
Juan Gris Man in the café 1912

The future wants its future back.
• The Illusion of Prosperity (Lebowitz)
For the last 50 years, the consumer, that means you and me, have been the most powerful force driving the U.S. economy. Household spending now accounts for almost 70% of economic growth, about 10% more than it did in 1971. Household spending in the U.S. is also approximately 10-15% higher than most other developed nations. Currently, U.S. economic growth is anemic and still suffering from the after-shocks of the financial crisis. Importantly, much of that weakness is the result of growing stress on consumers. Using the compelling graph below and the data behind it, we can illustrate why the U.S. economy and consumers are struggling.
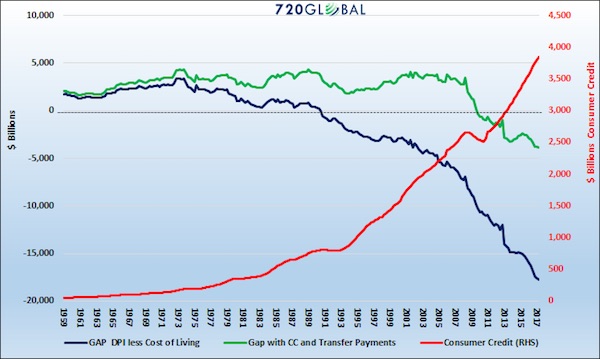
The blue line on the graph above marks the difference between median disposable income (income less taxes) and the median cost of living. A positive number indicates people at the median made more than their costs of living. In other words, their income exceeds the costs of things like food, housing, and insurance and they have money left over to spend or save. This is often referred to as “having disposable income.” If the number in the above calculation is negative, income is not enough to cover essential expenses. From at least 1959 to 1971, the blue line above was positive and trending higher. The consumer was in great shape. In 1971 the trend reversed in part due to President Nixon’s actions to remove the U.S. dollar from the gold standard.
Unbeknownst to many at the time, that decision allowed the U.S. government to run consistent trade and fiscal deficits while its citizens were able to take on more debt. Other than rampant inflation, there were no immediate consequences. In 1971, following this historic action, the blue line began to trend lower. By 1990, the median U.S. citizen had less disposable income than the median cost of living; i.e., the blue line turned negative. This trend lower has continued ever since. The 2008 financial crisis proved to be a tipping point where the burden of debt was too much for many consumers to handle. Since 2008 the negative trend in the blue line has further steepened. You might be thinking, if incomes were less than our standard of living, why did it feel like our standard of living remained stable? One word – DEBT.

Lance has a lot of detail in his assessment. Worth a read.
• Trump Tax Plan Economic Outcomes Likely Disappointing (Roberts)
Do not misunderstand me. Tax rates CAN make a difference in the short run particularly when coming out of a recession as it frees up capital for productive investment at a time when recovering economic growth and pent-up demand require it. However, in the long run, it is the direction and trend of economic growth that drives employment. The reason I say “direction and trend” is because, as you will see by the vertical blue dashed line, beginning in 1980, both the direction and trend of economic growth in the United States changed for the worse. Furthermore, as I noted previously, Reagan’s tax cuts were timely due to the economic, fiscal, and valuation backdrop which is diametrically opposed to the situation today.
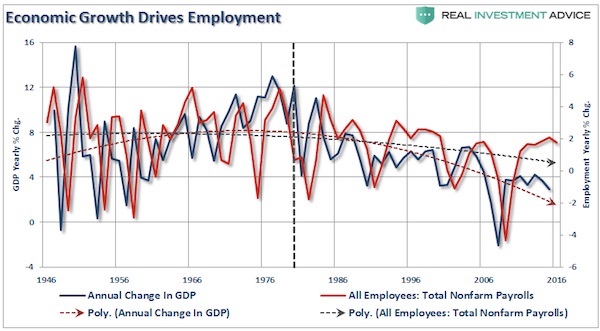
“Importantly, as has been stated, the proposed tax cut by President-elect Trump will be the largest since Ronald Reagan. However, in order to make valid assumptions on the potential impact of the tax cut on the economy, earnings and the markets, we need to review the differences between the Reagan and Trump eras.

[..] Of course, as noted, rising debt levels is the real impediment to longer-term increases in economic growth. When 75% of your current Federal Budget goes to entitlements and debt service, there is little left over for the expansion of the economic growth. The tailwinds enjoyed by Reagan are now headwinds for Trump as the economic “boom” of the 80’s and 90’s was really not much more than a debt-driven illusion that has now come home to roost. Senator Pat Toomey, a Pennsylvania Republican who sits on the finance committee, said he was confident that a growing economy would pay for the tax cuts and that the plan was fiscally responsible. “This tax plan will be deficit reducing,”
The belief that tax cuts will eventually become revenue neutral due to expanded economic growth is a fallacy. As the CRFB noted: “Given today’s record-high levels of national debt, the country cannot afford a deficit-financed tax cut. Tax reform that adds to the debt is likely to slow, rather than improve, long-term economic growth.” The problem with the claims that tax cuts reduce the deficit is that there is NO evidence to support the claim. The increases in deficit spending to supplant weaker economic growth has been apparent with larger deficits leading to further weakness in economic growth. In fact, ever since Reagan first lowered taxes in the ’80’s both GDP growth and the deficit have only headed in one direction – lower.

The economy lost its balance. It will tip over.
• The Top 1% Of Americans Now Control 38% Of The Wealth (CNBC)
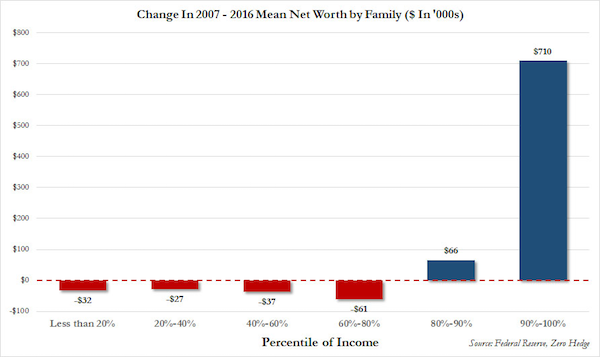
America’s top 1% now control 38.6% of the nation’s wealth, a historic high, according to a new Federal Reserve Report. The Federal Reserve’s Surveys of Consumer Finance shows that Americans throughout the income and wealth ladder posted gains between 2013 and 2016. But the wealthy gained the most, driven largely by gains in the stock market and asset values. The top 1% saw their share of wealth rise to 38.6% in 2016 from 36.3% in 2013. The next highest nine% of families fell slightly, and the share of wealth held by the bottom 90% of Americans has been falling steadily for 25 years, hitting 22.8% in 2016 from 33.2% in 1989. The top income earners also saw the biggest gains. The top 1% saw their share of income rise to a new high of 23.8% from 20.3% in 2013. The income shares of the bottom 90% fell to 49.7% in 2016.

I smell danger.
• This Chart Defines the 21st Century Economy (CHS)
One chart defines the 21st century economy and thus its socio-political system: the chart of soaring wealth/income inequality. This chart doesn’t show a modest widening in the gap between the super-wealthy (top 1/10th of 1%) and everyone else: there is a veritable Grand Canyon between the super-wealthy and everyone else, a gap that is recent in origin. Notice that the majority of all income growth now accrues to the the very apex of the wealth-power pyramid. This is not mere chance, it is the only possible output of our financial system. This is stunning indictment of our socio-political system, for this sort of fast-increasing concentration of income, wealth and power in the hands of the very few at the top can only occur in a financial-political system which is optimized to concentrate income, wealth and power at the top of the apex.
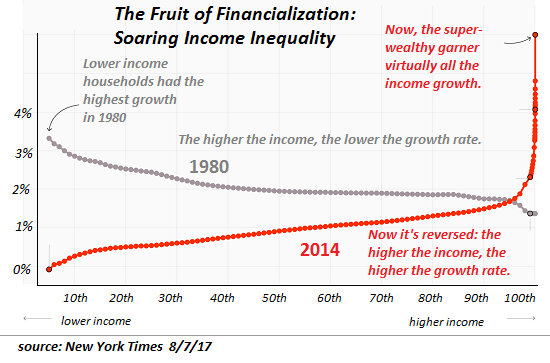
[..] the elephant in the room few are willing to mention much less discuss is financialization, the siphoning off of most of the economy’s gains by those few with the power to borrow and leverage vast sums of capital to buy income streams–a dynamic that greatly enriches the rentier class which has unique access to central bank and private-sector bank credit and leverage. Apologists seek to explain away this soaring concentration of wealth as the inevitable result of some secular trend that we’re powerless to rein in, as if the process that drives this concentration of wealth and power wasn’t political and financial. There is nothing inevitable about such vast, fast-rising income-wealth inequality; it is the only possible output of our financial and pay-to-play political system.

China just took two giant steps back from being a functioning economy.
• China’s Traders Have an Excuse to Take the Rest of Year Off
Financial markets in the world’s second-largest economy are set to turn listless in the fourth quarter as party officials keep a lid on volatility around a seminal Communist Party gathering. That’s the finding of Bloomberg surveys of market participants. The benchmark Shanghai Composite Index is projected to end the year 0.3% higher than Wednesday’s close. The yuan will be at 6.64 per dollar, unchanged from the current level, while the 10-year sovereign bond yield is expected to slip to 3.59% from 3.63%. “I don’t expect any big swings,” said Ken Chen, Shanghai-based analyst with KGI Securities Co. “Regulators would want to ensure the markets are stable for the 19th Party Congress.”
Authorities have stressed the need for stability in the lead-up to what will be China’s most important political event in years. The twice-a-decade party congress, which starts on Oct. 18, is expected to replace about half of China’s top leadership and shape President Xi Jinping’s influence into the next decade. The China Securities Regulatory Commission has ordered local brokerages to mitigate risks and ensure stable markets before and during the event, people familiar with the matter have said. The CSRC has also banned brokerage bosses from taking holidays or leaving the country from Oct. 11 until the congress ends, according to the people.
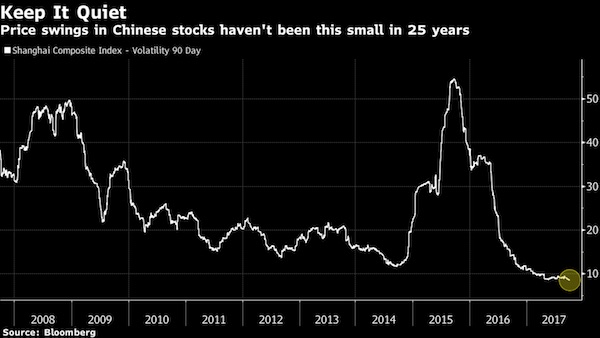

Why that forced low volatility is so dangerous. No price discovery.
• China’s Mortgage Debt Bubble Raises Spectre Of 2007 US Crisis (SCMP)
Young Chinese like Eli Mai, a sales manager in Guangzhou, and Wendy Wang, an executive in Shenzhen, are borrowing as much money as possible to buy boomtown flats even though they cannot afford the repayments. Behind the dream of property ownership they share with many like-minded friends lies an uninterrupted housing price rally in major Chinese cities that dates back to former premier Zhu Rongji’s privatisation of urban housing in the late 1990s. Rapid urbanisation, combined with unprecedented monetary easing in the past decade, has resulted in runaway property inflation in cities like Shenzhen, where home prices in many projects have doubled or even tripled in the past two years. City residents in their 20s and 30s view property as a one-way bet because they’ve never known prices to drop. At the same time, property inflation has seen the real purchasing power of their money rapidly diminish.
“Almost all my friends born since the 1980s and 1990s are racing to buy homes, while those who already have one are planning to buy a second,” Mai, 33, said. “Very few can be at ease when seeing rents and home prices rise so strongly, and they will continue to rise in a scary way.” The rush of millions young middle-class Chinese like Mai into the property market has created a hysteria that eerily resembles the housing crisis that struck the United States a decade ago. Thanks to the easy credit that has spurred the housing boom, many young Chinese have abandoned the frugal traditions of earlier generations and now lead a lifestyle beyond their financial means. The build-up of household and other debt in China has also sparked widespread concern about the health of the world’s second largest economy.
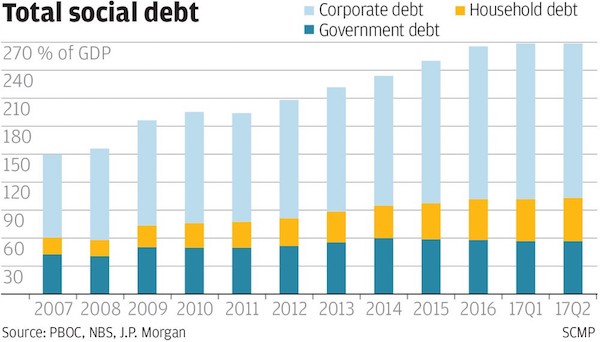
[..] Mai and Wang have been playing it fast and loose to deal with their debts. Mai has lent 600,000 of the 800,000 yuan he got from a bank after using his first flat as collateral to a money shark promising an annualised return of 20 per cent. Wang gave the bank fake documents showing her monthly income was 18,000 yuan – about 1.6 times her actual salary. It did not ask any questions. Neither see any problem, because the value of their underlying assets, the flats, have risen. The value of Mai’s two flats rose from 3.8 million yuan last year to 6.4 million yuan last month, while the value of Wang’s unit is now 2.93 million yuan, up from 2.6 million yuan. “I think I made a smart and successful decision to leverage debt,” Mai said.
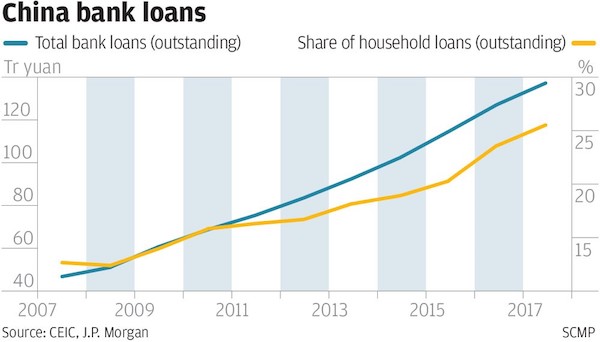

Watch India.
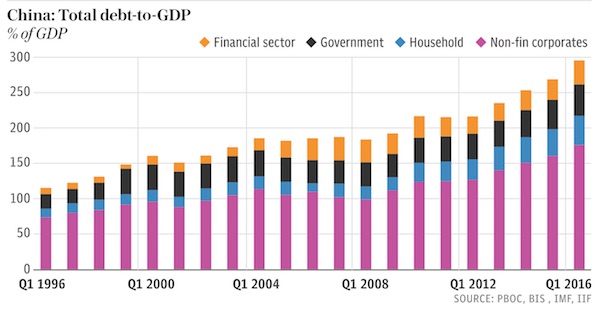
• Debt Boom In India And China Threatens New Financial Crisis – WEF (Tel.)
Banks across the world are more vulnerable to a crisis now than they were in the build up to the credit crunch, the World Economic Forum has warned. Bad loans in India have more than doubled in the past two years, while in China’s financial system “business credit is building up similarly to the United States pre-crisis, and could be a new source of vulnerability.” China’s credit boom has been the subject of several warnings from global finance groups and regulators in recent months. Last week the Bank of International Settlements warned that higher interest rates in the US could have a knock on effect in the world’s second-largest economy, forcing rates higher in China, making the debt mountain more expensive to maintain and hitting the economy hard.
Britain, the US and other developed economies have taken major steps to shore up their banking systems as they were at the heart of the financial crisis, but the global financial system as a whole faces new and growing risks. Other parts of the financial system are taking risks instead, such as fund managers in the so-called shadow banking sector. The eurozone banks have still not fully recovered from the crash either. “In general, there is still too much debt in parts of the private sector, and top global banks are still ‘too big to fail’,” the WEF’s Global Competitiveness Report said. “The largest 30 banks hold almost $43 trillion in assets, compared to less than $30 trillion in 2006, and concentration is continuing to increase in the US, China, and some European countries. “In Europe, banks are still grappling with the consequences of 10 years of low growth and the enduring non-performance of loans in many countries.”

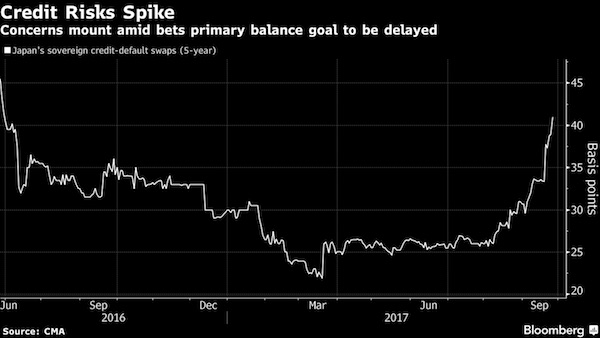
Abe’s power gamble.
• Japan Downgrade Risk Seen Rising as Default Swaps Climb (BBG)
Japan’s credit rating could be in the cross hairs after Prime Minister Shinzo Abe indicated the nation may abandon its goal of covering key expenditures through taxes. The cost of insuring Japan’s government debt against default rose to a 15-month high on Tuesday, with policy uncertainty adding to concerns about tensions with North Korea. On Monday, Abe said he would dissolve parliament later this week and he’d pay for economic measures with funds from a consumption-tax increase originally intended to rein in the nation’s swollen debt. Japanese government bonds extended declines Wednesday after S&P Global Ratings said it expects “material” fiscal deficits to continue through 2020.
S&P’s ratings assume fiscal improvements will be gradual over the next few years, sovereign analyst Craig Michaels said. “The prospect for extra revenue to be spent rather than being used to pay down Japan’s debt is a factor of higher bond yields,” said Shuichi Ohsaki, chief rates strategist for Japan at Bank of America Merrill Lynch. “There also appears to be some speculation that such a policy move will lead to a sovereign downgrade.” Yield on Japan’s five-year note added 2.5 basis points to minus 0.090% Wednesday, which would be the steepest increase since March 9. The benchmark 10-year yield climbed 2.5 basis points to 0.055%, a level unseen since early August.
The challenges in meeting the long-standing objective of achieving a primary balance surplus, add to concerns about Japan’s debt load, which is the world’s heaviest. Getting to that goal would allow the government to pay for programs including social security and public works projects from tax revenue, rather than through new debt financing. Abe is betting he can crush a weak opposition in next month’s election, which he has framed in part as a vote on his plans to use revenue from the upcoming consumption-tax hike to fund an $18 billion economic package aimed at tackling the challenges of an aging society.

It’s the mob. One question. Who’s going to end up paying?
• JPMorgan Ordered To Pay Over $4 Billion To Widow And Family (ZH)
A Dallas jury ordered JPMorgan Chase to pay more than $4 billion in damages for mishandling the estate of a former American Airlines executive. Jo Hopper and two stepchildren won a probate court verdict over claims that JPMorgan mismanaged the administration of the estate of Max Hopper, who was described as an airline technology innovator by the family’s law firm. The bank, which was hired by the family in 2010 to independently administer the estate of Hopper, was found in breach of its fiduciary duties and contract. In total, JP Morgan Chase was ordered to pay at least $4 billion in punitive damages, approximately $4.7 million in actual damages, and $5 million in attorney fees.
The six-person jury, which deliberated a little more than four hours starting Monday night and returned its verdict at approximately 12:15 a.m. Tuesday, found that the bank committed fraud, breached its fiduciary duty and broke a fee agreement, according to court papers. “The nation’s largest bank horribly mistreated me and this verdict provides protection to others from being mistreated by banks that think they’re too powerful to be held accountable,” said Hopper in a statement. “The country’s largest bank, people we are supposed to trust with our livelihood, abused my family and me out of sheer ineptitude and greed. I’m blessed that I have the resources to hold JP Morgan accountable so other widows who don’t have the same resources will be better protected in the future.” “Surviving stage 4 lymphoma cancer was easier than dealing with this bank and its estate administration,” Mrs. Hopper added.
Max Hopper, who pioneered the SABRE reservation system for the airline, died in 2010 with assets of more than $19 million but without a will and testament, according to the statement. JPMorgan was hired as an administrator to divvy up the assets among family members. “Instead of independently and impartially collecting and dividing the estate’s assets, the bank took years to release basic interests in art, home furnishings, jewelry, and notably, Mr. Hopper’s collection of 6,700 golf putters and 900 bottles of wine,” the family’s lawyers said in the statement. “Some of the interests in the assets were not released for more than five years.”
The bank’s incompetence caused more than just unacceptably long timelines; bank representatives failed to meet financial deadlines for the assets under their control. In at least one instance, stock options were allowed to expire. In others, Mrs. Hopper’s wishes to sell certain stock were ignored. The resulting losses, the jury found, resulted in actual damages and mental anguish suffered by Mrs. Hopper. With respect to Mr. Hopper’s adult children, the jury found that they lost potential inheritance in excess of $3 million when the Bank chose to pay its lawyers’ legal fees out of the estate account to defend claims against the Bank for violating its fiduciary duty.

“A world in recovery”, Stephen?
• The Courage to Normalize Monetary Policy (Stephen Roach)
Central banks’ unconventional monetary policies – namely, zero interest rates and massive asset purchases – were put in place in the depths of the 2008-2009 financial crisis. It was an emergency operation, to say the least. With their traditional policy tools all but exhausted, the authorities had to be exceptionally creative in confronting the collapse in financial markets and a looming implosion of the real economy. Central banks, it seemed, had no choice but to opt for the massive liquidity injections known as “quantitative easing.” This strategy did arrest the free-fall in markets. But it did little to spur meaningful economic recovery. The G7 economies (the United States, Japan, Canada, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy) have collectively grown at just a 1.8% average annual rate over the 2010-2017 post-crisis period.
That is far short of the 3.2% average rebound recorded over comparable eight-year intervals during the two recoveries of the 1980s and the 1990s. Unfortunately, central bankers misread the efficacy of their post-2008 policy actions. They acted as if the strategy that helped end the crisis could achieve the same traction in fostering a cyclical rebound in the real economy. In fact, they doubled down on the cocktail of zero policy rates and balance-sheet expansion. And what a bet it was. According to the Bank for International Settlements, central banks’ combined asset holdings in the major advanced economies (the US, the eurozone, and Japan) expanded by $8.3 trillion over the past nine years, from $4.6 trillion in 2008 to $12.9 trillion in early 2017. Yet this massive balance-sheet expansion has had little to show for it.
Over the same nine-year period, nominal GDP in these economies increased by just $2.1 trillion. That implies a $6.2 trillion injection of excess liquidity – the difference between the growth in central bank assets and nominal GDP – that was not absorbed by the real economy and has, instead been sloshing around in global financial markets, distorting asset prices across the risk spectrum. Normalization is all about a long-overdue unwinding of those distortions. Fully ten years after the onset of the Great Financial Crisis, it seems more than appropriate to move the levers of monetary policy off their emergency settings. A world in recovery – no matter how anemic that recovery may be – does not require a crisis-like approach to monetary policy. Monetary authorities have only grudgingly accepted this. Today’s generation of central bankers is almost religious in its commitment to inflation targeting – even in today’s inflationless world. While the pendulum has swung from squeezing out excess inflation to avoiding deflation, price stability remains the sine qua non in central banking circles.

Chaos looms in Germany. Merkel will be forced to accept a FinMin she doesn’t want. Greece will be squeezed even more. And Italy, Spain etc.
• German Finance Minister Wolfgang Schäuble To Be Bundestag Speaker (G.)
Wolfgang Schäuble, a man revered and reviled in equal measure for his tenacious austerity economics, is to relinquish his powerful role as Germany’s finance minister and instead become the speaker of the parliament, his party has announced. Schäuble, 75, was asked to take on the role by the chancellor, Angela Merkel, who is keen on someone with authority and experience to steer future debate in the Bundestag after the success in Sunday’s election of the rightwing radical Alternative für Deutschland (AfD). The AfD is due to take up 94 seats in the house, having secured 12.6% of the vote, and its leadership has pledged to shake up the debating culture in the Bundestag, making it considerably rowdier than the calm and consensus-based mood that has characterised it in the past.
The role of speaker has been empty since Norbert Lammert, a veteran CDU MP, recently announced he would retire at the end of the last parliamentary term. In terms of protocol it ranks second only to that of federal president, and ahead of the chancellor, but in reality it is considerably less powerful than his current post. Schäuble, a lawyer by training, is the longest-serving MP in the Bundestag, having been elected in 1972. Once one of Merkel’s staunchest rivals, he has since become one of her closest confidantes as well as the most experienced and high-profile minister in her cabinet. He has been finance minister since 2009 and is held in high regard in Germany, particularly by the conservative base, who revere him for acting in Germany’s interests as the dogged protector of austerity economics in the eurozone.
He is also admired at home for his insistence – some would say obsession – with a balanced budget or the “black zero”. Germany today has a record budget surplus. But elsewhere he is a hugely controversial figure, particularly in Greece and in Ireland, where he has often faced criticism for his handling of the euro crisis that has dominated almost his entire time as finance minister. Schäuble has yet to respond to the reports of his new appointment, but it was confirmed on Wednesday afternoon by Volker Kauder, the chairman of the CDU parliamentary bloc.








