
Russell Lee Street scene. Spencer, Iowa 1936

The inbuilt and inevitable downfall of our formerly ‘rich economies’ in a nutshell: “Companies do not exist to create jobs. You don’t get rewarded for creating jobs..”
• This Labor Day, Let’s Acknowledge Why Our Job-Creation Machine Is Broken (MW)
It’s Labor Day weekend, and despite unemployment under 5% and nearly 15 million private-sector jobs created since February 2010, nobody’s celebrating. Workforce participation is stuck near historic lows, six million people are part-timers but want to work full time, and wage growth remains subdued. Both presidential candidates have talked a good game about jobs and the economy, but neither addresses the real problem. The U.S. job-creation machine—once the envy of the world—is broken, because American corporations cannot create steady, well-paying jobs here in the USA while also providing maximal returns to their investors, who are really in charge. So says Gerald Davis, a professor at the University of Michigan’s Ross School of Business, who has studied these issues for years.
A short piece he wrote late last year for Brookings and a new book, “The Vanishing American Corporation,” trace the big changes in American corporations from the job-rich giants of the post-World War II era to job killers now, because the mission of the corporation has changed radically. Corporations’ new, exclusive emphasis on shareholder value—enforced by executive-compensation packages in which equity comprised 62.2% of S&P 500 CEOs’ total compensation in 2015, according to Equilar—has pushed top executives to replace humans with robots, send jobs overseas or bring in lower-paid immigrants to do them here, hire part-time or temporary workers (or glorified day laborers and Uber “contractors”) instead of full-time ones, and lay off thousands of employees even when profits are soaring.
Cutting labor costs boosts earnings, which tends to push stock prices (and executive compensation) higher, and frees up cash for more “important” things like dividends or share buybacks. As of March, S&P 500 companies had bought back more than $2 trillion in stock over the last five years, making buybacks the biggest source of demand for stocks since 2009, HSBC estimated. That makes big pension funds and “activist” investors like Carl Icahn happy, but it’s bad news for the millions of Americans who still yearn for well-paying middle-class jobs that offer career advancement, decent health-care coverage, and retirement security. “Under our current conditions, creating shareholder value and creating good jobs are largely incompatible,” Davis wrote in his Brookings piece. “Corporations are ‘job creators’ only as a last resort.” “Companies do not exist to create jobs. You don’t get rewarded for creating jobs..”

Hollowing out.
• US Factory Orders Tumble For Longest Streak In History (ZH)
21 Months… US Factory Orders have decline year-over-year every month since October 2014 (the end of QE3). This is the longest period of decline in US history (since 1956) and has always indicated the US economy is in recession… While headlines will crow of 1.9% MoM gain (which missed expectations of a 2.0% rise), the trend is simply ugly: Year-over-year Factory Orders fell 3.5%. As Bloomberg also notes, there’s one key takeaway from the Commerce Department’s report Friday on U.S. factory orders. The value of unfilled orders dropped in July to the lowest level in two years, indicating producers are having an easier time meeting demand.
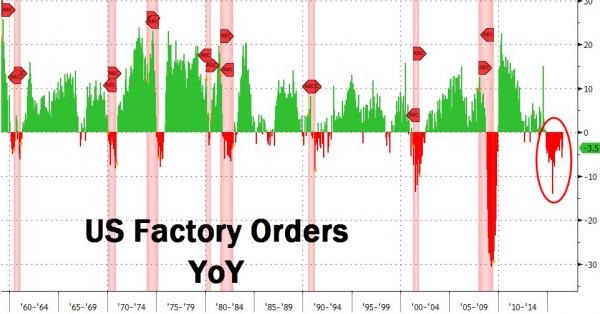
With soft sales, factories have little reason to add as many workers to their payrolls and may find it difficult to raise prices. Employment in manufacturing dropped 14,000 in August, the most in three months, another report from the Labor Department showed Friday. • Unfilled orders to all manufacturers fell 0.1% to $1.13 trillion, the lowest since June 2014, after a 0.9% slump. • Unfilled orders have increased just once since November. • Total factory orders rose 1.9% in July after a 1.8% drop. Just another WTF chart to ignore.

The whole economy turns to junk.
• Number Of Credit-Crimped US Companies Rises to 2009 Level, S&P Says (BBG)
You’d have to go back to the months following the financial crisis to find so many companies facing potentially ruinous debt problems. That’s according to the latest tally by S&P Global Ratings of “weakest link” issuers. S&P counted 251 with ratings at the low end of junk status and a negative outlook, the most since October 2009, when the total was 264. The issuers collectively have about $359 billion of debt outstanding, led by energy companies, according to S&P’s Sept. 1 report. “Weakest links maintain an important role as potential default indicators,” Diane Vazza, S&P’s head of global fixed income research, said in the report.
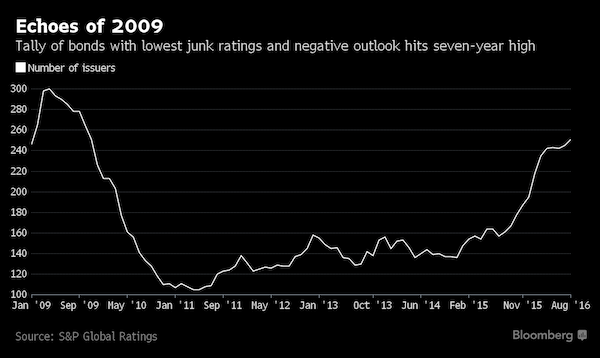
They’re almost 10 times more likely to miss payments than ordinary speculative-grade issuers, Vazza wrote, adding that 71 of 100 companies that defaulted this year had been previously tagged as weakest links. The oil and gas sector contributed 62 issuers, or about 25% of the total, as stress on commodities markets continues. Eight of the August additions were from that industry, including Chesapeake Energy and Hornbeck Offshore Services. Financial institutions followed with 34 issuers, or 14%. Other newcomers included Tesla Motors, Elon Musk’s cash-strapped electric-car maker, and Intelsat SA, the satellite operator that proposed a private bond exchange offer, which S&P labeled “a distressed restructuring and tantamount to default.”
S&P assembled the list based on the number of borrowers rated B- or lower with either negative outlooks or negative implications on Credit Watch that indicate a strong possibility of further downgrades. The number hit its record high of 300 issuers in April 2009. The U.S. speculative-grade corporate default rate grew to 4.8% in August after seven defaults, and is expected to reach 5.6% by June 2017, S&P said in a separate report. The U.S. speculative-grade default rate for energy issuers is 21.7% as of July 31, Vazza said.

The power of buybacks. “..the American economy has transformed from a system of value creation to one of value extraction.”
• US Exchanges Trade Fewest Stocks In 32 Years (ZH)
The number of common stocks traded on major U.S. exchanges are the fewest in three decades. As CNBC reports, “Currently, there are just 3,267 stocks in the University of Chicago’s CRSP data, and this is the lowest since 1984,” wrote longtime Jefferies equity strategist Steven DeSanctis. What’s behind this phenomenon? DeSanctis explains: “Between the lack of IPO activity, the pickup of M&A, and buybacks, the U.S. equity world is becoming smaller and smaller, and this could be one of many reasons why active managers are lagging behind their indexes. Companies may not want to come public due to the additional cost of Sarbanes-Oxley or the fact that the private market has become a bigger source of financing than it has been in the past.”
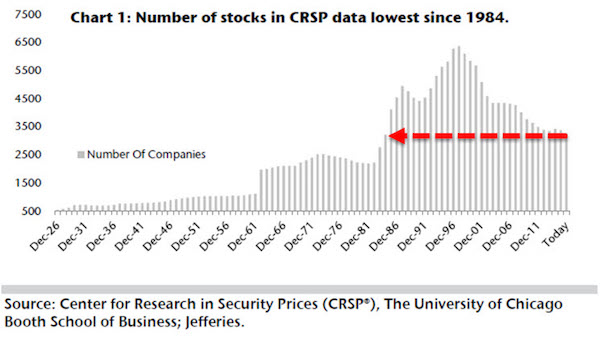
So whether it’s the total number of stocks or the amount of shares for each company outstanding, the stock market is shrinking. Or as Dark Bid’s Daniel Drew previously noted, The Stock Market Is Disappearing In One Giant Leveraged Buyout It’s easy to find critics and doomsayers who predict that the next stock market crash is just around the corner. They could be right, but another possibility is that the stock market itself will disappear entirely. Anyone who is familiar with mergers and acquisitions knows what happens when a company is being slowly acquired. The price climbs higher, slowly yet relentlessly. Liquidity evaporates as offers are lifted. If the price moves up too quickly, buy programs are canceled. The buyer waits until the froth dies down a little before resuming purchases.
Eventually, the bids reappear, and the process continues. Once the buyer acquires 5% of the company, a legal requirement is triggered: the SEC requires the buyer to file Schedule 13D, otherwise known as a “beneficial ownership report.” Once this report is filed, everyone can see the buyer, and the stock price will usually jump. This same process has been underway in the stock market over the last 6 years. The market is up well over 200%. Liquidity has evaporated in the S&P 500 futures market, and the central banks themselves are buying S&P 500 futures. Companies are spending nearly all of their profits on stock buybacks. All of this activity harms employees. William Lazonick discussed the negative effects in a Harvard Business Review article called “Profits Without Prosperity.” According to Lazonick, the American economy has transformed from a system of value creation to one of value extraction.

Please do it before the election.
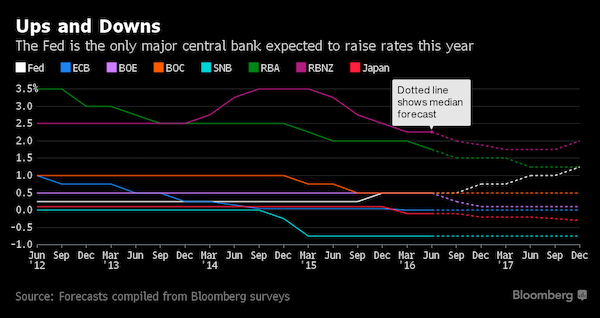
• US Economy May Need Much Higher Interest Rates: Fed’s Lacker (R.)
The U.S. economy appears strong enough to warrant significantly higher interest rates, Richmond Federal Reserve Bank President Jeffrey Lacker said on Friday. Lacker, who is not a voting member of the U.S. central bank’s rate-setting committee this year, said he still favors raising rates sooner than later and that the Fed’s last policy meeting in July would have been a “good time” to tighten policy. Speaking to a group of economists in Richmond, Lacker argued that a range of economic analysis suggests the Fed’s benchmark overnight interest rate – the federal funds rate – is currently too low. “It appears that the funds rate should be significantly higher than it is now,” he said in the speech. He made his comments after the U.S. government reported a hiring slowdown in August that could effectively rule out a rate increase later this month.
While Lacker is not due to have a vote on policy until 2018, he does participate in discussions on interest rates. The Fed has appeared sharply divided between policymakers who favor rate increases soon and those who urge more caution. Those favoring caution appeared to get a boost on Friday when a report showed 150,000 U.S. jobs were created last month, fewer than expected. But Lacker said the weaker pace of hiring still left the job market on a strengthening path and the case for higher rates would only grow stronger unless job growth slowed “significantly in the months ahead.” He suggested there were increased risks in waiting to raise rates. “The way the data is playing out I think the longer we wait there is a material increase in risks that we run,” Lacker told reporters after his speech.

Pity. I’d love to see Draghi do a rate hike.
• US Economic Misery Finds Company, Just Not In a Rate Hike (BBG)
The Federal Reserve is expected, sooner or later, to raise its key interest rate for a second time since the financial crisis – a feat not in sight for other major developed-nation central banks. It’ll depend on if the economy is doing well, and policy makers may take comfort that the U.S. ranking has fallen in a gauge of economic misery. With the unemployment rate at 4.9% and inflation at 0.8%, the U.S. Misery Index score of 5.7 has improved since the financial crisis, though it lags behind Switzerland, Japan, the U.K. and New Zealand. All these nations’ central banks are poised to hold rates at record lows, or cut them further, according to surveys conducted by Bloomberg. The Misery Index is a simple calculation adding the rate of unemployment and inflation, with lower scores indicating a healthier economy.
But if you think the four countries that are beating out the U.S. in terms of misery are doing everything right, think again. Japan and Switzerland, both of which have brought their rates to negative levels in an attempt to boost lending, are suffering from deflation, which is helping bring down their Misery Index scores. New Zealand, though faring a bit better economically, is also expected to cut its central bank rate as inflation remains suppressed, and the U.K. will do so as policy makers attempt to counteract the fallout from Brexit.

All they have left is zeroes.
• ECB Throws Twelfth Zero at Inflation (BBG)
The European Central Bank has added a digit to its odometer to read 1,000,000,000,000. Euros, not kilometers. That’s the amount of excess liquidity now sloshing through the financial system – equivalent to almost €3,000 ($3,360) for each of the 340 million people in the 19-nation region. The money is created by the ECB through a program of quantitative easing and bank loans, and is aimed at bringing inflation closer to its goal of just under 2%. It’s labeled “excess” because it’s the amount over and above what’s immediately needed by the banking system to serve the economy. That’s why it’s inflationary. But no matter how often the money is lent to companies and households, at the end of each day it lands at the central bank where commercial institutions have their accounts.
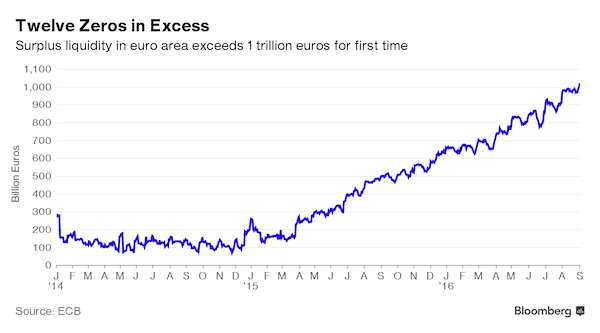
And because the ECB’s stimulus package also includes a negative deposit rate of 0.4%, lenders are charged for that surplus cash. With excess liquidity passing €1 trillion as of Sept. 1, the ECB now makes more than €11 million a day in interest from the deposit facility alone. Though that’s just a fraction of the institution’s revenue. “Earnings related to QE are more decisive for net income,” said Michael Schubert, an economist at Commerzbank in Frankfurt. “It was the bigger factor in the past years.” There is no single profit and loss account for the 19 national central banks and the ECB; everyone publishes their own. Germany’s Bundesbank, which implements monetary policy in Europe’s largest economy, made €248 million last year from charging interest for deposits and nearly €2 billion from past and present asset-purchase programs.

Please make it stop!
• Any ECB Move Into Stocks Unlikely To Be Plain Sailing (R.)
The ECB may soon be forced to follow the Bank of Japan’s example and buy equities as part of any expanded stimulus programme, but it faces significant hurdles in helping all 19 euro zone members equally without distorting a key market for investors. The European Central Bank could run out of eligible bonds for its €1.7 trillion bond-buying scheme, meaning alternative options are on the table should it decide to loosen policy further to lift growth and inflation across the bloc. Analysts say these could include large-scale share buying, a policy that the BOJ has already adopted after it started purchasing equity exchange traded funds (ETFs) for its own quantitative easing scheme six years ago.
ETFs allow an investor to trade a range of assets, from a basket of stocks to government debt. ETFs, which offer a convenient way to purchase a broad basket of securities in a single transaction from an exchange, have risen in popularity with investors due to their simplicity and lower fees. But buying ETFs in the 19-nation euro zone would be far from simple for the ECB, both practically and politically. “How do you buy an index which favours all countries within the euro zone? Obviously the ECB doesn’t want to be seen favouring one market above another,” said Commerzbank economist Peter Dixon.
The BOJ doubled its ETF purchases in late July to an annual pace of 6 trillion yen ($58 billion). According to SPDR ETFs, the BOJ is now estimated to hold almost 50% of the total Japanese ETF market. Investments in Europe-listed ETFs are worth just over $500 billion, compared with nearly $200 billion in Japan and more than $2 trillion in the United States, according to consultancy firm ETFGI. Although the European ETF market is bigger than Japan’s, such a scheme would have to benefit 19 member states, from heavyweight Germany to much smaller Slovakia.

Washington should leave them alone.
• Retailers Seek US Government Help With Shipping Crisis (WSJ)
U.S. retailers, bracing for a blow as they stock up for the crucial holiday sales season, asked the government to step in and help resolve a growing crisis caused by the near-collapse of South Korea’s Hanjin Shipping , one of the world’s largest container shipping companies. “While the situation is still developing, the prospect of harm is significant and apparent,” Sandra Kennedy, president of the Retail Industry Leaders Association, wrote in a letter to the Department of Commerce and the Federal Maritime Commission. Hanjin’s recent bankruptcy filing “presents an enormous challenge to U.S. shippers,” she said, and “could have a substantial impact on consumers and the economy at large.”
The trade group is urging the U.S. to work with ports, cargo handlers and the South Korean government to resolve the widespread disruption in freight shipments caused by the Hanjin bankrupcy filing. A spokesman for the Retail Industry Leaders Association said they’re hoping the South Korean government could help provide clarity and speed to the bankruptcy proceedings, which are being considered by courts there. Hanjin handles about 7.8% of the trans-Pacific trade volume for the U.S. market, Ms. Kennedy’s letter said. Since the shipping company filed for bankruptcy protection in a Seoul court Wednesday, terminal operators, ports, cargo handlers, truckers and others have refused to handle its cargo, for fear they won’t get paid. That is causing turmoil at U.S. ports and beyond, said shippers, importers and freight forwarders.

There’s no maybe involved. The only way to finance Tesla was to agree to buy back its own second hand cars from lenders, or in other words: “..Tesla began providing “residual value guarantees” to those “leasing partners.”
• Tesla’s Cash Crunch Worse Than You Think (Fortune)
It’s well known that Tesla is deploying gigantic amounts of capital to boost sales from a projected 50,000 vehicles this year to half-a-million in 2018. That’s arguably the most ambitious goal in corporate America. To make it happen, Musk has grown Tesla’s asset base from $1.3 billion at the end of 2013 to $11.9 billion by June 30, following a $1.7 billion equity raise in the second quarter. Now, Tesla will need to accelerate its capital-raising program to fund the SolarCity deal. It’s absolutely typical for a startup racing to build new plants and R&D centers to burn a lot more cash than it generates. Investors and analysts are mostly optimistic, predicting that Tesla will in a few years exploit its heavy investment by generating big positive and fast-growing cash flows.
Hence, it’s crucial to examine the arc of Tesla’s cash flows to project when, and if, it will become profitable. As with its other pro-forma measures, Tesla’s version of cash from operations looks a lot better than the official numbers. So which is the right figure for investors? As it reported in its 10K for 2015, Tesla made a major concession to an important group of customers. The shift was aimed at strengthening a fast-growing business, sales of vehicles to banks that lease its model S and X vehicles to end-customers. In the past, Tesla simply sold the autos to its leasing customers, with no strings attached. The banks had no right to get money back from Tesla if, for example, the market for used electric vehicles dropped, forcing them to sell at lower-than-expected prices when the leases ended.
But starting in the fourth quarter of 2014, Tesla began providing “residual value guarantees” to those “leasing partners.” Those guarantees state that when the lease expires, typically after three years, the bank has the option of selling the car back to Tesla at a fixed, pre-determined price. Or, if the lessor chooses to sell the cars on its own and receives less than the guarantee amount, Tesla must cover the shortfall. Of course, customers have the option of buying the Model S or Model X for a fixed price at the end of the lease period, and if a customer does keep the car, Tesla’s liability ends. But if a customer decides not to buy, the bank can return the car to Tesla and pocket the guaranteed price, or sell the three-year old vehicle on the nascent green used car market. Either way, Tesla takes a big loss, and effectively returns a lot of the original “purchase” price, if rates for used S and X’s drop.

“..Australia’s real estate bubble, which is being held aloft by foreign capital..”
• Apartment Correction To Cause Australia-Wide Recession (SMH)
A “correction” in the apartment market could see sharp falls in all Australian home prices and a nationwide recession, a gloomy bank analyst report on the housing market warns. The report by analysts CLSA paints a “base case” scenario which says Australia’s housing cycle has “peaked,” with household debt now extending the country’s property bubble. The shift by big banks to tighten lending standards is likely to cause a “correction” and “crisis” in cheap apartments which will spread, leading to defaults among smaller developers and a sharp contraction in construction, CLSA says.
The “worst case” scenario foresees “dwelling prices falling sharply in all areas, eventually leading to a recession,” the report’s authors, respected former banking analyst Brian Johnson, and his colleagues say. “Issues of affordability and household debt are overextending Australia’s real estate bubble, which is being held aloft by foreign capital,” they say. “Our base case has the crisis starting with cheap apartments and later spreading to other flats in close proximity.” The authors put a “sell” recommendation on stocks of companies most likely to be affected by the crunch, including the country’s biggest bank CBA and listed property giant Lendlease. Another property player Mirvac would also be impacted, they said.
Mr Johnson and co. said they believe a correction in the housing market will start with settlement problems among apartment buyers, where purchasers who stumped up a 10% deposit simply walk away leaving developers to recoup the money or resell the unit. Under the “base case” scenario the contagion from falling apartment prices has a “muted” impact on single-family homes and is not enough to push the economy into recession. The risk of the “worst case” happening, which predicts sharp price falls and a recession, is increased because Australian household’s are holding debt that is at 122% of GDP and house prices are 12 times price to income ratios, the authors say.

No matter how the Apple case turns out, golden taxation days in Europe are over. Next up for scrutiny: Netherlands.
• Starbucks, Amazon Pay Less Tax Than A Sausage Stand, Austria Says (R.)
Multinationals like coffee chain Starbucks and online retailer Amazon pay less tax in Austria than one of the country’s tiny sausage stands, the republic’s center-left chancellor lamented in an interview published on Friday. Chancellor Christian Kern, head of the Social Democrats and of the centrist coalition government, also criticized internet giants Google and Facebook, saying that if they paid more tax subsidies for print media could increase. “Every Viennese cafe, every sausage stand pays more tax in Austria than a multinational corporation,” Kern was quoted as saying in an interview with newspaper Der Standard, invoking two potent symbols of the Austrian capital’s food culture.
“That goes for Starbucks, Amazon and other companies,” he said, praising the European Commission’s ruling this week that Apple should pay up to €13 billion in taxes plus interest to Ireland because a special scheme to route profits through that country was illegal state aid. Apple has said it will appeal the ruling, which Chief Executive Tim Cook described as “total political crap”. Google, Facebook and other multinational companies say they follow all tax rules. Kern criticized EU states with low-tax regimes that have lured multinationals – and come under scrutiny from Brussels. “What Ireland, the Netherlands, Luxembourg or Malta are doing here lacks solidarity towards the rest of the European economy,” he said.
He stopped short of saying that Facebook and Google would have to pay more tax but underlined their significant sales in Austria, which he estimated at more than 100 million euros each, and their relatively small numbers of employees – a “good dozen” for Google and “allegedly even fewer” for Facebook. “They massively suck up the advertising volume that comes out of the economy but pay neither corporation tax nor advertising duty in Austria,” said Kern, who became chancellor in May.

Always thought that ‘kills 99% of bacteria can’t be a good thing’. Without bacteria, there are no people.
• Antibacterial Soaps Banned In US Amid Claims They Do ‘More Harm Than Good’ (G.)
Antibacterial soaps were banned from the US market on Friday in a final ruling by the Food and Drug Administration, which said that manufacturers had failed to prove the cleansers were safe or more effective than normal products. Dr Janet Woodcock, director of the FDA’s center for evaluation and research, said that certain antimicrobial soaps may not actually serve any health benefits at all. “Consumers may think antibacterial washes are more effective at preventing the spread of germs, but we have no scientific evidence that they are any better than plain soap and water,” she said in a statement. “In fact, some data suggests that antibacterial ingredients may do more harm than good over the long term.”
Manufacturers had failed to show either the safety of “long-term daily use” or that the products were “more effective than plain soap and water in preventing illness and the spread of certain infections”. The new federal rule applies to any soap or antiseptic product that has one or more of 19 chemical compounds, including triclocarbon, which is often found in bar soaps, and triclosan, often in liquid soaps. It does not affect alcohol-based hand sanitizers and wipes, which the FDA is still investigating, or certain healthcare products meant specifically for clinical settings. The FDA has given manufacturers a year to change their products or pull them off shelves.








