
Underwood&Underwood Chicago framed by Gothic stonework high in the Tribune Tower 1952
For the second time in three years, I’m fortunate enough to spend some time in New Zealand (or Aotearoa). In 2012, it was all mostly a pretty crazy touring schedule, but this time is a bit quieter. Still get to meet tons of people though, in between the relentless Automatic Earth publishing schedule. And of course people want to ask, once they know what I do, how I think their country is doing.
My answer is I think New Zealand is much better off than most other countries, but not because they’re presently richer (disappointing for many). They’re better off because of the potential here. Which isn’t being used much at all right now. In fact, New Zealand does about everything wrong on a political and macro-economic scale. More about that below.
I’ve been going through some numbers today, and lots of articles, and I think I have an idea what’s going on. Thank you to my new best friend Grant here in Northland (is it Kerikeri or Kaikohe?) for providing much of the reading material and the initial spark.
To begin with, official government data. We love those, don’t we, wherever we turn our inquisitive heads. Because no government would ever not be fully open and truthful. This is from Stuff.co.nz, March 19 2015:
New Zealand GDP grew 3.3% last year
New Zealand’s economy grew 3.3% last year, the fastest since 2007 before the global financial crisis, Statistics NZ said. Most forecasts expect the economy to keep growing this year and next, although slightly more slowly than in the past year. For the three months ended December 31, GDP grew 0.8%, in line with Reserve Bank and other forecasts. That was led by shop sales and accommodation.
That sounds great compared to most other nations. But then we find out where the alleged growth has come from (I say alleged because other data cast a serious doubt on the ‘official’ numbers):
The economy grew a revised 0.9% in the September quarter, down from 1% reported earlier. Retail and accommodation increased 2.3% in the December 2014 quarter, buoyed by a 15% increase in international tourist spending, as reported on Wednesday. New Zealand household spending also increased 0.6%. [..]
“Spending by Chinese, US, and UK visitors all increased in 2014, though Australians spent less.” Australia is New Zealand’s biggest tourism market, but the New Zealand dollar has been high against the Australian currency, trading at A96.5c on Thursday. The exchange rate was under A80c at the start of 2013. Total visitor spending last year hit $7.4 billion, up 13% on the previous year. [..]
(Note: $1 US = $1.3156 NZ today.)
Increased banking activity was reflected in a 1.1% rise in financial services this quarter, while housing investment rose 5.2%.
[..] The figures also showed the first fall in real incomes since the middle of 2012. The inflation-adjusted purchasing power of disposable income was down 0.5% in the December quarter.
We’ll get back to housing in a bit. And by all means, keep those last few numbers in mind: while the economy ostensibly grew by 3.3%, disposable income was down. That’s what you call a warning sign.
But let’s focus first on tourism and especially on China. While overall tourist spending rose 15% in 2014, as part of a later quote in this article we will even see that “tourism from China was up 40% in the first two months of this year from a year ago..”
Still, that cannot make up for that other big trade with China, exports, in particular of New Zealand’s biggest industry, dairy, and the second biggest, timber. There things are not looking nearly as rosy. And after reading the next piece, I’m wondering how the economy could possibly have grown by 3.3%. More from Stuff.co.nz, dated March 25:
Dairy Slump Hits New Zealand Exports To China
New Zealand posted a small trade surplus of just $50 million in February with dairy exports down heavily, especially to China, New Zealand’s top export market. Some economists had expected a monthly surplus of about $350 million. The trade shortfall for the year ended February 2015 was a deficit of $2.2 billion. Exports to China have boomed in the past few years, but melted down last year as dairy product prices plunged. Total exports to China in February were down more than 36% on the same month last year.
China remains New Zealand’s biggest export market, worth almost $9b in the past year, just slightly ahead of Australia. But the trend for exports to China has been falling for the past year, and is down 45% from the peak in late 2013. In fact, it has returned to levels seen in 2012. [..] Total exports were worth $3.9b for the month, just barely ahead of monthly imports which were also about $3.9b.
So sure, the 3.3% was over 2014, and this piece concerns this year. But it also says ‘the trend for exports to China has been falling for the past year,’ and ‘..The trade shortfall for the year ended February 2015 was a deficit of $2.2 billion..’ and that can only leave me wondering again what real GDP growth was. This is from RadioNZ, April 3:
Confidence among manufacturers and exporters has taken a hit with export sales in February down 27% compared with a year ago. A survey found net confidence – which includes measures of cash flow, profitability, investment, staff and sales – fell into negative territory for the first time since April 2013. Net confidence was minus 13, down from 21 in January. The sample of Manufacturers and Exporters Association members covered companies with combined annual sales of $178 million, with 68% of those from exports. Association president Tom Thomson said currency volatility was the biggest issue for exporters, with the big jump in the US dollar forcing up the price of some raw materials.
Now I’m wondering which raw materials this fine man has in mind. See, I can imagine currency volatility being a bit of a drag, but not too much for New Zealand manufacturers, because as far as I can see the country’s exporters don’t seem to import much in the way of raw materials. The main exports, as I said, are dairy and timber, with a bit of meat thrown in, none of which require raw materials imports, and what the US dollar drives up in there would help New Zealand more than hurt it. That the New Zealand dollar itself has gained vs various other currencies, while true, is a whole other story.
New Zealand’s dairy industry has been thrown together since the start of the century in co-op Fonterra, good for 30% of global dairy exports – most dairy farmers are shareholders (mind you, no country the size of New Zealand should ever even think of exporting 30% of the world’s anything, of course, unless it’s something unique on the planet and it comes in small quantities). Fonterra’s by far biggest clients are the lactose-intolerant Chinese, who import about all the milkpowder – for their babies – they can lay their hands on, following a domestic tainted milk scandal a few years back. Still, to establish your biggest industry around one single client is obviously a very risky venture. And now there’s the added problem of dropping prices. The New Zealand Herald, April 2:
World Dairy Prices Slide 10.8% On Supply Concerns
International dairy prices continued to reverse gains made early this year at this morning’s GlobalDairyTrade (GDT) auction, putting downward pressure on Fonterra’s $4.70 a kg farmgate milk price forecast and raising concerns about next season’s likely payout. The GDT price index fell by 10.8% compared with the last sale a fortnight ago, when prices dropped by 8.8%. Big falls were recorded for the key products of wholemilk powder – down 13.3% to US$2,538 a tonne, skim milk powder – down 9.9% to US$2,467/tonne.
That 10.8% price drop occurred in just 2 weeks. There can be no doubt that if your economy depends so much on one sector and one client, you’re vulnerable. Probably as much as oil producers, who saw their prices drop more, but who mostly have higher profit margins. What hasn’t helped New Zealand dairy farmers is the Russian ban on EU milk products; these will now have to be sold on world markets. What won’t help either is the recent lifting of EU milk quotas, which will bring a huge flood of additional milk on the market. A market that is already drowning in milk. RadioNZ, April 2:
The Government is blaming a slump in milk prices on the world market being awash with milk. But New Zealand First leader Winston Peters said National’s economic policies and the high value of the New Zealand dollar were not helping dairy farmers. In the Global Dairy Trade auction prices dropped 10.8% overnight to $US2746 a tonne, the second fall in a fortnight. Mr Peters said he predicted the fall and it was a sign of rural areas lagging behind. “I’ve been saying it for a long long time – what you’ve got is a fixation with Auckland, hollowing out the provincial economies and sucking all the attention and money to Auckland and that is not going to go on any longer.”
Mr Peters said New Zealand had a free market system that no other country followed and he would legislate to control the exchange rate, similar to Singapore’s system. “The one country that’s not devaluing at the moment is New Zealand – every other economy has. [..] Economic Development Minister Steven Joyce firmly rejected that idea. “Well, with the greatest respect to Winston I am old enough, and so is he, to remember the last time we tried to set the exchange rate in this country and it wasn’t that successful…
“What he is basically saying is that he would legislate, presumably, to put the exchange rate at a level it won’t naturally go and that means effectively increasing costs for the consumer and decreasing costs for exporters.” [..] Meanwhile, the Fonterra Shareholders Council said some frustrated farmers were considering leaving the co-operative due to the price slump.
For more than a few farmers, the situation has already proved too much. NZ Herald, Jan 11:
At least four farmers have taken their lives since Fonterra cut its milk payout forecast for the coming season. On December 10, the dairy giant dropped its payout forecast for 2014-15 to an eight-year low of $4.70 a kilogram of milk solids. That’s nearly half the $8.40 paid in the 2013-14 season and is estimated to mean an income drop for farmers of $6.6 billion. Federated Farmers dairy industry group vice-chairman Kevin Robinson confirmed to the Herald on Sunday that it was aware of the December deaths. “There’s been discussion through Federated Farmers email about them,” he said.
Several industry experts blame high levels of rural debt for increased stress on farmers. In total, 14 farmers have taken their lives in the past six months, Chief Coroner Judge Neil MacLean said. The most recent four deaths were also confirmed by Te Aroha farmer Sue McKay, the administrator of a private Facebook-based support group. She added: “I also know some local hospitals have a number of farmers in them from attempted suicide. If there’s three in one ward alone, there will be more in other hospitals.”
Whole milk powder prices were down 11% in the month and 52% lower than a year earlier. Cheese also dropped 5% over the month.
But New Zealand also has a whole different side. If anything could explain the 3.3% GDP growth number for 2014, I’m guessing it must be this: a real estate bubble that would put most of Charles Ponzi’s heirs to shame. Not 10 years ago, mind you, Americans, but today. Will they never learn, you ask? No, they will have to have their faces pushed squarely through the stucco walls. And they’ll probably still have hope for a recovery when they come out at the other side. NZ Herald, April 5:
Hot Properties: Auckland Valuations Out Of Date Within Months
Council valuations are already out of date, with homes selling in Auckland’s overheated property market on average for more than 15% above their figure of six months ago. And previously unfashionable suburbs have recorded some of the biggest spikes as desperate buyers look for their first home. Mt Roskill made the biggest jump in the Real Estate Institute figures, which are based on Auckland sales in February and compared against capital valuations made in July last year. The valuations, which do not involve a property inspection or include chattels, were made public on October 1.
Even suburbs among the 10 with lowest rises, such as Remuera and Te Atatu Peninsula, were up 13%. Properties sold by Bayleys Real Estate last month included a West Harbour home bought for $700,000 more than its capital valuation of $900,000 and a Glendowie home with a capital value of $1.13m that sold for $1.575m. An Avondale home sold for $590,000 — $130,000 above valuation.
REINZ chief executive Colleen Milne wasn’t surprised because city fringe suburbs were now out of reach for many. The hot market made it hard for capital values to keep up, Milne said. “There has been a 19.9% median movement in Auckland in the last 18 months. I thought the CVs seemed to be quite appropriate at the time, but the whole thing is just supply and demand — we have a lack of houses,” she told the Herald on Sunday.
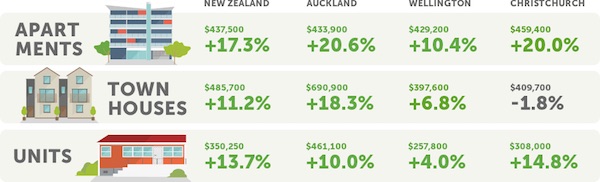
A ‘19.9% median movement in Auckland in the last 18 months’ is about 13.25% per year, a doubling time of just over 7 years. Auckland apartment prices in the Trade.me graph below, which covers February 2014-February 2015, would double every 3-4 years.
It must be an Anglo-Saxon disease. You can see it in London, in Sydney, Melbourne, New York, Toronto. The new normal way to make your failing economy look ‘healthy’ is to sell assets to any rich foreigner or investment fund who comes knocking, no matter what the consequences, short term or long term. In all these cities, young people can forget about buying a home, that allegedly government supported dream.
And everyone but the rich are pushed out ever further into the boondock burbs. It’s a ‘policy’ that kills cities, of necessity. Cities need people, real people, all people, poor and rich and old and young, that have grown up where they live, they love where they live, they are interested in making it look good and feel good. This is an ongoing and organic process, because cities are alive, and yes, you can kill them. But that’s for another story.
Back to New Zealand’s reality for the vast majority of people, who will never be able to fork over 100s of 1000s of dollars for a house. People like the workers in the timber industry, who see slowing Chinese demand translated into job cuts both for those who cut the trees and those who transport them.
Again, a dumb idea to base a whole industry around one client, but the men and women who did the job were just glad they had work. And now they don’t anymore. Jobs that in all likelihood will never come back again. China won’t have another debt-financed growth spurt, and there are no other candidates waiting on the horizon.
And that’s all a big shame. New Zealand is not poor, but it’s by no means as rich as Australia or Canada or Germany or the US. What it does have is the potential to be largely self-sufficient. A potential that is being squandered in order to play with the big boys of globalized trade.
New Zealand has only 4.5 million citizens, one third of which live in Auckland. It has vast tracts of productive land that are now used to feed export oriented cows and American pines, neither of which are even native. It could have a great shoe industry, plenty of leather, and a textile industry, plenty of wool. But New Zealand, like everyone else, imports such basic needs from China. While having scores of unemployed people. When will that light go off?
The country’s prime minister since 2008, John Key, used to work at Merrill Lynch and the New York Fed, and that sort of background guarantees valiant efforts to sell anything in the country that’s not bolted down, and take an axe to what is. It also guarantees zero initiative to become self-sufficient.
But then there are many tragic countries and societies in the world who all suffer from the same maladie. I’ll leave you with some reflections by the man who I’m told is New Zealand’s best business writer, Bernard Hickey in the NZ Herald:
New Zealand’s Economic Winds Of Change
Chaos theory calls it the butterfly effect. It’s the idea that a butterfly flapping its wings in the Amazon could cause a tornado in Texas. The New Zealand economy has plenty of its own butterflies changing the weather for GDP growth, jobs, interest rates, inflation and house prices. [..] One of the flappiest at the moment is the global iron ore price.
It’s barely noticed here but it’s an indicator of growing trouble inside our largest trading partner, China, and it is knocking our second-largest partner, Australia, for six. It fell to a 10-year low of almost US$50 a tonne this week and is down from a peak of more than US$170 a tonne in early 2011.
China embarked on an infrastructure spree after the global financial crisis. Over the three years to 2013, China poured 6.4 gigatonnes of concrete, which was more than was poured in the US in the entire 20th century. All that concrete needed reinforcing with steel and China didn’t have enough iron ore and coking coal to make it. That building boom created a glut of apartments and debt, which China now needs to digest. [..]
.. iron ore production in Australia has only now ramped up to its peak levels. Weak demand met high supply to produce a price slump. This all may seem irrelevant to New Zealand, but it’s not. The Australian dollar has fallen in response to the iron ore crash, while New Zealand’s dollar has remained strong because our economy is humming along, thanks to building surges in Christchurch and Auckland and plenty of spending and investment.
That divergence between the Australasian economies drove the New Zealand dollar to a record high of well over AUD$98 this week. Dollar parity would make all those winter holidays on the Australia Gold Coast and trips to shows in Sydney and Melbourne cheaper and generate a fierce headwind for manufacturing exporters and tourism businesses here that sell to Australians.
President Xi has reinforced the contrasting effects of the changes in China on Australia and New Zealand by encouraging consumers and investors to spend more of China’s big trade surpluses overseas. Tourism from China was up 40% in the first two months of this year from a year ago, and there remains plenty of demand from investors in China for New Zealand assets.
The dark side of this tornado in New Zealand after the flapping of the butterfly’s wings in China was felt in Nelson this week. The region’s biggest logging trucking firm, Waimea Contract Carriers, was put into voluntary administration owing $14m, partly because of a slump in log exports to China in the past six months.
That’s because New Zealand’s logs are now mostly shipped to China to be timber boxing for the concrete being poured in its new “ghost” cities. The Chinese iron ore butterfly has flapped and now we’re seeing Gold Coast winter breaks become cheaper and logging contracts rarer.







