
Paul Gauguin Christ in the garden of olives 1889

50 million empty apartments. ‘Real’ estate holds 75% of Chinese private ‘assets’. There can hardly be a more dangerous concept for the global economy.
• China Can Never Allow Its Housing Bubble To Burst (ZH)
Back in 2017, we explained why the “fate of the world economy is in the hands of China’s housing bubble.” The answer was simple: for the Chinese population, and growing middle class, to keep spending vibrant and borrowing elevated, it had to feel comfortable and confident that its wealth would keep rising. However, unlike the US where the stock market is the ultimate barometer of the confidence boosting “wealth effect”, in China it has always been about housing as three quarters of Chinese household assets are parked in real estate, compared to only 28% in the US, with the remainder invested financial assets. Beijing knows this, of course, which is why China periodically and consistently reflates its housing bubble, hoping that the popping of the bubble, which happened in late 2011 and again in 2014, will be a controlled, “smooth landing” process.
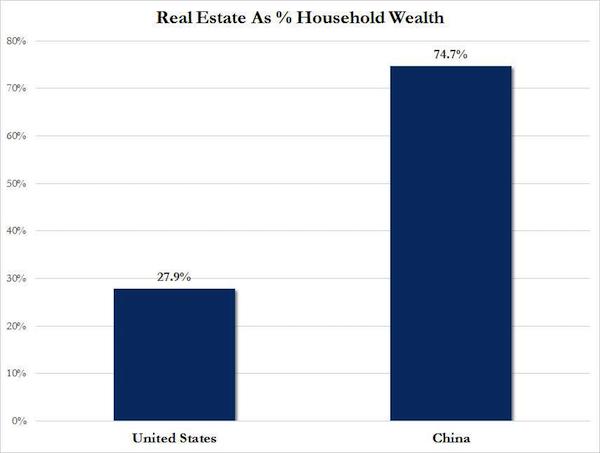
For now, Beijing has been successful in maintaining price stability at least according to official data, allowing the air out of the “Tier 1” home price bubble which peaked in early 2016, while preserving modest home price appreciation in secondary markets. How long China will be able to avoid a sharp price decline remains to be seen, but in the meantime another problem faces China’s housing market: in addition to being the primary source of household net worth – and therefore stable and growing consumption – it has also been a key driver behind China’s economic growth, with infrastructure spending and capital investment long among the biggest components of the country’s goalseeked GDP.
One result has been China’s infamous ghost cities, built only for the sake of Keynesian spending to hit a predetermined GDP number that would make Beijing happy. Meanwhile, in the process of reflating the latest housing bubble, another dire byproduct of this artificial housing “market” has emerged: tens of millions of apartments and houses standing empty across the country. According to Bloomberg, soon-to-be-published research will show that roughly 22% of China’s urban housing stock is unoccupied, according to Professor Gan Li, who runs the main nationwide study. That amounts to more than 50 million empty homes.

Britain is shrinking away from not just Europe, but the world, unable to focus on anything other than its domestic squabbles.
• One Thing Unites Britain (O.)
[..] Theresa May has always hung on in the belief that, when it came to the crunch moment, when a deal was on offer that would take the UK out of the EU on 29 March next year, her party and the country would unite sufficiently behind her to allow a withdrawal agreement to pass through parliament. The country would rally behind her vision of Brexit. But instead, as people become more aware of what leaving the EU entails, many MPs believe the reverse may be happening. [..] With more Tory Remainers and Leavers now opposing her, May’s task is daunting. Downing Street’s immediate task is to get her deeply split cabinet to unite around the final unresolved element of a potential deal with the EU: the legally complex issue of how to avoid a hard border between Northern Ireland and the Republic after Brexit.
Downing Street knows it is in a race against time. May is desperate to put a motion before the House of Commons before Christmas, in the hope that, somehow, it will pass. No 10 has pencilled in a cabinet meeting for early this week, probably on Tuesday. But disagreements remain among her most senior ministers over how the UK would exit from the so-called “backstop” agreement, under which the whole of the UK would remain in the EU customs union until a final UK-EU trade deal is struck. Several cabinet ministers are unhappy with what they fear will be fudged wording in the withdrawal agreement that fails to chart a clear path to exit the backstop. They want to see the full legal advice and want guarantees that the EU will not be able to prevent the UK breaking free from its system once and for all, so that it can strike its own trade deals.

It’s still the Irish hard border. And they’re still no closer to a solution.
• Four UK Ministers On Verge Of Quitting, EU Rejects Latest Plan (R.)
Four British ministers who back remaining in the European Union are on the verge of quitting Theresa May’s government over Brexit, the Sunday Times reported, as pressures built on the prime minister from all sides. The newspaper also said that the European Union had rejected May’s plan for an independent mechanism to oversee Britain’s departure from any temporary customs arrangement it agrees. The newspaper sourced the development to British sources, and not sources in the EU team. May is trying to hammer out the final details of the British divorce deal but the talks have become stuck over how the two sides can prevent a hard border from being required in Ireland.
Britain has proposed a UK-wide temporary customs arrangement with the EU to resolve the issue but Brexiteers in her party want London to have the final say on when that arrangement would end, to prevent it from being tied indefinitely to the bloc. A senior cabinet minister was quoted in the paper as saying: “This is the moment she has to face down Brussels and make it clear to them that they need to compromise, or we will leave without a deal.” An EU diplomat told Reuters earlier on Saturday that they were cautiously hopeful that an EU summit could happen in November to endorse the deal but that the volatile situation in Britain made it very difficult to predict.

Well, May herself doesn’t appear to know what to do with that power.
• Top Tory Says Theresa May Is ‘Handing Power To EU’ In Brexit Deal (G.)
Theresa May was accused last night by a former cabinet colleague of planning the “biggest giveaway of sovereignty in modern times”, as she faced a potentially devastating pincer movement from Tory remainers and leavers condemning her Brexit plans. The day after Jo Johnson, the pro-remain brother of former foreign secretary Boris Johnson, resigned from the government and called for a second referendum on Brexit, former education secretary Justine Greening launched an attack on the prime minister, saying her plans would leave the country in the “worst of all worlds”. Piling yet more pressure on May, Greening – who resigned from the cabinet in January – backed the former transport minister’s call for another public vote and said MPs should reject the prime minister’s deal.
Greening told the Observer: “The parliamentary deadlock has been clear for some time. It’s crucial now for parliament to vote down this plan, because it is the biggest giveaway of sovereignty in modern times. “Instead, the government and parliament must recognise we should give people a final say on Brexit. Only they can break the deadlock and choose from the practical options for Britain’s future now on the table.” Greening added: “Like many of us, Jo Johnson is a pragmatist on Britain’s relationship with the EU. But Conservative MPs can increasingly see that this sovereignty giveaway from No 10 leaves our country with less say over rules that govern our lives … That is not in the national interest, it’s the worst of all worlds and it resolves nothing.”

Even as the UK has also received the audio from Turkey.
• Khashoggi Murder Fails To Stop Britain Selling Arms To The Saudis (O.)
Britain has pursued its assiduous courtship of Saudi Arabia despite the murder of the journalist Jamal Khashoggi, with diplomats and Ministry of Defence officials meeting their counterparts in the kingdom to discuss closer economic, military and political ties. The discussions have taken place as Britain enters the final phase of negotiations to sell more Typhoon jets to Riyadh. They are similar to those used in the Saudi-led bombing of Yemen in a war that has caused a humanitarian disaster.
Britain sells billions of pounds of weapons to the countries bombing Yemen and is keen to strengthen its ties after Brexit. In July last year, the government confirmed it had created a dedicated Gulf region working group to promote “high-level dialogue with key trading partners to progress our trade and investment relationships”. Since then, civil servants have regularly visited the region for confidential talks to prepare for future deals once Britain leaves the European Union. A delegation from the Department for International Trade visited the Eastern Province chamber of commerce in Dammam in Saudi Arabia on 2 October – the day Khashoggi was murdered.
Alastair Long, the UK’s deputy trade commissioner for the Middle East and director of trade for Saudi Arabia, stressed that Britain was keen to create alternative markets and that Saudi Arabia “is at the head of these markets”. On 31 October, another UK government delegation visited Riyadh for a meeting with the Gulf Cooperation Council secretariat. A press release from the council said the meeting discussed expanding “the horizons of political, security, military and commercial cooperation”

Much discussed before: smaller producers have only one reaction to falling prices: produce more (if they can).
• Saudi Arabia Wants To Cut OPEC Allies Oil Output By Up To 1 Million Bpd (R.)
Saudi Arabia is discussing a proposal to cut oil output by up to 1 million barrels per day by OPEC and its allies, two sources close to the discussions told Reuters on Sunday. The sources said the discussions were not finalized as much depended on the reduction in Iranian exports. “There is a general discussion about this. But the question is how much is needed to reduce by the market,” one of the sources said, speaking in Abu Dhabi where a market monitoring committee is due to be held on Sunday, attended by top exporters Saudi Arabia and Russia.
Asked by reporters in Abu Dhabi if the market is in balance, Saudi Energy Minister Khalid Al-Falih said: “We will find out. We have our meeting later.” Al-Falih last month said there could be a need for intervention to reduce oil stockpiles after increases in recent months. The United States this month imposed sanctions curtailing Iran’s oil exports as part of efforts to curb Tehran’s nuclear and missile programs as well as its support for proxy forces in Yemen, Syria, Lebanon and other parts of the Middle East.

Smearing M5S has become less easy.
• Court Clears Rome’s Mayor Of Cronyism And Abuse Of Power (G.)
The Rome mayor, Virginia Raggi, has been cleared of cronyism and abuse of power after a judge ruled that the alleged offence did not constitute a crime. Prosecutors had called for a 10-month jail term over allegations that Raggi, from the anti-establishment Five Star Movement, lied to investigators over the appointment of Renato Marra, the brother of one of her close aides, as Rome’s tourism chief. His brother Raffaele, the former head of staff at Rome city hall, faces separate corruption allegations. The accusations emerged not long after Raggi was elected as Rome’s first female mayor in June 2016. Had she been convicted she would have been forced to resign as mayor, in line with the Five Star Movement’s code of ethics.
She wept upon hearing the ruling, saying afterwards: “This sentence wipes out two years of mud-slinging. We’ll go forward with our heads held high for Rome, my beloved city, and for all citizens.” Luigi Di Maio, the Five Star Movement leader and Italy’s deputy prime minister, celebrated the court ruling while using the opportunity to criticise journalists whom he accused of “attacking Italy’s most massacred mayor” for two years and generating “fake news” to bring her down. “Go Virginia! I am happy for always having defended you and believed in you,” he wrote on Facebook.

There are people who genuinely want peace. Get out of their way.
• 2 Koreas Complete The Disarming Of 22 Guard Posts (AP)
The North and South Korean militaries completed withdrawing troops and firearms from 22 front-line guard posts on Saturday as they continue to implement a wide-ranging agreement reached in September to reduce tensions across the world’s most fortified border, a South Korean Defense Ministry official said. South Korea says the military agreement is an important trust-building step that would help stabilize peace and advance reconciliation between the rivals. But critics say the South risks conceding some of its conventional military strength before North Korea takes any meaningful steps on denuclearization — an anxiety that’s growing as the larger nuclear negotiations between Washington and Pyongyang seemingly drift into a stalemate.
South Korea reportedly has about 60 guard posts — bunker-like concrete structures surrounded with layers of barbed-wire fences and manned by soldiers equipped with machine guns — stretched across the ironically named Demilitarized Zone. The 248-kilometer (155-mile) border buffer peppered with millions of land mines has been the site of occasional skirmishes between the two forces since the 1950-53 Korean War. The North is believed to have about 160 guard posts within the DMZ.

In this Nov. 4, 2018, photo provided by South Korea Defense Ministry, a yellow flag is raised at a guard post of South Korea in the demilitarized zone, South Korea. A South Korean Defense Ministry official said on Saturday, Nov. 10, 2018, the North and South Korean militaries have completed withdrawing troops and firearms from 22 front-line guard posts as they continue to implement a wide-ranging agreement reached in September to reduce tensions. The flag marks the post that is to be dismantled so that each side can observe the work in progress.

Sorry, but no. Using much less energy of any kind is the future. Voluntarily or forced. That’s what we should prepare our societies for.
• Moorside’s Atomic Dream Was An Illusion. Renewables Are The Future (G.)
Toshiba’s decision to pull out of building a nuclear power station in Cumbria last week will cause shockwaves far beyond the north-west of England. The outcome is a disaster for the surrounding area, which is heavily reliant on the nuclear industry for jobs and prosperity. Local politicians admit it is a blow and a disappointment for Cumbrians hoping for roles at the proposed Moorside plant. They say they genuinely believe a new buyer for the site will come forward. But that looks like wishful thinking. To an extent, the demise of Moorside can be attributed to problems with it as a specific project. It has looked doomed since Toshiba’s US nuclear unit, Westinghouse, declared bankruptcy in 2017 and the company ruled out new nuclear investments outside of Japan.
Efforts to woo the South Korean energy company Kepco as a buyer then floundered. The executive leading the sale for Toshiba blamed the failure to find a buyer on being “caught between a series of unplanned and uncontrollable events”. But the end of Moorside is also emblematic of the wider challenges that new nuclear faces. It took a decade from Tony Blair signalling the UK’s renewed interest in nuclear power in 2006 for France’s EDF Energy and the British government to sign a generous subsidy deal and green-light Hinkley Point C, the UK’s first new nuclear plant in a generation. In all likelihood, it will not be generating electricity until 2027. Ministers insist new nuclear power stations are still an essential way of hitting the country’s greenhouse gas emission targets and providing energy security as old plants are switched off in the 2020s.
Losing Moorside means there are just five other new nuclear projects planned, including Hinkley Point C. Eyes will now turn to Hitachi’s proposed Wylfa Newydd plant on Anglesey. The project is the furthest along the line after Hinkley, but it’s far from a done deal. The new nuclear drive was meant to be solely funded by the private sector, but the government has already made a striking exception in the case of Wylfa. Ministers have promised Hitachi they will use public money to take a £5bn stake in the scheme. Such a dramatic U-turn on policy is explained by the fact that Wylfa is about more than the UK’s desire for new nuclear: it is also about cooperation with Tokyo and bringing forth other investment from Japanese firms, such as carmakers, after Brexit.

We get the drift, but we also know only a small part of 1 or 2 generations of mankind have ever ‘seen’ coral reefs. And most people only do ‘see’ them in pics and movies. You might want to think about that. it’s definitely not about you ‘seeing’ coral reefs or rhino’s or orangutans. It’s about something else.
• Next Generation ‘May Never See The Glory Of Coral Reefs’ (G.)
Children born today may be the last generation to see coral reefs in all their glory, according to a marine biologist who is coordinating efforts to monitor the decline of the world’s most colourful ecosystem. Global heating and ocean acidification have already severely bleached 16 to 33% of all warm-water reefs, but the remainder are vulnerable to even a fraction of a degree more warming, said David Obura, chair of the Coral Specialist Group in the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. “It will be like lots of lights blinking off,” he told the Observer. “It won’t happen immediately but it will be death by 1,000 blows. Between now and 2 degrees Celsius, we will see more reefs dropping off the map.”
Obura added: “Children born today may be the last generation to see coral reefs in all their glory. Today’s reefs have a history going back 25 million to 50 million years and have survived tectonic collisions, such as that of Africa into Europe, and India into Asia. Yet in five decades we have undermined the global climate so fundamentally that in the next generation we will lose the globally connected reef system that has survived tens of millions of years.”

Headline obviously for effect. But interesting theme. Still, is it capitalism that is to blame for suppressing women, or patriarchy?
• Why Women Have Better Sex Under Socialism (G.)
This book has a simple premise: “Unregulated capitalism is bad for women,” Kristen Ghodsee argues, “and if we adopt some ideas from socialism, women will have better lives.” Ghodsee is an ethnographer who has researched the transition from communism to capitalism in eastern Europe, with a particular focus on gender-specific consequences. “The collapse of state socialism in 1989 created a perfect laboratory to investigate the effects of capitalism on women’s lives,” she writes. Less regulated economies, she finds, place a disproportionate burden on women. Women subsidise lower taxes through their unpaid labour at home. Cuts to the social safety net mean more women have to care for children, the elderly and the sick, forcing them into economic dependence.
Ghodsee contends that without state intervention, the private sector job market punishes those who bear and raise children and discriminates against those who might one day do so. The government is better at ensuring wage parity across different groups than the private sector, and economies with more public sector jobs tend to have more gender equality, too. Women bear the brunt of capitalism’s cyclical instability, and are often the last to be hired and the first to be fired in economic downturns. They are paid less, they have less representation in government and, she writes, all of this affects their sexuality. The less economic independence women have, the more sexuality and sexual relationships conform to the marketplace, with those who are disadvantaged in the free market pursuing sex not for love or pleasure but for a roof over their heads, health insurance, or access to the wealth or status that capitalism denies them.










