Salvador Dali Eggs on the plate (without the plate) 1932

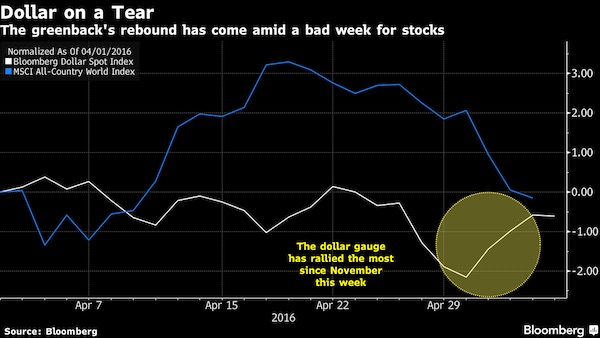
Well, they delivered something. But that’s a much bigger topic than just tax cuts, that’s Fed policy.
Lance is trying to utterly confuse us with an absolute overkill of graphs all in one place. But the gist is clear.
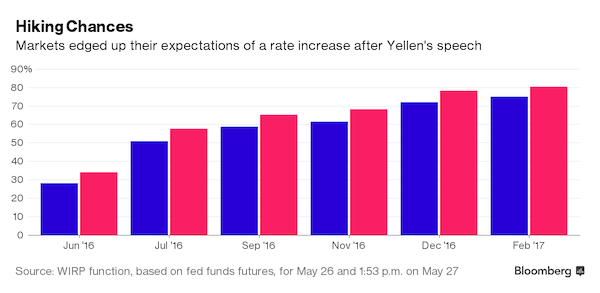
• Tax Cuts A Year Later – Did They Deliver? (Roberts)
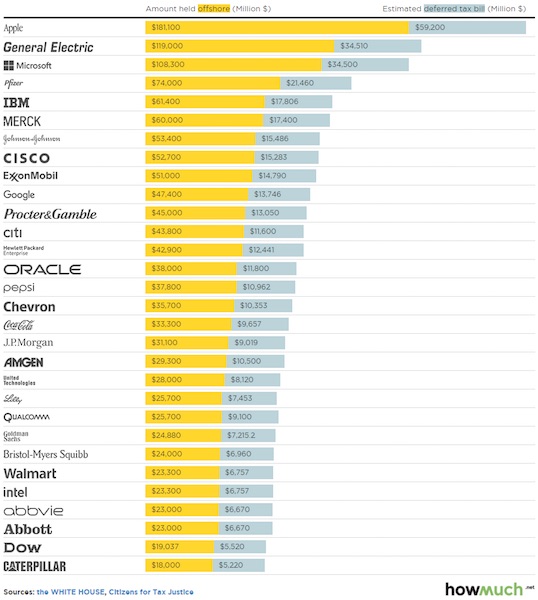
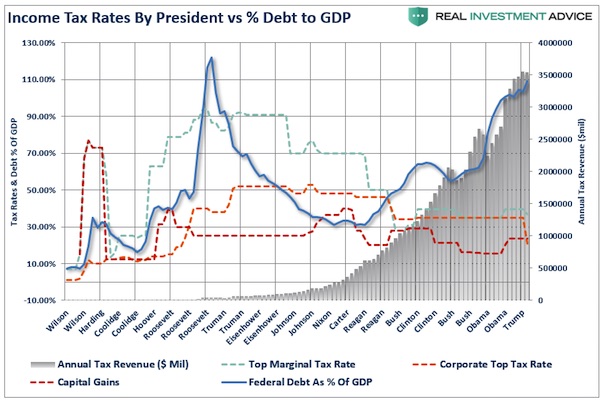
I received a lot of push back on my views when the “mainstream” analysis was the tax cuts would jump start economic growth. Of course, with 2017’s Q1 economic growth coming in at a meager 0.7% annualized, it would certainly seem to be needed. But as I questioned then: “Do tax reductions lead to higher economic growth, employment and incomes over the long-term as promised?” Speaking to NBC’s Meet the Press, VP Mike Pence argued at the time he was confident that eventually, the deficit would decline as it would be overcome by surging economic “growth” thanks to the tax cuts it will fund. [..] As shown in the chart below, changes to tax rates have a very limited impact on economic growth over the longer term.
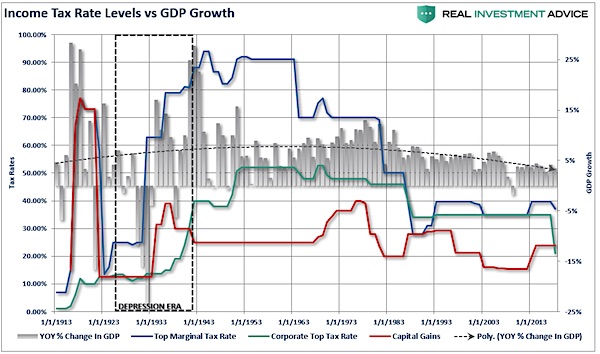
Reagan’s tax cuts were effective because they were “timely” due to the economic, fiscal, and valuation backdrop which is diametrically opposed to the situation today. “Importantly, as has been stated, the proposed tax cut by President-elect Trump will be the largest since Ronald Reagan. However, in order to make valid assumptions on the potential impact of the tax cut on the economy, earnings and the markets, we need to review the differences between the Reagan and Trump eras. My colleague, Michael Lebowitz, recently penned the following on this exact issue.
‘Many investors are suddenly comparing Trump’s economic policy proposals to those of Ronald Reagan. For those that deem that bullish, we remind you that the economic environment and potential growth of 1982 was vastly different than it is today.” [..] The differences with today’s economic and market environment could not be starker. The tailwinds provided by initial deregulation, consumer leveraging, declining interest rates, and inflation provided huge tailwinds for corporate profitability growth. The chart below shows the ramp up in government debt since Reagan versus subsequent economic growth and tax rates.
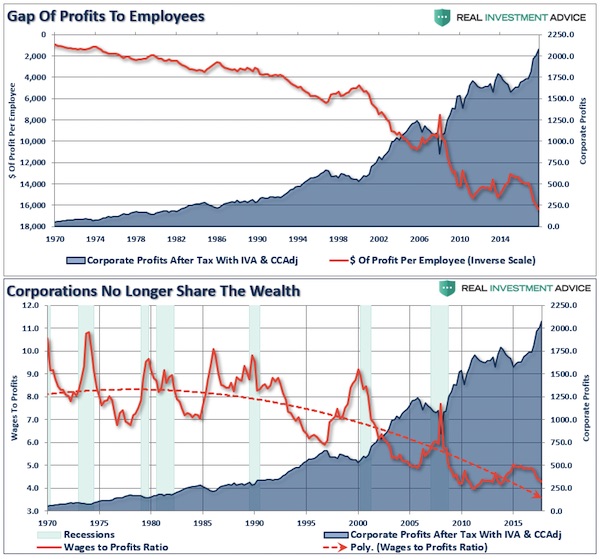
While wages did rise marginally over the last, due more to tightness in the labor market rather than tax cuts, corporations failed to share the wealth. In fact, the ratio of profits to workers wages have materially worsened since the enactment of tax cuts.

Going to the mattresses. To be honest, it’s always been clear that trying turn the US into a cashless society is the stuff for revolution.
• The Death Of Cash Has Been Greatly Exaggerated – Look At The $100 Bill (MW)
The stock market is coming off its best January in years, the economy appears to be holding up well, interest rates are still low, cryptos and mobile payments continue to gain traction — it’s not exactly a cash-friendly climate at the moment. Then what’s going on with the $100 bill? A decade ago, $20 and $1 bills were both far more prevalent than the Benjamins. As you can see by this chart from Deutsche Bank’s Torsten Slok, the currency hierarchy has shifted dramatically since then.
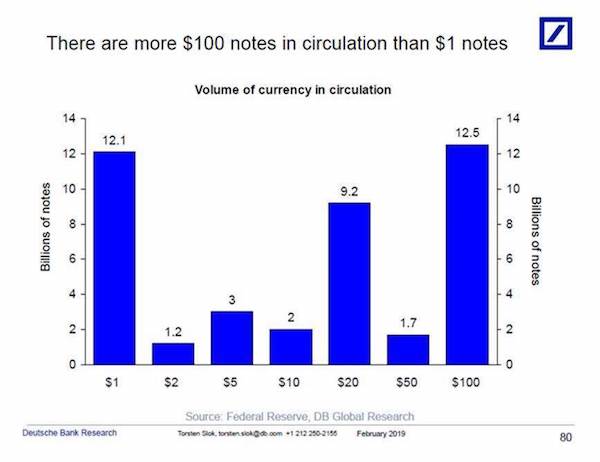
In 2017, the $100 bill took the crown as the most popular U.S. bill, doubling since 2007, which has helped drive the sharp rise in currency and other liquid assets as a share of GDP:
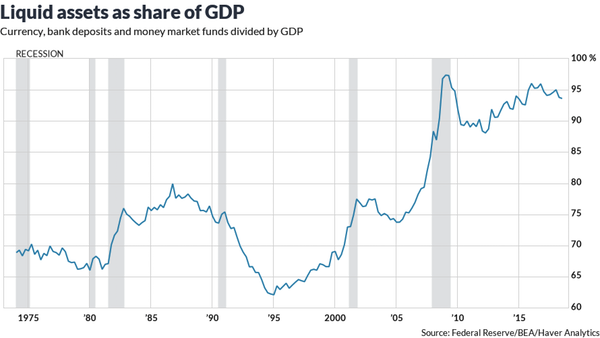
But why? Deutsche Bank’s Slok mulled a few possibilities. “It could be driven by a global fear of negative interest rates in Europe and Japan,” he said. “Or it could be a savings vehicle for U.S. households worried about another financial crisis, or it could be driven by more demand from the global underground economy.” Of course, we know it’s not because more people are using the $100 bill as pocket money. Smaller bills are still far more popular in that regard. Just look at the average lifespan of each bill:
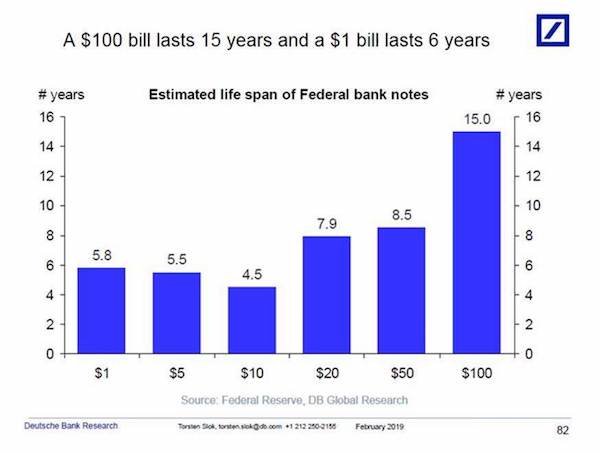
So what’s that telling us? Mattresses everywhere are getting increasingly stuffed with $100 bills instead of being put to work in the stock market or elsewhere. That speaks to the frame of mind of the Average Joe as much as anything else.

“Lighthizer said after the testimony [..] that formal steps would be taken to abandon plans of raising tariffs on Chinese goods.”
• China Trade Talks Made ‘Fantastic’ Progress Last Week -Kudlow (CNBC)
National Economic Council Director Larry Kudlow said Thursday that trade talks between the U.S. and China are going great, noting the two countries are making “fantastic” progress in meetings last week. “Last week was fantastic,” Kudlow told CNBC’s “Squawk on the Street.” “We’re making great headway on nontariff barriers and tariffs regarding various commodities such as soybeans and energy and beef. We have mechanisms with regard to enforcement, which is -I think- unparalleled.” “The progress has been terrific,” Kudlow added. But “we have to hear from the Chinese side. We have to hear from President Xi Jinping, of course. I think we’re headed for a remarkable, historic deal.” U.S. equities briefly pared some of their losses following Kudlow’s remarks.
Kudlow also said China has expressed willingness to make key structural changes to prevent intellectual property theft, a highly contested issue in these negotiations. Kudlow’s comments follow testimony from Robert Lighthizer, the U.S. trade representative. Lighthizer told members of the House Ways and Means Committee that China needed to do more than just buy more U.S. goods for the two countries to strike a permanent trade deal. But Lighthizer said after the testimony, according to The Wall Street Journal, that formal steps would be taken to abandon plans of raising tariffs on Chinese goods. This is a clear signal that a trade deal could come in the near future. “Lighthizer has worked miracles on this Chinese deal,” Kudlow said. “We’ve never come this far on China trade.”

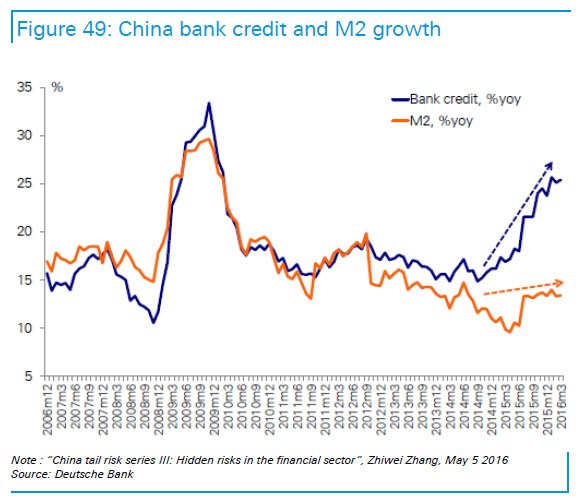
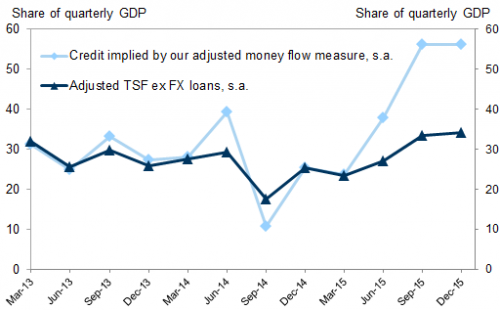
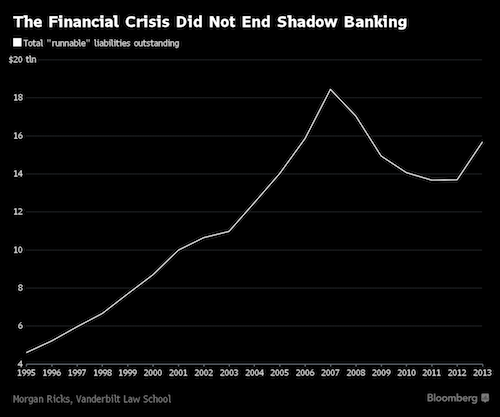
News item by news item my long held ideas of the importance of the shadow banks for China’s official growth numbers are being confirmed.
• China’s Shadow Debt Burden Much Larger Than Believed (ZH)
[..] a team of S&P credit analysts warned in an October report that China’s debt burden might be much larger than previously believed. Against a backdrop of soaring corporate defaults, the team from S&P warned that investors could safely tack on another ~40% of debt/GDP to China’s total (with even more likely hidden from view) after a careful analysis of a new source of shadow debt being tapped by local governments to further their development plans. These Local Government Financing Vehicles, or LGFVs, represented “an iceberg with titanic credit risks” as local officials had increasingly turned to these sources of shadow financing to finance development projects while bureaucrats in Beijing struggled to turn off the credit taps.
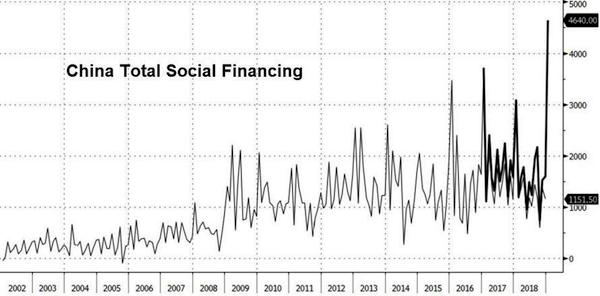
Now that Beijing has reckoned with the idea that now is not the time to try and contain the country’s massive debt load, even as the percentage of bad debt balloons, it increasingly appears that these measures might be too little, too late for investors who financed these LGFVs, as the Wall Street Journal revealed in a report about how a local government in China’s impoverished South had caused a stir by stiffing its creditors after racking up a debt pile – largely through these LGFVs – equivalent to roughly three times the government’s annual revenue.
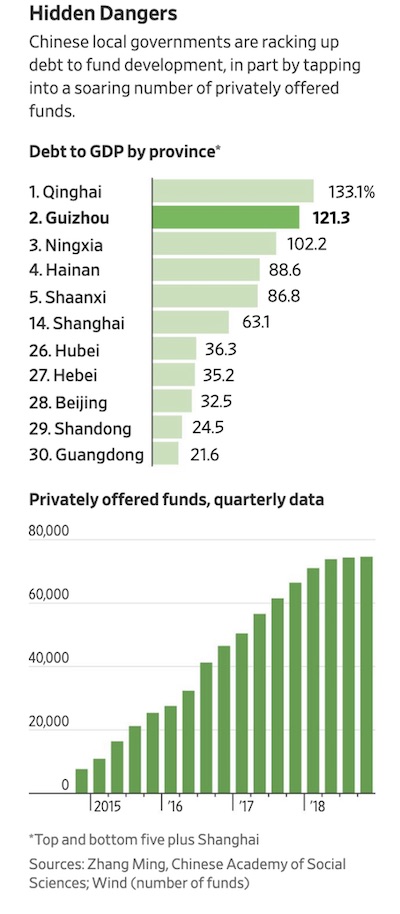
While putting a number on the amount of shadow debt in the system is difficult due to the opacity of the Chinese financial system, one economist at a domestic think tank estimated that off-balance-sheet borrowings by local governments could be as much as 23.6 trillion yuan, as of the end of 2017, meaning that total is likely higher today, as governments have been forced to tap these vehicles during Beijing’s deleveraging campaign. The proliferation of private funds and other money-raising channels for local governments makes it difficult for economists and for Beijing to track the total amount of borrowings. Official figures pegged the sum of local and central government debt at 29.95 trillion yuan ($4.457 trillion) in 2017, roughly 36% of the economy.

South Korea “exports contracted 11.1 percent in February from a year earlier, their biggest drop in nearly three years, with shipments to major buyer China slumping 17.4 percent.”
• Growing China Downdraft Chills Asia Factory Activity (R.)
Weak demand in China and growing global fallout from the Sino-U.S. trade war took a heavier toll on factories across much of Asia in February, business surveys showed on Friday. Activity in China’s vast manufacturing sector contracted for the third straight month, pointing to more strains on its major trading partners and raising questions over whether Beijing needs to do more to stabilize the slowing economy. In many cases, business conditions were the worst Asian companies have faced since 2016, with demand weakening not only in China but globally. Japan’s factory gauge fell at the sharpest pace in 2-1/2 years as slumping orders prompted plants to cut production, while separate data from South Korea showed its exports plummeted.
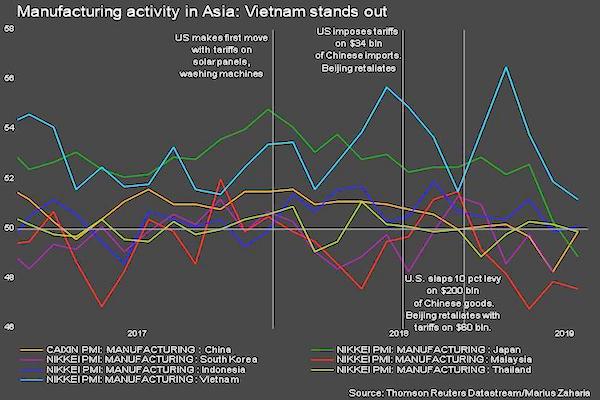
“The weakening trend in Chinese import demand weighed heavily on exports across the rest of the region,” said Sian Fenner, lead Asia economist at Oxford Economics. [..] China watchers are looking to Premier Li Keqiang’s work report to the annual meeting of parliament next week for clues on further stimulus plans. Li will set out the government’s economic targets for the year on Tuesday. Sources have told Reuters Beijing will set a 2019 growth target of 6.0-6.5 percent, down from around 6.5 percent in 2018. China reported economic growth cooled to 6.6 percent last year, its weakest pace since 1990, but some analysts believe actual activity is much weaker.
[..] In Japan, the Markit/Nikkei Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) fell into contraction territory as both domestic and foreign orders slumped. “We need to be mindful that uncertainty over the global economic outlook is heightening,” Bank of Japan board member Hitoshi Suzuki said on Thursday, after data showed the biggest drop in industrial output in a year in January. Readings from South Korea — the first economy in Asia to report trade data each month – were equally grim. Its exports contracted 11.1 percent in February from a year earlier, their biggest drop in nearly three years, with shipments to major buyer China slumping 17.4 percent.

“Once deeply resistant to Trump, CPAC is now like a religious gathering full of Trump idolatry. “Make America Great Again” (Maga) hats and sweaters are much in evidence..”
• CPAC On Socialism, Bernie Sanders And 2020: ‘Trump Will Win, 100%’ (G.)
“The favourite in the Democratic race is Bernie Sanders because the way he makes socialism sound,” said Brandon Morris, 32, wearing a Maga cap. “Most citizens don’t know how the system works; once I tell them, they see it will fall apart.” Morris, a nurse from Gainesville, Florida, who is African American, added: “I’m against socialism because I see it as a form of slavery. The rich will get richer and the poor will get poorer. Cory Booker and Kamala Harris talk about Medicare for All and that will kill doctors’ incentives to work hard. Look at Cuba.” Like Trump, Sanders ran in 2016 warning of a rigged system and the downsides of global trade and, like Trump, he thrived in midwestern states against Hillary Clinton. Less than a week after declaring his 2020 candidacy, Sanders had already raised $10m, well ahead of any of his rivals.
Wearing a Maga cap and stars and stripes jacket, Sam Lee, the communications director of conservative group Grand Opportunity USA, said: “I think Sanders has the ability to generate a base. He’s genuine. It’s the same thing as Trump: they’re very upfront about who they are. But Trump will win, 100%.” Lee rejected candidates such as Harris and Elizabeth Warren as “background noise”, adding: “Every election has people who aren’t going to make it and I don’t think they could.” Fran Wendelboe, the treasurer of the conservative organisation the 603 Alliance in New Hampshire, the first state to hold a primary, said: “Among the young voters, Bernie Sanders still seems popular. I think he still has great traction. Elizabeth Warren doesn’t seem to be getting much – she should get out of the race. But they’re all trampling themselves to get as far to the left as they can. Nobody’s going to beat Trump.”
Mike Wertz, a self-employed property appraiser, said: “It’s hard to run against Santa Claus: Bernie Sanders is Santa Claus because he says he would give everything away free. But Trump is still popular.” Wertz, 52, from Stevensville, Maryland, dismissed the prospects of Joe Biden, the former vice-president who is yet to declare whether he will mount a third bid for the White House. “Biden would get exposed. He stumbles around and says silly things. Trump would bring that out of him; he wouldn’t let Biden get away with it. If Biden said something stupid, Trump would tweet it in about 30 seconds.”

Just to show you my views are not alone. Jimmy Dore and Aaron Maté.
Someone mailed me yesterday talking about the conservatism of my columns. Never saw that before. And I don’t agree. Raging against the empty narratives of the anti-Trump machine does not make me a Trump supporter. People should read more carefully. The world is not divided into two camps.
• Claim Trump Had Prior Knowledge Of WikiLeaks Fails Hilariously (Dore)

Cohen and the Democrats lost it all when he said at the start he never wanted a White House job.
• Trump Says Cohen Lied ‘95% Instead Of 100%’ In Testimony To Congress (G.)
Donald Trump claimed on Thursday that Michael Cohen lied about almost everything during his explosive congressional testimony the day before – but told the truth by saying he had no evidence that Trump colluded with Russia. Speaking in Vietnam after meeting the North Korean leader, Kim Jong un, Trump said Cohen, his former legal fixer, lied “95% instead of 100%” of the time during a hearing of the House oversight committee on Wednesday. “I was impressed,” said Trump. Trump falsely claimed several times that Cohen had testified that there had been “no collusion”. In fact, Cohen said he did not know any “direct evidence” of collusion. “But I have my suspicions,” he told members of Congress.
Trump said of Cohen: “He lied a lot, but it was very interesting, because he didn’t lie about one thing. He said no collusion with the Russian hoax. And I said, ‘I wonder why he didn’t just lie about that too, like he lied about everything else.’” Cohen delivered a scathing account of his 10 years as Trump’s enforcer, calling the president a racist conman, implicating him in a series of felonies and estimating that Cohen had threatened 500 people on Trump’s behalf. He said Trump’s eldest son, Donald Jr, had been involved in a criminal conspiracy to pay hush money to a pornographic actor, Stormy Daniels, who alleged she had an affair with the elder Trump. Federal prosecutors in New York continue to investigate.
Cohen confirmed that Trump was under federal investigation for undisclosed crimes and warned that Trump may try to cling to power even if his re-election campaign fails next year. He also alleged that Trump knew in advance of plans by WikiLeaks to publish Democratic party emails, which US authorities say were stolen by Russian intelligence operatives, and that Donald Jr was to meet with Russians at Trump Tower. But, Cohen said, he knew of no direct evidence that Trump or his campaign colluded with Russia’s interference in the 2016 election campaign. US intelligence agencies concluded that the Russian operation was aimed at boosting Trump’s chances.

Trudeau’s riding has lots of SNC-Lavalin jobs. But he may have gone too far.
• The Case That Could Bring Down Canada’s Justin Trudeau (G.)
What is going on in Canada? Canada’s prime minister, Justin Trudeau, is facing the biggest political scandal of his administration. The affair centres around allegations that his former attorney general, Jody-Wilson Raybould, was improperly pressured by some of his closest advisers to prevent the prosecution of a large Canadian engineering firm over accusations of fraud and bribery. Thus far, the scandal has been politically costly; Gerald Butts, a longtime friend of Trudeau’s, and his closest adviser, resigned two weeks ago. Wilson-Raybould has resigned, too. A handful of polls are showing the scandal is politically unpopular for the governing Liberals – which is worrying for them, given there is a federal election in October.
What is the company accused of? SNC-Lavalin, based in Montreal, is accused of paying C$48m worth of bribes in Libya to Muammar Gaddafi’s family, in order to secure lucrative contracts. The bribery is alleged to have occurred between 2001 and 2011. If found guilty, the company would be barred from bidding on federal projects for a decade. SNC-Lavalin employs nearly 50,000 people worldwide, with 3,400 in Quebec. Company executives have been lobbying fora “deferred prosecution agreement”, which in effect allows them to pay a fine in lieu of a criminal prosecution, with no ban on bidding for contracts. But federal prosectors have decided to pursue a trial.
This is where the scandal is centred: the prime minister and his aides, along with the finance minister, have been accused of pressing Wilson-Raybould to intervene and asking prosecutors to accept a deferred prosecution agreement. Wilson-Raybould declined to override the judgment of her top legal team.

Nobody is willing to say yes to intervention.
• Anti-Maduro Allies Regroup After The Fight For Humanitarian Aid (CNBC)
Venezuela’s opposition has formally urged the international community to keep all options on the table, after deadly clashes broke out in border towns over the weekend. On Saturday, at least three people were killed and hundreds more were left injured, Reuters reported, as opposition activists tried to defy a government ban to bring food supplies, hygiene kits and nutritional supplements into the country. It comes at a time when the South American nation is in the midst of the Western Hemisphere’s worst humanitarian crisis in recent memory. President Donald Trump has consistently refused to rule out the prospect of military intervention in Venezuela and the country’s opposition leader, Juan Guaido, has called on the international community to “keep all options open.”
U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo tweeted over the weekend that Washington would “take action against those who oppose the peaceful restoration of democracy in Venezuela.” To be sure, the prospect of U.S.-led military intervention is clearly being signaled as a form of “action.” “I think large-scale U.S. military intervention remains unlikely, though the chances are increasing — that’s worrying,” Tom Long, assistant professor in the department of politics and international studies at the University of Warwick, told CNBC via email. “More than the deadly clashes, what I worry could push towards military action is the lack of options remaining for the opposition and its international allies to increase pressure,” he added.

We can only guess as to why Chelsea picks the NYT to divulge details about this. We don’t have to guess as to why the NYT picks it up; it wants to repeat this one again:
” In recent years, Mr. Assange and WikiLeaks have become notorious for their role in disseminating Democratic emails stolen by Russian hackers as part of the Russian government’s covert efforts to damage the 2016 Democratic presidential nominee, Hillary Clinton, and help Donald J. Trump win.”
And Chelsea now helps them do it.
• Disclosing Subpoena for Testimony, Chelsea Manning Vows to Fight (NYT)
Chelsea Manning, the former Army intelligence analyst convicted in 2013 of leaking archives of secret military and diplomatic documents to WikiLeaks, revealed in an interview on Thursday that she had been subpoenaed to testify before a grand jury — and vowed to fight it. The subpoena does not say what prosecutors intend to ask her about. But it was issued in the Eastern District of Virginia and comes after prosecutors inadvertently disclosed in November that Julian Assange, the founder of WikiLeaks, has been charged under seal in that district. Ms. Manning, who provided a copy of the subpoena to The New York Times, said that her legal team would file a motion on Friday morning to quash it, arguing that it would violate her constitutional rights to force her to appear.
She declined to say whether she would cooperate if that failed. “Given what is going on, I am opposing this,” she said. “I want to be very forthright I have been subpoenaed. I don’t know the parameters of the subpoena apart from that I am expected to appear. I don’t know what I’m going to be asked.” [..] Ms. Manning said that her lawyers have been talking about the subpoena with an assistant United States attorney in the Eastern District, Gordon D. Kromberg. After an inadvertent court filing revealed that Mr. Assange has been charged under seal, it was Mr. Kromberg who successfully argued before a judge that any such charges remain a secret and should not be unsealed. Moreover, she said, Mr. Kromberg told her lawyers in vague terms that prosecutors wanted to talk to her about her past statements.
During her court-martial, Ms. Manning delivered a lengthy statement about how she came to copy archives of secret documents and send them to WikiLeaks, including her online interactions with someone who was likely Mr. Assange. “It’s disappointing but not surprising that the government is continuing to pursue criminal charges against Julian Assange, apparently for his role in uncovering and providing the public truthful information about matters of great public interest,” said Barry Pollack, a lawyer for Mr. Assange. [..] In recent years, Mr. Assange and WikiLeaks have become notorious for their role in disseminating Democratic emails stolen by Russian hackers as part of the Russian government’s covert efforts to damage the 2016 Democratic presidential nominee, Hillary Clinton, and help Donald J. Trump win.

“Since 2003, China has poured more cement every two years than the US managed in the entire 20th century.”
• The Grey Wall Of China: Inside The World’s Concrete Superpower (G.)
In the suburbs south of Beijing, what could one day be the world’s busiest airport is rapidly taking shape. Nicknamed “the starfish” due to the striking design by Zaha Hadid Architects, the Beijing Daxing international airport is set to open in October, and could eventually handle more than 100 million passengers a year. While the 52,000-tonne steel exoskeleton covering the airport’s six concourses immediately catches the eye, what lies beneath is familiar to many Chinese mega-projects: concrete – 1.6m cubic metres of it. Located 67km south of the capital, the airport sprawls across 780,000 sq metres – about a third of the size of Edinburgh. It aims to process 72 million passengers a year, and will have four runways by 2025, but there is a longer-term vision for additional runways and talk of 200 million passengers. Beijing’s existing international airport in the north-east, which will stay open, already handles around 96 million passengers a year.
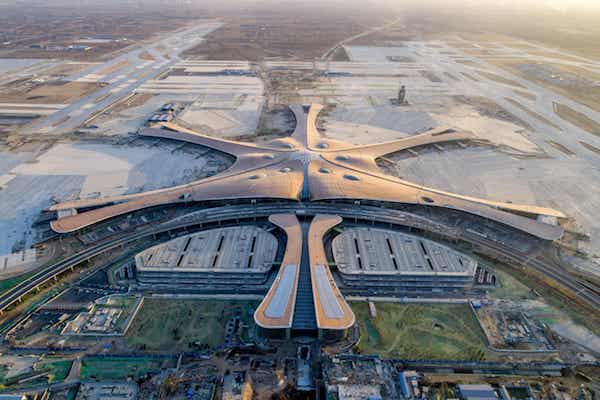

Photograph: Sipa Asia/Rex/Shutterstock
The new airport is just the latest chapter in the story of how China became the concrete superpower of the 21st century. Since 2003, China has poured more cement every two years than the US managed in the entire 20th century. Even after a dip in recent years, China uses almost half the world’s concrete. The construction sector – roads, bridges, railways, urban development and other concrete-and-steel projects – accounted for one-third of the expansion of the Chinese economy in 2017. China is already home to the largest concrete structure in the world – the Three Gorges Dam across the Yangtze River. Sometimes touted as China’s “new Great Wall”, the dam includes 27.2m cubic metres of concrete and its hydroelectric power station is the world’s largest power station in terms of capacity.
Like all of China’s concrete achievements, the Three Gorges Dam has been mired in controversy. Around 1.4 million people were displaced by the project, and there were complaints that the rehousing settlements were inadequate or that compensation money disappeared into local government coffers. More than 100 workers died in the construction process, and archaeological and cultural sites were flooded. None of this prevented Li Yongan, general manager of the Three Gorges Corporation, from declaring in 2006 that the dam was “the grandest project the Chinese people have undertaken in thousands of years”.
Li only had to wait seven more years to be outdone by yet another Chinese feat of concrete. In 2013, the eastern route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project opened, connecting the Grand Canal in China’s east with the capital in the north. The project is a multi-decade plan to divert the water from China’s lush south to its arid north, where water scarcity is an acute problem. The waterway has already cost around $80bn (£61bn), making it the most expensive infrastructure project in the world. In the first phase alone, it has used more than double the amount of concrete in the Three Gorges Dam: 65m cubic metres. The project ultimately aims to transport fresh water a distance of more than 4,300km.