due to the impact of dams that are drastically reducing the benefits healthy rivers provide people and nature, according to a global analysis. Billions of people rely on rivers for water, food and irrigation, but from the Danube to the Yangtze most large rivers are fragmented and degraded. Untouched rivers are largely confined to remote places such as the Arctic and Amazonia. The assessment, the first to tackle the subject on a worldwide level, examined 12m kilometres of rivers and found that just 90 of the 246 rivers more than 1,000km (621 miles) long flowed without interruption.
The scientists, whose research, published in the journal Nature, was led by Günther Grill, at McGill University in Canada, were particularly concerned to discover that only a quarter of long rivers that once flowed freely to the sea, rather than to an inland lake or other river, still had such a course. Separate research in Britain, which included the effects of smaller infrastructure such as weirs, fords and culverts, suggests that 97% of the nation’s river network has been interrupted by human-built structures. Thriving wildlife in rivers is crucial to keeping water clean but freshwater habitats were found to be the hardest hit of all the ecosystems, with wildlife populations having plunged by an average of 83% since 1970 due to dams, overuse of water and pollution.
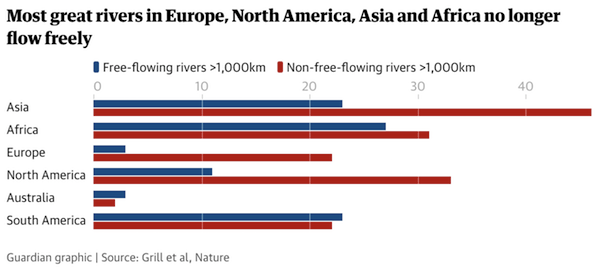
Great rivers that flow freely are now rare in populated areas. Heavily fragmented rivers include the Danube, Nile, and Euphrates, the Paraná and Missouri in the Americas, the Yangtze and Brahmaputra in Asia, and the Darling in Australia. The Congo and Amazon were found to be among the least affected. The biggest impact comes from physical barriers created by dams, but reservoirs also seriously affect the natural seasonal flow of rivers. “It can be really freaky sometimes, when the electricity is produced one hour on, one hour off, and the river goes up and down by a metre, which is very stressful to the ecosystems downstream,” said Grill. The study estimates that there are about 60,000 large dams worldwide and 3,700 in planning or construction, in addition to millions of smaller dams.

A cheap way to get young votes. Don’t fall for it. Thes countries fail even their Paris commitments.
• Proposal To Spend 25% Of EU Budget On Climate Change (BBC)
Eight European countries have called for an ambitious strategy to tackle climate change – and to spend a quarter of the entire EU budget on fighting it. The joint statement says the EU should have net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 “at the latest”. It was signed by France, Belgium, Denmark, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, and Sweden. The group says their plan can “go hand in hand with prosperity” and “set an example for other countries to follow.” The position paper comes ahead of a major summit of European leaders in the Romanian city of Sibiu, beginning on Thursday, which will discuss the future of Europe and the EU’s strategy for the next five years. But not everyone is on board – there are 28 countries in the EU, and several of those absent from the joint position statement are significant players – including Germany.
The position of the eight countries is that climate change has “profound implications for the future of humanity” and that its impacts are already apparent – citing “the heat waves and scorching fires of last summer”. [..] “The EU budget currently under negotiation will be an important tool in this respect: at least 25% of the spending should go to projects aimed at fighting against climate change,” the paper said. Annual EU budgets have spending limits set by what is known as the multiannual financial framework (MFF). The current one allowed the EU to spend more than €900bn between 2014-2020. The eight-nation group is eyeing the next framework, which is set to cover 2021-2027. [..] At the moment, EU countries are required to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 20% from their 1990 levels by 2020, with the aim of raising that to a 40% reduction by 2030. But many are set to miss these targets – some by a wide margin.









