Joan Miro The tilled field 1924

And the parasite is killing its host.
• CEO Stock Buybacks Parasitize the Economy (Ralph Nader)
The monster of economic waste—over $7 trillion of dictated stock buybacks since 2003 by the self-enriching CEOs of large corporations—started with a little noticed change in 1982 by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) under President Ronald Reagan. That was when SEC Chairman John Shad, a former Wall Street CEO, redefined unlawful ‘stock manipulation’ to exclude stock buybacks. Then after Clinton pushed through congress a $1 million cap on CEO pay that could be deductible, CEO compensation consultants wanted much of CEO pay to reflect the price of the company’s stock. The stock buyback mania was unleashed. Its core was not to benefit shareholders (other than perhaps hedge fund speculators) by improving the earnings per share ratio. Its real motivation was to increase CEO pay no matter how badly such burning out of shareholder dollars hurt the company, its workers and the overall pace of economic growth.
In a massive conflict of interest between greedy top corporate executives and their own company, CEO-driven stock buybacks extract capital from corporations instead of contributing capital for corporate needs, as the capitalist theory would dictate. Yes, due to the malicious, toady SEC “business judgement” rule, CEOs can take trillions of dollars away from productive pursuits without even having to ask the companies’ owners—the shareholders—for approval. What could competent management have done with this treasure trove of shareholder money which came originally from consumer purchases? They could have invested more in research and development, in productive plant and equipment, in raising worker pay (and thereby consumer demand), in shoring up shaky pension fund reserves, or increasing dividends to shareholders.
The leading expert on this subject—economics professor William Lazonick of the University of Massachusetts—wrote a widely read article in 2013 in the Harvard Business Review titled “Profits Without Prosperity” documenting the intricate ways CEOs use buybacks to escalate their pay up to 300 to 500 times (averaging over $10,000 an hour plus lavish benefits) the average pay of their workers. This compared to only 30 times the average pay gap in 1978. This has led to increasing inequality and stagnant middle class wages. [..] In a review of 64 companies, including major retailers such as JC Penny and Macy’s, these firms spent more dollars in stock buybacks “than their businesses are currently worth in market value”! [..] The scholars concluded that “Buybacks are a way of disinvesting – we call it ‘committing corporate suicide’..

How much time do I have?
• The Economy Is Humming. Bankers Are Cheering. What Could Go Wrong? (NYT)
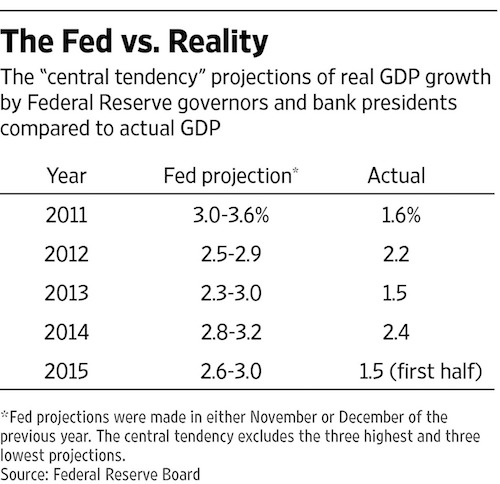
For decades, the global economy has been defined by dissonance. There has been the Japanese recession. The financial crises in the United States and Europe. And drama in emerging markets throughout. But as central bankers, finance ministers and money managers descend on Washington this week for the fall meetings of the IMF, they will confront an unusual reality: global markets and economies rising in unison. Never mind political turmoil, populist uprisings and threats of nuclear war. From Wall Street to Washington, economists have been upgrading their forecasts for the global economy this year, with the consensus now pointing to an expansion of more than 3% — up noticeably from 2.6% in 2016. Economists from the IMF are likely to follow suit when the fund releases its biannual report on the global economy on Tuesday.
The rosy numbers are noteworthy. But what’s more startling is that virtually every major developed and emerging economy is growing simultaneously, the first time this has happened in 10 years. “In terms of positive cycles, it is difficult to find very many precedents here,” said Brian Coulton, the chief economist at Fitch, the debt ratings agency. “It is the strongest growth we have seen since 2010.” In Japan, a reform-minded government and aggressive action by the central bank have pushed growth to 1.5% — up from 0.3% three years ago. In Europe, strong domestic demand in Germany and robust recoveries in countries like Spain, Portugal and Italy are expected to spur 2.2% growth in the eurozone. That would be more than double its average annual growth in the previous five years.
Aggressive infrastructure spending by China; bold economic reforms by countries including Brazil, Indonesia and India; and rising commodities prices (helping countries such as Russia) have spurred growth in emerging markets. And in the United States, despite doubts about President Trump’s ability to pass a major tax bill, the economy and financial markets chug along. In fact, one of the few large economies not following an upward path is Britain, whose pending exit from the European Union is taking a toll. Having grown at an average annual pace of just over 2% from 2012 to 2016, the British economy is expanding just 1.5% this year. [..] “We are in a boom today, but we should not forget that the financial system is still relatively unstable,” said Jim Reid, a credit strategist at Deutsche Bank.
Mr. Reid, who spices up his market analyses by regaling clients with pop songs on the piano, recently published a detailed study on what he expects will be the causes of the next global financial crisis. Pick your poison: an abrupt slowdown in China, the rise of populism, debt problems in Japan or an ugly outcome to Britain’s move to leave the European Union. His overriding worry, though, is that investors and policy makers aren’t prepared for what will happen when global central banks put a halt to their easy-money policies. Since the 2008 crisis, Mr. Reid noted, central banks have accumulated more than $14 trillion in assets — an amount that exceeds the annual output of China by $3 trillion. What happens when the central banks all start to sell? “This is unprecedented,” Mr. Reid said. “And no one knows what the outcome will be.”

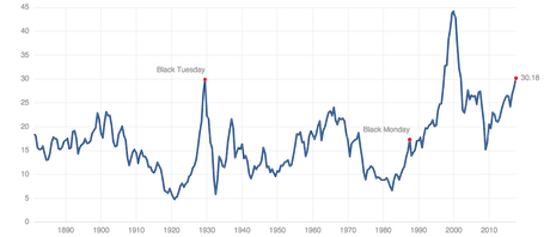
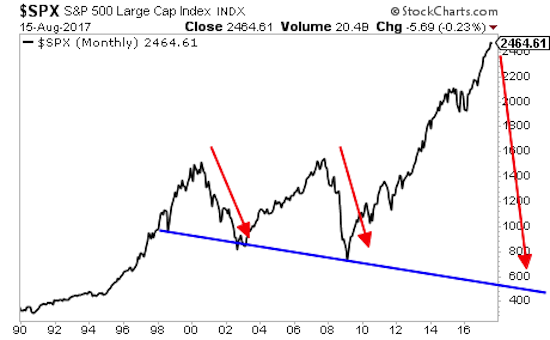
Compressed volatility.
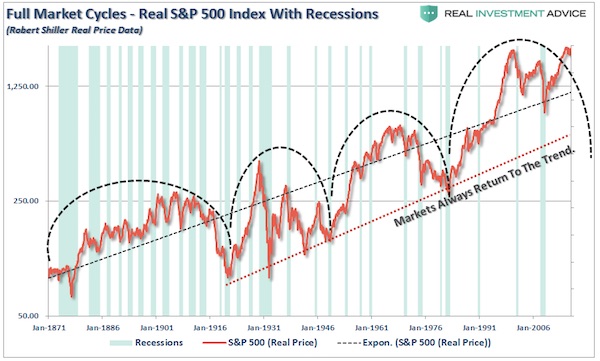
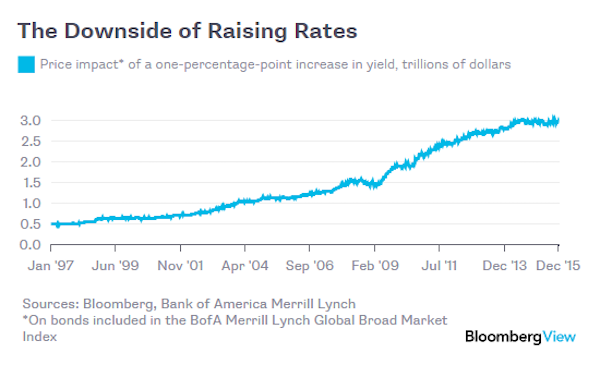
We find ourselves in a very unique point in history and in a world dominated by false narratives. It is a challenge to keep an analytical grip on reality, but I’ll try to tie a few threads together here to put everything in a macro context. Firstly the underlying base reality: Free money, easy money, whatever you want to call it, permeates everything we see in financial markets. Indeed I would argue price appreciation has been paid for with unprecedented and, in my view, unsustainable volatility compression. A couple of charts really highlight this. Most clearly perhaps is the precise trend line tagging we can observe in the correlated picture of price appreciation and volatility compression since the February 2016 lows:
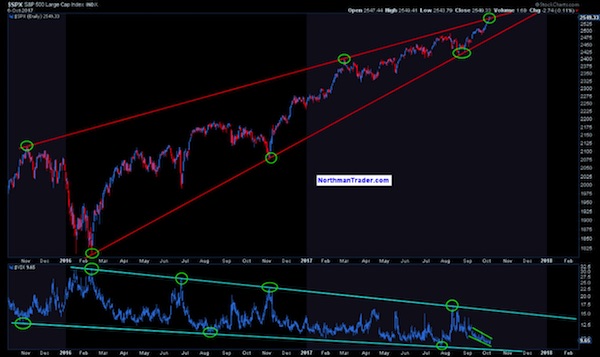
The $VIX’s corollary, the inverse $XIV, embarked on an explosive near one way journey since the US election coinciding with over $2 trillion central bank intervention in just the first 9 months of 2017:
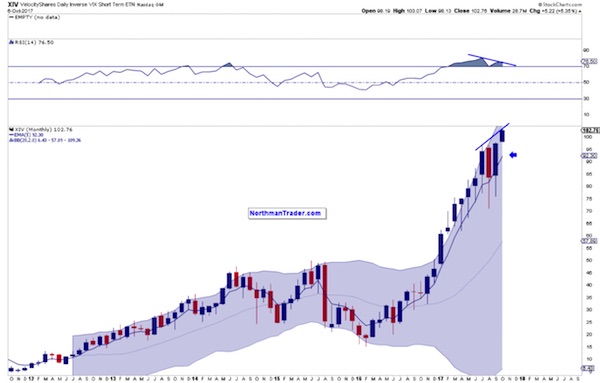
And it has continued to this day and just made another all time high this past week on a massive negative divergence. It is the magnitude of this volatility compression that explains the current trading environment we find ourselves in. Aside from the obvious artificial liquidity avalanche we’ve had speculated about the driver of all this and the answer may simply be the promise of even more free money, specifically tax cuts. As some of you may recall from my analysis over the past year I’ve been very clear that math ultimately will bring out truth in any narrative. In this case that notion that tax cuts pay for themselves is a fantasy. It always has been. Can it result in a short term bump in spending or even growth? Yes it is possible, especially if structured right.
But any historical analysis will show you that tax cuts, especially already coming from a relatively low base, will just add to debt via larger deficits. Recently the White House budget director finally acknowledged this very reality: “a tax plan that doesn’t add to the deficit won’t spur growth” My criticism has been that all this marketing talk is simply a lie and will structurally put the country further at risk of trillion dollar deficits and a massive debt explosion that is already baked in even without tax cuts.

But he makes no attempt to apologize?!
• Schäuble: Another Financial Crisis Is Coming Due To Spiraling Global Debt (ZH)
Schauble warned that the world was in danger of “encouraging new bubbles to form”. “Economists all over the world are concerned about the increased risks arising from the accumulation of more and more liquidity and the growth of public and private debt. I myself am concerned about this, too,” he said echoing the concern voiced just one day earlier by IMF head Christine Lagarde, said the world was enjoying its best growth spurt since the start of the decade, but warned of “threats on the horizon” from “high levels of debt in many countries to rapid credit expansion in China, to excessive risk-taking in financial markets”. Schäuble also echoed the latest warning from the BIS, which last month said that the world had become so used to cheap credit that higher interest rates could derail the global economic recovery.
Meanwhile, Schäuble defended austerity, saying the word was, “strictly speaking, an Anglo-Saxon way of describing a solid financial policy which doesn’t necessarily see more, or higher deficits as a good thing.” The soon to be former finance minister also took a pot shot at the UK: “The UK always made fun of Rhineland capitalism,” he said, contrasting Germany’s consensus-driven, social market model with Anglo-American free markets and deregulation. “[But] we have seen that the tools of the social market economy were more effective at dealing with the [financial] crisis…than in the places where the crisis arose.”
Of course, Germany’s success – almost entirely a function of the common currency which has effectively kept the Deutsche Mark from soaring – has come at the expense of crisis after crisis among Europe’s southern states. Unfortunately it has resulted in an entire generation of unemployed youth in countries like Greece, Italy and Spain. Still, in keeping with his dour image, Schäuble’s last words were pessimistic: “We have to ensure that we will be resilient enough if we ever face a new economic crisis,” he added. “We won’t always have such positive economic times as we have now” concluded the jolly 75-year-old. Perhaps Wolfi is worrying too much: after all, according to Janet Yellen, “we will not see another crisis in our lifetime.” And if we do, well central banks are primed and ready to injects trillions more to keep the artificial “recovery” and market “all time highs” can kicked just a little bit further.

They’ll screw this one up, too.
• EU Plan To Prevent Bank Runs Could Backfire, Create Panic (BBG)
Three years since their banking union began to take shape, European Union regulators are seeking fresh powers to deal with lenders in trouble. Their plan would let them stop withdrawals from a failing bank for a few days while they address the problem, with the aim of preventing a run. But this approach could easily have the opposite effect, spreading panic to the whole financial system. There’s a better way. Instead of freezing bank accounts, EU governments should enable regulators to keep a bank going while they restructure it and search for a new owner. This will require EU governments to commit additional resources for the task. The ECB and the euro zone’s Single Resolution Board have been calling for the power to freeze bank accounts – a so-called moratorium – since the swift resolution of Banco Popular in June.
They succeeded in winding down the troubled Spanish lender by selling it to rival Banco Santander, but had to do it on a weekday night with a run on deposits in progress. The regulators say that next time it might be impossible to find a buyer overnight. A moratorium would relieve that pressure and perhaps allow them to sell the bank at a better price. This approach would mirror an arrangement which is currently in place in Germany, and it’s superficially appealing: Closing a bank would certainly stop a run. But it could also have unintended consequences. Depositors may run from a bank in trouble sooner — fearing that if they wait too long they may not be able to withdraw their money. It could also lead depositors to empty their accounts as soon as the bank re-opens. Most dangerous of all, freezing accounts in one bank could spread panic to the rest of the system, as other depositors fear the same will happen to them.
The idea also puts international cooperation on bank resolution at risk. The EU regulators’ plan threatens to disrupt measures put in place after the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in 2008. Bank of England economists recently warned in a working paper that adopting the new moratorium might prompt banks to back out of the existing arrangements for handling financial emergencies.

An extensive look at crypto. Much better than the headline makes you think.
• Hackers And Fraudsters Are Causing Cryptocurrency Chaos (Ind.)
Cryptocurrencies were supposed to offer a secure, digital way to conduct financial transactions but they have been dogged by doubts. Concerns have largely focused on their astronomical gains in value and the likelihood of painful price crashes. Equally perilous, though, are the exchanges where virtual currencies are bought, sold and stored. These exchanges, which match buyers and sellers and sometimes hold traders’ funds, have become magnets for fraud and mires of technological dysfunction, posing an underappreciated risk to anyone who trades digital coins. Huge sums are at stake. As the prices of bitcoin and other virtual currencies have soared this year – bitcoin has quadrupled – legions of investors and speculators have turned to online exchanges.
Billions of dollars’ worth of bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies, which aren’t backed by any governments or central banks, are now traded on exchanges every day. “These are new assets. No one really knows what to make of them,” said David L Yermack, chairman of the finance department at New York University’s Stern School of Business. “If you’re a consumer, there’s nothing to protect you.” Regulators and governments are still debating how to handle cryptocurrencies, and Mr Yermack says the US Congress will ultimately have to take action. Some of the freewheeling exchanges are plagued with poor security and lack investor protections common in more regulated financial markets. Some Chinese exchanges have falsely inflated their trading volume to lure new customers, according to former employees.
There have been at least three dozen heists of cryptocurrency exchanges since 2011; many of the hacked exchanges later shut down. More than 980,000 bitcoins have been stolen, which today would be worth about $4bn. Few have been recovered. Burned investors have been left at the mercy of exchanges as to whether they will receive any compensation. Nearly 25,000 customers of Mt. Gox, once the world’s largest bitcoin exchange, are still waiting for compensation more than three years after its collapse into bankruptcy in Japan. The exchange said it lost about 650,000 bitcoins. Claims approved by the bankruptcy trustee total more than $400m.

Not without China, no.
• Is This The Geopolitical Shift Of The Century? (OP)
The geopolitical reality in the Middle East is changing dramatically. The impact of the Arab Spring, the retraction of the U.S. military, and diminishing economic influence on the Arab world – as displayed during the Obama Administration – are facts. The emergence of a Russian-Iranian-Turkish triangle is the new reality. The Western hegemony in the MENA region has ended, and not in a shy way, but with a long list of military conflicts and destabilization. The first visit of a Saudi king to Russia shows the growing power of Russia in the Middle East. It also shows that not only Arab countries such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE, but also Egypt and Libya, are more likely to consider Moscow as a strategic ally.
King Salman’s visit to Moscow could herald not only several multibillion business deals, but could be the first real step towards a new regional geopolitical and military alliance between OPEC leader Saudi Arabia and Russia. This cooperation will not only have severe consequences for Western interests but also could partly undermine or reshape the position of OPEC at the same time. Russian president Vladimir Putin is currently hosting a large Saudi delegation, led by King Salman and supported by Saudi minister of energy Khalid Al Falih. Moscow’s open attitude to Saudi Arabia—a lifetime Washington ally and strong opponent of the growing Iran power projections in the Arab world—show that Putin understands the current pivotal changes in the Middle East.

Direct result of Turkey’s deal with Russia on Syria.
• Tensions Rise As US, Turkey Halt Visitor Visas, Send Lira Tumbling (BBG)
The U.S. and Turkey each suspended visa services for citizens looking to visit the other country, a sharp escalation of a diplomatic spat that sent the lira down more than 6% against the U.S. dollar. The moves followed the Oct. 4 arrest of a Turkish national who works at the U.S. consulate in Istanbul for alleged involvement in the July 2016 coup attempt against President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. Hours after the Trump administration halted visa services in Turkey on Sunday, Erdogan’s government responded in kind, even repeating verbatim much of the U.S. statement. Both sides said “recent events” had forced them to “reassess the commitment” of the other to the security of mission facilities and personnel.
Only two weeks ago, U.S. President Donald Trump had heaped praise on Erdogan when they met on the sidelines of the United Nations General Assembly in New York, saying the Turkish leader “is becoming a friend of mine” and “frankly, he’s getting high marks.” The U.S. on Thursday called charges against the man “wholly without merit,” saying it was “deeply disturbed” by the arrest and “by leaks from Turkish government sources seemingly aimed at trying the employee in the media rather than a court of law.” Turkey responded by saying the arrested Turkish citizen wasn’t part of the U.S. Consulate’s staff but a “local employee.” The lira was at 3.7323 per dollar as of 10:37 a.m. in Singapore on Monday, down more than 3% from Friday’s close, and touched as low as 3.8533. The currency is heading for a seventh day of declines, the longest stretch since May 2016.
Relations between Turkey, a NATO member, and some Western countries soured after the failed 2016 coup. Erdogan has accused U.S.-based Turkish preacher Fethullah Gulen of organizing the attempted overthrow, and has become increasingly impatient with the U.S. for not turning him over. “I would expect that there will be some sort of de-escalation at the leadership level – Trump and Erdogan will speak or meet,” said Murat Yurtbilir, who specializes in Turkish affairs at the Australian National University. “But the underlying problems won’t go away: the Gulen issue, Turkey’s slow switch toward Russia’s policy in Syria and the economy. ”

But but but….
• Sanctions Against Russia Have Cost European Union €30 Billion (RT)
New research by the Austrian Institute of Economic Research (WIFO) suggests the EU’s economic sanctions against Russia introduced three years ago have cost European countries billions of euro. The survey, which was conducted at the request of the European Parliament and published on Friday, showed EU exports to Russia declining annually by 15.7% since 2014. Up to 40% of that decrease was due to sanctions, it said. As a result of the penalties, Russia has lost its place as EU’s fourth largest trading partner and currently ranks fifth behind the US, Switzerland, China, and Turkey. WIFO calculated EU exports to Russia nosedived from €120 billion four years ago to €72 billion in 2016. According to the research, Cyprus was hit most as exports to Russia plunged 34.5% over the past two years. Greece suffered a 23.2% fall; Croatia’s exports were down 21%.
Austrian exports to Russia dropped by almost ten% or by €1 billion, WIFO said. Poland and the UK have lost €3 billion each. The researchers said the impact of sanctions was most damaging during the first year, as “not much progress has been made in switching trade flows to other countries.” EU sanctions against Russia were introduced in 2014 over the country’s alleged involvement in the conflict in eastern Ukraine. The penalties targeted Russia’s financial, energy, and defense sectors, along with some government officials, businessmen, and public figures. Moscow responded by imposing an embargo on agricultural produce and food and raw materials on countries that joined the anti-Russian sanctions. Since then the sides have repeatedly broadened and extended the restrictive measures.

“You can always write a law and claim it is unconstitutional to separate. That does not make it legal, moral, or ethical.”
Moreover, it contradicts the UN Charter.
• Spain is the Blueprint for How All Governments Will Act (Martin Armstrong)
What is going on in Spain is the blueprint what what other governments will do. The Spanish people themselves outside of Catalonia are deeply divided. Many see this as offensive and others see the government as offensive. We are looking at the breakup of the USA as well and do not forget the civil war to prevent separatists in America. The real issue is that people ban together for creating society and civilization and then government abuses its power and the process of decline begins. This is throughout history and it really does not matter what culture or country. It is all the same. Spain’s Constitutional Court, the puppet of Rajoy, on Thursday ordered the suspension of Monday’s session of the regional Catalan parliament. Rajoy is demonstrating that government will not tolerate losing power.
You can always write a law and claim it is unconstitutional to separate. That does not make it legal, moral, or ethical. Reuters reported: “The suspension order further aggravated one of the biggest crises to hit Spain since the establishment of democracy on the 1975 death of General Francisco Franco. But Spanish markets rose on perceptions the order might ward off, at least for now, an outright independence declaration.” The structure of the EU in attempting to federalize Europe required a single federal debt. That is what they failed to do so you ended up with a half-baked cake. This is why we have the problems in Europe as we do. But make no mistake about it, this is a political problem and what happens in Europe will be a contagion as it was in 1931. This will eventually cause major problems politically in the States as well.

Justice Scalia I greatly admired. However, his letter on the separatist movement in the USA said that the civil war decided there was no right to separate. I disagree with that opinion, but that is my opinion. There are those who object to my writing about Catalonia from the Madrid side. They create a list of hateful names directed at me personally and then say I know nothing of Spain. They are making the same mistake as government. They assume that government and Rajoy is Spain. The people are the sovereign of Spain – not Rajoy nor his Constitutional Court. If you cannot see that government is supposed to be “elected” by the people, they are not to be the ruler of the people as some monarch, they you have missed the entire point of history. You can hate me all you want, but it is your life you are surrendering to government and that of your posterity. We have a choice. We either understand that government when unchecked will go too far and surrender as sheep, or we stand up and try to make the future better for our posterity.

Someone better intervene.
• Catalans Call for Talks as Spain Enters Crunch Week (BBG)
A senior member of the Catalan administration called for dialogue with Spain, warning that all of Europe faces economic damage unless a resolution is found to his region’s standoff with the central government in Madrid. After a weekend of mass demonstrations in favor of Spanish unity, Raul Romeva, foreign affairs chief for the separatist government in Barcelona, insisted that the door was open for talks if Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy would grasp the chance of dialogue. “We need two to tango, we need the other side to be at the table,” Romeva said in an interview in Barcelona on Sunday. “We’re always going to be at the negotiation table, but to start negotiations we need the other party to negotiate with.”
The hint of an olive branch came as both sides hurtle toward crunch time in a dispute that threatens the breakup of Spain. Catalan President Carles Puigdemont has vowed to press ahead with his independence drive in a declaration due as soon as Tuesday, while Rajoy pledged that “national unity will be maintained” by using all instruments available to him. “The risk of this getting a lot worse, with correspondingly bad market development for Spanish assets, is still too great for my risk appetite,” said Erik Nielsen, chief economist at UniCredit. He predicted at least another week of pressure on Spanish and Catalan debt and assets before “things will eventually normalize.”
[..] Romeva invoked the crisis in the euro area that sent yields soaring on Spanish government debt and curbed access to finance, warning that the economic fallout of any worsening of the situation won’t be limited to Catalonia. “This simply won’t affect the Catalan economy, it’s going to affect the Spanish economy, it’s going to affect the European economy,” Romeva said. He blamed Madrid for causing the political uncertainty that’s prompted a stampede for the exit. “What causes uncertainty is the incapability of the political central state – or the Spanish state – to provide a political solution,” he said.

Since Greece entered the bailout mechanism, foreclosures are down by 89%. Good.
• Greece Foreclosures Target Seems Unattainable (K.)
Foreclosures, which have been practically frozen for the last eight years, represent the credit system’s Achilles’ heel. The impact from the paralysis of the auction system is already obvious in banks’ financial results on the reduction of nonperforming loans and threatens to undermine the target set for containing nonperforming exposures (NPEs). The ECB’s Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM) has asked Greek lenders to bring down their NPEs by €11.5 billion through liquidations (property auctions) up to 2019. Meeting this target requires foreclosures worth €5.5 billion per year while takings from auctions have been poor.
The foreclosures scheduled for this year only concern 5,600 properties, worth €1.1 billion. This is the smallest number of auctions in recent years, given that 2016 (when auctions were held for 4,800 properties) was practically wasted due to protracted strikes by Greece’s lawyers and notaries. This year’s figures actually concern mostly auctions demanded by the state or private lenders, while banks have only instigated few auctions, mainly concerning commercial or industrial properties. For comparison purposes, one has to see the statistics from 2009, before Greece entered the bailout mechanism, when foreclosures numbered 52,000 and their value reached €4.2 billion. This means an 89% drop since then.

I’ve said it before: the EU is the mafia.
• Nearly There, But Never Further Away (FP)
The guard forced the migrants to kneel and began barking orders in Arabic, a language that few of the once-hopeful souls who had traveled to Libya from sub-Saharan Africa spoke. A gaunt, elderly man in ripped jeans and a tattered T-shirt failed to comply. The guard, wearing a crisp new uniform emblazoned with the insignia of Libya’s anti-illegal immigration police division, raised his wooden club and brought it down hard on the man’s back, driving him face down into the ground with the first blow. It was early May, three weeks after the staff at the Triq al-Sikka migrant detention center in the Libyan capital of Tripoli had received human rights training from the International Organization for Migration (IOM). The guard struck the elderly man again on the back and clubbed the back of his legs.
Then he moved methodically down the line of kneeling migrants, beating each man as if he were responsible for his fellow prisoner’s infraction. Cries of pain echoed through the barren, warehouse-like facility, where more than 100 half-starved migrants were locked away in crowded cells. Some had been there for months, enduring regular beatings and surviving on a few handfuls of macaroni and a single packet of juice each day. Others had recently been rounded up off the streets in raids targeting black African migrants. Soon after the beatings began, other guards at the facility noticed my presence and quickly ushered me into a waiting area outside the well-appointed office of Col. Mohamed Beshr, the urbane head of Libya’s anti-illegal immigration police.
Beshr is a key player in recent joint EU-Libyan efforts to halt migration to Europe, including intercepting migrants at sea and detaining them on land. He has welcomed high-level European diplomats and U.N. representatives to the Triq al-Sikka facility, and his office is filled with certificates from workshops run by IOM, the European Union, and Britain’s development agency. Yet Beshr seemed frustrated by my questions about the abuses openly taking place at the detention center he oversaw. To hear him tell it, his European partners cared about only one thing, even if they wouldn’t say it: preventing migrants from showing up on Italy’s shores. “Are they looking for a real solution to this humanitarian crisis?” Beshr asked, smirking and raising his eyebrows. “Or do they just want us to be the place where migrants are stopped?”
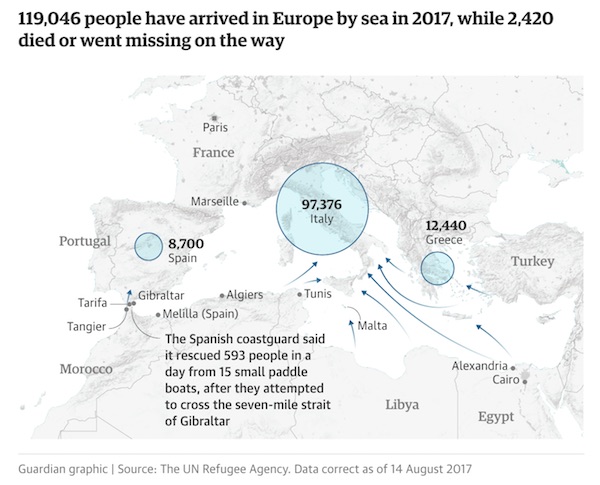
Eighteen months after the EU unveiled its controversial plan to curb illegal migration through Libya — now the primary point of departure for sub-Saharan Africans crossing the Mediterranean Sea to Europe — migrants have become a commodity to be captured, sold, traded, and leveraged. Regardless of their immigration status, they are hunted down by militias loyal to Libya’s U.N.-backed government, caged in overcrowded prisons, and sold on open markets that human rights advocates have likened to slave auctions. They have been tortured, raped, and killed — abuses that are sometimes broadcast online by the abusers themselves as they attempt to extract ransoms from migrants’ families.
The detention-industrial complex that has taken hold in war-torn Libya is not purely the result of a breakdown in order or the work of militias run amok in a state of anarchy. Visits to five different detention centers and interviews with dozens of Libyan militia leaders, government officials, migrants, and local NGO officials indicate that it is the consequence of hundreds of millions of dollars in pledged and anticipated support from European nations as they try to stem the flow of unwanted migrants toward their shores.