
Pablo Picasso Massacre in Korea 1951
In the New Year, after a close to the old one that was sort of terrible for our zombie markets, do prepare for a whole lot of stories about China (on top of Brexit and Yellow Vests and many more windmills fighting the Donald). And don’t count on too many positive ones that don’t originate in the country itself. Beijing will especially be full of feel-good tales about a month from now, around Chinese New Year 2019, which is February 5.
And we won’t get an easy and coherent true story, it’ll be bits and pieces stitched together. What will remain is that China did the same we did, just on steroids. It took us 100 years to build our manufacturing capacity, they did it in under 20 (and made ours obsolete). It took us 100 years to borrow enough to get a debt-to-GDP ratio of 300%, they did it in 10.
In the process they also accumulated 10 times more non-productive assets than us, idle factories, bridges to nowhere and empty cities, but they thought that would be alright, that demand would catch up with supply. And if you look at how much unproductive stuff we ourselves have gathered around us, who can blame them for thinking that? Perhaps their biggest mistake has been misreading our actual wealth situation; they didn’t see how poorly off we really are.
Xiang Songzuo, “a relatively obscure economics professor at Renmin University in Beijing”, expressed some dire warnings about the Chinese economy in a December 15 speech. He didn’t get much attention, not even in the West. Not overly surprising, since both Beijing and Wall Street have a vested interest in the continuing China growth story.
But with the arrival of 2019, that attention started slowly seeping through. Former associate professor of business and economics at the Peking University HSBC Business School in Shenzhen, Christopher Balding, left China 6 months ago after losing his job. At the time, he wrote: “China has reached a point where I do not feel safe being a professor and discussing even the economy, business and financial markets..”. And, noting a change that very much seems related to what is coming down the road:
”One of my biggest fears living in China has always been that I would be detained. Though I happily pointed out the absurdity of the rapidly encroaching authoritarianism, a fact which continues to elude so many experts not living in China, I tried to make sure I knew where the line was and did not cross it. There is a profound sense of relief to be leaving safely knowing others, Chinese or foreigners, who have had significantly greater difficulties than myself. There are many cases which resulted in significantly more problems for them. I know I am blessed to make it out.”
A few days ago, Balding wrote this on Twitter:
“Most experts dismissed the speech by Xiang Songzuo (claiming Chinese GDP growth could be as low as 1.67%) as implausible…”. No, we didn’t. The GS PE guy and the PKU dean have every reason to deny it. Car and mobile phone shipment down 2% and 16% are not a 6.5% growth economy.”
That certainly sets the tone of the discussion. GDP growth of 1.67% vs the official 6.5%; smartphone shipments down 16%, car sales slumping. Not the kind of numbers you’ll hear from Beijing. And Balding does know China, whether they like it or not. On Monday, Bloomberg, where he was/is a regular contributor, published this from his hand:
China Has a Dangerous Dollar Debt Addiction
Officially, China lists its outstanding external debt at $1.9 trillion . For a $13 trillion economy, that’s not a major amount. But focusing on the headline number significantly understates the underlying risks. Short-term debt accounted for 62% of the total as of September, according to official data, meaning that $1.2 trillion will have to be rolled over this year .
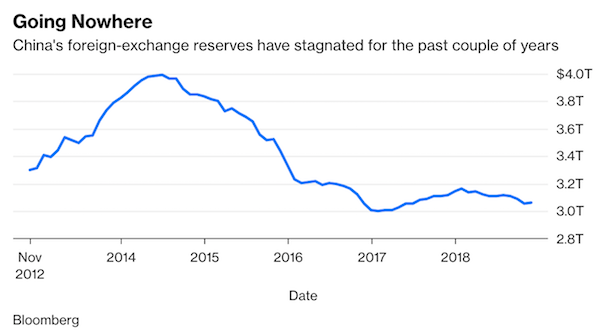
Just as worrying is the speed of increase: Total external debt has increased 14% in the past year and 35% since the beginning of 2017 . External debt is no longer a trivial slice of China’s foreign-exchange reserves, which stood at just over $3 trillion at the end of November, little changed from two years earlier. Short-term foreign debt increased to 39% of reserves in September, from 26% in March 2016.
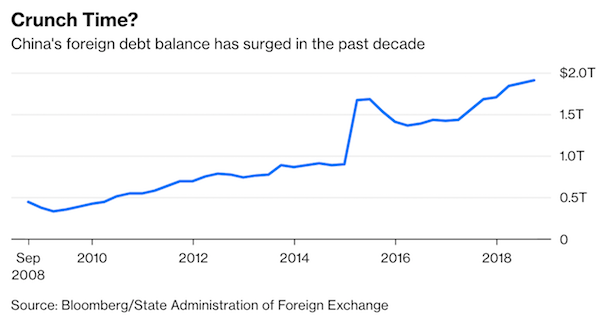
The true picture may be more precarious. China’s external debt was estimated at between $3 trillion and $3.5 trillion by Daiwa Capital Markets in an August report. In other words, total foreign liabilities could be understated by as much as $1.5 trillion after accounting for borrowing in financial centers such as Hong Kong, New York and the Caribbean islands that isn’t included in the official tally. Circumstances aren’t moving in China’s favor.
The nation’s companies rushed to borrow in dollars when there was a 3% to 5% spread between Chinese and U.S. interest rates and the yuan was expected to strengthen. Borrowing offshore was cheaper and offered the additional bonus of likely currency gains. Now, the spread in official short-term yields has shrunk to near zero and the yuan has been depreciating for most of the past year. Refinancing debt in dollars has become harder, and more risky.
Beijing’s policies have exacerbated the buildup of foreign debt. To promote Xi Jinping’s Belt and Road Initiative, the president’s landmark foreign policy endeavor, China has been borrowing dollars on international markets and lending around the world for everything from Kenyan railways to Pakistani business parks. With this year and 2020 being the peak years for repayments, China faces dollar funding pressure.
To repay their dollar debts, Chinese firms will either have to draw from the central bank’s foreign-exchange reserves (a prospect Beijing is unlikely to allow) or buy dollars on international markets. This creates a new set of problems. There are only 617 billion yuan ($90 billion) of offshore renminbi deposits in Hong Kong available to buy dollars . If China was to push firms to bring debt back onshore, this would necessitate significant outflows that would push down the yuan’s value against the dollar.
The Xiang Songzuo speech was also noted by the Financial Times this week. Their conclusions are not much rosier. Recent US imports from China look good only because both buyers and sellers try to stay ahead of tariffs. And whole some truce or another there may smoothen things a little, China must launch a massive stimulus against the background of twice as much investment being needed for a unit of GDP growth.
Nervous Markets: How Vulnerable Is China’s Economy?
A relatively obscure economics professor at Renmin University in Beijing sparked a minor furore last month when he claimed a secret government research group had estimated China’s growth in GDP could be as low as 1.67% in 2018 — far below the officially published rate of 6.7% for the year up to September.
Most experts dismissed the speech by Xiang Songzuo as implausible, despite longstanding doubts about the reliability of China’s official GDP data. Yet although discussion of his claims was quickly scrubbed from the Chinese internet, the presentation has been viewed more than 1.2m times on YouTube — an indication of the raw nerve Mr Xiang touched with his doom-laden warnings.
[..] the question that is hanging over global markets is just how vulnerable is China to a much sharper slowdown? Ominously, the recent downturn has occurred even though the expected hit to Chinese exports from the trade war has not yet materialised. In fact, analysts say exports probably received a one-off boost in recent months as traders front-loaded shipments to beat the expected tariff rise from 10% to 25% that US president Donald Trump threatened would take effect in January. That rise is now on hold due to the 90-day truce that Mr Trump agreed with Chinese president Xi Jinping at the G20 meeting in Argentina last month.
[..] The amount of new capital investment required to generate a given unit of GDP growth has more than doubled since 2007 , according to Moody’s Analytics. In other words, investment stimulus produces little bang for Beijing’s buck, even as it adds to the debt levels.
[..] “They [Beijing] will soon have no choice but to launch massive stimulus,” says Alicia Garcia Herrero, chief Asia Pacific economist at Natixis in Hong Kong. “They do not want to give away their credibility because they said they wouldn’t do it, but there is no time to be cautious any more. Not having growth is ultimately the worst outcome of all.”
Christopher Whalen picks up on Xiang Songzuo’s speech as well, and quotes him saying that “Chinese stock market conditions resemble those during the 1929 Wall Street Crash”. Whereas the China Beige Book states that sales volumes, output, domestic and export orders, investment, and hiring fell on a year-over-year and quarter-over-quarter basis. Which leads to the conclusion that deflation is, or should be, Beijing’s main worry.
Oh, and Chinese consumer demand has weakened, something we’ve seen more off recently. Reuters headlines “China To Introduce Policies To Strengthen Domestic Consumption” today, but that headline could have come from any of the past 5 years or so. Domestic consumption is precisely China’s problem, and they can’t achieve nearly enough growth there.
Foreign investors have convinced themselves that the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) is superior in terms of economic management, this despite ample evidence to the contrary, thus accepting the official view is easy but also increasingly risky. In a December 15 speech , Renmin University’s Xiang Songzuo warned that Chinese stock market conditions resemble those during the 1929 Wall Street Crash. He also suggested that the Chinese economy is actually shrinking.
China growth, Tesla profitability, or the mystical blockchain all require more credulity than ever before. For example, in the first half of 2016 global capital markets stopped due to fear of a Chinese recession. Credit spreads soared and deal flows disappeared. But was this really a surprise? In fact, the Chinese government had accelerated official stimulus in 2015 and 2016 to counter a possible slowdown and, particularly, ensure a quiet domestic scene as paramount leader Xi Jinping was enshrined into the Chinese constitution.
Today western audiences are again said to be concerned about China’s economy and this concern is justified, but perhaps not for the reasons touted in the financial media. The China Beige Book (CBB) fourth-quarter preview, released December 27, reports that sales volumes, output, domestic and export orders, investment, and hiring fell on a year-over-year and quarter-over-quarter basis. CBB is a research service that surveys thousands of companies and bankers on the ground in China every quarter.
Contrary to the positive foreign narrative about “growth” in China, CBB contends that deflation is the bigger threat compared to inflation. “Because of China’s structural problems, deflation has very clearly emerged as the bigger threat in a slowing economy than inflation. Consumer demand has weakened, and you see that reflected in retail and services prices,” CBB Managing Director Shehzad Qazi said in an interview.
So, China phone shipments are down 16%, as per Balding. But Tim Cook says Apple’s never done better. Still, if that 16% number is correct, either Apple or its Chinese suppliers are doing worse, not better. And 16% is a lot.
Despite Recent Battering, Tim Cook Says Apple’s ‘Ecosystem Has Never Been Stronger’
Apple Inc. stock has taken a beating in recent months, but Chief Executive Tim Cook defended his company Tuesday, and expressed optimism that trade tensions with China would soon ease. Apple shares have fallen by more than one-third since their peak on Oct. 3, and tumbled further last week after the tech giant warned of disappointing iPhone sales in its holiday quarter. But in an interview Tuesday with CNBC’s Jim Cramer, Cook said the company was still going strong, and its naysayers were full of “bologna.” “Here’s the truth, what the facts are,” Cook said about reports of slow iPhone XR sales, according to a CNBC transcript.
“Since we began shipping the iPhone XR, it has been the most popular iPhone every day, every single day, from when we started shipping, until now. . . . I mean, do I want to sell more? Of course I do. Of course I’d like to sell more. And we’re working on that.” Slower sales in China also contributed to Apple’s lowered forecast, and Cook said Tuesday he believes that situation to be “temporary.”
“We believe, based on what we saw and the timing of it, that the tension, the trade-war tension with the U.S. created this more-sharp downturn,” he said. Cook said he’s “very optimistic” a trade deal between the U.S. and China will be reached . “I think a deal is very possible. And I’ve heard some very encouraging words,” he said.
16% fewer phones, that gets you the second production cut at Apple and its ‘magnificent ecosystem’ in short order. Now sure, Cook can try and blame the tariffs. but Samsung’s Q4 2018 sales fell 11%, and its operating profit fell by 29%. It’s a bigger and wider issue, and China is at the heart of it.
Apple Cuts Q1 Production Plan For New iPhones By 10%
Apple, which slashed its quarterly sales forecast last week, has reduced planned production for its three new iPhone models by about 10% for the January-March quarter, the Nikkei Asian Review reported on Wednesday. That rare forecast cut exposed weakening iPhone demand in China, the world’s biggest smartphone market, where a slowing economy has also been buffeted by a trade war with the United States.
Many analysts and consumers have said the new iPhones are overpriced. Apple asked its suppliers late last month to produce fewer-than-planned units of its XS, XS Max and XR models, the Nikkei reported, citing sources with knowledge of the request. The request was made before Apple announced its forecast cut, the Nikkei said.
And very much not least there was this graph of Chinese investments in Africa. What are the conditions? At what point will they call back the loans? And when countries can’t pay back, what’s the penalty? How much of this has been provided by Beijing in US dollars it doesn’t have nearly enough of?
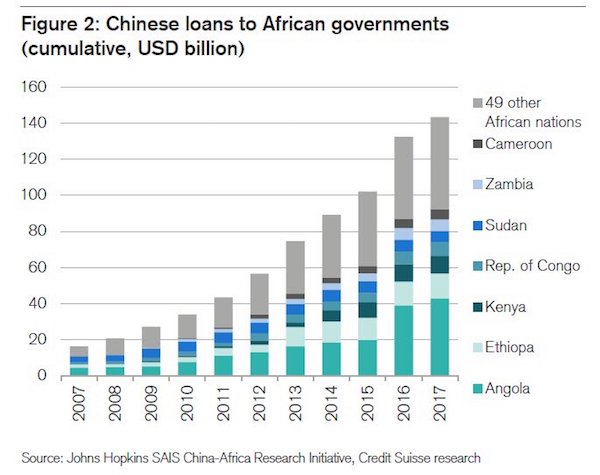
It’s like the much heralded Belt and Road project, or Silk Road 2.0, isn’t it, where the first batch of participating nations have started sounding the alarm over loan conditions. Yes, it sounds great, I admit, but I have long said that in reality Belt&Road is China’s ingenious scheme to export its industrial overcapacity and force other countries to pay for it. It’s like the model Rome had, and the US still do, just all in one single project. And this one has a name, and it can be expanded to Africa.
But no, I don’t see it. I think China’s debt, combined with the vast distance it still has from owning a global reserve currency, will call the shots, not Xi Jinping.
China won’t be taking over. At least, not anytime soon.








