Paul Cézanne Les (Grandes) Baigneuses 1905



Trump NBC

RFK Brand
.@RobertKennedyJr talks to Russell Brand about how the NSA was in charge of Operation Warp Speed, the history of the United States bioweapons program, and why Anthony Fauci is the highest-paid government official in history:
"The weird thing about the pandemic was this constant… pic.twitter.com/qunw3Bn6pP
— KanekoaTheGreat (@KanekoaTheGreat) September 18, 2023



Stoltenberg
WAR: NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg revealed that Russia offered not to invade Ukraine if the alliance would agree to deny Zelenskyy membership. Our refusal triggered the war – we are complicit. pic.twitter.com/Rj9jbOoLVA
— @amuse (@amuse) September 18, 2023



“Much as the deck is stacked against Mr. Trump, his enemies have stupidly stuffed that deck full of jokers that are liable to shriek and giggle their way out of court when turned face-up..”
• Boldly Into the Chaos (Kunstler)
The Ukraine war caper has pretty clearly lost its appeal as a supposed crusade for “democracy.” The yellow and blue flags vanished from the front porches and car bumpers months ago. It was a lie from the get-go that we have any national interest in that sad sack country. Our own government engineered the fiasco, and from every angle it has been a dead loss for all parties on our side. Ukraine has been reduced to a failed state in-waiting; Euroland has sacrificed its industrial economy for nothing; and the USA has squandered its last bits of prestige among other nations in this ignominious game of Lets You and Him Fight. Also, Americans have begun to notice that the billions funneled into Mr. Zelensky’s cadre of neo-Nazis and kleptocrats is money that is not going to places like East Palestine, Ohio, Lahaina, Maui, and the towns along our tortured southern border from Matamoros to Tijuana.
Even the people who supposedly elected “Joe Biden” are becoming a little concerned about blundering into World War Three over the mess created by Victoria Nuland & Company. How did we come to the point that it is now illegal to question the veracity of elections in America? And to charge a former president of the US for doing it? Much as the deck is stacked against Mr. Trump, his enemies have stupidly stuffed that deck full of jokers that are liable to shriek and giggle their way out of court when turned face-up. Judge Tanya Chutkan of the DC District Court is one of the jokers, having already branded Mr. Trump a seditious insurrectionist in the trails of many J-6 demonstrators she sent to jail on longer sentences than the prosecutors even asked for.
DA Fani Willis of Fulton County, Ga, is another joker who constructed a career-ending booby-trap for herself, and DA Alvin Bragg of New York County (Manhattan) will not be the one laughing when he’s finally bum-rushed out of his law license. An interesting fate awaits “Joe Biden” in the months ahead as the revenue stream of the Biden family foreign consulting firm gets audited in a House impeachment Inquiry. And an interesting-er fate awaits the Party of Chaos when it finally has to admit that it doesn’t have a candidate for the 2024 presidential election — at least a candidate anyone has ever heard of. The “president” stands (shakily) bestride a dilemma. He can gracefully bow out of office and avoid the historic humiliation of being unmasked as the crookedest chief executive ever — but if he does that, he loses the ability to pardon the son he so loves in any upcoming indictments, or pardon himself as CEO of Biden Consulting Inc.
Or, just maybe, the Blob will steal into the White House residence some gloomy pre-dawn morn, and settle its quivering, gelatinous endoplasm over “JB’s” face until his struggles with Congress and everything else on this plane of existence come mercifully (for us) to their end.

“House Republicans will have to break through the labyrinth of Biden paywalls and find how much money was rerouted into Biden coffers.”
• How Biden Will Circle the Wagons (Hanson)
The strategies of saving the Biden presidency from an impeachment and a Senate trial despite overwhelming evidence of his corruption are starting to emerge. The Family is confronted with damning evidence from the laptop, from the testimonies of Hunter’s business associates Bobulinksi and Archer, from Ukrainian oligarchs and Viktor Shokin, from IRS whistleblowers, from FBI writs, from a likely pseudonymous Biden trove of 4,000 emails to his son and associates, and from the absolute paranoia of a White House that must constantly change its narrative of denials to adjust to a growing portrait of utter corruption, bribery, and perhaps even the treason of warping U.S. policy to fit Biden family interests.
One of their strategies is to deny, then hedge, then ignore, then grow silent—and repeat the wash/rinse/spin cycle of stonewalling as many times as necessary to evade the mounting truth. Insidiously Joe Biden has retreated from his once loud protestations that he supposedly had no idea of what Hunter and his associates were doing. Such a patently dishonest denial set the model that the President would have no compunction about lying to the American people until the evidence of his wrongdoing becomes overwhelming. But this first line of defense did not crumble for years—only to be replaced by a second line of denial: Biden may have known of Hunter’s shenanigans, but he had no business interests with him. That was another blatant untruth.
And that additional stalling also allowed Biden to ignore the closing walls of incrimination for even more months. When these two forward lines of defense collapsed, as the Biden consortium knew they eventually would, a retreat to a third line of defense followed: yes, Joe knew, after all, of Hunter’s miscreant shakedowns; and, yes, Joe, after all, conceded that from time to time he did meet Hunter’s business associates, and upon requests made phone calls to Hunter’s clientele. But he did not profit from such knowledge and associations. Instead an upright old Joe from Scranton was playing along with the “illusion” of influence peddling: Scranton naiveté is not D.C. criminality. Biden’s tripartite lines of defense always got shorter and shallower as evidence mounted. But so far Biden has managed to consume 31 months of his presidency through these strategic retreats.
His fourth and final line of defense will likely be that he was involved, that he had rather than feigned contact, but that he did nothing other than what scores of other high-ranking politicians do who rub shoulders with would-be miscreants, sycophants, and crooks—and so did not knowingly take “loans” and “gifts” that had strings attached. To breach this fourth defense line, House Republicans will have to break through the labyrinth of Biden paywalls and find how much money was rerouted into Biden coffers. And then they must additionally compare what came into the Biden hands with a) what the family reported on their respective income tax returns, and b) whether their various properties and lifestyles were remotely possible without such massive hidden income. And getting bank records from the Bidens will be near impossible.

“I was asked to speak, and I was the President of the United States. I’m allowed to do that.”
• ‘It Was My Decision’: Trump Defends 2020 Election Challenge (ET)
Special counsel Jack Smith is now prosecuting the Washington case against President Trump, alleging conspiracy to obstruct an official proceeding, obstructing an official proceeding, conspiracy to defraud the United States, and conspiracy against rights. They relate to Jan. 6 only in terms of his calls to delay the vote certification in Congress on that day. “First of all, I had very little to do with January 6th,” he said, referring to the Capitol breach. “I was asked to speak, and I was the President of the United States. I’m allowed to do that.” He said that “hundreds of thousands of people were there, and it was a beautiful, beautiful sight,” and that he spoke “peacefully and patriotically” at the event. He told Ms. Welker he had thought about going into the Capitol that day, but Secret Service advised him to go back to the White House.
“I wanted to go down peacefully and patriotically to the Capitol. Secret Service, who I have great respect for, said, ‘Sir, it’s better if you don’t do that. It could be unsafe,'” President Trump said. He clarified they didn’t mean they anticipated a riot, but because with such a large crowd, a single assailant would have significant cover. “So I didn’t have a dispute with them.” He further alleged that the breach happened because then-Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) turned down his offer of 10,000 additional National Guard. “She’s responsible for January 6th,” he alleged. “And the J6 Committee refused to interview her.” He noted that the treatment of those who were present was one reason he decided to run for reelection. “People that went [there], that didn’t even go into the building, have suffered gravely,” he said, pointing out that rioters in cities across the country calling to “defund the police” were not prosecuted in the same way.
The Department of Justice has thus far brought 1,100 cases against those who were present on Jan. 6, and efforts continue. “When you launched your campaign in March, you told the crowd, quote, ‘I am your retribution.’ What does that mean? What does that look like?” Ms. Welker asked President Trump. “I think retribution is talking in terms of I have to protect people,” he said. “What they’re doing to people is so horrible. They’re putting people in jail for long periods of time. Firemen, policemen, accountants, even lawyers. They’re in prisons for years now and don’t even have trials in some cases.” “I’m talking about fairness,” he said, adding he was open to pardoning those who were wrongly imprisoned, and dismissing rumors that he planned to fire or target his political opponents. “I’m looking to appoint an attorney general who’s going to be tough on crime and fair. Very simple.”

The lion’s den?!
“Every fiber of our union is being poured into fighting the billionaire class and an economy that enriches people like Donald Trump at the expense of workers..”
• Trump to Skip Second GOP Debate, Address Detroit Auto Workers Instead (Sp.)
Former US President Donald Trump is reportedly set to address current and former members of the United Auto Workers (UAW) union in Detroit instead of participating in the upcoming Republican primary debate.An insider with the Trump reelection campaign relayed to US media that the former commander-in-chief is looking to speak with a crowd of current and former union members, as well as blue-collar workers in the plumbing and electrical industries. However, early reports of the speaking event have not been warmly accepted by the UAW union, whose president issued a statement noting Trump is part of the problem the agency is trying to combat. “Every fiber of our union is being poured into fighting the billionaire class and an economy that enriches people like Donald Trump at the expense of workers,” UAW President Shawn Fain said told US media.
“We can’t keep electing billionaires and millionaires that don’t have any understanding what it is like to live paycheck to paycheck and struggle to get by and expecting them to solve the problems of the working class.” Last week, some 13,000 workers from the auto industry initiated strikes following a call by the UAW. The strikes affected the so-called “Big Three” automakers in the United States – Ford, General Motors and Stellantis. The strikes commenced after negotiations failed to secure wage increases for workers by the deadline set for late Thursday night. Should Trump deliver on the speaking event, it would mark the second occasion in which he has decided to sidestep a Republican debate. The first instance took place in August and saw Trump participate in a pre-recorded interview with former Fox News host Tucker Carlson that was released as the initial debate came underway. The second GOP debate is scheduled to take place on September 27 at the Reagan Library in California.

“..the Biden camp argued that the indictment was politically motivated and “unconstitutional.”
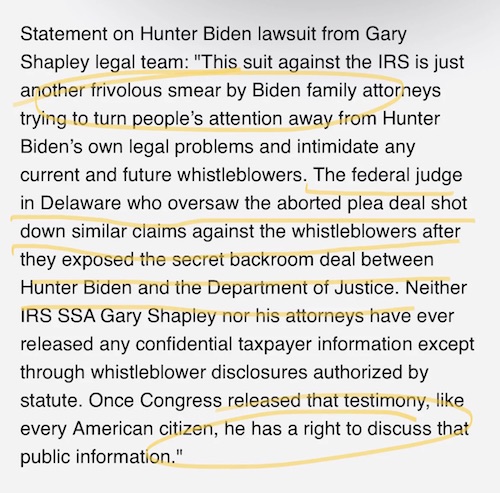
• Hunter Biden Sues IRS for ‘Violating His Privacy’ (Sp.)
Hunter Biden was indicted on September 14 on three charges related to his alleged false statements to purchase a firearm. The First Son faces up to 25 years in prison if convicted. Hunter Biden’s legal team filed a lawsuit against the US Internal Revenue Service (IRS) on Monday. The suit alleges that the privacy of the president’s son was violated by the two whistleblowers who went before Congress to testify against him. It adds that agents “targeted and sought to embarrass” the First Son. The filing, according to media reports, names IRS Agents Gary Shapley and Joseph Ziegler, accusing them of having “mishandled” certain aspects of the investigation into Hunter Biden. According to the lawsuit, the IRS “willfully, knowingly, and/or by gross negligence, unlawfully disclosed Mr. Biden’s confidential tax information.”
But that is not all. The younger Biden is seeking $1,000 in damages for “each and every unauthorized disclosure of his tax returns.” A US federal court released a three-count indictment against the president’s son, Hunter Biden, on September 14. Two of the charges are related to the fact that Hunter Biden lied about not using illegal drugs when completing a gun purchase form for a Colt Cobra revolver. The third charge relates to the actual possession of a weapon while using narcotics. He faces up to 25 years in prison if convicted on the charges, according to court documents. According to the state prosecutors’ line of inquiry, the crimes were committed by the US president’s son in October 2018. In response, the Biden camp argued that the indictment was politically motivated and “unconstitutional.” The indictment came just weeks after an earlier plea agreement on tax and gun charges tied to Hunter fell apart in July after the presiding judge raised concerns about the terms of the deal.

”The obvious value in not claiming income is to avoid taxes. However, claiming income also highlights not just the receipt of these funds but their sources..”
• The Surgical Charging of Hunter Biden Ignores a Pattern of Concealment (Turley)
Thus far, the Justice Department has surgically avoided charges that would implicate the president. This may simply be a coincidence, and correlation does not constitute causation. However, the other charges (including those that the Justice Department effectively killed by slow-walking its investigation) have an obvious potential connection: They all worked to help conceal the influence-peddling operation. None of this means that this unifying theory is true, but it cannot be ignored by anyone investigating this corruption scandal. First, there are the tax violations. While Hunter may be charged with some tax violations, the statute of limitations has now run out on the most controversial payments in the 2014 and 2015 period for foreign sources such as Ukraine’s Burisma.
The obvious value in not claiming income is to avoid taxes. However, claiming income also highlights not just the receipt of these funds but their sources. Likewise, falsely claiming income as a “loan” can keep the money off the books or make it less likely to trigger scrutiny on the source and purpose of payments. Second, there are the money transfers. The House has now detailed millions in transfers to Biden family members from a dizzyingly array of dozens of companies and accounts. The use of a complex labyrinth raises obvious concerns that it is a tactic used by individuals to conceal money transfers. Third, many of us have noted that there seems ample basis for charging Hunter Biden under the Foreign Agents Registration Act, particularly given previous charges against such defendants as Trump campaign chair Paul Manafort.
Registering as a foreign agent obviously invites much greater scrutiny over foreign dealings and the specific nations involved in lobbying efforts. Again Hunter could still eventually face charges for avoiding taxes. But there is little evidence that the Justice Department has actively pursued these broader implications or motivations. For many, the marginalization of these charges raises troubling concerns, particularly in light of the failed sweetheart deal and the allegations from the whistleblower. Even if the tax charges are brought, the framing of the investigation has been on the income rather than the influence sought in these dealings.

“..under a presumption that the rights that apply to every other American citizen do not apply to Mr. Biden..”
• Hunter Biden Claims Whistleblowers Tried To ‘Target’ And ‘Embarrass’ Him (ZH)
Fresh off his felony indictment for gun charges, Hunter Biden is suing the IRS, alleging that agents have “targeted and sought to embarrass” him. Yes, the same Hunter who tried to deduct hookers from his tax return. And the same IRS that let him ‘call in’ for interviews (so he never did), and abruptly swapped out the team investigating him in May – leading to several whistleblowers coming forward to allege not just slow-walking the case, but a coverup involving (obviously) preferential treatment. So, on Monday morning, with Hunter in congressional crosshairs, Hunter’s lawyers filed a lawsuit Monday morning which cites two major examples in IRS whistleblowers Gary Shapley and Joseph Ziegler, who claimed that the agency mishandled aspects of the Biden investigation.
Biden’s lawyers allege that the IRS “willfully, knowingly, and/or by gross negligence, unlawfully disclosed Mr. Biden’s confidential tax information,” and have demanded $1,000 in damages for “each and every unauthorized disclosure of his tax returns,” Fox News reports. “Biden is the son of the President of the United States. He has all the same responsibilities as any other American citizen, and the IRS can and should make certain that he abides by those responsibilities,” reads the filing. “Similarly, Mr. Biden has no fewer or lesser rights than any other American citizen, and no government agency or government agent has free rein to violate his rights simply because of who he is.” “Yet the IRS and its agents have conducted themselves under a presumption that the rights that apply to every other American citizen do not apply to Mr. Biden,” the filing continues.

How much longer can the EU exist?
• European Elite’s Dream Of Power Crumbles (RMX)
For a long time, the major capitals of Western Europe dreamed their beautiful dream about how the EU, as a power, would become an increasingly important actor in building security policy after the end of the Cold War. In this dream, Great Britain was supposed to be the European anchor in transatlantic relations with America. Somewhere at the turn of the first and second decade of the 21st century, French President Nicolas Sarkozy and German Chancellor Angela Merkel established a key division of labor between themselves. According to this, Paris was responsible for the security of the Mediterranean basin and West Africa, while Germany, due to its relations with Russia, was supposed to “take care” of the security of Eastern Europe and the Black Sea basin. However, recent years have shown the complete failure of these plans. One by one, elements of the beautiful dream of power fell apart.
Brexit ejected Great Britain from the orbit of European integration. With Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Germany’s Eastern policy collapsed. The disastrous intervention in Libya, followed by subsequent military coups in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger, as well as the entrenchment of Russian mercenaries from the Wagner Group there, clearly indicate that French leadership in European security policy toward Africa has ended in complete disaster for the time being. One might think that all these events would be enough for the European elite to realize the need to abandon dreams and return to reality. However, the only reaction to the geopolitical crisis in Europe is the proposal to establish majority decisions in the area of the EU’s foreign and security policy, which de facto means accepting the dominance of Paris and Berlin.
The current situation, however, requires a fundamental change in Europe’s thinking and action. Some time ago, there was an idea circulating to create a European Security Council by EU countries. Perhaps it is worth returning to it, provided it would establish a mechanism based on the real military resources of states and their competencies in the field of international policy. The current way of thinking about Europe’s security policy is still, unfortunately, some kind of mirage growing out of the old imperial and colonial ambitions of powers. It ignores the growing potential of Central and Eastern European countries, mainly Poland, but also the Baltic and Scandinavian states. Above all, however, it has proven to be completely ineffective.

“..after Kiev announced that it would sue the three nations for banning the import of Ukrainian produce..”
• Hungary, Poland and Slovakia Pull Out Of EU Grain Platform (RT)
Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia are withdrawing from an EU platform coordinating Ukrainian grain imports after Kiev announced that it would sue the three nations for banning the import of Ukrainian produce, Polish media reported on Monday. The Ukrainian government announced on Monday that it would bring a case against the three countries at the World Trade Organization (WTO), after they announced unilateral bans on the import of Ukrainian seeds and grains. Earlier this summer, the EU allowed five Eastern European nations to block the import of these products for domestic sale, but refused to reauthorize the ban on Friday. As a result, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia imposed bans of their own.
Citing an anonymous source in Brussels, Poland’s PAP news agency said that these countries would withdraw from the EU platform that coordinated the first ban. The decision was made “out of caution and the fact that Ukraine could use information provided within the framework of the coordination platform against these three countries during WTO proceedings,” the source said. Officials in Budapest, Warsaw, and Bratislava argue that Ukrainian agricultural imports undercut domestic prices and threaten the livelihoods of local farmers. Speaking to Politico on Monday, Ukrainian trade representative Taras Kachka dismissed these concerns, arguing that “prices are global.”
Bulgaria and Romania have not imposed unilateral bans. In response, Bulgarian farmers staged a nationwide protest on Monday, causing blockades at dozens of highways and border crossings. In Bucharest, Romanian Prime Minister Marcel Ciolacu said that he would consider a ban if Ukrainian produce began to flow into the country. The EU has condemned the unilateral bans, as has Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelensky. The decision by Brussels not to extend the ban “is an example of true unity and trust between Ukraine and the EU. Europe always wins when the rules work and the treaties are fulfilled,” he said on Friday.

” Western nations should create their own “agreed formula for … the vision of Ukraine’s victory” and also “enshrine military assistance to Ukraine in … legislation..”
• Kiev Demands West Take Measures To Combat ‘War Fatigue’ (RT)
Ukraine faces the threat of its “carefully woven web of foreign assistance” being slowly unraveled due to waning optimism and growing disappointment among its Western backers, the head of the National Security and Defense Council, Aleksey Danilov, wrote in an opinion piece published on Saturday in the newspaper Ukrainskaya Pravda. The security chief accused “reputable and influential” Western media outlets of publishing materials suggesting Ukraine’s much-hyped summer counteroffensive is failing, Kiev’s troops are unable to take back territory from Russia, and Moscow’s resources are “limitless.” These sentiments slow down the Western military assistance to Kiev and stand in the way of Ukraine’s “peace formula,”Danilov added. He stated that the only solution to the conflict between Moscow and Kiev, which has been going on for more than a year and a half, is a military solution.
“The peace formula is the weapons formula,” he said in the article. Danilov urged the West to combat its own growing skepticism about Ukraine’s prospects in the conflict. Western nations should create their own “agreed formula for … the vision of Ukraine’s victory” and also “enshrine military assistance to Ukraine in … legislation,” he said, adding that election cycles might affect “the stability of the partnership” between Ukraine and the West. The US and its allies should also “develop and implement a set of measures to neutralize so-called ‘war fatigue,’” Danilov maintained. He also admitted that “a sprint” – i.e. a short conflict – had been “replaced by a long run.” His words came more than three months into the Ukrainian counteroffensive, which has so far failed to bring about any meaningful changes to the front lines but has seen Kiev’s troops suffer heavy losses in attempts to penetrate Russian defenses.
Numerous Western media outlets have reported on the growing skepticism among Western officials about the prospects for the operation. The New York Times reported in August that US and UK officials were “perplexed” by Kiev’s tactics, while the Wall Street Journal said Washington would reduce military aid to Ukraine in 2024. Moscow has repeatedly expressed its willingness to engage in peace talks as long as its interests are taken into account and the “reality on the ground” is respected. However, Ukrainian President Vladimir Zelensky has imposed a legal prohibition on all discussions with Russia. He also insisted on his own “peace formula” – the one Danilov was referring to – which includes the withdrawal of Russian troops from all territories claimed by Kiev, reparations from Moscow, and a criminal tribunal for the members of Russian government.

“The Clinton Foundation has been illegally raising money, in theory, for HIV/AIDS projects in Ukraine since 2004, without seeking or obtaining approval for these efforts, as is required in advance..”
• Clintons Look to Cash in on ‘Aid’ for Ukraine (Sp.)
The Clinton Global Initiative (CGI) has announced plans to launch a “Ukraine Action Network,” ostensibly to facilitate the delivery of humanitarian aid to Ukrainians amid the West’s ongoing proxy war against Russia in the troubled Eastern European country. The campaign, set to be formally unveiled Tuesday at the CGI’s annual conference in New York, is said to be the outcome of a collaborative effort between former First Lady and Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and current First Lady of Ukraine Olena Zelenskaya that began a year ago. The Ukraine Action Network is expected to help “mobilize existing CGI partners, as well as new leaders from around the world, to create and finance new commitments for Ukrainians.” The details of the program, including which “Ukrainians” specifically are expected to benefit, have yet to be elaborated.
The Clintons shut down the CGI component of their Clinton Foundation non-profit in 2017, firing dozens of employees and shuttering the CGI’s New York office after donations by businesses and foreign nations dried up following Mrs. Clinton’s surprise loss in the 2016 presidential election. The Clintons revived the CGI in 2022, with thousands of donors and hundreds of partnering organizations announcing the launch of over 140 different projects at last year’s conference. In a letter to attendees of the upcoming Tuesday gathering, the foundation indicated that the 2023 meeting would “hear from those who are tackling some of today’s most pressing issues, including climate change, health inequities, food insecurity, economic inequality, threats to democracy around the world, and record-breaking refugee displacement.”
Officials, business leaders, and celebrities expected to attend include Bill Clinton, Biden Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, California Governor Gavin Newsom, former Obama and Biden Press Secretary Jen Psaki, Pope Francis, NBA Hall-of-Famer Dwayne Wade, Google President Ruth Porat, former British Prime Minister Tony Blair and others. Charles Ortel, a Wall Street analyst who has been investigating the Clintons’ charity-related activities for about eight years, told Sputnik last month that the foundation’s plans to incorporate Ukraine into its agenda may be a sign that they’re hoping to cash in on some of the potentially vast package of reconstruction support for Kiev by Western countries. “The Clinton Foundation has been illegally raising money, in theory, for HIV/AIDS projects in Ukraine since 2004, without seeking or obtaining approval for these efforts, as is required in advance, from numerous domestic and foreign government authorities. No outsider actually knows exactly what they have been doing for nearly 20 years in that ransacked remnant of a country,” Ortel said.

“The war is good, very good for the oil tanker companies which can run the gauntlet of the Americans”, says a Greek source. The international shipping media are fearful of reporting this publicly..”
• US Sanctions War Is Good For Russian Shipping, Greeks Too (Helmer)
The US-led sanctions war against Russian fossil fuel exports, especially oil, has been the best thing to have happened to Sovcomflot, Russia’s leading shipping company and operator of the world’s largest oil and gas tanker fleets. Revenues are up, earnings and profits are multiplying; Sovcomflot has never had so much cash in the bank; its debt is down to the lowest level in more than twenty years – and none of it is in American or European bank hands. Released on August 28 and expressed in discreet language, the new company financial report says: “Revenues from tanker business segments (transportation of crude oil and petroleum products) are supported by favourable market conditions against the background of increased demand for tanker tonnage, taking into account the changing geography of international trade in oil and petroleum products.
Despite the presence of a seasonal reduction in freight rates in the summer, the company believes that the market fundamentals, including the limited growth of the global tanker fleet due to the small number of orders for the construction of new vessels, suggests a high probability of stability in the medium term of freight rates at a level above the historically average.” “Favourable market conditions” is Sovcomflot’s phrase for the US and NATO sanctions, first imposed on Sovcomflot’s financing and payment operations in February 2022, and escalated this year in EU and UK sanctions targeting Dubai and Hong Kong fleet management companies. The reference to “changing geography” means what shipping experts and analysts from London to Oslo, Piraeus to Singapore acknowledge privately:
“The war is good, very good for the oil tanker companies which can run the gauntlet of the Americans”, says a Greek source. The international shipping media are fearful of reporting this publicly. London-based shipping publications like Lloyds List, sold by the London-listed Informa group to the Montagu investor group, are not reporting what their industry sources agree is happening. “Some people tend to close doors behind them”, a veteran maritime news reporter coyly describes the news blackout. Seatrade, another Informa outlet, is restricting its reporting to NATO tracking of sanctions busting.
US maritime media like GCaptain (California) and Marine Money (Connecticut) refuse to respond to questions about their news blackout. Equally quiet, although for different reasons, are the Indian, Chinese and Singaporean shipping press. Sovcomflot is now confidently predicting the worldwide split between the Russian and US- NATO fleets will continue for the foreseeable future. “Despite the presence of a seasonal reduction in freight rates in the summer, the company believes that the fundamental market fundamentals, including the limited growth of the global tanker fleet due to the small number of orders for the construction of new vessels, suggests a high probability of stability in the medium term of freight rates at a level above the historically average.”

“The newly expanded BRICS, after all, is now a Commodity Powerhouse. So, who now controls inflation in the U.S.: A trapped Fed, or the new commodity king?”
• The BRICS Commodity Powerhouse: Can It Force a New Economic ‘Order’? (Crooke)
Although many in the West think everything ‘is fine’ – that the U.S. Fed likely will bring inflation under control, and soon will be cutting interest rates. Yet oil prices are up 37% and rising. This has been the case since the price bottomed out a few months ago. “People forget oil prices fell almost 50% from their peak, and that fall ended in May of this year. And that big decline in oil prices was the major factor in bringing headline inflation [down] from 9% to 3%”. Energy is a major cost input that needs to be passed on to consumers. And so is interest on debt, which increases as interest rate rises cut across the economic spectrum. Everybody is waiting for the Fed to cut rates, because the only way for the U.S. government, American consumers, and businesses to manage their present debt (on which they loaded-up – at zero rates) is if interest rates drop.
People may understand this, but they just assume that it’s not going to be an issue because, of course, the Fed ‘is going to cut rates’. It is very unlikely however, that the western authorities will be able to get rates down again to zero. Selling further oil from the U.S. Strategic Reserve just isn’t going to happen: At this point, the U.S. economy can only run for 20 days on its current oil reserves. And the Fed is not going to be able to launch much of another round of money-printing, should the economy drop into recession. The Fed may try to rescue the economy in this way, though when inflation is the problem, it is not possible to solve an inflation problem by creating more inflation. Inflation (and interest rates), after a short lag, would again rise.
The point is that much of the ruling strata still do not ‘get it’: the decades-long experience of near-zero inflation that the West has experienced has imprinted itself on the collective mindset – but that world of effortless money-making was an aberration, not a norm. Plainly put, the West now is somehow trapped in various diverse financial ways, such as fiscal exhaustion (i.e. U.S. deficit spending has reached 8.5% of GDP). Whilst true, that many in the West do not understand that the zero-inflation era was an aberration, caused by factors that no longer pertain – for sure, the aberration is well understood in Beijing and Moscow. Liam Halligan notes similarly that oil prices are up almost a third over the last three months: “It’s a hugely significant increase that could seriously aggravate the cost of living crisis. Yet the surge seems to have barely been noticed by much of our political and media class”.
Crude markets began to tighten earlier this summer after the Opec exporters’ cartel agreed to withhold oil supplies in a bid to raise prices, and Halligan tartly observes: “Anyone who downplays the power of Opec knows nothing about worldwide energy markets and even less about geopolitics”. Is it happenstance that a quiet financial war, triggered by the drip-drip of de-dollarisation and higher energy costs, might finally give BRICS the leverage to coerce a change of policy in the West? And should western reluctance to re-structure persist, might the BRICS leadership ratchet higher? The newly expanded BRICS, after all, is now a Commodity Powerhouse. So, who now controls inflation in the U.S.: A trapped Fed, or the new commodity king?

“The US can’t win the geopolitical chess game anymore without trying to change the conditions of the test or the rules, or by cheating..”
• Biden Wants to Salvage US Hegemony by Reforming UN Security Council (Sp.)
US President Joe Biden will urge the UN to expand the Security Council to water down Russia and China’s influence in the body, the Western press says. Could Biden succeed? Joe Biden “will take a look at the architecture of the Security Council,” US National Security Council spokesman John Kirby announced ahead of the UN General Assembly meeting. Still, the British media assumes that the US president will advocate adding new members to the United Nations Security Council in order to weaken Russia and China’s role. Reportedly, Biden wants to add India, Brazil, Germany, South Africa, and Japan to the international body. Currently, the Security Council has 15 members: five of them are “permanent” (P5) and enjoy veto powers (Russia, China, France, the UK, and the US); and 10 are “non-permanent,” with five of them being elected each year by the General Assembly for a two-year term.
“It is empty posturing, because Biden knows that the UNSC can only be expanded by an amendment to the Charter, and any of the P5 can veto it,” Professor Alfred de Zayas, former UN independent expert on international order and author of 10 books, including The Human Rights Industry and Building a Just World Order, told Sputnik. “One can surmise that Biden is joining the ‘bandwagon’ of many countries and academics who are similarly asking for expansion. Perhaps Biden’s noises will be well received in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where the prestige of the US has been in decline, and the US could score points at low cost,” the former UN independent expert continued.
Biden is by no means an innovator: at the 15th BRICS Summit, which convened in August in Johannesburg, the core nations of the group (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) stated in their final declaration that they are in favor of reforming the UN Security Council and expanding developing countries’ representation. The BRICS declaration named Brazil, India, and South Africa as potential new members of the UNSC. Thus, the US president de facto wants to add two of Washington’s ardent allies to the list – Germany and Japan. The two weren’t added to the original composition of the UNSC (which was formed immediately after the Second World War) since they were the two major WW2 aggressors. In addition, Team Biden seemingly wants to curry favors with major powers of the Global South in an apparent bid to drag them to Washington’s side.
“Since [the West’s] desperate efforts to expel Russia, a permanent member, from the principal organ of the UN have failed thus far, they are trying a different tactic of overhauling the P5 to salvage Western decline and one that only further demonstrates how disconnected the foreign policy establishment is from reality. The US can’t win the geopolitical chess game anymore without trying to change the conditions of the test or the rules, or by cheating,” Max Parry, a US independent journalist and geopolitical analyst, told Sputnik. According to Parry, “the reasons surrounding the timing of this attempt to propose changes could not be more clear, with Washington striking out virtually everywhere in proxy theaters of conflict and spheres of influence.”
“US hegemony is shrinking with more and more countries throughout the global south shifting away from the West toward Moscow and Beijing’s camps and the Ukraine proxy war has been yet another foreign policy disaster that has geostrategically backfired,” the journalist said.




Bowie America

Water ant
https://twitter.com/i/status/1703836863847366841

Starling
https://twitter.com/i/status/1703840569716269160

Platypus
Platypus! pic.twitter.com/uE8I3e4m34
— Fascinating (@fasc1nate) September 18, 2023

Wait for it
https://twitter.com/i/status/1703826158712713610

Fairy tale
This is straight out of a fairy tale book, absolutely beautiful… pic.twitter.com/aDm99ULO2Z
— Nature is Amazing ☘️ (@AMAZlNGNATURE) September 18, 2023


Support the Automatic Earth in wartime with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.