V&APA Bowie age 16 in the Kon-Rads 1963



As things shape up the very way we always said they would, others claim ownership of the story.
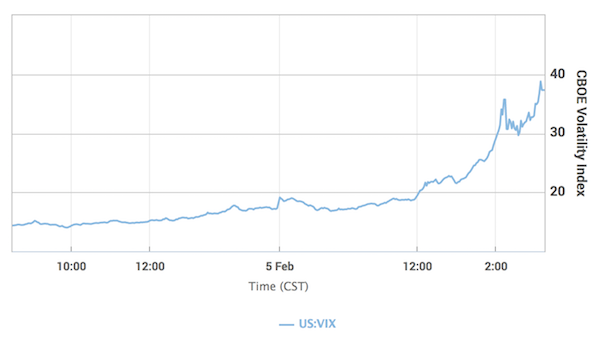
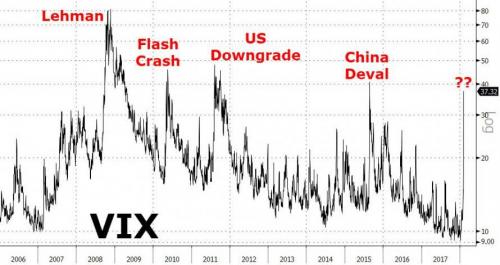
“China has set off a major correction and it is going to snowball. Equities and credit have become very dangerous, and we have hardly even begun to retrace the ‘Goldlocks love-in’ of the last two years..”
• RBS Cries ‘Sell Everything’ As Deflationary Crisis Nears (AEP)
RBS has advised clients to brace for a “cataclysmic year” and a global deflationary crisis, warning that major stock markets could fall by a fifth and oil may plummet to $16 a barrel. The bank’s credit team said markets are flashing stress alerts akin to the turbulent months before the Lehman crisis in 2008. “Sell everything except high quality bonds. This is about return of capital, not return on capital. In a crowded hall, exit doors are small,” it said in a client note. Andrew Roberts, the bank’s credit chief, said that global trade and loans are contracting, a nasty cocktail for corporate balance sheets and equity earnings. This is particularly ominous given that global debt ratios have reached record highs. “China has set off a major correction and it is going to snowball. Equities and credit have become very dangerous, and we have hardly even begun to retrace the ‘Goldlocks love-in’ of the last two years,” he said.
Mr Roberts expects Wall Street and European stocks to fall by 10pc to 20pc, with even an deeper slide for the FTSE 100 given its high weighting of energy and commodities companies. “London is vulnerable to a negative shock. All these people who are ‘long’ oil and mining companies thinking that the dividends are safe are going to discover that they’re not at all safe,” he said. Brent oil prices will continue to slide after breaking through a key technical level at $34.40, RBS claimed, with a “bear flag” and “Fibonacci” signals pointing to a floor of $16, a level last seen after the East Asia crisis in 1999. The bank said a paralysed OPEC seems incapable of responding to a deepening slowdown in Asia, now the swing region for global oil demand Morgan Stanley has also slashed its oil forecast, warning that Brent could fall to $20 if the US dollar keeps rising.
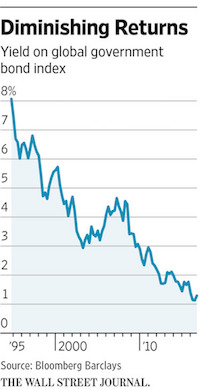
It argued that oil is intensely leveraged to any move in the dollar and is now playing second fiddle to currency effects. RBS forecast that yields on 10-year German Bunds would fall time to an all-time low of 0.16pc in a flight to safety, and may break zero as deflationary forces tighten their grip. The European Central Bank’s policy rate will fall to -0.7pc. US Treasuries will fall to rock-bottom levels in sympathy, hammering hedge funds that have shorted US bonds in a very crowded “reflation trade”. RBS first issued its grim warnings for the global economy in November but events have moved even faster than feared. It estimates that the US economy slowed to a growth rate of 0.5pc in the fourth quarter, and accuses the US Federal Reserve of “playing with fire” by raising rates into the teeth of the storm. “There has already been severe monetary tightening in the US from the rising dollar,” it said.
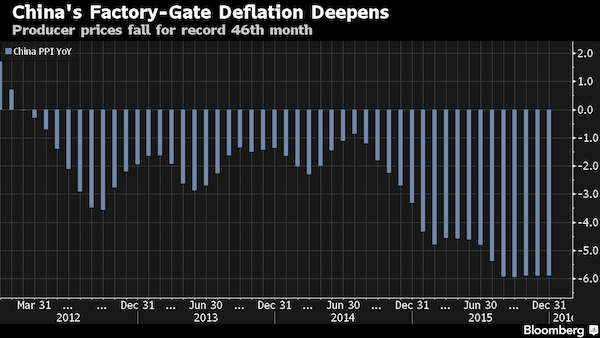
It is unusual for the Fed to tighten when the ISM manufacturing index is below the boom-bust line of 50. It is even more surprising to do so after nominal GDP growth has fallen to 3pc and has been trending down since early 2014. RBS said the epicentre of global stress is China, where debt-driven expansion has reached saturation. The country now faces a surge in capital flight and needs a “dramatically lower” currency. In their view, this next leg of the rolling global drama is likely to play out fast and furiously. “We are deeply sceptical of the consensus that the authorities can ‘buy time’ by their heavy intervention in cutting reserve ratio requirements (RRR), rate cuts and easing in fiscal policy,” it said.
Read more …

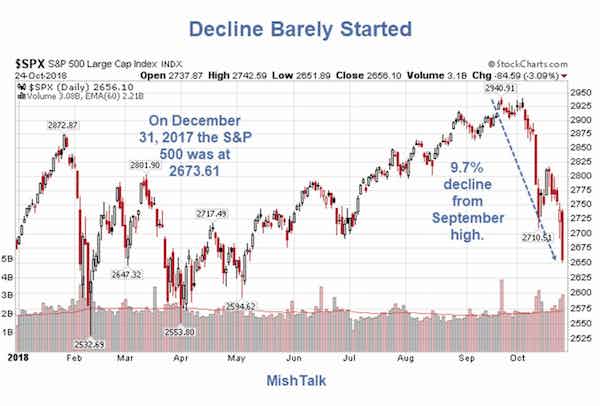
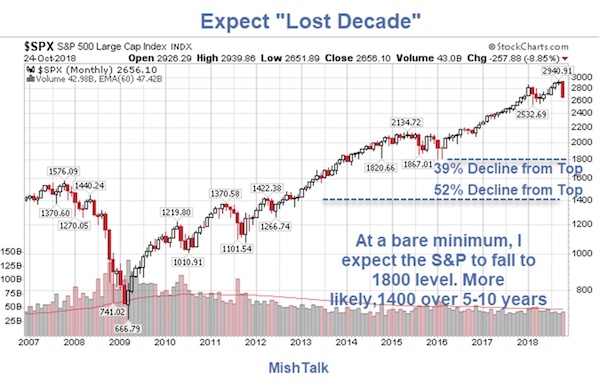
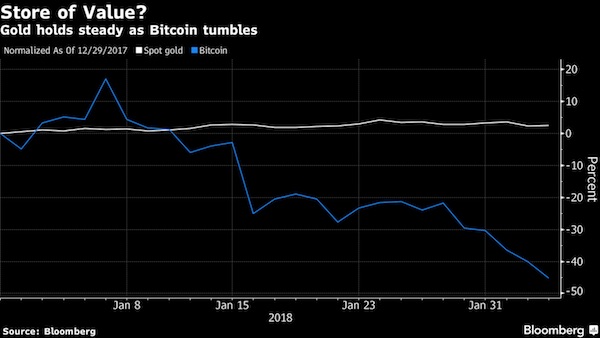
How about 50%? Standard & Poor’s 1500 index – a broad basket of large, mid and small company stocks – is already down -26.9% from its 52-week high.
• An ‘Extremely Normal And Realistic’ 26% S&P 500 Drop Is Taking Shape (MW)
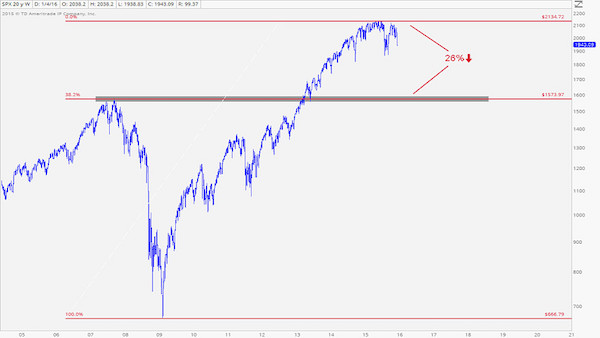
It’s been a brutal start to 2016 in the markets. But the way this chart is setting up, there’s a lot more pain on the way, according to J.C. Parets of the All Star Charts blog. “We’re down 9% from the all-time highs in the S&P 500 SPX, +0.09% and I see people acting like two-year-olds that just had their favorite toy taken away from them,” he said. “Why, because the market is down 9% from its highs last year after rallying over 220% over the prior 6 years? Please.” He goes on to explain how this recent spate of selling action isn’t unusual and how “things get absolutely destroyed all the time.” Like the British pound, energy, emerging markets and agricultural commodities, to name just a few.
“And these are real collapses in prices, not this 9% nonsense that people are getting all worked up about because it’s the S&P 500, or Apple or something that they’re too sensitive about,” Parets wrote in his blog post. He used the chart above to support his prediction that the S&P is headed toward the 1,570 level, which would be an “extremely normal and realistic” 26% correction from the top. Or another 20% from where it stands now. “This is a ‘sell rallies’ market, not a ‘buy the dip’ environment,” he added. That’s not to say there won’t be bounces. “Go look at a list of the best days in stock market history, they all come during massive selloffs,” Parets said. “I would expect this decline to be no different and the rallies we do get should be vicious.”
Read more …

And now Lybia comes on line…
• Oil Down 20% Since Start Of Year, $10 Target Looms (Reuters)
Crude oil prices continued a relentless dive early on Tuesday, falling almost 20% since the beginning of the year as analysts scrambled to cut their 2016 oil price forecasts and traders bet on further price falls. U.S. crude West Texas Intermediate was trading at $30.66 per barrel at 0531 GMT on Tuesday, down 75 cents from the last settlement and about 20% lower than at the beginning of the year. Earlier it traded at $30.60, the lowest since December 2003. Brent crude futures fell 83 cents to $30.72 a barrel. Earlier they declined to $30.66, their lowest since April 2004. Brent has fallen nearly 20% in January and, like WTI, has declined on every day of trading so far this year.
Trading data showed that managed short positions in WTI crude contracts, which would profit from a further fall in prices, are at a record high, implying that many traders expect further falls. “It’s going to be a very interesting year in oil,” said Ric Spooner at CMC Markets in Sydney. “The lower the price goes, the faster in time we are likely to form a base and recover.” Analysts also adjusted to the early price rout in the year, with Barclays, Macquarie, Bank of America Merrill Lynch, Standard Chartered and Societe Generale all cutting their 2016 oil price forecasts on Monday. “A marked deterioration in oil market fundamentals in early 2016 has persuaded us to make some large downward adjustments to our oil price forecasts for 2016,” Barclays bank said.
“We now expect Brent and WTI to both average $37/barrel in 2016, down from our previous forecasts of $60 and $56, respectively,” it added. But it was Standard Chartered that took the most bearish view, stating that prices could drop as low as $10 a barrel. “Given that no fundamental relationship is currently driving the oil market toward any equilibrium, prices are being moved almost entirely by financial flows caused by fluctuations in other asset prices, including the USD and equity markets,” the bank said. “We think prices could fall as low as $10/bbl before most of the money managers in the market conceded that matters had gone too far,” it added.
Read more …

It’ll be epic.
• Plunging Prices Could Force A Third Of US Oil Firms Into Bankruptcy (WSJ)
Crude-oil prices plunged more than 5% on Monday to trade near $30 a barrel, making the specter of bankruptcy ever more likely for a significant chunk of the U.S. oil industry. Three major investment banks – Morgan Stanley, Goldman Sachs and Citigroup – now expect the price of oil to crash through the $30 threshold and into $20 territory in short order as a result of China’s slowdown, the U.S. dollar’s appreciation and the fact that drillers from Houston to Riyadh won’t quit pumping despite the oil glut. As many as a third of American oil-and-gas producers could tip toward bankruptcy and restructuring by mid-2017, according to Wolfe Research.
Survival, for some, would be possible if oil rebounded to at least $50, according to analysts. More than 30 small companies that collectively owe in excess of $13 billion have already filed for bankruptcy protection so far during this downturn, according to law firm Haynes & Boone. Morgan Stanley issued a report this week describing an environment “worse than 1986” for energy prices and producers, referring to the last big oil bust that lasted for years. The current downturn is now deeper and longer than each of the five oil price crashes since 1970, said Martijn Rats, an analyst at the bank. Together, North American oil-and-gas producers are losing nearly $2 billion every week at current prices, according to a forthcoming report from AlixPartners, a consulting firm. “Many are going to have huge problems,” said Kim Brady at consultancy Solic Capital.
Read more …

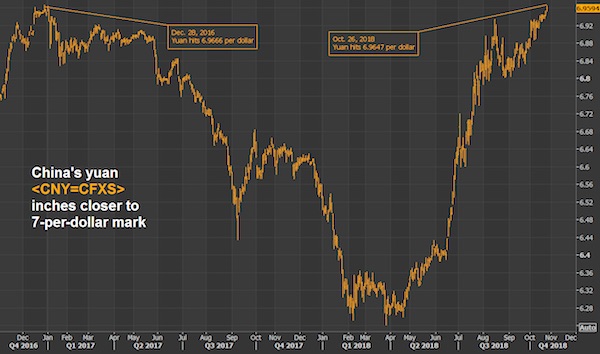
“Its actions are comparable to steps taken by other central banks when they previously fought against international speculators, such as George Soros..”
• China Resorts To ‘Nuclear Strength’ Weapons To Defend The Yuan (Guardian)
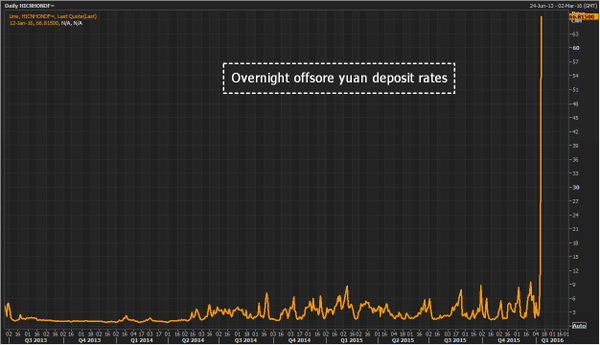
The Chinese authorities have resorted to “nuclear strength” weapons to deter an attack on the yuan by short sellers and convince sceptical investors that they are in control of the country’s spluttering financial system. China’s central bank fixed the currency firmer again on Tuesday but traders were not persuaded and the currency slipped in early trade despite what dealers called aggressive intervention to support the currency. The gap between the mainland yuan and its offshore counterpart had grown in recent days but suspected intervention by China’s state-owned banks brought them almost into line on Tuesday. The action sent the rate at which banks charge each other to borrow yuan in Hong Kong to a record high of 67% on Tuesday.
“The market suspects that the People’s Bank of China is possibly using major state banks to directly drain yuan liquidity in offshore markets,” said a dealer at an European bank in Shanghai. The dealer described the strength of the central bank’s actions as being of “nuclear-weapon” level strength. “Its actions are comparable to steps taken by other central banks when they previously fought against international speculators, such as George Soros,” he said. [..] Perceived mis-steps by China’s authorities have stoked concerns in global markets that Beijing might be losing its grip on economic policy, just as the country looks set to post its slowest growth in 25 years. Amid suspicions by some in the market that China wants the yuan to devalue in order to boost its ailing exporters, sources suggested there were moves afoot for China’s cabinet to take a bigger role in overseeing financial markets.
The state council has set up a working group to prepare for upgrading the cabinet’s financial department to bureau level, said a source close to the country’s leadership. Officials were doing their best to talk up the currency [..] The central bank’s chief economist Ma Jun said on Monday that the bank planned to keep the yuan basically stable against a basket of currencies, and fluctuations against the US dollar would increase. Han Jun, deputy director of the office of the Chinese Communist party’s leading group on financial and economic affairs, said a more substantial decline in the yuan was “ridiculous” and “impossible”.
Read more …

The louder their claims, the lower confidence goes.
• Chinese Official: Bets Against Yuan Are ‘Ridiculous and Impossible’ (WSJ)
Wagers that the yuan will slump 10% or more against the dollar are “ridiculous and impossible,” a senior Chinese economic official said Monday, warning that China had a sufficient tool kit to defeat attacks on its currency. “Attempts to sell short the renminbi will not succeed,” said Han Jun, deputy director of the office of the Central Leading Group on Financial and Economic Affairs, at a briefing at the Chinese Consulate in New York. “The expectations of markets can be changed.” The comments are the latest demonstration of Chinese officials’ determination to defeat those betting that yuan declines will intensify. They echo comments such as ECB President Mario Draghi’s 2012 “whatever it takes” speech, made when European government bonds issued by weaker countries were under attack.
Yet analysts said China’s plan carries considerable risks, potentially creating tension with the government’s efforts to integrate itself into the global financial architecture. Currency-market interventions are costly and risk confusing investors by adding to volatility, some said. “These interventions work well only if they’re undertaken in the context of much broader reforms,” said Eswar Prasad, a former top China hand at the International Monetary Fund and now an economics professor at Cornell University. Bets against the yuan, or renminbi, have picked up in 2016, sending the currency to its lowest level in nearly five years against the dollar and widening the gap between the official Chinese yuan fixing and the so-called offshore market in Hong Kong, where the government is less involved.
On Monday, the yuan rose 0.3% against the dollar in China and rose 1.5% in the offshore market, to 6.5863 per dollar. In late New York trading, the yuan was up 0.4% to 6.5666 per dollar. The debate over the direction of the yuan has captivated Wall Street since last August, when China roiled financial markets by reducing the currency’s value against the dollar by 2% on Aug. 11, its largest single-day decline in two decades. Further yuan devaluation would threaten to exacerbate existing problems in the global economy, where sluggish demand for goods and services is tripping up growth. Many nations have sought to bolster flagging domestic growth by increasing exports, but a sharp decline in the yuan would likely undermine such efforts by making Chinese goods cheaper and more competitive abroad.
Read more …

“China’s banks could require up to $7.7 trillion of new capital and funding over the next three years…” But that’s just part of the story; it’s still based on very low amounts of bad loans -“barely 1% at the big lenders, and 1.8% at mid-tier banks this year-, and that doesn’t seem realistic. Fitch puts it at 21%(!).
• China Banks Feel The Heat Of Meltdown (FT)
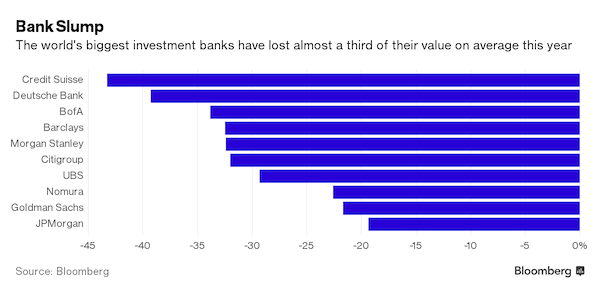
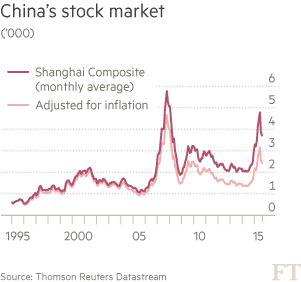
If the US or Europe had experienced the kind of equity market slump that China has suffered of late, its financial institutions would be quaking and leading the list of biggest fallers in Shanghai and Hong Kong trading. As it is, the big banks have seen their share prices tumble by about 10% over the past two or three weeks, far less than the 15% slump in the Shanghai Composite index. On the face of it, there may be good reason for that. Traditionally China’s large financial institutions are not big stock market players — retail investors make up the bulk of the market. In reality, the banks are the most exposed to China’s ills. They are directly bound up in the stock market turmoil and the government’s efforts to shore up sentiment against the flood of selling. Figures relating to the past week or so are not yet available.
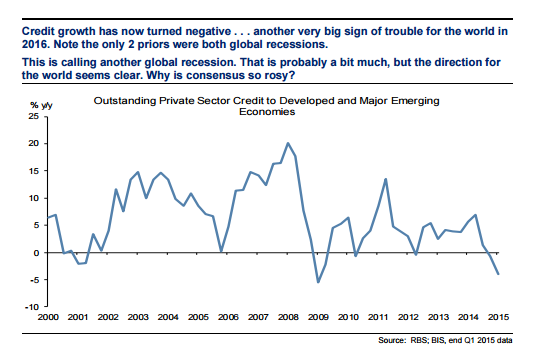
But during a similar rout in early July last year, 17 banks — including the big five listed but partly state-owned groups — lent more than $200bn to facilitate broker purchases of shares and funds. Even without the seizure of their balance sheets to prop up the equity market, China’s banks are pretty troubled. Like banks in the west before the financial crisis, China’s lenders — with government encouragement — have inflated a vast credit bubble, funding the country’s ambitious companies and fast-expanding property market. Chinese banking assets now amount to more than $30tn. Over the past decade, credit growth has consistently topped 10% a year. (It peaked at close to 35% in 2009.) Even this year, it is expected to be double the 6-7% forecast rate of GDP growth.
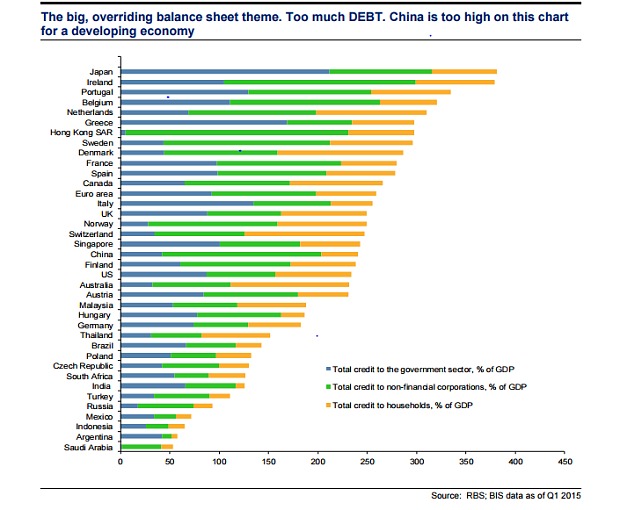
Last August, JPMorgan estimated China’s non-financial industry private sector debt at 147%, half as much again as in 2007. The downturn in China’s fortunes — particularly across its heartland heavy industry — is already hitting the banks. Annual non-performing loan rates have been doubling annually since 2012. China Merchants Bank, China Everbright and ICBC are seen as among the most troubled. China bulls point to the still low level of NPLs — barely 1% at the big lenders, and 1.8% at mid-tier banks this year, according to analyst forecasts. As a gauge, NPLs in Greece have risen to between 30 and 40% amid that country’s crisis. But China experts at independent research house Autonomous suggest investors are underestimating a spiralling problem. Across the board, loan losses will rise by $845bn this year, Autonomous predicts. That, they think, will be enough to shrink profits by 6% at big banks.
[..] Investors in China’s banks may well recognise that the lenders cannot be compared with institutions that operate along western lines and will expect hazier disclosures and readier state interference. They are also likely to think that China will not allow its banks to fail. But if analysts, like those at Autonomous are to be believed, China’s banks could require up to $7.7tn of new capital and funding over the next three years.
Read more …

Exporting deflation.
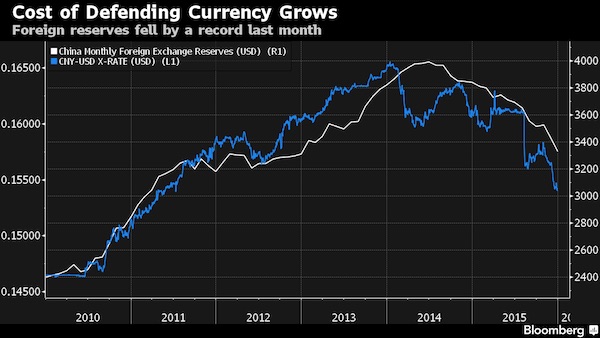
• China FX Reserve Sell-Off To Soon Move Beyond US Treasuries (Reuters)
The unwinding of China’s foreign exchange reserves could soon extend beyond U.S. Treasuries, with U.S. corporate and euro zone sovereign bonds among the assets most vulnerable to selling from Beijing, Bank of America Merrill Lynch said on Monday. China sold a record $510 billion of FX reserves last year to counter the damaging impact on an already decelerating economy from the surge of capital fleeing the country. The lion’s share of that came from $292 billion sales of U.S. Treasury debt, followed by $92 billion sales of U.S. stocks, $3 billion of U.S. agency bonds and $170 billion of non-U.S. assets, according to BAML estimates. China increased its U.S. corporate bond investments by $44 billion last year to $415 billion, BAML strategists estimated, adding that it won’t be long before investors turn their attention to other assets Beijing could potentially sell.
“In the next two months I would still say Treasuries. But if the pressure continues beyond that, it’s non-U.S. assets, and in the U.S. space it’s definitely corporates and agencies,” said Shyam Rajan, rates strategist at BAML in New York. Rajan and his colleagues estimate that China’s $3.33 trillion FX reserves comprise $1.15 trillion non-U.S. assets (mostly short-dated euro-denominated bonds), $415 billion U.S. corporate bonds, $212 billion in agencies, $266 billion stocks and $1.29 trillion of Treasuries. Selling across these bonds may not automatically trigger a sharp rise in their yields though, Rajan said, pointing to the experience of Treasuries in the latter part of last year when swap spreads moved below zero.
“The way to trade the reserve flow story is through relative value trades, such as the swap spread tightening in Treasuries. I would imagine it plays out the same way in other markets too,” Rajan said. Last year’s record unwind brought China’s total FX reserves to a three-year low of $3.33 trillion. Most analysts expect that to be depleted further this year. JP Morgan estimates that capital flight from China since the second quarter of 2014 has totaled $930 billion, while credit ratings agency Fitch on Monday put the figure at over $1 trillion. U.S. investment bank Morgan Stanley on Monday joined Goldman Sachs in lowering its forecast for the Chinese yuan, citing the ongoing flow of capital out of the country and need for a weaker currency to support the economy.
Read more …

Nothing much has changed, other than suspicions that Beijing can’t handle the downfall. But global exposure to China is still the same, it’s just been ridiculously downplayed.
• Why China’s Market Illness Has Gotten More Contagious (WSJ)
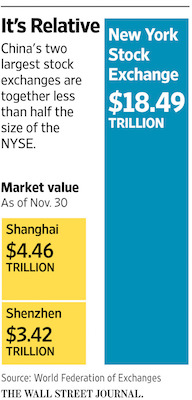
The Shanghai stock market is undersized and isolated. Its market capitalization is less than one-quarter the size of New York’s. Just 37% of its shares are available to trade, and foreigners own only a tiny fraction. Yet the tide of selling by Chinese investors last week—along with an unexpectedly sharp move to weaken the yuan—rolled through stocks, commodities and currencies across the globe. The chain reaction heralds a new era for China, whose financial-market muscle has long been underdeveloped compared with its economic heft. On Monday, Chinese shares resumed their slide. The Shanghai Composite Index dropped 5.3%, leaving it down 15% in the new year. U.S. shares stumbled but covered their losses in the final hour of trading and closed up slightly.
Oil fell to a new 12-year low in the U.S., and currencies in countries like South Africa and Russia fell sharply. Until last year, few in global markets took their cue from Shanghai, which has a history of roller-coaster trading. In the summer of 2015, a sharp plunge in the Shanghai Composite, after a 60% rise earlier in the year, combined with a surprise yuan devaluation to trigger a global selloff. Attention soon faded, and Shanghai’s market ended the year up 9.4%. But last week’s meltdown again showed China’s market influence. And to many, it suggested an even more ominous possibility: that Beijing may be fumbling its management of China’s economy. That could have disastrous consequences for the prices of goods and commodities, and thus markets, around the world.
Today, China accounts for about 11% of world gross domestic product, 12% of the globe’s oil consumption and about half the demand for steel. It is the No. 1 trading partner for countries from South Korea and Australia to Brazil and soaks up exports worth more than 10% of GDP from Singapore and Taiwan. Despite tight controls over the currency and the banking system that wall off China from much of the global financial system, China’s huge presence in global trade means the country is more tightly tied to the rest of the world than ever. Its roaring growth has been a boon to Western stock markets like Germany’s, whose exchange is filled with manufacturers that sell machines and factory equipment there.
Now, China ties may be a liability. In Europe, whose companies get 10% of their revenue from the Asia-Pacific region, the pan-European Stoxx Europe 600 is down 7% in 2016 through Monday, and Germany’s DAX is down 8.5%. Europe is especially vulnerable to a China slowdown: Its own economic growth has been weak for years, and the Continent has been counting on exports to plug the gap. Nearly 10% of the exports from the 28-member EU go to China. The story isn’t the same everywhere, though. U.S. companies get only 5% of their revenue from Asia-Pacific. They also can rely on a more buoyant domestic economy. The S&P 500 was down 6% this year through Friday.
Read more …

And India is one of the first victims of the popping China Ponzi.
• China Rout Threatens to Spawn India Crisis (BBG)
A deepening slowdown in China threatens to derail India’s economic growth, triggering financial market upheaval and a falling currency, Vishal Kampani, the nation’s top investment banker, said. “If China keeps getting hit like this, the yuan has to devalue, and we will see another crisis in India,” Kampani at JM Financial, the South Asian country’s top M&A adviser last year, said in a Jan. 8 interview. “I refuse to believe that India will stand out and will look very different.” Indian stocks and the rupee fell Monday, tracking declines in other emerging markets as volatility in China sapped risk appetite globally. China’s efforts to stabilize the yuan failed to halt equity losses, reviving concern about the Communist Party’s ability to manage an economy set to grow at its weakest pace since 1990. India’s benchmark S&P BSE Sensex Index fell 0.4% on Monday in Mumbai after dropping as much as 1.4% earlier.
The rupee weakened 0.2% to 66.7725 against the dollar as of 4:11 p.m. local time. A devaluation of the yuan could weaken the rupee, creating “huge problems” for Indian companies that have to pay back dollar loans, Kampani said. China is India’s largest trade partner and third-largest export market, so a slowdown there could prolong a record slump in the South Asian nation’s overseas shipments, which declined 12 straight months through November. A China-led rout in Indian markets also risks damping private investment, already hurt by credit lines choked by bad debt and a legislative gridlock that’s blocked economic bills. That would boost pressure on Prime Minister Narendra Modi to sustain public spending even at the risk of worsening Asia’s widest budget deficit. Modi has seen his economic agenda stall in parliament, disappointing investors who bet that his landslide win in 2014 would speed up reforms.
Read more …

In which the richer nations can once again overpower the poorer.
• EU Set To Weigh China’s Eligibility For Lower Import Tariffs (BBG)
European Union policy makers are poised to kick off deliberations to determine whether EU industries ranging from steel to solar can keep relying on import tariffs to fend off aggressive Chinese competitors, the opening salvo in a political and economic battle due to last all year. The European Commission, the EU’s executive arm, will hold an initial debate Jan. 13 about whether the bloc should recognize China as a market economy starting in December. Such a step would make it more difficult for European manufacturers such as ArcelorMittal and Solarworld AG to win sufficiently high EU duties meant to counter alleged below-cost – or “dumped” – imports from China.
The talks will pit free-trade governments in northern Europe against more protectionist ones in the south, put Europe on a possible track that the U.S. is staying off and produce a political verdict on whether communist China has come of age economically 15 years after it joined the World Trade Organization. In addition to being a political prize for Beijing, market-economy status would be a business boost for China, whose growth has slumped to the weakest since 1990 and which suffered a 10% fall in stocks last week. “This is one of the hottest issues on the agenda,” Jo Leinen, a German MEP who chairs its delegation for relations with China, said by phone from Saarbruecken, Germany, on Jan. 7. “It’s a hot potato. The Chinese are pushing for market-economy status and interests are divided in Europe.”
The matter combines top-level political calculations with tricky economic and legal considerations. With the EU struggling to bolster economic growth and keep Greece in the euro area, leaders across Europe have courted China for investment in infrastructure and orders of goods such as Airbus planes. While it’s the EU’s No. 2 trade partner behind the U.S., China is grouped with the likes of Belarus, Kazakhstan and Mongolia in seeking market-economy designation by Europe and faces more European anti-dumping duties than any other country. The import levies cover billions of euros of Chinese exports such as stainless steel, solar panels, aluminum foil, bicycles, screws, paper, kitchenware and office-file fasteners, curbing competition for producers across the 28-nation EU. Market-economy status for China would signal more European trust in Beijing by ensuring the EU uses Chinese data for trade investigations affecting the country.
Read more …

Emerging markets will start collapsing outright, Brazil, South Africa, China and more.
• South Africa’s Flash Crash Exposes Cracks in Currency Liquidity (BBG)
It took just 15 minutes on Monday morning for South Africa’s rand to plummet 9% in what traders said may be a prelude of the new normal in the global $5.3 trillion-a-day currency market. Such flash crashes will probably become more common in foreign-exchange trading as liquidity shrinks amid tighter regulation and reduced demand for emerging-market assets, according to Insight Investment and Citigroup.The rand slid to record lows versus the dollar and yen in Asian trading before recovering the bulk of the day’s losses almost as swiftly. “The rand isn’t alone in this,” said Paul Lambert at Insight Investment, a Bank of New York Mellon unit, which manages more than $582 billion.
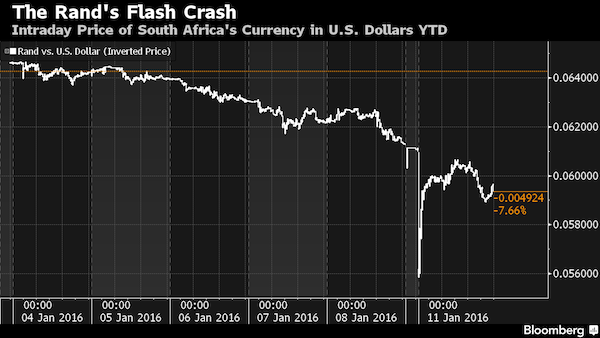
“The rand is another reflection of the change in the liquidity environment in which we’re all operating. We’re learning that unless there are clients on the other side, banks are very unwilling to take risk onto their books.” Volatility in the rand versus the dollar surged toward the highest level in four years, while a measure of global currency price swings climbed to the most since October. The difference between prices at which traders are willing to buy and sell the rand, used as a gauge of liquidity, was about 1.5 times wider on average in the past six months than it was during the first half of 2015, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
In a phenomenon that’s also hit U.S. stock markets in recent years, regulation is pushing banks to reduce their size and cut down on market making, making it more difficult to trade without prices moving adversely. A reduction in liquidity has contributed to similar price swings in fixed-income securities, including the $13 trillion U.S. government bond market. Bursts of volatility in currency markets and diminishing liquidity are another affliction for emerging economies such as South Africa, which seek to secure overseas investments amid slowing growth, a rout in commodities and domestic political challenges. Boosting international trade and capital inflows is made harder by currency turmoil as investors and banks become less willing to take on additional risk.
Read more …

A rock and an impossible place.
• Saudi Arabia Plays Down Riyal Peg Fears (FT)
Saudi Arabia sought to cool talk about the future of its currency peg, saying movements in the forward market were the result of market “misperception” about the state of the kingdom’s economy. Oil price declines and rising tensions between Saudi Arabia and Iran have pushed up the cost of riyal-dollar forward prices and questioned the validity of the 30-year-old peg. In a statement, the governor of the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency said it would “uphold its mandate” of maintaining the peg at SR3.75 to the dollar, “backed up by the full range of monetary policy instruments including its foreign exchange reserves”. The statement was prompted by forward market volatility, said governor Fahad al-Mubarak, which he attributed to “mispricing linked to market operators’ misperception about Saudi Arabia’s overall economic backdrop”.
Economic and financial indicators were stable, underpinned by its net creditor position and a sound and resilient banking system, Mr al-Mubarak said. Oil price woes are weighing on several commodity currencies, not least Russia’s rouble, which dropped more than 1% to a 13-month low. Further rouble declines would cut across the Central Bank of Russia’s strategy for resuming its easing cycle, said Rabobank’s Piotr Matys, and increased the risk of a prolonged recession. Oil’s impact on the Saudi kingdom would prompt markets to “worry more” about falling reserves and the exchange rate pegs of Saudi Arabia and other Gulf states, said Kamakshya Trivedi of Goldman Sachs in a note, “especially if attempts at fiscal adjustment are not credible or unsuccessful”.
Simon Quijano-Evans at Commerzbank acknowledged that Saudi Arabia had four years’ worth of reserves to cover budget and current account deficits. But he added that without a sustained upward oil price move, market speculation about the peg would increase. “History has shown us that if a policy peg is not economically viable, there really is little point in holding on as the intrinsic benefits from the set-up eventually become its principal vulnerabilities,” he said. Gulf bankers were unconcerned, saying the peg had survived worse financial backdrops. In the late 1990s, when oil prices were even lower, the finance ministry toiled under domestic debts totalling more than 100% of gross domestic product. Sama still has $627bn in foreign reserves, down 14% on last November, as the kingdom burns through its savings to fund the deficit and an expensive war in Yemen.
“Traders are forgetting about Saudi firepower,” said one senior Gulf banker. “This is a low-cost trade with a huge potential payout,” said another senior financier. “Those bearish oil may want to bet that pressure will become too great for Saudi. Possible, but not my scenario.”
Read more …

Nothing has changed, nothing at all. The bankers still write the rules that are supposed to keep them in check.
• Banks’ Worst Fears Eased as Basel Soft-Pedals Capital Overhaul (BBG)
Global banking regulators pledged to refrain from further tightening capital requirements with new rules to be finalized in 2016, dispelling industry fears that triggered intense lobbying efforts over the past year. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision doesn’t plan to raise capital requirements across the board in the remaining projects of its post-crisis bank rule overhaul, it said Jan. 11 after a meeting of its oversight body, chaired by ECB President Mario Draghi. The group, which includes the Bank of England and U.S. Federal Reserve, said it will assess the potential costs of any additional action. “The committee will conduct a quantitative impact assessment during the year,” the group said in a statement. “As a result of this assessment, the committee will focus on not significantly increasing overall capital requirements.”
Basel’s slate of rules for this year, including a review of trading risks that the committee endorsed on Jan. 10, have faced heavy criticism from bankers, who say onerous new capital charges would crimp their ability to lend. The overhaul of how banks value risky assets has led industry executives to warn a regulatory onslaught – sometimes referred to as Basel IV – is still ahead, even after the last decade of new rules designed to prevent another market meltdown. Karen Shaw Petrou at Federal Financial Analytics said the Basel’s latest statement is a response to bankers’ warnings. “Global regulators clearly hope to tamp down continuing talk of a ‘Basel IV’ rule, emphasizing in both action and statements that continuing changes are recalibrations, not hikes,” Petrou said in an e-mail.
Draghi said the agreements reached by the Basel committee and the upcoming agenda seek to provide greater clarity about the capital framework and, “a clear path for completing post-crisis reforms.” As part of this process, the regulator will hold a public consultation on removing internal-model approaches for some risks, such as the Advanced Measurement Approach for operational risk, as well as on “setting additional constraints on the use of internal model approaches for credit risk, in particular through the use of floors.” The committee also sounded a soft note on another lingering worry of bankers, the unweighted leverage ratio. It will keep the minimum amount of capital per total assets unchanged at 3%, when it becomes a binding requirement in 2018, it said. For the world’s biggest banks, there may be an add-on, it said, without elaborating.
Read more …

Canada has so much more to go.
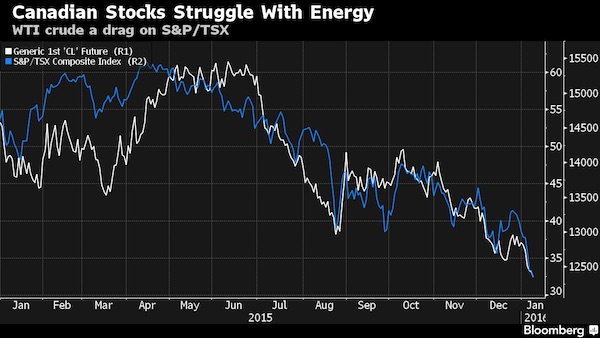
• Canadian Stocks Fall in Longest Slump Since 2002 (BBG)
Energy’s drag on Canadian stocks showed no signs of abating as the nation’s benchmark equity gauge slumped a ninth straight day, the longest losing streak since 2002. Canadian equities have lost 7.4% during this period with the Standard & Poor’s/TSX Composite Index failing to post a positive trading day in 2016. Crude futures in New York tumbled to a 12-year low. Analysts at Morgan Stanley projected Brent oil may slump to as low as $20 a barrel on strength in the dollar. Brent dropped 6.7% to $31.32 a barrel in London. Bank of America Corp. cut its average 2016 Brent forecast to $46 a barrel from $50. “Risk appetite will not return until we start to see crude carve out a bottom,” said David Rosenberg at Gluskin Sheff in a note to clients.
The S&P/TSX fell 1% to 12,319.25 at 4 p.m. in Toronto. The gauge capped a 20% plunge from its September 2014 record on Jan. 7, hitting a magnitude in declines commonly defined as a bear market. Canada was the second Group of 7 country to see its benchmark enter a bear market, after Germany’s DAX Index did in August. Energy producers sank 2.7%. The group, which accounts for about 20% of the broader index, was the worst-performing sector in the S&P/TSX last year.
Read more …

The demise of retail.
• Discovery (Jim Kunstler)
It looks like 2016 will be the year that humanfolk learn that the stuff they value was not worth as much as they thought it was. It will be a harrowing process because a great many humans are abandoning ownership of things that are rapidly losing value — e.g. stocks on the Shanghai exchange — and stuffing whatever “money” they can recover into the US dollar, the assets and usufructs of which are also going through a very painful reality value adjustment. Of course this calls into question foremost exactly what money is, and the answer is: basically a narrative construct. In other words, a story explaining why we behave the way we do around certain things. Some parts of the story have a closer relationship with reality than other parts. The part about the US dollar has a rather weak connection.
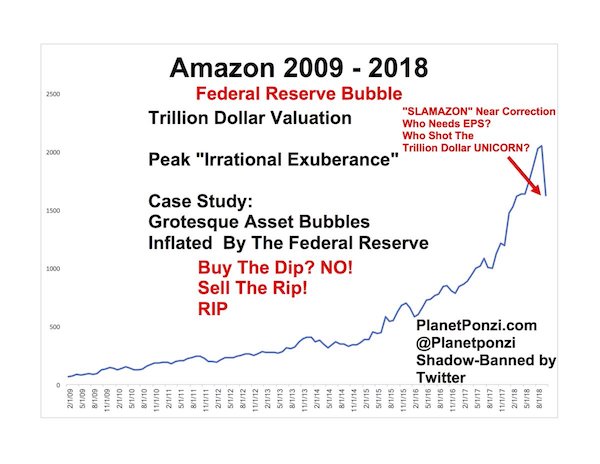
When various authorities — the BLS, the Federal Reserve, The New York Times — state that the US economy is “strong,” we can translate that to mean giant companies listed on the stock exchanges are able to put up a Potemkin façade of soundness. For instance, Amazon.com. The company continues to seem like a good idea. And it reinforces that idea in the collective imagination by sending a lot of low-priced goods to your door, (all bought on credit cards), which rings your (nearly) instant gratification bell. This has prompted investors to gobble up Amazon stock. It’s well-established by now that the “brick-and-mortar” retail operations are majorly sucking wind. Meaning, fewer people are driving to the Target store and venues like it to buy stuff. Supposedly, they are buying stuff at Amazon instead.
What interests me in that story is the idea that every single object purchased these days has a UPS journey attached to it. Of course, people also drive to the Target store, though I doubt they leave the place with just one thing. That dynamic ought to call into question just how people are living in the USA, and the answer to that is: spread out all over the place in a suburban sprawl living arrangement that has poor prospects for being reformed or mitigated. Either you drive yourself to the Target store for a slow-cooker and a few other things, or Amazon has to send the brown truck to each and every house. Either way includes an insane amount of transport, and sooner or later both the brick-and-mortar chain store model and the Amazon home delivery model will fail.
Read more …

Joris is primarily funny here. But he wants to ‘reform’ the EU, and that’s a dead end. One point is good: EU’s finance center can’t be in a country outside of it. So the UK threat to leave would force banks and multinationals out of London.
• It’s Time For Europe To Turn The Tables On Bullying Britain (Luyendijk)
So let us start talking now, out loud in Brussels as well as in Europe’s opinion pages and in national parliaments, about the offer we are going to make to the Scots, should they prefer Brussels to London in the event of Brexit. Let’s also discuss in which ways we are going to repatriate financial powers from London to the European mainland. It is strange enough that Europe’s financial centre lies outside the eurozone, but to have it outside the EU? That would be like placing Wall Street in Cuba. Clearly multinational corporations from China, Brazil or the US cannot have their European HQs outside the EU. So let’s have an EU summit about which European capitals these headquarters should ideally move to. Make sure the English can hear these discussions, and in the meantime keep an eye on how the value of commercial real estate in London plummets.
Or consider the UK-based Japanese car industry – would Greece, with its excellent port and shipping facilities, not be its ideal new home? Oh yes, and sooner or later, the 1.3 billion Indians will object again to not having a permanent seat on the UN security council when 55 million English do. Let’s work out what favours we want from India in exchange for our support. The best way for the EU to prevent Brexit is to start preparing for it, loudly. But this is not enough. European politicians and pundits must not be shy of cutting England down to size. This is the chief problem for those in England trying to make the EU case: they must acknowledge first how irrelevant and powerless their country has become. Except that is still a huge taboo. Seen from China or India, the difference between the UK and Belgium is a rounding error: 0.87% of world population versus 0.15%.
But this is not at all how Britain sees itself – consider the popular derogatory expression “a country the size of Belgium”. But alas, what a missed opportunity this referendum is. A child can see that the EU needs fundamental reform and just imagine for a moment that England had argued not for a better deal for Britain, but for all of us Europeans. How electrifying it would have been if Cameron had demanded an end to the insanely wasteful practice of moving the European parliament back and forth between Strasbourg and Brussels. If he had insisted on a comprehensive overhaul of the disastrous common agricultural policy, on the long overdue reduction in salaries and tax-free perks for Eurocrats, and on actual prosecution of corrupt officials. Instead he has set his sights on largely symbolic measures aimed at humiliating and excluding European migrants, safeguarding domestic interests versus those of the eurozone and, no surprises here, guarantees for London’s financial sector.
Ultimately, as far as the EU is concerned, the English are only in it for themselves. All the more reason, then, for Europeans to stop imploring them to stay in, and begin using their strength in the negotiations.
Read more …

These clowns actually believe they’re in control.
• Migrant Flows ‘Still Way Too High,’ EU Tells Turkey (AFP)
The number of migrants crossing the Aegean Sea from Turkey to Greece is “still way too high”, a top EU official said Monday, a month and a half after a deal aimed to limit the flow. EU vice president Frans Timmermans said Turkey and Brussels had to speed work up on implementing the action plan, while Ankara reaffirmed it was looking at a measure to tempt more Syrians to stay in Turkey by granting them work permits. “The numbers are still way too high in Greece, between 2,000-3,000 people (arriving) every day. We cannot be satisfied at this stage,” Timmermans told reporters after talks with Turkey’s EU Affairs Minister Volkan Bozkir in Ankara. “The goal of this (action plan) is to stem the flow. 2,000-3.000 (arrivals) a day is not stemming the flow. But we are in this together and we will work on that,” he added.
Under the November 29 deal, EU leaders pledged €3 billion in aid for the more than 2.2 million Syrian refugees sheltering in Turkey, in exchange for Ankara acting to reduce the flow. Under pressure from voters at home, EU leaders want to reduce the numbers coming to the European Union after over one million migrants reached Europe in 2015. Yet there has so far been no sign of a significant reduction in the numbers of migrants from Syria, Afghanistan and other troubled states undertaking the perilous crossing in rubber boats from Turkey’s western coast to EU-member Greece. Turkish authorities on a single day last week found the bodies of at least 36 migrants, including several children, washed up on beaches and floating off its western coast after their boats sank.
In the latest tragedy Monday, two women and a five-year-old girl died when a boat carrying 16 Afghan migrants sank in bad weather off the Aegean coast, reports said. “I believe we need to speed our work to get some of the projects in place,” said Timmermans. “I also said to the minister that we need… to be very explicit on what elements of the action plan have already been implemented and where we still need work.” Bozkir said that Turkey was expending “intense efforts” on halting the migrant flow, saying the Turkish authorities were stopping 500 people every day. “We will try to reduce the pressure on illegal immigration by giving work permits to Syrians in Turkey,” he added.
Read more …

Dead on. Not a bright future. As long as the right wing keeps rising in the face of incompetence.
• Mass Migration Into Europe Is Unstoppable (FT)
In the 18th and 19th centuries, Europeans populated the world. Now the world is populating Europe. Beyond the furore about the impact of the 1m-plus refugees who arrived in Germany in 2015 lie big demographic trends. The current migration crisis is driven by wars in the Middle East. But there are also larger forces at play that will ensure immigration into Europe remains a vexed issue long after the war in Syria is over. Europe is a wealthy, ageing continent whose population is stagnant. By contrast the populations of Africa, the Middle East and South Asia are younger, poorer and rising fast. At the height of the imperial age, in 1900, European countries represented about 25% of the world’s population. Today, the EU’s roughly 500m people account for about 7% of the world’s population. By contrast, there are now more than 1bn people in Africa and, according to the UN, there will be almost 2.5bn by 2050.
The population of Egypt has doubled since 1975 to more than 80m today. Nigeria’s population in 1960 was 50m. It is now more than 180m and likely to be more than 400m by 2050. The migration of Africans, Arabs and Asians to Europe represents the reversal of a historic trend. In the colonial era Europe practised a sort of demographic imperialism, with white Europeans emigrating to the four corners of the world. In North America and Australasia, indigenous populations were subdued and often killed — and whole continents were turned into offshoots of Europe. European countries also established colonies all over the world and settled them with immigrants, while at the same time several millions were forcibly migrated from Africa to the New World as slaves. When Europeans were populating the world, they often did so through “chain migration”.
A family member would settle in a new country like Argentina or the US; news and money would be sent home and, before long, others would follow. Now the chains go in the other direction: from Syria to Germany, from Morocco to the Netherlands, from Pakistan to Britain. But these days it is not a question of a letter home followed by a long sea voyage. In the era of Facebook and the smartphone, Europe feels close even if you are in Karachi or Lagos. Countries such as Britain, France and the Netherlands have become much more multiracial in the past 40 years. Governments that promise to restrict immigration, such as the current British administration, have found it very hard to deliver on their promises.
The EU position is that, while refugees can apply for asylum in Europe, illegal “economic migrants” must return home. But this policy is unlikely to stem the population flows for several reasons. First, the number of countries that are afflicted by war or state failure may actually increase; worries about the stability of Algeria are rising, for example. Second, most of those who are deemed “economic migrants” never actually leave Europe. In Germany only about 30% of rejected asylum seekers leave the country voluntarily or are deported. Third, once large immigrant populations are established, the right of “family reunion” will ensure a continued flow. So Europe is likely to remain an attractive and attainable destination for poor and ambitious people all over the world.
Read more …